Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Vacuum Tower Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vacuum tower
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, sourcing a vacuum tower that meets the specific needs of your operations can be a daunting challenge. With the increasing demand for efficient crude oil processing and the complexities introduced by heavier crude slates, international B2B buyers must navigate a multifaceted market landscape. This comprehensive guide addresses the diverse types and applications of vacuum towers, providing crucial insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and operational efficiencies.
As you delve into this guide, you will discover actionable strategies for selecting the right vacuum tower tailored to your unique operational requirements. From understanding the nuances of deep cut operations to evaluating the latest technological advancements in structured packing, our guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. We also highlight regional considerations and supplier profiles, particularly beneficial for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Vietnam and Germany.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge presented in this guide, you can confidently engage with suppliers, optimize your procurement processes, and ultimately enhance your refinery’s performance. The insights provided here are designed to help you streamline your operations, improve yield, and reduce costs, ensuring your investment in a vacuum tower yields substantial returns.
Understanding vacuum tower Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Vacuum Tower | Standard design utilizing trays or random packing | Crude oil refining | Pros: Simple design, lower capital costs. Cons: Lower efficiency in heavy feed processing. |
| Deep Cut Vacuum Tower | Optimized for higher gas oil yields with structured packing | Heavy crude processing | Pros: Increased yield, better profitability. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex operation. |
| High-Pressure Vacuum Tower | Designed to operate at higher pressures for specific feeds | Specialty chemical production | Pros: Enhanced separation efficiency. Cons: Increased operational complexity, maintenance demands. |
| Batch Vacuum Tower | Operates in batch mode for flexibility in product types | Small-scale refining | Pros: Versatile, tailored production. Cons: Inefficient for large-scale operations. |
| Continuous Vacuum Tower | Operates continuously for high throughput | Large-scale oil refining | Pros: High efficiency, consistent output. Cons: Significant capital investment, less flexibility. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Conventional Vacuum Towers?
Conventional vacuum towers are the backbone of many refineries, typically employing trays or random packing for separation. They are designed to operate at lower pressures, making them suitable for processing lighter crude oils. B2B buyers should consider their simplicity and lower capital costs, which make them an attractive option for initial setups. However, their efficiency diminishes when handling heavier crude types, which are becoming increasingly prevalent in global markets.
How Do Deep Cut Vacuum Towers Enhance Refinery Operations?
Deep cut vacuum towers utilize advanced structured packing to maximize gas oil yields while reducing residue production. By operating at higher cut points, they allow refiners to extract more valuable products from heavier crude feeds, leading to significant economic benefits. Buyers interested in optimizing their operations should weigh the initial investment against potential long-term gains in profitability and efficiency. However, they must also be prepared for the complexities of operating such advanced systems.
What Are the Advantages of High-Pressure Vacuum Towers?
High-pressure vacuum towers are engineered to handle specific feeds that require enhanced separation efficiency. They are ideal for specialty chemical production, where precise control over the distillation process is critical. Buyers should consider the operational complexities and maintenance requirements that come with these systems. While they offer superior performance, the higher operational pressures can lead to increased risks and costs.

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
When Should Buyers Consider Batch Vacuum Towers?
Batch vacuum towers are ideal for operations that require flexibility in product types and smaller scale production. They allow for tailored processing, making them suitable for niche markets or pilot plants. However, buyers should be aware that while they provide versatility, batch systems are often less efficient for large-scale operations. This trade-off must be carefully evaluated against production needs and market demands.
What Are the Benefits of Continuous Vacuum Towers for Large Operations?
Continuous vacuum towers are designed for high throughput, making them the preferred choice for large-scale oil refining operations. They ensure consistent output and high efficiency, which are critical for meeting market demands. However, the significant capital investment and reduced flexibility in product types can be challenging for some buyers. Companies looking to scale operations should assess their long-term production goals to determine if a continuous system aligns with their strategic objectives.
Key Industrial Applications of vacuum tower
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vacuum tower | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas Refining | Crude oil distillation for fractionation | Increased yield of valuable products from crude oil | Compatibility with various crude types; energy efficiency |
| Petrochemicals | Production of feedstocks for chemical synthesis | Enhanced quality and quantity of feedstock production | Material compatibility; advanced technology for process efficiency |
| Heavy Industries | Recovery of heavy vacuum gas oil (HVGO) | Improved profitability through better product recovery | Equipment durability; maintenance support |
| Renewable Energy | Processing of biofuels and alternative fuels | Efficient separation of biofuel components | Adaptability to different feedstocks; regulatory compliance |
| Environmental Management | Treatment of hazardous waste through distillation | Reduction of waste volume and recovery of reusable materials | Robustness of materials; environmental impact assessments |
How is a Vacuum Tower Used in the Oil and Gas Refining Sector?
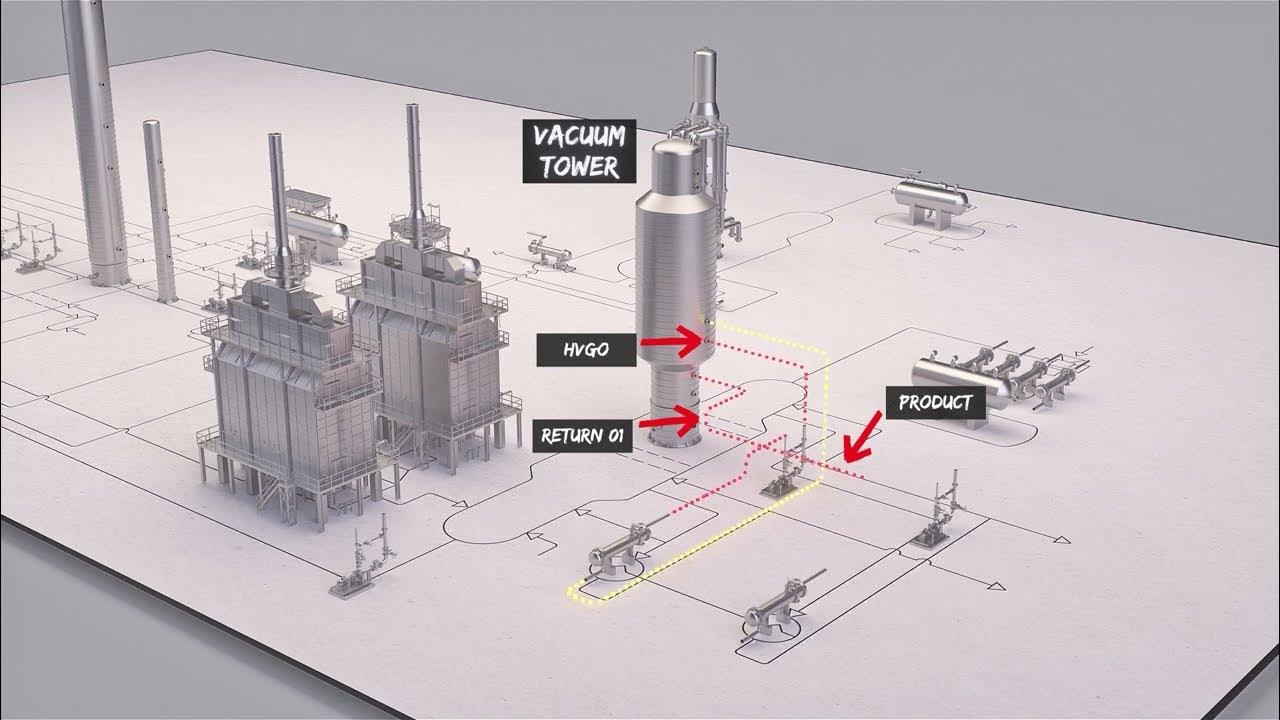
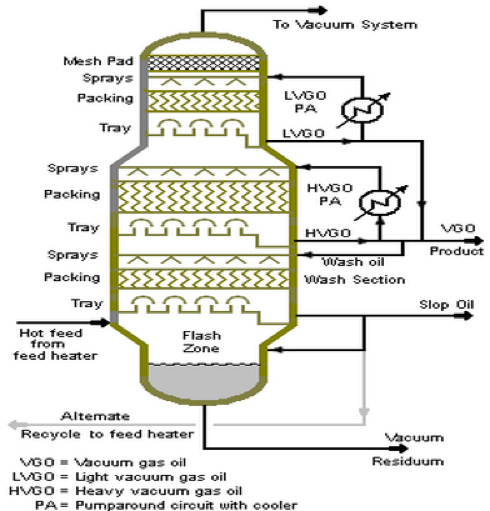
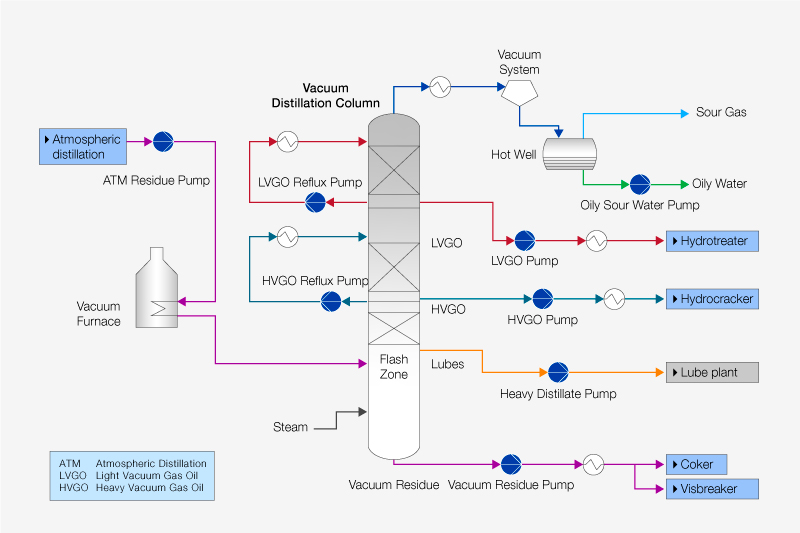
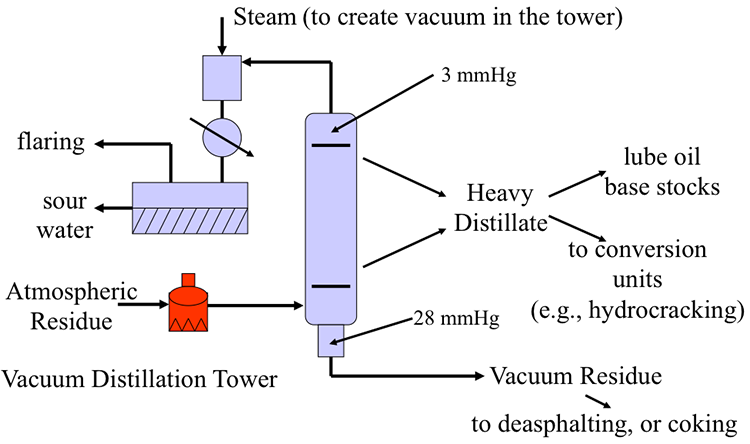
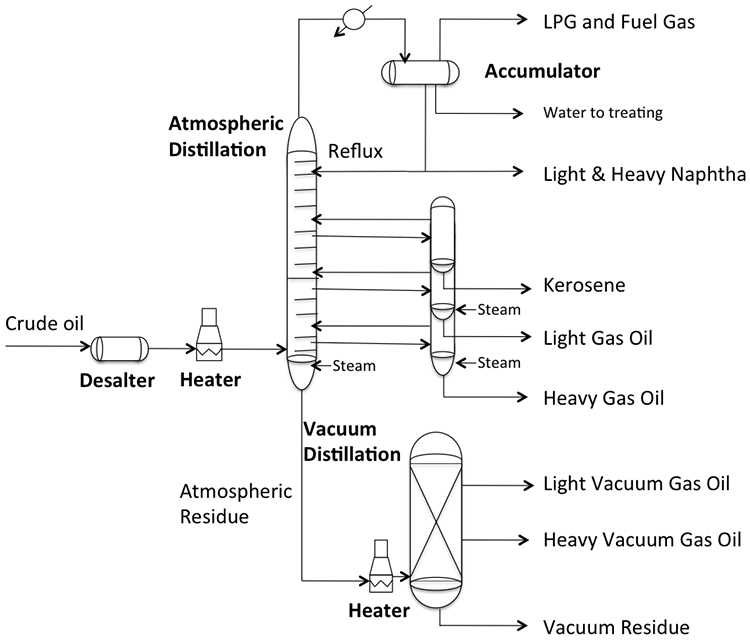
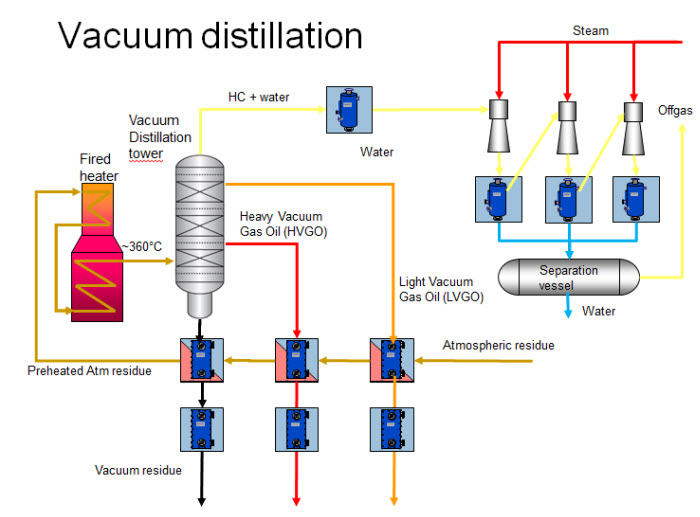
In the oil and gas refining sector, vacuum towers are crucial for distilling crude oil into various fractions. By operating under reduced pressure, these towers enable the separation of heavier fractions like vacuum gas oil (VGO) and residue. This process not only maximizes the yield of valuable products but also mitigates thermal degradation of the crude, which is particularly important given the increasing heaviness of crude oils. International buyers should consider the compatibility of vacuum towers with different crude types and ensure energy efficiency to enhance profitability.
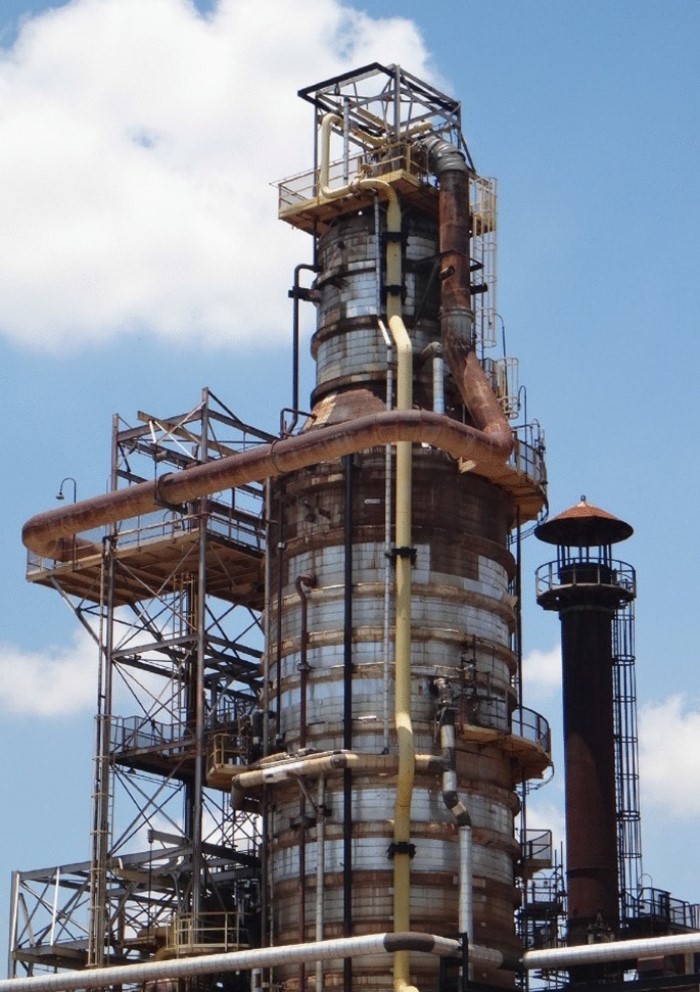

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
What Role Does a Vacuum Tower Play in Petrochemical Production?
In petrochemical manufacturing, vacuum towers are employed to produce high-quality feedstocks necessary for chemical synthesis. These feedstocks are critical for producing a wide range of chemicals, including plastics and fertilizers. The use of vacuum distillation allows for the efficient separation of lighter fractions, which can significantly enhance the quality and quantity of feedstock produced. When sourcing vacuum towers, buyers must focus on material compatibility and the technology employed to ensure process efficiency and product quality.
How Does a Vacuum Tower Benefit Heavy Industries?
Heavy industries utilize vacuum towers to recover heavy vacuum gas oil (HVGO), which is essential for various industrial applications. By optimizing the distillation process, companies can increase the profitability of their operations through better recovery rates of valuable products. This is particularly beneficial in regions with a heavy crude slate. Buyers should prioritize equipment durability and maintenance support when sourcing vacuum towers to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
In What Ways Can Vacuum Towers Support Renewable Energy Initiatives?
Vacuum towers are increasingly being adapted for the processing of biofuels and alternative fuels, allowing for the efficient separation of biofuel components. This application is vital for meeting the growing demand for sustainable energy sources. The ability to process a variety of feedstocks while maintaining high separation efficiency provides a significant advantage in the renewable energy market. Buyers should consider the adaptability of vacuum towers to different feedstocks and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
How Do Vacuum Towers Aid in Environmental Management?
In environmental management, vacuum towers are used to treat hazardous waste through distillation, effectively reducing waste volume and recovering reusable materials. This application is critical for companies looking to minimize their environmental footprint and adhere to regulatory requirements. When sourcing vacuum towers for waste treatment, businesses should assess the robustness of materials used in construction and conduct environmental impact assessments to ensure compliance with local and international standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vacuum tower’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Characterizing Heavy Crude Feed for Optimal Yield
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when characterizing heavy crude feeds that are intended for processing in vacuum towers. This issue is exacerbated when there is a lack of detailed assay data on the heaviest fractions of crude oil. Inadequate characterization can lead to inefficient operation, as estimations of gas oil recovery may be inaccurate. This results in missed economic opportunities and increased operational costs due to suboptimal processing conditions.
The Solution: To overcome this problem, buyers should invest in advanced analytical techniques that provide a more comprehensive view of the feed’s composition. This may include employing laboratory methods such as high-temperature gas chromatography or utilizing specialized software for molecular weight estimation and boiling point distribution analysis. Additionally, establishing relationships with reputable testing laboratories that focus on heavy fraction analysis can provide the necessary data for accurate simulation and modeling. By gaining a precise understanding of the crude feed, operators can optimize their vacuum tower settings for improved yield, ultimately enhancing profitability.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Operation Due to Inadequate Maintenance Practices
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the inefficiency stemming from poor maintenance practices of vacuum towers. Over time, the accumulation of residues and potential fouling of heat exchangers can reduce the efficiency of the distillation process. This not only affects the quality of the end products but can also lead to increased downtime for maintenance and repairs, thereby impacting overall production timelines and costs.
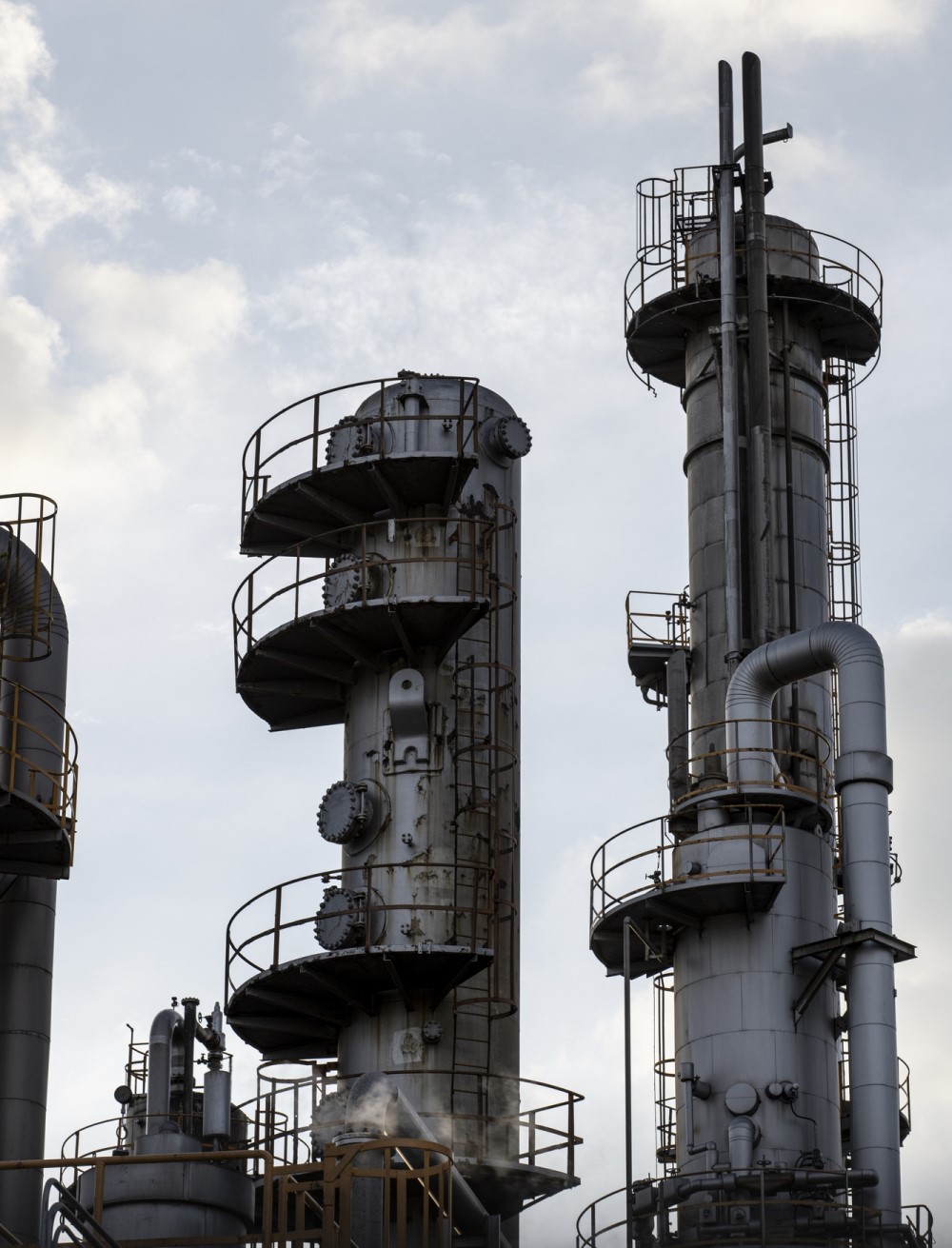

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance-related inefficiencies, buyers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular cleaning and inspection of vacuum towers and associated equipment. Utilizing predictive maintenance technologies, such as IoT sensors, can provide real-time monitoring of equipment conditions, enabling operators to identify potential issues before they escalate. Moreover, investing in training programs for personnel on best practices for equipment upkeep can ensure that maintenance is carried out effectively, reducing unexpected downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Economic Challenges in Upgrading Equipment for Deep Cut Operations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are hesitant to upgrade their vacuum towers to facilitate deep cut operations due to perceived high capital investment and uncertainty regarding return on investment (ROI). This is particularly relevant in regions with fluctuating crude prices, where the financial risk associated with such upgrades can deter decision-making. Consequently, buyers may continue to operate with outdated systems, missing out on the economic benefits of enhanced gas oil recovery.
The Solution: To address these economic concerns, buyers should conduct a thorough feasibility study that assesses the potential economic incentives of upgrading to deep cut vacuum tower operations. This study should factor in the specific characteristics of the crude being processed, potential yield improvements, and the projected ROI over time. Engaging with engineering firms that specialize in refinery upgrades can provide valuable insights and help in developing a phased implementation plan that minimizes upfront costs. Additionally, exploring financing options, such as government grants or low-interest loans for energy efficiency projects, can make the transition to more advanced operations financially viable. By approaching the upgrade strategically, buyers can enhance their production capabilities while managing financial risks effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vacuum tower
What Are the Key Materials Used in Vacuum Towers?
When selecting materials for vacuum towers, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they align with operational requirements. The choice of materials directly impacts performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in vacuum towers: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and glass-lined steel.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Vacuum Towers?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, with a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and pressure ratings suitable for many applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
Pros & Cons: The advantages of carbon steel include its low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can lead to maintenance challenges and reduced lifespan, particularly in corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is typically used in vacuum towers handling non-corrosive media. Its performance can be compromised in environments with high sulfur or chloride content.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that carbon steel components meet local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, to ensure compatibility with local environmental conditions.
What About Stainless Steel in Vacuum Towers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, with temperature ratings up to 1,500°F (815°C) and pressure ratings that vary based on specific grades.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for a wide range of media. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for vacuum towers processing corrosive materials, ensuring long-term reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the specific grade of stainless steel, as compliance with standards like EN or ASTM is critical for ensuring material performance in varying climates.
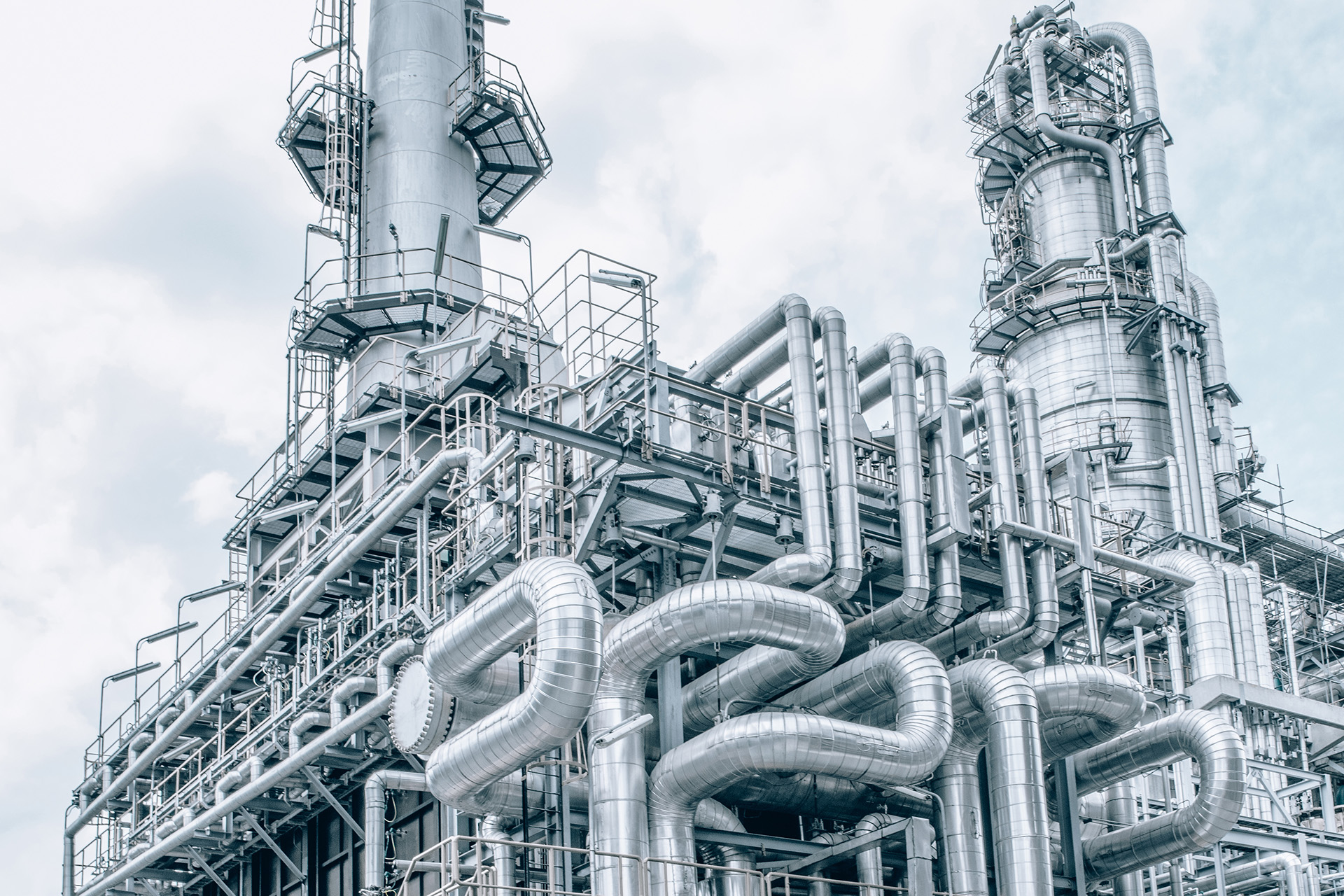

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
How Do Alloy Steels Compare in Vacuum Tower Applications?
Key Properties: Alloy steels are engineered to enhance specific properties, such as strength and corrosion resistance, with temperature ratings often exceeding 1,000°F (538°C).
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steel is its ability to handle high-stress environments, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, the cost can be significantly higher than both carbon and stainless steels, and the manufacturing process can be complex.
Impact on Application: Alloy steels are often used in vacuum towers that process heavy crude oils and other challenging materials, providing enhanced performance under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with stringent regulations, like Germany, must ensure that alloy steels meet specific standards, such as DIN 17100, to ensure compliance and reliability.
What Role Does Glass-Lined Steel Play in Vacuum Towers?
Key Properties: Glass-lined steel combines the strength of steel with the corrosion resistance of glass, with temperature ratings typically around 400°F (204°C).
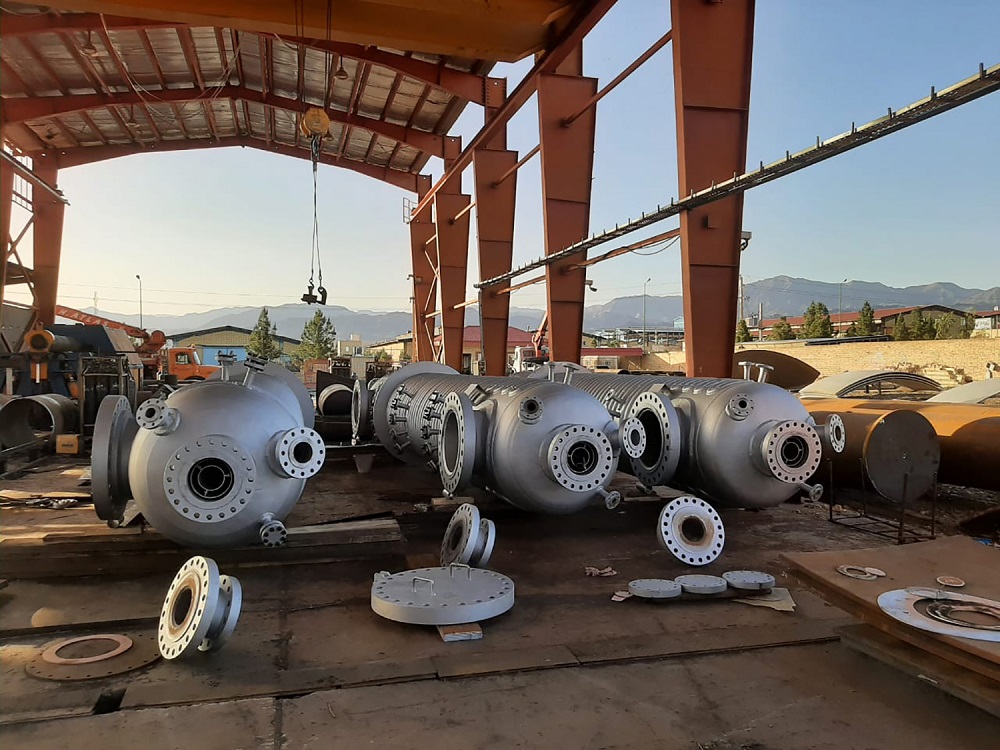

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
Pros & Cons: The main advantage is its exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. However, it is more fragile than other materials and can be prone to chipping, which may necessitate careful handling during installation.
Impact on Application: Glass-lined steel is particularly suited for vacuum towers processing aggressive chemicals, where corrosion resistance is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fragility of glass-lined steel and ensure that their suppliers provide adequate handling and installation guidelines to prevent damage.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Vacuum Towers
| Material | Typical Use Case for vacuum tower | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Non-corrosive media processing | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive media processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex mfg | High |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy-duty applications for crude oils | High strength and durability | Higher cost and complex mfg | High |
| Glass-Lined Steel | Aggressive chemical processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Fragility and risk of chipping | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for vacuum towers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vacuum tower
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Vacuum Towers?
The manufacturing process of vacuum towers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and operational requirements. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality vacuum towers.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The foundation of any vacuum tower lies in its raw materials. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialized alloys designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. Material selection is crucial, as it impacts the tower’s durability and efficiency. Suppliers typically procure materials that comply with international standards, such as ASTM or ASME specifications, ensuring quality and reliability.
Before forming, raw materials undergo rigorous testing for chemical composition and mechanical properties. This stage often includes a thorough inspection of the materials to identify any defects or inconsistencies that could affect the tower’s performance.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
The forming stage is where raw materials are transformed into specific components of the vacuum tower. This process can include techniques such as:
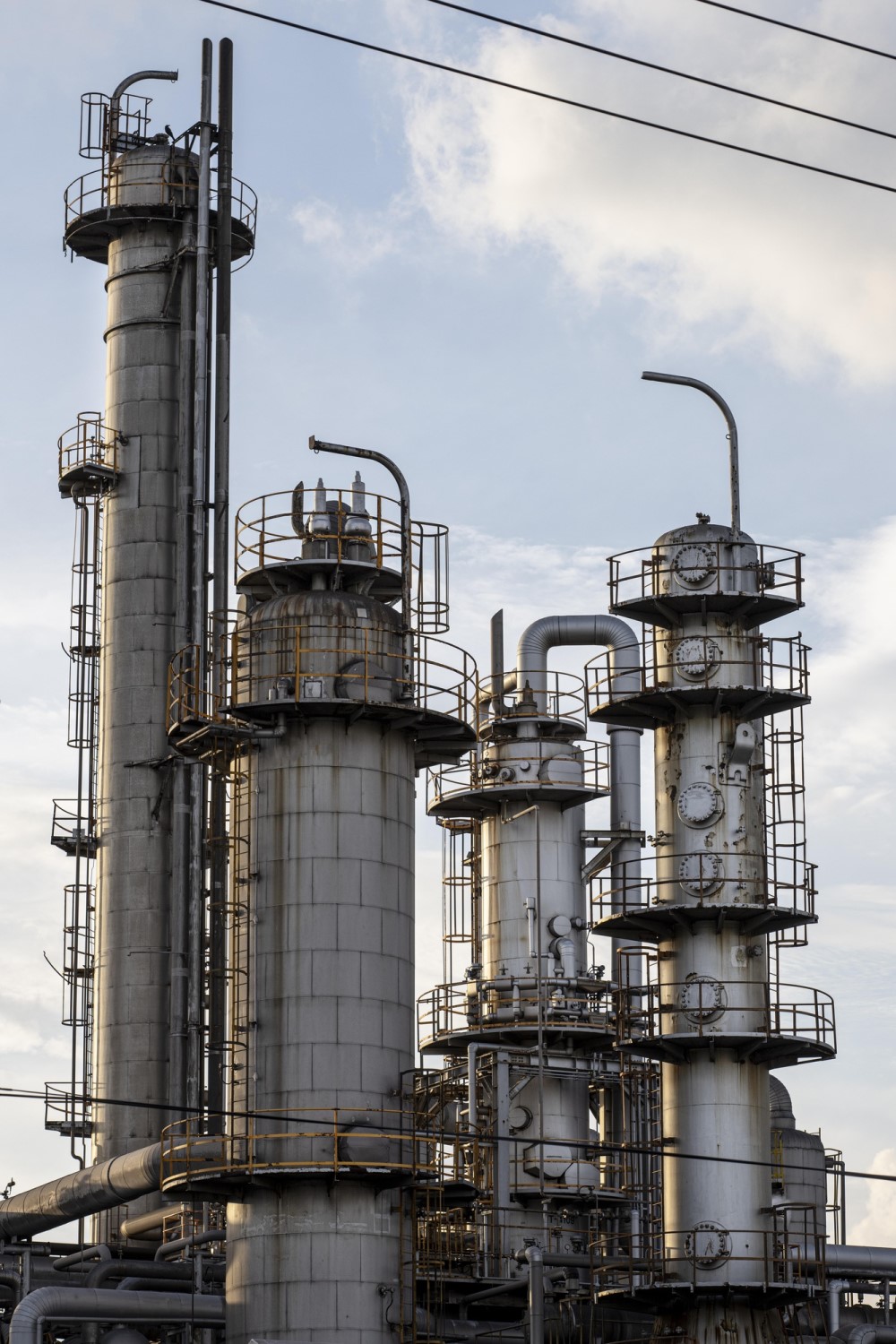

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
- Welding: Automated and manual welding methods are used to join metal sheets and pipes. High-quality welds are essential for maintaining structural integrity under vacuum conditions.
- Bending and Rolling: Metal sheets are bent or rolled into cylindrical shapes for the tower’s body, ensuring precise dimensions to optimize performance.
- Machining: Components may require machining to achieve the necessary tolerances and surface finishes. This step is critical for fittings and connections that must seal effectively.
Each of these processes must be carefully monitored to maintain quality, and any deviations can lead to inefficiencies or failures in the final product.
3. Assembly: What Are the Steps in Component Integration?
Once all components are formed, the assembly stage begins. This involves:
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller components, such as internals and trays, are assembled first. This step allows for easier handling and inspection.
- Main Assembly: The main body of the tower is constructed, integrating all sub-assemblies. Alignment and fit-up are crucial to ensure the tower operates efficiently under vacuum conditions.
- Quality Checks: At various points during assembly, quality control checks are performed to ensure components meet design specifications and regulatory requirements.
B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly processes and any relevant certifications that suppliers hold.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared?
The finishing stage enhances both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the vacuum tower. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting, painting, or coating are applied to protect against corrosion and improve durability.
- Insulation: Thermal insulation may be added to improve energy efficiency and maintain operational temperatures.
- Final Inspection: Before shipping, the tower undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all specifications and quality standards.
Buyers should verify that suppliers have established protocols for finishing processes to ensure longevity and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Practices in Vacuum Tower Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of vacuum towers. Implementing robust QA practices ensures that the final product meets or exceeds expectations.
International Standards: Which Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to recognized international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, particularly important for buyers in Europe.
- API Certifications: For those in the oil and gas sector, certifications from the American Petroleum Institute (API) ensure that products meet specific industry standards.
These certifications provide assurance of quality and reliability, which is crucial for high-stakes applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Essential Stages?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing ensures that processes remain within specified limits. This may include dimensional checks and material tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the completed vacuum tower assesses performance, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Implementing these checkpoints helps catch defects early, reducing costs and enhancing product reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that vacuum towers meet operational requirements. Common techniques include:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that the tower can withstand the operational vacuum and pressure conditions.
- Leak Testing: Identifies any leaks that could compromise performance. This is often done using helium leak detection methods.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or radiography assess the integrity of welds and materials without damaging the components.
These tests provide critical data that can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the vacuum towers.

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that a supplier’s quality control practices are robust, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
1. Conduct Supplier Audits: What Should Be Included?
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes and QC practices firsthand. Audits should focus on:
- Quality management systems and certifications.
- Equipment and technology used for manufacturing and testing.
- Employee training and qualifications in quality assurance.
2. Request Documentation: What Reports Are Essential?
Buyers should request documentation that outlines the supplier’s QA processes, including:
- Quality assurance and control manuals.
- Inspection and testing reports for previous orders.
- Certificates of compliance with international standards.
Having access to this information can help buyers make informed decisions.
3. Consider Third-Party Inspections: When Are They Necessary?
Engaging third-party inspection services provides an additional layer of assurance. Independent inspectors can verify compliance with quality standards and perform random sampling of products before shipment. This can be particularly beneficial for international buyers concerned about quality consistency.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Challenges for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing vacuum towers from suppliers in different regions, international buyers may face unique challenges:

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in business practices can impact negotiations and quality expectations. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings.
- Logistical Issues: International shipping and customs can complicate quality assurance. Buyers should work with suppliers who have experience in managing logistics to ensure timely delivery of compliant products.
By addressing these challenges proactively, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies and secure high-quality vacuum towers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vacuum tower’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a vacuum tower can be a complex process, especially for international buyers looking to optimize their refining operations. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed to streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring you acquire the right equipment for your needs while maximizing operational efficiency and economic returns.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical to ensure the vacuum tower meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as processing capacity, desired cut-points, and compatibility with existing refinery equipment. Additionally, assess the types of crude oil you will be processing, as different crudes may necessitate specific design features.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
Step 2: Conduct Market Research on Suppliers
Thorough market research allows you to identify potential suppliers that specialize in vacuum towers. Look for companies with a proven track record in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Pay attention to their experience with similar projects and the technologies they employ, which can significantly impact performance and efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Evaluate their experience with deep cut operations or specific technologies like structured packing, as these can enhance the efficiency of the vacuum tower.
- Key Questions to Ask:
- What is your experience with vacuum tower installations?
- Can you provide examples of successful projects with similar requirements?
Step 4: Assess Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with international standards and possess relevant certifications. This step is vital to mitigate risks associated with safety, environmental regulations, and operational reliability. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and any specific local standards applicable to your region.
Step 5: Request Detailed Proposals and Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline the specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. This will allow for a comprehensive comparison of offerings. Pay attention to the breakdown of costs, including installation, support, and any potential hidden fees.
- Consider Including:
- Warranty details and after-sales support.
- Training and documentation for your operational team.
Step 6: Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the equipment’s lifespan. Analyze the potential return on investment (ROI) based on projected increases in yield and efficiency from the vacuum tower.

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Terms
Once you select a supplier, ensure that all contractual terms are clear and agreed upon. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and penalties for delays or non-compliance. Engaging a legal expert familiar with international contracts can provide additional security and clarity.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for vacuum towers, ensuring they select the right equipment and supplier for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vacuum tower Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vacuum Tower Sourcing?
When sourcing vacuum towers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The total cost can be broken down into several key components:
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
-
Materials: The primary materials used in vacuum towers include stainless steel, specialized alloys, and various insulation materials. The choice of materials can significantly impact both the cost and performance. High-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both manufacturing and assembly. Skilled labor is often required for precision engineering and installation, which can increase costs. Additionally, factors such as location and labor market conditions can influence these expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which is crucial for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for producing specific components of vacuum towers. This one-time investment is often amortized over large production runs, impacting the pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure that vacuum towers meet industry standards and specifications. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the design and regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the destination, size, and weight of the vacuum tower. International shipments may incur additional costs due to tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers gauge whether the margin is reasonable based on the value offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Vacuum Tower Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of vacuum towers, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant cost savings. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, allowing buyers to reduce their per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed vacuum towers tailored to specific operational needs may come with higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the availability of quality certifications (such as ISO) can affect pricing. High-quality materials and certifications often lead to higher costs but can ensure better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may command higher prices due to perceived value and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can significantly impact the total cost. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears the responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit.
What Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips Should Buyers Consider?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and a focus on cost-efficiency can lead to better deals:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may not always represent the best long-term value.
-
Leverage Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Open communication about needs and expectations can foster collaboration and mutual benefit.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of global market trends, supply chain dynamics, and technological advancements can provide leverage in negotiations. This knowledge can help buyers make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
-
Be Clear About Specifications: Clearly outlining specifications and requirements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that suppliers provide accurate quotes, reducing the risk of unexpected costs later.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of vacuum tower sourcing requires a thorough understanding of cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. Always consult with multiple suppliers and conduct comprehensive market research to obtain the best value for your investment.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vacuum tower With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Vacuum Towers
In the competitive landscape of industrial refining and processing, choosing the right technology for distillation is crucial. While vacuum towers have long been the standard for separating heavy hydrocarbons into lighter fractions, several alternative solutions exist that may better serve specific operational needs. This analysis compares vacuum towers with two viable alternatives: Atmospheric Distillation Units (ADUs) and Continuous Fractionation Columns (CFCs). Each of these technologies has its unique strengths and weaknesses that may appeal to different buyers based on their operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Vacuum Tower | Atmospheric Distillation Unit (ADU) | Continuous Fractionation Column (CFC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High yield of heavy fractions | Limited to lighter fractions | Excellent for continuous operation |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Lower capital costs | High initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled personnel | Easier to implement | Complex setup |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Generally lower maintenance | High maintenance due to continuous operation |
| Best Use Case | Processing heavy crudes | Light crude processing | High-volume, continuous applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Atmospheric Distillation Units?
Atmospheric Distillation Units (ADUs) primarily handle lighter crude oils and are often less expensive to install than vacuum towers. They operate under atmospheric pressure, which simplifies the design and operation. However, their performance is limited when it comes to extracting heavier fractions, making them less suitable for refiners who primarily deal with heavy crudes. ADUs may also require additional downstream processing units to handle heavier components, which can increase overall complexity and costs.
How Do Continuous Fractionation Columns Compare?
Continuous Fractionation Columns (CFCs) are designed for high-volume operations and provide a consistent output of separated fractions. They excel in applications where continuous operation is essential, such as in petrochemical production. The downside is that CFCs often come with a higher initial investment and require complex setups that can be challenging to implement. Maintenance can also be demanding due to the continuous nature of the process, necessitating regular checks and repairs to ensure optimal performance.
Which Solution Should B2B Buyers Consider for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate distillation technology, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific operational needs, including the type of crude they process, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Vacuum towers are ideal for facilities handling heavy crudes requiring high yield and recovery rates. In contrast, if the focus is on lighter crudes and lower capital expenditures, ADUs may be a more suitable choice. For operations needing continuous processing and high efficiency, CFCs could provide the best return on investment despite their higher costs.
Ultimately, the decision should be informed by a thorough analysis of the operational goals, potential economic benefits, and the challenges of each technology. Understanding these aspects will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vacuum tower
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Vacuum Tower?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a vacuum tower is critical for B2B buyers involved in oil refining and petrochemical industries. Here are the key specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
Vacuum towers are typically constructed from high-grade stainless steel or carbon steel, chosen for their resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The material grade influences the tower’s durability and maintenance costs, impacting the long-term operational efficiency of the refinery. Buyers should ensure that the material meets industry standards such as ASTM or ASME to guarantee reliability. -
Design Pressure and Temperature
The design pressure and temperature specifications define the operational limits of the vacuum tower. These parameters ensure that the tower can handle the specific conditions of the distillation process without risk of failure. Understanding these specifications is crucial for buyers to match the equipment to their operational needs and avoid costly downtimes. -
Vacuum Level
The vacuum level is a critical specification that directly affects the distillation efficiency of the tower. A higher vacuum level allows for lower boiling points, enabling the separation of heavier fractions without thermal cracking. Buyers should assess the vacuum requirements based on the feedstock quality and desired output to optimize yield. -
Column Height and Diameter
The physical dimensions of the vacuum tower, including its height and diameter, influence the separation efficiency and capacity. A taller column can enhance separation but may increase construction and maintenance costs. Buyers must balance the need for efficiency with budget constraints while considering the refinery’s throughput requirements. -
Packing Type and Configuration
The type of packing used in the vacuum tower—whether structured packing or random packing—affects mass transfer efficiency and pressure drop. Structured packing, for instance, offers lower pressure drops and higher capacity, making it suitable for modern refining operations. Understanding the packing configuration helps buyers make informed decisions to maximize operational performance. -
Heat Exchanger Integration
The integration of heat exchangers within the vacuum tower system is vital for energy efficiency. Effective heat exchange reduces energy consumption by preheating feedstock and recycling heat from the process. Buyers should evaluate the design and efficiency of heat exchangers to ensure optimal performance and cost savings.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Vacuum Towers?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and procurement processes. Here are some essential terms:
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce equipment that may be marketed under another company’s brand. In the context of vacuum towers, buyers should look for reputable OEMs to ensure quality and reliability in equipment specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to assess inventory needs and budget constraints, especially when planning large-scale purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. For vacuum towers, issuing an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive offers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions based on cost and specifications. -
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and costs, facilitating smoother cross-border trade. -
CAPEX (Capital Expenditure)
CAPEX refers to the funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as equipment and buildings. Understanding CAPEX implications is critical for buyers assessing the long-term investment in vacuum towers, including installation and maintenance costs. -
O&M (Operations and Maintenance)
O&M refers to the activities necessary for the ongoing operation and upkeep of equipment. Buyers should consider O&M factors when evaluating vacuum towers, as they directly influence operational efficiency and overall lifecycle costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and make informed decisions when investing in vacuum tower technology.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vacuum tower Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Vacuum Tower Sector?
The vacuum tower sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by global economic shifts, technological advancements, and an increasing demand for efficient crude oil processing. A primary driver is the growing complexity of crude oil compositions, particularly with the rise of heavier crude grades. This complexity necessitates more advanced vacuum distillation technologies, such as deep cut vacuum towers, which enhance distillate yields while reducing operational costs. For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing and investment decisions.
Emerging trends include the integration of digital technologies like process simulation and data analytics, which allow for precise modeling of refinery operations. These technologies facilitate better decision-making regarding equipment upgrades and maintenance schedules. Moreover, as global refineries aim for higher operational efficiency, the adoption of structured packing over traditional tray designs in vacuum towers is becoming commonplace. This shift not only improves capacity but also enhances separation efficiency, making it an attractive option for refiners looking to optimize their processes.

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
In addition, the focus on sustainability is reshaping market dynamics. As regulatory pressures increase and the global shift toward cleaner energy sources accelerates, vacuum tower operations must adapt. Buyers should be aware of these trends to align their procurement strategies with suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing in the Vacuum Tower Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor in the sourcing of vacuum tower technologies and materials. The environmental impact of refinery operations is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprints. This includes the use of energy-efficient technologies and materials with lower environmental impacts.
Ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important as companies strive for transparency in their supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as obtaining certifications for green materials and processes. For instance, some manufacturers are now offering vacuum towers that are designed to minimize waste and maximize energy recovery, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is rising, as businesses recognize the value of sustainability in enhancing their brand reputation and meeting regulatory requirements. For B2B buyers, collaborating with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability not only contributes to environmental stewardship but also offers potential cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced regulatory compliance costs.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
What Is the Historical Context of Vacuum Tower Development and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of vacuum towers dates back to the early 20th century when they were first introduced in the oil refining process. Initially, these units operated on simple distillation principles, primarily designed to separate lighter fractions from heavier crude oils. Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have transformed vacuum towers into sophisticated systems capable of handling increasingly complex crude oil mixtures.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the introduction of structured packing significantly enhanced the efficiency of vacuum distillation, allowing for better separation and higher yields. This evolution is particularly relevant today as refineries face the challenge of processing heavier crude slates, which have become more prevalent due to geopolitical shifts and market demands.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of investing in modern technologies that not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with evolving market needs. By leveraging the advancements in vacuum tower technology, buyers can ensure they are well-positioned in a competitive and increasingly sustainable landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vacuum tower
-
How do I select the right vacuum tower for my refinery?
Choosing the right vacuum tower depends on several factors, including the type of crude oil processed, desired product yields, and operational efficiency. Assess your refinery’s specific needs, such as throughput capacity and the characteristics of the crude being refined. Collaborate with engineering specialists to conduct feasibility studies, which can provide insights into potential configurations and technologies, such as structured packing versus traditional trays. Additionally, consider the long-term operational costs and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and profitability. -
What are the key benefits of using a deep cut vacuum tower?
Deep cut vacuum towers offer significant advantages, including increased yields of high-value products like heavy vacuum gas oil (HVGO) and reduced production of lower-value residues. By operating at higher cut points, these towers can enhance the profitability of refining operations. They are particularly beneficial for processing heavier crudes, allowing refineries to adapt to changing feedstock characteristics. Conducting a thorough economic analysis can help determine the potential return on investment and operational efficiencies achievable through deep cut operations. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for vacuum towers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering vacuum towers that meet international standards. Request case studies or references from previous clients, particularly those with similar operational contexts. Evaluate their technical capabilities, including customization options and support services. Additionally, consider suppliers’ responsiveness to inquiries and their ability to provide after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact your long-term partnership. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering a vacuum tower?
Lead times for vacuum tower orders can vary significantly based on factors such as customization requirements and supplier capabilities. Generally, standard models may have a lead time of 16 to 24 weeks, while customized solutions can take longer, often exceeding 30 weeks. It’s essential to communicate your project timelines with suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure they can meet your deadlines. Planning for potential delays due to logistics or regulatory approvals is also crucial, especially for international shipments. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing vacuum towers?
Minimum order quantities for vacuum towers can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the equipment. Some suppliers may allow single-unit orders for standard models, while others may require bulk purchases for custom designs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Additionally, inquire about the flexibility in scaling orders, as this can impact your procurement strategy and overall project budget. -
What payment terms are common in B2B transactions for vacuum towers?
Payment terms in B2B transactions for vacuum towers typically range from 30% to 50% upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans, especially for larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow requirements and project timelines. Always review the terms of the contract carefully, including any penalties for late payments or conditions for refunds, to ensure clarity and protection for both parties. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my vacuum tower purchase?
To ensure quality assurance for your vacuum tower, select suppliers who adhere to recognized industry standards, such as ISO certifications. Request detailed specifications and quality control processes that the supplier implements during manufacturing. Additionally, consider conducting site visits or audits of the supplier’s facility to evaluate their production practices. Establish clear acceptance criteria and conduct thorough inspections upon delivery to confirm that the equipment meets the agreed-upon specifications and performance standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a vacuum tower?
When importing a vacuum tower, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations in your country. Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders who understand the complexities of transporting large industrial equipment. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations, is prepared to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in lead times for customs inspections and any potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your shipment, as these can impact overall project costs.
Top 5 Vacuum Tower Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ascent Engineering – Deep Cut Vacuum Towers
Domain: ascentengineering.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Deep cut vacuum towers are designed for the hydrocarbon and renewable processing industries, offering significant economic and operational benefits. They allow for increased gas oil yields and lower column bottoms flowrates, with a higher residue initial boiling point and greater HVGO production. The technology has evolved from trays to structured packing, improving efficiency and capacity. Deep c…
2. KECO – K-Tower with Vacuum Base
Domain: kecotabs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: KECO K-Tower with Vacuum Base and KECO Pulling Accessories
3. Goodway – CTV-1501 Cooling Tower Vacuum
Domain: goodway.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: CTV-1501 Cooling Tower Vacuum
– Input Power:
– 15 Amps, 115V, 60 Hz AC
– 15 Amps, 115V, 50 Hz AC
– 7.5 Amps, 230V, 60 Hz AC
– 7.5 Amps, 230V, 50 Hz AC
– Overview:
– Designed to remove dangerous bacteria and debris from cooling tower basins without draining the system.
– Quickly vacuums bacteria-filled slime, algae, mud, and contaminants.
– Saves time and water loss.
– Me…
4. WIKA – Advanced Temperature Measurement Systems
Domain: blog.wika.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Advanced temperature measurement systems for vacuum towers, designed to improve yield and product quality in vacuum distillation units (VDU). These systems include flexible multi-sensor setups that allow for the insertion of over 45 sensors to measure cross-sectional temperature differentials. They help detect maldistribution of vapor flow, control wash oil feed rates, and prevent coke formation, …
5. Chem Drop – Vacuum Tower Bottoms Recovery
Domain: chemdropenergy.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Chem Drop provides recovery of Vacuum Tower Bottoms (VTB) to meet client specifications, ensuring a consistent supply chain and logistics. Services include recovery, terminal purchases, pipeline shipping, barge allotments, rail car, and general transportation for various fuel oils. VTBs are the leftover bottom product of distillation, processed in cokers for upgrading into gasoline, diesel, and ga…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vacuum tower
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Vacuum Tower Market?
In the competitive landscape of refining, the strategic sourcing of vacuum towers is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and maximizing yield. Buyers should prioritize advanced technologies such as structured packing and deep cut operations, which can significantly enhance gas oil recovery while minimizing operational costs. Understanding the nuances of feed characterization and leveraging sophisticated process simulations can further inform investment decisions, ensuring alignment with market demands and economic viability.

Illustrative image related to vacuum tower
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Refinery Operations?
Investing in high-quality vacuum towers not only streamlines production but also positions your facility to adapt to the increasingly heavy crude slates prevalent in today’s market. As refineries pivot towards more efficient and environmentally sustainable practices, sourcing advanced vacuum distillation technologies will be paramount. This approach not only mitigates operational risks but also provides a pathway to capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
What Is the Future of Vacuum Tower Operations?
As the global energy landscape evolves, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should take proactive steps to integrate cutting-edge vacuum tower solutions into their operations. Embrace the future of refining by conducting feasibility studies and engaging with technology providers to unlock the full potential of your refinery’s capabilities. Now is the time to act—ensure your operations are equipped to meet the demands of tomorrow’s market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to vacuum tower