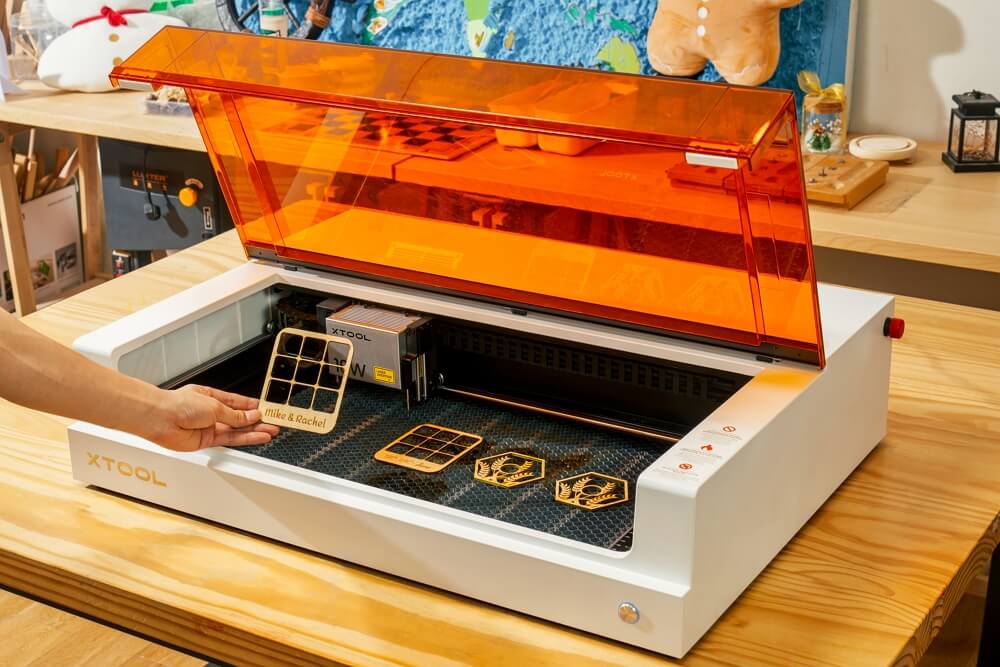
Wooden Cut Machine Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wooden cut machine
In an increasingly competitive global marketplace, sourcing the right wooden cut machine presents unique challenges for B2B buyers. Whether you’re looking to enhance production efficiency or diversify your product offerings, navigating the complexities of laser cutting technology is essential for achieving business success. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of wooden cut machines, focusing on key factors such as types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Brazil) seek reliable solutions, understanding the nuances of different technologies—like CO2 and fiber lasers—becomes crucial. Our guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by offering insights into the operational capabilities of various machines, their maintenance requirements, and potential return on investment.
By addressing common challenges, such as ensuring quality and efficiency while managing costs, this resource equips you with the knowledge needed to select a wooden cut machine that aligns with your specific operational needs. Whether you’re a small-scale artisan or a large manufacturing enterprise, this guide aims to facilitate your journey in sourcing the ideal equipment to elevate your business’s capabilities in woodworking.
Understanding wooden cut machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutters | Utilizes CO2 gas for laser generation; suitable for various woods | Sign making, furniture design, crafts | Pros: High precision, versatile; Cons: Higher initial cost, requires maintenance. |
| CNC Router Machines | Computer-controlled cutting tool with rotating bits | Custom furniture, cabinetry, architectural elements | Pros: Great for complex shapes; Cons: Slower than laser cutters, can be less precise. |
| Diode Laser Cutters | Compact and more affordable; suitable for light-duty tasks | Small-scale crafts, prototypes | Pros: Affordable, easy to operate; Cons: Limited power, not ideal for thick materials. |
| Plasma Cutters | Uses high-velocity plasma to cut through materials | Heavy-duty applications, industrial settings | Pros: Fast cutting for thick materials; Cons: Less detail, rougher edges. |
| Engraving Machines | Focuses on surface engraving rather than cutting through | Branding, personalized gifts | Pros: High detail, good for customization; Cons: Limited to engraving, not cutting. |
What Are CO2 Laser Cutters and Their Key Benefits for B2B Buyers?
CO2 laser cutters are among the most popular choices for wood processing in the B2B sector due to their versatility and precision. These machines use a CO2 gas mixture to produce a focused laser beam, allowing for intricate designs and clean cuts. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including sign making, furniture design, and various crafts. Buyers should consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance, as the higher performance comes with a higher cost.
How Do CNC Router Machines Operate and What Are Their Applications?
CNC router machines are computer-controlled devices that utilize rotating bits to cut and shape wood. They excel in creating complex shapes and intricate designs, making them ideal for custom furniture, cabinetry, and architectural elements. While they offer great flexibility, B2B buyers need to be aware of their slower cutting speeds compared to laser options and may require more setup time for intricate designs.
What Advantages Do Diode Laser Cutters Offer for Small-Scale Applications?
Diode laser cutters are compact and more affordable, making them suitable for light-duty tasks and small-scale crafts. These machines are user-friendly and ideal for prototyping and small custom projects. However, their power limitations mean they may not be suitable for cutting through thicker materials. B2B buyers should assess their production needs to determine if these machines meet their requirements.
In What Scenarios Are Plasma Cutters Most Effective for Wood Cutting?
Plasma cutters utilize high-velocity plasma to cut through materials, making them effective for heavy-duty applications. While they can handle thicker wood, the cuts may lack the detail and precision found in laser or CNC options. B2B buyers in industrial settings may find plasma cutters beneficial for rapid cutting tasks, but they should also consider the trade-off in edge quality.
How Do Engraving Machines Enhance Customization in Wooden Products?
Engraving machines focus on applying designs to wood surfaces rather than cutting through them. They are perfect for branding and personalized gifts, offering high detail and customization options. However, businesses should note that these machines are limited to engraving, making them less versatile than cutting machines. Buyers should consider their specific needs for branding and personalization when selecting these machines.
Key Industrial Applications of wooden cut machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wooden cut machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture components cutting | Enables precise, intricate designs and reduces waste | Need for high-speed, durable machines with precise control |
| Advertising & Signage | Engraving and cutting custom signage | Enhances brand visibility and personalization options | Consider material compatibility and engraving quality |
| Arts & Crafts | Production of decorative items and toys | Allows for unique, customizable products for niche markets | Look for versatility in materials and ease of operation |
| Architecture & Design | Architectural models and prototypes | Facilitates rapid prototyping and design visualization | Ensure machine size and precision meet project requirements |
| Construction & Renovation | Custom wood paneling and fixtures | Provides tailored solutions for aesthetic and functional needs | Evaluate machine capability for large or complex cuts |
How is the wooden cut machine utilized in furniture manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing industry, wooden cut machines are used to create custom components such as tabletops, chair parts, and intricate carvings. This technology allows manufacturers to achieve high precision and reduce material waste, thus enhancing cost-efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and South America, should consider machines that offer adaptability for various wood types and thicknesses, as well as high-speed capabilities to meet production demands.
What role do wooden cut machines play in advertising and signage?
Wooden cut machines are crucial for the advertising and signage sector, where they are employed to engrave and cut custom signs. This application enables businesses to create visually appealing and personalized branding elements, which are vital for customer engagement. Buyers should prioritize sourcing machines that provide high-quality engraving options and support a variety of materials, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal in outdoor settings.
How do wooden cut machines enhance arts and crafts production?
In the arts and crafts industry, wooden cut machines facilitate the production of unique decorative items and toys, allowing artisans to explore creative designs with precision. This capability not only enhances product quality but also opens up opportunities for customization in niche markets. International buyers should seek machines that are user-friendly and versatile, accommodating different types of wood and design intricacies to foster creativity.
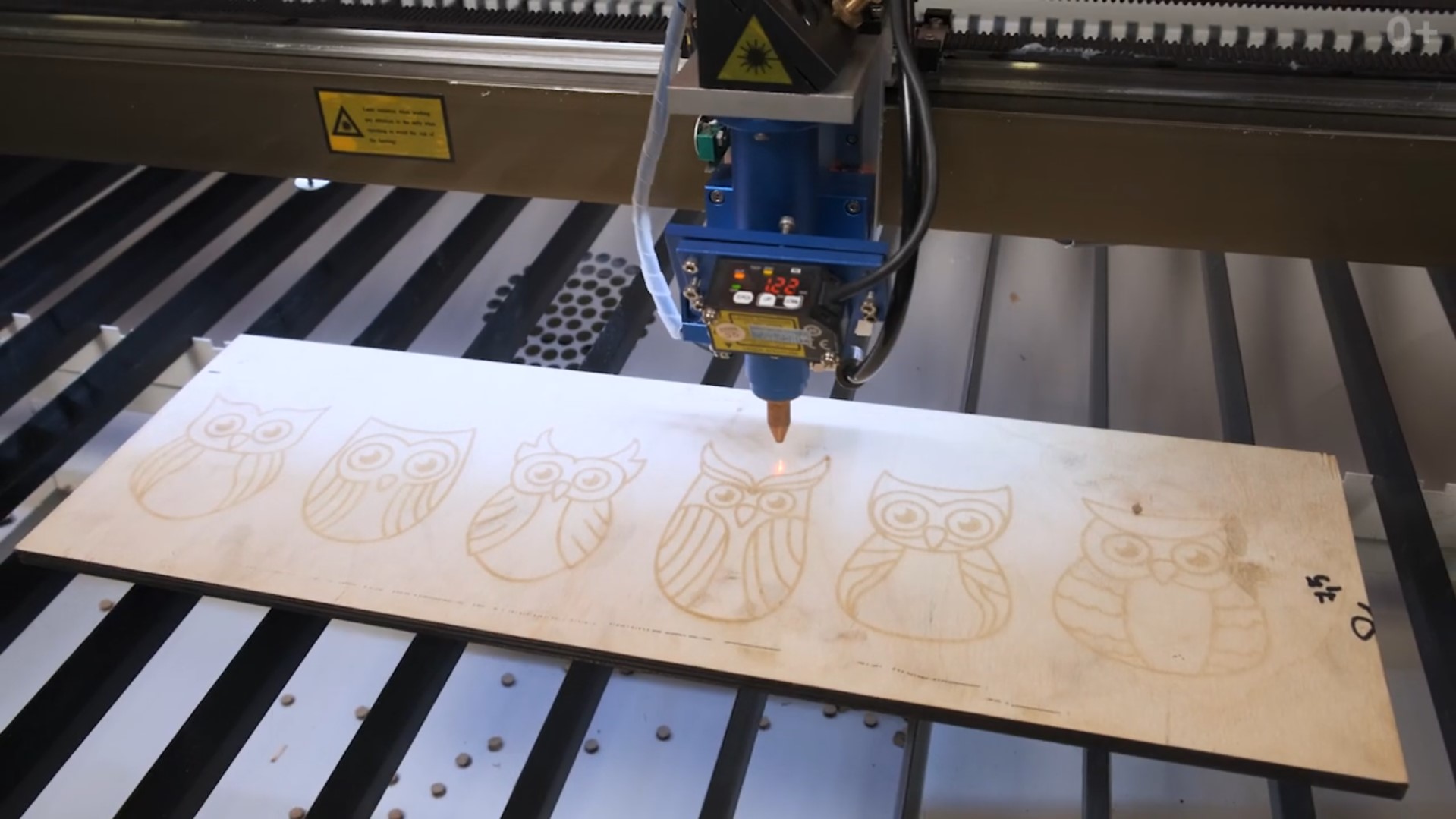

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
What benefits do wooden cut machines offer in architecture and design?
Architects and designers utilize wooden cut machines to create detailed architectural models and prototypes, which are essential for visualizing concepts and client presentations. This technology streamlines the prototyping process, enabling rapid adjustments and iterations. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing machines that offer high precision and the ability to handle complex cuts, ensuring that their designs are accurately represented.
How are wooden cut machines used in construction and renovation projects?
In the construction and renovation sectors, wooden cut machines are employed to produce custom wood paneling and fixtures tailored to specific project requirements. This application allows for both aesthetic enhancement and functional solutions in residential and commercial spaces. Buyers should assess the machine’s capacity for large-scale cuts and its compatibility with various wood materials, ensuring that it meets the diverse needs of construction projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘wooden cut machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Cutting Quality Across Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with inconsistent cutting quality when using wooden cut machines on different types of wood, such as hardwood versus softwood. For instance, a furniture manufacturer may find that their laser cutter produces clean cuts on pine but struggles with oak, resulting in burned edges or incomplete cuts. This inconsistency not only affects production efficiency but also compromises the quality of the final products, leading to potential customer dissatisfaction and increased material waste.
The Solution: To mitigate issues of inconsistent cutting quality, it is crucial to invest in a machine that features adjustable settings for different materials. Buyers should prioritize wood laser cutters with advanced technology that allows for precise control over power, speed, and frequency settings. For instance, utilizing a machine with a robust software interface enables operators to input specific parameters for each wood type, optimizing the cutting process. Additionally, conducting material tests before large runs can help establish the best settings for each type of wood, ensuring quality results. Regular maintenance of the machine, including lens cleaning and alignment checks, is also vital to maintain cutting precision over time.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs and Energy Consumption
The Problem: Many businesses are concerned about the operational costs associated with running wooden cut machines, especially in regions where electricity is expensive. A typical example is a small craft business in Brazil that finds their energy bills skyrocketing due to the continuous operation of their laser cutter. This situation can severely impact the profitability of the business, especially when margins are tight.
The Solution: To address high operational costs, B2B buyers should look for energy-efficient models that utilize advanced laser technology, such as fiber or CO2 lasers that are optimized for lower power consumption. Additionally, implementing a workflow that maximizes machine utilization can significantly reduce energy waste. For example, scheduling cutting tasks during off-peak energy hours can lower costs. Buyers may also consider investing in machines that come with built-in energy-saving features, such as automatic standby modes when idle. Moreover, conducting an energy audit of the facility can identify other areas for improvement, enabling businesses to lower their overall energy consumption.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Training Staff for Effective Operation
The Problem: One common pain point for companies investing in wooden cut machines is the steep learning curve associated with operating advanced machinery. This is particularly prevalent in regions with limited access to technical training resources. A furniture maker in South Africa may find it challenging to train staff quickly, leading to operational delays and reduced productivity as employees struggle to understand the software and machinery.
The Solution: To overcome training difficulties, businesses should prioritize purchasing machines that come with comprehensive training programs, including tutorials and on-site support. Manufacturers that offer extensive user manuals, video tutorials, and customer support can greatly enhance the training experience for staff. Additionally, investing in a user-friendly interface is essential; machines that feature intuitive software can significantly reduce the time required for training. Implementing a mentorship program where experienced operators guide new staff can also foster a culture of learning and ensure efficient machine operation. For ongoing improvement, companies might consider regular workshops or refresher courses to keep staff updated on best practices and new features as they become available.
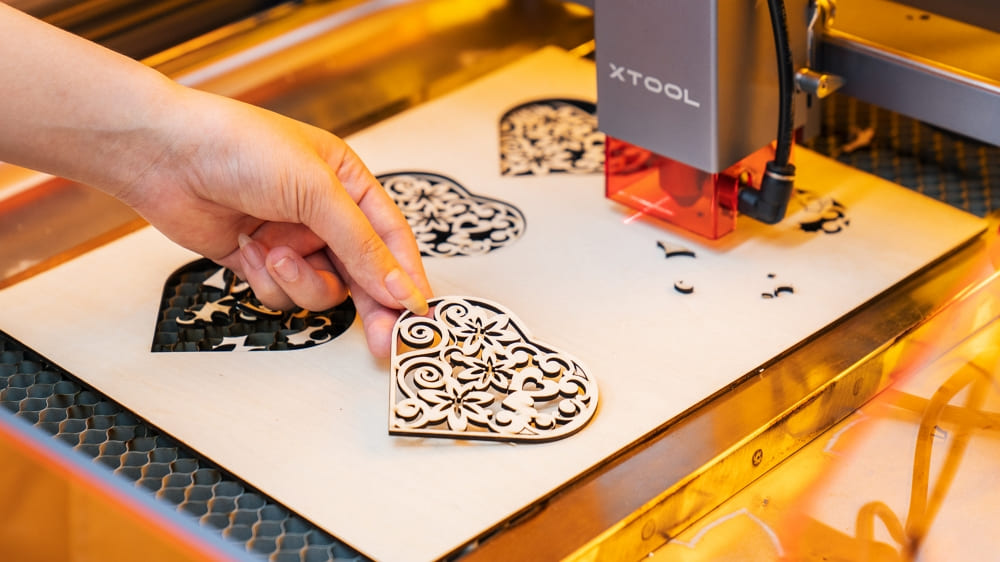

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wooden cut machine
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Wooden Cut Machines?
When selecting materials for wooden cut machines, understanding the properties and performance characteristics of each option is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials: softwood, hardwood, plywood, and MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard). Each material presents unique advantages and challenges, influencing their suitability for various applications.
How Do Softwoods Perform in Wooden Cutting Applications?
Softwoods, such as pine and cedar, are characterized by their lightweight and ease of processing. They typically have lower density, which allows for faster cutting speeds and less wear on the cutting equipment. However, softwoods can be less durable than hardwoods and may not withstand heavy use over time.
Pros: Softwoods are generally less expensive and easier to work with, making them ideal for quick production runs or prototype development. They also have a lower thermal conductivity, which can reduce the risk of burning during laser cutting.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Cons: The lower durability means that softwoods may not be suitable for products requiring high strength or long-term use. Additionally, the surface finish may not be as refined as that of hardwoods, which can affect aesthetic quality.
Impact on Application: Softwoods are often used for decorative items, toys, and temporary structures. They are compatible with various finishing processes, but care must be taken to avoid excessive heat during cutting.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Hardwoods?
Hardwoods, such as oak and cherry, are known for their density and durability. They provide a high-quality finish and are often preferred for high-end products. The cutting process for hardwoods typically requires more power and time due to their density.
Pros: Hardwoods offer excellent durability and a premium appearance, making them suitable for furniture and high-value items. They also provide better engraving contrast, enhancing the visual appeal of finished products.
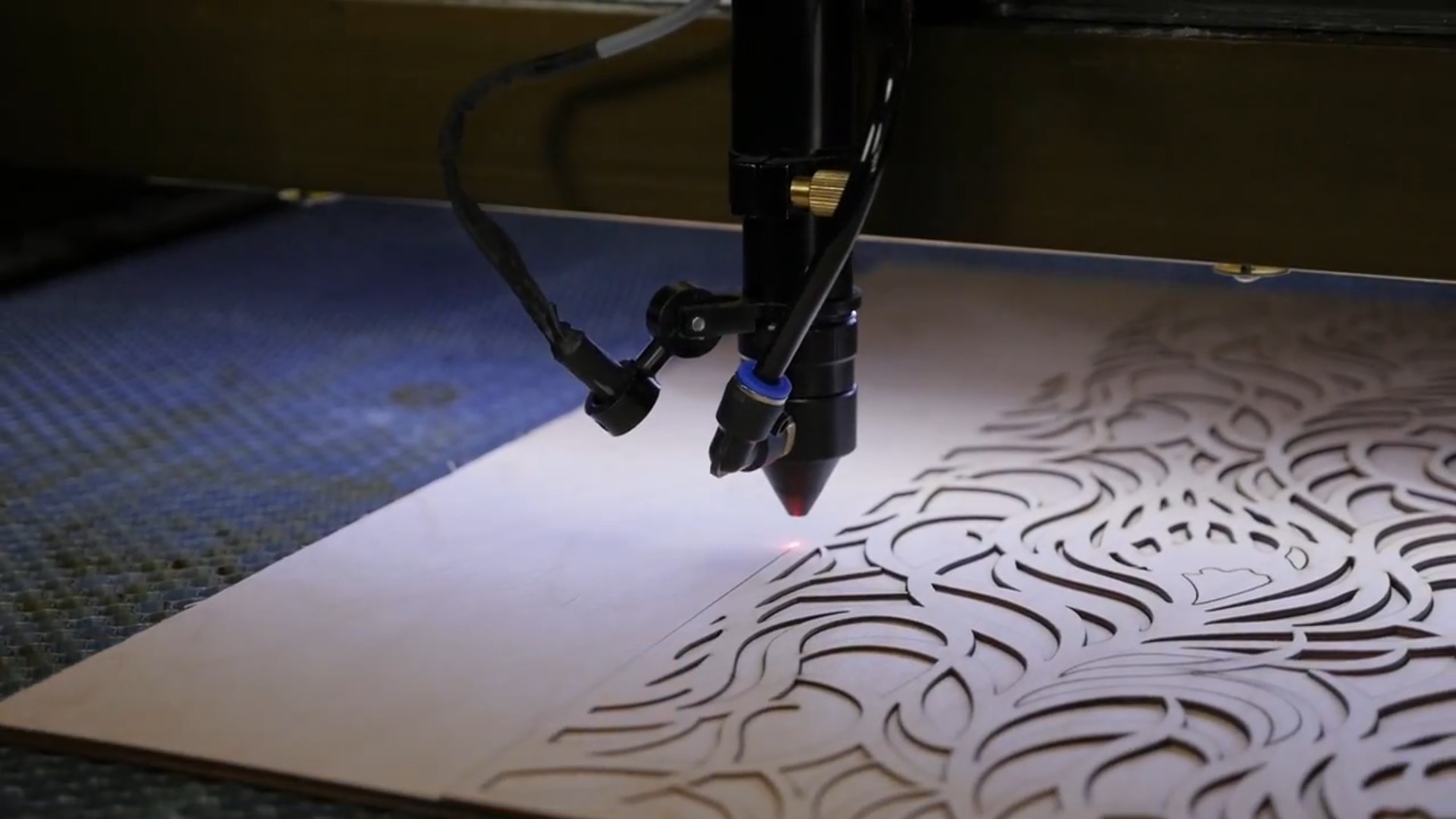

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Cons: The higher cost and increased manufacturing complexity can be a barrier for some businesses. Additionally, the cutting process may require specialized equipment to achieve optimal results without damaging the material.
Impact on Application: Hardwoods are commonly used for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items. They align with international standards for quality, making them a preferred choice in markets that prioritize craftsmanship, such as Germany and other European countries.
How Does Plywood Compare in Wooden Cutting Processes?
Plywood is a composite material made from layers of wood veneer glued together. Its structure provides strength and stability, making it a versatile choice for various applications. The type of adhesive used can significantly affect its compatibility with laser cutting.
Pros: Plywood is generally more cost-effective than solid hardwoods and offers good dimensional stability. It can be cut and engraved effectively, making it suitable for a wide range of products.
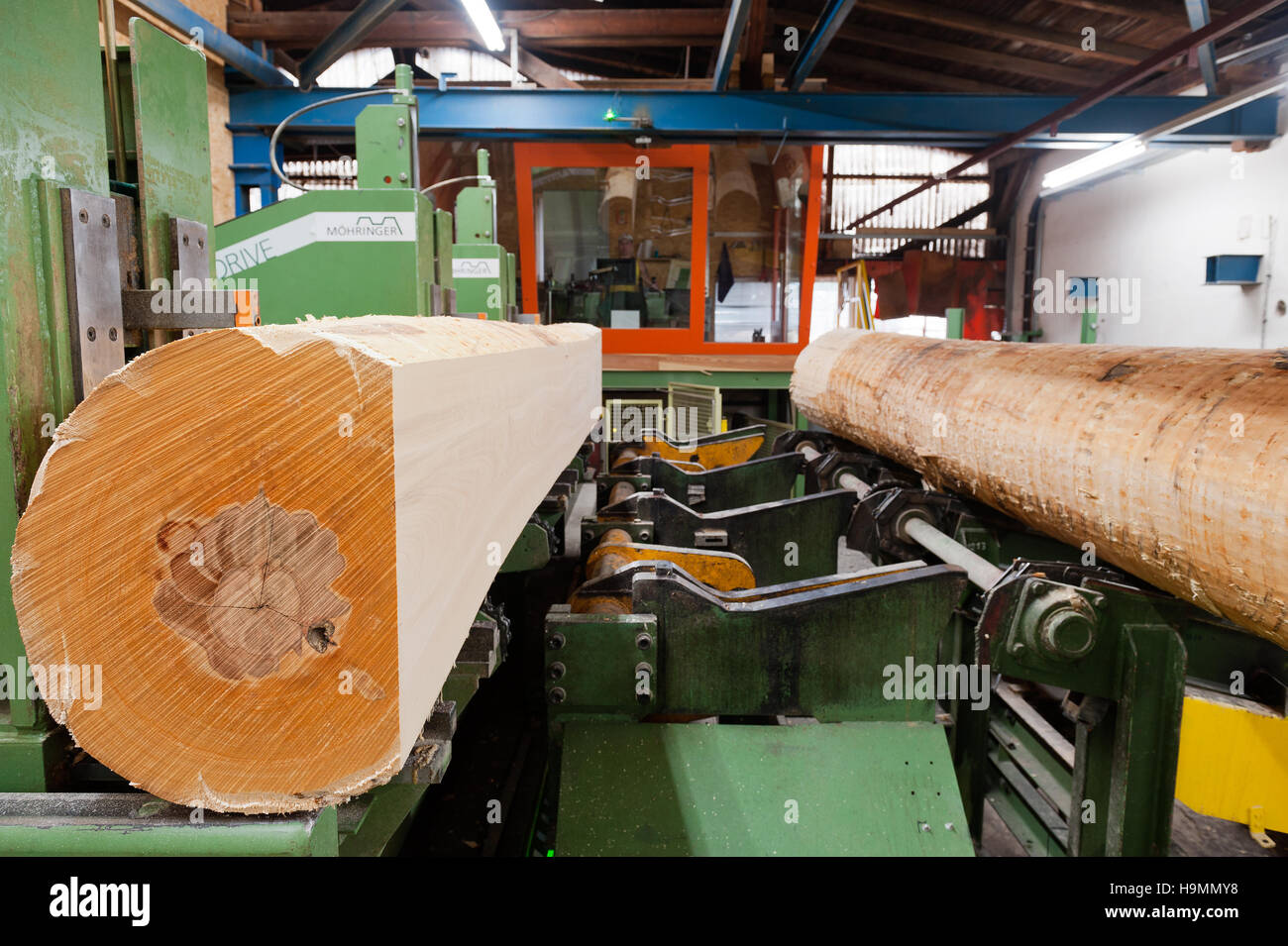

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Cons: The quality of the finish can vary depending on the type of plywood and adhesive used. Some plywoods may produce dark edges when cut, which can detract from the final appearance.
Impact on Application: Plywood is widely used in construction, furniture, and decorative applications. Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards regarding adhesives and finishes, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
What Are the Key Considerations for Using MDF in Wooden Cutting Machines?
MDF is a manufactured wood product made from wood fibers combined with adhesives. Its smooth surface makes it ideal for laser cutting and engraving, allowing for intricate designs.
Pros: MDF is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with, making it suitable for mass production. It provides a smooth finish that is ideal for painting and veneering.
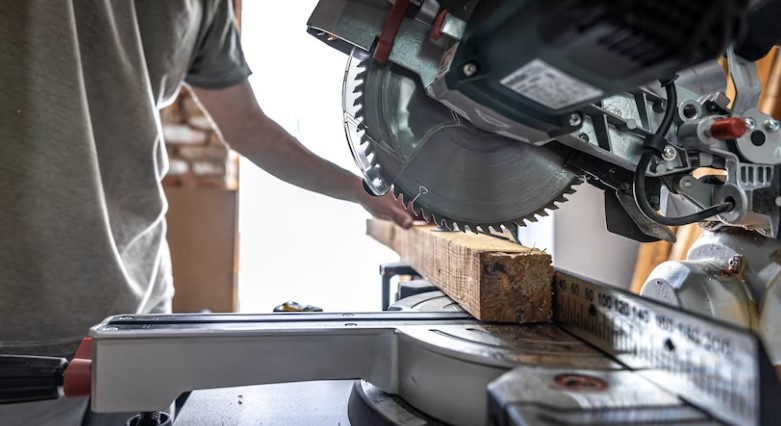

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Cons: MDF is less durable than solid wood and can be susceptible to moisture damage. Additionally, the cutting process can produce fine dust, which may require additional safety measures.
Impact on Application: MDF is commonly used for prototypes, display items, and furniture components. Buyers should consider the environmental impact of MDF production and ensure compliance with relevant standards, particularly in European markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Wooden Cut Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for wooden cut machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood | Decorative items, toys | Lightweight and easy to cut | Less durable than hardwood | Low |
| Hardwood | Furniture, cabinetry | High durability and premium finish | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Plywood | Construction, furniture | Cost-effective and stable | Variable finish quality | Medium |
| MDF | Prototypes, display items | Smooth surface for intricate designs | Susceptible to moisture | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for wooden cut machines, helping to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wooden cut machine
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for wooden cut machines are crucial for ensuring that the final products meet the high standards expected by international B2B buyers. This section delves into the typical stages of manufacturing, key techniques employed, and the comprehensive quality control (QC) measures that underpin the production of these machines.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Wooden Cut Machine?
The production of wooden cut machines can be broken down into several key stages, each critical to ensuring the machine’s performance and durability.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include high-quality steel for the frame, aluminum for components, and specialized alloys for the laser tubes. Each material is chosen for its specific properties, such as strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear.
Before assembly, materials undergo various pre-treatment processes, including cutting, machining, and surface finishing to remove any imperfections. This ensures that all components fit together seamlessly and function correctly.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
The next stage involves forming the individual components of the wooden cut machine. This can include processes such as:
-
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to create precise shapes and dimensions. This technology allows for high repeatability and accuracy, which is essential in producing parts that need to fit together perfectly.
-
Laser Cutting: For specific parts, laser cutting may be employed to achieve intricate designs and precise cuts. This method is particularly useful for components that require high levels of detail.
-
Welding and Joining: Various joining techniques, including welding and bolting, are utilized to assemble the frame and internal components. The choice of technique depends on the material and the required strength of the joint.
Assembly: How Are Machines Put Together?
Once all components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage typically involves:
-
Component Integration: Each part is carefully integrated, starting with the frame and moving to internal components like the laser tube and cooling systems.
-
Electrical Wiring: Proper wiring is crucial for the machine’s functionality. This includes connecting the control board, laser ignition unit, and positioning system.
-
Calibration: After assembly, machines undergo calibration to ensure that all components are functioning correctly and efficiently. This includes adjusting the laser beam focus and ensuring that the movement systems are precise.
Finishing: What Final Touches Are Added?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings, such as paints or anodizing, to prevent corrosion and enhance aesthetic appeal. Additionally, quality checks are performed to ensure that the machine meets design specifications and performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that wooden cut machines are reliable and perform as expected. International standards and industry-specific certifications play a significant role in this process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards is crucial. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is crucial for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their ability to provide consistent products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet certain safety and environmental standards. The CE marking indicates compliance with EU legislation, making it essential for manufacturers targeting the European market.
-
API Standards: For certain applications, especially in industries like oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet quality specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and assembly accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the machines are shipped, a comprehensive final inspection is performed. This ensures that all aspects of the machine, from functionality to appearance, meet quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential to mitigate risks associated with procurement.
What Methods Can Be Used for Verification?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This can include on-site visits to assess equipment, procedures, and employee training.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request quality assurance reports that detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. These reports can highlight the consistency and reliability of the supplier’s production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an impartial assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes and the final product. This is particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with the supplier’s practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
Navigating the nuances of quality control and certification can be challenging for international buyers.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can influence quality expectations and communication. Buyers should be aware of regional practices and standards.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with the regulations relevant to their target markets.
-
Language Barriers: Communication can pose challenges, especially when discussing technical specifications and quality standards. Utilizing translators or local representatives can help facilitate clearer communication.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for wooden cut machines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the intricacies of production and maintaining rigorous quality control, suppliers can deliver reliable machines that meet the diverse needs of international markets. Buyers equipped with this knowledge can make informed decisions, ensuring that their investments yield maximum returns.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘wooden cut machine’
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers seeking to procure a wooden cut machine, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before starting the procurement process. Consider the types of wood you intend to cut, the thickness of the materials, and the complexity of designs. This will guide you in selecting a machine with the appropriate power, size, and technology (e.g., CO2 laser vs. diode laser) that meets your production needs.
Step 2: Research Different Machine Types
There are various types of wooden cut machines, including laser cutters, CNC routers, and traditional saws. Each type has its advantages and limitations. Investigate which technology aligns best with your business model, whether you prioritize speed, precision, or versatility in material handling.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s vital to assess their reliability and reputation. Request detailed company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies from businesses in similar sectors. A supplier’s experience with your specific market can significantly influence service quality and support.
- Check certifications: Ensure that the supplier meets international standards (e.g., ISO certifications).
- Review warranty and service agreements: Understand what support is offered post-purchase.
Step 4: Assess Machine Features and Capabilities
Investigate the specific features of the machines you are considering. Look for capabilities such as adjustable cutting speeds, precision settings, and the ability to handle various wood types.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
- Control systems: Ensure the machine has an intuitive control panel for ease of operation.
- Safety features: Evaluate built-in safety measures to protect operators and maintain compliance with local regulations.
Step 5: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond the initial purchase price, calculate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
- Energy efficiency: Look for machines that minimize energy consumption.
- Spare parts availability: Ensure that parts are readily available to reduce downtime during repairs.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Whenever possible, arrange for a demonstration of the machine or request sample cuts from the supplier. This is critical to understanding the machine’s performance and quality of output.
- Evaluate cut quality: Inspect the edge finish and precision of the cuts.
- Test user interface: Make sure the machine is user-friendly for your operators.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly defined in the contract. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and support agreements.
- Negotiate terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing and support terms that suit your budget and operational needs.
- Include training provisions: Ensure that operator training is part of the agreement for a smooth transition to new equipment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can strategically navigate the procurement process for wooden cut machines, ensuring that they select the right equipment that meets their operational needs while also providing value and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wooden cut machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing a Wooden Cut Machine?
When sourcing a wooden cut machine, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The overall cost can be broken down into several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include the laser tube, frame, motors, and electronics. The choice of materials directly impacts the machine’s durability and performance. For instance, higher-quality metals and advanced laser tubes can lead to better cutting precision and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both manufacturing and assembly. Skilled technicians are necessary for the assembly of complex components like the laser system and electronic controls. Labor costs can vary significantly by region; countries with lower labor costs may offer cheaper machines, but this can affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers with higher operational efficiencies may pass these savings onto buyers. It’s essential to assess the manufacturer’s production capabilities and overhead management.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized machine configurations. This is particularly relevant for machines designed for unique applications or non-standard materials.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and inspection processes ensure that machines meet quality standards. This component can add to the upfront cost but is vital for ensuring reliability and performance in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance and the chosen shipping method. Consideration must also be given to customs duties and taxes, which can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to the total cost of production. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning and the perceived value of the machine.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Wooden Cut Machines?
Several factors influence the pricing of wooden cut machines, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to discounts. Suppliers often have a lower price per unit for larger orders, making it beneficial for companies looking to scale operations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced cutting capabilities or specific software integrations, will increase the price. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials Used: The type of laser technology (e.g., CO2 vs. fiber lasers) and the quality of components can significantly influence pricing. Buyers should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of different materials and technologies.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines with certifications (such as CE or ISO) may come at a premium but provide assurance of quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and service offerings of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and customer support services.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect logistics costs. Understanding terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers better manage shipping expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can benefit from strategic negotiation:
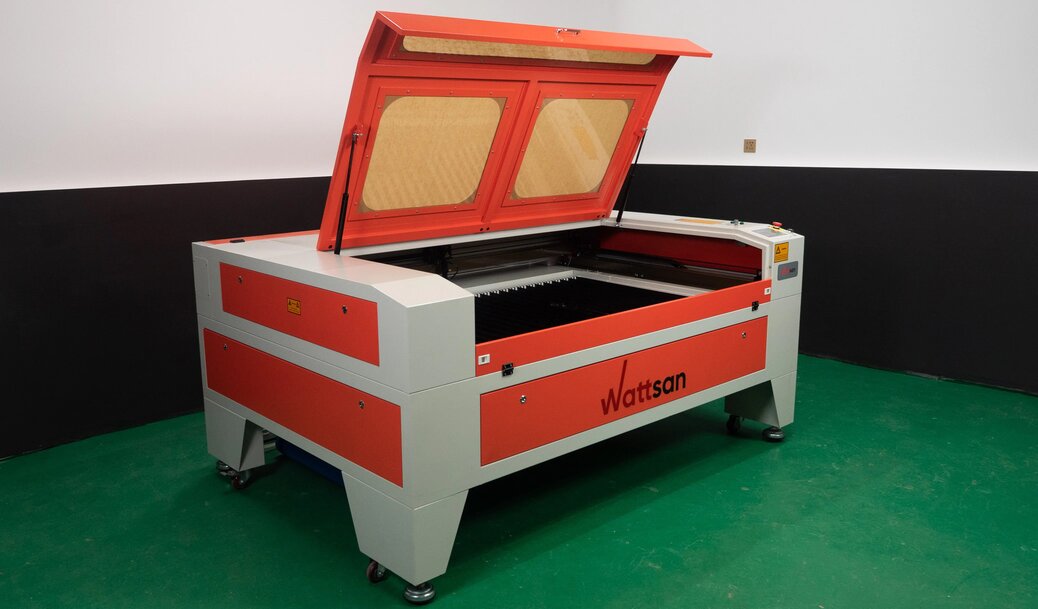

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. A machine with a higher upfront cost may offer lower operational costs, making it more economical in the long run.
-
Leverage Competitive Quotes: Obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers to understand market pricing. This information can be a powerful negotiation tool.
-
Focus on Long-term Relationships: Building a rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Consider factors like after-sales support and availability of spare parts, which can affect long-term costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different markets may have varying pricing structures due to local demand, currency fluctuations, and trade policies. Understanding these nuances can provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for wooden cut machines can vary widely based on specifications, supplier location, and market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and directly consult suppliers for the most accurate pricing and cost estimates tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing wooden cut machine With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Wooden Cut Machines
In the realm of wood processing, the wooden cut machine—particularly laser cutting technology—stands out for its precision and efficiency. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit the specific needs of different businesses. These alternatives vary in terms of performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these options can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Comparison Table of Wooden Cut Machine and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Wooden Cut Machine | CNC Router | Band Saw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; intricate designs | Versatile; good for large cuts | Efficient for thick materials |
| Cost | Moderate to high investment | Varies; generally lower initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Easier to set up; user-friendly | Straightforward operation |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires specific care | Low; regular lubrication needed | Low; blade replacement only |
| Best Use Case | Fine details, engraving | General woodworking, large projects | Straight cuts in thick wood |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Router
CNC routers are computer-controlled cutting machines that can handle a variety of materials, including wood. They excel in creating intricate designs and can be programmed for high-speed operations. The initial investment is generally lower than that of laser cutters, making them an attractive option for startups and smaller businesses. However, while they offer versatility, CNC routers might not achieve the same level of precision for fine details as a laser machine.
Band Saw
The band saw is a traditional woodworking tool that excels in making straight cuts through thick materials, making it ideal for larger projects. Its lower initial cost and simplicity of operation appeal to many businesses. However, band saws are limited in their ability to perform intricate designs and engraving, which could be a disadvantage for companies focused on customized or detailed wood products. Maintenance is minimal, primarily involving blade changes, but the quality of cuts may not match that of a wooden cut machine.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wood Processing Solution
When selecting a wood processing solution, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs, including the types of products they intend to create, their budget, and their operational capabilities. While the wooden cut machine offers precision and versatility for detailed work, alternatives like CNC routers and band saws may better suit businesses focused on larger cuts or those operating within tighter budget constraints. By carefully considering these factors, companies can select the most appropriate technology to enhance their production efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wooden cut machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Wooden Cut Machine?
Understanding the critical specifications of a wooden cut machine is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
1. Power Output (Wattage)
The power output of a laser cutter is usually measured in watts (W). This specification directly affects the cutting speed and the thickness of wood that can be processed. For instance, machines with higher wattage can cut through thicker materials more quickly, making them ideal for mass production scenarios. In B2B contexts, selecting the appropriate power output can lead to enhanced productivity and efficiency.
2. Cutting Area (Work Envelope)
The cutting area, or work envelope, refers to the maximum size of the material that can be processed in the machine. It is typically measured in millimeters (mm). A larger cutting area allows for more extensive projects without needing to reposition the material, which is crucial for businesses that handle large wood panels or multiple items simultaneously. Ensuring the cutting area meets your operational needs can significantly reduce setup times and increase throughput.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
3. Precision and Tolerance
Precision refers to how accurately the machine can cut or engrave, often defined by the tolerance level, which is the acceptable limit of variation in a physical dimension. High precision and low tolerance are vital for projects requiring intricate designs or tight-fitting components. In B2B applications, this can lead to reduced material waste and improved product quality, which are key factors for customer satisfaction and repeat business.
4. Cooling System
A robust cooling system is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and extending the lifespan of the machine. Laser cutting generates significant heat, which can affect performance if not adequately managed. Machines with efficient cooling systems can operate for longer periods without overheating, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For businesses, this can translate into higher productivity and lower operational expenses.
5. Material Compatibility
Different wooden cut machines are designed to work with various types of materials, such as hardwood, softwood, plywood, and MDF. Understanding the material compatibility of a machine is crucial for businesses that aim to diversify their product offerings. Choosing a machine that can handle a wider range of materials can provide competitive advantages in terms of versatility and market reach.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Wooden Cut Machine Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and collaborations. Here are some common trade terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of wooden cut machines, knowing about OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers for replacement parts or new machines, ensuring quality and compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses, especially when planning inventory and budgeting for purchases. This term can significantly impact cash flow and inventory management strategies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the B2B sector, submitting an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms can help businesses understand their obligations regarding shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, which can influence total procurement costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the context of wooden cut machines, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management. Shorter lead times can improve responsiveness to market demands and enhance customer satisfaction.
By grasping these essential technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, streamline their procurement processes, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the wooden cut machine Sector
What Are the Current Trends and Dynamics in the Wooden Cut Machine Market?
The wooden cut machine sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. Global demand for precision and efficiency in woodworking is elevating the importance of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and laser-cutting technology. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, seek reliable and high-performance machinery, they must navigate a landscape marked by rapid innovation. Key trends include the increasing integration of automation and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, which enhance operational efficiency and enable remote monitoring and diagnostics.

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Additionally, the demand for custom and intricate designs is rising, necessitating machines that can handle diverse materials and complex cuts. The growing popularity of eco-friendly products is also influencing sourcing decisions. Manufacturers are exploring sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and optimizing material usage to minimize waste. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also caters to the preferences of environmentally conscious consumers.
The market is also characterized by competitive pricing and the emergence of regional suppliers offering localized services. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide robust after-sales support and easy access to spare parts, especially in developing markets. Consequently, understanding the unique needs of different regions is crucial for suppliers aiming to establish a foothold in this dynamic sector.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing of Wooden Cut Machines?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies within the wooden cut machine sector. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing wood from certified forests, ensuring that the materials used in manufacturing are responsibly harvested, and opting for machines that minimize energy consumption.
The environmental impact of production processes is under scrutiny, leading to a demand for ‘green’ certifications. Certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) are increasingly sought after by buyers looking to ensure that their supply chains are ethical and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, machines that utilize energy-efficient technologies or alternative energy sources not only reduce carbon footprints but also lower operational costs, making them more attractive to buyers.
Importantly, the emphasis on ethical sourcing extends to the entire supply chain, prompting businesses to evaluate their suppliers’ practices. Buyers must ensure that their partners uphold labor rights and adhere to ethical production standards, which can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty in an increasingly competitive market.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Wooden Cut Machines in B2B?
The evolution of wooden cut machines has significantly shaped the woodworking industry, particularly in the B2B sector. Historically, woodworking relied heavily on manual labor and rudimentary tools, which limited precision and scalability. The introduction of mechanized tools in the early 20th century revolutionized the sector, paving the way for more consistent and efficient production methods.
The advent of CNC technology in the late 20th century marked a pivotal moment, allowing for complex designs to be executed with unmatched precision. This technological leap not only enhanced product quality but also reduced waste, aligning with the increasing emphasis on sustainability.
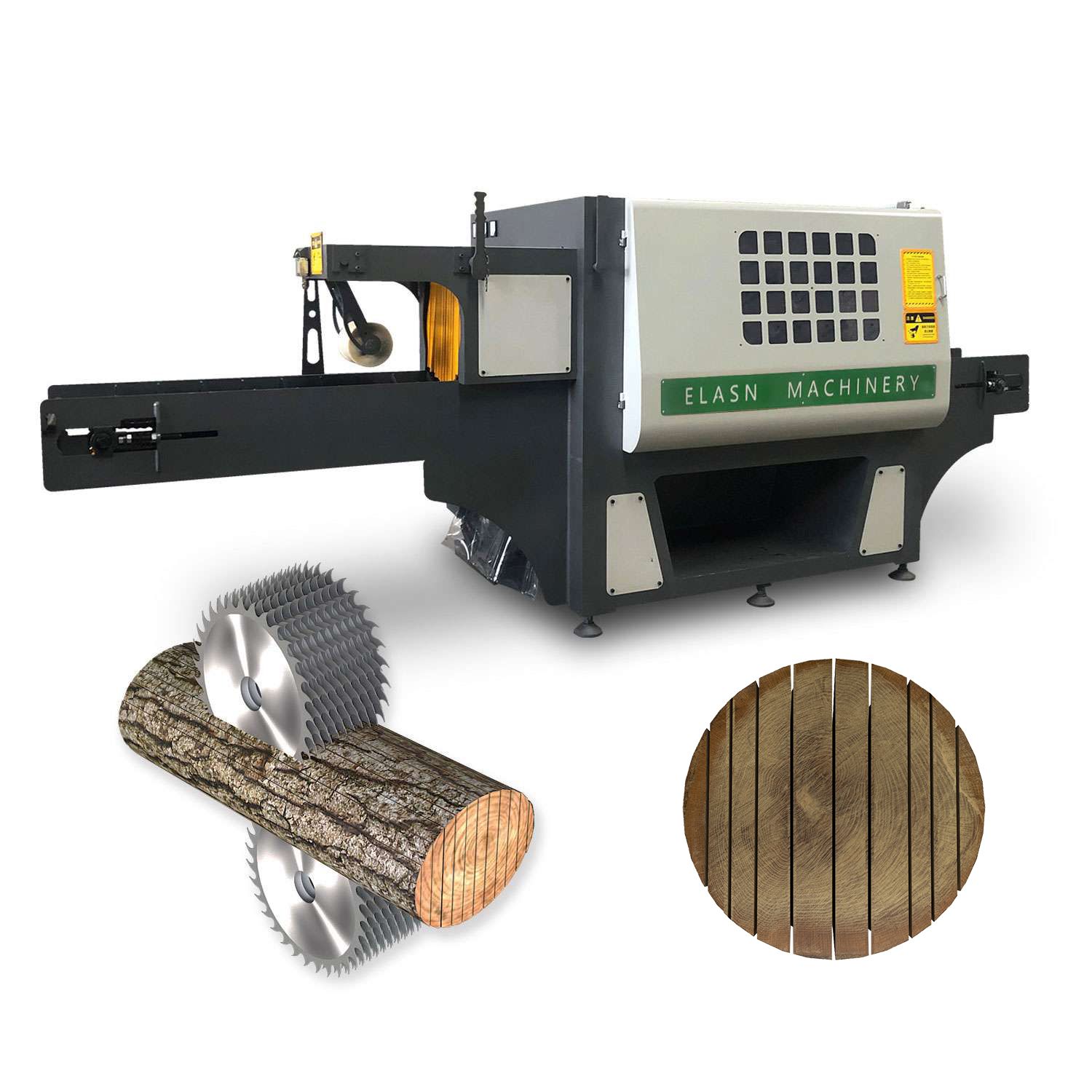

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
In recent years, the integration of laser cutting technology has further transformed the landscape, enabling intricate designs and faster processing times. As the industry continues to evolve, understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and the importance of selecting machines that meet contemporary demands for efficiency, sustainability, and customization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wooden cut machine
-
How do I choose the right wooden cut machine for my business?
Choosing the right wooden cut machine involves assessing your specific needs, such as the types of wood you will be processing and the intricacy of designs you aim to create. Consider the machine’s cutting speed, power, and precision, as well as the size of the work area. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s versatility—whether it can also engrave—and its compatibility with various materials like plywood, MDF, and hardwoods. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers or manufacturers to understand the technical specifications that best suit your production requirements. -
What is the best laser cutting technology for wood?
The best laser cutting technology for wood typically involves CO2 lasers due to their efficiency in cutting and engraving various wood types. They provide high-quality cuts with minimal burn marks and can handle both softwoods and hardwoods effectively. When selecting a machine, look for features such as adjustable power settings, a robust cooling system, and a precise positioning mechanism. These features ensure optimal performance and longevity, making CO2 lasers a preferred choice for businesses engaged in wood processing. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for wooden cut machines?
When vetting suppliers for wooden cut machines, prioritize their experience and reputation in the industry. Check for certifications and compliance with international quality standards, as well as customer reviews and case studies. Inquire about their manufacturing processes and after-sales support, including maintenance services and availability of spare parts. Additionally, assess their ability to provide customization options that meet your specific production needs, as well as their responsiveness and communication style during the negotiation phase. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for wooden cut machines?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for wooden cut machines can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the machine. Generally, MOQs may range from one unit for smaller, custom orders to several units for bulk purchases, particularly with established manufacturers. It’s essential to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies, as negotiating lower MOQs may be possible for first-time buyers or long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a wooden cut machine internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of wooden cut machines typically include options such as a deposit upfront (often 30% to 50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or escrow services for added security. Be sure to clarify the accepted payment methods, such as bank transfers, PayPal, or credit cards, and consider the impact of currency fluctuations on your transaction. Establishing clear payment terms helps ensure a smooth transaction and builds trust with your supplier. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my wooden cut machine?
To ensure quality assurance for your wooden cut machine, request detailed specifications and certifications from the supplier. Consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible, or ask for video demonstrations of the machine in operation. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s QA processes, including testing procedures and warranty policies. Establishing a solid communication channel with the supplier can facilitate ongoing support and troubleshooting, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a wooden cut machine?
When importing a wooden cut machine, logistics considerations include understanding shipping options, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Determine whether the supplier offers freight services or if you will need to arrange for a freight forwarder. Evaluate shipping costs and insurance options to protect your investment during transit. Additionally, be aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply, and ensure that all necessary documentation is in order to avoid delays in customs clearance. -
Can I customize my wooden cut machine to fit specific production needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for wooden cut machines to cater to specific production needs. Customizations can include adjustments in cutting area size, power output, and additional features like advanced cooling systems or software integration for design flexibility. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers, and don’t hesitate to request prototypes or samples if necessary. Customized solutions can enhance operational efficiency and ensure that the machine aligns perfectly with your business objectives.
Top 4 Wooden Cut Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wattsan – 6090 LT Wood Laser Cutting Machine
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Wattsan offers a range of wood laser cutting machines, including the 6090 LT model with a work area of 900 x 600 mm, tube power of 80-90 W, and a maximum engraving speed of 700 mm. The dimensions of the machine are 1490x1030x670 mm, plus an additional 315 mm if on wheels. Key features include a robust frame construction to reduce vibration, a precise positioning system with three-phase drives, hig…
2. CNC Router – Precision Cutting Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The user is looking for a cutting machine that can achieve precision similar to a laser cutter without leaving burn marks. They are working with 3/32 inch thick basswood and require the ability to cut complex shapes. Suggestions from the community include CNC routers, water jet cutting (with caution regarding moisture), and craft machines like Cricut or Silhouette for cutting craft foam. A scroll …
3. Robotime – Wood Laser Cutting Machine
Domain: robotimeonline.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Best Wood Laser Cutting Machine for Crafts: Advantages include precision, consistency, speed (up to 600m/s), flexibility, versatility (can cut and engrave various materials), waste reduction, contactless cutting, and reduced need for finishing. Common uses include wooden signs, keychains, jewelry, Christmas ornaments, wooden toys, and organizers. Factors to consider when selecting a machine includ…
4. Opt Lasers – XT8 45W Plug&Play Laser Kit
Domain: optlasers.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Opt Lasers offers two main laser wood cutters: 1. XT8 45W Plug&Play Laser Kit for All CNC Machines – Specs: 45W Optical Power, HD 125DPI 180um spot, max wood cutting thickness 20mm (¾”); Best For: CO2-like Ultra High Speed Cutting and Engraving, Thick Materials Cutting. Price: $1,299.00. 2. XT-50 6W Plug&Play Laser Kit for All CNC Machines – Specs: 6W Optical Power, Ultra HD 550DPI 45um spot, max …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wooden cut machine
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of wooden cut machines offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the technology behind laser cutting—such as the benefits of CO2 lasers for precision and efficiency—companies can make informed decisions that enhance their production capabilities and product quality. The ability to process various wood types, from softwoods to MDF, opens up diverse opportunities for creating marketable products, ranging from decorative items to functional components.
Investing in high-quality machinery not only ensures reliability and longevity but also supports sustainable practices in woodworking. As businesses look to innovate and expand, the importance of sourcing the right equipment cannot be overstated.
Moving forward, companies should explore partnerships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers to leverage the latest advancements in wood cutting technology. Embrace the potential of laser cutting to elevate your product offerings and meet the growing demands of your market. Start your sourcing journey today to capitalize on the benefits of modern woodworking solutions!

Illustrative image related to wooden cut machine
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.