Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Types Of Alumina Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of alumina
In the ever-evolving global market, sourcing the right types of alumina can present significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With diverse applications ranging from cutting tools to electrical components, understanding the specific characteristics of various alumina grades is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the different types of alumina, including smelter grade, low soda, reactive, tabular, fused, and high-purity alumina, providing insights into their applications and benefits.
Moreover, we will explore essential factors such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends that affect procurement strategies. By equipping international buyers with in-depth knowledge about alumina types and their respective properties, this guide aims to empower businesses to select the most suitable materials for their unique needs. Whether you are a manufacturer in Nigeria seeking high-purity alumina for specialized applications or a procurement officer in Saudi Arabia looking for reliable suppliers, this comprehensive resource will serve as your go-to reference for navigating the complexities of the alumina market. As you embark on this journey, you will gain the insights necessary to enhance your supply chain efficiency and achieve your operational goals.
Understanding types of alumina Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smelter Grade | Used for aluminum metal production; requires high temperatures. | Aluminum manufacturing, metallurgical processes. | Pros: Essential for aluminum production. Cons: Not suitable for specialized applications. |
| Low Soda | Contains <0.1% soda; suitable for electronic applications. | Electronics, electrical components. | Pros: Low contamination levels enhance performance. Cons: More expensive processing methods. |
| Reactive | High purity and fine crystal size; sinters at lower temperatures. | Chemical processing, wear-resistant components. | Pros: High chemical inertness and strength. Cons: Limited availability may affect sourcing. |
| Tabular | Sintered α-alumina with large corundum crystals; high density. | Catalyst beds, grinding media. | Pros: Versatile applications; customizable sizes. Cons: Requires specific processing techniques. |
| High Purity | Purity of 99.99% and above; made from specialized processes. | Specialty ceramics, high-tech applications. | Pros: Exceptional quality and performance. Cons: Higher cost and sourcing challenges. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Smelter Grade Alumina?
Smelter grade alumina is primarily used for producing aluminum metal, necessitating high temperatures during processing. This type of alumina is generated through the calcination of aluminum hydroxide, making it essential for metallurgical operations. B2B buyers should consider the scale of their aluminum production needs, as this grade is crucial for creating aluminum products, but it may not fit specialized applications requiring additional properties.
How Does Low Soda Alumina Benefit Electronic Applications?
Low soda alumina is characterized by its minimal soda content, typically less than 0.1%, making it ideal for electronic and electrical components. This low soda level reduces contamination, enhancing the performance and reliability of electronic parts. B2B buyers in the electronics sector should prioritize this grade when sourcing materials to ensure high-quality performance in their applications, despite the potentially higher costs associated with its production.
Why Choose Reactive Alumina for Chemical Processing?
Reactive alumina is known for its high purity and fine crystal size, which allows it to sinter into a dense body at lower temperatures compared to other grades. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring high chemical inertness, such as in chemical processing and wear-resistant components. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, as sourcing reactive alumina may be limited and can affect lead times.
What Makes Tabular Alumina Versatile?
Tabular alumina features large, flat-shaped corundum crystals and is produced through a sintering process. Its high density and customizable sizes make it suitable for various applications, including catalyst beds and grinding media. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific processing techniques required for this type, as it can influence the cost and effectiveness of the final product.
Why is High Purity Alumina Essential for Specialty Applications?
High purity alumina, with a purity level of 99.99% or higher, is crucial for high-tech and specialty ceramic applications. This alumina is produced through advanced processes that ensure its exceptional quality. B2B buyers looking for top-tier materials for demanding applications should consider high purity alumina, keeping in mind that its higher cost and potential sourcing challenges may impact procurement strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of types of alumina
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of alumina | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | High-purity alumina for advanced ceramics | Enhanced performance in high-stress environments | Ensure consistent purity levels and reliable supply chains |
| Electronics | Low soda alumina in semiconductor packaging | Improved reliability and performance of components | Look for suppliers with expertise in low soda processing |
| Automotive | Reactive alumina in catalytic converters | Increased efficiency and reduced emissions | Verify compliance with environmental regulations |
| Construction | Tabular alumina in refractory materials | Superior thermal stability and longevity | Assess thermal properties and sourcing certifications |
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Fused alumina for abrasive applications | High durability and efficiency in grinding processes | Evaluate the material’s hardness and consistency |
How is High-Purity Alumina Used in Aerospace & Defense Applications?
High-purity alumina is critical in aerospace and defense sectors, where materials must withstand extreme conditions. It is utilized in advanced ceramics for components like insulators and protective coatings. These applications require alumina with a purity of 99.99% or higher to ensure reliability and performance under high temperatures and stresses. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality and compliance with stringent aerospace standards, especially when sourcing from regions like Europe or the Middle East.
What Role Does Low Soda Alumina Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Low soda alumina is essential in the electronics industry, particularly in the production of semiconductor packaging materials. This type of alumina minimizes the risk of contamination, which can adversely affect the performance of electronic components. The low soda content, typically less than 0.1%, is crucial for ensuring high reliability. Buyers in Africa and South America should seek suppliers with advanced processing capabilities to meet these stringent requirements, ensuring that the alumina maintains its integrity throughout the manufacturing process.
Why is Reactive Alumina Important for Automotive Catalytic Converters?
Reactive alumina is widely used in automotive catalytic converters due to its excellent chemical inertness and thermal stability. This type of alumina helps enhance the efficiency of catalytic reactions, leading to reduced emissions and improved fuel economy. As global regulations tighten on vehicle emissions, sourcing high-quality reactive alumina becomes increasingly important for automotive manufacturers. Buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and performance data to meet regulatory requirements.
How Does Tabular Alumina Benefit Construction Refractory Applications?
Tabular alumina is a preferred material in the construction industry, especially for refractory applications. Its unique structure offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Applications include linings for furnaces and kilns, where durability is essential. International buyers should consider the thermal properties and sourcing certifications of tabular alumina to ensure it meets the demands of construction projects across various regions, including Africa and the Middle East.
What Advantages Does Fused Alumina Offer in Mining & Mineral Processing?
Fused alumina is widely utilized in mining and mineral processing as an abrasive material due to its exceptional hardness and durability. It is commonly used in grinding and polishing applications, providing high efficiency and effectiveness. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the hardness and consistency of fused alumina products, ensuring they meet industry standards. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers with reliable delivery capabilities is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in mining operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of alumina’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Grade of Alumina for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the daunting task of selecting the appropriate grade of alumina for their unique applications. With various grades like smelter, reactive, and high-purity alumina, buyers may struggle to understand the differences and implications of each type. This lack of clarity can lead to suboptimal product performance, increased costs, and potential project delays, especially when the chosen alumina does not meet the specific requirements for chemical resistance, thermal stability, or mechanical strength.
The Solution: To effectively address this challenge, buyers should start by conducting a thorough needs analysis to understand the specific properties required for their application. This involves collaborating closely with engineers and product designers to outline critical factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands. Once these requirements are clear, buyers should engage with reputable suppliers who can provide samples and technical data sheets for various alumina grades. Testing these samples in real-world scenarios can further validate their suitability. Additionally, leveraging industry forums and expert consultations can provide insights into best practices for selecting alumina grades tailored to specific applications. This proactive approach minimizes risks and ensures that the chosen alumina enhances product performance.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions in Alumina Procurement
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions can significantly impact the availability and cost of alumina, creating anxiety for B2B buyers who rely on timely delivery for their projects. Fluctuations in prices and extended lead times can result in project delays and unexpected budget overruns, making it critical for buyers to maintain smooth procurement processes. Furthermore, buyers in regions like Africa and South America may face additional challenges related to transportation and import regulations.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions, buyers should diversify their supplier base by establishing relationships with multiple alumina manufacturers across different geographic regions. This strategy allows for flexibility in sourcing and can provide alternative options in case one supplier experiences delays. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can help manage stock levels effectively, reducing the risk of excess inventory or shortages. Buyers should also consider forming long-term contracts with suppliers to lock in prices and ensure consistent supply. Staying informed about global market trends, geopolitical factors, and potential disruptions can further empower buyers to make timely decisions and adjust their procurement strategies as needed.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality Control in Alumina Products
The Problem: Quality inconsistencies in alumina products can lead to severe performance issues, particularly in high-stakes applications like aerospace or electronics. Buyers may receive batches of alumina that do not meet the specified purity levels or have undesirable physical properties, resulting in compromised product quality and costly rework or recalls. This challenge is exacerbated by the varying quality standards across suppliers, especially for international buyers.
The Solution: To ensure quality control, B2B buyers should establish clear specifications and standards for the alumina they procure. This includes defining purity levels, particle size distribution, and other relevant properties. Implementing a robust quality assurance program that involves regular audits and inspections of supplier facilities can help ensure compliance with these standards. Additionally, requesting certificates of analysis (CoA) for each batch received can provide critical insights into the material’s quality. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about their quality control processes and testing methodologies can foster transparency and build trust. Lastly, conducting periodic performance evaluations of alumina in actual applications can help identify any potential quality issues early, allowing for timely corrective actions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of alumina
What Are the Key Properties of Smelter Grade Alumina?
Smelter grade alumina, primarily used in aluminum production, exhibits high thermal stability and excellent mechanical properties. Its temperature rating can exceed 1,000°C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. The material’s low impurity levels enhance its performance in metallurgical processes, ensuring a high yield of aluminum metal. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and energy-intensive, impacting overall costs.
From a B2B perspective, smelter grade alumina is critical for industries in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where aluminum production is a key economic driver. Buyers should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN to ensure product quality and consistency. Additionally, logistical considerations, including transportation and storage, are crucial due to the material’s bulkiness.
How Does Low Soda Alumina Benefit Specialized Applications?
Low soda alumina is characterized by its minimal sodium content, typically less than 0.1%. This property is essential for applications in electronics and electrical components, where even trace amounts of sodium can adversely affect performance. The material offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
While low soda alumina provides significant advantages, it can be more expensive than standard grades due to the additional processing required to reduce sodium levels. For international buyers, especially in regions like South America and Europe, understanding the specific requirements for low soda alumina can help in selecting the right supplier. Compliance with local and international standards is also crucial to ensure product reliability.
What Are the Advantages of Reactive Alumina?
Reactive alumina is known for its high purity and fine particle size, which allows it to sinter at lower temperatures. This property makes it ideal for applications requiring high chemical inertness and wear resistance, such as in catalysts and advanced ceramics. Its excellent mechanical properties also contribute to its versatility across various industries.
However, the production of reactive alumina can be complex and may involve higher costs compared to other grades. B2B buyers should assess the specific needs of their applications to determine if the benefits outweigh the costs. Additionally, understanding the regulatory landscape in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia is essential for ensuring compliance with local standards.
Why Choose Tabular Alumina for High-Temperature Applications?
Tabular alumina is a sintered form of alumina that features large, flat-shaped corundum crystals. It is known for its high refractoriness, low porosity, and excellent mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature applications such as refractories and abrasives. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions without degrading is a significant advantage.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
On the downside, tabular alumina can be more expensive to produce due to the energy-intensive manufacturing process. For international buyers, especially those in Europe, understanding the specific applications and performance characteristics of tabular alumina is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Ensuring that suppliers meet relevant standards can also mitigate risks associated with product quality.
Summary Table of Alumina Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of alumina | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smelter Grade | Aluminum production | High thermal stability | Complex and energy-intensive manufacturing | High |
| Low Soda | Electronics and electrical components | Minimal sodium content for better performance | Higher cost due to additional processing | Medium |
| Reactive | Catalysts and advanced ceramics | High purity and fine particle size | More complex production process | High |
| Tabular | Refractories and abrasives | Excellent mechanical strength and refractoriness | Higher production costs | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of alumina
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Alumina?
The manufacturing of alumina involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the specific requirements of various applications. The main stages are material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Alumina Production?
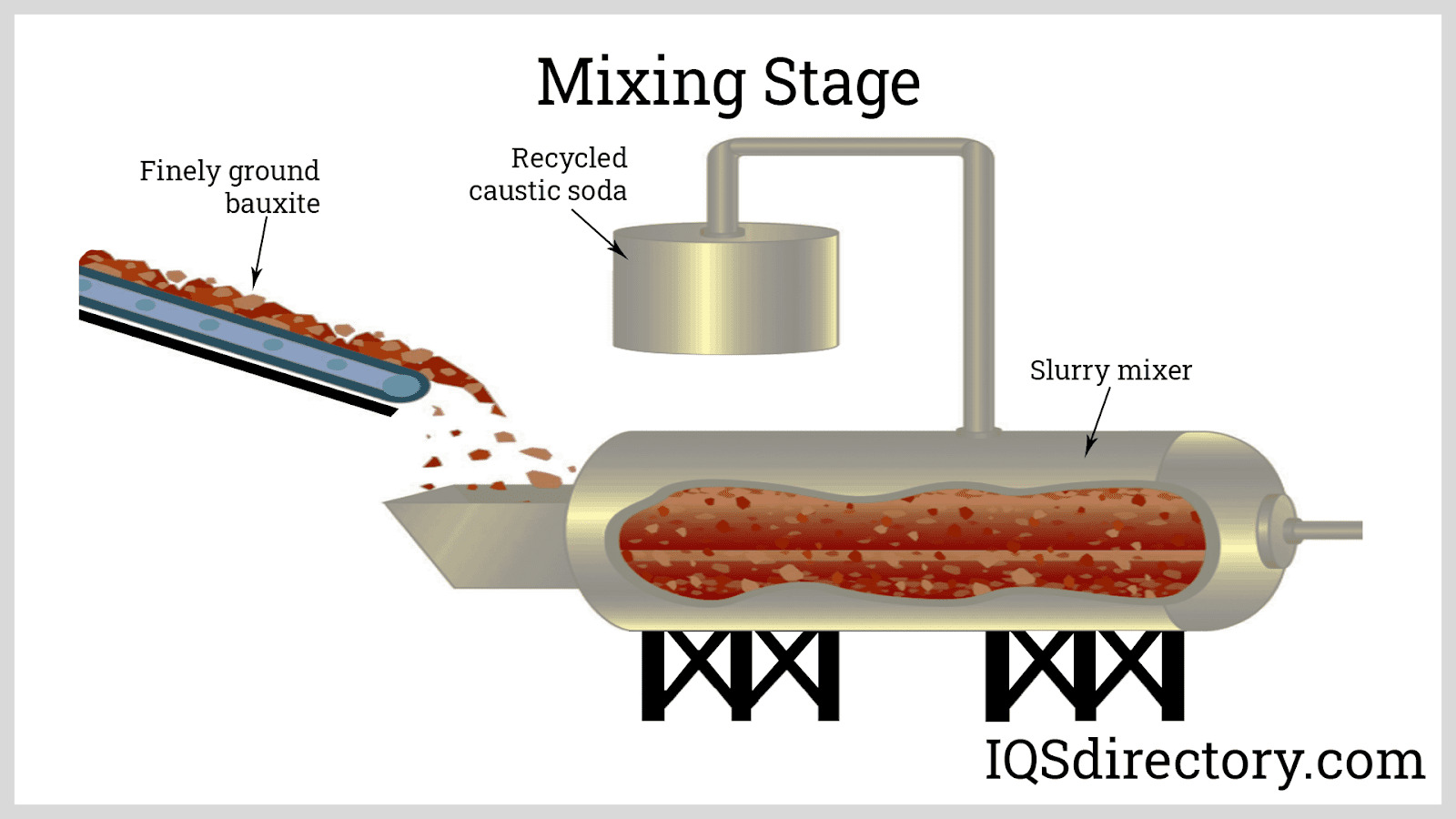
The initial stage begins with the sourcing of high-quality aluminum hydroxide or bauxite. The quality of the raw material significantly influences the final alumina product. In the case of smelter-grade alumina, aluminum hydroxide is processed through fluidized bed calciners or fluid flash calciners. This process involves removing both free and chemically bound water from the aluminum hydroxide. The material is then subjected to high temperatures, typically exceeding 1000°C, to initiate calcination, transforming it into alumina.
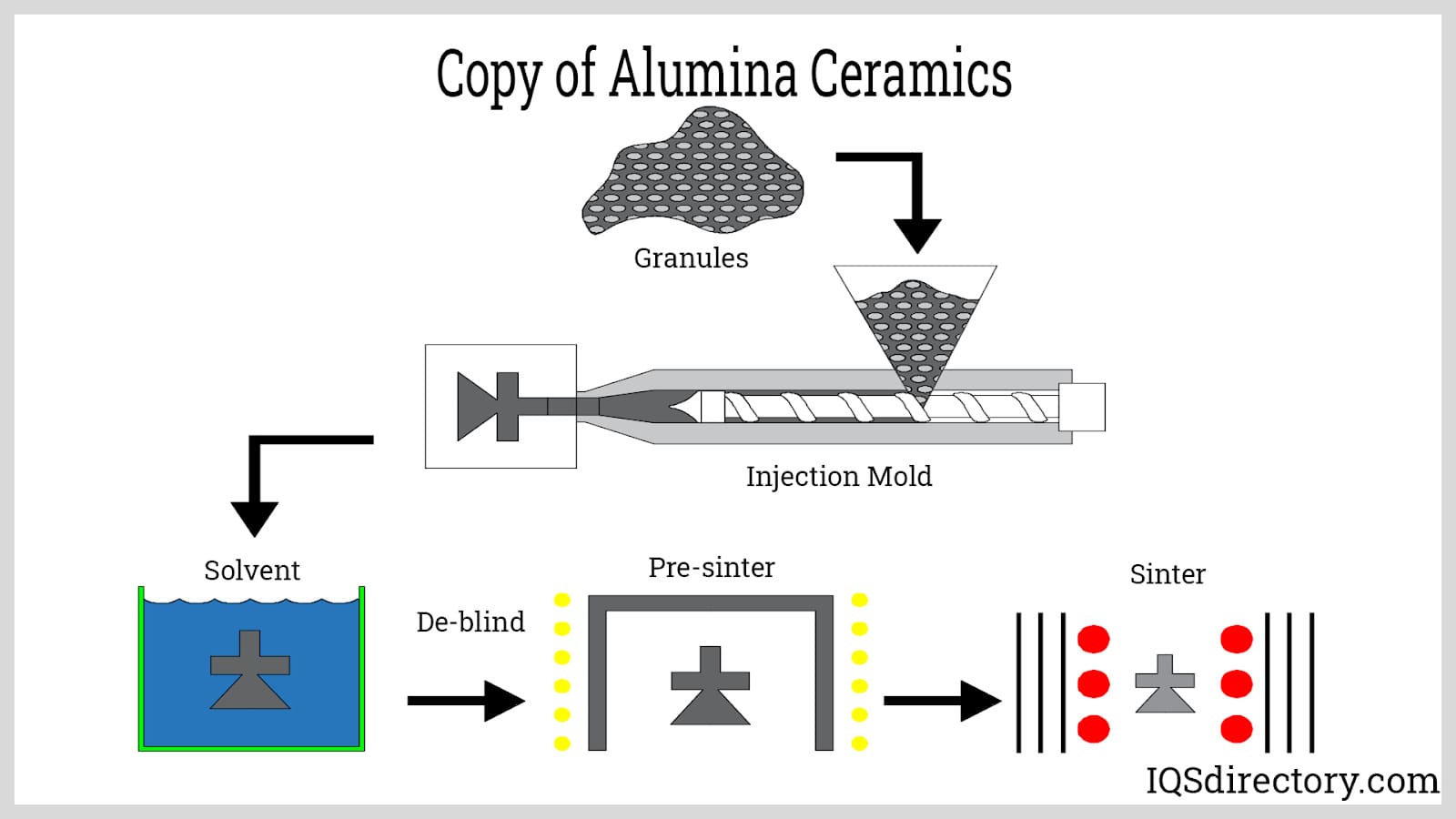
Illustrative image related to types of alumina
For specialized grades, such as low-soda or reactive alumina, additional purification steps may be necessary. Techniques such as acid washing or the addition of boron and chlorine can be employed to reduce soda content to below 0.1%. This level of purity is essential for applications in electronics and electrical industries.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Assembling Alumina?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. Various techniques are utilized depending on the desired grade and application of the alumina:
-
Injection Molding: This is commonly used for creating complex shapes and designs. The alumina powder is mixed with a binder and injected into a mold to achieve the desired form.
-
Pressing: In this technique, alumina powder is compacted under high pressure to form a dense body. It is often used for tabular alumina, which requires a specific morphology for applications such as catalyst supports.
-
Extrusion: This method allows for continuous shapes and is often used in producing tubes and rods.
Following forming, assembly may involve combining different alumina parts or integrating alumina with other materials to create a composite product.
How is Finishing Achieved for Alumina Products?
The finishing stage includes several processes designed to enhance the properties of the alumina product. These may include:

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
-
Sintering: After forming, parts are subjected to sintering at high temperatures to achieve densification and improve mechanical properties. This process can vary based on the type of alumina, with tabular alumina often being sintered at temperatures around 1800°C.
-
Grinding and Polishing: These processes are employed to achieve the required surface finish and dimensional tolerances. Fine grinding is crucial for high-purity alumina used in advanced ceramics.
-
Coating and Surface Treatment: For specific applications, alumina parts may undergo additional treatments, such as coating, to enhance properties like corrosion resistance or wear resistance.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Essential for Alumina Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in alumina manufacturing to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Several key elements define the QA process.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered in Alumina Quality Control?
B2B buyers should be aware of various international quality standards relevant to alumina manufacturing. ISO 9001 is the most recognized standard for quality management systems and serves as a foundational requirement for manufacturers. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply, depending on the end-use of the alumina products.
Manufacturers should also be familiar with local regulations and standards, particularly for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Compliance with these standards not only ensures quality but also facilitates smoother international trade.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are critical for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves testing the raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter the production process. This step is essential to prevent defective materials from compromising the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensional accuracy are monitored. This continuous oversight helps identify any deviations from established norms.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished alumina products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all specifications. Common testing methods include physical property tests (e.g., density, porosity), chemical composition analysis, and performance tests tailored to specific applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa and South America, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
Illustrative image related to types of alumina
-
Conducting Audits: Engaging in regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. Audits can help identify any gaps in compliance or areas for improvement.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide comprehensive quality reports detailing their QC processes and results from recent tests. These documents serve as evidence of compliance with international standards.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: Employing independent third-party inspectors can enhance credibility and provide an objective assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes. This step is particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers’ practices.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
When sourcing alumina from international suppliers, buyers must navigate various nuances that can impact quality control. These include:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the business culture and practices in different regions can influence communication and expectations regarding quality assurance.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks related to product handling and storage. Buyers should discuss these factors with suppliers to ensure appropriate measures are in place to safeguard product quality during transit.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the regulatory landscape in their target markets. Ensuring that suppliers meet these regulations can help avoid complications during importation and distribution.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing different types of alumina, ensuring they acquire high-quality products that meet their specific application needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of alumina’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, finding the right type of alumina is crucial for meeting your specific technical requirements. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, in sourcing the appropriate alumina types for their applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, it’s essential to outline your specific needs. Determine the grade of alumina required based on application—whether it’s smelter grade for aluminum production, low soda for electrical components, or high-purity alumina for specialized uses. Understanding these requirements will help streamline your sourcing process.
Illustrative image related to types of alumina
Step 2: Research Different Alumina Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of alumina available. Key grades include reactive alumina, tabular alumina, and fused alumina, each offering unique properties. Knowing the differences will allow you to select the most suitable type for your application, ensuring performance and cost-effectiveness.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure they meet your standards. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from previous clients in your industry. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in delivering quality alumina products that align with your specifications.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your chosen suppliers possess relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or other quality management standards. Certifications indicate adherence to quality control processes and can assure you of the material’s reliability. This step reduces the risk of sourcing inferior products that may impact your operations.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing any purchase, request samples of the alumina types you are considering. Testing samples in your specific application conditions will help validate their performance and compatibility. This step is critical in avoiding costly mistakes that could arise from unsuitable materials.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and delivery schedules. Establishing clear terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings later. Ensure that you discuss any potential price fluctuations and how they will be managed.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After the procurement process, consider establishing a long-term partnership with your supplier. A reliable supplier can provide consistent quality and support, enabling you to adapt to changing market demands. Regular communication and performance reviews can help strengthen this relationship, ensuring mutual growth.
By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing alumina more effectively, ultimately ensuring that your procurement aligns with your operational goals and quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of alumina Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alumina Sourcing?
When sourcing alumina, B2B buyers must consider several cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The type of alumina selected—be it smelter grade, high purity, or reactive alumina—significantly impacts costs. High-purity alumina, for instance, requires advanced processing and purification, leading to higher material costs compared to standard grades.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. For example, regions with higher wage standards may see increased labor costs, affecting the final pricing for alumina products.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, contributing to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific alumina applications can involve significant upfront investments. Buyers should factor in these costs, especially for specialized products requiring unique molds or processing equipment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of alumina products through rigorous testing and certification can add to costs. However, high-quality materials typically yield better performance and durability, justifying the investment.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary dramatically, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and the need for special handling can all influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the final price. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can help buyers negotiate more effectively.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Alumina Pricing?
Price influencers such as volume and customization play a significant role in alumina sourcing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Buying in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may have minimum order quantities (MOQs), which can impact pricing strategies. Negotiating favorable terms for bulk purchases can lead to substantial savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized alumina products tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to ensure accurate pricing and avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The presence of quality certifications can influence price. Materials with verified purity levels or specific performance characteristics often command a premium, reflecting their enhanced value.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms can clarify who is responsible for costs associated with shipping, insurance, and duties, thus influencing the total landed cost of the product.
What Are Effective Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies are crucial for cost efficiency.
-
Research and Preparation: Conduct thorough research on market prices and supplier capabilities. Understanding the competitive landscape can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating prices, consider the TCO, which includes all associated costs over the product’s lifecycle. This approach can reveal that a higher upfront cost may result in lower long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority access to new products. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate more favorably with loyal customers.
-
Flexibility in Terms: Be open to negotiating terms beyond just price. This could include payment terms, delivery schedules, or volume commitments, which can all contribute to a more advantageous overall deal.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for alumina products can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier negotiations. Buyers should seek multiple quotes and engage in thorough discussions to ensure they are receiving the best value for their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of alumina With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Types of Alumina
In the quest for advanced materials, B2B buyers often encounter various options that serve similar functions as alumina, or aluminum oxide. While alumina is renowned for its durability, thermal stability, and versatility across numerous industries, alternative materials and methods can also meet specific needs and applications. Understanding these alternatives allows buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and suitability for their unique requirements.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
| Comparison Aspect | Types Of Alumina | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Zirconia (ZrO2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal stability, excellent wear resistance, and chemical inertness. | Superior hardness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent thermal stability. | High toughness, good wear resistance, and thermal insulation properties. |
| Cost | Generally moderate; varies by grade and purity. | Typically higher due to processing complexity. | Higher initial cost but may reduce overall lifecycle costs due to durability. |
| Ease of Implementation | Widely available, easy to mold and shape; various grades for specific applications. | More complex to process; requires specialized equipment for machining. | Can be challenging to work with due to its brittleness and requires careful handling. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durability and resistance to wear. | Low maintenance; resistant to oxidation and thermal shock. | Requires careful maintenance due to susceptibility to cracking under stress. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for electrical insulators, cutting tools, and wear-resistant applications. | Best for high-performance applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing and automotive components. | Excellent for applications requiring high strength and toughness, such as dental and orthopedic implants. |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Alternatives
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is a compound semiconductor known for its exceptional hardness and thermal conductivity. It performs well in high-temperature applications and is often used in industries such as automotive and aerospace. The primary drawback is its higher cost and the complexity of machining, which may require specialized tools and techniques. Despite the initial investment, its durability can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
Zirconia (ZrO2)
Zirconia is another alternative that offers impressive toughness and thermal insulation. It is particularly valuable in applications where strength is critical, such as in dental and orthopedic implants. However, zirconia can be brittle, making it less suitable for high-stress applications unless carefully engineered. Its higher price point compared to alumina may be offset by the long-term benefits in specific use cases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate material for your application, consider factors such as performance requirements, cost constraints, and the ease of implementation. Types of alumina provide a versatile option suitable for a wide range of applications, while alternatives like silicon carbide and zirconia may offer superior performance in niche scenarios. B2B buyers should weigh these aspects carefully to identify the best solution that aligns with their operational goals, budget, and application requirements. Engaging with suppliers and manufacturers can also provide insights into the latest advancements and options available, ensuring a well-informed purchasing decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of alumina
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of Alumina?
Understanding the technical properties of alumina is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right type for their specific applications. Here are several key specifications that play a vital role in decision-making:
-
Material Grade
– Alumina comes in various grades, each tailored for different applications. For instance, smelter grade is used for aluminum production, while high-purity alumina (99.99% purity) is preferred for advanced ceramics. Choosing the appropriate grade directly impacts the performance and longevity of the final product. -
Purity Level
– The purity of alumina influences its thermal and chemical stability. High-purity alumina is essential in applications such as electronics and biomedical devices, where impurities can affect performance. A higher purity level often correlates with increased manufacturing costs, making it vital for buyers to balance cost and application needs. -
Particle Size Distribution
– The size of alumina particles can affect sintering behavior and final product characteristics. For example, reactive alumina has smaller crystal sizes (<1μm) that sinter at lower temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring high strength and chemical inertness. Understanding particle size is essential for optimizing production processes and achieving desired mechanical properties. -
Thermal Stability
– Alumina’s ability to withstand high temperatures is a critical factor in applications such as refractories and abrasives. Tabular alumina, for instance, exhibits excellent thermal stability due to its dense structure. Buyers should assess the thermal requirements of their applications to select the right alumina type. -
Density and Porosity
– The density and porosity of alumina affect its mechanical strength and durability. Fused alumina, known for its low porosity and high density, is commonly used in demanding applications. Understanding these properties helps buyers anticipate how alumina will perform under operational stresses.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Dealing with Alumina?
Navigating the procurement process requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are several essential terms that every B2B buyer should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Buyers must identify OEM partners who can provide the specific grades of alumina needed for their applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is vital for budgeting and inventory management, especially for international buyers who may face additional shipping costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal document requesting a supplier to provide pricing for specific quantities and specifications. Submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for buyers to understand their liabilities and costs in cross-border transactions. -
Sourcing Strategy
– This refers to the approach buyers take in selecting suppliers and negotiating terms. A well-defined sourcing strategy can lead to cost savings and better quality products, making it an essential aspect of B2B procurement. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period from order placement to delivery. Understanding lead times is critical for planning production schedules and managing supply chain logistics, especially in industries where timing is crucial.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alumina, ensuring they select the right materials for their unique applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of alumina Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Alumina Sector?
The global alumina market is experiencing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for aluminum, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. Emerging economies in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are significantly contributing to this demand, fueled by urbanization and infrastructure development. Notably, countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are ramping up their aluminum production capacities, further stimulating the need for various grades of alumina.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing the efficiency of alumina production and quality control processes. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt these technologies, as they ensure better product consistency and traceability. Additionally, 3D printing is gaining traction, allowing for innovative applications of alumina in custom manufacturing, which appeals to industries looking for tailored solutions.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is witnessing a shift as suppliers are consolidating to optimize their supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who seek reliable partners capable of meeting fluctuating demands while maintaining quality. Overall, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing alumina effectively.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alumina Sector?
The sustainability discourse is becoming increasingly vital within the alumina sector, as environmental regulations tighten globally. B2B buyers are now more aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. The alumina production process, particularly the Bayer process, can have significant ecological footprints, including greenhouse gas emissions and water usage. Thus, buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and minimizing waste.
Ethical sourcing has also emerged as a key concern. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate commitment to corporate social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Responsible Care® can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainable and ethical practices.
In addition to these certifications, there is a growing interest in ‘green’ alumina alternatives. These products are derived from more sustainable methods or raw materials, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. By choosing suppliers that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the global environment.

Illustrative image related to types of alumina
What Has Been the Evolution of the Alumina Market?
The alumina market has evolved significantly over the past century, with its origins tracing back to the early industrial applications of aluminum. The development of the Bayer process in the late 19th century revolutionized alumina production, making it more cost-effective and efficient. This process enabled the widespread use of alumina in various applications, from ceramics to refractories.
As technology advanced, the market saw the introduction of different grades of alumina tailored for specialized applications, such as high-purity alumina for electronics and low-soda alumina for electrical components. This diversification has allowed the alumina sector to adapt to the evolving needs of industries, solidifying its position as a critical material in modern manufacturing.
In recent years, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing has marked the latest evolution of the market. Buyers are now not only concerned with product performance but also with the environmental and social implications of their sourcing choices. This shift is likely to shape the future of the alumina sector, driving innovation and responsible practices in production and supply chain management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of alumina
-
How do I determine the right type of alumina for my application?
To select the appropriate type of alumina, start by assessing the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength. For instance, reactive alumina is ideal for applications requiring high purity and low sintering temperatures, while smelter-grade alumina is essential for aluminum production. Consult with suppliers to discuss your needs and review technical data sheets to ensure the chosen alumina meets your specifications. -
What is the best alumina grade for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, tabular alumina is often the preferred choice due to its exceptional thermal stability and low permeability. It is sintered at high temperatures to produce a dense material that can withstand extreme heat without degradation. Ensure you also evaluate the specific requirements of your application, as other grades like fused alumina may also provide excellent high-temperature performance depending on the context. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alumina products?
Minimum order quantities for alumina products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific type of alumina required. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms for specialized grades to several tons for bulk orders. It is essential to communicate your needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to accommodate smaller orders, especially for new customers or trial purposes. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of alumina?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certifications, and experience in the alumina market. Request references and case studies to understand their reliability and product quality. Additionally, assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. Engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alumina internationally?
Payment terms can vary among suppliers but typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60/90 days. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow needs. Be aware that international transactions may involve additional costs such as currency exchange fees and import duties, so factor these into your budgeting process. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in alumina suppliers?
Quality assurance measures are vital to ensure the alumina you receive meets industry standards. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications and robust testing protocols for their products. Inquire about their quality control processes, including batch testing, purity analysis, and consistency checks. A reputable supplier should be willing to provide documentation and certificates of analysis for their alumina products. -
How do logistics and shipping affect the sourcing of alumina?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in the timely delivery of alumina products. Consider the supplier’s location, shipping methods, and estimated delivery times when making your decision. It’s advisable to discuss freight options and costs upfront, as international shipping can significantly impact your overall expenses. Additionally, ensure that your supplier has experience with customs regulations and can assist with necessary documentation for smooth transit. -
Can I customize alumina products to suit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for alumina products to meet specific application requirements. Customization may include adjustments in particle size, purity levels, or even specific formulations tailored to your needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to explore available options and ensure that they have the capability to deliver customized solutions effectively.
Top 6 Types Of Alumina Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wundermold – Alumina Ceramics Grades
Domain: wundermold.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 7 Different Grades of Alumina Ceramics: 1. Smelter Grade: Used for manufacturing aluminum metal, made from aluminum hydroxide, undergoes high temperatures and calcination. 2. Low Soda: Contains <0.1% soda, suitable for electronic and electrical applications, achieved through various processes. 3. Reactive: High purity and small crystal sizes (<1μm), sinters at lower temperatures, ideal for high ch…
2. Digital Fire – Alumina Products
Domain: digitalfire.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Alumina, also known as Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), is a white granular or fine silky powder used in ceramics. It is the most widely used high-tech ceramic material, with types including hydrated, calcined, and tabular alumina, each having various grades. Calcined aluminas are used in porcelain and whiteware, while super high purity grades (99.99%) are for optical and electronic applications. Alumina c…
3. GlobalSpec – Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
Domain: globalspec.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminum oxide (Al2O3), commonly known as alumina, is a white high-hardness ceramic with excellent wear characteristics, chemical resistance, compressive strength, high-temperature properties, and dielectric strength. It is used widely due to its versatility and low cost. Main drawbacks include relatively poor thermal-shock resistance. Types include calcium aluminate, sapphire, and alumina-zirconi…
4. Glenn Klockwood – Alumina Ceramics
Domain: glennklockwood.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Alumina (Al2O3) is a widely studied ceramic known for its ease of manufacturing, corrosion resistance, creep resistance, low cost, and high-temperature refractory nature. It is commonly used as a ceramic electronic substrate, in milling media, spark plugs, and wear-resistant applications such as pump seals and welding nozzles. Key classifications of alumina include: 1. Corundum – Single crystal al…
5. AZOM – Alumina (Aluminium Oxide)
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Alumina (Aluminium Oxide) is the most widely used oxide ceramic material with applications in spark plugs, tap washers, abrasion resistant tiles, and cutting tools. Key properties include high compression strength, high hardness, resistance to abrasion and chemical attack, high thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shock, high degree of refractoriness, high dielectric strength, high electric…
6. IQS Directory – Alumina Ceramics
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Alumina ceramics are robust industrial oxide ceramics derived from bauxite, known for exceptional hardness and strength. They can be fabricated using techniques such as injection molding, die pressing, isostatic pressing, slip casting, diamond machining, and extrusion. They serve as insulating materials for electrical applications and are resistant to wear, corrosion, chemicals, and high temperatu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of alumina
The diverse grades of alumina—ranging from smelter grade to high-purity varieties—present significant opportunities for strategic sourcing across various industries. Understanding the specific characteristics and applications of each type enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational needs. For instance, low-soda alumina is essential for electronics, while fused alumina excels in refractories and abrasives.
Moreover, the growing demand for advanced technical ceramics in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and electronics underscores the importance of sourcing high-quality materials that enhance product performance and durability. By partnering with reputable suppliers who prioritize innovation and quality, businesses can ensure they remain competitive in the global market.
Illustrative image related to types of alumina
Looking ahead, the alumina market is poised for growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing applications in emerging markets. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seize the opportunity to expand their sourcing strategies. Embrace the potential of alumina to enhance your product offerings and drive your business forward. Engage with reliable manufacturers today to secure a competitive advantage in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.