Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Shredder Design Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shredder design
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing effective shredder design solutions presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil. The need for efficient shredding equipment that meets both operational requirements and sustainability goals has never been more pressing. This guide addresses these challenges by providing an in-depth exploration of various shredder types, including those designed for plastic, metal, and cardboard, as well as their specific applications in diverse industries.
Navigating the global market for shredders involves understanding the nuances of supplier vetting, cost implications, and the latest technological advancements. This comprehensive resource empowers buyers by offering actionable insights into the selection process, ensuring that decision-makers can confidently assess the best options for their unique needs. Additionally, we will delve into best practices for maximizing the return on investment in shredding solutions, highlighting key considerations that influence both performance and durability.
Whether you’re operating in the Middle East, South America, or Europe, this guide serves as a strategic tool, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the intricacies of shredder design and the associated market dynamics, you can enhance your operational efficiency while contributing to sustainable practices in your industry.
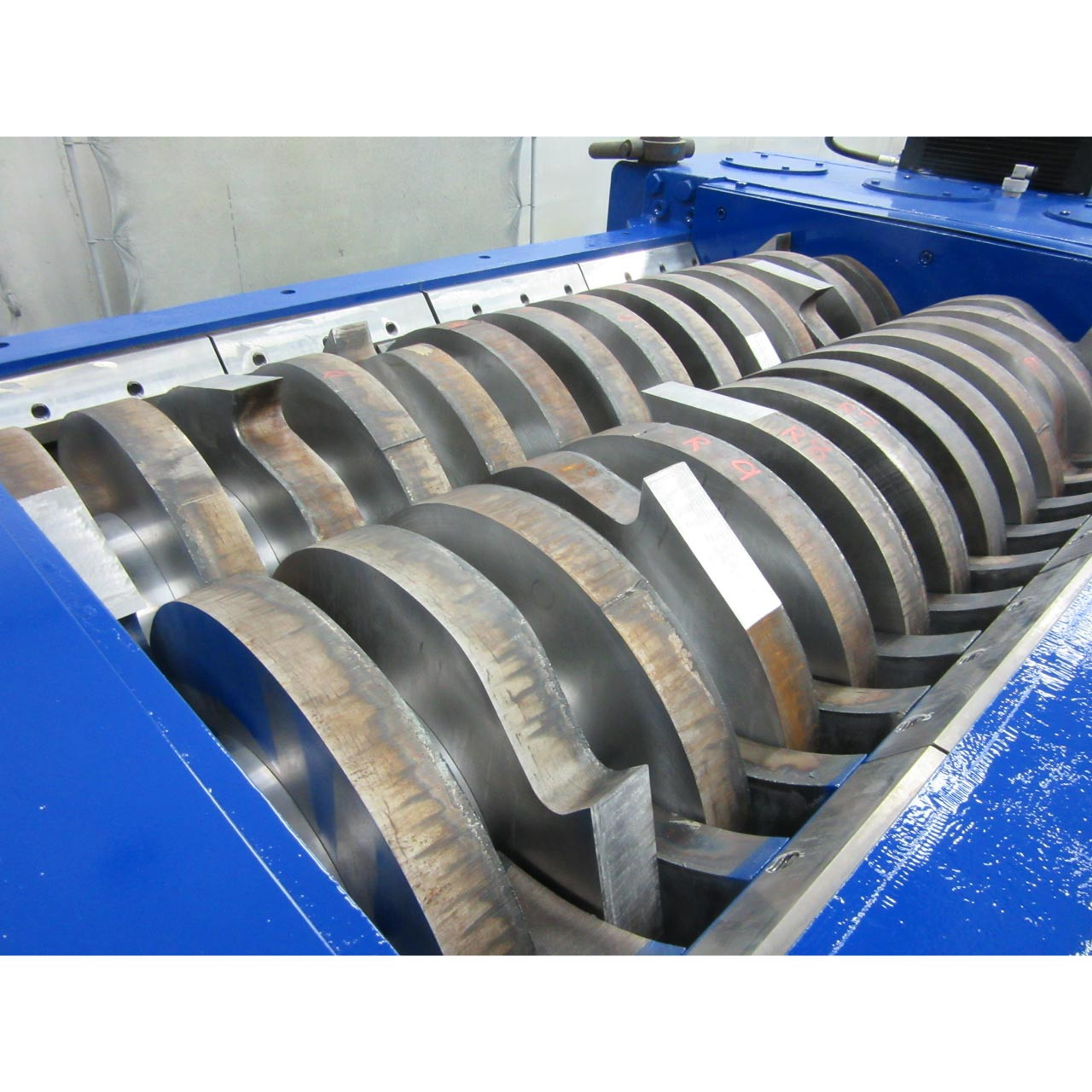
Understanding shredder design Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Shredders | Designed for various plastic types; often includes modular designs for flexibility. | Recycling facilities, manufacturing plants | Pros: Versatile, eco-friendly; Cons: May require specific maintenance for different plastics. |
| Metal Shredders | Heavy-duty construction; capable of handling tough materials like steel and aluminum. | Scrap yards, metal recycling operations | Pros: High durability, efficient; Cons: Higher initial investment and energy consumption. |
| Cardboard Shredders | Specialized for processing cardboard; often creates perforated material for packing. | Warehouses, packaging companies | Pros: Reduces waste volume, cost-effective; Cons: Limited to cardboard materials. |
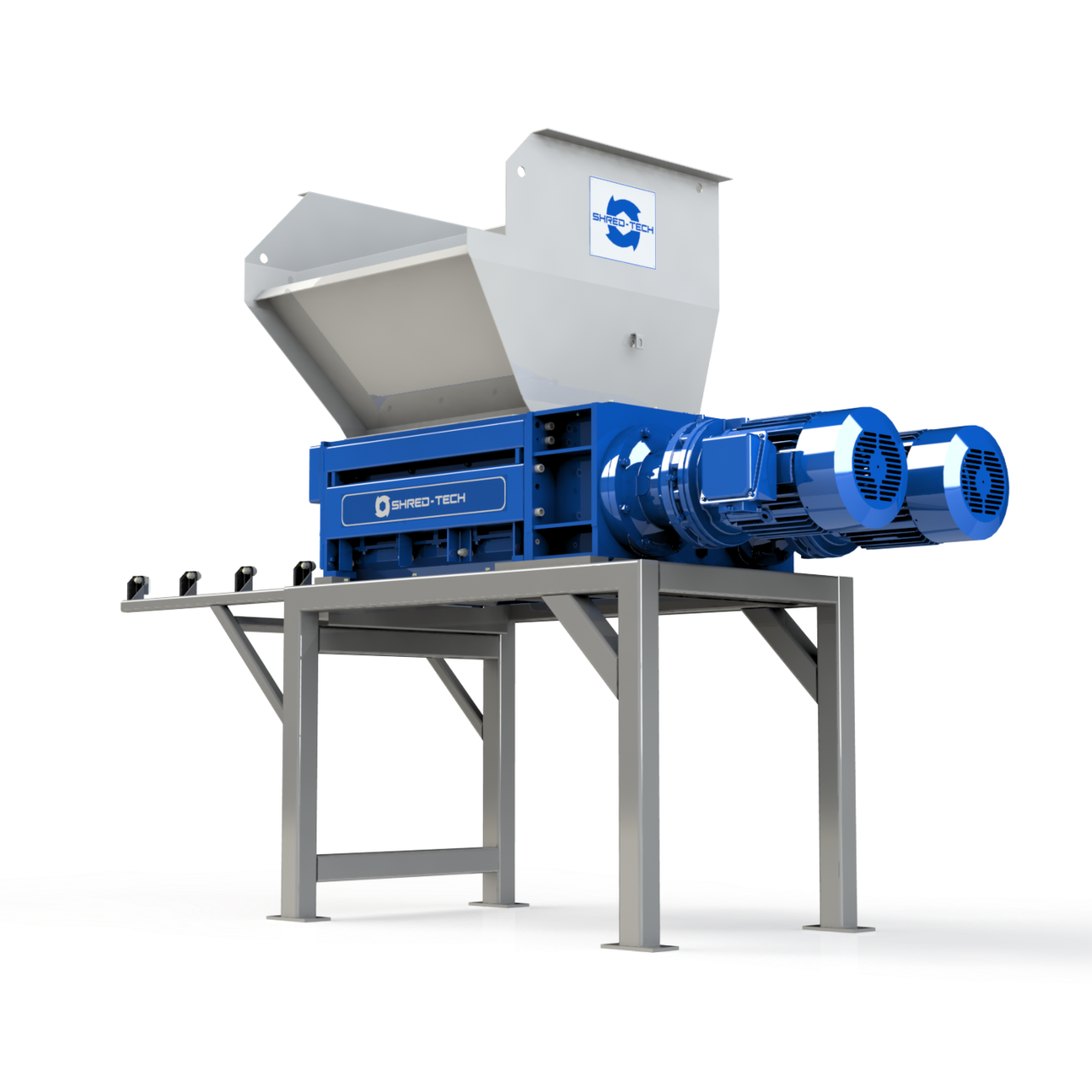
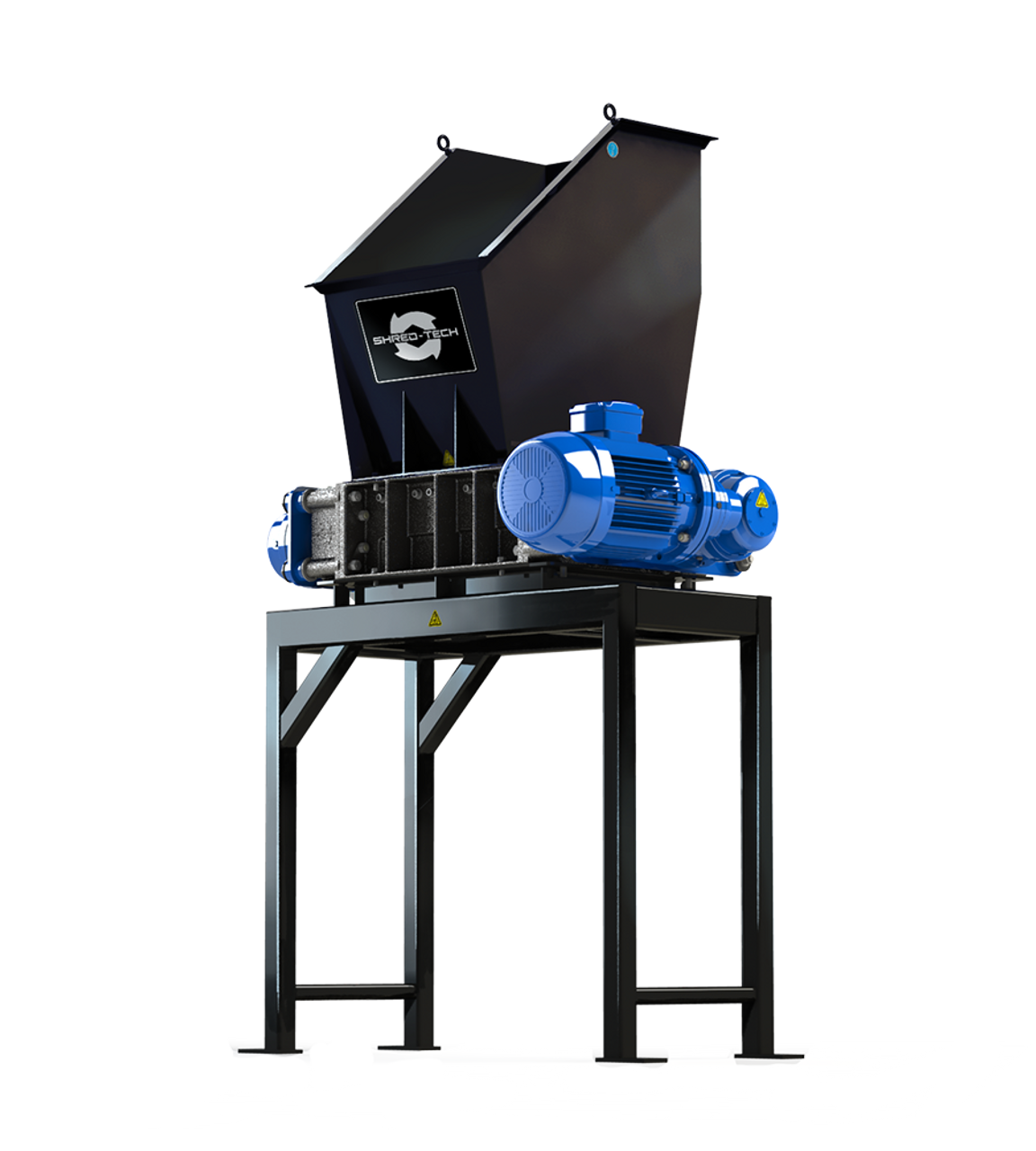
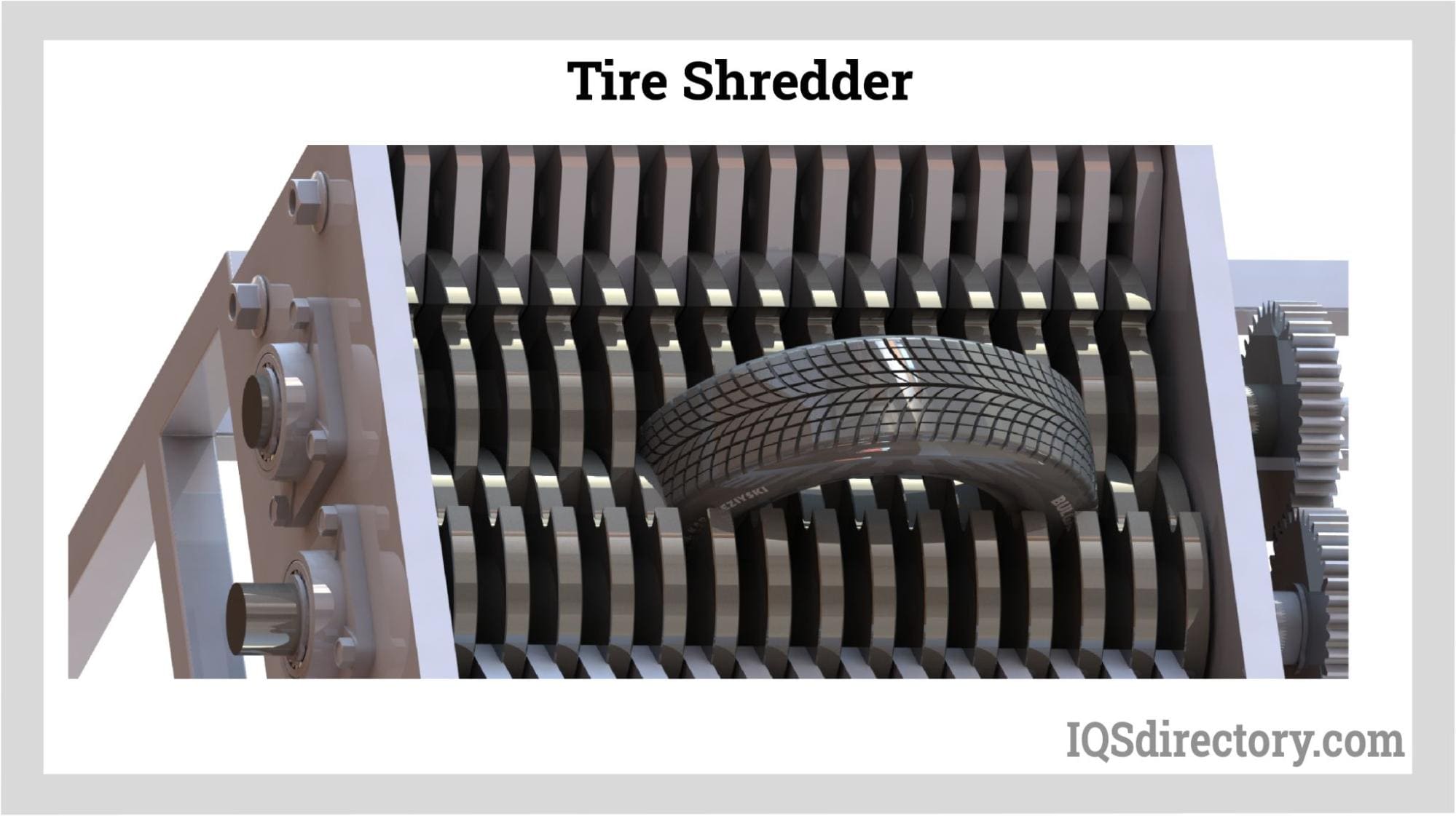
| Tire Shredders | High torque systems designed for breaking down tires; often equipped with multiple shredding stages. | Tire recycling plants, waste management | Pros: Effective in reducing tire volume; Cons: Requires significant power and maintenance. |
| Organic Waste Shredders | Focused on processing organic materials; often includes features for composting. | Agricultural sectors, waste management | Pros: Supports sustainability, reduces landfill waste; Cons: Limited to organic materials, may require regular cleaning. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Plastic Shredders?
Plastic shredders are engineered to handle a range of plastic materials, making them essential in recycling operations. They often feature modular designs that allow for easy upgrades or adjustments to meet specific processing needs. B2B buyers should consider the types of plastics they will be shredding, as different models may be optimized for various plastic compositions. Additionally, maintenance requirements can vary, necessitating a thorough understanding of the operational environment.
How Do Metal Shredders Stand Out in the Market?
Metal shredders are built to withstand the rigors of processing tough materials like steel and aluminum. Their robust construction and high torque capabilities make them ideal for scrap yards and metal recycling facilities. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the shredder’s capacity and power requirements, as these can significantly impact operational costs. While they offer excellent durability and efficiency, the initial investment can be substantial, and ongoing energy use should be factored into budgeting.
What Makes Cardboard Shredders Essential for Warehouses?
Cardboard shredders are specifically designed to process cardboard waste, transforming it into manageable sizes or perforated sheets for packaging. This capability is particularly beneficial for warehouses and packaging companies looking to minimize waste and optimize storage. Buyers should assess the shredder’s output quality and speed, as well as its compatibility with existing waste management systems. While they offer cost-effective waste reduction, their utility is limited to cardboard materials.
Why Are Tire Shredders Critical for Recycling Operations?
Tire shredders utilize high torque systems capable of breaking down tires into smaller, manageable pieces. This is crucial for tire recycling plants that aim to repurpose rubber and metal components. B2B buyers must consider the shredder’s power requirements and maintenance needs, as these machines can be demanding in terms of energy and upkeep. Although they are effective in reducing tire volume, the complexity of operation can pose challenges for some businesses.
How Do Organic Waste Shredders Contribute to Sustainability?
Organic waste shredders are designed to process biodegradable materials, making them vital for agricultural sectors and waste management initiatives. They often include features that facilitate composting, aligning with sustainability goals. Buyers should evaluate the types of organic materials they plan to shred and the shredder’s efficiency in processing these inputs. While they significantly reduce landfill waste and promote recycling, their application is limited to organic materials, necessitating careful consideration of waste streams.
Key Industrial Applications of shredder design
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Shredder Design | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Processing of municipal solid waste | Efficiently reduces waste volume, facilitating easier transport and disposal | Durability, capacity, and compatibility with local waste types |
| Recycling | Plastic recycling for sustainable materials | Converts waste into reusable materials, enhancing sustainability efforts | Material type compatibility, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency |
| Manufacturing | Shredding of scrap metal and production waste | Maximizes material recovery, lowering raw material costs | Shredder power, size, and adaptability to different metal types |
| Automotive | Tire shredding for recycling and material recovery | Reduces disposal costs and recycles valuable materials | High torque capability, safety features, and compliance with local regulations |
| Packaging | Cardboard shredding for packaging material | Creates flexible packaging solutions, reducing material costs | Shredder size, throughput rate, and ease of integration with existing systems |
How is Shredder Design Used in Waste Management?
In the waste management sector, shredders are employed to process municipal solid waste, including organic materials, plastics, and metals. By reducing the volume of waste, shredders facilitate more efficient transport and disposal, minimizing landfill use. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable shredders that can handle diverse waste types is crucial. Additionally, understanding local waste regulations and ensuring compliance can help prevent operational setbacks.
What Role Does Shredder Design Play in Recycling?
Shredder design is pivotal in the recycling industry, particularly for plastics. These machines convert waste plastics into smaller particles, making them easier to process and repurpose. This not only supports sustainable practices but also offers significant cost savings by providing a reliable source of raw materials. Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe must consider the shredder’s compatibility with various plastic types and its energy efficiency to optimize their recycling operations.
How is Shredder Design Beneficial for Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, shredders are utilized to process scrap metal and production waste, which maximizes material recovery. This process reduces raw material costs and minimizes waste disposal expenses. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe, selecting a shredder with the right power and size is essential to accommodate different metal types. Furthermore, ensuring the shredder can adapt to various production environments enhances operational efficiency.
What is the Importance of Shredder Design in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry relies on tire shredders to efficiently recycle tires, turning them into reusable materials. This process not only lowers disposal costs but also recycles valuable materials such as rubber and steel. International buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, should prioritize shredders with high torque capabilities and robust safety features to handle the tough nature of tire materials while adhering to local environmental regulations.
How Does Shredder Design Enhance Packaging Solutions?
Shredders are increasingly used in the packaging sector to process cardboard into flexible material for packaging. This application not only reduces material costs but also improves packaging efficiency. B2B buyers in regions like Brazil should focus on the shredder’s size and throughput rate to ensure it meets their production needs. Additionally, ease of integration with existing systems is a key consideration to streamline operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘shredder design’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Waste Reduction in Diverse Industries
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing, construction, or food services often struggle with the effective management of waste materials. This can lead to excessive costs related to waste disposal, regulatory fines, and environmental concerns. For instance, a manufacturing plant may generate a variety of waste types—plastic, metal, and cardboard—that require different handling processes. If not managed properly, the mishandling of these materials can result in operational inefficiencies and increased disposal costs.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest in a versatile shredder design that accommodates multiple material types. Shredders designed to handle a variety of waste can streamline the recycling process, reducing the need for multiple machines. When sourcing shredders, look for models that come equipped with interchangeable blades and adjustable settings to effectively process different materials. Additionally, consider integrating a shredding system with a built-in baler to compact materials, making them easier to store and transport. This dual-functionality not only saves space but also enhances efficiency in waste management.
Scenario 2: Navigating Equipment Assembly and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity associated with assembling and maintaining shredding equipment. Many buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, may lack the technical expertise required for proper setup and ongoing maintenance of sophisticated machines. This can lead to prolonged downtime, increased operational costs, and frustration among staff, ultimately impacting productivity.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should prioritize equipment that comes with comprehensive assembly guides and customer support. For instance, opting for shredders that offer a step-by-step assembly guide and readily available technical support can significantly reduce the learning curve. Additionally, consider purchasing shredders that allow for modular components, which can be easily replaced or upgraded as needed. This approach simplifies maintenance and allows for quick repairs, minimizing downtime. Investing in training sessions for staff can also enhance their understanding of the equipment, leading to better performance and longevity of the shredders.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Environmental Regulations
The Problem: With increasing regulatory pressure related to waste management and environmental protection, B2B buyers often find themselves challenged by compliance issues. Businesses that fail to adhere to local and international waste disposal regulations may face hefty fines or reputational damage. For example, a company operating in a region with strict environmental laws may struggle to ensure that their shredders effectively reduce waste to compliant levels.
The Solution: Buyers should seek shredders designed with compliance in mind. When sourcing equipment, ensure that it meets both local and international standards for waste reduction and recycling efficiency. Collaborate with manufacturers who provide certifications and detailed specifications regarding their shredders’ capabilities. Additionally, integrating a monitoring system that tracks shredding performance and waste output can help businesses stay compliant. Regular audits and consultations with environmental experts can also keep your operations aligned with evolving regulations, ultimately safeguarding your business from potential penalties.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shredder design
What Are the Key Materials for Shredder Design?
In the design of shredders, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and operational efficiency. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in shredder design, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Impact Shredder Design?
Stainless steel is a popular choice for shredder components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and strength. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various shredding applications, particularly in environments prone to moisture or chemical exposure.
Pros: Stainless steel offers exceptional durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Its resistance to rust and corrosion makes it ideal for outdoor or humid conditions.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other materials like carbon steel. Manufacturing complexity can also increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective for shredding materials that may contain moisture, such as organic waste or plastics. Its strength ensures consistent performance across diverse media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may also consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Shredder Design?
Carbon steel is another widely used material in shredder construction, known for its high tensile strength and affordability. It is often used for blades and frames, providing a good balance between performance and cost.
Pros: The lower cost of carbon steel makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. Its strength allows for effective shredding of various materials, including wood and plastic.
Cons: Carbon steel is more susceptible to rust and corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or regular maintenance to prolong its lifespan.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for shredding dry materials and is often used in industrial applications where cost efficiency is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for protective treatments to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates. Compliance with local manufacturing standards is also essential.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
How Does Aluminum Enhance Shredder Performance?
Aluminum is less common but increasingly used in specific shredder designs due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It is particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is a priority.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature allows for easier handling and reduced energy consumption during operation. It also resists corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
Cons: The primary limitation is its lower strength compared to steel, which may affect performance in high-load applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for shredding lighter materials or in portable shredding machines where weight is a critical factor.
Illustrative image related to shredder design
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the trade-offs between weight and strength when selecting aluminum. Compliance with international standards is essential to ensure quality and safety.
What Advantages Does Polypropylene Offer in Shredder Design?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer used in some shredder components, particularly hoppers and casings, due to its lightweight and chemical resistance.
Pros: Polypropylene is cost-effective and offers good resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for shredding various materials without degrading.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Cons: Its lower mechanical strength compared to metals limits its use in high-stress applications. It may also be less durable over time under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is suitable for shredding non-metallic materials, particularly in industries focused on recycling plastics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polypropylene components meet relevant safety and quality standards, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Shredder Design
| Material | Typical Use Case for shredder design | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Shredding wet or corrosive materials | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Industrial shredding of dry materials | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to rust and corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight or portable shredders | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium to High |
| Polypropylene | Shredding plastics and non-metallics | Cost-effective and chemical-resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions tailored to specific operational needs and regional considerations.
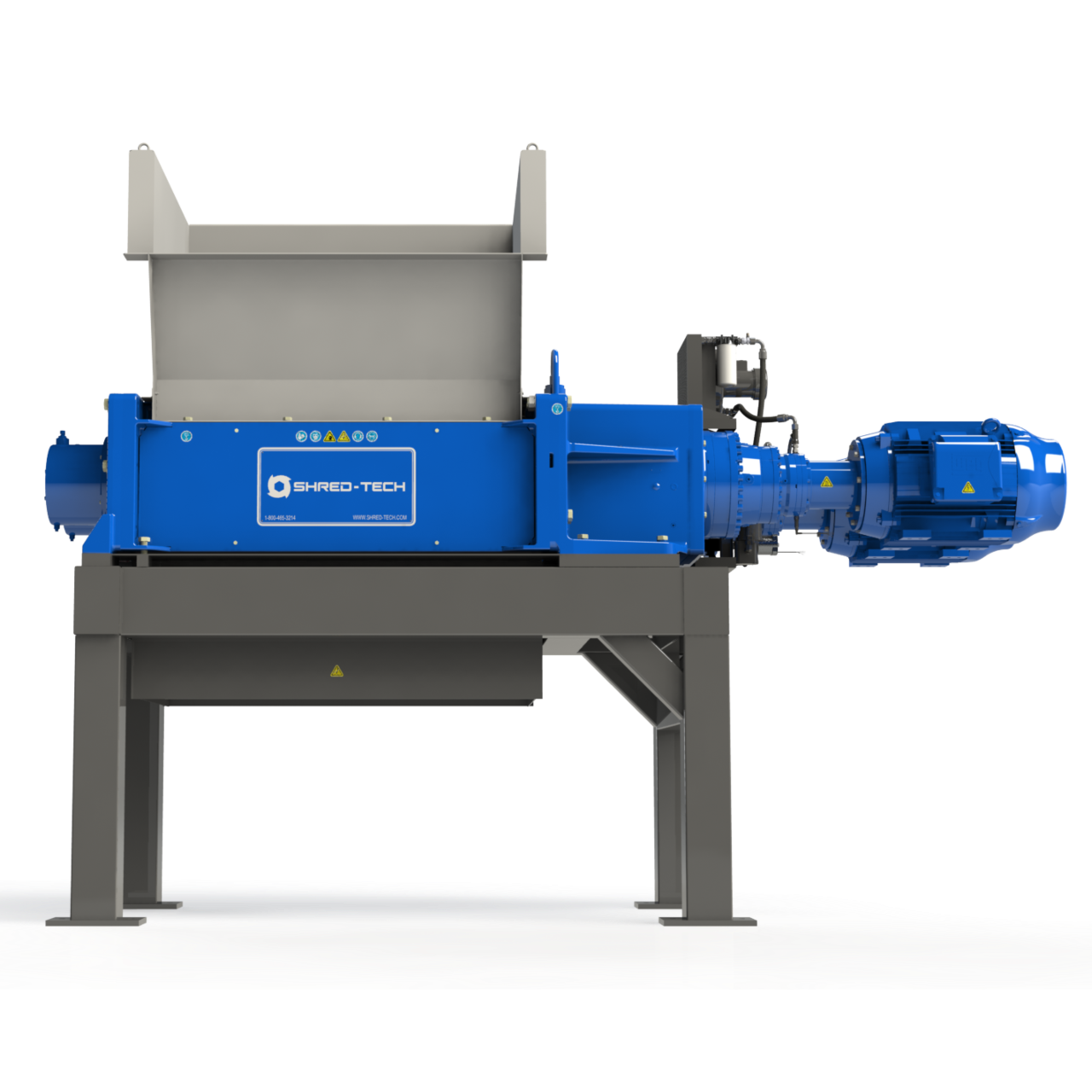
Illustrative image related to shredder design
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shredder design
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Shredder Design?
The manufacturing process of shredders involves several crucial stages, each contributing to the overall quality and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Shredder Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting high-quality raw materials suited for shredders. Common materials include stainless steel for its durability and resistance to corrosion, as well as various alloys for specific applications. The selection of materials is critical, as it affects the shredder’s lifespan and performance. Suppliers should provide documentation on material specifications to ensure compliance with international standards.
How Is the Forming Process Executed in Shredder Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into components through techniques such as laser cutting, welding, and machining. For instance, laser cutting is often used to create precise shapes and dimensions for the shredder’s housing and blades. Machining processes, such as turning and milling, are utilized to achieve the required tolerances for moving parts like shafts and gears. It’s essential for manufacturers to implement strict controls during this phase to ensure that all components meet the design specifications.
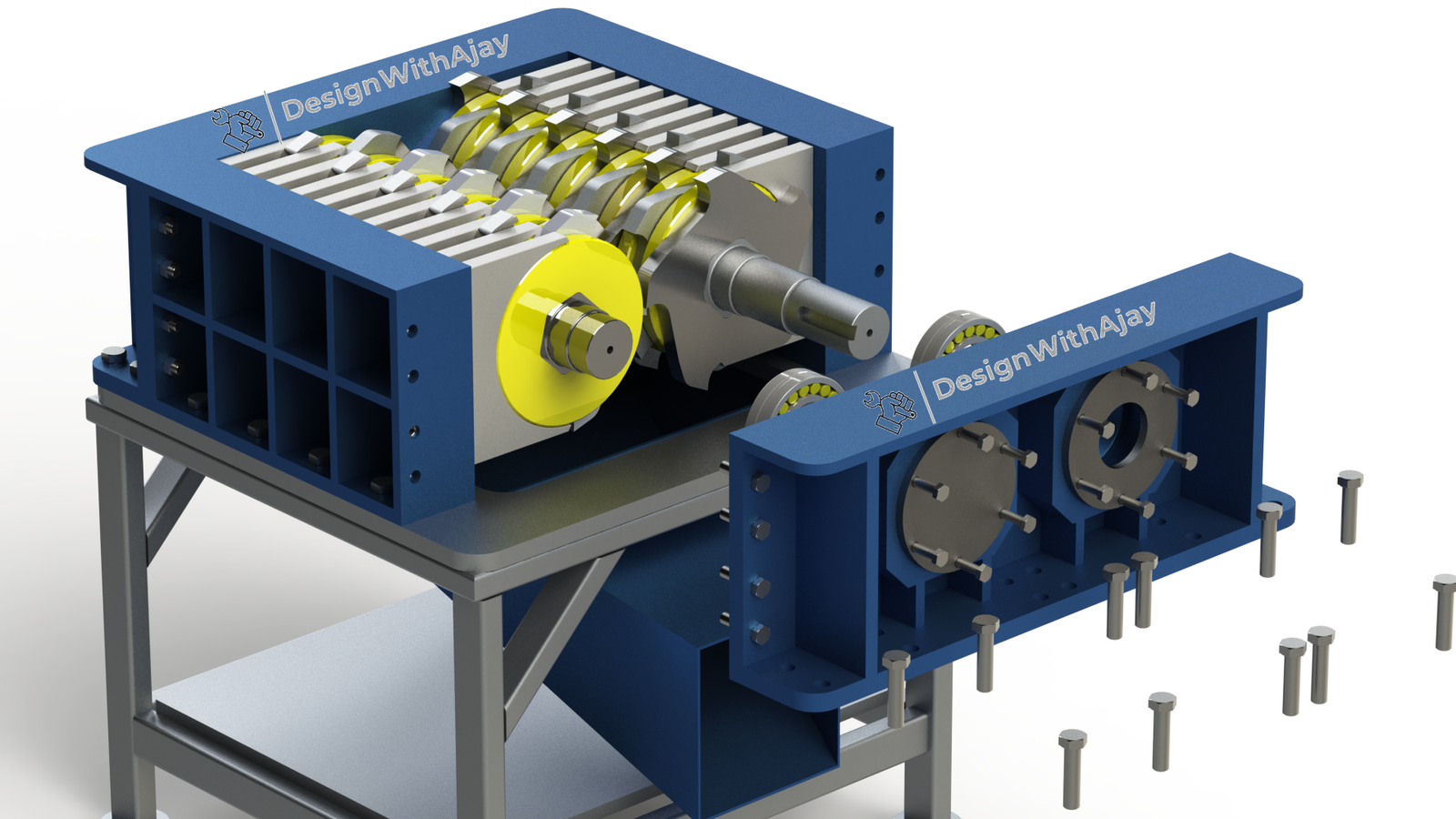
Illustrative image related to shredder design
What Does the Assembly Process Entail in Shredder Design?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage may involve both manual and automated assembly techniques. Skilled technicians typically perform critical assembly tasks, such as aligning blades and securing the housing, while automated systems may handle repetitive tasks like fastening screws or applying adhesives. Effective assembly processes are vital for achieving the desired performance and reliability of the shredder. Manufacturers should document their assembly procedures and provide training records to demonstrate their workforce’s expertise.
Which Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Shredder Manufacturing?
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the shredder. Techniques such as powder coating, anodizing, or polishing are applied to protect against wear and corrosion while providing an appealing finish. This stage may also include quality checks to ensure that the finish is uniform and free from defects. Buyers should inquire about the finishing methods used by suppliers, as these can significantly impact the shredder’s durability and maintenance needs.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Shredder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that shredders meet specified standards and performance criteria. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes of potential suppliers is essential for minimizing risks associated with product quality.
What International Standards Are Relevant to Shredder Manufacturing?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE mark (for products sold in Europe) and API standards (for certain industrial applications) should also be verified. Buyers should request copies of these certifications to ensure that their suppliers meet the necessary quality benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to detect defects and ensure compliance with design specifications. Key checkpoints include:
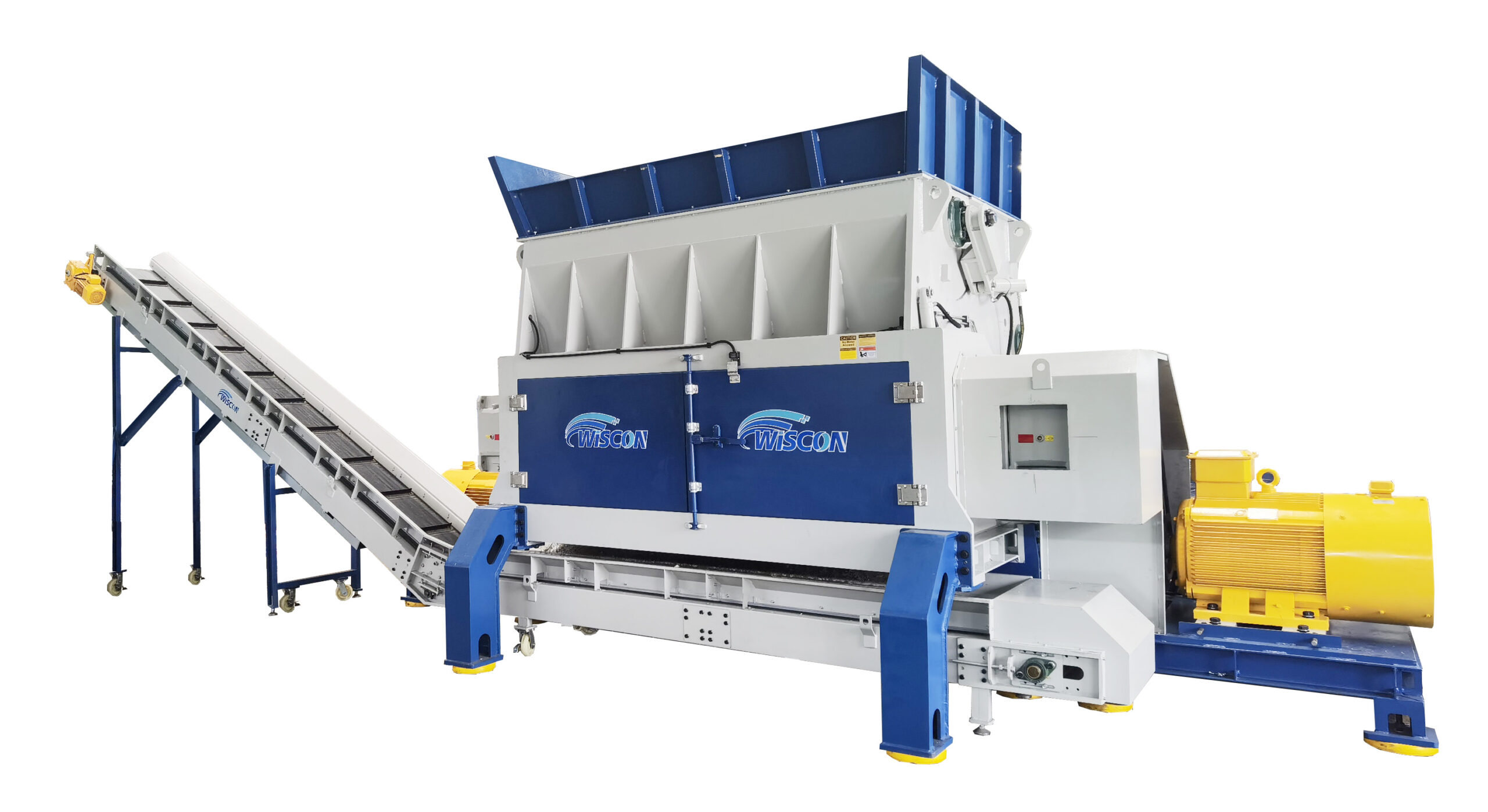

Illustrative image related to shredder design
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to confirm they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages helps identify issues early, allowing for corrective actions to be taken.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage includes comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets performance and safety standards.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC measures implemented by suppliers, as these can vary significantly between manufacturers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in Shredders?
Testing methods are essential for validating the performance and safety of shredders. Common techniques include:
- Functional Testing: Evaluating the operational capabilities of the shredder, such as its shredding efficiency and noise levels.
- Durability Testing: Assessing how well the shredder withstands stress and wear over time under normal operating conditions.
- Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with safety standards, particularly regarding electrical components and mechanical safety features.
Buyers should request documentation of testing protocols and results to verify the quality of the shredders they are considering.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several effective methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This allows buyers to assess the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports can help track a supplier’s performance over time. These reports should detail QC results, including any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly valuable for international buyers, who may not have the resources to conduct audits themselves.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Factors such as different regulatory environments, import/export standards, and cultural practices can influence quality assurance processes. Buyers should:
- Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize themselves with local laws regarding product safety and environmental standards to ensure compliance.
- Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication about quality expectations and standards.
- Consider Logistics: Assess how logistics might impact the quality of the product upon delivery, including transportation conditions and handling practices.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for shredder design and ensure they receive high-quality, reliable products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘shredder design’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure shredders, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can ensure that your investment in shredder design aligns with your operational needs and sustainability goals.
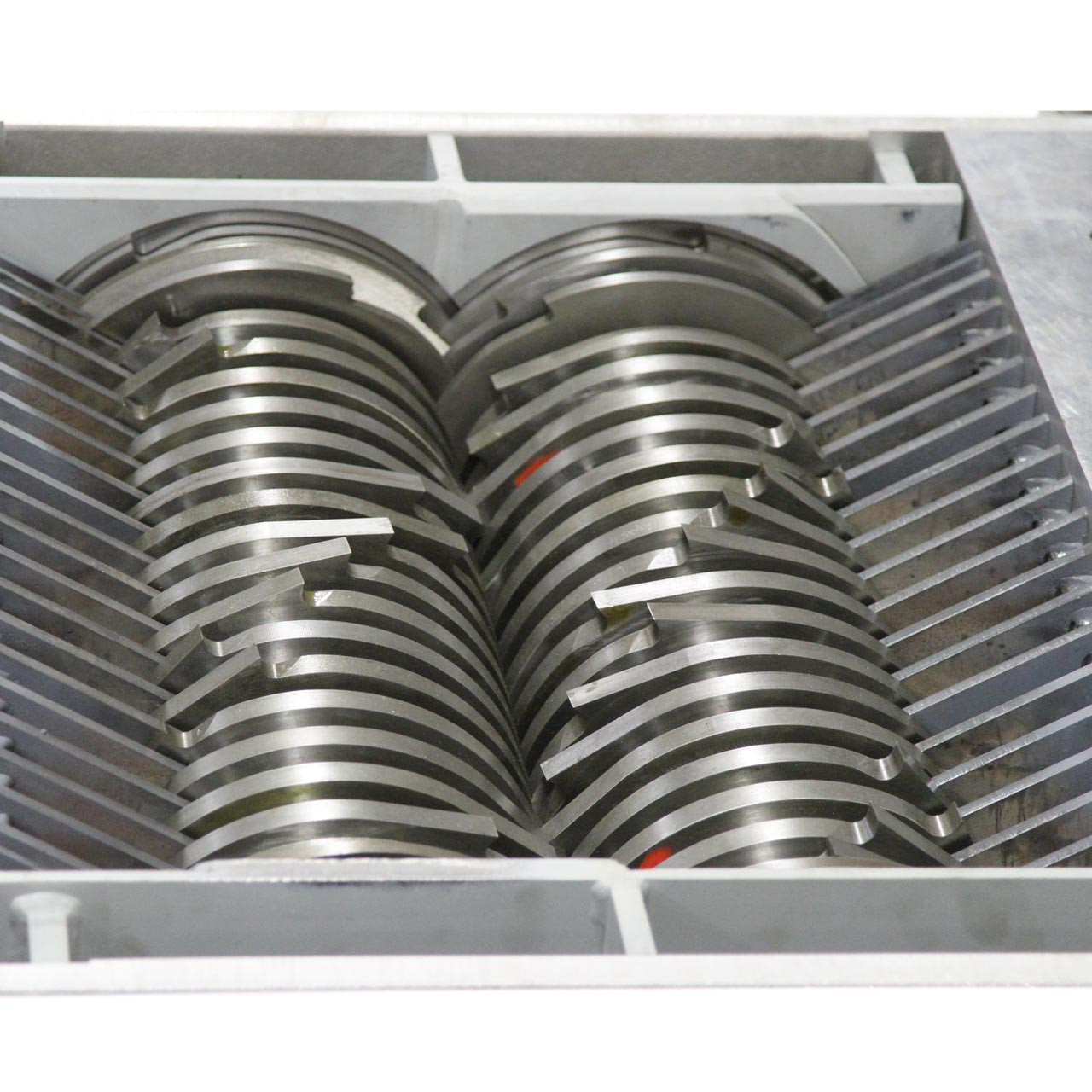

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before approaching suppliers, clarify your shredding requirements. This includes the type of materials you intend to shred (e.g., plastic, metal, cardboard) and the desired output size. Knowing the specifications helps in selecting a shredder that meets your operational efficiency and processing capabilities.
- Material Types: Identify whether you need a multi-purpose shredder or a specialized machine.
- Output Size: Determine the granule size required for your recycling or processing needs.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Understanding the industry standards is crucial for ensuring safety and operational efficiency. Familiarize yourself with international and local regulations that apply to shredders, including environmental compliance and safety certifications.
- ISO Certifications: Look for suppliers with ISO certifications that indicate adherence to quality standards.
- Local Regulations: Be aware of any specific regulations in your region that might affect shredder operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they have a proven track record in the industry. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar sectors or regions.
- Experience: Prioritize suppliers with extensive experience in manufacturing shredders for your specific material type.
- Customer Feedback: Seek testimonials or reviews from other clients to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Features
Not all shredders are created equal. Investigate the build quality and additional features that can enhance performance, such as adjustable shredding sizes, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
- Materials Used: Ensure that the shredder is constructed from durable materials, such as stainless steel, to withstand heavy use.
- Maintenance Requirements: Check if the supplier provides comprehensive maintenance guidelines and support.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Ensure that the quotes include all costs associated with the machine, such as shipping, installation, and after-sales support.
Illustrative image related to shredder design
- Breakdown of Costs: Look for transparency in pricing to avoid unexpected costs later.
- Long-term Value: Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs over time.
Step 6: Confirm After-Sales Support and Warranty
After-sales support is vital for the longevity of your shredder. Ensure that the supplier offers robust support services, including maintenance, spare parts availability, and warranty terms.
- Warranty Duration: Verify the length and coverage of the warranty provided.
- Support Channels: Check if they offer multiple support channels (e.g., phone, online chat) for troubleshooting and assistance.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Logistics
Once you’ve selected a supplier, confirm your order and discuss logistics. Coordinate shipping options that are cost-effective and timely, especially if your operations are dependent on the shredder’s arrival.
- Shipping Options: Evaluate different shipping methods based on cost and delivery time.
- Installation Services: Inquire if the supplier offers installation services to ensure proper setup and operation.
By adhering to this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process and secure a shredder that meets your business needs while promoting sustainability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shredder design Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Shredder Design Sourcing?
When sourcing shredders, understanding the cost structure is paramount. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the total cost. For instance, stainless steel, while more expensive than plastic, offers durability and longevity, which can be beneficial in the long run, especially for industrial applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor associated with manufacturing. Skilled labor may be required for assembly and quality control, which can increase costs, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the factory’s operation, such as utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of equipment. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds for producing specific shredder designs add to the initial setup costs. These can be amortized over higher production volumes to reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that shredders meet safety and performance standards, which can add to upfront costs but reduce long-term liabilities.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the origin and destination, especially for international shipments. Factors such as freight forwarding and customs duties need to be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market standard for margins can help buyers assess whether the pricing is competitive.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Shredder Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of shredders:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Suppliers are more likely to offer favorable terms for larger orders, which can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials that meet industry standards or certifications can command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in certified products.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and manufacturing capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher quality but at a premium, while emerging suppliers might provide competitive pricing but with varying quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international purchases. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping logistics, which can significantly affect the overall cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Shredder Prices?
Negotiating prices can lead to more favorable terms. Here are some strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Buyers should research market prices and supplier offerings to establish a baseline for negotiations. Having data on competitor pricing can strengthen your position.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Flexibility on Specifications: Being flexible on certain specifications can open up opportunities for cost savings. Discussing alternative materials or designs with suppliers might yield a more cost-effective solution.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, exclusive offers, and priority support.
-
Understand Local Market Dynamics: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding local market conditions, including tariffs and import regulations, can provide insights into negotiating better terms.
Conclusion: Why Are Prices Indicative and Subject to Change?
Prices for shredders can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is essential for buyers to approach negotiations with a clear understanding of these dynamics and to remain adaptable to changing market conditions. Always request updated quotes and be aware that prices may fluctuate due to material availability, exchange rates, or global supply chain issues.
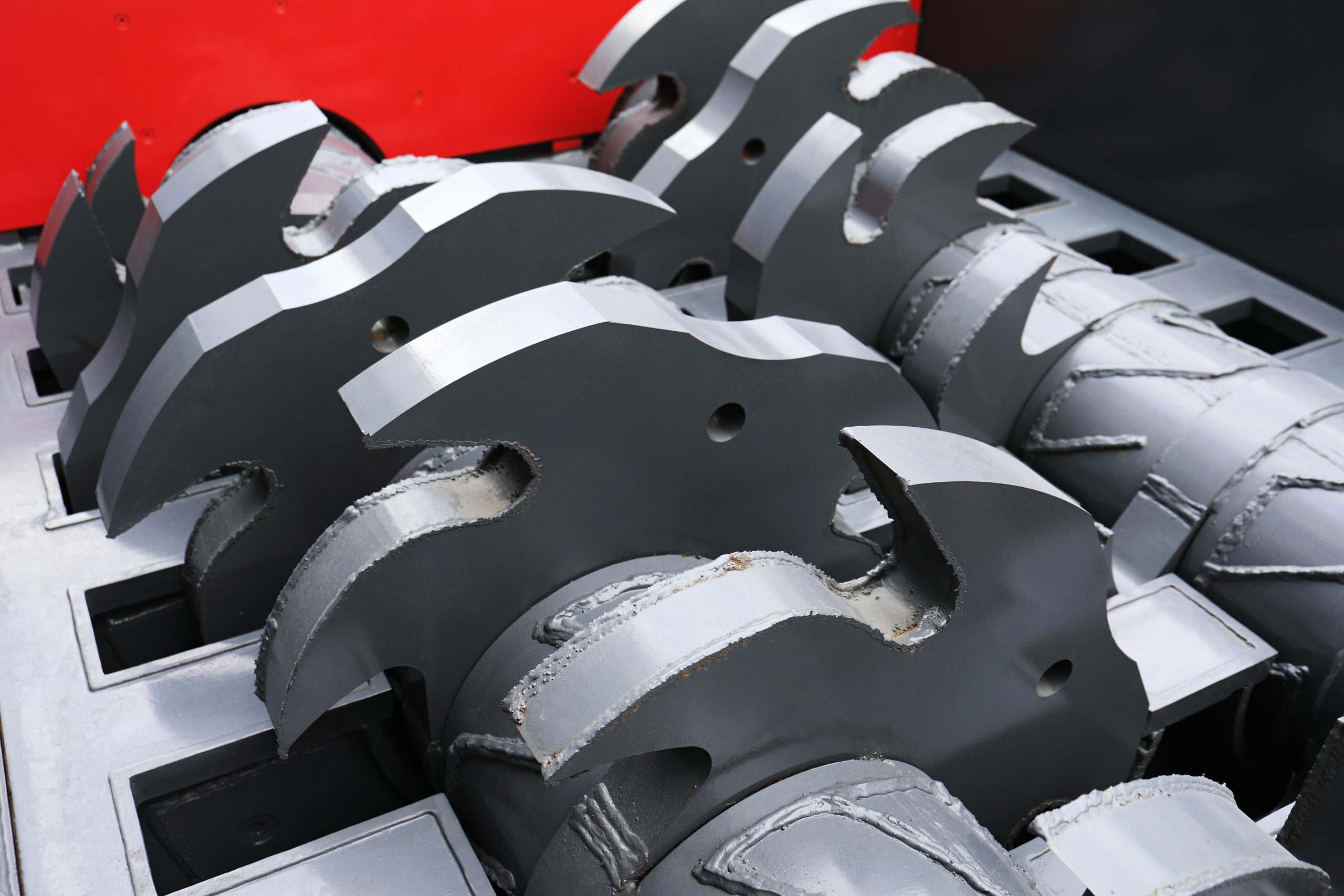

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing shredder design With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Shredder Design
In the landscape of waste management and recycling, various technologies exist to reduce material size for easier handling and processing. While shredder design remains a popular choice for many businesses, it’s essential to explore other viable alternatives that can also meet specific operational needs. This analysis compares shredder design against baler machines and compactor systems, focusing on key performance aspects to aid decision-making for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Shredder Design | Baler Machines | Compactor Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for mixed materials; produces uniform size | Compresses materials into dense bales for storage | Reduces volume significantly; suitable for large quantities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; operational costs vary | Higher upfront costs; economical for high-volume operations | Varies by size and type; generally cost-effective for large waste |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space and setup; user training needed | More complex installation; requires space for bales | Generally easy to set up; minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts can wear out | Low maintenance; occasional servicing required | Routine checks; may require more maintenance depending on usage |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for diverse waste types; recycling facilities | Excellent for paper, cardboard, and plastics | Best for high-volume waste reduction in commercial settings |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Baler Machines?
Baler machines excel in compressing recyclable materials into manageable bales, making them easy to transport and store. They are particularly effective for paper and cardboard recycling, where density and space-saving are critical. However, the initial investment for balers can be significantly higher than shredders, which may deter smaller operations. Furthermore, balers require sufficient space to accommodate the bales and a more complex installation process, which can delay operational readiness.
How Do Compactor Systems Compare?
Compactor systems offer a powerful solution for reducing the volume of waste, making them ideal for businesses dealing with large quantities of refuse. They operate efficiently, compressing various materials into dense blocks that facilitate easier handling and disposal. The ease of setup and minimal training required for operation make compactors an appealing choice for many businesses. However, they may not be as versatile as shredders when it comes to processing mixed materials, and the effectiveness can vary based on the specific type of compactor used.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs?
When deciding between shredder design and its alternatives, consider your specific operational requirements, including the types of materials you handle, your budget, and available space. If your business deals with a variety of waste types and requires consistent particle size for recycling, a shredder may be the best option. On the other hand, if you primarily process large volumes of paper or cardboard, investing in a baler could yield better efficiency and savings in the long run. For businesses focused on waste reduction and space management, compactor systems may provide the most effective solution.
By thoroughly evaluating the pros and cons of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shredder design
What Are the Essential Technical Properties in Shredder Design?
When designing a shredder, several key technical properties are critical to ensure efficiency, durability, and overall performance. Understanding these specifications not only aids in selecting the right equipment but also helps in optimizing operational costs and improving sustainability efforts. Below are some of the essential technical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in constructing the shredder significantly impacts its longevity and performance. Stainless steel is often preferred for its corrosion resistance and strength. This is particularly important for shredders used in recycling applications where exposure to various substances is common. For B2B buyers, selecting high-grade materials can result in reduced maintenance costs and extended service life. -
Shredding Capacity
This specification refers to the volume of material a shredder can process within a given time frame, usually measured in tons per hour (TPH). Understanding the shredding capacity is crucial for businesses looking to match their operational needs with the right machine. A higher capacity shredder can lead to increased productivity, making it a worthwhile investment for large-scale operations. -
Motor Power
The motor power, typically measured in kilowatts (kW), determines the shredder’s efficiency and ability to handle tough materials. A robust motor ensures that the shredder can operate continuously without overheating, which is essential for businesses with high throughput requirements. Selecting the right motor power can enhance the operational efficiency and durability of the shredder. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in dimensions or physical properties of the shredder components. Precise tolerances are essential for ensuring the parts fit correctly and function efficiently. This specification is particularly important in applications where precision is critical, as improper tolerances can lead to mechanical failures or reduced shredding efficiency. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in shredder design. Key features may include emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and automatic shut-off systems. For B2B buyers, understanding the safety specifications can help mitigate risks associated with operating heavy machinery and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Shredder Design?
Navigating the world of shredder design involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
Illustrative image related to shredder design
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of shredders, partnering with an OEM can provide businesses with reliable components that meet specific design requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses looking to manage inventory costs effectively. It enables buyers to negotiate better terms and ensures that they have enough products on hand to meet operational demands. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process that allows businesses to compare costs and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand shipping logistics, costs, and risk management during the procurement of shredders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead time is essential for businesses to plan their operations and inventory management effectively, ensuring that they receive shredders when they need them without unnecessary delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in shredder design.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the shredder design Sector
What Are the Current Trends and Dynamics in the Global Shredder Design Market?
The global shredder design market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for recycling and waste management solutions. Key trends include the rise of automation and smart technology integration, where manufacturers are developing shredders equipped with advanced sensors and IoT capabilities. These innovations not only enhance operational efficiency but also allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which are crucial for international buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where resource optimization is paramount.
Moreover, the shift towards sustainability is reshaping purchasing decisions. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing machines that facilitate recycling and waste reduction. In Europe and other developed markets, regulatory frameworks promoting circular economy practices are encouraging investments in shredders designed for specific materials, such as plastics and metals. This focus on material-specific solutions is especially relevant for markets in Nigeria and Brazil, where local regulations are evolving to enforce stricter waste management practices.
Additionally, the availability of modular and customizable shredder designs is becoming a key consideration. International buyers prefer solutions that can be tailored to specific operational needs, allowing for scalability and adaptability as market demands change. This trend is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to enter or expand in emerging markets, where flexibility can provide a competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability Shaping B2B Sourcing in Shredder Design?
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it is a fundamental aspect of B2B sourcing in the shredder design sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their procurement choices and are seeking suppliers that align with ethical practices. The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, as they play a vital role in reducing the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting shredders.
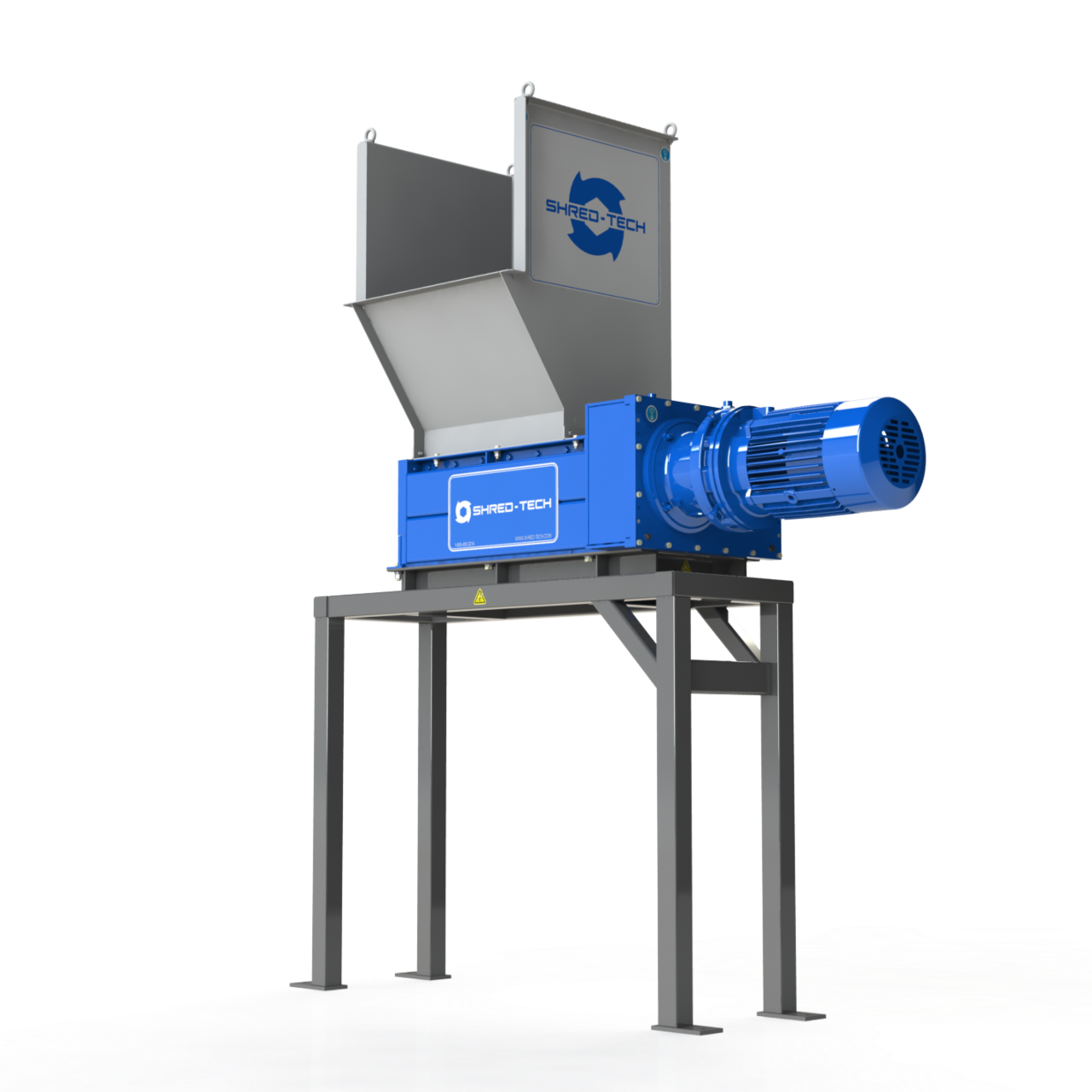
Illustrative image related to shredder design
In this context, ‘green’ certifications and the use of sustainable materials are becoming essential criteria for sourcing decisions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to guidelines for responsible sourcing are highly valued by international buyers. Moreover, the incorporation of recycled materials in shredder components not only enhances the sustainability profile of products but also appeals to eco-conscious consumers and businesses.
As sustainability regulations tighten globally, especially in European markets, buyers from Africa and South America must also consider the long-term implications of their sourcing strategies. Investing in shredders designed with sustainability in mind not only ensures compliance with local regulations but also positions companies as responsible players in the global market.
What Is the Historical Context of Shredder Design for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of shredder design dates back to the early 20th century when shredders were primarily used for agricultural waste management. Over the decades, technological advancements have transformed these machines into sophisticated systems capable of processing a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and electronic waste.
The introduction of electric motors and hydraulic systems in the mid-20th century significantly improved shredding efficiency and capacity. By the late 1990s, the focus shifted towards automation, with manufacturers integrating computer controls to enhance precision and reduce labor costs. This evolution has not only increased the performance of shredders but has also opened new avenues for recycling and waste management, making them indispensable for businesses looking to optimize operations and meet regulatory standards.
In today’s context, understanding this historical evolution is crucial for B2B buyers. It provides insights into the technological capabilities of current models and helps identify which features are essential for meeting modern recycling challenges. As companies continue to adapt to changing market demands, the history of shredder design offers valuable lessons in innovation and sustainability that can guide sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shredder design
1. How do I choose the right shredder design for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate shredder design involves assessing your specific requirements, including the type of materials you plan to shred (e.g., plastic, metal, cardboard), volume, and desired output size. Consider the shredding capacity (tonnage per hour), energy efficiency, and maintenance needs. Additionally, evaluate whether you need a single-shaft, multi-shaft, or granulator design based on the material characteristics. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can help align the shredder’s capabilities with your operational goals.
2. What are the key features to look for in industrial shredders?
When sourcing industrial shredders, focus on features such as blade design, motor power, safety mechanisms, and ease of maintenance. Look for robust construction materials that enhance durability, especially for heavy-duty applications. Advanced models may offer variable speed settings, automatic feed systems, and noise reduction technology. Ensure that the shredder complies with international safety standards, which is crucial for protecting your workforce and minimizing operational risks.
3. Can I customize the shredder design to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for their shredder designs. You can specify features such as blade configurations, shredding capacity, and material types to optimize performance for your unique applications. Discussing your needs with suppliers will help them provide tailored solutions, ensuring you receive a machine that fits your operational processes effectively. Be prepared to share detailed information about your shredding requirements to facilitate this customization.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for shredders?
Minimum order quantities for shredders can vary significantly between suppliers, depending on their production capabilities and inventory. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for specialized equipment to larger quantities for standard models. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about MOQs and whether they offer flexible options for smaller businesses or startup operations. Understanding these terms is essential for budgeting and planning your acquisition strategy.
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing shredders internationally?
Payment terms for international shredder purchases typically include options such as upfront payments, letters of credit, or installment payments based on delivery milestones. Discuss these terms with suppliers to find an arrangement that suits your financial strategy. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or discounts for early payments. Ensure that you understand the implications of currency exchange rates and any additional fees associated with international transactions.
6. How do I vet suppliers for shredder design?
Vetting suppliers requires a thorough evaluation of their credentials, experience, and customer feedback. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality management practices. Request references from previous clients and review case studies to assess their reliability. Additionally, visiting manufacturing facilities, if possible, can provide insight into their production capabilities and quality control processes. Engaging in direct communication can also help establish rapport and gauge their responsiveness.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing shredders?
Logistics considerations for importing shredders include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Assess the best shipping options based on your timeline and budget, considering air freight for speed versus ocean freight for cost-effectiveness. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and compliance certificates. Familiarize yourself with local import regulations to avoid delays and unexpected costs during the shipping process.
8. How do I ensure quality assurance for shredders purchased internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally purchased shredders, request detailed product specifications and quality control documentation from your supplier. Establish quality benchmarks that the equipment must meet upon delivery. Consider conducting pre-shipment inspections or audits to verify that the machines conform to your standards. Additionally, inquire about warranties and after-sales support to address any potential issues that may arise post-purchase, ensuring long-term satisfaction with your investment.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Top 4 Shredder Design Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sustainable Design – Shredder Box
Domain: sustainabledesign.studio
Introduction: 3.3 Shredder Box in Stainless Steel
Price: from £445.00
Description: A small mountable plastic shredder box designed for recycling plastic. Can be hand powered or attached to a motor.
What’s Included:
– Fully Built Kit (if selected) or Flat Packed for Self Assembly
– Lasercut Parts in Stainless Steel (tapped and countersunk where required)
– 30mm Machined Hex Shaft (With Keyway)
– Pre Welded Mesh…
2. IQS Directory – Industrial Shredders
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Industrial shredders are powerful and versatile tools designed for recycling and waste management. They handle a variety of materials, from confidential documents to bulky items like tires and metals. Key types include: 1. Single Shaft Shredder: Features a single rotating shaft with hardened blades, ideal for plastics, wood, and textiles. Produces uniformly-sized particles (1-2 inches). 2. Double …
3. Precious Plastic – The Shredder
Domain: davehakkens.nl
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The Shredder is part of the Precious Plastic machine development project. It is designed to be built on a budget, with considerations for using non-CNC facilities for construction. The user, Glen Pcal, is exploring the use of a pneumatic socket driver powered by a compressor instead of an electric motor. Feedback from other community members suggests that a pneumatic impact driver may not be effec…
4. Instructables – $50 Plastic Shredder
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: $50 Plastic Shredder / Grinder / Recycler; Designed for DIY community, especially for 3D printing enthusiasts; Utilizes a cross-cut paper shredder mechanism; Requires a powerful motor and metal gear drive; Recommended shredder: AmazonBasics 12-Sheet Cross-Cut Paper, CD, and Credit Card Shredder; Project duration: approximately 48 hours; Tools needed: PH screwdriver, basic electrical tools, saw or …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shredder design
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing in shredder design is essential for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability. As highlighted throughout this guide, choosing the right shredding solution can significantly impact not only material processing capabilities but also cost-effectiveness and environmental compliance. By investing in advanced shredders tailored for specific materials—such as plastics, metals, and cardboard—companies can optimize their recycling processes and reduce waste, ultimately contributing to a circular economy.
Furthermore, the importance of sourcing high-quality components, such as stainless steel parts and reliable motors, cannot be overstated. These elements ensure durability and performance, which are critical for meeting the rigorous demands of industrial operations. For international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics and supplier capabilities will be key to successful procurement.
As we look ahead, the integration of innovative technologies in shredder design—such as automation and IoT—promises to revolutionize the industry. We encourage buyers to stay informed about emerging trends and seek partnerships that align with their sustainability goals. Invest in quality shredding solutions today to secure a more efficient and eco-friendly tomorrow.

Illustrative image related to shredder design
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
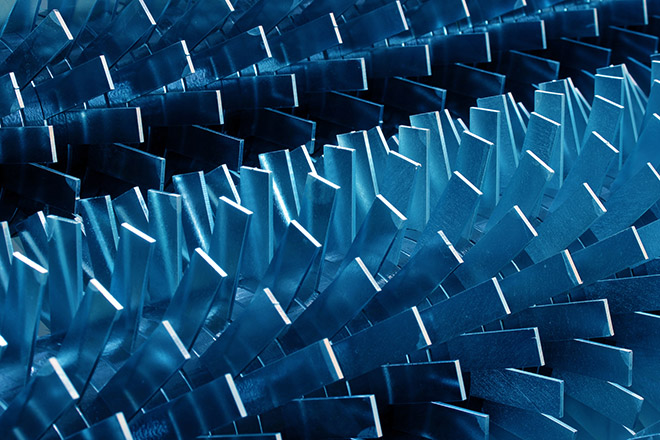
Illustrative image related to shredder design