Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Insulation Ceramic Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for insulation ceramic
Navigating the complexities of sourcing insulation ceramic materials can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers across various global markets. With the increasing demand for high-performance thermal insulation solutions, international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key players like Germany and Saudi Arabia—must ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of insulation ceramics, providing detailed insights into various types such as ceramic fiber blankets, their diverse applications in industries ranging from manufacturing to energy, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Our comprehensive exploration covers essential aspects such as cost considerations, shipping logistics, and product specifications, equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to select the right insulation materials for their unique requirements. Whether you are looking to enhance the thermal efficiency of industrial furnaces or seeking reliable insulation for high-temperature applications, this guide serves as a valuable resource. By empowering you with actionable insights and best practices, we aim to streamline your procurement process, minimize risks, and ultimately drive value in your operations. Join us as we navigate the global market for insulation ceramics, ensuring you are well-prepared to make strategic purchasing decisions that meet your business objectives.
Understanding insulation ceramic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber Blanket | High-temperature resistance, lightweight, flexible | Furnace linings, kiln insulation, steam turbine wraps | Pros: Excellent thermal efficiency, reusable; Cons: Can be costly if not sourced properly. |
| Fiberfrax Durablanket | High strength, needled ceramic fibers, low shrinkage | Industrial heat processing, fire protection, insulation jackets | Pros: Durable, versatile; Cons: Limited chemical resistance to specific acids. |
| High-Purity Ceramic Fiber | Superior thermal performance, low thermal conductivity | Aerospace, nuclear insulation, high-performance furnaces | Pros: Exceptional thermal stability; Cons: Higher price point, requiring careful sourcing. |
| Ceramic Fiber Mat | Flexible mat made from spun fibers, good for filtration | Gas filtration, hot gas velocity resistance | Pros: Lightweight, easy to handle; Cons: May require additional support in certain applications. |
| Mullite-Based Insulation | High chemical stability, lightweight, low thermal mass | Petrochemical industries, high-temperature applications | Pros: Excellent thermal and mechanical properties; Cons: Often requires custom solutions for specific needs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Ceramic Fiber Blankets?
Ceramic fiber blankets are renowned for their high-temperature resistance, typically rated up to 2300°F. They are lightweight and flexible, making them easy to handle and install. These blankets are ideal for applications such as furnace linings and kiln insulation, where thermal efficiency is critical. Buyers should consider the sourcing of these blankets, as costs can vary significantly based on purity and manufacturer reputation.
How Do Fiberfrax Durablankets Stand Out in the Market?
Fiberfrax Durablankets are characterized by their high strength and needled construction, providing low shrinkage at elevated temperatures. This makes them suitable for a variety of industrial applications, including heat processing and fire protection. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the specific temperature requirements and chemical exposure of their operations, as certain acids may affect performance.
What Benefits Do High-Purity Ceramic Fibers Offer to B2B Buyers?
High-purity ceramic fibers provide superior thermal performance and low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for demanding applications in aerospace and nuclear sectors. These materials ensure exceptional thermal stability and can withstand extreme conditions. However, the higher price point may necessitate a careful evaluation of the long-term benefits versus initial costs, making them a premium choice for specialized applications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Ceramic Fiber Mats?
Ceramic fiber mats are flexible and made from spun fibers, offering good performance for gas filtration and high-temperature applications. Their lightweight nature allows for easy installation, but they may require additional structural support in certain scenarios. B2B buyers should assess the specific filtration needs and installation environments when considering these products.
Why Choose Mullite-Based Insulation for High-Temperature Applications?
Mullite-based insulation is valued for its high chemical stability and low thermal mass, making it suitable for use in the petrochemical industry and other high-temperature settings. It offers excellent thermal and mechanical properties, but often requires customized solutions to meet specific operational needs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of performance against the potential for increased complexity in sourcing and installation.
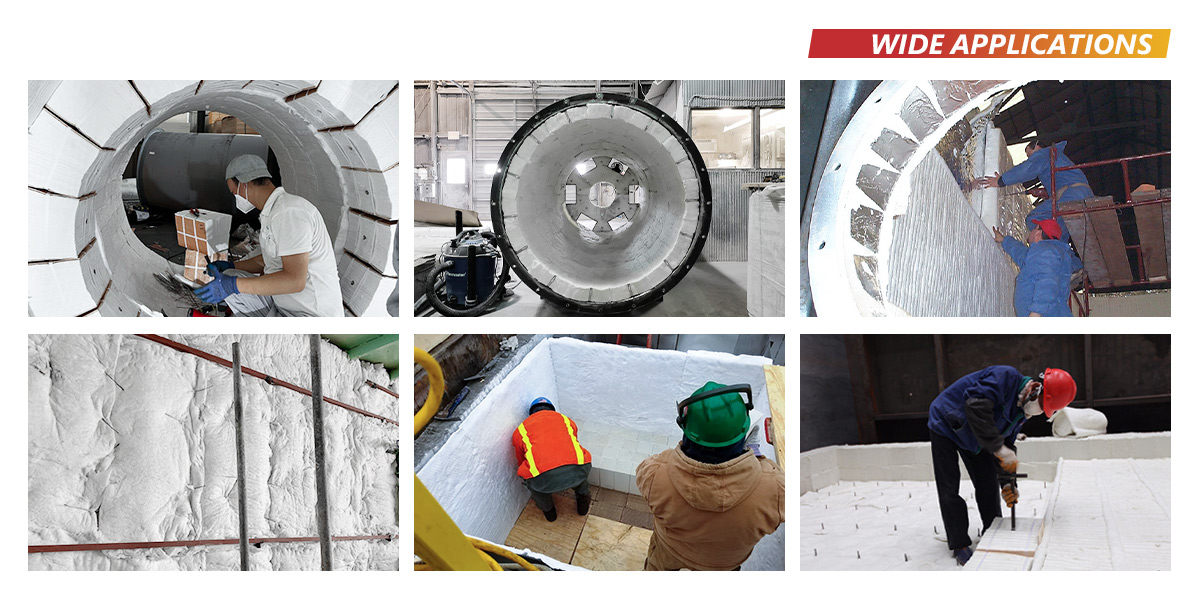
Key Industrial Applications of insulation ceramic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Insulation Ceramic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel and Metal Processing | High-Temperature Furnace Linings | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs. | Sourcing high-purity grades for durability and performance. |
| Oil and Gas | Insulation for Pipelines and Vessels | Prevents heat loss, maintaining optimal operating temperatures. | Consider local suppliers for quick delivery and compliance with international standards. |
| Power Generation | Insulation for Steam and Gas Turbines | Improves thermal efficiency and extends equipment lifespan. | Evaluate insulation thickness and temperature ratings for specific turbine applications. |
| Glass Manufacturing | Furnace Crown Insulation | Reduces energy consumption and improves production rates. | Ensure compatibility with high-temperature processes and chemical stability. |
| Nuclear Energy | Reactor Insulation | Enhances safety and operational efficiency in high-radiation environments. | Look for certified materials that meet safety regulations and international standards. |
How is Insulation Ceramic Utilized in Steel and Metal Processing?
In the steel and metal processing industry, insulation ceramics are primarily used for high-temperature furnace linings. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures while providing excellent thermal efficiency, which is crucial for energy-intensive processes. By utilizing high-purity grades, businesses can significantly reduce heat loss, thereby lowering operational costs. Buyers should prioritize sourcing options that offer durability and performance under high-stress conditions to ensure long-term reliability.
What Role Does Insulation Ceramic Play in Oil and Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas sector, insulation ceramics are essential for pipelines and vessels to prevent heat loss and maintain optimal temperatures for fluid transport. This insulation not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to safety by reducing the risk of thermal expansion and contraction. International buyers should consider local suppliers who can provide timely delivery and ensure compliance with global standards, enhancing supply chain reliability.
Why is Insulation Ceramic Important in Power Generation?
Insulation ceramics are used extensively in steam and gas turbines within the power generation industry. These materials improve thermal efficiency by minimizing heat loss, which is critical for maximizing energy output and extending equipment lifespan. Buyers should evaluate insulation thickness and temperature ratings specific to their turbine applications, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry regulations.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
How Does Insulation Ceramic Benefit Glass Manufacturing?
In glass manufacturing, insulation ceramics are employed for furnace crown insulation to reduce energy consumption and enhance production rates. The ability of these materials to withstand high temperatures and resist thermal shock is vital in maintaining consistent product quality. Buyers must ensure that the insulation materials are compatible with the specific high-temperature processes used in glass production, focusing on both thermal efficiency and chemical stability.
What is the Significance of Insulation Ceramic in Nuclear Energy?
In the nuclear energy sector, insulation ceramics are crucial for reactor insulation, enhancing safety and operational efficiency in high-radiation environments. These materials help maintain thermal stability while preventing radiation leakage. Buyers in this field should prioritize sourcing certified insulation products that meet stringent safety regulations and international standards, ensuring compliance and reliability in critical applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘insulation ceramic’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Temperature Resistance Needs
The Problem: Many industries, particularly those in manufacturing and energy, face challenges when it comes to insulation materials that can withstand extreme temperatures. Buyers often struggle to find ceramic insulation solutions that not only meet the required thermal ratings but also maintain performance over time. For instance, a steel manufacturing plant may need insulation that can endure temperatures up to 2300°F without significant degradation, which can lead to costly downtime and increased energy consumption.
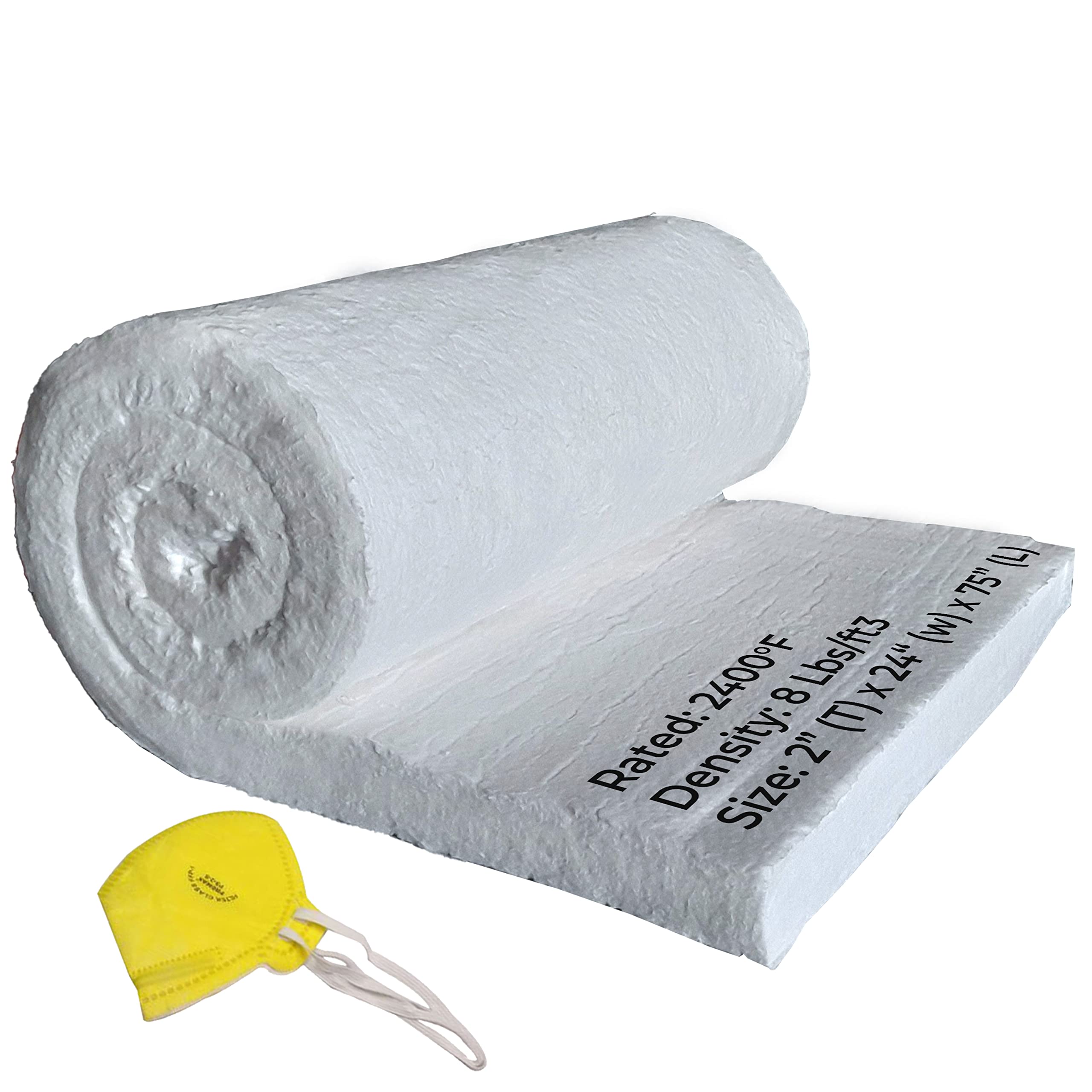

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-purity ceramic fiber insulation products specifically designed for high-temperature applications. When evaluating suppliers, look for detailed technical data sheets that specify temperature ratings, density, and durability under extreme conditions. Opt for products that feature low thermal conductivity and high tensile strength, such as needled ceramic fiber blankets, which can provide excellent thermal efficiency and resistance to thermal shock. Additionally, consider engaging with suppliers who offer customizable solutions, allowing you to tailor the insulation to your specific operational needs. Regular maintenance checks and assessments can also help identify potential issues before they lead to failure, ensuring that your insulation performs optimally over its lifespan.
Scenario 2: Cost-Effectiveness in Material Selection
The Problem: In competitive markets, B2B buyers often encounter pressure to reduce operational costs, including expenses related to insulation materials. Many find themselves torn between opting for cheaper alternatives that may compromise on quality and performance versus investing in premium insulation ceramics that promise long-term savings but come at a higher upfront cost. This dilemma can be particularly pronounced in industries such as petrochemicals, where insulation is critical for energy efficiency.
The Solution: A strategic approach to overcoming this challenge is to conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis. Buyers should compare the initial costs of insulation ceramics with potential long-term savings in energy efficiency, maintenance, and equipment lifespan. For instance, high-quality ceramic fiber insulation may have a higher upfront cost but can significantly reduce energy losses, translating into lower utility bills over time. Additionally, investing in durable materials that require less frequent replacement can lead to substantial savings. Collaborating with suppliers who offer detailed ROI calculations and case studies from similar industries can provide valuable insights into making a well-informed decision. This approach not only aids in selecting the right product but also justifies the investment to stakeholders.
Scenario 3: Navigating Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions have made it increasingly difficult for B2B buyers to secure timely deliveries of insulation ceramic materials. Industries reliant on just-in-time inventory practices often face project delays due to unexpected shortages or extended lead times. This situation can lead to increased costs, operational inefficiencies, and missed deadlines, particularly in sectors such as construction and manufacturing.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should develop a proactive sourcing strategy that emphasizes building strong relationships with multiple suppliers. Diversifying your supply chain can help cushion against disruptions and provide alternative options in case of shortages. Additionally, it is beneficial to maintain an open line of communication with suppliers regarding their production schedules and inventory levels. Implementing an inventory management system that tracks usage and anticipates future needs can also help in planning orders well in advance. Buyers should consider establishing contracts with suppliers that include provisions for expedited shipping or priority service, ensuring that you receive materials when needed. Finally, keeping abreast of market trends and potential geopolitical issues affecting supply chains can inform your procurement strategy and enhance your resilience against future disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for insulation ceramic
What Are the Key Properties of Common Insulation Ceramic Materials?
When selecting insulation ceramics for high-temperature applications, understanding the properties of various materials is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in insulation ceramics: Ceramic Fiber, Mullite, Zirconia, and Alumina.
How Does Ceramic Fiber Stand Out in High-Temperature Applications?
Ceramic fiber is known for its lightweight and flexible nature, making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal efficiency. It typically withstands temperatures up to 2300°F (1260°C) and exhibits low thermal conductivity, which enhances energy efficiency. However, while it is dimensionally stable at high temperatures, it can be sensitive to chemical attacks from strong acids and bases.
Pros:
– Excellent thermal insulation properties
– Lightweight and easy to handle
– High resistance to thermal shock
Cons:
– Potential degradation in chemically aggressive environments
– Requires careful installation to avoid damage
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Additionally, buyers should consider local regulations regarding the use of ceramic fibers, as some countries have stringent guidelines on fiber emissions.
What Advantages Does Mullite Offer for Insulation?
Mullite is a type of ceramic that combines alumina and silica, providing exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength. It is capable of withstanding temperatures up to 3200°F (1760°C) and exhibits good resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion.
Pros:
– High-temperature resistance
– Superior mechanical strength
– Good chemical stability
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to other insulation materials
– More complex manufacturing process
Mullite’s properties make it suitable for applications in industries such as steel manufacturing and glass production. For B2B buyers in South America and Africa, the cost may be a significant factor, as budget constraints can limit the choice of materials.
How Does Zirconia Enhance Thermal Insulation?
Zirconia is recognized for its exceptional thermal insulation properties and can withstand temperatures exceeding 3000°F (1650°C). It also has excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for applications involving aggressive media.
Pros:
– Extremely high-temperature tolerance
– Excellent chemical resistance
– Low thermal conductivity
Cons:
– Very high cost compared to other options
– Limited availability in some regions
For international buyers, particularly in Germany and Saudi Arabia, the high cost of zirconia may be a barrier. However, its long-term performance in harsh environments can justify the investment, especially in industries where downtime is costly.
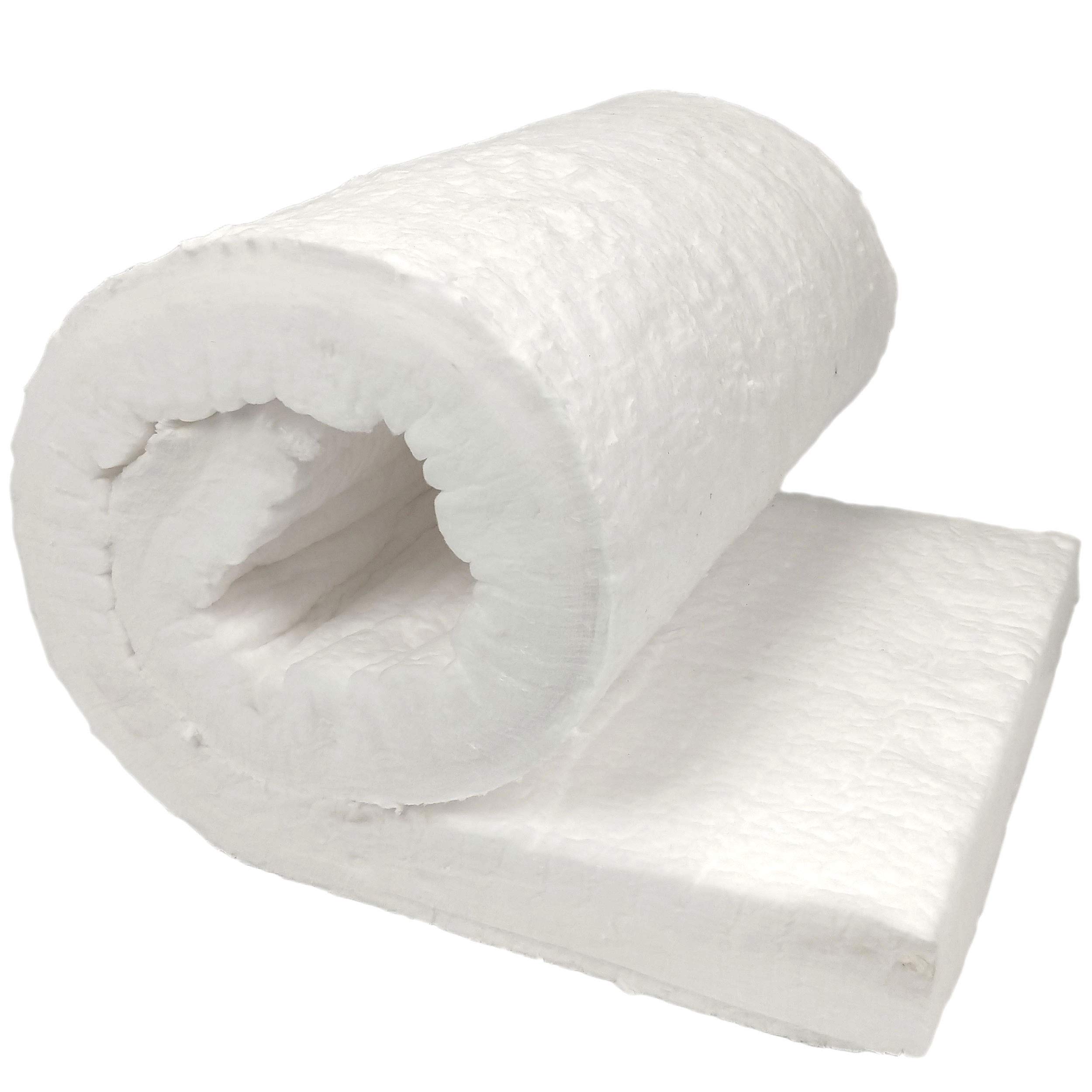
What Role Does Alumina Play in Insulation Ceramics?
Alumina is a versatile ceramic material that can be formulated to provide varying levels of thermal resistance. It is commonly used in applications that require moderate thermal insulation, typically up to 2000°F (1093°C). Its durability and resistance to wear make it a popular choice in various industrial applications.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
Pros:
– Cost-effective compared to other high-temperature materials
– Good mechanical strength
– Versatile applications
Cons:
– Lower temperature rating compared to mullite and zirconia
– Can be brittle under certain conditions
For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Africa, the cost-effectiveness of alumina makes it an attractive option for various applications, including furnace linings and kiln insulation. Compliance with local standards is crucial, especially when dealing with industrial applications.
Summary Table of Insulation Ceramic Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for insulation ceramic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber | Furnace linings, kiln insulation | Lightweight and flexible | Sensitive to chemical attacks | Medium |
| Mullite | Steel manufacturing, glass production | High-temperature resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconia | Chemical processing, aerospace | Extremely high-temperature tolerance | Very high cost | High |
| Alumina | Furnace linings, kiln insulation | Cost-effective and durable | Lower temperature rating | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when selecting insulation ceramics tailored to their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for insulation ceramic
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Insulation Ceramics?
The manufacturing process of insulation ceramics, particularly ceramic fiber products, is intricate and involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial to ensure the final product meets the required thermal and physical specifications.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing high-purity raw materials, typically including alumina, silica, and zirconia. These materials are often subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet predefined specifications. The materials are then processed into fibers through methods such as spinning or blowing, which create the lightweight and flexible structure essential for insulation applications.
How Is the Forming Process Executed?
Once the fibers are prepared, the forming process begins. The fibers are needled together to create blankets or mats. This technique enhances the handling strength and dimensional stability of the product. In some cases, additional components, such as binders, may be introduced to improve the mechanical properties of the insulation. The forming process is critical as it directly influences the insulation’s performance at high temperatures.
What Does the Assembly Stage Entail?
After forming, the next step is assembly. This may involve cutting the blankets to specific dimensions or layering them for enhanced thermal efficiency. Depending on the intended application, products may be combined with other materials, such as metal foils, to provide additional benefits like moisture resistance or structural integrity.
What Are the Key Techniques in Finishing?
The finishing stage includes drying and curing the insulation products to eliminate any residual moisture and enhance thermal stability. This stage may also involve additional treatments, such as coating or surface treatment, to further improve performance characteristics. The final products undergo stringent inspections to ensure they meet the desired specifications before being packaged for shipment.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
What Quality Control Measures Are In Place for Insulation Ceramics?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of insulation ceramics, particularly given the high-temperature applications they serve. International standards, such as ISO 9001, along with industry-specific certifications like CE and API, play a crucial role in ensuring product quality and reliability.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing the need for consistent quality and customer satisfaction. This standard is recognized globally, making it a significant consideration for B2B buyers looking to ensure their suppliers adhere to best practices. Additionally, compliance with CE marking indicates that the products meet European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
The quality control process typically involves several checkpoints, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC). IQC focuses on the quality of raw materials before they enter production. IPQC monitors the manufacturing process to catch any deviations early, while FQC ensures that the final products meet all specifications before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods commonly employed include thermal conductivity tests, dimensional stability assessments, and chemical resistance evaluations. These tests help verify that the insulation ceramics can withstand the demanding conditions they will face in their applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical. This can be achieved through several means:
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control practices. During an audit, buyers can review production processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards. Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s capabilities.
How Important Are Quality Control Reports?
Requesting quality control reports is another way to gain insight into a supplier’s practices. These reports should detail the results of various quality tests and inspections conducted throughout the manufacturing process. Regular reporting demonstrates a commitment to transparency and accountability.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further bolster confidence in a supplier’s quality control. These organizations specialize in evaluating compliance with international standards and can provide certifications that reinforce product quality. This is particularly important for B2B buyers operating in regions where local regulations may vary.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control and certification requirements, which can differ significantly by region. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on local compliance standards. Understanding these nuances is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential supply chain disruptions.
How Can Regional Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Regional differences can impact not only the standards required but also the materials available and the manufacturing techniques employed. For example, suppliers in Europe might have access to advanced technologies that enhance quality, while manufacturers in other regions may rely on traditional methods. Buyers should consider these factors when selecting suppliers to ensure they meet their specific quality requirements.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for insulation ceramics are complex and multifaceted. B2B buyers must engage deeply with their suppliers, understanding the manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and regional certification nuances to ensure they receive high-quality products. By taking a proactive approach to supplier verification and quality assurance, businesses can secure reliable insulation solutions that meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘insulation ceramic’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure insulation ceramic materials. Given the diverse applications of ceramic insulation in various industries—from manufacturing to energy production—it’s essential to approach the sourcing process methodically. This guide will help you identify key considerations and actions to ensure you select the right product and supplier for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for successful procurement. Determine the required temperature ratings, density, and application types for the insulation ceramic products you need. For instance, products like ceramic fiber blankets can vary significantly in properties, such as thermal resistance and flexibility, depending on your specific use case.
- Consider applications: Identify if the insulation will be used in high-temperature furnaces, kilns, or other specialized equipment.
- Assess environmental conditions: Take into account factors such as exposure to chemicals or moisture that may affect the insulation’s performance.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards and regulations. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management, or specific certifications relevant to your region.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
- Check for experience: Investigate the supplier’s history in the insulation ceramic market and their experience with similar projects.
- Request documentation: Ask for quality assurance documents, safety data sheets, and product data sheets to verify compliance.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Quality
Before making a purchase, assess the quality of the insulation ceramic products offered. Request samples to evaluate their properties and suitability for your applications.
- Test for durability: Ensure the insulation can withstand the required temperatures and environmental conditions without degrading.
- Look for performance data: Review any available test results or performance metrics that demonstrate the product’s efficacy.
Step 4: Compare Pricing Structures
Understanding pricing is vital for budget management. Compare quotes from multiple suppliers, but be cautious of choosing the lowest price without considering quality.
- Analyze cost per unit: Evaluate the cost in relation to the specifications and expected lifespan of the product.
- Consider bulk purchasing discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders, as many suppliers offer better rates for bulk purchases.
Step 5: Verify Shipping and Delivery Options
Shipping logistics can significantly impact project timelines. Confirm the supplier’s shipping capabilities and delivery times to ensure they align with your project schedule.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
- Choose the right shipping method: Depending on your order size, consider whether LTL (Less Than Truckload) or UPS is more appropriate.
- Discuss lead times: Clarify expected lead times for production and shipping to avoid project delays.
Step 6: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication with suppliers is key to successful sourcing. Ensure that you have established clear lines of communication to address questions or concerns promptly.
- Set up regular updates: Arrange for periodic check-ins during the order process to monitor progress and address any issues.
- Create a point of contact: Designate a representative from your organization to liaise with the supplier for streamlined communication.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Review Before Purchase
Before finalizing your order, conduct a comprehensive review of all gathered information. Ensure that all specifications, pricing, and delivery details meet your requirements.
- Confirm order details: Revisit all terms and conditions, including warranties and return policies.
- Assess supplier reliability: Finally, consider feedback from previous customers or industry peers to gauge the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for insulation ceramic, ensuring they make informed decisions that meet their technical and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for insulation ceramic Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Insulation Ceramic Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing insulation ceramics, several key components must be taken into account:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the raw materials used in the production of insulation ceramics. High-purity ceramic fibers, for instance, can range significantly in price depending on their thermal performance and chemical composition. Buyers should note that variations in material quality can lead to price fluctuations.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the manufacturing process, particularly for high-quality insulation ceramics that require precise handling and assembly. Labor costs can vary by region, impacting overall pricing strategies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, but they are often passed onto the buyer.
-
Tooling: The development of specialized tooling for custom or high-volume orders can add to initial costs. Buyers looking for specific dimensions or properties should consider these tooling expenses in their total cost analysis.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that insulation ceramics meet specific standards requires robust QC processes. The cost of testing and certification can significantly impact the final price, particularly for products that require compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: The transportation of insulation ceramics, which can be bulky and fragile, must be factored into the cost structure. Shipping methods (LTL, UPS, etc.) and distances can vary dramatically, influencing the overall expense.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin based on their operational costs and market conditions. Buyers should be aware that margins can vary widely across different suppliers and regions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Insulation Ceramic Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers are generally more willing to negotiate pricing for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers should balance the need for specialized products with their budgetary constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) typically command higher prices. It’s crucial for buyers to assess whether the additional investment aligns with their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is vital for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping costs and risks, affecting the total landed cost of the products.
What Negotiation Tips Can Buyers Use to Enhance Cost Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to improve cost efficiency when sourcing insulation ceramics:
-
Leverage Bulk Orders: Negotiating discounts for larger volumes can lead to significant savings. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing over time.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and replacement costs. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Investigate Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly by region due to labor costs, supply chain dynamics, and market demand. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct market research to identify competitive pricing.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to larger orders, requesting samples can ensure product quality meets expectations without incurring significant upfront costs.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends, such as material innovations and regulatory changes, can provide leverage in negotiations and sourcing strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers for insulation ceramics is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on key cost components, utilizing effective negotiation strategies, and considering the total cost of ownership, buyers can enhance their sourcing decisions and achieve better outcomes. Always remember that the indicative prices provided may vary based on market conditions and specific supplier agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing insulation ceramic With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Insulation Ceramic: What Are Your Options?
When considering insulation solutions for high-temperature applications, it’s essential for B2B buyers to evaluate various materials available in the market. Insulation ceramic is a popular choice due to its excellent thermal resistance and stability. However, several alternatives offer unique benefits that may align better with specific operational needs or budget constraints. Below, we compare insulation ceramic with two viable alternatives: mineral wool and fiberglass insulation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Insulation Ceramic | Mineral Wool | Fiberglass Insulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal resistance (up to 2300°F), low thermal conductivity | Good thermal and acoustic insulation, lower max temp (up to 1200°F) | Moderate thermal resistance, suitable for lower temperatures (up to 1000°F) |
| Cost | $85.00 – $775.00 per unit | Generally lower, $50.00 – $150.00 per unit | Moderate, $30.00 – $200.00 per unit |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and installation techniques | Easy to cut and install; less specialized training needed | Simple installation; widely available |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; durable and long-lasting | May require periodic checks for moisture | Requires regular checks for insulation integrity |
| Best Use Case | High-temperature applications like kilns, furnaces, and reactors | Industrial applications needing soundproofing and moderate heat resistance | Residential and commercial buildings for standard insulation needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mineral Wool?
Mineral wool, made from natural or synthetic fibers, provides good thermal and acoustic insulation. It is particularly effective in environments where sound attenuation is critical, making it ideal for construction projects. The lower cost of mineral wool can be attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, its thermal resistance is lower than that of insulation ceramic, making it less suitable for extreme high-temperature applications.
How Does Fiberglass Insulation Compare?
Fiberglass insulation is another popular alternative. It is lightweight, easy to install, and offers reasonable thermal resistance for temperatures up to 1000°F. It is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. One drawback is that fiberglass can absorb moisture, which may compromise its insulating properties and necessitate regular inspections. Additionally, it doesn’t perform as well in high-temperature industrial settings compared to insulation ceramic.
Conclusion: How Do You Choose the Right Insulation Solution?
Selecting the appropriate insulation material depends on your specific needs, including temperature requirements, budget, and installation capabilities. Insulation ceramic is ideal for high-temperature applications and environments requiring robust thermal stability. However, for projects with lower temperature demands or where cost is a primary concern, mineral wool or fiberglass insulation may be more suitable. Assessing these factors will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with operational goals and financial constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for insulation ceramic
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Insulation Ceramic?
When selecting insulation ceramic materials, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the purity and composition of the ceramic fibers. For example, high-purity grades (such as 8lb and 6lb) are designed for high-temperature applications, offering superior thermal stability. B2B buyers should prioritize high-purity grades when dealing with extreme thermal environments, as they enhance durability and reduce the risk of chemical reactions. -
Temperature Rating
This specification defines the maximum temperature the insulation can withstand without degrading. Insulation ceramics are often rated for temperatures up to 2300°F (1260°C). Understanding the temperature rating is critical for applications like furnaces and kilns, as exceeding this limit can lead to insulation failure, compromising safety and efficiency. -
Density
Measured in pounds per cubic foot (lb/cu.ft), density affects the insulation’s thermal efficiency and handling characteristics. Higher-density materials typically provide better thermal resistance but may be heavier and less flexible. B2B buyers need to balance density with application requirements, especially in industries where weight and flexibility are significant factors. -
Thermal Conductivity
This property measures how well heat is transferred through the material. Low thermal conductivity indicates better insulation performance. In B2B contexts, selecting insulation ceramics with low thermal conductivity can lead to energy savings, reduced heat loss, and improved operational efficiency, which are critical for industries like manufacturing and energy. -
Dimensional Stability
This refers to the material’s ability to maintain its shape and integrity under varying temperature conditions. Insulation ceramics with high dimensional stability resist warping and shrinkage, which is vital for maintaining structural integrity in high-heat applications. Buyers should seek products with proven dimensional stability to minimize maintenance and replacement costs. -
Chemical Resistance
Insulation ceramics should be resistant to various chemicals, especially in industrial applications where exposure to corrosive substances is common. B2B buyers must ensure that the selected insulation can withstand specific chemicals present in their operational environments to prevent degradation and ensure longevity.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Insulation Ceramic Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the insulation ceramic market, OEMs often supply custom insulation solutions tailored to specific equipment or machinery, making it crucial for buyers to establish strong relationships with reputable OEMs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process allows buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. A well-structured RFQ can streamline procurement and improve supplier negotiations. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining responsibilities and risks associated with shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms is critical for international buyers to understand shipping costs, insurance, and liability, which can significantly impact total procurement costs. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. Understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management, as delays can affect production schedules and operational efficiency. -
Thermal Shock Resistance
This property describes a material’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing. For buyers, selecting insulation ceramics with high thermal shock resistance ensures reliability and longevity in fluctuating temperature environments, essential for industries such as glass manufacturing and metal processing.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing insulation ceramics, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the insulation ceramic Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Insulation Ceramic Market?
The global insulation ceramic market is witnessing significant growth, propelled by several key drivers. An increase in high-temperature applications across industries such as metallurgy, petrochemicals, and power generation has heightened the demand for advanced insulation materials. Additionally, the push for energy efficiency and cost reduction is leading companies to invest in high-performance insulation solutions, which can withstand extreme conditions without compromising thermal efficiency.
Emerging technologies such as advanced manufacturing techniques and digital supply chain solutions are reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging online platforms to access a wider range of suppliers and products, allowing for more competitive pricing and better service. Furthermore, innovations in material science, such as the development of lightweight and flexible ceramic fiber blankets, are enhancing product offerings and expanding application possibilities.
Market dynamics indicate a growing trend toward regional sourcing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are prioritizing suppliers who can provide localized support and rapid delivery to reduce lead times and transportation costs. Countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia are becoming pivotal hubs for sourcing high-quality insulation ceramics, driven by robust industrial sectors and a focus on sustainability.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Insulation Ceramic Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the insulation ceramic sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products is becoming increasingly scrutinized by buyers. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste. This shift is driven not only by regulatory requirements but also by consumer demand for greener products.
Ethical sourcing is integral to sustainability efforts. B2B buyers are seeking suppliers who uphold responsible labor practices and ensure safe working conditions throughout their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection, as they signify adherence to international sustainability standards.
Moreover, the trend towards ‘green’ materials is gaining momentum. Buyers are interested in insulation ceramics that utilize recycled content or are free from harmful chemicals. These materials not only meet performance standards but also align with corporate sustainability goals, enhancing brand reputation and consumer trust.
How Has the Insulation Ceramic Industry Evolved Over Time?
The insulation ceramic industry has undergone significant transformations since its inception. Initially, the focus was primarily on basic thermal insulation properties. However, as industrial applications expanded, the demand for advanced, high-performance solutions emerged. The introduction of ceramic fiber technologies in the 1960s marked a turning point, offering superior thermal stability and lightweight characteristics.
In recent years, the industry has evolved further with the advent of high-purity materials and innovative manufacturing processes that enhance product durability and efficiency. This evolution reflects a broader trend toward customization and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to cater to specific industry needs and applications.
As the market continues to grow, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing will likely shape the future of the insulation ceramic sector, driving innovation and fostering partnerships between buyers and suppliers committed to shared values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of insulation ceramic
-
How do I choose the right insulation ceramic product for my application?
Selecting the appropriate insulation ceramic product depends on several factors including temperature rating, density, and application specifics. For high-temperature applications, look for products rated above 2300°F, such as high-purity ceramic fiber blankets. Evaluate the physical properties, such as flexibility and dimensional stability, to ensure they meet the demands of your project, whether it’s furnace linings or thermal reactor insulation. Consulting with suppliers about your specific needs can help narrow down options. -
What is the best insulation ceramic for high-temperature industrial processes?
High-purity ceramic fiber products, particularly those with a temperature rating of 2300°F, are ideal for high-temperature industrial processes. Products like Fiberfrax Durablanket or similar needled insulating blankets provide excellent thermal efficiency and low heat storage, making them suitable for applications such as kiln and furnace insulation. Always consider the specific operational environment and consult product datasheets to ensure compatibility with your process requirements. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for insulation ceramics?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, product certifications, and customer reviews. Assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Inquire about their ability to provide technical support and customization options. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, especially if sourcing from different regions, to ensure timely delivery and responsiveness to your needs. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for insulation ceramic products?
Minimum order quantities for insulation ceramic products can vary widely depending on the supplier and the product type. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 square feet for blankets and rolls. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with suppliers, as many are willing to accommodate smaller orders or offer flexible arrangements for regular customers, especially for custom specifications. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing insulation ceramics internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but typically include options such as upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, or net 30/60 days after delivery. When negotiating, consider your cash flow and the reliability of the supplier. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services for large transactions, minimizing risk while ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. -
How can I ensure the quality of insulation ceramics before purchase?
To ensure product quality, request samples and technical data sheets from potential suppliers. Conduct audits or site visits if feasible, and ask for third-party testing certifications to verify compliance with industry standards. Additionally, establish a clear quality assurance process, including inspection upon delivery, to confirm that the products meet your specifications and performance criteria. -
What shipping options are available for insulation ceramic products?
Shipping options for insulation ceramics depend on the order size and destination. For larger shipments, Less Than Truckload (LTL) freight is often recommended, while smaller orders may be suitable for standard courier services like UPS. Be sure to discuss shipping arrangements with your supplier, including costs, delivery timelines, and customs handling, especially for international orders to ensure smooth logistics. -
What are the advantages of using ceramic fiber blankets in industrial applications?
Ceramic fiber blankets offer several advantages, including excellent thermal insulation properties, lightweight design, and flexibility, making them easy to handle and install. They are dimensionally stable at high temperatures and exhibit low thermal conductivity, which helps reduce energy costs. Additionally, these blankets are resistant to thermal shock and chemical degradation, making them ideal for various applications, including furnace linings and insulation for steam and gas turbines.
Top 7 Insulation Ceramic Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ceramaterials – Ceramic Fiber Blanket High Purity Grade 8lb 2300°F
Domain: ceramaterials.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Ceramic Fiber Blanket High Purity Grade 8lb 2300°F”, “Price Range”: “$90.00 – $240.00”, “Temperature Rating”: “2300°F”, “Grade”: “High Purity”, “Density”: “8lbs/cu.ft”, “Shipping Methods”: [“UPS”, “LTL FREIGHT”], “Sizes Available”: [“0.25\” x 24\” x 50′”, “0.5\” x 24\” x 50′”, “0.5\” x 48\” x 25′”, “1\” x 24\” x 25′”, “1\” x 48\” x 25′”, “1.5\” x 24\” x 17′”, “1.5\” x 48\” x 17′”…
2. Unitherm – Ceramic Fiber Blanket
Domain: shop.unitherm.com
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Ceramic Fiber Blanket”, “Part Number”: “CF6-1-24X25”, “Price”: “$166.80”, “Density”: “6#”, “Thickness”: “1 inch”, “Width”: “24 inches”, “Length”: “25 feet”, “Total Area”: “50 square feet”, “Continuous Use Limit”: “1922°F (1149°C)”, “Max Use Limit”: “2300°F (1260°C)”, “Material”: “Pure alumina-silica”, “Manufacturing Process”: “Modern spinning process”, “Features”: “Exceptional le…
3. Thermaxx – Fiberfrax® Ceramic Fiber Insulating Blankets
Domain: thermaxxjackets.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Thermaxx uses Fiberfrax® Ceramic Fiber Insulating Blankets and Mats, which are lightweight, thermally efficient, and resistant to thermal shock. The product family includes Durablanket® ceramic fiber products, which are high strength, needled insulating blankets made from spun Fiberfrax ceramic fibers. They are available in various temperature grades, densities, and sizes. Key products include:
-…
4. Zircar Ceramics – Alumina Type AL-25/1700
Domain: zircarceramics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Alumina Type AL-25/1700″,”description”:”Cost-effective medium duty 1700°C rated hot face insulation.”,”temperature_rating”:”1700°C”},{“name”:”Alumina Type AL-28/1800″,”description”:”Cost effective, utility-grade hot face insulation for use in kilns, furnaces and other thermal process systems operating to temperatures of 1800°C (3272°F).”,”temperature_rating”:”1800°C”},{“name”…
5. Precision Ceramics – Thermal Conductivity Materials
Domain: precision-ceramics.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Precision Ceramics offers a variety of ceramic materials with distinct thermal conductivity properties. Key materials include: 1. **Alumina**: Thermal conductivity ranging from 25 to 40 W/mK. 2. **Zirconia**: Typically around 3 W/mK. 3. **Alumina Toughened Zirconia**: Approximately 6 W/mK. 4. **Macor**: Low thermal conductivity of 1.5 W/mK. 5. **Silicate Ceramics** (e.g., Cordierite, Steatite, Por…
6. LizardSkin – Ceramic Insulation
Domain: shop.lizardskin.com
Introduction: Ceramic Insulation LizardSkin Ceramic Insulation (CI) is a premium spray-on thermal insulation product designed for cars, trucks, street rods, customs, and racecars. Key features include:
– Reduces heat entering the interior by 30°F or more
– Water-based composition with high-grade acrylic binders and ceramic insulation particles
– Coverage: 1-gallon can covers 23-25 square feet at 0.040″ (40 m…
7. Taofiber – Ceramic Fiber Insulation
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Ceramic fiber insulation rated for temperatures of 2300°F or above. Recommended thickness is 50mm (2 inches) using 2 layers of 25mm each. Mention of a product called “rigidizer” to reduce friability. Suggested supplier: Taofiber, which sells insulation by the roll.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for insulation ceramic
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Insulation Ceramic Market?
In the dynamic realm of insulation ceramics, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. High-purity ceramic fiber products, such as blankets and insulation mats, offer exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making them indispensable in industries ranging from manufacturing to energy. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide detailed technical data, competitive pricing, and robust shipping options to ensure a seamless procurement process.
How Can B2B Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing for Competitive Advantage?
Investing in strategic sourcing not only reduces costs but also enhances product quality and reliability. By establishing long-term relationships with reputable manufacturers, businesses can gain access to innovative insulation solutions tailored to their specific needs. This approach is particularly beneficial for companies operating in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where demand for high-performance insulation is growing.

Illustrative image related to insulation ceramic
What Does the Future Hold for Insulation Ceramic Buyers?
As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and energy efficiency, the demand for advanced insulation materials is set to rise. B2B buyers should stay informed about technological advancements and market trends to make proactive sourcing decisions. By embracing a forward-thinking sourcing strategy, companies can position themselves advantageously in a competitive landscape. Engage with suppliers today to explore how insulation ceramics can enhance your operational efficiency and contribute to your business’s long-term success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.