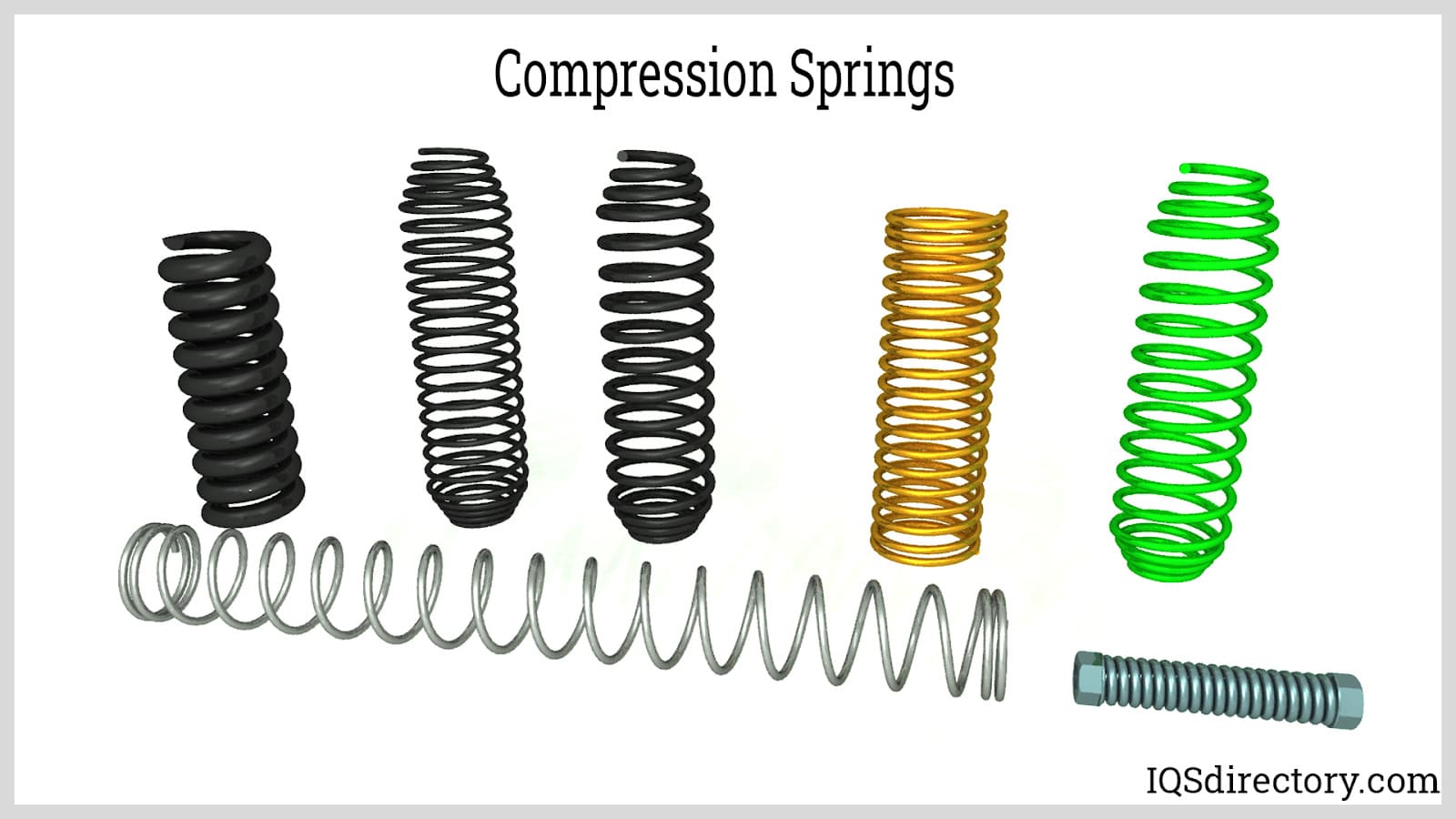
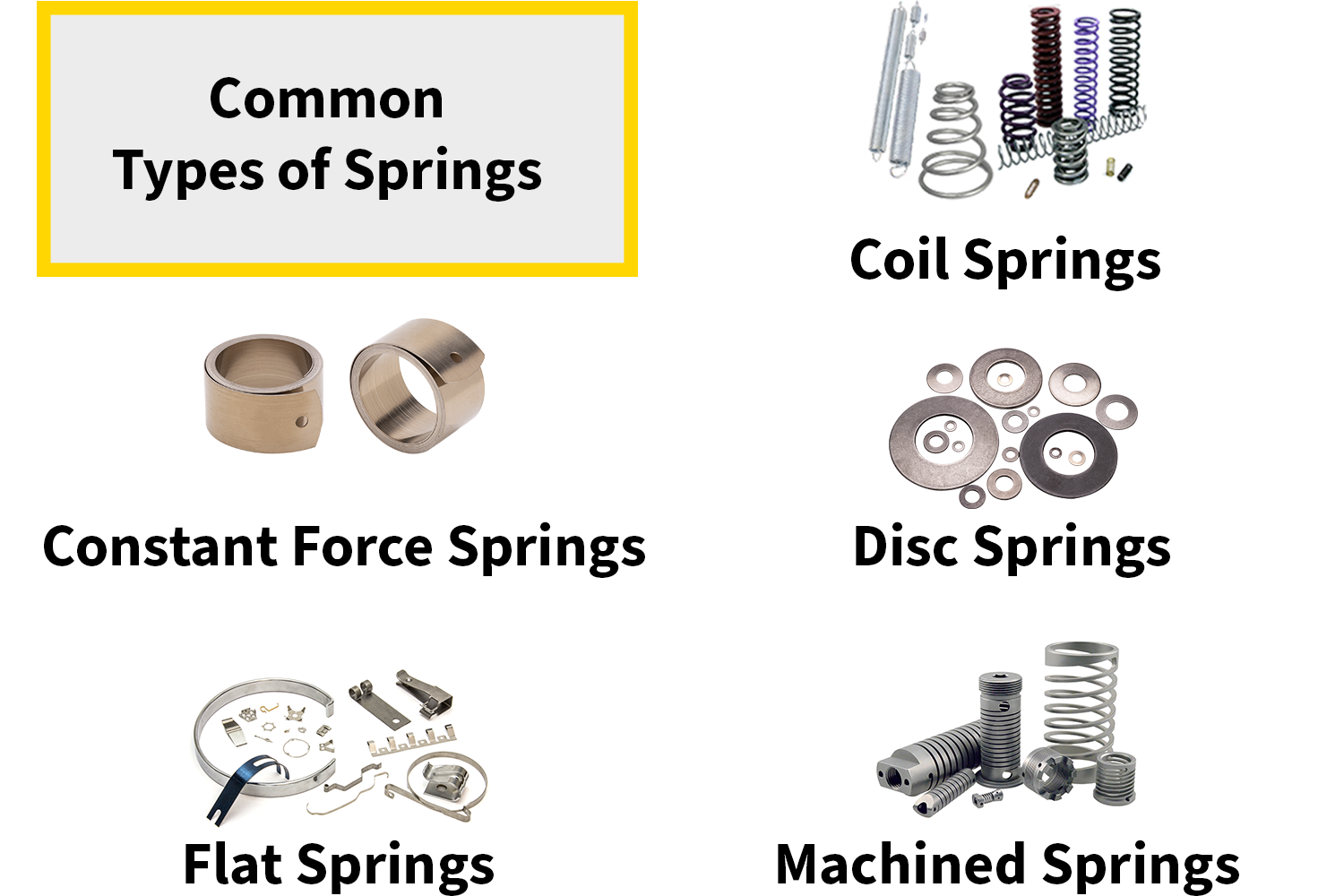
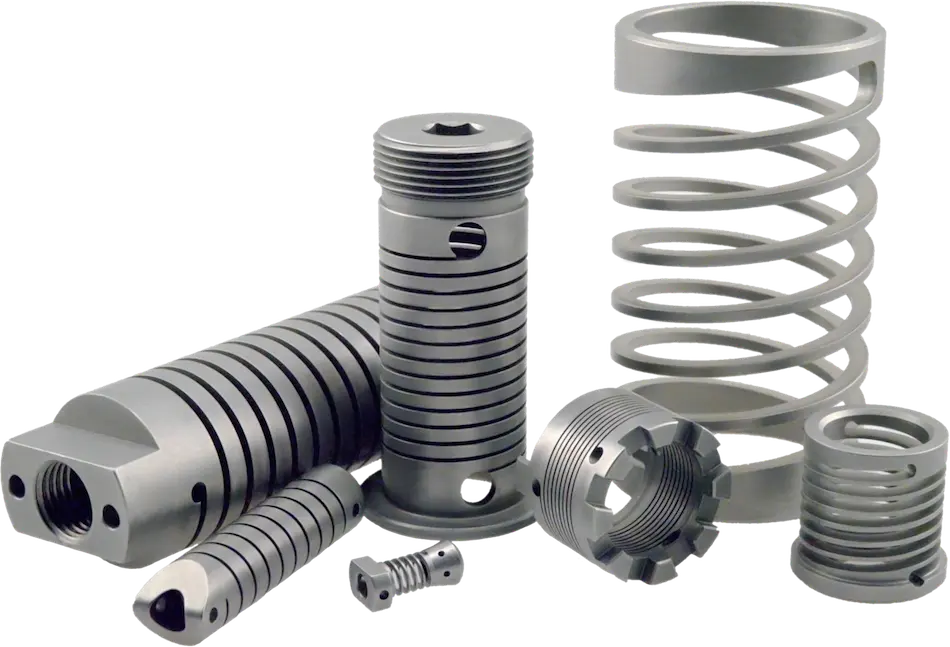
What Are Springs Made Of Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what are springs made of
In today’s global marketplace, understanding what springs are made of is crucial for B2B buyers who seek reliable components for their machinery and products. Sourcing high-quality springs can be a daunting task, especially when navigating diverse materials and manufacturing processes across different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies in selecting the right spring material that not only meets specific performance criteria but also aligns with budgetary constraints and regulatory standards.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of spring materials—ranging from high-carbon steel to brass and stainless steel—highlighting their unique properties and applications. It provides insights into the manufacturing processes, enabling buyers to appreciate how these factors influence spring performance and longevity. Additionally, the guide offers actionable advice on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the importance of quality assurance in the procurement process.
By empowering international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide serves as an essential resource for those looking to optimize their supply chains and enhance product reliability. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or manufacturing sectors, understanding the nuances of spring materials will help you achieve your operational goals while ensuring cost-effectiveness and compliance with local standards.
Understanding what are springs made of Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Music Wire | High tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance | Automotive, general industrial applications | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited corrosion resistance. |
| Oil Tempered Wire | Enhanced fatigue resistance, good performance at elevated temperatures | Aerospace, heavy machinery | Pros: Durable, suitable for high-stress environments. Cons: More expensive than standard options. |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, maintains strength in moist conditions | Food processing, marine applications | Pros: Long lifespan, hygiene-friendly. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Phosphor Bronze | Good fatigue resistance, excellent electrical conductivity | Electronics, musical instruments | Pros: Non-magnetic, resistant to corrosion. Cons: Limited load capacity compared to steel. |
| Brass | High corrosion resistance, good machinability | Plumbing, decorative applications | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, easy to work with. Cons: Lower strength than steel options. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Music Wire Springs?
Music wire springs are made from high-carbon steel, providing exceptional strength and fatigue resistance, making them suitable for a wide array of applications, especially in the automotive and general industrial sectors. Their affordability and versatility make them a preferred choice for many manufacturers. However, buyers should consider that music wire lacks corrosion resistance, which may limit its use in environments prone to moisture or harsh chemicals.
How Do Oil Tempered Wire Springs Perform in High-Stress Environments?
Oil tempered wire springs undergo a special heat treatment that enhances their fatigue resistance, making them ideal for applications in aerospace and heavy machinery where high performance under stress is crucial. These springs maintain their strength at elevated temperatures, but they come at a higher cost than standard options. When purchasing, buyers should weigh the benefits of durability and performance against the increased investment required.
Why Choose Stainless Steel Springs for Corrosion Resistance?
Stainless steel springs are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to maintain strength in moist environments, making them ideal for food processing and marine applications. While their lifespan is significantly longer than that of other materials, the initial cost is higher. B2B buyers must consider the long-term savings associated with reduced maintenance and replacement when evaluating the investment in stainless steel springs.
What Advantages Do Phosphor Bronze Springs Offer?
Phosphor bronze springs are characterized by their good fatigue resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making them particularly valuable in the electronics and musical instrument industries. Their non-magnetic properties and resistance to corrosion further enhance their appeal. However, buyers should note that these springs have a limited load capacity compared to steel options, which may restrict their use in high-load applications.
In What Scenarios are Brass Springs Most Effective?
Brass springs are notable for their high corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, often used in plumbing and decorative applications. Their ease of machinability allows for intricate designs, but they do not match the strength of steel springs. B2B buyers should consider the specific application requirements, including load-bearing needs and environmental exposure, when deciding on brass springs as a suitable option.
Key Industrial Applications of what are springs made of
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what are springs made of | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Suspension systems using high-carbon steel springs | Enhanced vehicle stability and ride comfort | Durability under high loads, resistance to fatigue |
| Aerospace | Compression springs in aircraft control systems | Improved safety and performance in critical applications | Compliance with stringent safety standards, lightweight materials |
| Industrial Machinery | Oil-tempered wire springs in conveyor systems | Increased operational efficiency and reliability | Corrosion resistance, ability to withstand heavy loads |
| Electronics | Phosphor bronze springs in connectors and switches | Reliable electrical performance and longevity | Conductivity, resistance to wear, and environmental factors |
| Medical Devices | Stainless steel springs in medical equipment | Ensured safety and hygiene in sensitive applications | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and regulatory compliance |
How Are Springs Used in the Automotive Sector and What Are the Benefits?
In the automotive industry, high-carbon steel springs are integral to suspension systems. These springs provide essential support, enhancing vehicle stability and ride comfort. By absorbing shocks and vibrations, they help maintain tire contact with the road, which is crucial for safety. International buyers should consider sourcing springs that can endure high loads and resist fatigue, ensuring long-lasting performance in various driving conditions.
What Role Do Springs Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, compression springs made from high-quality alloys are vital components in aircraft control systems. They contribute to the safety and performance of critical mechanisms, such as landing gear and throttle controls. Buyers in this sector must prioritize materials that meet stringent safety regulations and can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, ensuring reliability in demanding environments.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Why Are Springs Important in Industrial Machinery?
Oil-tempered wire springs are commonly utilized in conveyor systems within industrial machinery. These springs enhance operational efficiency by maintaining consistent tension and facilitating smooth movement. For businesses, sourcing springs with corrosion resistance and the ability to handle heavy loads is critical to prevent downtime and ensure continuous production processes, particularly in harsh working conditions.
How Do Springs Enhance Electronics Performance?
In the electronics sector, phosphor bronze springs are often used in connectors and switches. Their unique properties ensure reliable electrical performance and longevity, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent connectivity. International buyers should focus on sourcing springs that offer excellent conductivity, resistance to wear, and durability against environmental factors, ensuring the reliability of electronic devices.
What Is the Importance of Springs in Medical Devices?
Stainless steel springs are crucial in various medical devices, where safety and hygiene are paramount. These springs are used in equipment like syringes and diagnostic tools, ensuring they function correctly while maintaining biocompatibility. Buyers in the medical field must prioritize sourcing springs that meet regulatory compliance and offer corrosion resistance, safeguarding patient health and device efficacy.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what are springs made of’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Selecting the Right Material for Extreme Conditions
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the oil and gas industry is tasked with sourcing springs for downhole equipment that must withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. The buyer is overwhelmed by the variety of materials available and fears selecting the wrong one could lead to equipment failure, costly repairs, and safety hazards. The pressure to meet stringent industry standards adds to their anxiety, as any downtime could result in significant financial losses.
The Solution: To ensure the selection of appropriate spring materials for extreme conditions, buyers should focus on high-performance alloys specifically designed for such environments. Stainless steel and Inconel are excellent choices due to their high corrosion resistance and ability to retain strength at elevated temperatures. When specifying springs, buyers should consult with suppliers who offer material certifications and detailed performance data. Additionally, engaging with engineering services that specialize in downhole applications can provide insights into the best material choices based on operational conditions. Prioritize suppliers that can offer a range of heat treatments and coatings to enhance the longevity of the springs.
Scenario 2: Balancing Cost with Performance Needs
The Problem: A manufacturer in the automotive sector is struggling to balance budget constraints with the need for high-quality springs in their vehicle designs. The buyer knows that using low-cost materials could compromise the performance and safety of the vehicles, yet the pressure to reduce costs is mounting from management. This dilemma leaves them uncertain about how to achieve an optimal balance between affordability and quality.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis of different spring materials. High-carbon steel springs, such as music wire, offer a cost-effective option without sacrificing performance, especially in non-corrosive environments. Buyers should also explore the possibility of bulk purchasing to leverage discounts while ensuring they are working with reputable suppliers who understand industry standards. Furthermore, collaborating with the design team can lead to innovative solutions that reduce the amount of material needed without compromising strength. Engaging in open discussions with suppliers about potential alternatives or composite materials can also yield effective solutions that meet both performance and budgetary needs.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Scenario 3: Ensuring Consistency in Quality and Supply
The Problem: A buyer in the aerospace industry faces the challenge of inconsistent quality in the springs they are sourcing, leading to variability in product performance. This inconsistency is causing delays in production and raising concerns about compliance with safety regulations. The buyer is worried that failure to resolve this issue could jeopardize contracts with major clients and damage their reputation in the market.
The Solution: To address quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing springs from manufacturers with robust quality assurance processes in place. Implementing a vendor qualification program that includes on-site audits and performance evaluations can help ensure that suppliers consistently meet quality standards. Additionally, establishing long-term partnerships with select suppliers can lead to better communication and reliability in supply chains. Buyers should also invest in a comprehensive testing regimen for incoming materials, including tensile testing and fatigue analysis, to verify that the springs meet the specified criteria before they are integrated into the final products. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can significantly reduce the risks associated with quality inconsistency and enhance the overall reliability of their supply chain.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what are springs made of
What Are the Key Properties of Common Spring Materials?
When selecting materials for springs, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in spring manufacturing: music wire, stainless steel, oil-tempered wire, and phosphor bronze.
How Does Music Wire Perform in Spring Applications?
Key Properties: Music wire is a high-carbon steel known for its exceptional tensile strength and elasticity. It can withstand high loads and has a temperature rating of up to 200°F (93°C).

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Pros & Cons: The advantages of music wire include its cost-effectiveness and high fatigue resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive and industrial equipment. However, it is not corrosion-resistant, which limits its use in moist or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Music wire springs are ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, such as compression springs in vehicle suspensions. They are not suitable for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A228 for music wire. Additionally, they should consider the availability of high-carbon steel and its sourcing implications.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Springs?
Key Properties: Stainless steel springs are highly resistant to corrosion due to the presence of chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer. They can typically handle temperatures up to 800°F (427°C) and are suitable for various environmental conditions.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as marine or food processing industries. The downside is that stainless steel is more expensive than other materials, and manufacturing can be more complex due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel springs are commonly used in applications where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount, such as in medical devices and food processing equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like DIN 1.4310 in Germany or JIS G4305 in Japan is essential for stainless steel springs. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Why Choose Oil-Tempered Wire for Springs?
Key Properties: Oil-tempered wire is a high-carbon steel that undergoes a specific heat treatment process, enhancing its fatigue resistance. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 400°F (204°C).
Pros & Cons: This material is cost-effective and provides good performance under cyclic loading conditions. However, it may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as stainless steel, which can be a limitation in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Oil-tempered wire springs are often used in automotive and industrial applications where high strength and fatigue resistance are required, such as in suspension systems and machinery.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with ASTM A313 standards and be aware of the material’s sourcing and availability in their region.
What Role Does Phosphor Bronze Play in Spring Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Phosphor bronze is an alloy of copper, tin, and phosphorus, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue strength. It performs well in temperatures up to 300°F (149°C).
Pros & Cons: The advantages of phosphor bronze include its electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for electrical applications. However, it is generally more expensive than steel alternatives and may not be as strong under heavy loads.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Impact on Application: Phosphor bronze springs are ideal for applications in electronics and marine environments, where corrosion resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B150 is important for buyers in regions like South America, where sourcing high-quality alloys can be challenging.
Summary Table of Spring Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for what are springs made of | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Music Wire | Automotive suspension systems | High strength and fatigue resistance | Not corrosion-resistant | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Oil-Tempered Wire | Industrial machinery, automotive applications | Cost-effective and fatigue resistant | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Phosphor Bronze | Electrical applications, marine environments | Good corrosion resistance and conductivity | Generally more expensive | Medium |
This strategic guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in spring manufacturing, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what are springs made of
What Are the Key Stages in the Spring Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of springs involves several meticulous stages that ensure both the quality and performance of the final product. Each stage is essential in transforming raw materials into reliable spring components suited for various applications.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Spring Manufacturing?
The first step in spring manufacturing is the selection and preparation of materials. Springs are predominantly made from high-carbon steels, stainless steels, and alloys such as phosphor bronze and brass. High-carbon steels, known for their strength and durability, are typically used for music wire springs. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for moist or chemically aggressive environments.
Before the manufacturing process begins, the raw material is inspected for quality and consistency. This includes checking for the correct diameter, tensile strength, and any surface imperfections that could affect the spring’s performance. These checks ensure that only suitable materials are used, minimizing the risk of defects in the final product.
How Are Springs Formed During the Manufacturing Process?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming the springs. This can be achieved through various methods, including cold coiling and hot coiling.
-
Cold Coiling: This method is typically employed for thinner wires. The wire is wound around a mandrel at room temperature, allowing for precise control over the spring’s dimensions.
-
Hot Coiling: For thicker wires or bar stock, the wire is heated to increase flexibility before being wound. This method helps in creating larger springs that require greater strength. After coiling, the springs are quenched in oil or water to harden them, which also relieves any internal stresses.
The forming stage is crucial as it determines the spring’s dimensions and initial properties. Any inaccuracies at this stage can lead to performance issues later.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Spring Manufacturing?
After the springs are formed, they undergo several finishing processes to enhance their performance and durability. These processes include:

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
-
Heat Treatment: This involves heating the springs to specific temperatures and then cooling them in a controlled manner to relieve stresses and improve tensile strength.
-
Shot Peening: This technique involves bombarding the surface of the springs with small steel balls, which creates compressive stresses on the surface, significantly enhancing fatigue resistance.
-
Surface Coating: To protect against corrosion and wear, springs are often coated with materials like zinc, chromium, or rubber. This step is particularly important for springs used in harsh environments.
These finishing techniques play a vital role in ensuring that the springs meet the required performance standards and can withstand operational demands.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Spring Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the spring manufacturing process, as it ensures that the final products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look for in Spring Manufacturing?
For B2B buyers, understanding the quality standards that manufacturers adhere to is crucial. The most recognized international standard is ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure consistent product quality.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific standards such as CE marking (for compliance with European health and safety standards) and API standards (for the oil and gas industry) are also important. These certifications provide assurance that the springs are manufactured to meet specific performance and safety criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Spring Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection occurs when raw materials arrive at the facility. It ensures that the materials meet specified requirements before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections are conducted to monitor the production process and ensure compliance with specifications. This includes checking dimensions and material properties at different stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the springs are manufactured, a final inspection is performed to verify that the finished products meet all quality standards. This includes testing for tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and dimensional accuracy.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure reliability and performance.
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These audits can reveal the effectiveness of their quality management systems and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Control Reports: Buyers can ask for detailed QC reports that outline the tests conducted during production, including the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. This documentation is vital for understanding the quality assurance practices in place.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent bodies can conduct thorough inspections and tests, providing unbiased verification of the supplier’s claims.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing springs. Differences in regional manufacturing standards, material availability, and environmental conditions can affect the quality and suitability of springs for certain applications.
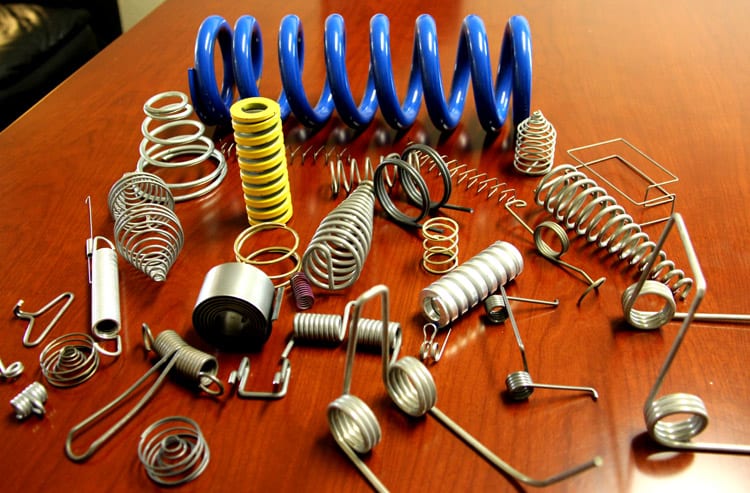

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial, as compliance can vary significantly across countries. Additionally, cultural differences may influence communication and negotiation processes regarding quality expectations.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for springs are critical factors that B2B buyers must consider when sourcing components. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification practices, buyers can ensure that they procure high-quality springs that meet their specific requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what are springs made of’
Introduction:
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to understand the materials used in spring manufacturing. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right springs for your applications, optimize performance, and minimize the risk of failure due to material inadequacies.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements of your application, including load capacity, environmental conditions, and size constraints. Understanding these specifications helps in determining the most suitable spring materials, such as high-carbon steel for strength or stainless steel for corrosion resistance. Accurate specifications ensure you procure springs that meet your operational needs and standards.
Step 2: Research Material Properties
Familiarize yourself with the different types of materials commonly used in spring manufacturing. Key materials include:
– Music Wire: Known for its high strength and versatility.
– Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance for humid or harsh environments.
– Oil Tempered Wire: Ideal for applications requiring fatigue resistance.
Understanding these properties will guide your selection process and help you match materials to specific application requirements.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it is crucial to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers who demonstrate a robust quality assurance process and have experience with your specific application needs. A reliable supplier can significantly impact the performance and durability of your springs.
Step 4: Request Material Certifications
Ensure that the materials used in the springs are certified and meet industry standards. Certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific material compliance documents, provide assurance of quality and consistency. This step is vital for maintaining product integrity and ensuring that the springs will perform as expected in their intended application.
Step 5: Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Analyze the cost versus the benefits of the springs based on the selected materials. While cheaper options might seem attractive, they can lead to higher long-term costs due to potential failures or replacements. Evaluate factors like durability, performance, and lifecycle costs to make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and operational needs.
Step 6: Inquire About Manufacturing Processes
Understanding the manufacturing processes used by your supplier can provide insight into the quality of the springs. Ask about methods such as heat treatment, shot peening, and coating, as these processes can enhance the performance and lifespan of the springs. A supplier that invests in advanced manufacturing techniques is more likely to deliver high-quality products.
Step 7: Review Testing and Quality Control Measures
Finally, ensure that the supplier has robust testing and quality control measures in place. Inquire about their testing protocols, such as fatigue testing and dimensional inspections, to confirm that the springs meet your specified requirements. A stringent quality control process can prevent issues and ensure the reliability of the springs in your applications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing springs, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and reduced operational risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what are springs made of Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Spring Manufacturing?
When sourcing springs, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers to make informed decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials typically represent a significant portion of the total cost, with choices ranging from high-carbon steel to stainless steel, each with unique pricing implications. For instance, music wire and oil-tempered wire are popular for their strength and fatigue resistance but may vary in price based on market demand and availability.
Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the spring design and the skill level required for assembly and quality checks. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America or Africa, may provide competitive pricing for standardized products, but specialized springs may still incur higher labor expenses due to the need for skilled workers.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses expenses related to the production facility, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, ultimately affecting the final price of the springs.
Tooling costs involve the initial investment in molds and machinery required to produce specific spring designs. For custom springs, these costs can be substantial but are amortized over large production runs, making it crucial to consider the minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating.
Quality control (QC) is vital in ensuring the springs meet industry standards. Rigorous QC processes can increase costs but ultimately lead to better reliability and customer satisfaction, which can justify a higher price point.
Logistics costs include transportation and warehousing, which can vary based on the shipping terms (Incoterms) and the distance from the supplier. For international buyers, understanding these costs is crucial, as they can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
Margins are influenced by the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape. Suppliers with established reputations may command higher prices but often provide better service and product reliability.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Springs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of springs, particularly for international B2B buyers. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) play a critical role; larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
Specifications and customization also impact pricing. Custom springs designed for specific applications often require more intricate manufacturing processes and can lead to higher costs compared to off-the-shelf products. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to obtain accurate quotes.
Material selection is another significant factor. High-performance materials like titanium or specialized alloys may increase costs but provide long-term benefits in durability and performance. Understanding the material properties and their suitability for specific applications is vital for making cost-effective decisions.
Quality certifications can affect pricing as well. Springs that meet industry standards or possess specific certifications may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability they provide.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Supplier factors such as reputation, location, and service levels can also influence prices. Suppliers with a strong track record may charge a premium, but the reliability and support they offer can provide long-term value.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Springs?
Negotiating effectively can lead to significant cost savings. Buyers should research the market to understand average prices and identify potential suppliers. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing and terms.
Consider discussing volume discounts and exploring flexible payment terms to ease cash flow. Additionally, being open to alternative materials or designs may lead to cost reductions without compromising quality.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial for international buyers. This includes not just the initial purchase price but also logistics, potential tariffs, and future maintenance costs. A holistic view of costs can help buyers make better sourcing decisions.
Lastly, for B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, being aware of pricing nuances related to currency fluctuations, local economic conditions, and trade agreements can enhance negotiation strategies. Always consider obtaining multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for springs can vary widely based on materials, specifications, and market conditions. It is essential for buyers to consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what are springs made of With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Springs: What Are the Options?
In the realm of mechanical design and engineering, springs are vital components utilized in a variety of applications, from automotive to consumer electronics. However, alternatives exist that can perform similar functions, often with distinct advantages. By comparing what springs are made of—primarily high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and other alloys—against alternative solutions like pneumatic systems and elastomeric materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Are Springs Made Of | Pneumatic Systems | Elastomeric Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity, fatigue resistance | Excellent for dynamic applications | Good elasticity, limited load capacity |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, variable over time | Higher installation costs, variable | Generally lower initial costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise manufacturing processes | Requires skilled installation | Easy to implement, low complexity |
| Maintenance | Moderate; periodic inspections needed | High; requires regular checks | Low; generally durable |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, automotive suspension | Robotics, manufacturing automation | Cushioning, sealing applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Pneumatic Systems: An Efficient Alternative
Pneumatic systems utilize compressed air to create movement, making them a viable alternative to traditional springs. They excel in applications requiring rapid motion and flexibility, such as robotics and assembly lines. The performance of pneumatic systems is outstanding in dynamic applications, allowing for smooth and precise control. However, the initial cost of setting up a pneumatic system can be significantly higher than that of traditional springs, and ongoing maintenance is crucial to ensure system reliability. Additionally, the need for skilled technicians for installation and upkeep can be a barrier for some businesses.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Elastomeric Materials: Flexibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Elastomeric materials, such as rubber or silicone, provide an alternative to metal springs in specific applications. They offer good elasticity and can absorb shocks, making them suitable for cushioning and sealing functions. The initial costs for elastomers are often lower compared to springs, and they are relatively easy to implement in designs. However, their load-bearing capacity is limited, and they may not perform well under high-stress conditions. Therefore, while elastomeric materials are cost-effective for certain applications, they may not be suitable for high-load scenarios where traditional springs excel.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When evaluating whether to use traditional springs or explore alternative solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific application requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and installation complexities. While springs made from high-carbon steel or stainless steel offer excellent durability and performance in high-stress environments, pneumatic systems and elastomeric materials present unique benefits that may align better with certain operational demands. By carefully considering these factors, businesses can choose the most effective solution to meet their mechanical design needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what are springs made of
What Key Technical Properties Should B2B Buyers Consider for Spring Materials?
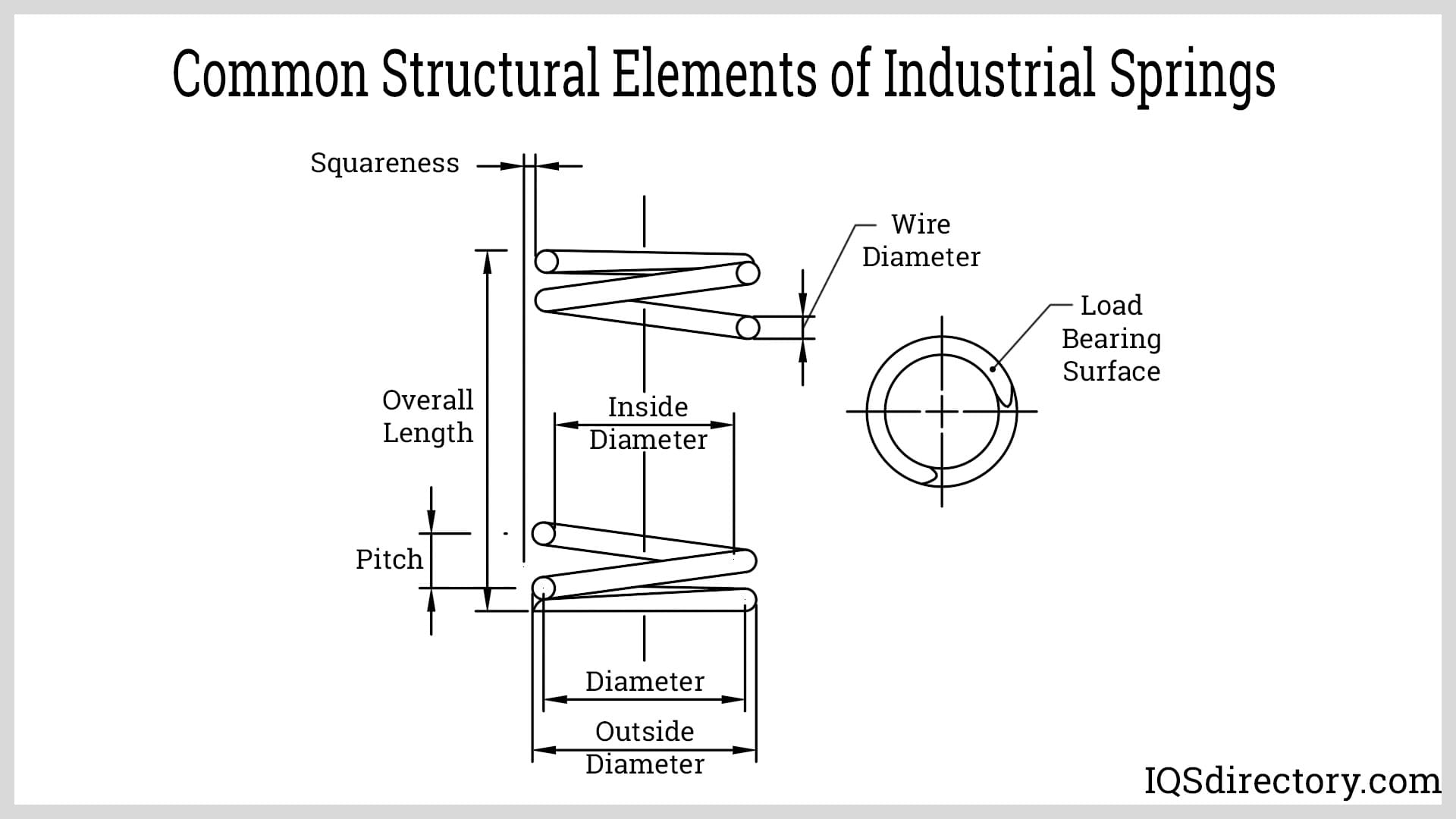
When selecting springs for industrial applications, understanding critical technical properties is essential. These specifications not only influence performance but also ensure longevity and reliability in demanding environments.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the spring’s raw material, which can significantly affect its mechanical properties. Common grades include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Each grade has unique characteristics such as tensile strength, elasticity, and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring that the spring can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions typical of its intended application.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit of variation in a spring’s dimensions and mechanical properties. Tight tolerances are critical in applications requiring precise functionality, such as automotive or aerospace components. A spring manufactured within specified tolerances ensures compatibility with other parts and reduces the risk of mechanical failure. For buyers, understanding tolerance levels is vital to avoid costly adjustments or replacements down the line.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. In spring applications, a higher yield strength indicates that the spring can handle greater loads without losing its shape. B2B buyers must consider yield strength when evaluating springs for heavy-duty applications, as it directly impacts the spring’s performance and durability.
4. Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand repeated loading cycles without failure. Springs are often subject to cyclic stresses during operation, making fatigue resistance a critical property. Materials with high fatigue resistance are particularly important in industries like automotive and aerospace, where spring failure can lead to significant safety hazards and operational downtime.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is especially important for springs used in harsh environments, such as those exposed to moisture or chemicals. Stainless steel and phosphor bronze are commonly used for their excellent corrosion-resistant properties. For B2B buyers, selecting materials with high corrosion resistance can extend the lifespan of springs and minimize maintenance costs.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Spring Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communication between buyers and suppliers.
Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are then sold under another company’s brand. In the spring industry, OEMs often require specific spring designs that meet particular performance criteria. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers ensure that the springs they source will be compatible with their products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQs can help buyers negotiate better terms and avoid excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the spring industry, issuing an RFQ enables buyers to compare options and select the best supplier based on price, lead time, and quality. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transportation. Proper knowledge of these terms can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smoother logistics.
By grasping these essential technical properties and industry terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing springs, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and reliability in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what are springs made of Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting the Springs Manufacturing Sector?
The global springs manufacturing market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. Key market drivers include the increasing demand for automation in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where springs play a crucial role in functionality and performance. Additionally, the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) is prompting manufacturers to innovate and adapt their spring designs to meet the unique requirements of these vehicles.

Illustrative image related to what are springs made of
Emerging B2B sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital procurement platforms that facilitate easier access to suppliers and enable buyers to evaluate options based on material specifications, pricing, and lead times. This is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where access to a wide range of suppliers is essential for competitive sourcing. Furthermore, as global supply chains become increasingly interconnected, buyers are advised to consider not only the cost but also the reliability and quality of suppliers, particularly in the context of geopolitical shifts and economic fluctuations.
Another trend is the growing emphasis on customization, where manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements. This trend is particularly beneficial for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where industries demand high-quality, specialized spring solutions that can withstand rigorous operational conditions.
How Does Sustainability Influence Material Choices in the Springs Sector?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the springs manufacturing sector, as environmental impacts and ethical sourcing practices gain prominence. The production of springs typically involves materials that can have significant ecological footprints, particularly metals derived from mining activities. As a result, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing waste during the manufacturing process.
Ethical supply chains are also crucial, as companies face pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to ensure that their sourcing practices do not exploit labor or harm the environment. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of ‘green’ materials—like recycled stainless steel or eco-friendly coatings—are becoming important factors in supplier evaluations.
Moreover, the rise of circular economy principles is influencing material choices, encouraging manufacturers to design springs that can be easily recycled at the end of their lifecycle. This not only reduces waste but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers looking for sustainable solutions.
What Is the Historical Context of Springs Manufacturing?
The evolution of spring manufacturing can be traced back to ancient times, where simple metal coils were used for various mechanical purposes. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as advances in metallurgy and mass production techniques enabled the manufacture of springs in larger quantities and with greater precision.
Throughout the 20th century, the development of specialized materials—such as high-carbon steels and alloys—enhanced the performance and durability of springs, catering to an expanding range of applications in industries like automotive and aerospace. Today, the focus is not only on functionality but also on customization and sustainability, reflecting the changing needs of global markets.
This historical perspective highlights the importance of understanding material properties and manufacturing processes, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions in the dynamic springs sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what are springs made of
-
How do I choose the right material for my spring application?
Selecting the appropriate material for your spring depends on several factors, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and application specifics. Common materials include high-carbon steel for strength and durability, stainless steel for corrosion resistance, and specialty alloys for high-temperature environments. Assess the operational conditions your spring will face, such as moisture, temperature, and load cycles, to make an informed choice. Consulting with a spring manufacturer can also provide insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What is the best spring material for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, chrome silicon and chrome vanadium springs are ideal choices. These materials maintain strength and elasticity at elevated temperatures, making them suitable for automotive and industrial applications where heat is a factor. Additionally, Inconel and other nickel-based alloys can be used for extreme conditions. It’s crucial to evaluate the temperature range and potential stress factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the spring in its intended environment. -
How can I ensure the quality of springs sourced internationally?
To ensure high-quality springs from international suppliers, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Check for certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples for testing and inspect their manufacturing processes, including material sourcing and production techniques. Establish clear quality assurance protocols, including testing for fatigue resistance and dimensional accuracy, to mitigate risks associated with international sourcing. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for spring materials?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and are influenced by the type of spring and material required. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. For custom springs, the MOQ may be higher due to the specialized manufacturing processes involved. Always discuss your specific needs with the supplier to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your production schedule and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing springs?
Payment terms for sourcing springs can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, but upfront deposits may be required, especially for custom orders. Some suppliers offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing your order, as this can impact your cash flow and budgeting for projects. -
How can I customize springs for my specific application?
Customization of springs involves specifying dimensions, material types, and mechanical properties tailored to your application. Most manufacturers offer design consultations to help you determine the best spring design based on load requirements, space constraints, and environmental conditions. Providing detailed specifications and engaging in discussions about your application will facilitate the customization process and ensure the springs meet your exact needs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing springs?
Logistics plays a critical role in the timely delivery of springs, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. Consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that could affect delivery times and costs. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding shipping timelines and tracking information. Additionally, consider warehousing options if you require just-in-time inventory management to streamline production processes. -
How do I assess the environmental impact of spring materials?
Assessing the environmental impact of spring materials involves examining the sourcing, manufacturing, and disposal processes. Opt for suppliers who prioritize sustainability by using recycled materials or environmentally friendly manufacturing practices. Inquire about the lifecycle analysis of the materials used and their recyclability. Choosing springs made from sustainable materials not only reduces environmental impact but can also enhance your brand’s reputation in eco-conscious markets.
Top 5 What Are Springs Made Of Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Century Spring – Spring Materials & Types
Domain: centuryspring.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Century Spring offers a variety of spring materials and types, including compression springs, extension springs, torsion springs, tapered springs, die springs, disc springs, and custom springs. Key materials include high-carbon spring steels, stainless steel (specifically 316 stainless steel), and alloy steels. 316 stainless steel springs are noted for their medical and food-grade quality, featuri…
2. Lee Spring – Spring Materials
Domain: leespring.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Lee Spring offers a variety of spring materials including High Carbon Steels, Alloy Steels, Stainless Steels, Copper Alloys, and Composite materials. Key materials include: 1. High Carbon Steels: Music Wire, Hard Drawn MB, Oil Tempered MB. 2. Alloy Steels: Oil Tempered Chrome Vanadium, Oil Tempered Chrome Silicon. 3. Stainless Steels: Stainless Steel 302, 304, 316, 17-7 PH. 4. Copper Alloys: Phosp…
3. European Springs – Spring Materials
Domain: europeansprings.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Materials used for springs include: 1. Steel Springs: Low-Alloy Steel, Cold Formed Steel, Oil Tempered Steel, Bainitic Hardened Steel, Stainless Steel. 2. Other Alloys: Hastelloy, Elgiloy, Nimonic, Inconel, Beryllium Copper, Phosphor Bronze. 3. Pressings Materials: Steel, Beryllium Copper, Copper Alloy, Nickel Alloy, Aluminium, Brass, Melinex. 4. Manufacturing capabilities include precision stampi…
4. Tevema – Stainless and Carbon Steel Springs
Domain: tevema.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Springs: Pros – Corrosion Resistance, High Strength, Aesthetically Pleasing, Longevity; Cons – Higher Cost, Magnetic Properties. Carbon Steel Springs: Pros – Cost-Effective, High Strength, Wide Availability; Cons – Susceptibility to Corrosion, Limited Heat Resistance. Alloy Steel Springs: Pros – High Strength, Corrosion Resistance, Versatility; Cons – Higher Cost, Limited Availabil…
5. Industrial Springs – Precision Coil Springs
Domain: wired.com
Registered: 1992 (33 years)
Introduction: Springs are manufactured by Industrial Springs, which produces springs ranging from the thickness of a hair to the thickness of an arm. The manufacturing process involves placing a coil of carbon spring or stainless steel onto a former to shape it, grinding the top and bottom flat for stability, and tempering the springs by heating them to 920°C, cooling them in quenching oil, and reheating to 450…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what are springs made of
In the world of springs, material selection is paramount for ensuring performance, longevity, and reliability across diverse applications. Key materials such as music wire, stainless steel, and phosphor bronze each offer unique properties tailored to specific operational environments. By understanding the characteristics and applications of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and budget constraints.
Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in optimizing supply chains and ensuring that businesses obtain high-quality springs that meet stringent specifications. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for customized spring solutions will grow. Buyers are encouraged to collaborate closely with reputable manufacturers to leverage insights into material innovation and manufacturing processes.
Looking ahead, the emphasis on sustainable sourcing and advanced materials will shape the future of spring production. Companies that prioritize these aspects will not only enhance their operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem. For international buyers, now is the time to engage with suppliers who can provide the expertise and support necessary to navigate this dynamic landscape effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.