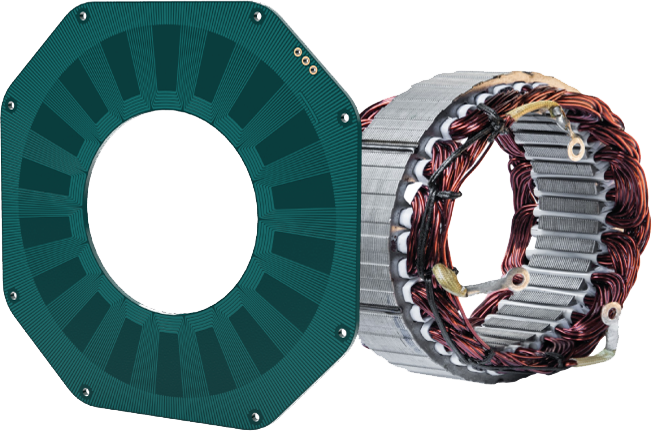
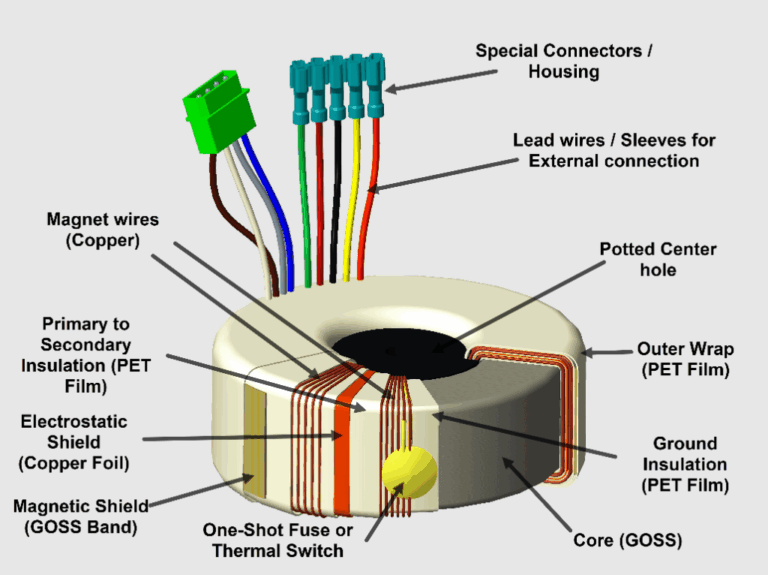
What Is The Function Of The Stator: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is the function of the stator
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, understanding the function of the stator is critical for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations and enhance energy efficiency. As the cornerstone of electric motors, the stator plays a pivotal role in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, making it essential for various applications ranging from HVAC systems to industrial machinery. However, sourcing high-quality stators that meet specific performance requirements can be challenging, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics vary significantly.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of stator functionality, exploring different types, applications, and the latest technological advancements. It also addresses key considerations for supplier vetting, cost analysis, and maintenance requirements, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By providing actionable strategies and best practices, this guide empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the global market effectively. Whether you are based in Brazil, Vietnam, or any other emerging market, understanding the critical role of the stator will enable you to enhance operational efficiency and drive sustainable growth within your organization.
Understanding what is the function of the stator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Stator | Utilizes alternating current, creates a rotating magnetic field | HVAC systems, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, robust; Cons: Less efficient under variable loads. |
| Permanent Magnet Stator | Uses permanent magnets for magnetic field generation | Electric vehicles, robotics | Pros: High efficiency, compact size; Cons: Higher initial costs. |
| Synchronous Stator | Operates at synchronous speed with constant frequency | Power generation, synchronous motors | Pros: Stable operation, precise speed control; Cons: Requires complex control systems. |
| DC Stator | Comprises a cylindrical armature with coils for magnetic interaction | Automotive applications, small motors | Pros: Simple design, effective for low-speed applications; Cons: Limited to DC applications. |
| Switched Reluctance Stator | Features variable reluctance to create magnetic fields | Electric drives, industrial pumps | Pros: High torque density, simple construction; Cons: Noisy operation, requires advanced control strategies. |
What Are the Characteristics of Induction Stators?
Induction stators are primarily used in HVAC systems and various industrial machinery. They generate a rotating magnetic field through alternating current, which induces motion in the rotor. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness and robustness of these stators, especially in environments where variable loads are common. However, their efficiency may drop under such conditions, making them less suitable for applications requiring consistent high performance.
How Do Permanent Magnet Stators Differ in Application?
Permanent magnet stators leverage the power of permanent magnets to produce a magnetic field, offering high efficiency and compactness. They are widely used in electric vehicles and robotics, where space and energy efficiency are paramount. While the initial investment may be higher compared to induction stators, the long-term savings in energy consumption and performance can justify the cost for B2B buyers looking for sustainable solutions.
What Advantages Do Synchronous Stators Provide?
Synchronous stators are designed to operate at a constant speed, making them ideal for power generation and synchronous motor applications. Their ability to maintain precise speed control enhances operational stability. However, the complexity of the control systems required can be a drawback for some buyers. Companies must weigh the benefits of stable operation against the potential challenges in system integration and maintenance.
What Are the Key Features of DC Stators?
DC stators consist of a cylindrical armature with coils that interact magnetically, making them suitable for automotive applications and small motors. Their simple design allows for effective performance in low-speed applications. Buyers should note that while they are easy to implement, DC stators are limited to direct current applications, which may restrict their versatility in diverse operational environments.
Why Consider Switched Reluctance Stators?
Switched reluctance stators utilize variable reluctance to create magnetic fields, finding applications in electric drives and industrial pumps. Their high torque density and simple construction are significant advantages for manufacturers seeking efficient solutions. However, potential buyers should be aware of the noise associated with these systems and the need for advanced control strategies to ensure optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of what is the function of the stator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is the function of the stator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| HVAC | Stators in electric motors for HVAC systems | Enhanced energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Compliance with local energy regulations and standards |
| Data Centers | Stators in cooling fan motors for data centers | Improved cooling efficiency and reduced energy consumption | Reliability and performance under high thermal loads |
| Manufacturing | Stators in industrial machinery motors | Increased productivity and reduced downtime | Availability of replacement parts and service support |
| Automotive | Stators in electric vehicle motors | Improved performance and energy savings | Compatibility with various vehicle models and regulations |
| Renewable Energy | Stators in wind turbine generators | Higher energy conversion efficiency | Durability in harsh environmental conditions |
How is the Stator Used in HVAC Systems and What Problems Does It Solve?
In HVAC systems, the stator plays a crucial role in electric motors that drive fans and compressors. By generating a magnetic field, the stator enables efficient energy conversion, which is essential for optimal air circulation and temperature control. For businesses, this translates into lower energy costs and improved system reliability. International buyers should consider energy efficiency ratings and compliance with local standards when sourcing HVAC motors, ensuring they meet regional regulations and operational demands.
What Role Does the Stator Play in Data Center Operations?
In data centers, stators are integral to the motors that power cooling systems. These cooling fan motors utilize stators to maintain consistent airflow, crucial for preventing overheating of servers and equipment. By optimizing cooling performance, businesses can significantly cut down on energy consumption, a critical factor given that cooling accounts for a substantial portion of data center energy use. Buyers should prioritize sourcing high-performance motors that can operate reliably in high-temperature environments to ensure continuous operation.
Why is the Stator Important in Manufacturing Machinery?
In the manufacturing sector, stators are essential components in the electric motors that drive various machinery. Their ability to create a stable magnetic field allows for precise control of motor speed and torque, enhancing operational efficiency. This leads to increased productivity and minimized downtime, which are vital for maintaining competitive advantage. When sourcing motors, manufacturers should consider the availability of technical support and the quality of components to ensure longevity and reliability.
How Does the Stator Impact Automotive Electric Motors?
For the automotive industry, particularly in electric vehicles, the stator is a key component of electric motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical power. An efficient stator design contributes to improved vehicle performance and energy savings, essential for meeting consumer expectations and regulatory requirements. Buyers should focus on sourcing motors that align with specific vehicle models and performance standards, ensuring compatibility and efficiency.
What is the Significance of the Stator in Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines, the stator is vital for converting kinetic energy from wind into electrical energy. A well-designed stator enhances energy conversion efficiency, making renewable sources more viable and cost-effective. International buyers in this sector should consider the durability of materials and design, ensuring that stators can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is the function of the stator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Role of the Stator in Motor Efficiency
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in manufacturing and industrial sectors, often struggle to grasp the critical function of the stator in electric motors. This lack of understanding can lead to poor purchasing decisions, such as opting for lower-quality motors that do not meet operational demands. For instance, a company that relies on HVAC systems may choose an inefficient motor, resulting in increased energy costs and frequent breakdowns due to inadequate cooling capacity. This not only impacts operational efficiency but also affects overall production output and profitability.
The Solution: To effectively address this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize education about the stator’s role in motor efficiency. When sourcing motors, it is essential to request detailed specifications on the stator design, including materials used and construction quality. Buyers should look for motors with laminated steel stators that enhance magnetic efficiency, which directly impacts energy consumption and performance. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who can provide insights into how stator configurations affect motor performance will help buyers make informed decisions. Regular training sessions and workshops with suppliers can further enhance understanding and ensure that the team is well-versed in selecting the right motors for their applications.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Installation and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: After purchasing electric motors, many companies face challenges during the installation and maintenance phases, particularly regarding the stator’s fixed position. Improper installation can lead to misalignment with the rotor, causing inefficient operation and increased wear on both components. Furthermore, lack of knowledge about the stator’s cooling needs can result in overheating issues, leading to costly downtimes and repairs. These challenges can be particularly daunting for businesses in regions with limited access to technical support or training resources.
The Solution: To overcome installation and maintenance challenges, B2B buyers should ensure that they work closely with suppliers who provide comprehensive installation guides and support. This includes detailed schematics that illustrate the correct alignment of the stator and rotor, as well as guidelines on ensuring adequate ventilation for cooling. Investing in training for maintenance staff on the specific requirements for stator upkeep can significantly reduce the risk of operational failures. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes checks on stator insulation and cooling efficiency can prolong the lifespan of the motor and optimize performance.
Scenario 3: Navigating Variability in Stator Types and Technologies
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter a wide array of stator types and technologies, which can create confusion when trying to determine the best fit for their specific applications. For example, a company may be unsure whether to choose a permanent magnet stator or an induction stator, leading to indecision and potential delays in procurement. This uncertainty can be particularly problematic for businesses operating in competitive markets where time-to-market is critical.
The Solution: To navigate the variability in stator types and technologies, buyers should conduct thorough research and engage with technical experts to understand the benefits and limitations of each type. Creating a matrix of requirements based on operational needs—such as torque, efficiency, and environmental conditions—can facilitate better decision-making. Buyers should also consider establishing partnerships with suppliers who offer a range of stator technologies, allowing for flexibility in sourcing and ensuring that they can meet evolving demands. By actively participating in industry forums and attending trade shows, buyers can gain insights into emerging technologies and trends, further enhancing their ability to choose the right stator for their applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is the function of the stator
When selecting materials for the stator in electric motors, it is crucial to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in stator construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Laminated Steel for Stators?
Laminated steel is the most widely used material for stators due to its excellent magnetic properties. The key properties of laminated steel include high magnetic permeability, which allows for efficient magnetic field generation, and good electrical resistance, which minimizes eddy current losses. Laminated steel can withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 150°C, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Laminated steel is durable and cost-effective, making it an ideal choice for mass production. Its magnetic efficiency contributes to improved motor performance, which is essential for applications in HVAC systems and data centers.
Cons: While laminated steel is robust, it can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precise lamination to optimize magnetic properties.
Impact on Application: Laminated steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including air and various gases, making it versatile for different motor types.
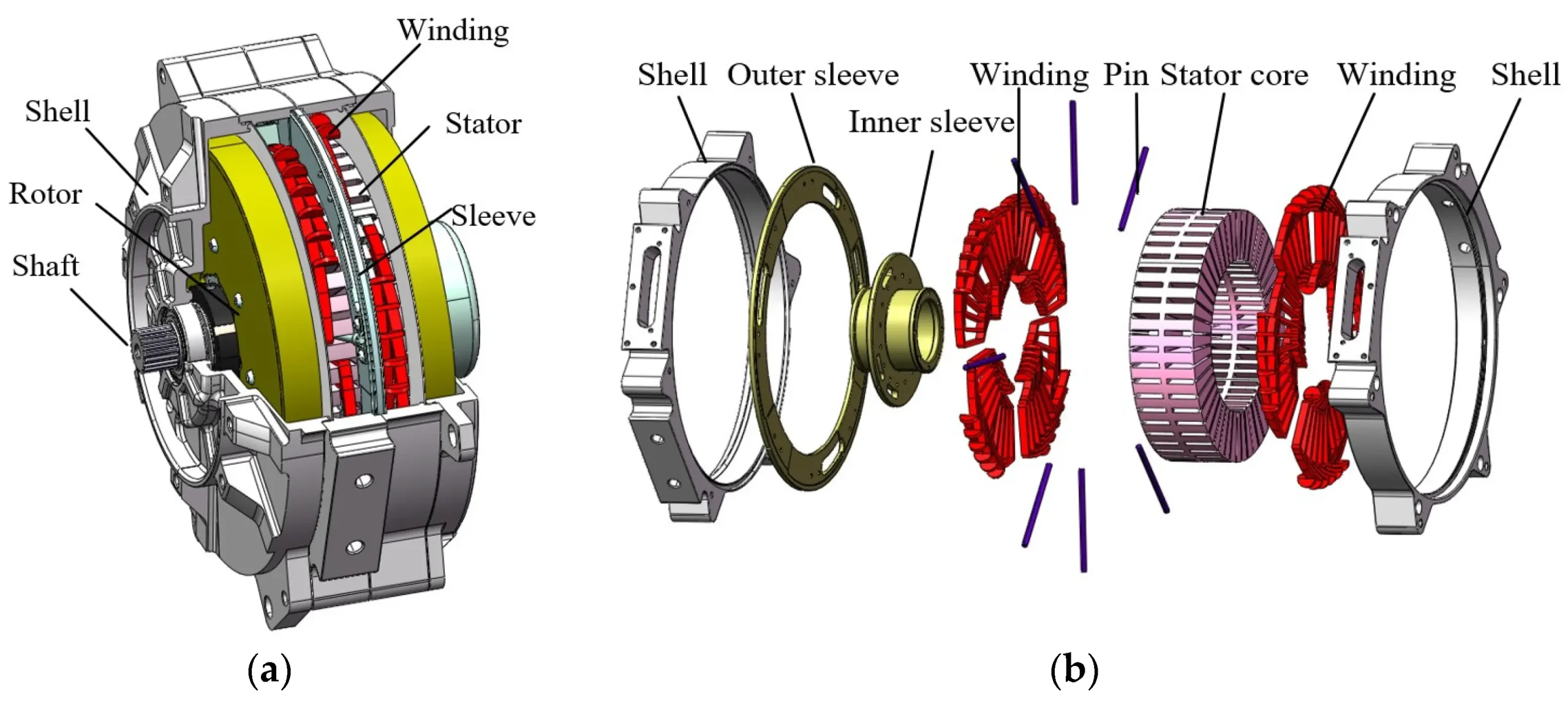
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards like ASTM or DIN for laminated steel quality. Corrosion resistance treatments may be particularly important in humid climates.
How Do Copper Windings Enhance Stator Functionality?
Copper is often used for windings in stators due to its superior electrical conductivity. Key properties include high thermal and electrical conductivity, which allows for efficient energy transfer and heat dissipation. Copper windings can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros: The high conductivity of copper results in lower energy losses, enhancing overall motor efficiency. It also has excellent fatigue resistance, contributing to the longevity of the stator.
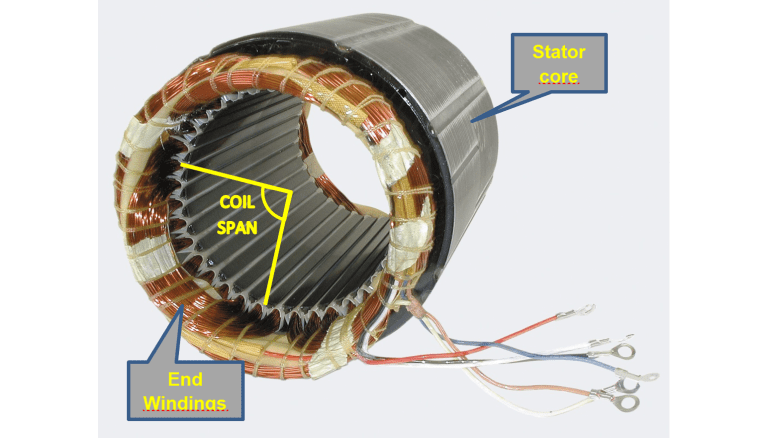
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Cons: Copper is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum, which can increase overall production costs. Additionally, copper is heavier, which may not be suitable for lightweight applications.
Impact on Application: Copper windings are ideal for applications requiring high performance, such as precision servo motors and industrial machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of fluctuations in copper prices and consider sourcing from regions with stable supply chains. Compliance with international trade regulations is also essential.
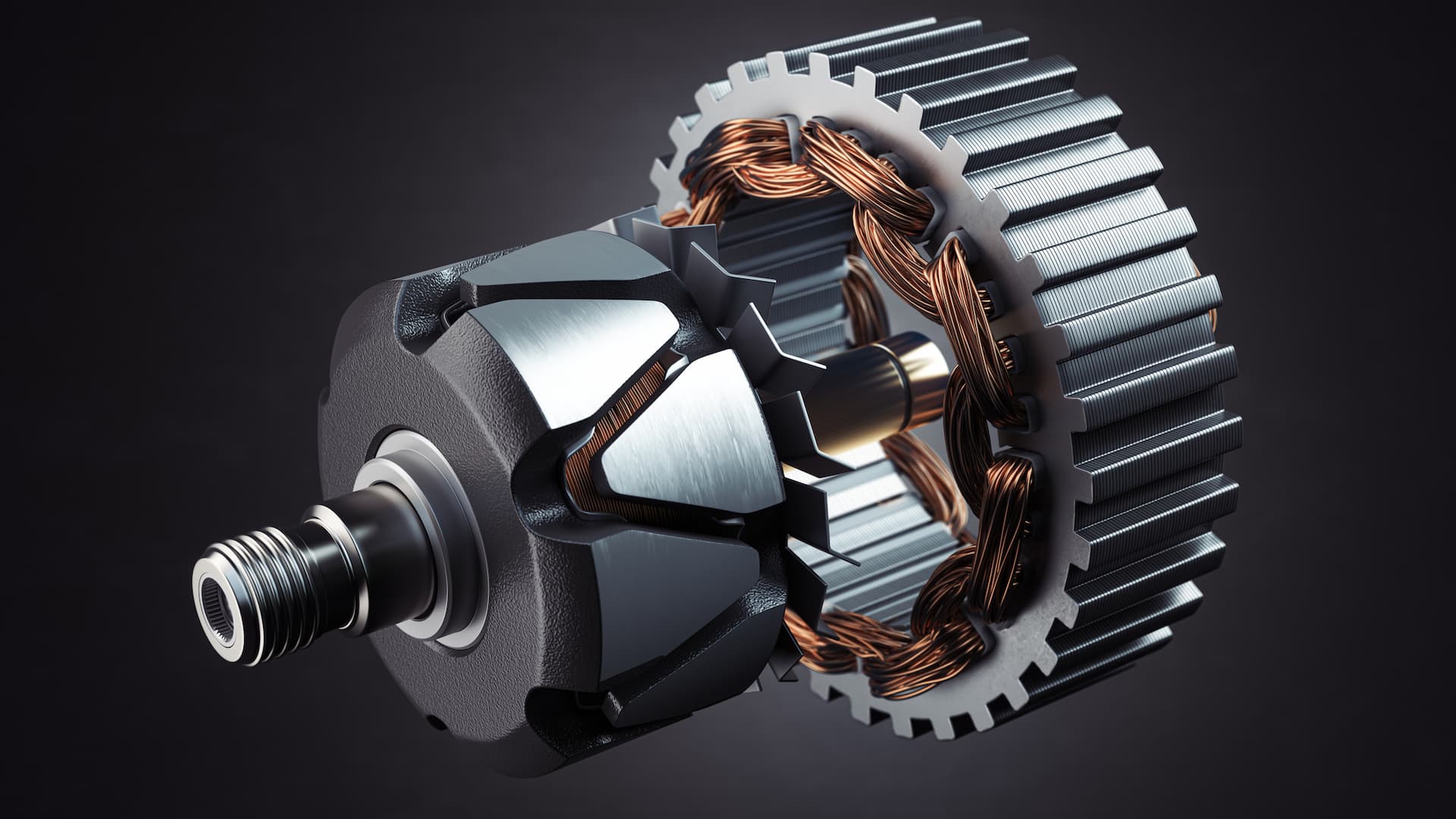
Why Is Aluminum a Popular Alternative for Stator Windings?
Aluminum is increasingly used as an alternative to copper in stator windings due to its lower cost and lighter weight. Key properties include decent electrical conductivity (about 60% that of copper) and good resistance to corrosion when properly treated.

Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects. Its lightweight nature is beneficial for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Cons: Aluminum’s lower conductivity means that it may not perform as efficiently as copper in high-demand applications. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to fatigue over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are prioritized, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards and are treated for corrosion resistance, especially in coastal regions of the Middle East.
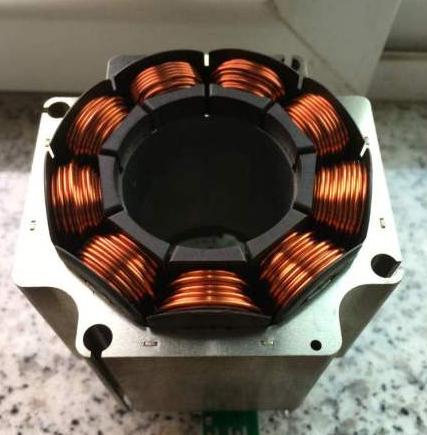
What Role Does Insulation Material Play in Stator Performance?
Insulation materials, such as epoxy resin and polyester, are crucial for the stator’s longevity and performance. Key properties include high dielectric strength and thermal stability, which protect the windings from electrical shorts and overheating.

Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Pros: High-quality insulation materials enhance the durability of the stator, allowing it to operate efficiently at higher temperatures. They also contribute to safety by preventing electrical failures.
Cons: The cost of high-performance insulation materials can be significant, impacting overall production costs. Additionally, the manufacturing process may require specialized techniques to ensure proper application.
Impact on Application: Insulation materials are essential for all types of motors, particularly in environments with high humidity or temperature fluctuations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that insulation materials comply with international standards and are suitable for their specific environmental conditions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is the function of the stator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laminated Steel | General use in electric motors | High magnetic efficiency | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Copper | High-performance motors | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Budget-sensitive applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Low |
| Insulation Material | All types of motors | Enhances durability and safety | Can increase production costs | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in stator construction, highlighting their significance in performance and longevity while addressing the specific needs of international B2B buyers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is the function of the stator
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Stators?
The manufacturing of stators involves a series of meticulous processes to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques and standards that contribute to the overall quality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Stator Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in stator manufacturing. The primary material used is laminated silicon steel, chosen for its magnetic properties and efficiency in conducting magnetic flux. The steel sheets are typically coated to prevent eddy current losses.
- Cutting and Laminating: The steel sheets are cut into specific dimensions and laminated to reduce energy losses. This process involves stacking multiple thin sheets to form the stator core.
- Coating: After cutting, the sheets undergo a coating process to enhance their electrical insulation properties. This is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of the stator.
What Techniques Are Used in Stator Forming?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired stator configuration.
- Stamping: The laminated sheets are stamped into slots where the windings will be placed. This is often done using high-precision dies to ensure consistent dimensions and minimize material waste.
- Winding: After stamping, copper wire is wound into the slots to create coils. Techniques such as automatic winding machines are commonly employed to enhance accuracy and speed.
How Is the Stator Assembled?
Once the components are formed, the next step is assembly.
- Core Assembly: The laminated core is first assembled, ensuring that all pieces fit together perfectly to maintain structural integrity.
- Coil Insertion: The wound coils are then inserted into the stator core. This step requires careful handling to prevent damage to the coils and ensure proper alignment.
- Connection: Electrical connections are made, and insulation is applied to prevent short circuits. Proper soldering techniques are essential to maintain connection integrity.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Stator Production?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the durability and performance of the stators.
- Insulation Treatment: After assembly, the stator undergoes insulation treatment to protect against environmental factors. This may involve varnishing or resin encapsulation to ensure a robust protective layer.
- Final Assembly: Additional components such as end caps and mounting brackets are attached to complete the stator.
- Painting and Labeling: Finally, the stator is painted to provide a protective coating and labeled for identification, including specifications and compliance standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Stator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of stator manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Various checkpoints and standards are adhered to throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Apply to Stator Manufacturing?
Manufacturers must comply with several international standards to assure quality and safety.
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard focuses on consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established a systematic approach to managing quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking demonstrates compliance with safety and health requirements.
- API Standards: For stators used in specific industries, such as oil and gas, adhering to API standards can be crucial for ensuring reliability and safety in operational environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Stator Production?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of production.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. It involves inspecting material certifications and conducting tests on samples.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that production methods are followed, and any deviations are addressed promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the stators are fully assembled, they undergo final inspections. This includes electrical testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections for surface defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential to ensure reliability.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of suppliers provides insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. This can include reviewing their quality management systems and production facilities.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the frequency and results of inspections, as well as any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not be able to visit facilities directly.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances in quality control must be considered.
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can be crucial. Some regions may prioritize cost over quality, which can affect the final product.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations that affect manufacturing practices. Buyers should be aware of local standards and ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks of damage or quality degradation. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping protocols to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for stators are intricate and vital for their performance in electric motors. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs. Engaging in thorough quality verification and establishing clear communication with suppliers can significantly enhance the procurement experience and foster long-term partnerships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is the function of the stator’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to understand the function of the stator in electric motors. A well-informed procurement process can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the machinery in which these components are utilized. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing decisions align with technical requirements and operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the stator. This includes dimensions, materials, and electrical characteristics necessary for your specific application.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify the type of motor (AC or DC) and its operational demands.
- Consider environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, that may affect the stator’s performance.
Step 2: Research Available Stator Types
Understand the different types of stators available and how they function within various motor designs. This knowledge will help you select a stator that best meets your operational needs.
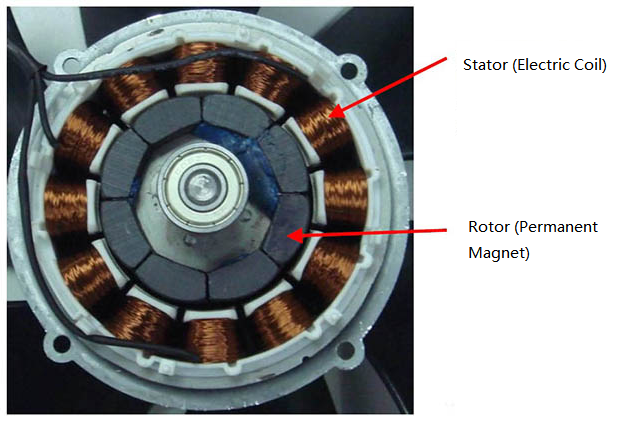
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
- Important Variants:
- Laminated Steel Stators: Common in AC motors for efficient magnetic flux.
- Cylindrical Steel Armatures: Typically found in DC machines, influencing torque generation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards and can deliver high-quality stators. A reliable supplier will have a proven track record in your specific sector.
- What to Look For:
- Request technical documentation and certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
- Seek references from other buyers in your region to gauge supplier reliability and quality.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Investigate the manufacturing processes used by your shortlisted suppliers. The quality of the stator is heavily influenced by the production techniques employed.
- Key Questions:
- What materials are used in production, and how do they impact the stator’s efficiency and durability?
- Are there advanced technologies utilized in manufacturing, such as PCB stator technology, that enhance performance?
Step 5: Consider Cost vs. Value
While cost is a significant factor, it’s essential to evaluate the value that a high-quality stator brings to your operations. Cheaper options may lead to higher long-term costs due to inefficiency or increased maintenance.
- Value Assessment:
- Analyze the expected lifespan and efficiency improvements associated with different stator options.
- Factor in energy savings and maintenance costs that high-quality stators can provide over time.
Step 6: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples or prototypes of the stators to test their performance in your specific applications. This step can help identify potential issues early in the process.
- Testing Considerations:
- Conduct performance tests to ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
- Evaluate the ease of installation and maintenance requirements.
Step 7: Finalize Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier and verified the stator’s performance, ensure that all terms and conditions are clearly outlined in the contract. This includes delivery timelines, warranty terms, and after-sales support.
- Key Elements to Include:
- Specify payment terms and any penalties for late delivery.
- Ensure there are clear guidelines for warranty claims and support services.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing stators effectively, ensuring that their procurement decisions lead to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced long-term costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is the function of the stator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Stator Sourcing?
When sourcing stators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary components influencing the cost of stators include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The materials used in stator manufacturing, typically laminated steel, copper windings, and insulation, significantly influence pricing. High-quality materials can improve performance and efficiency, but they also come at a premium. For international buyers, sourcing materials locally can mitigate costs but may affect quality and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can significantly impact the overall price. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or Brazil, may offer competitive pricing. However, the trade-off may be in the form of skill levels and production quality, making it essential to evaluate suppliers carefully.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to the factory’s operational expenses, including utilities and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers in the form of lower prices.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for customized stators. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating quotes, as they can significantly affect the overall price, particularly for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure that the stators meet specified performance standards. While implementing high-quality QC can increase costs, it is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of electric motors.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely, depending on the distance from the supplier and the shipping method chosen. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is critical for clarifying responsibilities for shipping and customs duties.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s business model. Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide insight into typical margins and help in negotiating better prices.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence the pricing of stators, which international buyers should consider for effective sourcing.
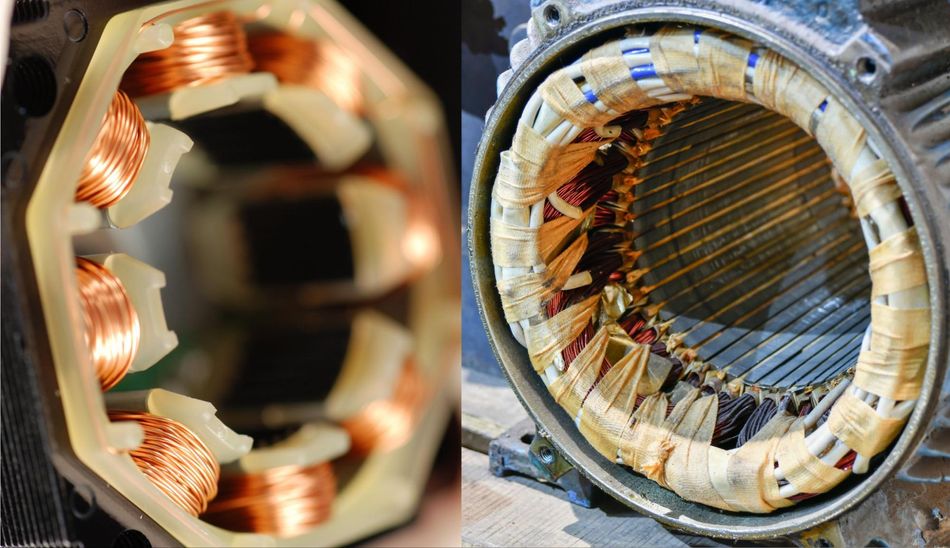
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often set minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing. Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs, but buyers must balance inventory costs against potential savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom stators designed for specific applications may lead to higher costs due to the complexity of production. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality and certified products typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in certified stators against their specific needs to ensure optimal performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and service levels, which can translate into lower risks and better performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can impact the total cost. For instance, choosing “Free On Board” (FOB) terms may lead to different pricing structures compared to “Cost, Insurance, and Freight” (CIF) terms.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International Buyers?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy efficiency, and replacement. A lower initial cost may result in higher TCO.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs and negotiate better pricing based on larger volumes.
-
Be Transparent About Requirements: Clearly communicate your needs and specifications to suppliers. This can lead to more accurate quotes and reduce the risk of unexpected costs.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Understanding regional market dynamics can give buyers leverage in negotiations. Knowledge of local supplier capabilities and competition can inform discussions around pricing and quality.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, flexibility in terms, and priority in production schedules.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is essential for international B2B buyers sourcing stators. By considering these elements, businesses can optimize their purchasing decisions and enhance their operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is the function of the stator With Other Solutions
The function of the stator in electric motors is critical for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. However, various alternative technologies can achieve similar outcomes, often with distinct advantages and disadvantages. This analysis explores these alternatives to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is The Function Of The Stator | Alternative 1: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) | Alternative 2: Induction Motors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in generating a magnetic field, supporting rotor movement. | Excellent torque and speed control; high efficiency across varying loads. | Robust performance, especially in high-torque applications. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long-term savings through efficiency. | Higher initial costs but lower operational costs due to efficiency. | Generally lower upfront costs; potential higher maintenance costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized knowledge for setup and integration. | More complex setup; needs precise alignment and control systems. | Easier to implement in existing systems; widespread familiarity. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; long lifespan if designed well. | Low maintenance; no brushes or windings to wear out. | Requires regular maintenance; wear on rotor and stator can lead to failures. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications needing precise control and efficiency, like HVAC systems. | Best for applications requiring high efficiency and variable speed control, like robotics. | Suitable for general-purpose applications and heavy machinery due to robustness. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM)?
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) offer notable benefits, such as high efficiency and excellent torque characteristics, making them ideal for applications requiring precision, like robotics and HVAC systems. Their ability to maintain performance across varying loads enhances their appeal in dynamic environments. However, PMSMs come with higher initial costs and require advanced control systems for optimal operation, which may complicate implementation.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Induction Motors?
Induction motors are widely recognized for their robustness and reliability, making them a preferred choice in heavy machinery and general-purpose applications. They typically have lower upfront costs and are easier to implement due to their straightforward design and the familiarity of technicians with their operation. However, they may require more frequent maintenance due to wear on components, and their efficiency can be lower compared to stators or PMSMs, especially under varying load conditions.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When choosing between the stator function and alternative technologies like PMSMs and induction motors, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific application requirements. Factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, ease of implementation, and maintenance capabilities will guide the decision-making process. Understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to select the solution that best aligns with their operational goals, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their systems.
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is the function of the stator
What are the Key Technical Properties of a Stator in Electric Motors?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a stator is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in electric motors. These specifications not only affect the performance of the motors but also impact cost-effectiveness and longevity. Below are critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The stator is typically made from laminated silicon steel, which minimizes energy losses due to eddy currents. The grade of this steel affects the efficiency and durability of the motor. For instance, higher-grade materials can improve magnetic properties and reduce heat generation, leading to better performance in demanding applications. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer high-quality materials to ensure long-term reliability.
2. Winding Configuration
The winding configuration of the stator, which can be either single-phase or three-phase, influences the motor’s torque and efficiency. Three-phase windings are generally preferred for industrial applications due to their superior performance and lower energy consumption. Understanding the winding configuration helps buyers select motors that meet their specific operational requirements.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the allowable variations in dimensions during the manufacturing process. High tolerance levels are critical for ensuring that the stator fits precisely with the rotor, which is essential for efficient energy transfer and minimizing wear and tear. For B2B buyers, selecting manufacturers with stringent tolerance standards is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
4. Insulation Class
The insulation class of the stator determines its ability to withstand temperature variations. Insulation classes (like Class B, F, or H) indicate the maximum temperature that the winding can handle. A higher insulation class often translates to a longer lifespan and reduced risk of failure. Buyers should assess the insulation class based on the specific environmental conditions in which the motor will operate.
5. Size and Footprint
The physical dimensions of the stator are crucial for determining the overall footprint of the motor. Smaller stators may be required in compact machinery, while larger applications may allow for bigger designs. Understanding the spatial constraints of your application helps in selecting the right motor that fits seamlessly into existing systems.
6. Cooling Mechanisms
Effective cooling is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of the stator. Various cooling methods, such as air or liquid cooling, can be employed depending on the application. Buyers should consider the cooling requirements based on the operational environment to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
What are Common Trade Terms Related to Stators?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source high-quality components, as OEM products often meet stringent industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively, especially when sourcing components for large projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing information for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and rights, reducing the risk of unexpected costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that operations run smoothly without delays.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards (like ISO or CE) indicate compliance with specific quality and safety regulations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications to ensure that the stators meet necessary industry benchmarks.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure successful procurement of electric motors and components.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is the function of the stator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends for Stators?
The global stator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electric motors across various industries, including HVAC, automotive, and industrial machinery. As the world moves towards electrification and automation, the stator’s function as a vital component in electric motors becomes even more critical. Key trends include the rise of energy-efficient and compact motor designs, which cater to modern applications like data centers and cleanroom environments. Additionally, the push for smarter motor technologies is reshaping the industry, with innovations such as PCB stators enhancing performance and energy savings.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality stators that not only meet technical specifications but also align with local energy efficiency regulations. Emerging markets are seeing a shift towards integrating advanced motor technologies to improve operational efficiency and reduce energy consumption. Buyers are advised to stay updated on technological advancements and assess suppliers based on their ability to provide innovative solutions that enhance system performance and reliability.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Stator Procurement?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the stator supply chain. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers must consider suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing emissions during production.
Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly materials in stator production can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of electric motors. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and have a clear sustainability strategy. This approach not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also appeals to end-users increasingly demanding environmentally conscious products.
What Is the Evolution of Stator Technology in the B2B Sector?
The stator has evolved significantly since the inception of electric motors, moving from simple designs to complex, highly engineered components essential for modern applications. Early stators were primarily made of solid iron, which limited efficiency and performance. The introduction of laminated steel sheets in stator construction allowed for better magnetic flux and reduced energy losses, enhancing overall motor efficiency.
In recent years, advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies have led to the development of high-performance stators that can support increased operational demands. Innovations such as the integration of smart sensors for real-time monitoring and control are paving the way for the next generation of electric motors. This evolution not only improves performance but also extends the lifespan of motors, making them more appealing to B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about these advancements will be crucial for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is the function of the stator
-
How does a stator function in an electric motor?
The stator is the stationary part of an electric motor that generates a magnetic field essential for motor operation. It consists of windings or coils that create this magnetic field when electrical current passes through them. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor, which is the moving part of the motor, enabling it to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Understanding the stator’s role is crucial for optimizing motor performance and efficiency. -
What are the different types of stators used in various motors?
Stators can vary based on the type of motor. In AC motors, the stator typically features a cylindrical shape made of laminated steel to minimize energy loss. For DC motors, stators are designed with a steel armature and pole pieces that generate the necessary magnetic field. Understanding the type of stator required for your application is important for ensuring compatibility and performance efficiency. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing stators for my business?
When sourcing stators, consider factors such as material quality, design specifications, and compatibility with existing systems. It’s also important to evaluate the manufacturer’s reputation and experience in the industry. Look for suppliers who can offer customization options to meet specific requirements and ensure compliance with international standards, particularly if you are operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
How can I verify the quality of stators from international suppliers?
To verify the quality of stators from international suppliers, request certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards, such as ISO or CE. Conduct factory audits if possible, or request samples for testing. Additionally, review customer testimonials and case studies that highlight the supplier’s reliability and product performance. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better quality assurance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for stators, and how do they affect my purchasing decisions?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between suppliers. Understanding the MOQ is essential as it impacts your inventory management and cash flow. If the MOQ is high, it may be necessary to negotiate with the supplier or explore alternative options to minimize upfront costs. Consider your production needs and storage capabilities when evaluating MOQs to ensure they align with your business strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing stators internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of stators can vary widely. Common practices include partial upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide you with sufficient security while also considering the supplier’s requirements. Ensure you understand the implications of currency fluctuations and additional fees that may arise during international transactions. -
How can logistics impact the procurement of stators from overseas suppliers?
Logistics plays a critical role in the procurement of stators, affecting delivery times, costs, and overall supply chain efficiency. It’s essential to work with reliable logistics partners who can navigate customs regulations and ensure timely delivery. Factor in shipping methods, potential tariffs, and lead times when planning your procurement strategy, especially when sourcing from regions like Europe, Africa, or South America. -
What customization options are available for stators, and how do they benefit my business?
Customization options for stators can include variations in size, winding configurations, and material types to suit specific applications. Custom stators can enhance motor efficiency, improve performance, and reduce energy consumption. Discuss your unique requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options, ensuring that the customized stators meet your operational needs and align with your business goals.
Top 4 What Is The Function Of The Stator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Area Cooling – Stator Solutions
Domain: areacooling.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: The stator is a fixed part of an electric motor that works with electrical energy to create a magnetic field. It is essential for the operation of the motor, acting as a reference point for the rotor, which is the moving part. The stator typically consists of laminated steel sheets that allow magnetic flux to pass through. It generates a rotating magnetic field and is crucial for the motor’s energ…
2. Brainly – Stator in Electric Motors
Domain: brainly.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The stator is a critical component in electric motors, primarily responsible for producing magnetic fields that interact with the rotor. This interaction is essential for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, allowing the motor to perform work. The stator generates a magnetic field through coils of wire carrying electric current, inducing movement in the rotor. It also plays a role …
3. GRWinding – Alternator Stator
Domain: grwinding.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: The alternator stator is the stationary part of an alternator responsible for generating AC voltage through electromagnetic induction. Key components include: 1. Stator Core – Made of laminated steel to minimize eddy current losses. 2. Coil Windings – Usually copper wires that produce electricity when exposed to a magnetic field. 3. Insulation – Keeps the windings safely separated to prevent short…
4. TLCLAM – Electric Motors
Domain: tlclam.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Electric motors consist of two main components: stators and rotors. Stators are stationary and produce a magnetic field when energized with alternating current (AC), while rotors are the moving parts that interact with the stator’s magnetic field to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. Stators are made from materials like iron, steel, or printed circuit boards (PCBs), and their major …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is the function of the stator
As we conclude our exploration of the stator’s function, it becomes evident that this component is integral to the efficiency and performance of electric motors. The stator generates the magnetic field essential for rotor movement, ultimately converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. For B2B buyers, understanding the significance of stator quality and design is critical; superior stators lead to improved energy efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced motor longevity.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality stators can yield substantial benefits, particularly in industries reliant on electric motors, such as HVAC, manufacturing, and renewable energy. By partnering with reputable suppliers who prioritize innovation and reliability, businesses can not only optimize their operations but also navigate fluctuating global supply chains effectively.
Illustrative image related to what is the function of the stator
Looking forward, the demand for efficient and sustainable motor solutions will continue to rise, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Now is the time for international buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to enhance their competitive edge. Engage with suppliers who are committed to technological advancements and sustainability, ensuring your business remains at the forefront of the electric motor industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.