Worm And Wheel Gear Uses: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for worm and wheel gear uses
In the dynamic landscape of industrial machinery, sourcing effective worm and wheel gear solutions presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. These gears, known for their unique ability to provide high torque and significant speed reduction in a compact design, are critical components across various sectors, including automotive, manufacturing, and robotics. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of worm and wheel gear applications, offering insights into their types, operational benefits, and challenges—such as lubrication requirements and material considerations.
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find this comprehensive resource invaluable for making informed purchasing decisions. We will explore essential factors like supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and industry-specific applications to ensure you select the right gear solutions for your operational needs. With a focus on empowering you to navigate the complexities of the global market, this guide aims to enhance your procurement strategy and ultimately drive efficiency and reliability in your machinery operations. By understanding the nuances of worm and wheel gears, you can optimize your supply chain and mitigate risks associated with sourcing and maintenance.
Understanding worm and wheel gear uses Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Worm Gear | High reduction ratio, non-reversible | Conveyors, lifts, and hoists | Pros: Compact design, fewer moving parts; Cons: Requires specialized lubrication. |
| High-Load Worm Gear | Enhanced material strength, often with steel wheels | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment | Pros: Handles higher loads; Cons: More expensive, complex lubrication needs. |
| Brass Worm Gear | Brass wheel for wear resistance | Light-duty applications, automation systems | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to replace wheels; Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Self-Locking Worm Gear | Prevents back-driving due to friction | Elevators, winches | Pros: Increased safety; Cons: Lower efficiency due to friction losses. |
| Worm Gear with Integrated Drive | Combines motor and gear in one unit | Robotics, compact machinery | Pros: Space-saving, simplified design; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Standard Worm Gears?
Standard worm gears are characterized by their high reduction ratios and non-reversible power transmission, making them ideal for applications requiring significant torque reduction in a compact space. They are commonly used in conveyors and lifting mechanisms. For B2B buyers, the primary consideration is the need for specialized lubricants due to the sliding friction inherent in their design, which can complicate maintenance.
How Do High-Load Worm Gears Differ from Standard Variants?
High-load worm gears are designed with enhanced material strength, often using steel wheels to accommodate greater loads. They are essential in heavy machinery and industrial applications where durability is critical. Buyers should be aware that while these gears offer increased load capacity, they also come with higher costs and more complex lubrication requirements, necessitating careful planning for maintenance and operation.
Why Choose Brass Worm Gears for Light-Duty Applications?
Brass worm gears feature a brass wheel, which serves as a sacrificial component, protecting the more robust worm from wear. These gears are suitable for light-duty applications, such as automation systems, where cost-effectiveness is a priority. However, buyers should consider their limited load capacity and the potential need for more frequent replacements compared to steel variants.
What Are the Advantages of Self-Locking Worm Gears?
Self-locking worm gears provide an added safety feature by preventing back-driving due to friction between the worm and the wheel. This makes them particularly useful in applications like elevators and winches, where safety is paramount. While they enhance operational safety, buyers must also consider the trade-off in efficiency, as the increased friction can lead to power losses.
How Do Integrated Drive Worm Gears Benefit Compact Machinery?
Worm gears with integrated drives combine the motor and gear into a single unit, offering significant space-saving advantages for robotics and compact machinery. This design simplifies installation and reduces the number of components needed. However, B2B buyers should evaluate the higher initial costs and ensure compatibility with existing systems before making a purchase.
Key Industrial Applications of worm and wheel gear uses
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of worm and wheel gear uses | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyors for material handling | High torque output with compact design, reducing space requirements | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and load specifications |
| Automotive | Power steering systems | Provides reliable gear reduction, enhancing steering precision | Focus on durability and lubrication compatibility |
| Food and Beverage | Processing equipment for mixing and grinding | Efficient torque transfer for heavy loads, ensuring operational efficiency | Consider hygiene standards and corrosion resistance |
| Mining and Minerals | Hoisting equipment for lifting heavy loads | High reduction ratios enable safe lifting and lowering of materials | Evaluate load ratings and environmental conditions |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine pitch control systems | Enhances system reliability and safety through non-reversible design | Assess lubrication needs and material compatibility |
How Are Worm and Wheel Gears Utilized in Manufacturing Applications?
In the manufacturing sector, worm and wheel gears are pivotal in conveyor systems that transport materials efficiently. Their high torque output and compact design allow for significant load handling in limited spaces, which is essential in manufacturing plants where floor space is at a premium. International buyers should consider compatibility with existing material handling systems and ensure that the gears can withstand the specific load requirements of their operations.
What Role Do Worm and Wheel Gears Play in Automotive Steering Systems?
Worm and wheel gears are integral to automotive power steering systems, providing a reliable method for gear reduction that enhances steering precision. The unique design prevents back-driving, ensuring that the steering remains responsive and safe. B2B buyers in the automotive sector must prioritize durability and lubrication compatibility, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures, to maintain performance and longevity.
How Are Worm and Wheel Gears Applied in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, worm and wheel gears are commonly used in processing equipment for mixing and grinding applications. Their ability to transfer high torque efficiently ensures that heavy materials are processed without compromising operational efficiency. Buyers should consider hygiene standards and corrosion resistance when sourcing these gears, as food-grade materials are essential for compliance with safety regulations.
Why Are Worm and Wheel Gears Important in Mining and Minerals Operations?
Worm and wheel gears are crucial in mining and minerals operations, particularly in hoisting equipment designed for lifting heavy loads. The high reduction ratios provided by these gears enhance safety when moving materials vertically. When sourcing for this application, it is vital to evaluate load ratings and the environmental conditions of mining sites, ensuring that the gears can withstand harsh operating environments.
How Do Worm and Wheel Gears Contribute to Renewable Energy Solutions?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, worm and wheel gears are employed in pitch control systems. They enhance the reliability and safety of turbine operations by preventing back-driving, which is critical for adjusting blade angles according to wind conditions. Buyers should assess lubrication needs and material compatibility to ensure optimal performance in varying environmental conditions, particularly in regions with high humidity or extreme temperatures.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘worm and wheel gear uses’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Lubrication Challenges in Worm Gear Applications
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges that B2B buyers face when using worm and wheel gears is the issue of lubrication. The unique sliding motion between the worm and the wheel creates high friction, which can lead to rapid wear and tear if not adequately lubricated. Many companies struggle to identify the right lubricants due to the need for high-viscosity options that can handle the specific conditions of their applications. Inadequate lubrication can result in increased downtime, costly repairs, and potential failure of machinery, leading to significant financial losses.
The Solution: To address lubrication challenges, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on suitable lubricants for your specific worm gear setup. Opt for high-viscosity gear oils, such as ISO 460 or ISO 680, which are designed to withstand the sliding friction inherent in worm gear systems. Engage with reputable lubricant suppliers who specialize in industrial applications and can provide tailored solutions based on your operating conditions. Regularly perform oil analysis to monitor lubricant effectiveness and wear metals, ensuring that the chosen lubricant is performing optimally. Additionally, consider implementing a dedicated lubrication management system to ensure consistent application and maintenance, ultimately prolonging the life of your worm gears and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Managing Heat and Wear in Worm Gear Systems
The Problem: Excessive heat generation is another common pain point for B2B buyers utilizing worm and wheel gears. The sliding friction between the worm and wheel not only leads to wear but can also elevate temperatures, resulting in thermal degradation of both the lubricant and the gear materials. This situation can compromise the efficiency and reliability of the entire system, leading to unexpected failures and costly downtime. For companies operating in high-load environments, this issue becomes even more critical, as the risk of overheating increases.
The Solution: To effectively manage heat and wear, it is essential to implement a proactive thermal management strategy. Start by selecting worm gears made from materials that can withstand higher temperatures, such as heat-treated steel or specialized alloys. Incorporate cooling systems, such as oil circulation or external cooling jackets, to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures. Regular maintenance checks should include inspecting gear integrity and lubricating components to prevent overheating. Additionally, consider using synthetic lubricants with superior thermal stability, which can help to reduce friction and wear, ultimately leading to a longer lifespan for your worm gear assembly.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compatibility of Materials in Worm Gear Configurations
The Problem: Compatibility of materials used in worm and wheel gear configurations can present significant challenges for B2B buyers. For instance, using a steel worm with a brass wheel can result in differential wear rates, leading to imbalanced performance and necessitating frequent replacements. Furthermore, certain lubricants may react adversely with specific materials, causing corrosion or degradation. This complexity can make it difficult to maintain optimal gear performance, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, conduct a comprehensive material compatibility analysis during the design phase of your worm gear system. Choose a steel worm paired with a brass wheel for applications where wear is a concern, as the brass will act as a sacrificial material, absorbing most of the wear. However, ensure that the selected lubricant is compatible with both materials to prevent corrosion. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights on material properties and recommend suitable combinations based on your operational requirements. Regularly review and update your maintenance protocols to include checks for material wear and lubricant compatibility, ensuring that your worm gear systems operate efficiently and effectively over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for worm and wheel gear uses
What Are the Key Materials Used in Worm and Wheel Gear Applications?
When selecting materials for worm and wheel gear systems, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material significantly impacts performance, durability, and the specific application requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these gear systems: brass, steel, bronze, and plastic.
How Does Brass Perform in Worm and Wheel Gear Applications?
Brass is a popular choice for the wheel component in worm gear systems due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically operates well under moderate loads and provides good wear characteristics when paired with a harder steel worm. The temperature and pressure ratings for brass can vary, but it generally performs well in environments with moderate thermal stress.
Pros: Brass is relatively inexpensive, easy to machine, and provides a sacrificial wear surface that protects the worm.
Cons: Its lower strength compared to steel limits its use in high-load applications. Additionally, brass is susceptible to corrosion when exposed to sulfur-containing lubricants, which can lead to significant wear.
Impact on Application: Brass is suitable for applications where moderate loads and corrosion resistance are critical. However, international buyers must be cautious about lubricant compatibility to avoid premature failure.
What Advantages Does Steel Offer for Worm Gear Systems?
Steel is often used for the worm in worm and wheel gear assemblies due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand high loads and is suitable for applications requiring significant torque. Steel’s temperature and pressure ratings are generally high, making it versatile for various industrial applications.
Pros: Steel provides excellent wear resistance and can handle high-stress environments. Its strength allows for compact designs with fewer components.
Cons: Steel is heavier and more expensive than brass. Additionally, it requires careful lubrication to prevent wear due to sliding friction.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications, but international buyers should ensure compliance with local standards for material strength and performance.
How Does Bronze Compare in Worm Gear Applications?
Bronze is another viable option for worm gear systems, particularly for the wheel component. It offers good corrosion resistance and wear characteristics, making it suitable for marine and industrial applications. Bronze typically has better load-bearing capabilities than brass, allowing for more robust designs.
Pros: Bronze has excellent resistance to corrosion and wear, making it suitable for harsh environments. It also has good machinability.
Cons: Bronze can be more expensive than brass and may require more complex manufacturing processes. Its mechanical properties can vary significantly based on the alloy composition.
Impact on Application: Bronze is particularly beneficial in applications exposed to moisture or corrosive environments. International buyers should consider the specific alloy and its compliance with regional standards.
When Is Plastic a Suitable Choice for Worm Gear Applications?
Plastic, particularly engineering plastics like nylon or acetal, is increasingly used in worm gear applications for lightweight and cost-effective solutions. These materials offer good wear resistance and can operate quietly, making them suitable for consumer products and light-duty industrial applications.

Illustrative image related to worm and wheel gear uses
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be produced at a lower cost than metals. It also allows for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: Plastics generally have lower load-bearing capabilities and can deform under high temperatures or pressures. Their longevity may be less than that of metal counterparts.
Impact on Application: Plastic gears are best suited for low-load applications. International buyers should evaluate the specific thermal and mechanical properties to ensure suitability for their needs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Worm and Wheel Gear Uses
| Material | Typical Use Case for worm and wheel gear uses | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Moderate load applications, sacrificial wheels | Good machinability and corrosion resistance | Susceptible to corrosion from certain lubricants | Low |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications requiring high torque | High strength and durability | Requires careful lubrication, heavier | High |
| Bronze | Marine and industrial applications | Excellent corrosion and wear resistance | More expensive, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Plastic | Lightweight, low-load applications | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower load-bearing capacity, deformation risk | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in various regions, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for worm and wheel gear uses
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Worm and Wheel Gears?
The manufacturing of worm and wheel gears is a meticulous process that involves several stages, ensuring high precision and quality. The main stages can be broadly categorized into material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Worm and Wheel Gears?
Material preparation is crucial, as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the performance of the finished gears. Typically, high-grade steel is used for the worm, while brass or bronze is preferred for the wheel due to its favorable wear properties. The materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specific mechanical and chemical standards.
Before machining, the materials are cut to size and shape, often using techniques such as saw cutting or shearing. Following this, they may be subjected to heat treatment to enhance hardness and strength, especially for the steel components. This step is vital in ensuring that the worm can withstand the high torque loads it will encounter in operation.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves machining processes that shape the worm and wheel to precise specifications. Key techniques include:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are employed to create complex geometries and ensure high accuracy in the gear profiles. This is particularly important for the helical threads of the worm and the teeth of the wheel.
- Hobbing: For the wheel, hobbing is a common method used to cut the teeth. This process allows for the efficient production of gear teeth with consistent quality.
- Grinding: After initial shaping, grinding may be used to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish required for optimal performance. This is especially critical for achieving the necessary tolerances in the gear teeth.
How Are Worm and Wheel Gears Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage in the manufacturing process, where the machined components are brought together. The assembly process typically follows these steps:

Illustrative image related to worm and wheel gear uses
- Inspection of Components: Before assembly, each component is inspected for dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Alignment and Fitting: The worm is aligned with the wheel to ensure proper meshing. This step is essential to minimize backlash and ensure smooth operation.
- Lubrication Application: Proper lubrication is applied to the contact surfaces to reduce friction and wear during operation.
Quality checks are performed at each stage to ensure that the components fit together correctly and function as intended.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing techniques are applied to enhance the surface quality and performance of the gears. Common finishing processes include:
- Deburring: This process removes any sharp edges or burrs that may have formed during machining, ensuring safety and better fitting.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as coating or plating may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and reduce wear. For example, a phosphating treatment can be used on steel worms to enhance their durability.
- Final Inspection: A final inspection is conducted to verify that the finished gears meet all specified tolerances and surface finish requirements.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Worm and Wheel Gear Production?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of worm and wheel gears is governed by various international standards, which help ensure consistency and reliability in production.
Which International Standards Are Relevant?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is widely adopted across industries. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure quality at every stage of production.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be required, ensuring that the gears are suitable for specific applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure that the final product meets customer expectations. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor the machining and assembly processes, ensuring adherence to tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive inspection of the finished gears is conducted, including dimensional checks and functional testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards and production processes. During these audits, buyers can assess the equipment, staff qualifications, and overall manufacturing environment.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality reports from suppliers can provide insight into their QC processes and the results of recent inspections. These reports should detail any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can include material testing, dimensional checks, and performance evaluations.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers must be aware of certain nuances when dealing with suppliers from different regions:

Illustrative image related to worm and wheel gear uses
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and communication styles can facilitate smoother interactions and negotiations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local and international regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Consideration of logistics, including shipping times and costs, can influence the overall supply chain efficiency. Buyers should discuss these aspects with suppliers upfront.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for worm and wheel gears, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘worm and wheel gear uses’
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring worm and wheel gears, ensuring a streamlined process that minimizes risk and maximizes performance. By following these steps, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and technical specifications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, it’s crucial to outline your specific requirements. This includes load capacity, gear ratio, material preferences (such as brass or steel), and operating environment conditions. Clearly defined specifications ensure that you select a product that meets your application needs, reducing the risk of costly modifications later.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in worm and wheel gears. Look for companies with a solid reputation, extensive experience, and positive customer reviews. Key indicators of reliability include industry certifications and adherence to international quality standards, which can provide assurance of product performance and durability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Offerings
It’s essential to assess the capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. Review their product range, manufacturing processes, and customization options. Ensure they can meet your volume requirements and delivery timelines, as this directly impacts your production schedules.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Samples
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples of the worm and wheel gears. This allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the product firsthand. Pay attention to the material finish, precision of the gear teeth, and overall construction, as these factors influence performance and longevity.
Step 5: Assess Lubrication and Maintenance Recommendations
Worm and wheel gears require specific lubrication to function optimally. Inquire about the recommended lubricants for your selected gears, including viscosity and type (such as mineral-based or synthetic oils). Understanding maintenance requirements will help you prepare for operational longevity and efficiency.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of your purchase. This includes pricing, payment terms, warranty conditions, and return policies. Clear agreements help prevent misunderstandings and protect your investment in case of defects or performance issues.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the performance of the worm and wheel gears post-purchase. Regular inspections and performance evaluations can identify issues early, ensuring that the gears maintain their operational integrity and efficiency over time. Consider setting up a feedback loop with the supplier to address any concerns that may arise.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing worm and wheel gears, ensuring that they secure reliable, high-quality products that meet their specific operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for worm and wheel gear uses Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Worm and Wheel Gears?
When sourcing worm and wheel gears, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Common combinations include steel worms with brass wheels, which offer a balance between durability and cost. Specialty materials or alloys can increase the price but may be necessary for high-performance applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage rates, the complexity of manufacturing processes, and the level of automation employed in production. In regions like Europe, labor costs may be higher compared to emerging markets in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, which is particularly important for suppliers aiming to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, especially for bespoke designs. Off-the-shelf components can reduce tooling expenses, but they may not meet specific application requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure that the gears meet the necessary specifications and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent expensive failures and downtime in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and the volume of goods ordered. International buyers should consider potential tariffs and customs duties, which can further impact total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market competition, demand, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Worm and Wheel Gear Costs?
Several factors influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the MOQ requirements can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized gears may incur additional costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of material not only affects initial costs but also influences durability and maintenance expenses. Opting for high-quality materials can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time.
-
Quality Certifications: Gears that meet international standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may command higher prices but ensure reliability and performance, which is crucial for industrial applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can directly affect the final cost of goods.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Maximize Cost Efficiency in Worm and Wheel Gear Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to explore bulk discounts, flexible payment terms, or value-added services that could reduce overall costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and replacement when evaluating gear options. A lower initial price may not always translate to cost savings over time.
-
Regional Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be mindful of regional differences in manufacturing capabilities, lead times, and logistical challenges. Local suppliers may offer advantages in terms of reduced shipping costs and faster delivery.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Trends: Regularly monitor market trends and material costs to make timely purchasing decisions. This can be particularly beneficial in volatile markets where material prices fluctuate.
-
Request Samples: Before placing large orders, request samples to assess quality and suitability. This helps prevent costly mistakes and ensures that the products meet specific requirements.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for worm and wheel gears can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to understand the pricing landscape accurately.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing worm and wheel gear uses With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Worm and Wheel Gear Uses
When considering mechanical power transmission systems, it is essential to evaluate various options beyond traditional worm and wheel gears. While worm gears offer unique advantages, such as high reduction ratios and compact design, other technologies may provide better performance, cost-efficiency, or ease of maintenance. This analysis compares worm and wheel gear uses with two viable alternatives: helical gears and planetary gears, providing insights into their respective benefits and drawbacks.
| Comparison Aspect | Worm And Wheel Gear Uses | Helical Gears | Planetary Gears |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High reduction ratio; limited reversibility | Good efficiency; moderate reduction ratios | Very high efficiency; high torque density |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; higher lubrication needs | Moderate cost; generally lower than worm gears | Higher initial cost due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward; requires precise alignment | Easy to install; standard mounting options available | Complex installation; requires precise engineering |
| Maintenance | High maintenance; specialized lubrication needed | Low maintenance; standard lubricants suffice | Moderate maintenance; depends on design complexity |
| Best Use Case | Applications needing high torque and low speed | General-purpose applications, including automotive | High-performance applications requiring compact design |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Helical Gears?
Helical gears are characterized by their angled teeth, which allow for smoother engagement and higher efficiency compared to worm gears. They provide a moderate reduction ratio and can transmit power in both directions, making them versatile for various applications. Their cost is generally lower than that of worm gears, and they require standard lubricants, simplifying maintenance. However, they may not achieve the same high reduction ratios as worm gears and can be more complex to manufacture.

Illustrative image related to worm and wheel gear uses
How Do Planetary Gears Compare?
Planetary gears consist of multiple gears rotating around a central sun gear, providing excellent torque density and efficiency. They are particularly suitable for high-performance applications, such as robotics and aerospace, due to their compact design and ability to handle significant loads. The complexity of planetary gear systems results in a higher initial cost and more involved installation process. While maintenance is generally moderate, it can vary based on the specific design. For applications requiring extreme efficiency and space-saving designs, planetary gears often present a superior alternative.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right gear system for your application depends on various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Worm and wheel gears are ideal for scenarios needing high torque and low speed, but their lubrication challenges may not fit all operational environments. Helical gears serve well in general applications with their ease of use and lower maintenance needs, while planetary gears excel in high-performance contexts despite their complexity and cost. By carefully analyzing the specific needs of your operation and weighing the pros and cons of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for worm and wheel gear uses
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Worm and Wheel Gears?
When considering worm and wheel gears for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The most common materials used in worm gear construction are brass for the wheel and steel for the worm. This combination is preferred due to its durability and the sacrificial nature of brass, which absorbs wear. Material grade affects not only the longevity of the gear but also its performance under load. Selecting the right material ensures optimal functioning and reduces maintenance costs. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum load that a worm and wheel gear can handle without failure. It is vital for B2B buyers to assess the load requirements of their applications to choose gears that can withstand operational stresses. An inadequate load capacity can lead to premature failure and costly downtimes. -
Reduction Ratio
The reduction ratio indicates how much speed is reduced from the input to the output. Worm gears can achieve high reduction ratios with minimal effort, making them ideal for applications requiring significant torque. Understanding this ratio helps in selecting the appropriate gear for specific applications, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in power transmission. -
Lubrication Requirements
Due to the sliding friction inherent in worm gears, lubrication is critical for reducing wear and maintaining performance. High-viscosity lubricants (ISO 320 and above) are often required. Buyers should be aware of these requirements to prevent gear failure and ensure longevity, as inadequate lubrication can lead to increased friction and wear. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the acceptable limits of variation in gear dimensions. High precision in manufacturing ensures smooth operation and reduces the risk of misalignment, which can cause operational inefficiencies. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing machinery. -
Temperature Resistance
The ability of worm and wheel gears to withstand varying temperatures affects their performance and lifespan. Different applications may require gears that can operate under high or low thermal conditions. Selecting gears with suitable temperature resistance is essential for maintaining operational efficiency in diverse environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Worm and Wheel Gears?
Navigating the B2B landscape requires familiarity with specific jargon and trade terms. Here are several essential terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture parts that are used in the products of another company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and ensure compatibility with existing equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is important for buyers to consider when planning inventory and assessing cost-effectiveness. Knowing the MOQ can help manage budgets and forecast demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. It is a critical tool for buyers to obtain competitive pricing and terms, facilitating better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions to clarify delivery, risk, and cost responsibilities, especially in international dealings. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for effective supply chain management, helping buyers plan their production schedules and inventory levels. -
Compatibility
This term indicates whether different components (like gears and motors) can work together without issues. Ensuring compatibility is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and avoiding costly modifications or replacements.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make informed decisions when sourcing worm and wheel gears, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the worm and wheel gear uses Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Worm and Wheel Gear Sector?
The worm and wheel gear market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in automation and the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy. Key trends include the integration of smart technologies, which enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. Automation in sectors like material handling and robotics is propelling the need for high-performance gear systems, creating opportunities for suppliers to innovate and differentiate their products.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note the importance of sourcing high-quality materials that meet stringent industry standards. Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing and advanced materials are reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing for the production of more complex and durable gear designs. Additionally, the growing trend of localization in supply chains is prompting companies to seek regional suppliers that can offer timely delivery and reduced shipping costs, particularly in areas with limited infrastructure.
Furthermore, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles is influencing the design and application of worm and wheel gears, necessitating adaptations to cater to these evolving requirements. Buyers should stay informed about these market dynamics to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with both current needs and future developments.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Worm and Wheel Gear Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly vital in the worm and wheel gear sector. The environmental impact of production processes and the materials used necessitate a shift toward greener practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable manufacturing processes, minimizing waste and energy consumption while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Ethical supply chains are crucial for fostering trust and transparency in B2B relationships. Buyers should seek suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical standards.
The use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals or biodegradable lubricants, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce the carbon footprint associated with gear production but also appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. By investing in suppliers that prioritize sustainability, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for responsible manufacturing practices in the global market.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Worm and Wheel Gears in the B2B Context?
Worm and wheel gears have a rich history that dates back to ancient times, serving as one of the six classical simple machines. Initially employed in applications requiring significant torque and minimal speed reduction, these gears have evolved through advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques. The introduction of high-strength alloys and precision machining has dramatically improved their performance and longevity.
In the B2B context, the design and application of worm gears have adapted to meet the demands of modern industries. The shift from manual to automated systems in the 20th century propelled the use of worm gears in various applications, from conveyor systems to automotive powertrains. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and reliability, worm and wheel gears remain a critical component in mechanical systems, demonstrating their enduring relevance in today’s technology-driven landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of worm and wheel gear uses
1. How do I choose the right worm and wheel gear for my application?
Choosing the right worm and wheel gear requires assessing your specific application needs, including load capacity, speed reduction ratio, and available space. Consider the material composition; for instance, a steel worm paired with a brass wheel is common for its sacrificial properties, allowing the wheel to wear down instead of the worm. Additionally, evaluate the lubrication requirements, as worm gears typically require specialized high-viscosity lubricants. Consulting with suppliers about your operational conditions and potential customization options can further guide your selection.
2. What is the best lubricant for worm and wheel gears?
The best lubricant for worm and wheel gears is typically a high-viscosity oil, such as ISO 460 or ISO 680, designed to handle the sliding friction present in these systems. Compounded gear oils and industrial extreme pressure (EP) gear oils are popular choices, but care must be taken with brass components due to potential corrosion from EP additives. It’s also essential to choose lubricants that ensure adequate film thickness to prevent metal-to-metal contact. Regular lubricant analysis can help maintain optimal performance and longevity.
3. What customization options are available for worm and wheel gears?
Customization options for worm and wheel gears include variations in gear ratios, materials, and dimensions to fit specific application requirements. Suppliers often offer tailored solutions to meet unique operational conditions, such as environment-specific lubrication or load-bearing capabilities. Additionally, some manufacturers may provide custom machining services to create gears that align perfectly with your machinery. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to explore available customization options that can enhance performance and efficiency.
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for worm and wheel gears?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for worm and wheel gears can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the gears. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 10 units for standard products to several hundred for customized solutions. It’s crucial to communicate your needs with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. If you require a smaller quantity, consider reaching out to multiple suppliers to compare options and possibly find a partner willing to accommodate your order size.
5. How do I vet suppliers for worm and wheel gears?
Vetting suppliers for worm and wheel gears involves assessing their industry reputation, experience, and quality assurance processes. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the gear manufacturing sector, preferably with certifications such as ISO 9001. Request references or case studies demonstrating their ability to meet quality standards and delivery timelines. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible or conducting virtual audits to evaluate their capabilities and ensure they align with your business needs.
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing worm and wheel gears?
Payment terms for sourcing worm and wheel gears can vary widely among suppliers and may depend on order size, customization, and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, but some suppliers might require upfront payments or deposits, especially for custom orders. Additionally, consider discussing payment options such as letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risk. Always clarify payment terms upfront to ensure mutual understanding and avoid potential disputes.
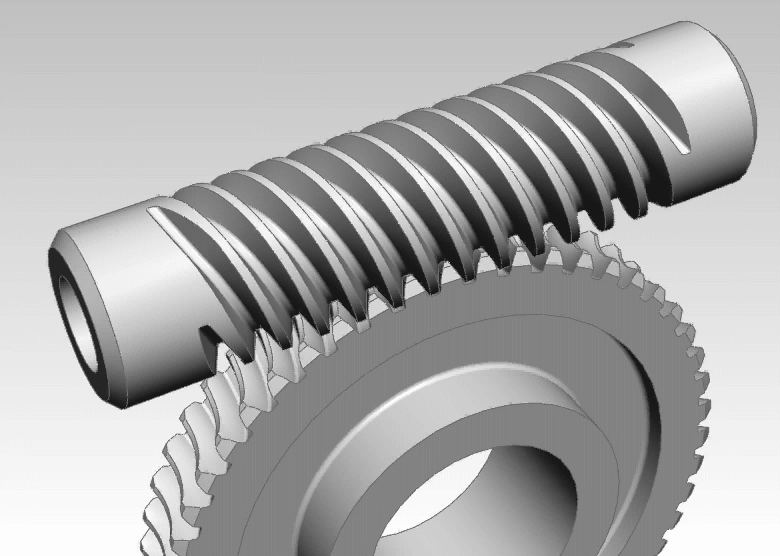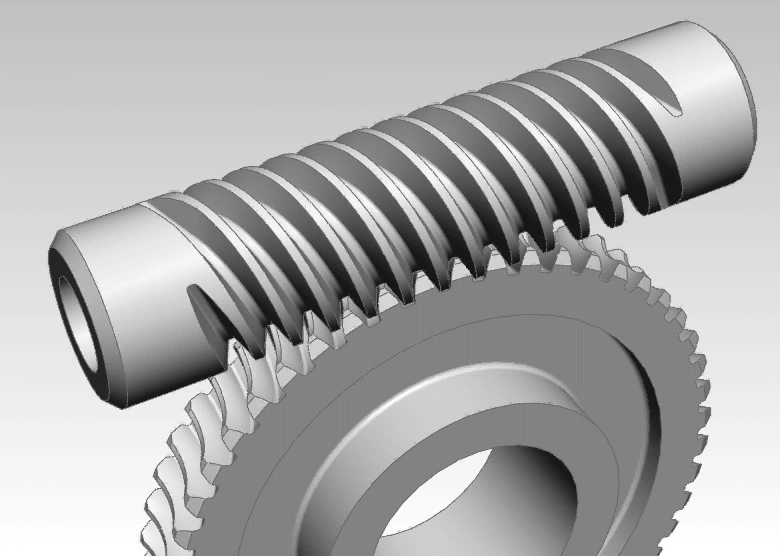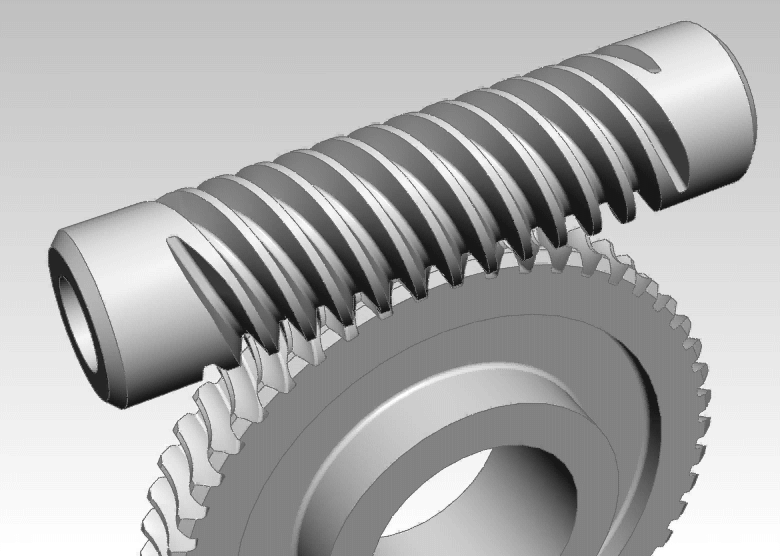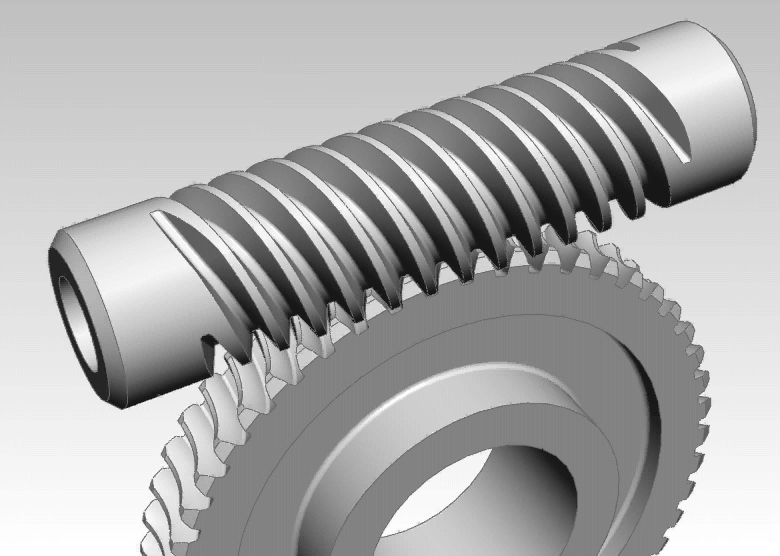
Illustrative image related to worm and wheel gear uses
7. What quality assurance measures should be in place for worm and wheel gears?
Quality assurance measures for worm and wheel gears should include rigorous testing protocols to assess material integrity, dimensional accuracy, and performance under load. Look for suppliers that implement in-process inspections and final audits, utilizing tools such as gear tooth calipers and hardness testers. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies and whether they conduct regular audits of their manufacturing processes. Ensuring that your supplier adheres to strict QA measures will help guarantee the reliability and longevity of the gears.
8. How can I ensure timely logistics and delivery for my worm and wheel gear orders?
To ensure timely logistics and delivery for worm and wheel gear orders, establish clear communication with your supplier regarding lead times and shipping methods. Discuss the logistics of your supply chain, including customs clearance and potential delays, especially for international shipments. Opt for suppliers with established logistics partnerships or those who can provide comprehensive shipping solutions. Implementing a buffer period in your project timeline can also help accommodate any unforeseen delays, ensuring your operations remain uninterrupted.
Top 4 Worm And Wheel Gear Uses Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machinery Lubrication – Worm Gears
Domain: machinerylubrication.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Worm gears consist of a shaft with a spiral thread that engages with a toothed wheel, typically made of steel (worm) and brass (wheel). They change rotational movement by 90 degrees and are known for high reduction ratios, allowing for increased torque or reduced speed with fewer moving parts. However, they require specialized high-viscosity lubricants (ISO 320 and greater) due to sliding friction…
2. IQS Directory – Worm Gears
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Worm gears are specialized staggered shaft gears designed for motion transfer between shafts through threads on a cylindrical rod, enabling speed reduction. They consist of two main parts: the worm and the worm wheel. Advantages include reduced noise, less vibration, compact design, and durability due to construction from hardened metals. Common manufacturing processes include hobbing, milling, an…
3. Superior Gearbox – Worm Gears
Domain: superiorgearbox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Worm gears are compact mechanical arrangements that facilitate high torque transmission with minimal noise. They are used in various applications including elevators and lifts, conveyor systems, automotive steering systems, tuning instruments, winches and hoists, packaging machinery, automatic gates and door openers, machine tools, and industrial mixers. Key benefits include high torque transmissi…
4. Rotalink – Worm Gear Motors
Domain: rotalink.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Worm gear motors offer high reduction ratios, compact design, and self-locking capabilities. They consist of a worm gear and a worm wheel, enabling significant speed reduction in a single stage. Key advantages include high reduction ratios, compact size, self-locking capability, and smooth, quiet operation. Applications include medical devices, robotics, packaging machinery, and lifts/hoists. Rota…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for worm and wheel gear uses
In conclusion, worm and wheel gears present unique advantages for various industrial applications, particularly in situations requiring high torque and compact design. Their ability to provide significant reduction ratios with fewer components minimizes potential points of failure, making them an appealing choice for machinery in sectors ranging from manufacturing to automotive. However, the challenges associated with lubrication and material compatibility, especially when using brass components, must be addressed through strategic sourcing to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
International B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize sourcing suppliers who not only understand the complexities of worm gear systems but also provide tailored lubrication solutions that enhance operational efficiency. As industries evolve, the demand for robust and efficient power transmission solutions will only increase.
Investing in high-quality worm and wheel gear systems today will prepare your operations for future challenges, ensuring sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore innovative materials, and consider advanced lubrication technologies to optimize your sourcing strategy and drive success in your projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.