Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Powdered Metal Process Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for powdered metal process
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, navigating the complexities of sourcing powdered metal processes can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The powdered metal process, known for its ability to produce high-strength, cost-effective components with minimal waste, offers a competitive edge in various industries, from automotive to medical devices. However, with diverse suppliers and varying material properties, making informed purchasing decisions is crucial.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of powdered metal manufacturing, covering essential topics such as types of powdered metals, their applications, and the key steps in the production process. We also provide insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the latest advancements in technology. By equipping B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as those in Brazil and Nigeria—with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market confidently.
As you explore the benefits and challenges associated with powdered metal processes, you will gain the knowledge needed to select the right materials and suppliers, ensuring high-quality production outcomes tailored to your specific needs. Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or streamline your manufacturing processes, this guide serves as a valuable resource for making strategic, informed decisions in the dynamic world of powdered metal manufacturing.
Understanding powdered metal process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomization | Involves creating metal powder by disintegrating molten metal. | Aerospace, automotive components | Pros: High purity, fine particle size. Cons: Higher cost due to equipment and energy requirements. |
| Mechanical Alloying | Combines multiple powders through high-energy milling. | Specialty alloys for high-performance applications | Pros: Tailored properties, complex compositions. Cons: Longer production times, more complex process. |
| Solid-State Reduction | Uses chemical processes to create powders from ores. | Magnetic components, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective for bulk materials. Cons: Limited to specific materials and properties. |
| Electrolysis | Produces powders through electrolytic processes. | Electronics, battery components | Pros: High purity and uniformity. Cons: Not suitable for large-scale production. |
| Chemical Reduction | Involves reducing metal oxides to pure metals using chemical agents. | Industrial applications, catalysts | Pros: Versatile for various metals. Cons: Requires careful handling of chemicals and processes. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Atomization in Powdered Metal Processes?
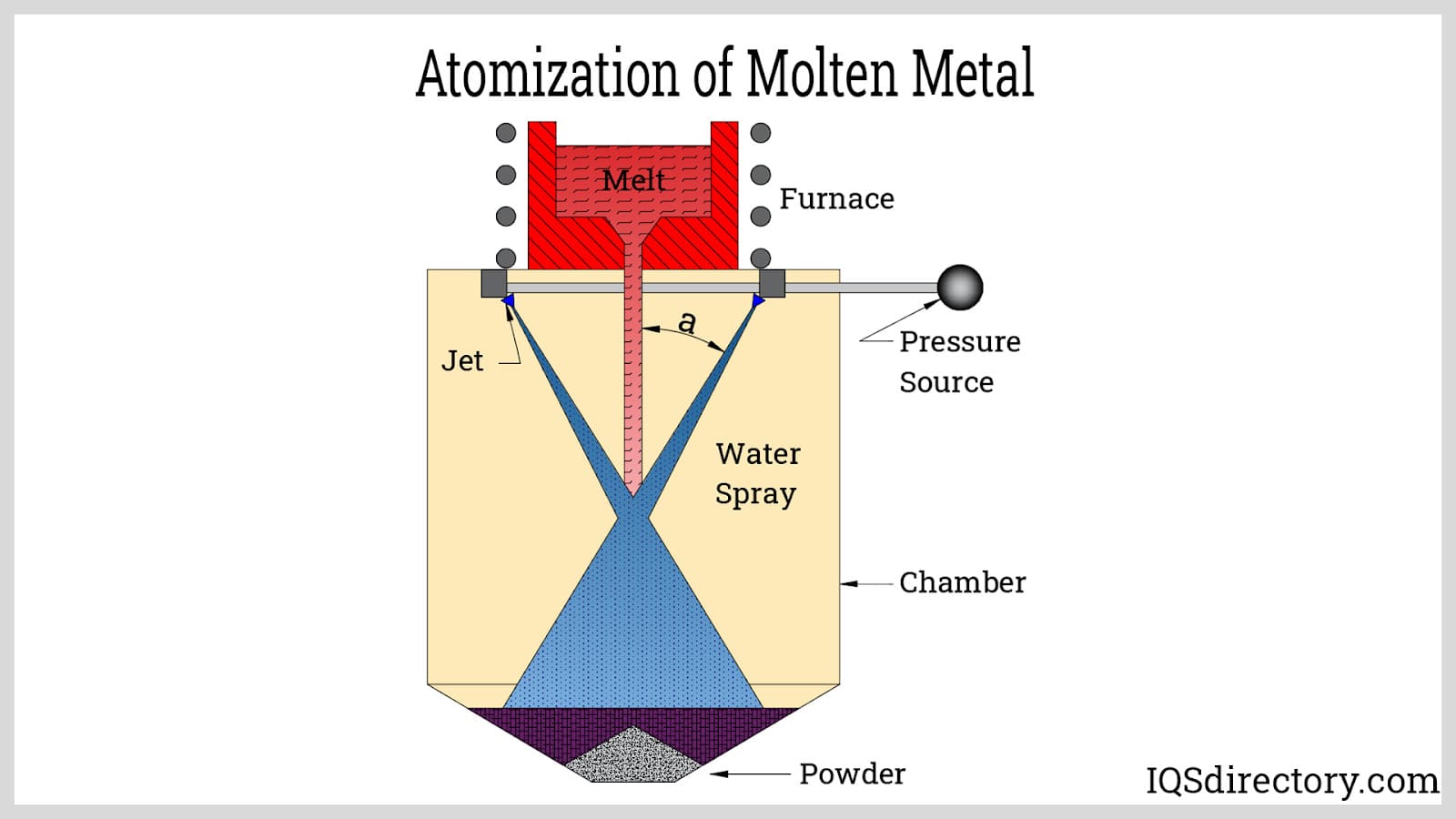
Atomization is a widely used method for producing metal powders, characterized by its ability to create high-purity and fine particles. This process involves the rapid cooling of molten metal, often using gas or liquid jets, which leads to a fine, spherical powder. It is particularly suitable for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, where the quality and consistency of materials are critical. Buyers should consider the higher costs associated with atomization equipment and energy consumption, but the benefits of superior material properties often justify the investment.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
How Does Mechanical Alloying Enhance Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Mechanical alloying is a unique process that combines different metal powders through high-energy milling to achieve specific material properties. This method allows for the creation of complex compositions and tailored performance characteristics, making it ideal for high-performance applications in industries such as aerospace and defense. However, the longer production times and complexity of the process can be drawbacks for buyers seeking rapid turnaround. Understanding the specific requirements of the application can help in deciding if this method is appropriate.
What Are the Advantages of Solid-State Reduction in Powder Production?
Solid-state reduction is a cost-effective technique used to produce metal powders from ores through chemical processes. This method is particularly advantageous for bulk materials and is commonly used in the production of magnetic components and automotive parts. While it offers lower production costs, buyers must consider that it may be limited to specific materials and properties. Evaluating the application requirements against the capabilities of this process is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Why Is Electrolysis Considered a Premium Method for Producing Metal Powders?
Electrolysis is a refined method for producing metal powders, known for its high purity and uniformity. This technique is particularly beneficial for producing components used in electronics and battery applications, where material consistency is paramount. While electrolysis yields high-quality powders, it is not typically suited for large-scale production due to its higher costs and slower processing times. Buyers should weigh the advantages of purity against the potential limitations in scalability.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
How Does Chemical Reduction Offer Versatility in Powdered Metal Applications?
Chemical reduction is a versatile technique that converts metal oxides into pure metals using various chemical agents. This method is widely applicable in industrial settings, particularly for catalysts and other specialized components. While it allows for a broad range of metals to be processed, buyers must be aware of the careful handling required in the chemical processes involved. Understanding the specific properties needed for the application will help buyers assess whether chemical reduction is the right choice for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of powdered metal process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of powdered metal process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine Components (e.g., gears, valves) | Enhanced performance, reduced weight, and cost savings | Material properties, precision manufacturing capabilities |
| Aerospace | Structural Components (e.g., brackets, frames) | High strength-to-weight ratio and reliability | Compliance with aerospace standards, material availability |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Instruments and Implants | Biocompatibility and precision manufacturing | Regulatory compliance, customization capabilities |
| Electronics | Connectors and Circuit Breakers | Improved conductivity and durability | Material selection, production scalability |
| Industrial Equipment | Gearboxes and Bearings | Increased efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Tolerance requirements, supply chain logistics |
How is the Powdered Metal Process Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, powdered metal processes are extensively used to manufacture critical engine components such as gears and valves. These components benefit from the high strength and lightweight characteristics achieved through sintering, which allows for more efficient fuel consumption and performance. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing requires a focus on the supplier’s ability to meet specific material properties and production tolerances to ensure compatibility with existing automotive designs.
What Are the Applications of Powdered Metal in Aerospace?
Aerospace applications leverage the powdered metal process to create structural components like brackets and frames that demand exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. The ability to produce complex geometries with high precision is crucial in this industry, where even minor defects can lead to significant safety issues. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with stringent aerospace standards and have a reliable supply chain for aerospace-grade materials.

Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
How is Powdered Metal Beneficial for Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, powdered metal processes are utilized to create surgical instruments and implants that require precise dimensions and biocompatibility. The customization capabilities of powdered metallurgy allow manufacturers to tailor materials to specific medical requirements, ensuring safety and efficacy. Buyers, especially from emerging markets, need to consider regulatory compliance and the supplier’s experience in producing medical-grade components to mitigate risks associated with product recalls or failures.
What Role Does Powdered Metal Play in Electronics?
The electronics sector employs powdered metal processes for producing connectors and circuit breakers, where improved conductivity and durability are paramount. The fine powder metallurgy allows for intricate designs that enhance electrical performance while reducing overall product size. For international B2B buyers, sourcing from manufacturers who can provide consistent quality and scalability is essential, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, where market demand is growing rapidly.
How Does Powdered Metal Improve Industrial Equipment Manufacturing?
In industrial equipment, powdered metal processes are used to manufacture gearboxes and bearings, which benefit from increased efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. The ability to achieve high tolerances with minimal machining leads to lower production costs and improved product reliability. Buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their capability to meet specific tolerance requirements and manage supply chain logistics effectively to ensure timely delivery of critical components.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘powdered metal process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Specification for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves struggling with the selection of the right powdered metal materials for their specific applications. The challenge often arises when clients require unique properties—such as high wear resistance or enhanced thermal conductivity—that standard materials do not provide. This can lead to delays in production timelines and increased costs, as trial and error with various material blends can be both time-consuming and expensive.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material specification, buyers should engage in detailed discussions with their suppliers about their specific application needs. Start by providing comprehensive information about the operational environment, including temperature ranges, load conditions, and corrosion factors. Collaborate with your supplier to explore custom alloy formulations that can meet your requirements. Utilizing advanced simulation tools and prototyping can also help in validating the performance of these custom materials before full-scale production, ensuring that the chosen solution is optimal and reducing the risk of costly revisions later in the process.
Scenario 2: Managing Production Costs While Ensuring Quality
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers in the powdered metal sector is balancing production costs with the quality of the final parts. In regions with fluctuating material prices, maintaining a cost-effective manufacturing process while ensuring high-quality outputs can feel like a daunting task. Buyers may find themselves at a crossroads, either compromising on material quality or facing unanticipated cost overruns.
The Solution: To address this, buyers should consider forming long-term partnerships with reliable powdered metal manufacturers who can provide transparent pricing structures and cost forecasts. Establishing a collaborative relationship can lead to insights on bulk purchasing or alternative materials that maintain quality while reducing costs. Additionally, leveraging techniques such as process optimization—like adjusting sintering temperatures or compaction pressures—can yield better material properties without incurring additional costs. Regular audits and performance reviews of the manufacturing process can also help identify inefficiencies and areas for cost reduction, ensuring that both quality and cost-effectiveness are achieved.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Part Consistency and Tolerances
The Problem: Buyers often face issues with achieving consistent part tolerances and geometries in high-volume production runs. Variability in the powdered metal process can lead to discrepancies in part dimensions, which can be especially problematic for components that require precise fitting in assemblies. Such inconsistencies not only affect product performance but can also lead to increased waste and rework, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is crucial for buyers to engage in a rigorous pre-production planning phase. This should include detailed discussions about tolerances and specifications with the manufacturer, ensuring that both parties have a clear understanding of expectations. Utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and finite element analysis (FEA), can help in refining part designs to ensure they are optimized for the powdered metal process. Furthermore, implementing robust quality control measures—like in-process monitoring and regular inspections—can help in maintaining consistency throughout production. Establishing a feedback loop with the manufacturer allows for continuous improvement, ensuring that part tolerances are consistently met in future production runs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for powdered metal process
What Are the Key Materials Used in Powdered Metal Processes?
When selecting materials for the powdered metal (PM) process, it is essential to consider various factors, including mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in PM, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Powdered Metal Applications?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures. Its composition typically includes chromium, which enhances its resistance to oxidation and rust.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as automotive and aerospace components. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing complexity may increase costs. Additionally, achieving specific mechanical properties may require secondary operations, such as heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for parts exposed to moisture or corrosive substances, making it a popular choice in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards, such as ASTM A276 or DIN 1.4301, to guarantee quality and performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using Iron in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Iron is a cost-effective material with excellent magnetic properties and good wear resistance. It can be alloyed with other elements to enhance its performance characteristics.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of iron is its low cost, making it an attractive option for high-volume production. However, it is prone to corrosion and may require protective coatings or treatments to enhance its durability. Additionally, the mechanical properties may not match those of higher-end alloys.
Impact on Application: Iron is commonly used in applications where magnetic properties are essential, such as in electrical components and automotive parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A1008 or JIS G3131 is crucial for ensuring the reliability of iron components in various applications across different regions.
Why Is Copper Popular in Powdered Metal Processes?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It is often alloyed with other metals to improve its mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, making it ideal for electrical components. However, it is more expensive than iron and may require careful handling to prevent oxidation. Additionally, its softness can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is widely used in electrical connectors, heat exchangers, and other applications requiring high conductivity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B193 for copper wire and ensure that the material meets regional specifications to guarantee performance.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance. It has good machinability and can be cast into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of bronze is its ability to withstand wear and tear, making it suitable for applications like bearings and bushings. However, it tends to be more expensive than iron and may not be as readily available in certain markets.
Impact on Application: Bronze is often used in marine applications and machinery where corrosion resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B505 is important for ensuring the quality and performance of bronze components, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary of Material Selection for Powdered Metal Processes
| Material | Typical Use Case for powdered metal process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Automotive and aerospace components | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Iron | Electrical components and automotive parts | Cost-effective for high volume | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Copper | Electrical connectors and heat exchangers | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation sensitivity | Med |
| Bronze | Marine applications and machinery | Excellent wear resistance | Higher cost and limited availability | Med |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection in the powdered metal process, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional standards.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for powdered metal process
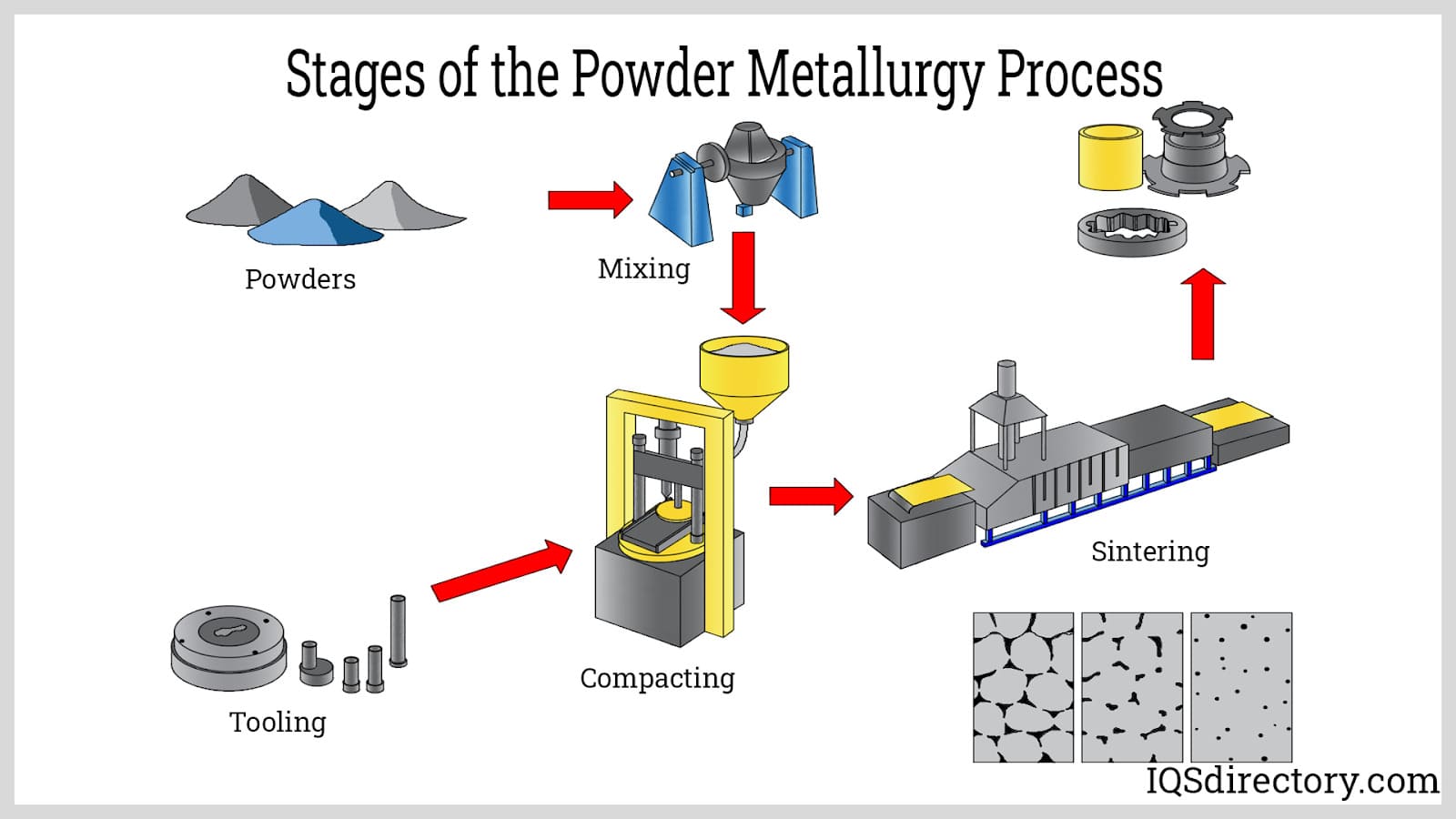
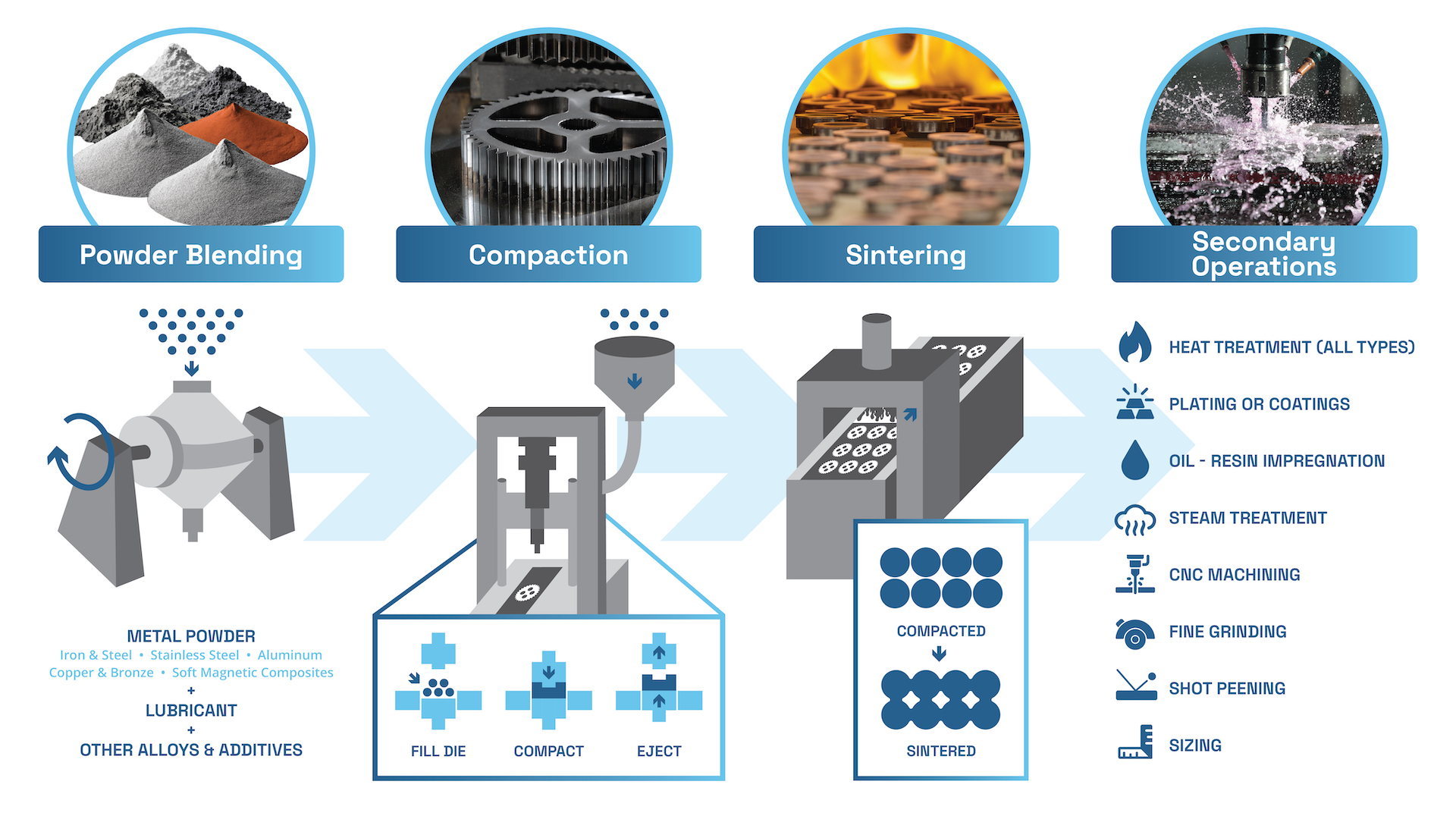
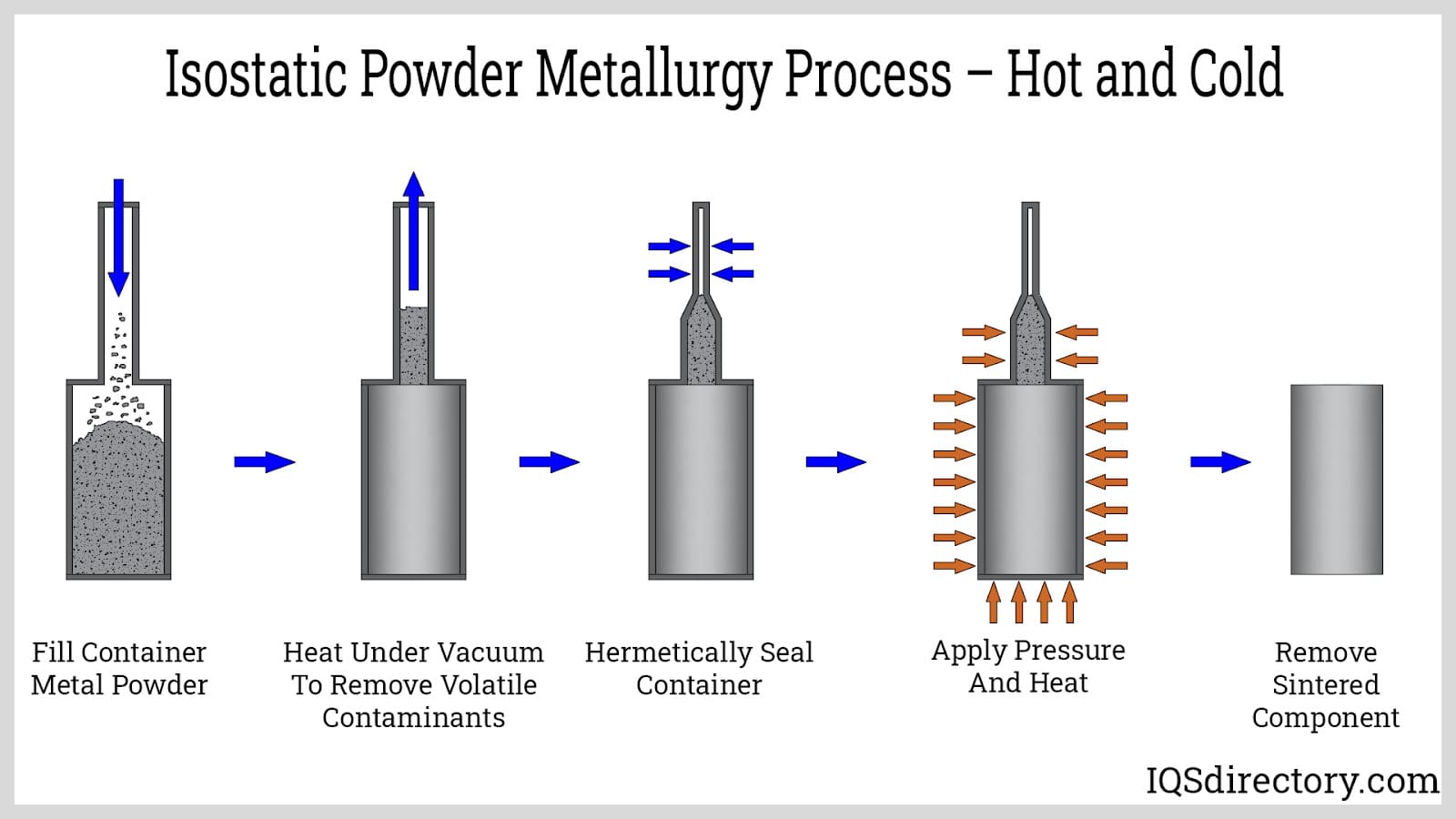
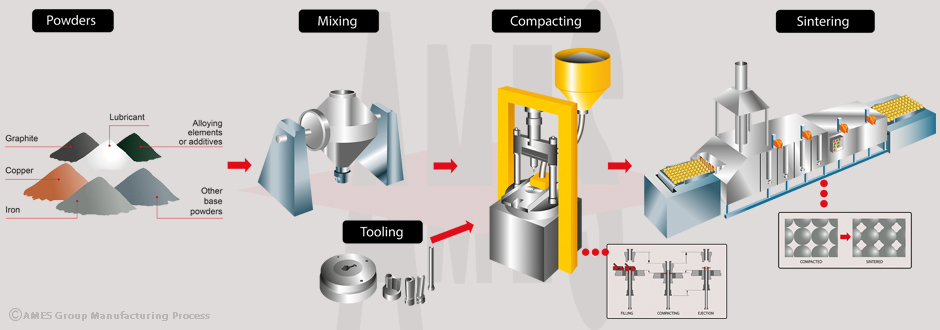
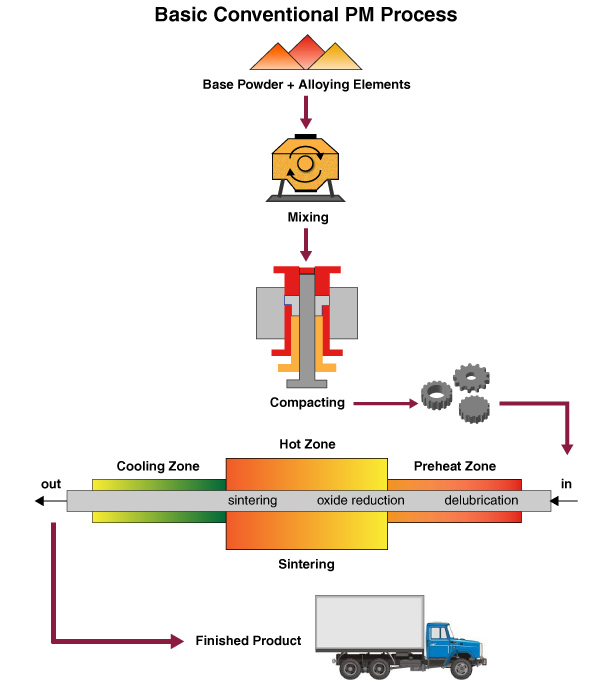
What Are the Main Stages of the Powdered Metal Manufacturing Process?
The powdered metal manufacturing process consists of several critical stages that transform raw materials into high-quality metal components. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chain and ensure the quality of their products.
How Is Material Prepared in Powder Metallurgy?
The first step in the powdered metal process involves the preparation of metal powders, which can be derived from various sources such as ore mining, recycling, or specialized manufacturing techniques like atomization and mechanical alloying. Each method has its advantages; for instance, atomization involves melting metal and breaking it into fine droplets that solidify into powder, offering excellent control over particle size and distribution.
Once the metal is powdered, it is essential to blend it with other materials, including alloying agents and lubricants. This blending enhances the properties of the final product, ensuring that it meets specific performance criteria. The formulation must be carefully tailored to achieve the desired characteristics, such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Powdered Metal Components?
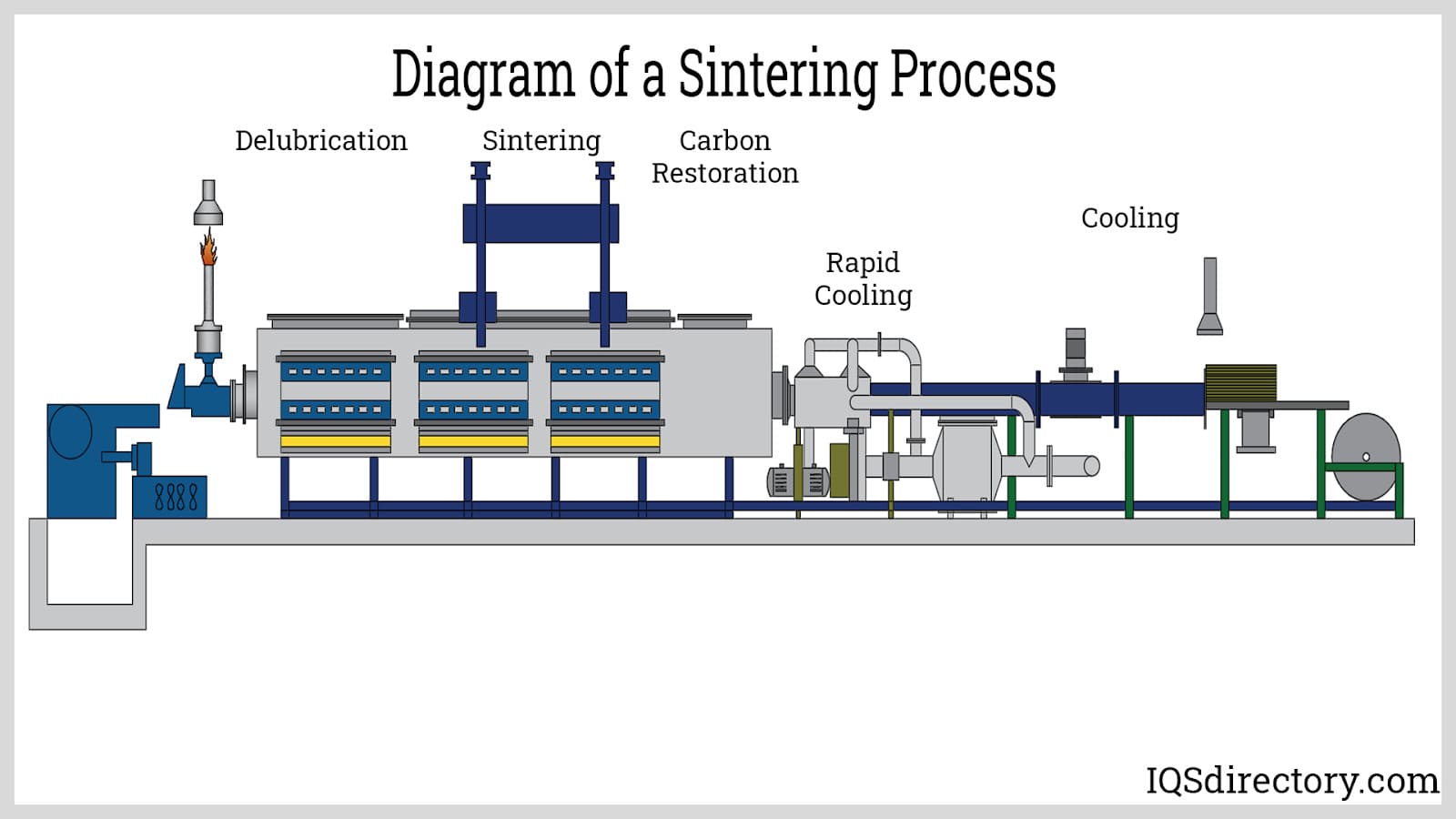
Forming is a critical stage in the powdered metal process. The blended powder is compacted into a “green” part using high-pressure dies and punches. This compaction process is crucial as it sets the shape and size of the final component. The compacted piece is then transported to a sintering furnace, where it undergoes a thermal process to achieve metallurgical bonding.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
Sintering typically occurs at temperatures just below the melting point of the metal, allowing particles to fuse together without fully melting. This process enhances the strength and structural integrity of the part. The atmosphere within the sintering furnace is controlled to prevent oxidation and ensure optimal bonding conditions.
What Finishing Processes Are Common in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
After sintering, parts may require various finishing operations to meet stringent performance standards. These operations can include heat treatment, machining, and surface coatings. Heat treatment processes like quenching or tempering improve hardness and durability, while machining allows for precise dimensional adjustments.
Finishing techniques such as deburring, tumbling, and plating enhance the surface quality and ensure that the parts meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements. The choice of finishing process largely depends on the intended application and industry standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the powdered metal manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding these quality measures is vital for selecting reliable suppliers.
What International Standards Govern Quality in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Several international quality standards are relevant to the powdered metal industry. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also apply, particularly for components used in critical applications like automotive or aerospace. These certifications ensure that products meet rigorous safety and performance standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production process. Ensuring that only high-quality materials are used is crucial for the overall integrity of the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors various parameters, including compaction pressure and sintering temperature. Regular checks at this stage help identify any deviations from specifications early in the process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the completion of manufacturing, FQC involves comprehensive testing and inspection of finished parts. This stage ensures that the components meet all design and performance criteria.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
A range of testing methods is employed to ensure the quality of powdered metal components. Common techniques include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Tools like calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are used to verify that parts meet specified dimensions.
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to assess the material properties of the finished components.
-
Surface Quality Assessment: Techniques like visual inspection, roughness measurement, and microscopic analysis are employed to evaluate surface finish and integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers to assess their quality management practices. This includes requesting documentation of ISO certifications, internal QC protocols, and records of previous audits. Suppliers should also provide test reports that detail the results of various quality assessments conducted during production.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services often conduct on-site inspections and testing, offering additional assurance that the supplier meets industry standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality assurance in international trade can be challenging. Buyers must be aware of regional regulations and standards that may differ from their own. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, while different certifications may apply in Africa or South America.
Understanding these nuances is crucial for establishing a successful partnership with suppliers. Clear communication regarding quality expectations and compliance requirements will help mitigate risks and ensure that the final products meet the necessary standards for their intended applications.
Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
Conclusion
The powdered metal manufacturing process encompasses various stages, each critical to producing high-quality components. For B2B buyers, particularly in diverse international markets, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is essential. By leveraging international standards, rigorous QC checkpoints, and thorough verification practices, buyers can confidently engage with suppliers and secure reliable, high-performance products tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘powdered metal process’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in navigating the procurement of powdered metal processing services. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you select a supplier who meets your technical requirements, budget, and quality standards, while also understanding the nuances of the powdered metallurgy process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your technical requirements before beginning the sourcing process. This includes details such as material types (e.g., iron, brass, copper), part dimensions, tolerances, and any specific mechanical properties needed for your application. A precise definition helps in identifying suppliers who can meet your needs effectively.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in powdered metallurgy. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry. Evaluate their market presence, the range of materials they offer, and their production capabilities to ensure they can handle your specific requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a decision, verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with industry-specific standards to ensure they meet your specifications.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Always ask for material samples to evaluate the quality of the powdered metal parts. Inspect the samples for consistency in composition, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. This step is crucial in assessing the supplier’s capability to produce parts that meet your expectations.
Step 5: Inquire About Production Processes
Understanding the supplier’s production processes can provide insight into their capabilities and efficiencies. Ask about their methods for powder production, compaction, and sintering, as well as any secondary operations they offer. This will help you gauge their ability to meet your technical specifications and production timelines.
Step 6: Assess Cost and Lead Times
Obtain detailed quotes from shortlisted suppliers, paying attention to cost structures and lead times. Evaluate not only the price per unit but also the overall value, including shipping costs and potential bulk discounts. Ensure that lead times align with your project timelines to avoid disruptions.
Step 7: Check References and Case Studies
Finally, request references and case studies from previous clients who have utilized the supplier’s services. This information can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability, quality of service, and responsiveness to client needs. Engaging with past customers can help you make a more informed decision.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process and select a powdered metal supplier that aligns with your technical requirements and business goals, ensuring successful project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for powdered metal process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Powdered Metal Process Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of the powdered metal process is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies. The main cost components include:

Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
-
Materials: The choice of metal powders significantly influences pricing. Common materials such as iron, stainless steel, and copper alloys vary in cost depending on market demand and availability. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs, which can lead to significant savings.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the production process, including skilled operators and technicians. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers may benefit from more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing practices, such as those found in high-capacity plants, can help mitigate these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling expenses refer to the costs associated with creating and maintaining molds and dies. Custom tooling can be costly, so it’s important to evaluate whether the required specifications justify these expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high quality through rigorous QC processes adds to the overall cost. However, investing in comprehensive QC can reduce long-term costs by minimizing defects and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for raw materials and finished products can vary widely based on distance and mode of transport. International buyers should consider the impact of Incoterms on logistics costs, as these terms dictate who is responsible for shipping and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing in Powdered Metal Sourcing?
Pricing in the powdered metal industry is heavily influenced by order volume and the degree of customization required. Higher volumes often lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Conversely, low minimum order quantities (MOQs) might result in higher prices due to setup costs being spread over fewer units.
Customization, such as unique material blends or intricate geometries, can significantly increase costs. It’s essential for buyers to clearly define their specifications early in the procurement process to receive accurate quotes. Additionally, the complexity of the design can necessitate advanced tooling and longer production times, further impacting pricing.
What Are the Quality and Certification Considerations for Powdered Metal Buyers?
Quality and certification play a critical role in the pricing structure. Suppliers with recognized certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) may charge a premium due to their commitment to quality assurance. Buyers should weigh the costs of certification against the potential risks associated with non-compliance, particularly in regulated industries such as automotive or aerospace.
What Negotiation Strategies Can B2B Buyers Use in Powdered Metal Sourcing?
Negotiation is key to achieving cost efficiencies in powdered metal sourcing. Buyers should:
- Research Market Prices: Understanding the market landscape helps in negotiating competitive rates.
- Leverage Volume Commitments: Offering to place larger orders can lead to better pricing.
- Discuss Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to favorable terms and pricing stability.
- Explore Alternative Suppliers: Seeking multiple quotes can provide leverage in negotiations.
How Can International Buyers Optimize Total Cost of Ownership in Powdered Metal Sourcing?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). TCO includes not only the purchase price but also costs related to logistics, inventory holding, and potential tariffs. Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
Different regions have unique pricing dynamics influenced by local market conditions, tariffs, and currency fluctuations. For instance, buyers in Brazil and Nigeria might face additional import duties that could affect overall costs. It’s crucial for buyers to factor in these nuances when evaluating suppliers from various geographical locations.

Illustrative image related to powdered metal process
Conclusion
While the powdered metal process offers numerous advantages, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is vital for effective sourcing. By considering these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to cost savings and improved product quality. Always remember to seek indicative pricing and tailor your sourcing strategy to suit your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing powdered metal process With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Powdered Metal Process
When evaluating manufacturing methods for metal components, it’s crucial to consider various alternatives to the powdered metal process. Each solution has distinct advantages and limitations that can impact production efficiency, cost, and final product quality. Below, we compare the powdered metal process with two notable alternatives: traditional machining and die casting.
| Comparison Aspect | Powdered Metal Process | Traditional Machining | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy and repeatability; excellent for complex geometries | Very high precision; limited to simpler shapes | Good surface finish; less precise than machining |
| Cost | Cost-effective for high-volume production; lower material waste | Higher costs for low-volume runs due to longer cycle times | Moderate initial setup costs; economical for high volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment; moderate learning curve | Widely understood process; accessible equipment | Requires specific molds; setup can be time-consuming |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance with wear on cutting tools | Moderate maintenance; mold wear can affect quality |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex, high-strength components in moderate to high volumes | Best for custom, low-volume parts needing high precision | Suitable for large, uniform parts in high-volume production |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Machining?
Traditional machining involves removing material from a solid block to create the desired part. This method excels in producing high-precision components with excellent surface finishes. However, it is often less cost-effective for large production runs due to longer cycle times and higher material waste. Machining is best suited for low-volume, highly customized components where precision is paramount, but it may not be ideal for complex geometries that require extensive tooling.
How Does Die Casting Compare?
Die casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into a mold to produce parts. This method allows for quick production of large quantities, making it cost-effective for high-volume runs. Die casting provides good surface finishes and can create complex shapes. However, it generally has a higher initial setup cost due to mold creation and may not achieve the same level of precision as traditional machining. Additionally, the mechanical properties of die-cast parts may not match those produced through the powdered metal process, particularly in terms of strength and durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing method hinges on specific project requirements, including production volume, component complexity, and cost constraints. For B2B buyers, understanding the unique strengths of each method is essential. If high precision and customization are paramount, traditional machining may be the preferred choice. In contrast, if producing complex parts in high volumes is the goal, the powdered metal process could be more advantageous due to its lower waste and cost-effectiveness. Meanwhile, die casting serves well for large, uniform components where speed and cost-efficiency are critical. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of project specifications and long-term objectives will guide buyers to the most suitable solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for powdered metal process
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
When engaging with powdered metal manufacturing, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
What is Material Grade and Why is it Important?
Material grade refers to the classification of metal powders based on their composition and properties. Common grades include stainless steel, copper, and bronze. Selecting the right material grade is vital because it affects the performance, durability, and suitability of the end product for specific applications. For instance, components intended for high-stress environments require materials with superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
How Do Tolerances Impact Manufacturing Quality?
Tolerances define the allowable variation in dimensions of a manufactured part. In powdered metal processes, tolerances can be as tight as ±0.001 inches. High precision in tolerances is essential for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, especially in assemblies where multiple components interact. Poor tolerance control can lead to increased production costs and compromised functionality.
What Role Does Density Play in Performance?
Density in powdered metal parts refers to the mass per unit volume and is a key indicator of the material’s quality and strength. Higher density generally results in enhanced mechanical properties, including strength and wear resistance. For buyers, understanding density is crucial as it directly correlates with the performance and lifespan of the final product.
Why is Sintering Temperature Critical?
Sintering temperature is the specific heat level applied during the sintering process, which is fundamental in bonding metal particles. The right temperature ensures optimal material properties, such as strength and ductility. It is essential for buyers to confirm that manufacturers maintain stringent controls over this aspect to guarantee high-quality outputs.
How Do Secondary Operations Enhance Product Performance?
Secondary operations include various finishing processes, such as heat treating and machining, that refine the properties of powdered metal parts. These operations can improve aspects like surface finish, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. Buyers should inquire about the availability of these services, as they can significantly enhance the functionality of the components.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Powdered Metal Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the powdered metal sector. Below are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
What Does OEM Mean in Powdered Metal?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer, which refers to a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s products. Understanding the role of OEMs is crucial for buyers looking to source components that need to meet specific quality and compatibility standards.
What is MOQ and Why Should Buyers Consider It?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must consider MOQ when budgeting and planning inventory, as it can affect cash flow and storage costs. Ensuring that MOQs align with production needs can lead to more efficient procurement processes.
How Does RFQ Facilitate the Procurement Process?
RFQ, or Request for Quotation, is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific quantities of products. This term is vital for establishing clear communication and expectations, ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing and timely delivery.
What Are Incoterms and Their Importance in International Trade?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are a series of predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, as they outline who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby minimizing risks in cross-border transactions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing powdered metal components, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and cost efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the powdered metal process Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Powdered Metal Process Market?
The global powdered metal process market is witnessing significant growth, primarily driven by increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength materials across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Emerging economies in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are particularly prominent, as they seek advanced manufacturing solutions to enhance local production capabilities. The trend towards automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies, with companies increasingly leveraging data analytics and IoT for improved production efficiency and supply chain management.
Another critical factor is the ongoing shift towards customization. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking tailored solutions that meet specific application requirements, which powdered metallurgy can efficiently provide through its ability to produce complex geometries and unique material properties. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms has transformed procurement processes, allowing international buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products, thereby fostering competitive pricing and innovation.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Trends in the Powdered Metal Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern in the powdered metal process sector. The inherent environmental advantages of powder metallurgy, such as minimal waste generation and the ability to recycle metal powders, align with the global push for greener manufacturing practices. The process utilizes up to 97% of the input materials, significantly reducing the environmental footprint compared to traditional methods like casting or machining.
B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers with strong sustainability credentials. This includes a preference for companies that adhere to ethical sourcing practices and possess certifications for environmentally friendly materials. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with international standards for sustainability and provide ‘green’ certifications are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market. Ethical supply chains not only mitigate risks associated with environmental degradation but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Powdered Metal Processes and Their Impact on Today’s B2B Market?
The powdered metal process has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, transitioning from a niche manufacturing technique to a mainstream production method. Initially used for producing small, intricate parts, advancements in technology have expanded its applications across various industries. The introduction of automated compaction and sintering processes has improved efficiency and precision, allowing for high-volume production without compromising quality.
This historical evolution has positioned powdered metallurgy as a viable alternative to traditional manufacturing methods. It not only meets the growing demand for customized solutions but also aligns with modern sustainability goals, making it an attractive option for international B2B buyers. As the market continues to innovate, the emphasis on high-performance, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly materials will likely drive further adoption across diverse sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of powdered metal process
-
How do I select the right powdered metal supplier for my business needs?
When selecting a powdered metal supplier, consider their experience, manufacturing capabilities, and reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers that offer a range of materials and customization options to meet your specific requirements. It’s also beneficial to check their quality assurance processes, certifications, and past client testimonials. Establishing direct communication with potential suppliers can provide insights into their responsiveness and support services, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for powdered metal components?
Minimum order quantities for powdered metal components can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 100 pieces for simpler designs to several thousand for more complex geometries. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and flexibility regarding MOQs, especially for international orders. -
What factors should I consider when customizing powdered metal parts?
When customizing powdered metal parts, consider the desired mechanical properties, dimensions, and any specific application requirements. The choice of metal powders, such as iron, stainless steel, or copper alloys, will influence performance characteristics like strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, think about secondary operations like heat treatment or surface finishing that may enhance the final product’s performance. Engaging with your supplier early in the design process can ensure optimal material selection and fabrication techniques. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by powdered metal suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among powdered metal suppliers, but common practices include net 30, net 60, or upfront payments for new customers. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or larger orders. It is essential to clarify payment terms during negotiations to ensure both parties have a clear understanding, which can help avoid potential cash flow issues and foster a positive business relationship. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in powdered metal products?
To ensure quality assurance in powdered metal products, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). Request detailed documentation on their testing methods, including mechanical property testing, dimensional inspections, and any certifications relevant to your industry. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality feedback and regular audits can also help maintain high standards throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing powdered metal components internationally?
When sourcing powdered metal components internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and import duties that may apply. It’s important to understand the supplier’s shipping capabilities and timelines, as well as their packaging standards to prevent damage during transit. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with international trade can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules. -
What are the environmental benefits of using powdered metal manufacturing?
Powdered metal manufacturing is recognized as an environmentally friendly process due to its high material utilization rate, often exceeding 97%. The process generates minimal waste and produces fewer harmful by-products compared to traditional metalworking methods. Additionally, many powdered metal suppliers employ sustainable practices, such as recycling metal powders and using energy-efficient technologies, making it a responsible choice for environmentally-conscious businesses. -
How can I assess the long-term performance reliability of powdered metal components?
To assess the long-term performance reliability of powdered metal components, request data on their testing results and performance in similar applications. Inquire about the materials used and any specific treatments applied during manufacturing. Additionally, consider seeking case studies or references from other clients who have used similar components in comparable environments. Understanding the operational conditions and the supplier’s track record can provide confidence in the durability and reliability of the components you are sourcing.
Top 7 Powdered Metal Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. James Engineering – MAX Deburring Machine
Domain: james-engineering.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The MAX Deburring Machine by James Engineering is designed for finishing powdered metal parts. It features compliance technology that adjusts pressure and action to ensure gentle, consistent deburring without damaging the parts. The machine offers multi-functionality, allowing for deburring, chamfering, radiusing, polishing, and washing in one unit, which minimizes handling of sensitive parts. It …
2. COMTEC – Powdered Metal Manufacturing
Domain: comtecmfg.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: The COMTEC Powdered Metal Manufacturing Process is an economical and environmentally clean method for producing parts with close to final dimensions, requiring little or no machining. The process involves creating solid ferrous and nonferrous metal parts from metal powder through powder metallurgy (P/M). Key steps include reducing metals to individual particles via atomization, chemical precipitat…
3. TWI Global – Powder Metallurgy Solutions
Domain: twi-global.com
Introduction: Powder metal (PM) manufacturing, also known as powder metallurgy, was first used in the early 1940s to create items such as porous bearings, cemented carbides, and electrical contacts. The process involves three basic steps: blending/preparing the metal powder, die compaction, and sintering. Additional heat treatment may be required after sintering to improve density, dimensions, and surface finis…
4. UARK – Powder Metallurgy Insights
Domain: uark.pressbooks.pub
Introduction: Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that uses metal powders to create parts, including composites with nonmetals like ceramics. Key advantages include the ability to produce complex shapes with minimal material waste and high precision. Typical size and weight limitations for parts are under 2 inches in thickness and under 35 lbs. The general powder metallurgy process includes generating …
5. Atlas Pressed Metals – Precision Powder Metallurgy Parts
Domain: atlaspressedmetals.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Powder Metallurgy (PM) is a manufacturing process used to create precise metal parts through several key steps: material selection, compacting, sintering, and additional operations like steam treating or machining. PM produces parts ranging from 0.68 grams to 6800 grams, suitable for moderate to high production volumes (hundreds to thousands of parts per hour). Key advantages include cost-effectiv…
6. TPIPM – Powder Metal Process
Domain: tpipm.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The Powder Metal Process involves several key steps: 1. Compaction: A pre-mixed metal powder is gravity fed into a die cavity and compacted to the final net shape, retaining its form without excessive damage. The compaction force is typically around 15-50 psi, and the parts have an indefinite shelf life due to a protective lubricant layer. 2. Sintering: Parts are heated in a furnace to 2050 F in a…
7. IQS Directory – Powder Metallurgy Components
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Powder metallurgy is a fabrication method that creates precise and highly accurate components by compacting powdered metals and alloys into a fixed die with intense pressure. Key products made using powder metallurgy include bushings, bearings, gears, high-strength gears, filters, magnets, and custom-designed metal parts. The process involves four fundamental stages: powder preparation, blending a…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for powdered metal process
Why Should International Buyers Consider Strategic Sourcing for Powdered Metal Processes?
In conclusion, the powdered metal process offers a multitude of advantages that make it an attractive option for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways highlight the cost-effectiveness, customization potential, and sustainability of powdered metallurgy. By utilizing more than 97% of input materials and producing minimal waste, this process aligns with the growing global emphasis on environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
Strategic sourcing in powdered metal can empower businesses to enhance their supply chains, ensuring high-quality components that meet specific application needs. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for precision-engineered components will only increase. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who can deliver tailored solutions and innovative technologies in powdered metallurgy.
Looking ahead, the landscape of powdered metal manufacturing is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing market demand. Now is the time for international buyers to explore partnerships with reputable manufacturers to leverage these benefits. By doing so, they can secure a competitive edge in their respective industries and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.