Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Thermoplastic Molding Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoplastic molding
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing high-quality thermoplastic molding solutions can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the demand for innovative and durable plastic components rising, understanding the intricacies of thermoplastic molding—ranging from injection molding to blow molding—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international buyers, providing in-depth insights into various molding processes, applications, and materials that can meet specific industry needs.
The complexities of selecting the right suppliers, assessing production costs, and ensuring compliance with regional regulations can overwhelm even the most experienced procurement teams. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable strategies for supplier vetting, material selection, and cost analysis, this guide aims to empower companies to navigate these challenges confidently. Additionally, it highlights the latest advancements in thermoplastic molding technologies, enabling buyers to stay ahead of market trends and demands.
Whether you are seeking to streamline your supply chain or enhance product quality, this guide is designed to facilitate informed decision-making, ultimately helping your business thrive in the global landscape of thermoplastic molding.
Understanding thermoplastic molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Injection Molding | High precision, mass production, complex geometries | Automotive parts, consumer goods, electronics | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes. Cons: High initial setup costs. |
| Blow Molding | Creates hollow parts, uses parison method | Bottles, containers, and large hollow items | Pros: Efficient for large volumes. Cons: Limited to hollow shapes. |
| Overmolding | Combines two materials in a single part for enhanced functionality | Handles, grips, and multi-material assemblies | Pros: Improved product performance. Cons: More complex tooling required. |
| Rotational Molding | Produces seamless, hollow parts using a rotating mold | Tanks, kayaks, and large containers | Pros: Versatile shapes, low tooling costs. Cons: Slower production rates. |
| Compression Molding | Uses heat and pressure to form parts, suitable for large items | Automotive parts, appliances, and electrical components | Pros: Good for high-strength applications. Cons: Longer cycle times. |
What Are the Characteristics of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that allows for the mass production of complex plastic components. It is characterized by its ability to create precise shapes and intricate designs, making it ideal for industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and electronics. Buyers should consider the high initial setup costs and the need for specialized molds, as these factors can impact the overall investment. However, once established, this method offers significant cost savings for large volume production.
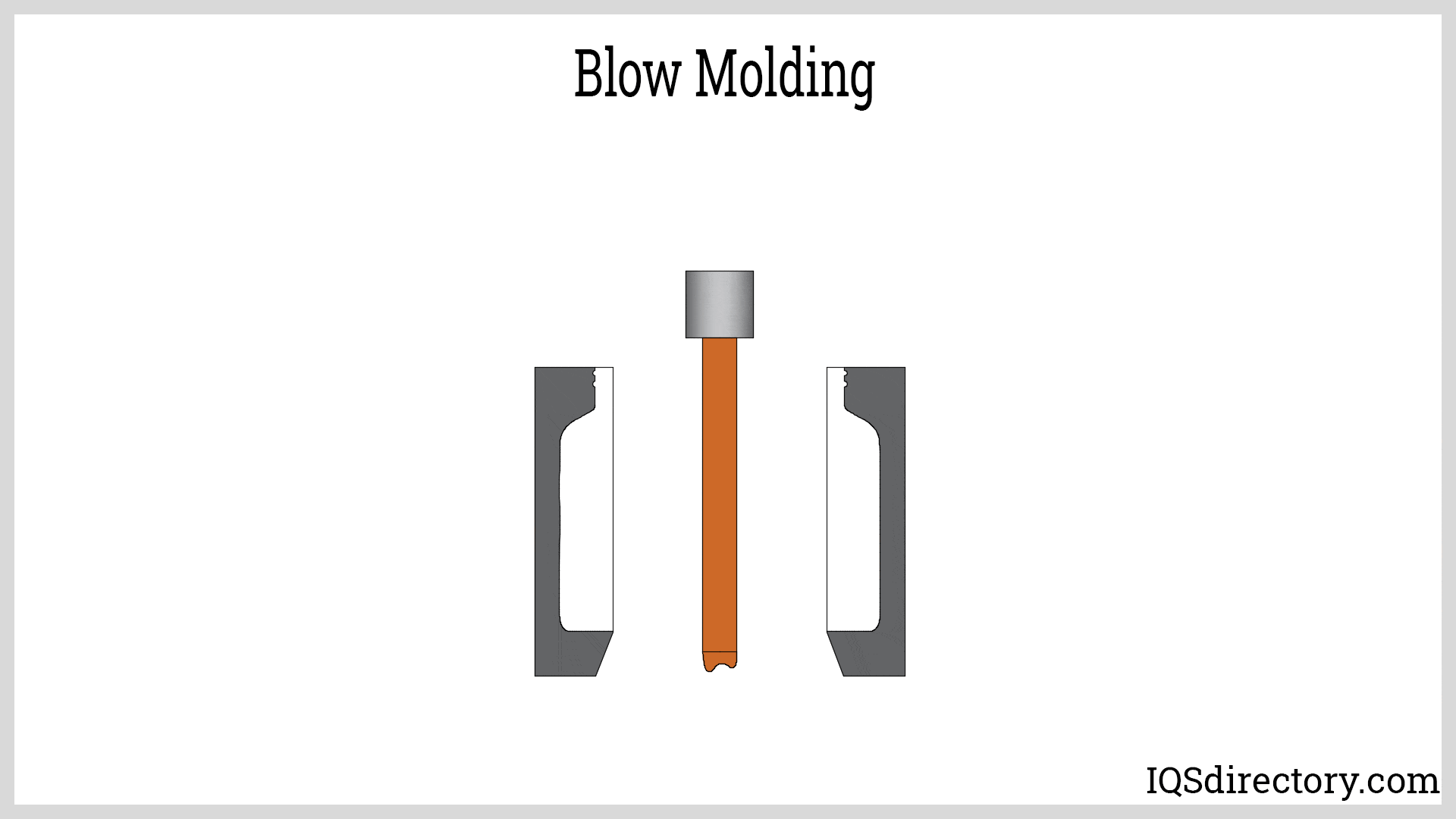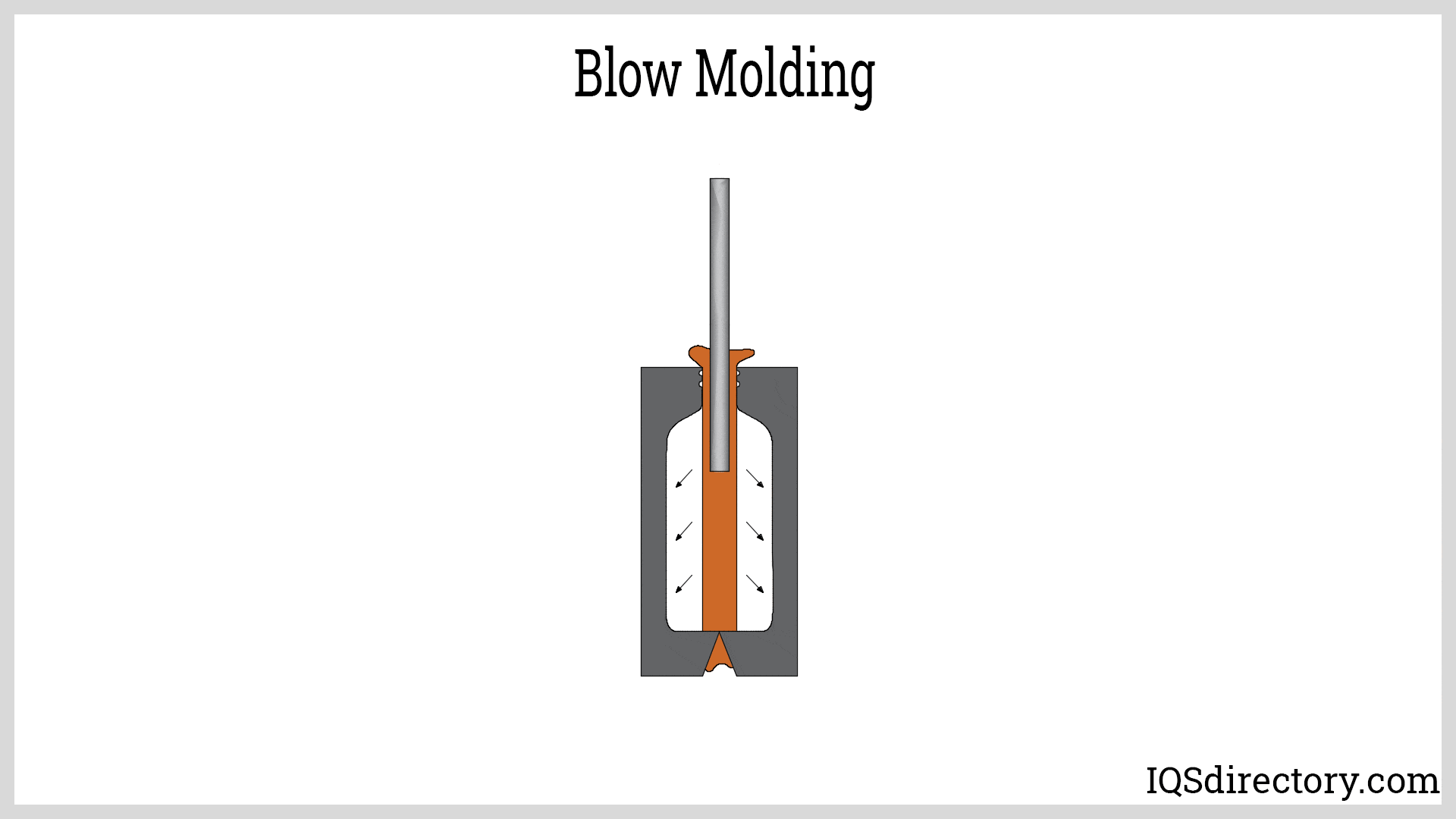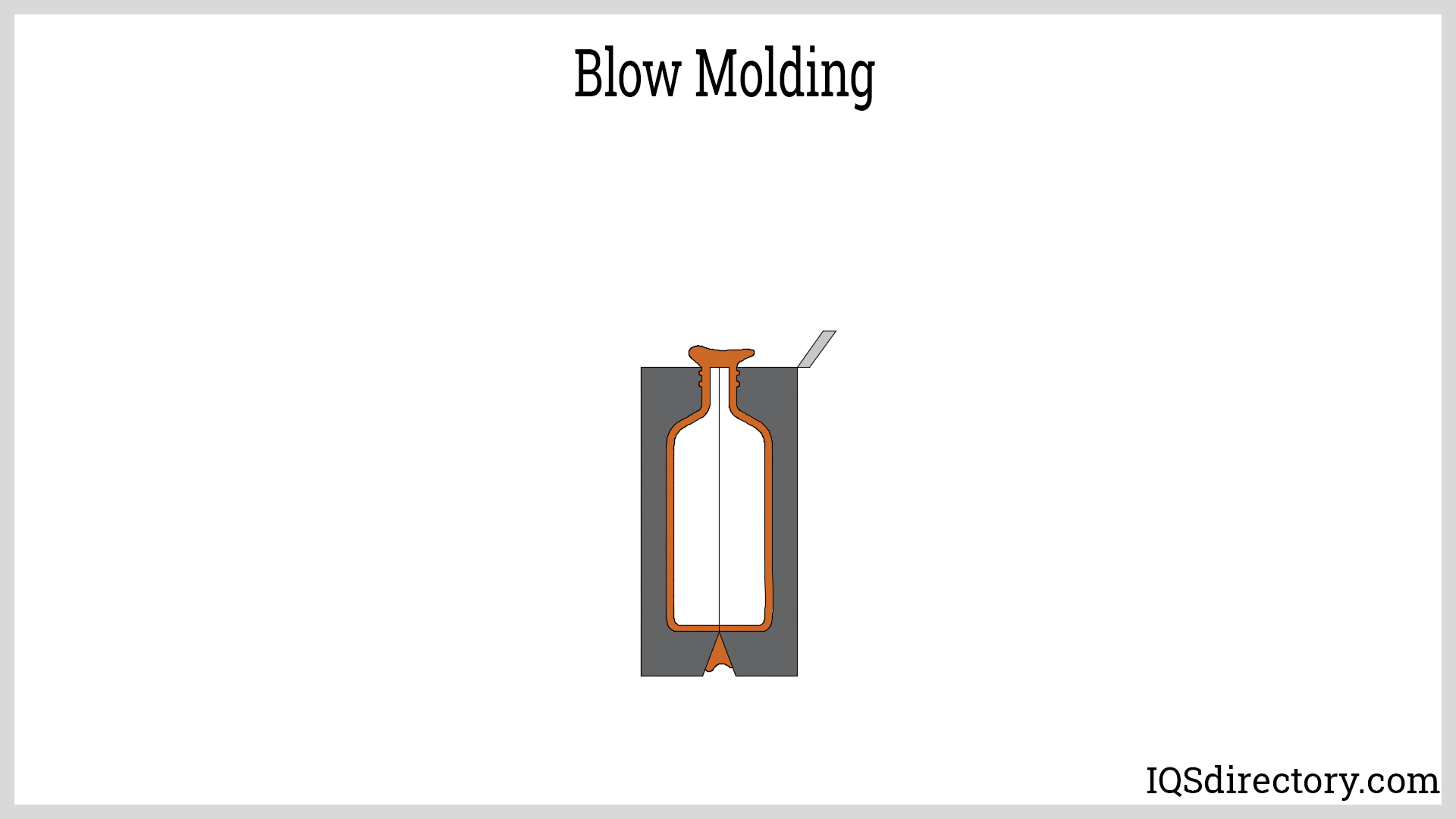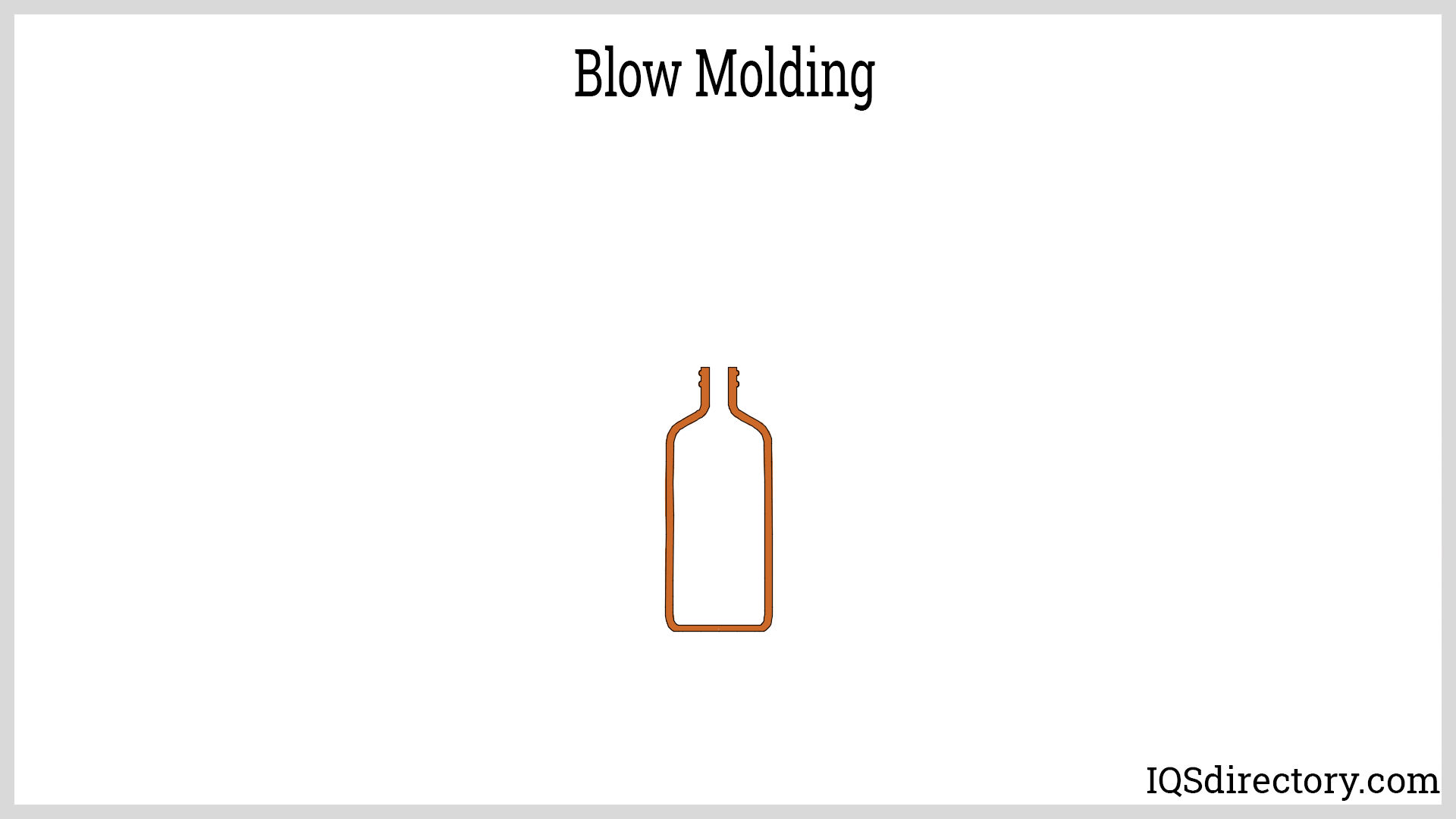
How Does Blow Molding Differ from Other Molding Techniques?
Blow molding is a unique process that specializes in creating hollow plastic products. By using a parison, or preform, which is heated and inflated, manufacturers can produce items such as bottles and large containers efficiently. The primary advantage for B2B buyers lies in its ability to handle high-volume production with relatively low material costs. However, the limitation to hollow shapes may restrict its applicability for more complex designs.
What Advantages Does Overmolding Provide for Product Design?
Overmolding is a versatile technique that allows for the combination of two different materials into a single product, enhancing functionality and ergonomics. This method is particularly beneficial in applications like handles and grips, where a softer material can improve user comfort. For B2B buyers, the main consideration is the complexity of tooling and design, which can lead to higher costs but ultimately results in superior product performance and differentiation in the market.
Why Choose Rotational Molding for Large, Hollow Products?
Rotational molding is an effective method for producing large, seamless, and hollow plastic parts. The process involves heating powdered resin in a rotating mold, allowing for even distribution and solidification. This technique is particularly well-suited for applications such as tanks and kayaks, where durability and flexibility are crucial. While the initial tooling costs are lower than some other methods, buyers must be aware of the slower production rates, which could affect lead times.
How Is Compression Molding Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Compression molding is a traditional method that employs heat and pressure to form parts, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Industries such as automotive and electrical components benefit from the strength and durability of products made through this technique. Buyers should note that while the process is effective for creating robust items, it typically involves longer cycle times and may not be as efficient for high-volume production compared to injection molding.
Key Industrial Applications of thermoplastic molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Thermoplastic Molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior components | Enhanced durability and design flexibility | Material specifications, compliance with safety standards, and lead times. |
| Electronics | Housing for electronic devices | Lightweight, cost-effective, and customizable designs | Supplier reliability, material certifications, and scalability of production. |
| Consumer Goods | Manufacturing of packaging solutions | Improved product protection and shelf appeal | Sustainability of materials, cost-effectiveness, and supply chain logistics. |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments | High precision and biocompatibility | Regulatory compliance, material traceability, and quality assurance processes. |
| Construction | Production of plumbing fittings | Resistance to corrosion and long-term durability | Material compatibility, availability of custom designs, and regulatory compliance. |
How Is Thermoplastic Molding Used in the Automotive Industry?
Thermoplastic molding plays a crucial role in the automotive sector by producing a variety of interior components such as dashboards, door panels, and trim pieces. The ability to create complex shapes while ensuring durability allows manufacturers to enhance vehicle aesthetics and functionality. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality thermoplastics that meet safety and environmental regulations is vital. Additionally, understanding local manufacturing capabilities and lead times can significantly impact supply chain efficiency.
What Are the Benefits of Thermoplastic Molding for Electronics?
In the electronics industry, thermoplastic molding is utilized to create housings for devices such as smartphones, computers, and appliances. This process enables the production of lightweight, cost-effective components that can be easily customized to meet specific design requirements. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is essential to consider the reliability of suppliers and their ability to provide materials that comply with international safety standards. Ensuring scalability of production is also critical to meet fluctuating market demands.
How Does Thermoplastic Molding Enhance Consumer Goods Packaging?
Thermoplastic molding is extensively used in the packaging sector to manufacture containers, bottles, and protective packaging. This method improves product protection while enhancing the visual appeal of packaging, which is vital for attracting consumers. B2B buyers, especially in developing markets, should prioritize sourcing sustainable materials that align with global environmental trends. Additionally, understanding the logistics of supply chains is crucial for ensuring timely delivery and cost efficiency.
Why Is Thermoplastic Molding Important in Medical Device Manufacturing?
The medical device industry relies on thermoplastic molding for the production of surgical instruments and components. This process offers high precision and the ability to create biocompatible parts necessary for patient safety. For international buyers, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory environments, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations is paramount. Furthermore, establishing a robust quality assurance process with suppliers is essential to maintain product integrity.
How Is Thermoplastic Molding Applied in Construction?
In construction, thermoplastic molding is used to create plumbing fittings and other durable components. The resistance of thermoplastics to corrosion and their long lifespan make them ideal for various applications in this sector. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should focus on sourcing materials that not only meet local building codes but also offer customization options to suit specific project needs. Additionally, considering the availability of local suppliers can enhance project timelines and reduce costs.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thermoplastic molding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the right thermoplastic material for their specific applications. With a myriad of options available, each with unique mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and chemical compatibility, the decision-making process can become overwhelming. For instance, a manufacturer in the automotive sector may struggle to choose between polycarbonate and polypropylene for a component that must withstand high temperatures and impact, leading to potential product failures and increased costs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material selection, buyers should start by conducting a thorough assessment of their application requirements. This includes understanding the environmental conditions the product will face, such as temperature fluctuations, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stresses. Collaborating closely with suppliers who specialize in thermoplastic materials can provide valuable insights into the most suitable options. Additionally, leveraging material datasheets and case studies from similar applications can help inform decisions. For instance, using polycarbonate for components that require high impact resistance, while opting for polypropylene for lightweight applications, can optimize performance and cost.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem: Another significant pain point is the rising production costs associated with inefficient thermoplastic molding processes. Many manufacturers may not have updated their machinery or processes, leading to longer cycle times, higher energy consumption, and increased waste. For example, an injection molding company may experience frequent machine breakdowns or require excessive manual intervention, resulting in delays and inflated operational costs.
The Solution: To combat high production costs, businesses should invest in process optimization and technology upgrades. Conducting a thorough audit of existing processes can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Implementing automation solutions, such as advanced robotics for material handling or predictive maintenance tools, can significantly enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Additionally, exploring options for recycling and reusing thermoplastic materials during production can minimize waste and cut costs. Partnering with equipment suppliers that offer training on best practices for machine operation and maintenance can also ensure that staff are well-equipped to maximize the efficiency of the molding process.
Scenario 3: Quality Control Issues Leading to Product Rejections
The Problem: Quality control is a critical concern for B2B buyers in thermoplastic molding, as poor-quality parts can lead to costly rejections and lost contracts. For instance, a company producing medical devices may find that the molded parts do not meet stringent regulatory standards due to inconsistencies in the molding process, resulting in delays and reputational damage. These quality issues often stem from inadequate monitoring of the molding parameters or insufficient training of the workforce.
The Solution: To address quality control issues, implementing a robust quality management system is essential. This includes establishing clear quality standards and specifications for each product, as well as regular training sessions for employees on quality control procedures. Investing in real-time monitoring technology can help track critical parameters during the molding process, such as temperature, pressure, and cooling times, enabling immediate adjustments if deviations occur. Additionally, conducting regular audits and product testing can ensure compliance with industry standards and enhance overall product reliability. Collaborating with third-party quality assurance providers can also provide an objective assessment of manufacturing processes and help identify areas for improvement.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoplastic molding
What Are the Key Properties of Common Thermoplastic Materials?
When selecting materials for thermoplastic molding, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance in various applications. Below are analyses of four commonly used thermoplastic materials in the industry.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a widely utilized thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It has a temperature rating of approximately 100°C and is resistant to a range of solvents, making it suitable for automotive and consumer goods applications.
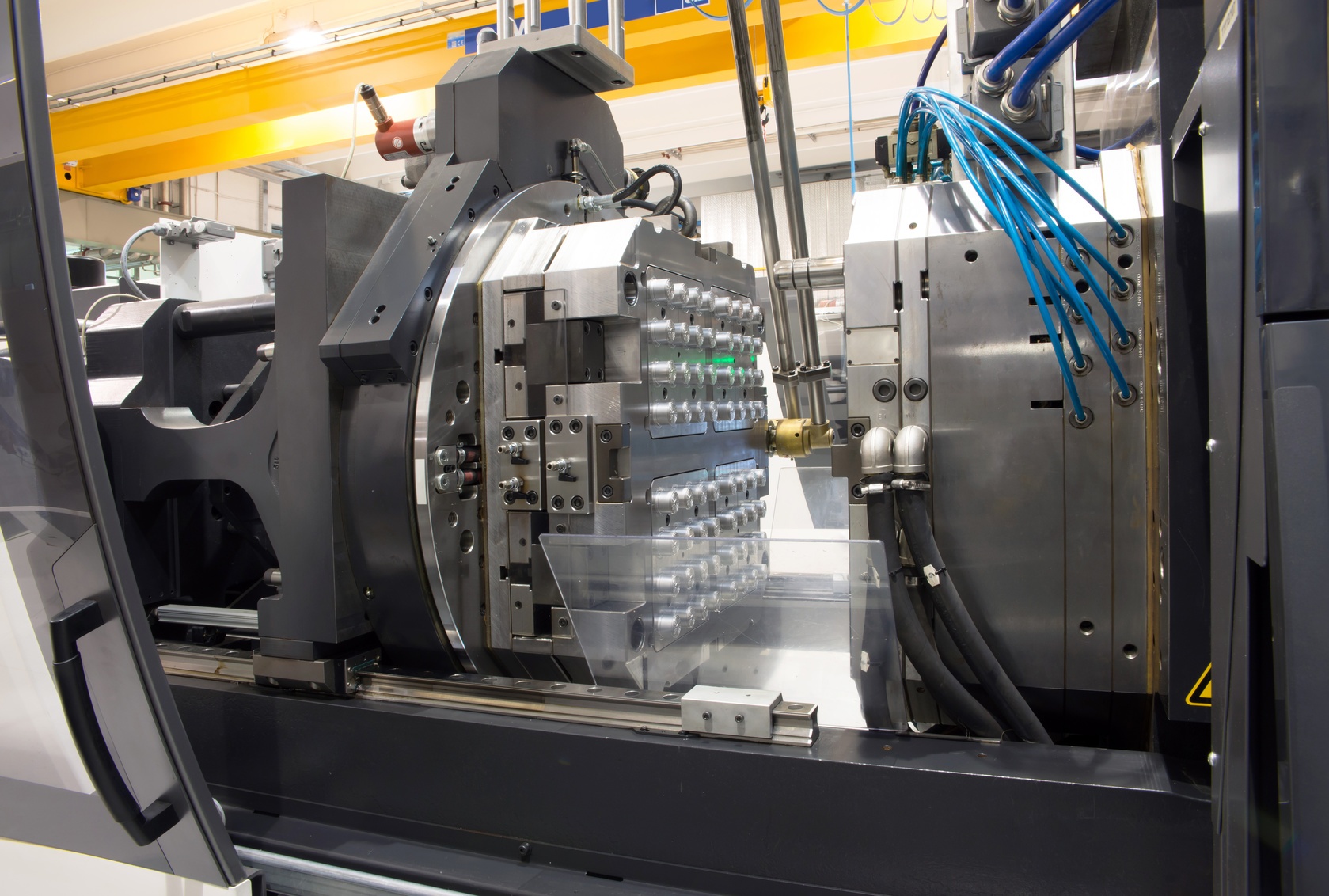
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
Pros: Polypropylene offers high durability and flexibility, making it ideal for products that require impact resistance. Its low cost and ease of manufacturing contribute to its popularity in mass production.
Cons: While it has good chemical resistance, it can be susceptible to UV degradation unless treated. Additionally, its lower heat resistance compared to other thermoplastics may limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is compatible with various media, including acids and bases, making it suitable for containers and packaging. However, its limitations in temperature resistance might affect its use in automotive engine components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, as well as international standards such as ASTM. The availability of polypropylene in local markets can also influence procurement strategies.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is renowned for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring transparency, such as safety goggles and light fixtures. It can withstand temperatures up to 135°C and is highly resistant to heat and UV light.
Pros: The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its strength and durability, which allows for thinner designs without compromising performance. Its ability to be easily molded into complex shapes enhances its versatility.
Cons: Polycarbonate tends to be more expensive than other thermoplastics and can be prone to scratching unless coated. Its processing can also be more complex, requiring precise temperature control.
Impact on Application: Its high impact resistance makes polycarbonate ideal for protective gear and electronic housings. However, the cost may be a barrier for some applications, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider compliance with safety standards, especially for consumer products. Understanding the local market demand for polycarbonate can aid in strategic sourcing.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a popular thermoplastic known for its strength, rigidity, and ease of processing. It has a temperature tolerance of up to 80°C and is commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive parts.
Pros: ABS is cost-effective and offers excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Its ability to be easily painted and finished enhances its aesthetic appeal.
Cons: While ABS is durable, it is less resistant to high temperatures and certain chemicals compared to other thermoplastics. This can limit its use in environments with extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: ABS is compatible with various media but may not perform well in high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments. Its versatility makes it a common choice for everyday consumer products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of ABS, particularly in electronics. Familiarity with standards such as JIS in Japan or DIN in Germany can facilitate compliance.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET is widely recognized for its excellent strength, thermal stability, and recyclability. It can withstand temperatures up to 70°C and is commonly used in packaging applications, such as bottles and containers.
Pros: PET’s recyclability is a significant advantage, aligning with global sustainability trends. Its clarity and barrier properties make it suitable for food and beverage applications.
Cons: PET can be more expensive than other thermoplastics and may require specific processing conditions to achieve optimal results. Its lower impact resistance compared to polycarbonate can also be a limitation.
Impact on Application: PET is particularly effective in packaging applications due to its barrier properties against moisture and gases. However, its limitations in high-temperature applications may restrict its use in certain sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and South America should consider the growing demand for sustainable materials, as well as compliance with food safety standards. Understanding local recycling capabilities can also influence material selection.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Thermoplastic Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoplastic molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive components, packaging | High durability and low cost | Susceptible to UV degradation | Low |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Safety goggles, electronic housings | Exceptional impact resistance | Higher cost and prone to scratching | High |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer electronics, automotive parts | Cost-effective with good mechanical properties | Less resistant to high temperatures | Medium |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Bottles, food packaging | Excellent recyclability and clarity | More expensive, lower impact resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and implications of various thermoplastics, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoplastic molding
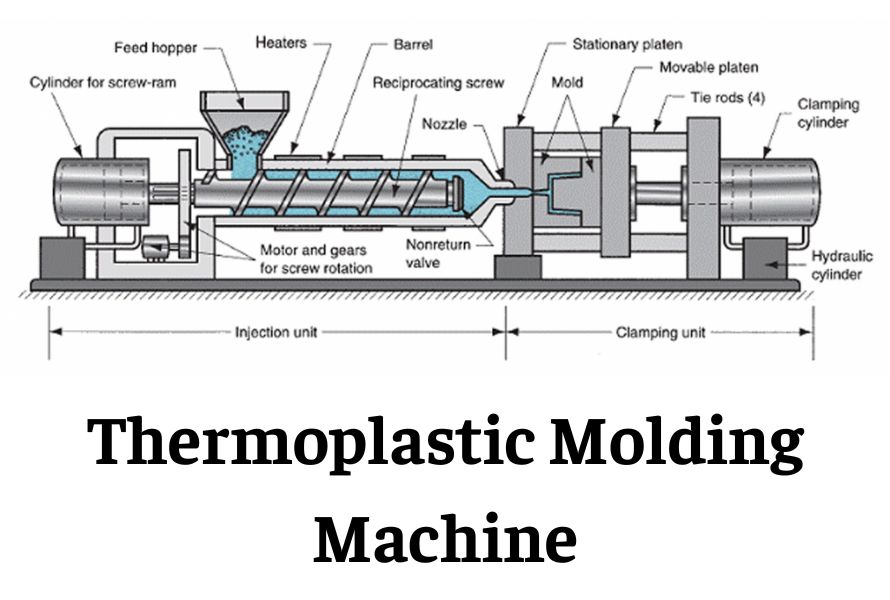
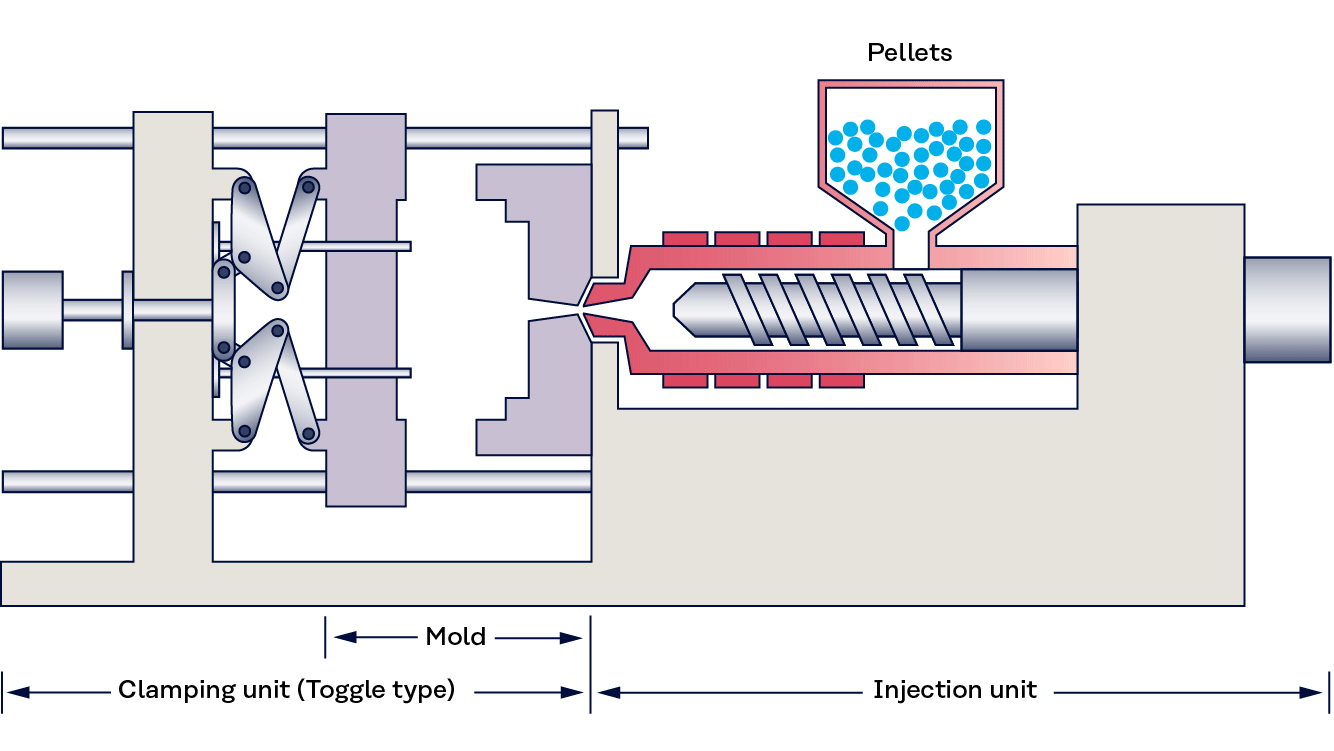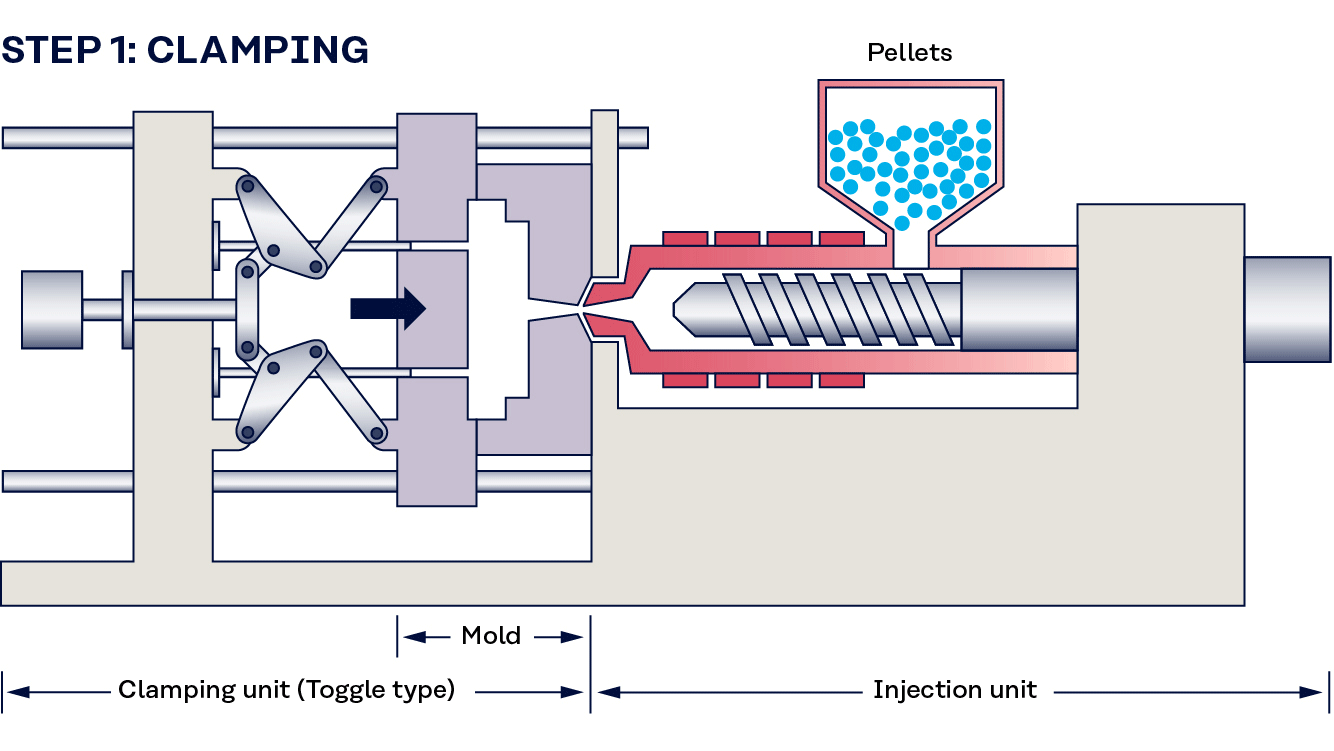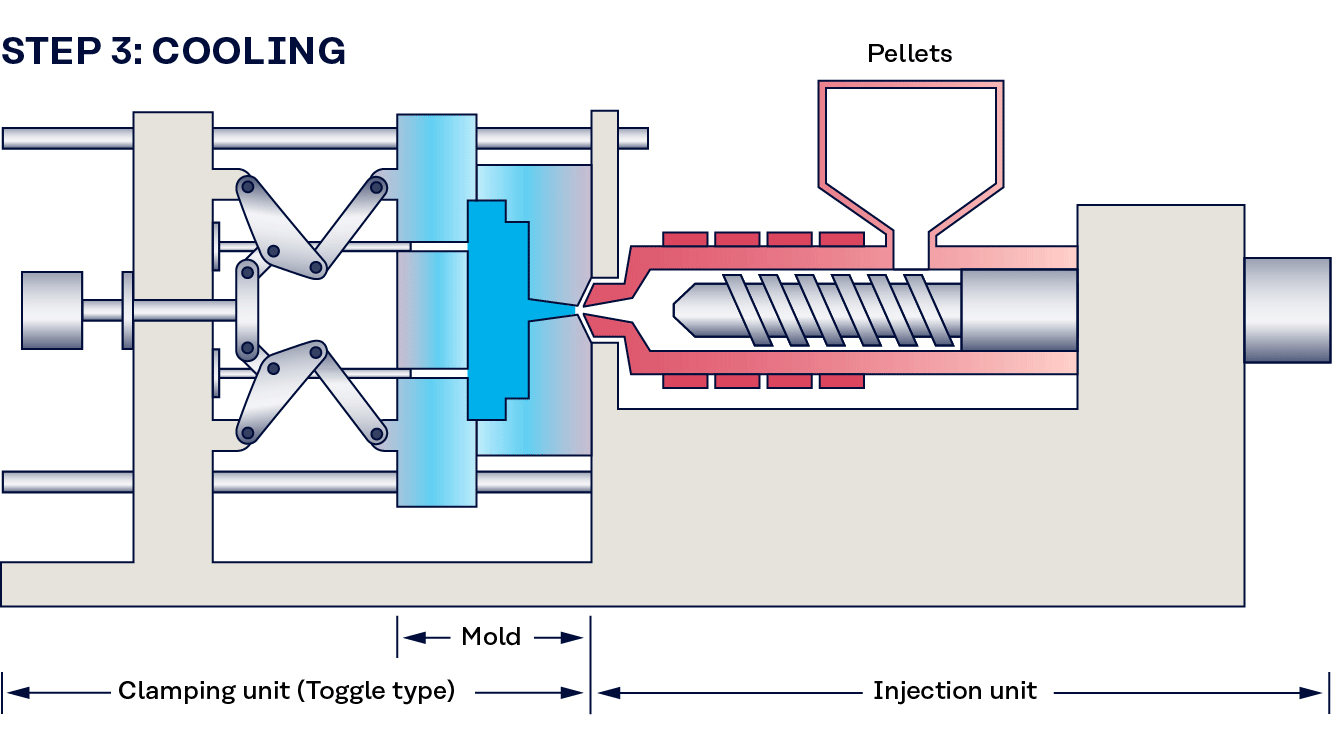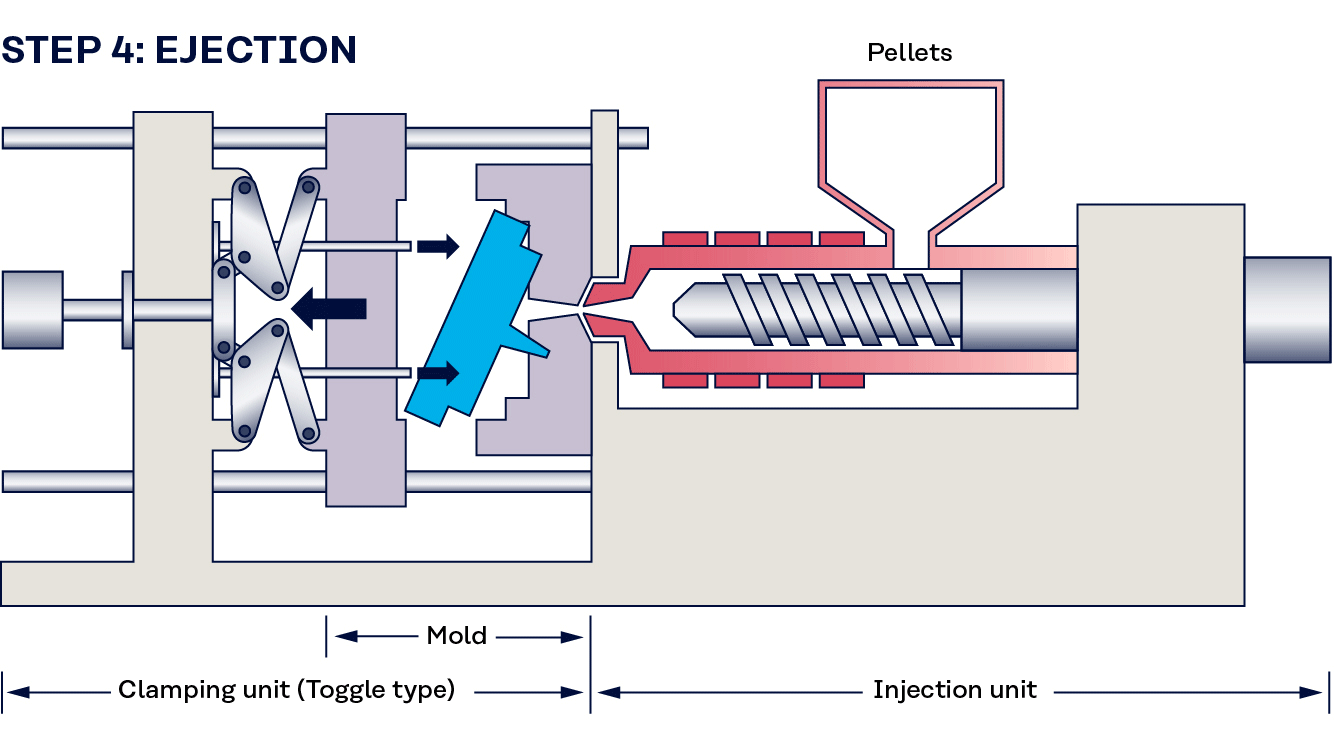
What Are the Main Stages of the Thermoplastic Molding Manufacturing Process?
The thermoplastic molding manufacturing process can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure quality and efficiency in production.
How Is Material Prepared for Thermoplastic Molding?
Material preparation is the foundational step in thermoplastic molding. It begins with the selection of appropriate thermoplastic materials based on the desired properties of the final product. Commonly used materials include polyethylene, polycarbonate, and polypropylene, each chosen for their mechanical strength, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
Once selected, the raw plastic pellets undergo drying to remove moisture, which can negatively affect the melting process and the quality of the molded parts. This step is vital, particularly for hygroscopic materials that absorb moisture from the environment. The dried pellets are then loaded into the injection molding machine’s hopper, ready for the subsequent melting process.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Thermoplastic Molding?
The forming stage involves several intricate techniques, primarily focused on transforming the prepared thermoplastic material into the desired shape. The two most prominent methods are injection molding and blow molding.
-
Injection Molding: This process involves melting the thermoplastic material and injecting it into a mold under high pressure. The precision of this technique allows for the creation of complex shapes and intricate designs, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from consumer products to automotive components.
-
Blow Molding: Used primarily for creating hollow plastic products, blow molding involves heating a plastic tube (parison) and inflating it within a mold. This technique is essential for producing items such as bottles and containers, providing an efficient method for mass production.
How Is Assembly Managed in Thermoplastic Molding?
In some cases, the molded parts may require assembly, particularly if they are components of a larger system. This could involve attaching additional elements, such as electronic components or hardware. The assembly process must be meticulously planned to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly and function as intended.
Automated assembly lines are often employed to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. However, manual assembly may still be necessary for intricate or sensitive components where precision is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the supplier’s capabilities in assembly, as this can significantly affect the overall production timeline and costs.
What Are the Key Finishing Techniques for Thermoplastic Molding?
Finishing is the final stage of the thermoplastic molding process, where additional treatments are applied to enhance the product’s appearance and functionality. Common finishing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
- Trimming and Deburring: Excess material from the molding process is removed to achieve the desired shape and smooth edges.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as polishing, painting, or coating may be used to improve aesthetics and durability. This step is especially important for products that will be exposed to harsh environments or require a specific visual appeal.
- Quality Checks: Each part undergoes rigorous quality checks during the finishing stage to ensure it meets the specified standards before being packaged and shipped.
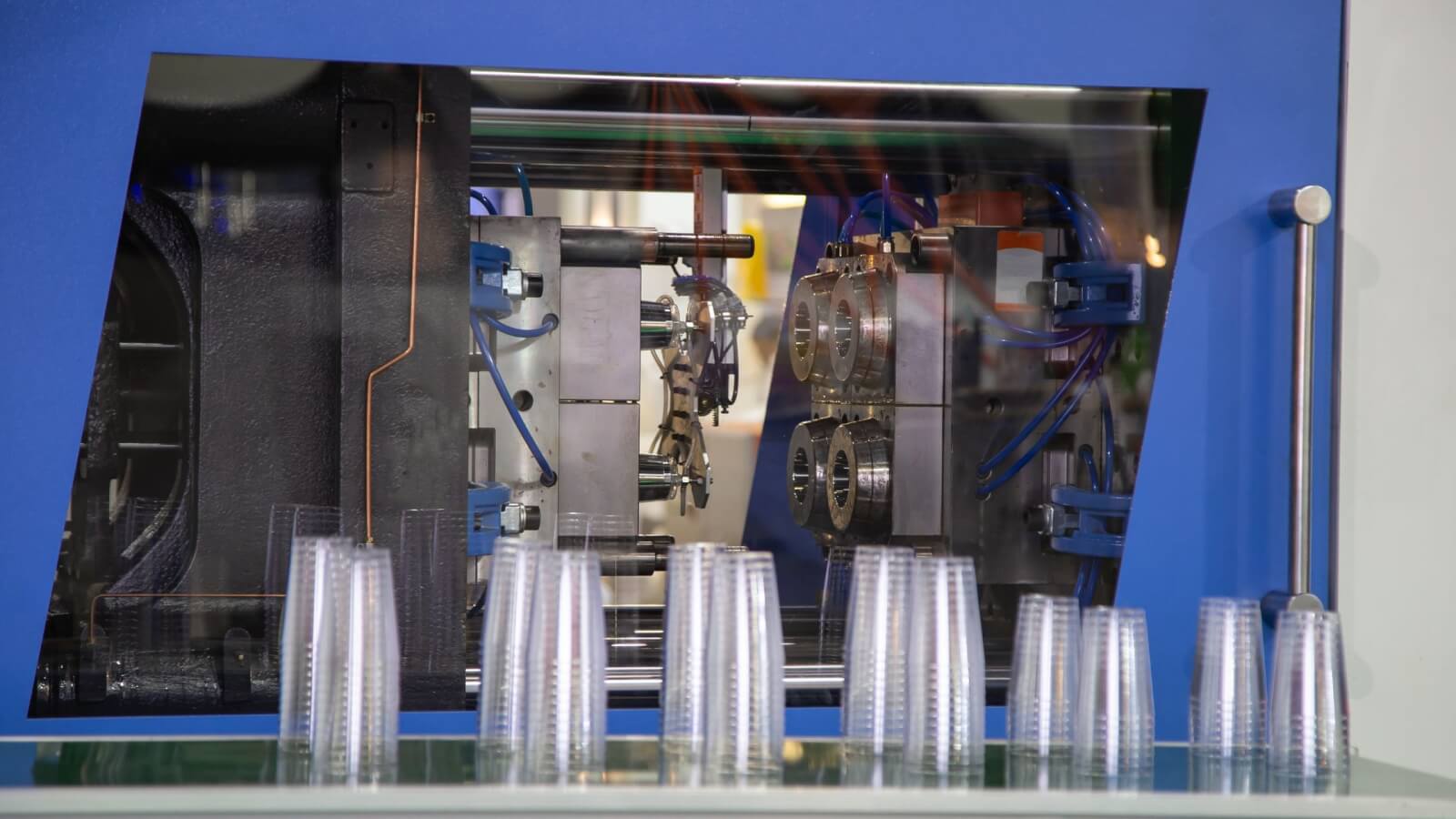
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards Relevant to Thermoplastic Molding?
Quality assurance is critical in thermoplastic molding, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is essential for verifying supplier capabilities.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems, applicable across various industries, including thermoplastic molding. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a supplier has established a robust quality management framework, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European market and API standards for oil and gas components are crucial for ensuring product safety and reliability. Buyers should inquire about these certifications during the supplier selection process to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into Thermoplastic Molding?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the thermoplastic molding process, ensuring that products meet the required specifications at various stages of production. Key QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on raw materials before they enter the production process. Suppliers should conduct thorough checks to verify that the materials meet quality standards and specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the molding process, regular inspections should be performed to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the finishing stage, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that each part meets the established quality criteria. This may involve dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Thermoplastic Molding?
B2B buyers should be aware of the various testing methods employed to ensure product quality in thermoplastic molding. Common testing methods include:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility of the molded parts to ensure they meet performance standards.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating the thermal properties of the materials, such as melting point and heat deflection temperature, to ensure suitability for the intended application.
- Dimensional Testing: Using precision measurement tools to verify that the molded parts adhere to specified dimensions and tolerances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards, B2B buyers can implement several verification strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and compliance with relevant standards. This direct observation can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting regular QC reports can help buyers stay informed about the supplier’s performance and any issues encountered during production. These reports should detail the results of inspections and tests conducted at various checkpoints.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations can conduct comprehensive evaluations and provide certifications that reassure buyers of the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards, necessitating thorough research and due diligence.
Buyers should also be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can mitigate these challenges and foster a successful partnership.
In conclusion, the thermoplastic molding process is a complex interplay of material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, supported by rigorous quality assurance practices. B2B buyers must navigate the intricacies of manufacturing and quality control to ensure they partner with suppliers who can deliver high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thermoplastic molding’
To successfully procure thermoplastic molding services, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide B2B buyers through the critical steps necessary to ensure effective sourcing, quality assurance, and long-term partnerships with suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of your thermoplastic parts, including dimensions, tolerances, and material properties. This step is crucial as it serves as the foundation for all subsequent discussions with potential suppliers. Be specific about the application of the parts to ensure that the supplier can meet the necessary performance criteria.
- Material Selection: Specify the type of thermoplastic required (e.g., ABS, polycarbonate) based on the application’s needs.
- Design Considerations: Provide detailed CAD files and any relevant design guidelines that may impact the molding process.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in thermoplastic molding. This involves looking for companies with a proven track record in your industry and a solid reputation for quality.
- Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers who have experience with the specific types of products you need.
- Geographical Considerations: Consider suppliers in regions that align with your logistics capabilities to minimize shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the technical capabilities of potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. This includes reviewing their machinery, technology, and production processes.
- Equipment Assessment: Confirm that the supplier uses advanced injection molding machines and has the necessary technology for precision manufacturing.
- Production Capacity: Ensure they can handle your order volume and meet delivery timelines without compromising quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a large commitment, request samples or prototypes of the thermoplastic parts. This allows you to evaluate the supplier’s quality and ability to meet your specifications.
- Quality Assessment: Inspect the samples for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material properties.
- Functional Testing: If applicable, perform tests to validate the part’s performance in real-world conditions.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen supplier holds the necessary certifications and complies with relevant industry standards. This is vital for maintaining quality and safety throughout the production process.
- Quality Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific quality standards that demonstrate a commitment to excellence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Verify that the supplier adheres to local and international regulations, particularly if your products will be sold in multiple markets.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Develop strong lines of communication with your supplier to facilitate a smooth collaboration. Clear communication helps in addressing any issues quickly and ensures that both parties are aligned.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss project progress, challenges, and any adjustments needed.
- Point of Contact: Designate a primary contact person on both sides to streamline communication and avoid misunderstandings.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms that protect your interests while fostering a mutually beneficial relationship. This includes pricing, lead times, and quality assurance measures.
- Contractual Agreements: Ensure that all agreements are documented, specifying responsibilities, timelines, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options that suit both parties, considering factors like upfront costs and milestone payments based on project phases.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for thermoplastic molding, ensuring quality, efficiency, and long-term success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoplastic molding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Thermoplastic Molding?
When sourcing thermoplastic molding services, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of thermoplastic materials significantly influences costs. Common materials like polyethylene and polycarbonate vary in price depending on their properties and availability. Specialty materials or those with certifications can elevate costs further.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both skilled and unskilled workers involved in the molding process. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, these expenses can be substantial. Conversely, countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the factory’s operational expenses, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Understanding the overhead rates of potential suppliers can provide insight into the overall pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be one of the most significant upfront investments in thermoplastic molding. Custom molds are essential for producing specific parts, and their design and manufacturing can vary widely in cost depending on complexity and material.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of molded parts incurs costs through testing and inspection processes. Suppliers with robust QC measures might charge higher prices, but this investment can prevent costly defects later.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs should be factored in, especially for international shipping. Incoterms can also affect these costs, influencing who bears the shipping risk and expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the market rates and competitive landscape can help buyers gauge whether a supplier’s margin is reasonable.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Pricing?
Pricing in thermoplastic molding is often influenced by volume and the specifications of the project.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts with specific design requirements or unique materials will generally incur higher costs. Clear communication regarding specifications can help avoid unexpected charges and ensure that the supplier can meet the necessary criteria.
What External Factors Affect Thermoplastic Molding Pricing?
Several external factors can also impact pricing in thermoplastic molding:
-
Material Availability: Fluctuations in the availability and price of raw materials can significantly affect overall costs. Buyers should stay informed about market trends that may influence material pricing.
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers offering products with specific quality certifications (ISO, ASTM, etc.) may charge a premium. However, these certifications can provide assurance of product reliability, which is crucial for certain industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may command higher prices but can offer peace of mind.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips to negotiate effectively:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial pricing. Consider logistics, potential tariffs, and quality assurance costs to determine the TCO. This holistic view can reveal hidden costs that might negate apparent savings.
-
Leverage Competition: Engage multiple suppliers to compare quotes and services. This not only provides leverage in negotiations but also helps identify the best fit for your needs.
-
Be Clear About Specifications: Provide detailed specifications and requirements upfront to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Explore Flexible Payment Terms: Discuss payment terms that can ease cash flow, such as extended payment periods or milestone payments aligned with production phases.
What Should Buyers Know About Indicative Pricing?
While indicative pricing can serve as a benchmark, it’s essential to recognize that actual costs can vary based on numerous factors. Market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements can all influence final pricing. Always request detailed quotes and clarify any assumptions to ensure transparency in the pricing process.
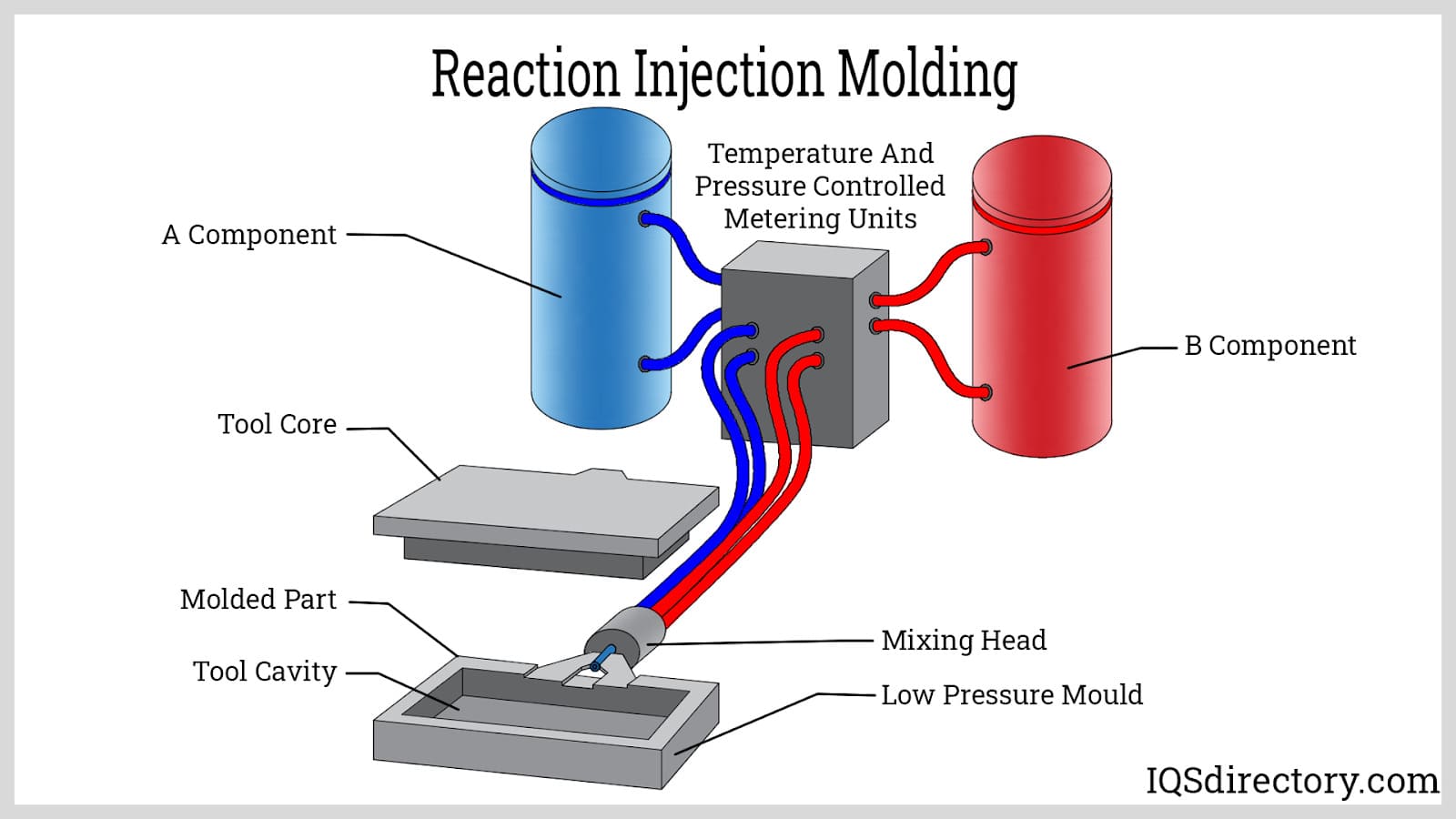
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thermoplastic molding With Other Solutions
In the quest for efficient manufacturing solutions, businesses often seek alternatives to thermoplastic molding. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various methods can guide international B2B buyers in selecting the most suitable technology for their production needs. This analysis compares thermoplastic molding against two prominent alternatives: compression molding and blow molding.
| Comparison Aspect | Thermoplastic Molding | Compression Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Good for large parts with less detail | Ideal for hollow objects and containers |
| Cost | Moderate setup and material costs | Generally lower material costs | Lower tooling costs for high volume |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and training | Easier to implement for simpler designs | Requires specific machinery but is straightforward |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks needed | Low; less wear on molds | Moderate; needs maintenance for blow molding machines |
| Best Use Case | Complex parts in automotive and consumer goods | Large parts, automotive components | Hollow containers, packaging, and toys |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Compression Molding?
Compression molding involves placing raw material into a heated mold and applying pressure. This method is particularly advantageous for producing larger parts with less intricate designs. One of its significant benefits is lower material costs, as it often requires less expensive raw materials compared to thermoplastics. However, compression molding is less suited for high-precision applications and can have longer cycle times, which may not meet the demands of industries requiring rapid production.
How Does Blow Molding Compare to Thermoplastic Molding?
Blow molding is specifically designed for creating hollow plastic products. This process is efficient for mass production of containers and packaging materials, making it a cost-effective solution when producing large volumes. The initial tooling costs are generally lower than thermoplastic molding, making it attractive for startups or companies testing new products. However, blow molding is limited to specific shapes and is not suitable for complex geometries, which may restrict its applicability in more demanding industries.
Conclusion: Which Solution Is Right for Your Business Needs?
Choosing the right manufacturing method hinges on your specific requirements, including product design, production volume, and budget constraints. Thermoplastic molding excels in applications requiring high precision and complex shapes, making it suitable for automotive and consumer goods. Compression molding can be a viable alternative for larger parts, while blow molding is best for hollow products. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each method, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoplastic molding
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thermoplastic Molding?
When engaging in thermoplastic molding, understanding critical technical properties is essential for making informed decisions. Here are several key specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type and quality of thermoplastic used in the molding process. Different grades possess unique mechanical and thermal properties, affecting durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals. For instance, high-performance grades like polycarbonate are suitable for demanding applications such as automotive components, while standard grades like polyethylene are often used for consumer products. Selecting the correct material grade is crucial for meeting product specifications and ensuring longevity. -
Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, which is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assembly processes. Tight tolerances are often required in applications where precision is paramount, such as in aerospace or medical devices. Conversely, looser tolerances may be acceptable for less critical applications. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers assess the feasibility of manufacturing processes and ensures that the final product meets functional requirements. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one cycle of the injection molding process, including injection, cooling, and ejection. Shorter cycle times can significantly enhance productivity and reduce manufacturing costs. For B2B buyers, understanding cycle time is vital for project planning and inventory management, enabling more efficient production scheduling and quicker market entry. -
Impact Resistance
Impact resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden forces or shocks without breaking. This property is particularly important in industries like automotive and consumer goods, where products may experience rough handling or impacts during their lifecycle. Selecting thermoplastics with high impact resistance ensures durability and customer satisfaction, making it a crucial consideration for B2B buyers. -
Thermal Stability
Thermal stability refers to a material’s ability to maintain its properties when exposed to heat. This is especially important in applications where parts may be subjected to high temperatures. Buyers must consider thermal stability to ensure that the molded components will perform effectively under their intended operating conditions, thus preventing failures and reducing warranty claims.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Thermoplastic Molding?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the thermoplastic molding sector. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In thermoplastic molding, buyers often work with OEMs to source custom parts tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate supply chains and secure high-quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant in thermoplastic molding as it affects inventory costs and production planning. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to ensure they can meet their production needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers inviting them to provide pricing for specific products or services. In the context of thermoplastic molding, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and optimal quality. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process. This knowledge can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses and ensure smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In thermoplastic molding, lead times can vary based on factors such as production schedules and material availability. Being aware of lead times is essential for buyers to manage their supply chains effectively and maintain production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes in thermoplastic molding, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thermoplastic molding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Thermoplastic Molding?
The thermoplastic molding sector is experiencing significant transformation, driven by various global factors. Increased demand for lightweight and durable materials, especially in the automotive, electronics, and consumer goods sectors, is propelling growth. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, manufacturers are increasingly adopting advanced technologies like automation and Industry 4.0, which streamline production processes and improve efficiency. For international B2B buyers, this trend translates to enhanced product quality and reduced lead times.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and additive manufacturing, are also gaining traction in thermoplastic molding. These innovations allow for rapid prototyping and customization, catering to specific market needs. Furthermore, the rise of smart manufacturing systems is enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics, fostering a more agile supply chain. As B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria and Vietnam navigate these trends, aligning with suppliers who leverage these technologies can lead to competitive advantages.
Sourcing strategies are evolving as well, with an increasing emphasis on local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. This shift is particularly relevant for markets in South America and the Middle East, where geopolitical factors can influence sourcing decisions. Buyers must remain vigilant and adaptable, embracing a dynamic approach to sourcing that aligns with these market changes.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Thermoplastic Molding?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the thermoplastic molding industry. The environmental impact of plastic production and disposal is drawing scrutiny, leading to a demand for more sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and implementing eco-friendly processes. This includes using recycled materials and adopting energy-efficient manufacturing practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial, as businesses face pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to ensure that their supply chains are free from labor abuses and environmental harm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and participation in global initiatives like the UN Global Compact can enhance a company’s reputation and align with the values of socially conscious buyers.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
The use of biodegradable thermoplastics and innovative materials that minimize environmental impact is also on the rise. Buyers should seek partnerships with suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications and demonstrate a clear commitment to sustainability. This not only meets regulatory requirements but also caters to the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Thermoplastic Molding Relevant to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The history of thermoplastic molding dates back to the early 1900s, with significant advancements that have shaped the industry into what it is today. The introduction of Bakelite by Leo Baekeland marked a turning point, as it was the first synthetic plastic, paving the way for the development of various thermoplastic materials. Over the decades, innovations in molding techniques, such as injection molding and blow molding, have revolutionized production capabilities, allowing for mass production of complex shapes and designs.
As the industry evolved, so did the applications of thermoplastics, expanding from simple household items to critical components in automotive and aerospace sectors. Understanding this historical context helps today’s B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and materials that have led to the current capabilities in thermoplastic molding. This knowledge can inform sourcing decisions and highlight the importance of partnering with suppliers who are not only well-versed in these advancements but also committed to continuous improvement and innovation in their processes.

Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoplastic molding
-
How do I choose the right thermoplastic molding process for my product?
Selecting the appropriate thermoplastic molding process depends on several factors, including the complexity of the part, production volume, and material specifications. Common methods include injection molding for high-volume production and complex shapes, blow molding for hollow products, and rotational molding for large, hollow items. Assess your product’s design requirements, desired material properties, and budget constraints to determine the most suitable process. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier can also provide insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What are the key materials used in thermoplastic molding?
Thermoplastic molding utilizes various materials, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and nylon, each offering unique characteristics. For instance, polypropylene is known for its chemical resistance and flexibility, while polycarbonate is valued for its strength and transparency. The choice of material should align with the application requirements, such as heat resistance, strength, and recyclability. Consult with suppliers to ensure optimal material selection based on your product’s performance and environmental considerations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for thermoplastic molded products?
Minimum order quantities for thermoplastic molded products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the part. Typically, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. High-volume orders often yield lower per-unit costs, while smaller quantities may incur higher production expenses. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production plans and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing thermoplastic molding?
Payment terms in the thermoplastic molding industry can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (often 30-50%), with the balance due upon completion or shipment of the order. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established customers. It’s important to clarify payment terms during negotiations to ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting processes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in thermoplastic molding?
Implementing a robust quality assurance process is crucial when sourcing thermoplastic molded products. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Ask about their testing protocols, including material inspections, dimensional checks, and functional testing. Request samples or prototypes before full-scale production to verify quality and ensure that the final product meets your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing thermoplastic molded products internationally?
When sourcing thermoplastic molded products from international suppliers, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to handle logistics and ensure they provide clear information about shipping methods and timelines. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs clearance and ensure compliance with import regulations in your country. -
How do I vet suppliers for thermoplastic molding services?
Vetting suppliers is essential to ensure reliability and quality. Start by researching potential suppliers’ industry reputation, certifications, and customer reviews. Request references from past clients and assess their experience with similar projects. Conduct site visits if possible or arrange virtual tours to evaluate manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. Establishing clear communication and understanding their production capacity is vital for a successful partnership. -
Can I customize thermoplastic molded products to meet specific requirements?
Yes, customization is a significant advantage of thermoplastic molding. Suppliers can often tailor designs, materials, and finishes to meet your specific needs. Discuss your product requirements in detail with potential suppliers, including design modifications, color matching, and material specifications. Providing detailed design files and specifications will help suppliers understand your needs and deliver products that align with your vision.
Top 7 Thermoplastic Molding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Thermoplastic Molding Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic molding involves forming plastic parts by injecting molten resin into a mold. Key features include:
– Thermoplastics can be reheated and reshaped, making them advantageous for recycling (up to 30% recycled content).
– Types of thermoplastic molding include rapid injection molding for prototypes and production injection molding for full-scale manufacturing.
– Applications span vari…
2. House of Adorn – Thermoplastics for Millinery
Domain: houseofadorn.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastics for Blocking & Sculpting in Millinery include materials such as Fosshape, WOrbla, Myla, Hatbond, and Crystoform. These materials become soft when treated with heat, allowing for molding, and retain their shape once cooled. They are suitable for various applications including masks, costumes, millinery, castings, and sculptural artworks. Key products include:
– Product Kit – Thermopl…
3. Toray – Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic
Domain: cf-composites.toray
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“Thermoplastic Molding Materials”: {“Short Fiber Pellet”: {“Description”: “Carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic (CFRTP) designed for injection molding.”, “Properties”: [“Light weight”, “Excellent strength”, “Stiffness”, “Dimensional accuracy”, “Sliding properties”], “Base Resins”: [“PP”, “PC”, “ABS”, “Nylon 6”, “Nylon 66”, “Nylon 610”, “PBT”, “PPS”], “Applications”: [“Automotive”, “Electric home…
4. Forged Acrylics – Thermoplastic Molding Solutions
Domain: forgedacrylics.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic molding is a versatile manufacturing process used to produce various plastic products. Key techniques include injection molding, blow molding, compression molding, and extrusion molding. Essential tools for beginners include an injection molding machine, CAD software for design, mold release agents, a drill press, an aluminum mold frame, a water bath for temperature control, and a bl…
5. Protolabs – Engineering-Grade Thermoplastics
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers a range of thermoplastic materials for injection molding, focusing on engineering-grade thermoplastics. Key materials include:
1. **ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)**
– **Benefits**: Tough, impact-resistant, low shrink, high dimensional stability, good resistance to acids and bases, relatively inexpensive.
– **Applications**: Cosmetic parts, handheld devices, hous…
6. Aline Components – Custom Injection Molding Services
Domain: alinecomponents.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic Injection Molding Process at Aline Components includes custom injection molding services since 1965. Key features include: High Quality Thermoplastic Materials, Custom Manufactured Molds made from high quality steel or aluminum, and Advanced Injection Molding Machines. Mold options available are Hot Runner Molds, Cold Runner Molds, Insert Molds, Two-Shot Molds, Stack Molds, Unscrewin…
7. Nova Stevensville – Advanced Thermoplastic Molding Solutions
Domain: novastevensville.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Nova Stevensville specializes in thermoplastic molding technology, focusing on advancements such as increased material selection with purpose-specific thermoplastics like polyetherimide (PEI), polysulfone (PSU), and polyether ether ketone (PEEK). These materials offer properties like chemical resistance, improved performance under mechanical stresses, and stability at high temperatures. The compan…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoplastic molding
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in thermoplastic molding is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains and enhance product quality. By understanding the diverse molding processes—such as injection, overmolding, and blow molding—companies can better select materials that meet specific application requirements while considering cost-effectiveness and sustainability. The adaptability of thermoplastics makes them invaluable across multiple industries, enabling businesses to innovate and respond to market demands swiftly.
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, forging strong relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to significant competitive advantages. As the global demand for sustainable and high-performance materials continues to rise, investing in strategic sourcing practices will not only streamline production but also ensure compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Looking ahead, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and explore new partnerships that can drive growth and efficiency. Embrace the opportunities presented by the thermoplastic molding industry to stay ahead in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Your next step could redefine your product line and bolster your business for future challenges.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic molding
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.