Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Parts Mechanical Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts mechanical
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing mechanical parts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. From navigating complex supply chains to ensuring quality and compliance, organizations must adopt strategic approaches to secure reliable components that meet their operational needs. This comprehensive guide on mechanical parts aims to equip businesses—particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Nigeria—with the insights necessary for effective procurement.
Covering a wide array of mechanical components, including linear motion parts, gears, bearings, and fasteners, this resource delves into the various applications and manufacturing processes associated with each category. Additionally, it provides detailed strategies for supplier vetting, cost analysis, and quality assurance, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.
By addressing key considerations such as supplier reliability, material specifications, and market trends, this guide empowers B2B buyers to enhance their purchasing strategies. With a focus on fostering successful partnerships and optimizing procurement processes, readers will gain the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the mechanical parts market confidently.
Understanding parts mechanical Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Motion Components | Enables movement in a straight line; includes shafts, bearings, and actuators. | Automation machinery, conveyor systems, robotics | Pros: High precision, reduced friction. Cons: Can be costly; requires precise alignment. |
| Fasteners | Includes screws, bolts, nuts, and washers; used to join parts. | Assembly lines, construction, automotive | Pros: Versatile, easy to use. Cons: Quality varies; may require specific tools. |
| Gears and Transmission | Transfers motion and torque; includes gears, sprockets, and pulleys. | Machinery, automotive, and aerospace applications | Pros: Increases efficiency, customizable ratios. Cons: Complex installation, potential for wear. |
| Seals and Gaskets | Prevents leakage of fluids or gases; includes O-rings and gaskets. | HVAC systems, automotive, and industrial equipment | Pros: Essential for durability, prevents contamination. Cons: Material degradation over time; must match specifications. |
| Pneumatic Components | Utilizes compressed air to perform work; includes cylinders and valves. | Manufacturing, packaging, and automation systems | Pros: High speed, energy-efficient. Cons: Requires air supply; can be sensitive to moisture. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Linear Motion Components?
Linear motion components are essential for systems requiring precise movement along a straight path. This category includes linear shafts, bearings, and actuators, which are pivotal in automation machinery, conveyor systems, and robotics. When considering these parts, B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as load capacity, material durability, and alignment requirements, as misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies.
How Do Fasteners Play a Role in Mechanical Assemblies?
Fasteners, encompassing screws, bolts, nuts, and washers, are fundamental in joining mechanical parts. Their versatility allows them to be used across various industries, from assembly lines to construction and automotive applications. Buyers should focus on the material quality, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with existing components when selecting fasteners to ensure long-lasting and reliable assemblies.
Why are Gears and Transmission Components Important?
Gears and transmission components are crucial for transferring motion and torque in mechanical systems. They include gears, sprockets, and pulleys, which enhance efficiency in machinery and automotive applications. Buyers need to consider gear ratios, material strength, and compatibility with other components to avoid issues related to installation and wear over time.
What are the Functions of Seals and Gaskets in Machinery?
Seals and gaskets are vital for preventing the leakage of fluids and gases in various applications, including HVAC systems and automotive engines. They come in various forms, such as O-rings and flat gaskets, and are essential for ensuring the durability of machinery. When purchasing, it’s crucial for buyers to match the specifications precisely to avoid degradation and ensure effective sealing over time.
How Do Pneumatic Components Enhance Mechanical Systems?
Pneumatic components utilize compressed air to perform work, making them essential in manufacturing, packaging, and automation systems. This category includes cylinders, valves, and fittings, which are known for their speed and energy efficiency. Buyers should consider the compatibility with air supply systems, potential moisture sensitivity, and maintenance requirements to optimize performance and longevity.
Key Industrial Applications of parts mechanical
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts mechanical | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Linear Motion Systems for Automation | Increased efficiency and precision in production | Quality certifications, lead times, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Automotive | Transmission Components in Vehicles | Enhanced performance and reliability of vehicles | Material specifications, compatibility with OEM standards, and durability under stress |
| Construction | Fasteners and Structural Components for Building | Improved safety and structural integrity | Compliance with local regulations, corrosion resistance, and load-bearing capacity |
| Agriculture | Bearings and Bushings in Machinery | Reduced maintenance costs and downtime | Availability of replacement parts, environmental resistance, and compatibility with existing machinery |
| Energy | Mechanical Seals in Pumps and Compressors | Enhanced efficiency and reduced leakage | Performance under temperature extremes, material compatibility, and supplier reliability |
How are Linear Motion Systems Used in Manufacturing Automation?
Linear motion systems, such as linear guides and ball screws, are critical in manufacturing automation. They facilitate the precise movement of machinery and robotic arms, ensuring high-speed operations with minimal friction. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing quality linear motion parts can significantly enhance production efficiency. Buyers must consider the compatibility of these components with existing systems and the certifications that guarantee their performance under varying operational conditions.
What Role Do Transmission Components Play in the Automotive Industry?
Transmission components, including gears and couplings, are essential for the functionality of vehicles. They ensure smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels, enhancing vehicle performance and reliability. For automotive manufacturers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing durable and high-quality mechanical parts is critical. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to OEM specifications and can provide proven reliability under diverse driving conditions.
Why are Fasteners Important in Construction?
Fasteners, such as bolts and screws, are foundational elements in construction projects. They secure structural components, ensuring the integrity and safety of buildings and infrastructure. For buyers in the construction sector across Africa and Europe, understanding local building codes and regulations is vital when sourcing fasteners. Additionally, factors like corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity must be considered to meet the demands of various environmental conditions.
How Do Bearings and Bushings Benefit Agricultural Machinery?
Bearings and bushings are key components in agricultural machinery, enabling smooth operation of moving parts. They reduce friction and wear, which translates to lower maintenance costs and decreased downtime. For agricultural equipment manufacturers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, sourcing high-quality bearings is essential for enhancing machinery reliability. Buyers should focus on the environmental resilience of these components, especially in harsh agricultural settings.
What Benefits Do Mechanical Seals Provide in Energy Applications?
Mechanical seals are crucial in pumps and compressors within the energy sector, preventing leaks and enhancing efficiency. They are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring the reliable operation of energy systems. For international buyers in the energy industry, sourcing seals that meet stringent performance standards is essential. Factors such as material compatibility and supplier reliability should be prioritized to ensure long-term operational success in diverse energy applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts mechanical’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Parts Amidst Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: In today’s global market, B2B buyers often face significant challenges in sourcing mechanical parts due to unpredictable supply chain disruptions. For example, a manufacturing company in Brazil may rely on specific linear motion parts, but sudden shipping delays or geopolitical issues can halt production lines, leading to financial losses and missed deadlines. This creates immense pressure to find reliable suppliers who can deliver quality components on time, which is further complicated by the variety of suppliers and the vast range of parts available.
The Solution: To navigate these challenges effectively, B2B buyers should adopt a dual sourcing strategy. This involves identifying multiple suppliers for the same parts, ideally from different geographical locations, to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. When selecting suppliers, prioritize those with proven track records and robust logistics capabilities. Establishing long-term relationships with local suppliers can also provide quicker access to essential components. Furthermore, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can reduce excess stock while ensuring that critical parts are available when needed. Regularly reviewing supplier performance and maintaining open lines of communication can also help in anticipating potential issues before they impact production.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Compatibility Issues with Mechanical Components
The Problem: Compatibility issues often arise when integrating new mechanical parts into existing machinery or systems. For instance, a company in Nigeria may purchase a new batch of bearings without thoroughly confirming their specifications, only to discover they do not fit with their current machinery. This oversight can lead to costly downtime and the need for re-engineering, which disrupts operations and delays project timelines.
The Solution: To prevent compatibility issues, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive specification documentation and utilize advanced CAD software for compatibility checks. Before purchasing, conduct a thorough analysis of the existing components and match them with the specifications of the new parts. Request detailed technical data sheets from suppliers, including material properties, dimensions, and tolerances. Engaging in pre-purchase prototyping can also help ensure that new parts fit seamlessly into existing systems. Additionally, fostering a collaborative relationship with suppliers can provide insights into alternative solutions that might better suit existing setups.
Scenario 3: Managing High Costs of Mechanical Parts
The Problem: The rising costs of mechanical parts can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating currency values like South America. A manufacturing firm may find that the cost of critical components like timing belts or bearings has increased substantially, impacting their overall production budget. This financial strain can force companies to compromise on quality or delay essential projects, ultimately affecting their competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To manage and reduce costs, buyers should explore bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers, which can provide discounts based on volume. Conducting a market analysis to understand pricing trends and potential alternative materials can also yield cost savings. Implementing an inventory management system that tracks usage patterns will help optimize stock levels and reduce waste. Furthermore, consider negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers to lock in prices and ensure a steady supply of critical components. By maintaining flexibility in sourcing and staying informed about market changes, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that balance cost and quality effectively.

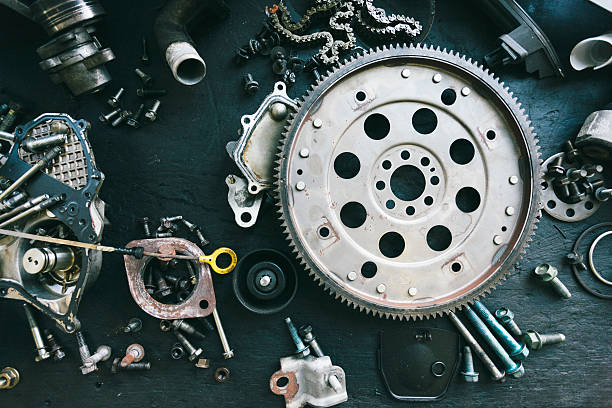
Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts mechanical
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Mechanical Parts?
When selecting materials for mechanical parts, understanding the properties of each material is essential for ensuring optimal performance in specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: steel, aluminum, plastic, and brass, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Mechanical Parts?
Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it a popular choice for mechanical components. Key properties include high tensile strength, excellent wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. However, steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can limit its use in certain environments unless treated or coated.
Pros and Cons: Steel offers exceptional durability and is relatively cost-effective, but its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where weight reduction is critical. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase when specific treatments for corrosion resistance are required.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and fuels, making it suitable for various industrial applications. However, its susceptibility to rust in humid environments necessitates careful consideration of protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding corrosion resistance and material certifications, such as ASTM standards. Compliance with international standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Mechanical Components?
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal and electrical conductivity. These properties make it suitable for applications where weight savings are essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Aluminum can be easily machined and formed, which simplifies manufacturing processes.
Pros and Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum is a significant advantage, but it is generally less strong than steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the cost of aluminum can be higher than that of steel, especially when considering the need for specialized alloys.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. However, it may not be suitable for high-temperature environments without specific alloy treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer aluminum for its lightweight properties and compliance with EU regulations on material safety. Understanding local alloy specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility with intended applications.
How Do Plastics Compare in Terms of Mechanical Parts?
Plastics, such as nylon or polycarbonate, are increasingly used in mechanical applications due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They exhibit good chemical resistance and can operate effectively in a variety of temperatures, depending on the type of plastic.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantages of plastics include low weight and cost-effectiveness, along with ease of manufacturing. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as well as metals, which can limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications involving moisture and chemicals, but compatibility with specific media must be assessed to avoid degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers from Brazil and Nigeria should consider local availability and compliance with international standards for plastics, such as those set by ASTM or ISO. Understanding the specific requirements for plastic materials in their applications is crucial.
What Role Does Brass Play in Mechanical Parts Manufacturing?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is valued for its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity and low friction.
Pros and Cons: The key advantages of brass include its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for plumbing and electrical applications. However, brass can be more expensive than other materials, and its mechanical strength is generally lower than that of steel.

Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with a range of media, including water and gases, but its use in high-pressure applications should be evaluated carefully.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East should be aware of the specific standards for brass components in plumbing and electrical applications. Compliance with local regulations and standards is essential for ensuring quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mechanical Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts mechanical | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, gears | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
| Plastic | Consumer products, housings | Low weight and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Excellent machinability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower strength | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for mechanical parts, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts mechanical
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Mechanical Parts?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for mechanical parts is crucial for B2B buyers seeking high-quality components. The production cycle typically consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Mechanical Parts Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational step where raw materials are selected based on the desired properties of the final product. Common materials include metals, plastics, and composites. In this phase, suppliers often conduct initial inspections to ensure material quality and compliance with specifications. This can involve checking for impurities, verifying dimensions, and confirming the mechanical properties of the material. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to inquire about the types of materials used and their sources to ensure they meet specific industry requirements.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Mechanical Parts Production?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired forms using various techniques. Key methods include:
- Injection Molding: Widely used for plastic components, this process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, allowing for complex shapes and high-volume production.
- Metal Stamping: This cold-working process transforms sheets of metal into specific shapes through the application of force, making it suitable for high-precision components.
- CNC Machining: Utilizing computer-controlled tools, CNC machining allows for high precision and flexibility in producing intricate designs from metals and plastics.
- Forging: A process that shapes metal by applying compressive forces, resulting in strong and durable parts.
Understanding these techniques helps B2B buyers identify which processes align with their quality and performance requirements.
How Does the Assembly Process Impact Quality in Mechanical Parts?
The assembly stage is where individual components are brought together to create the final product. This can involve mechanical fastening, welding, or adhesive bonding. The choice of assembly technique can greatly affect the durability and functionality of the parts. For instance, welded components may provide stronger joints than those that are merely bolted together.
In this stage, quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical. B2B buyers should ensure that manufacturers have established protocols to monitor the assembly process, as defects can often arise during this phase.

Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Applied to Mechanical Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the mechanical parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Methods like anodizing or plating can improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Painting and Coating: These processes not only provide a protective layer but can also enhance the appearance of the components.
- Polishing and Grinding: These techniques are used to achieve high surface finishes, which can be essential for certain applications.
Buyers should ask manufacturers about their finishing capabilities and how they align with industry standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Mechanical Parts Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the parts meet specified standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For mechanical parts, various international standards guide quality assurance practices. The most relevant include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to organizations of all sizes. It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
- CE Marking: This indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for products used in the oil and gas industry, these standards ensure that components meet specific performance criteria.
Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers assess the credibility and reliability of their suppliers.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Mechanical Parts Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. The most significant checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product before delivery.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC processes employed by manufacturers, including the frequency and methods of inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Mechanical Parts Quality?
Various testing methods are utilized to ensure the quality and performance of mechanical parts. These include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that components meet specified measurements.
- Functional Testing: Assessing whether the part performs as intended under operational conditions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or X-ray testing to detect internal flaws without damaging the part.
- Material Testing: Analyzing mechanical properties like tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance.
B2B buyers should request documentation of testing results and certifications to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation regarding their quality control measures, including inspection reports and compliance certificates.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
Understanding the nuances of quality assurance in international markets is particularly important for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Each region may have specific standards and regulations that need to be considered when sourcing mechanical parts.

Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
Conclusion
In-depth knowledge of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers in the mechanical parts sector. By understanding the main stages of manufacturing, relevant international standards, and effective QC practices, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the quality and reliability of the components they procure. This not only safeguards their operations but also enhances their competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts mechanical’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring mechanical parts. Whether you are sourcing components for manufacturing, assembly, or repair, following this checklist will ensure you make informed decisions, minimize risks, and secure high-quality products that meet your technical requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the mechanical parts you need. This includes dimensions, materials, tolerances, and performance requirements. Defining these specifications upfront helps streamline communication with suppliers and ensures that you receive parts that meet your exact needs.
- Consider industry standards: Identify relevant industry standards that may apply to the parts.
- Include application details: Provide context about how the parts will be used to help suppliers understand your requirements better.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in mechanical parts. Look for companies with a solid reputation and experience in your specific industry.
- Use online directories: Leverage platforms such as DirectIndustry or IQS Directory to find qualified suppliers.
- Check reviews and ratings: Look for customer testimonials and ratings to gauge supplier reliability and product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before entering into a contract, verify that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications. This may include ISO certifications or compliance with specific industry standards.
- Request documentation: Ask suppliers for copies of their certifications and quality control processes.
- Understand their quality assurance methods: Ensure that they have robust quality assurance protocols in place to maintain product consistency.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Always request samples of the mechanical parts before placing a bulk order. This allows you to evaluate the quality, fit, and functionality of the components.
- Test for compatibility: Ensure that the samples meet your technical specifications and integrate well with your existing systems.
- Assess material quality: Examine the materials used and their durability to ensure they align with your operational requirements.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare their pricing structures and payment terms. This step is critical for maximizing value and ensuring budget compliance.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate not just the unit price but also shipping costs, lead times, and potential discounts for bulk orders.
- Negotiate terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms or pricing to secure the best deal.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is essential throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear channels and protocols for updates, feedback, and any potential issues.

Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
- Set expectations: Clearly outline how often you expect updates on order status and any changes in timelines.
- Utilize technology: Consider using project management tools to facilitate communication and track progress.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Supplier Performance
After procurement, continuously monitor and evaluate your supplier’s performance based on quality, delivery time, and customer service.
- Create a performance checklist: Use criteria such as defect rates and delivery punctuality to assess ongoing supplier performance.
- Provide feedback: Share constructive feedback with suppliers to foster better relationships and improve future transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing processes, ensure quality, and build lasting partnerships with suppliers in the mechanical parts industry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts mechanical Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of mechanical parts sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the various components that contribute to the overall cost and the factors influencing pricing in this sector.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Mechanical Parts Sourcing?
The cost structure for mechanical parts typically encompasses several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences pricing. Common materials such as steel, aluminum, and plastics vary in cost due to market fluctuations and availability. Premium materials or specialized alloys can drive prices higher.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ widely based on geographic location and manufacturing processes. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but quality and expertise should not be compromised.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help reduce overhead, positively impacting pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling investments can be substantial, particularly for custom parts. The cost of molds, dies, and fixtures is often amortized over production runs, which affects pricing based on volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring quality through rigorous testing and inspection processes adds to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., ISO) can enhance product value but may also increase costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international orders. Factors like distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that varies based on their business strategy, competition, and market demand.
What Influences Pricing for Mechanical Parts?
Several factors impact the pricing of mechanical components, which international buyers should be aware of:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often decreases with larger order volumes due to economies of scale. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can also dictate pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts require additional design and manufacturing processes, leading to higher costs. Clear specifications can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality components and those with industry certifications command premium prices. Buyers should assess whether the added cost aligns with their quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may yield better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for pricing clarity. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Mechanical Parts Prices?
To optimize costs when sourcing mechanical parts, buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Build relationships with suppliers and negotiate terms based on volume and long-term commitments. Leverage competitive quotes to encourage better pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, maintenance, and operational efficiencies. Sometimes, a higher upfront investment in quality pays off in longevity and reduced operational costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, regional tariffs, and import regulations that may affect pricing. Being informed can lead to more strategic sourcing decisions.
-
Request Quotes with Transparency: Ask suppliers to break down quotes to understand the cost components better. This transparency helps in assessing the fairness of pricing and identifying areas for negotiation.
Final Thoughts
While indicative prices for mechanical parts can serve as a starting point, understanding the underlying cost structure and pricing influences is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Buyers from diverse regions, including Brazil and Nigeria, can benefit from these insights, ensuring they secure competitive pricing while maintaining quality and reliability in their sourcing strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts mechanical With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Parts Mechanical Solutions
When evaluating mechanical components, it is essential to consider alternative solutions that may offer comparable functionality or advantages. This analysis will compare traditional mechanical parts with two viable alternatives: Plastic Injection Molding and CNC Machining. Each option has unique characteristics that can influence a buyer’s decision based on their specific needs, budget, and operational context.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Mechanical | Plastic Injection Molding | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and reliability; suitable for heavy loads | Excellent for complex shapes; high precision | Exceptional precision; ideal for intricate designs |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower long-term costs due to durability | High setup costs; cost-effective for large volumes | Higher per-unit costs; economical for small batches |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation and integration | Requires specialized molds and setup | Needs skilled labor and sophisticated equipment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional lubrication required | Minimal maintenance post-production | Regular maintenance of machinery required |
| Best Use Case | Applications needing strong, durable components | Mass production of complex plastic parts | Custom parts with high precision requirements |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts with intricate shapes and designs. One of the major benefits of this method is its capacity for mass production, making it highly cost-effective when producing large quantities. However, the initial setup costs can be significant due to mold creation, making it less viable for smaller production runs. Additionally, while plastic parts may not match the durability of metal components, they are suitable for lightweight applications and can reduce overall product weight.
How Does CNC Machining Compare to Parts Mechanical Solutions?
CNC machining is a versatile manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to produce parts from various materials, including metals and plastics. It excels in producing highly precise and complex components, making it ideal for applications that demand tight tolerances. The downside is that the cost per unit is generally higher than traditional mechanical parts, particularly for low-volume production. CNC machining also requires skilled operators and regular maintenance of the machinery, which can increase operational overhead.
Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting between parts mechanical and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their operational requirements, including production volume, material needs, and budget constraints. If durability and long-term reliability are priorities, traditional mechanical parts may be the best option. However, for projects requiring intricate designs or rapid production, plastic injection molding or CNC machining could provide significant advantages. Ultimately, understanding the specific application and context of use will guide buyers toward the most suitable solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts mechanical
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Mechanical Parts?
In the realm of mechanical parts, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the composition and quality of the material used in the part, such as steel, aluminum, or plastic. High-grade materials often offer enhanced durability and performance, making them ideal for demanding applications. In B2B transactions, specifying material grades ensures that buyers receive parts that meet their operational requirements. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and is crucial for parts that must fit together precisely. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm ensures that parts will assemble correctly without excessive play. Accurate tolerances are vital in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision can affect safety and performance. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum load that a mechanical part can safely handle. It is particularly important for components such as bearings, shafts, and couplings. Understanding load capacity helps buyers select parts that will not fail under operational stress, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs. -
Corrosion Resistance
For parts exposed to harsh environments, corrosion resistance is a key property. Materials such as stainless steel or specially coated components can withstand moisture and chemical exposure. This property is particularly relevant for industries operating in humid or corrosive settings, such as marine or chemical processing. -
Fatigue Strength
This property measures a material’s ability to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles without failure. Parts with high fatigue strength are essential in applications where they experience dynamic stresses, such as in machinery and automotive components. This ensures longevity and reliability, which are critical for B2B buyers focused on minimizing lifecycle costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Mechanical Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are several important terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM specifications is vital for buyers looking to ensure compatibility and quality in replacement parts or components integrated into larger systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps companies plan their purchases and avoid excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific parts or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, ultimately leading to better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, particularly regarding shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate logistics, ensuring clarity on who bears the costs and risks at each stage of the transportation process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. This term is critical for inventory management, as longer lead times can affect production schedules. Buyers must consider lead times when planning their operations to avoid delays. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, signify that a product meets specific quality and safety benchmarks. Buyers should look for these certifications to ensure that the mechanical parts they procure comply with industry regulations and quality expectations, thus safeguarding their operations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing mechanical parts, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts mechanical Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global mechanical parts market is witnessing transformative dynamics driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and geopolitical influences. One of the key drivers is the increasing automation across industries, particularly in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace sectors. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are ramping up investments in automation technologies, thereby boosting the demand for precision-engineered mechanical components such as linear actuators, gears, and bearings.
Emerging B2B technology trends, including Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), are reshaping sourcing strategies. Companies are now leveraging data analytics and AI to optimize supply chains, enhance predictive maintenance, and improve inventory management. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is simplifying procurement processes, allowing international buyers to connect directly with manufacturers and suppliers, thus reducing lead times and costs.
Market dynamics are also influenced by the demand for customization and rapid prototyping. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide tailored solutions, leveraging techniques such as CNC machining and 3D printing to meet specific application needs. Moreover, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, are prompting companies to diversify their sourcing strategies, looking beyond traditional suppliers to mitigate risks.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As environmental concerns gain prominence, sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the mechanical parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and minimizing material waste, to enhance their eco-friendly credentials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate social responsibility in their operations. This includes fair labor practices, transparency in supply chains, and adherence to international labor standards. Buyers should look for suppliers that possess certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety), which indicate a commitment to sustainable and ethical practices.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals and biodegradable plastics, is on the rise. Suppliers offering products made from these materials can provide a competitive edge in the market, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. By integrating sustainability into their sourcing strategies, B2B buyers not only contribute to environmental preservation but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Brief Evolution/History
The mechanical parts industry has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from traditional manufacturing methods to advanced technologies. Early mechanical components were primarily crafted by hand, with limited precision and customization. However, the industrial revolution marked a turning point, introducing machine tools and mass production techniques that increased efficiency and lowered costs.
As industries advanced, so did the complexity and precision required in mechanical parts. The introduction of CNC machining in the late 20th century revolutionized manufacturing, allowing for high-precision parts to be produced at scale. Today, the industry is witnessing a shift towards automation and smart manufacturing, where data-driven decisions and real-time monitoring are becoming the norm. This evolution not only enhances production capabilities but also meets the demands of a rapidly changing global marketplace, positioning suppliers to better serve international B2B buyers across diverse sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts mechanical
-
1. How do I select the right mechanical parts for my project?
Choosing the right mechanical parts involves understanding your project requirements, including load capacity, operational environment, and specific functionality. Start by identifying the type of mechanical components you need, such as bearings, shafts, or fasteners. Consult with suppliers to compare materials, tolerances, and compatibility with existing systems. Additionally, consider the supplier’s expertise and the availability of customization options to ensure the parts meet your precise specifications. -
2. What are the key factors to consider when sourcing mechanical components internationally?
When sourcing mechanical components internationally, prioritize factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, and compliance with industry standards. Evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and past performance. Also, consider logistics aspects like shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Establish clear communication channels and understand the cultural nuances that may affect negotiations and transactions. -
3. How can I verify the credibility of a mechanical parts supplier?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, conduct thorough research including checking references and customer reviews. Look for industry certifications such as ISO or other relevant quality standards. Request product samples to assess quality firsthand and consider visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible. Engaging with a third-party inspection service can also provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s operations and product quality. -
4. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for mechanical parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mechanical parts can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific type of component. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for standard components to larger quantities for custom parts. It’s essential to discuss your needs with the supplier to negotiate MOQs that work for your business while considering cost-effectiveness and inventory management. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing mechanical components?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits, net 30, or net 60 terms. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. It’s advisable to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card) and consider using letters of credit for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the contract. -
6. How do I ensure quality assurance for mechanical parts?
Quality assurance can be maintained by establishing clear specifications and performance criteria with your supplier. Request certifications and quality control documentation that demonstrate compliance with industry standards. Implement regular quality checks during production and upon receipt of goods. Consider using third-party inspection services to verify that the products meet your quality expectations before final acceptance. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mechanical parts?
When importing mechanical parts, consider shipping methods, lead times, and costs. Understand the customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and additional fees. It’s also essential to have a reliable logistics partner who can manage the complexities of international shipping, including tracking and handling potential disruptions. Assess the risks of shipping delays and plan accordingly by keeping safety stock. -
8. Can I customize mechanical parts to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for mechanical parts, allowing you to tailor dimensions, materials, and features to meet your specific application requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to understand their capabilities and design constraints. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and possibly collaborate on prototypes to achieve the desired results.
Top 7 Parts Mechanical Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. JLCMC Mechatronics – Mechanical Parts
Domain: jlcmc.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: JLCMC Mechatronics offers a variety of mechanical parts including Linear Motion Parts (Linear Shafts, Linear Bearings, Ball Screws, etc.), Transmission Components (Shaft Couplings, Timing Belts, Gears, etc.), Fasteners (Screws, Bolts, Nuts, etc.), Positioning Parts (Locking Rings, Dowel Pins, etc.), Hardware & Transporting (Handles, Hinges, Casters, etc.), Pneumatics (Cylinders, Valves, etc.), Sen…
2. IQS Directory – Mechanical Components
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Introduction: Mechanical components are essential parts used in various manufacturing processes. They include items such as gears, bearings, fasteners, and springs, which are critical for the functionality of machines and equipment. These components are designed to provide support, movement, and stability in mechanical systems. They can be made from various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites,…
3. M&R – Mechanical Parts
Domain: mrprint.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Mechanical Parts include a wide range of components for M&R equipment and other print-related products. Categories include: Adhesives & Seals (30), Air Filters (3), Anchor (6), Axles (1), Ball Screw (10), Ball Transfer (1), Bearing Accessories (9), Bearing Assembly (1), Bearing Ball (3), Bearing- Linear (124), Bearings (106), Bearings – Spherical (4), Belts (6), Blankets & Assemblies (18), Blowers…
4. Mechanical Power – Industrial Parts
Domain: mechanicalpower.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Mechanical Power – Industrial Parts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. 7 Days to Die – Mechanical Parts
Domain: 7daystodie.fandom.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Mechanical Parts are an un-craftable multi-purpose part used for crafting various items, particularly in vehicles, tools, and mechanical electric devices and traps. They can be found in Destroyed Workbenches, Toolboxes, Mo Power Crates, and Working Stiffs Crates, or harvested from items like Air Conditioners, Gas Stations, Office Chairs, and broken down vehicles using a Wrench. Scrapping an Engine…
6. Tsurumi Pump – Mechanical Seals 3PN 4PN 8PN 12PN
Domain: tsurumipump.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: PARTS: Mechanical Seal 3PN 4PN 8PN 12PN, SKU: 025-000-78
7. Kinetic Labs – HMX Frog Tactile Switches
Domain: kineticlabs.com
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”HMX Frog Tactile Switches”,”price”:”$9.36″},{“name”:”HMX Latte Linear Switches”,”price”:”$8.10″},{“name”:”Kinetic Labs Keyboard Switch Tester Pack”,”price”:”$17.99″},{“name”:”Gateron Oil King Switches”,”price”:”$11.70″},{“name”:”Kinetic Labs Gecko Silent Linear Switches”,”price”:”$10.80″},{“name”:”Kinetic Labs Switch Container”,”price”:”$3.82 (15% off) $4.49″},{“name”:”Kineti…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts mechanical
In the dynamic landscape of mechanical parts sourcing, strategic procurement emerges as a vital component for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By focusing on key areas such as supplier diversity, quality control, and innovative manufacturing processes, businesses can significantly enhance their supply chain resilience. Understanding the specific needs of diverse markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, enables buyers to tailor their sourcing strategies effectively.
International buyers should prioritize building strong relationships with reliable manufacturers, leveraging technologies such as CNC machining and plastic injection molding to ensure high-quality standards. Additionally, embracing sustainability and ethical sourcing practices will not only foster trust but also align with the growing global emphasis on responsible business operations.
Looking ahead, the evolving market dynamics present vast opportunities for growth and collaboration. By staying informed about industry trends and continuously adapting sourcing strategies, businesses can position themselves competitively. Now is the time to take action—engage with trusted suppliers, explore innovative solutions, and strengthen your supply chain to thrive in the competitive world of mechanical parts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to parts mechanical
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.