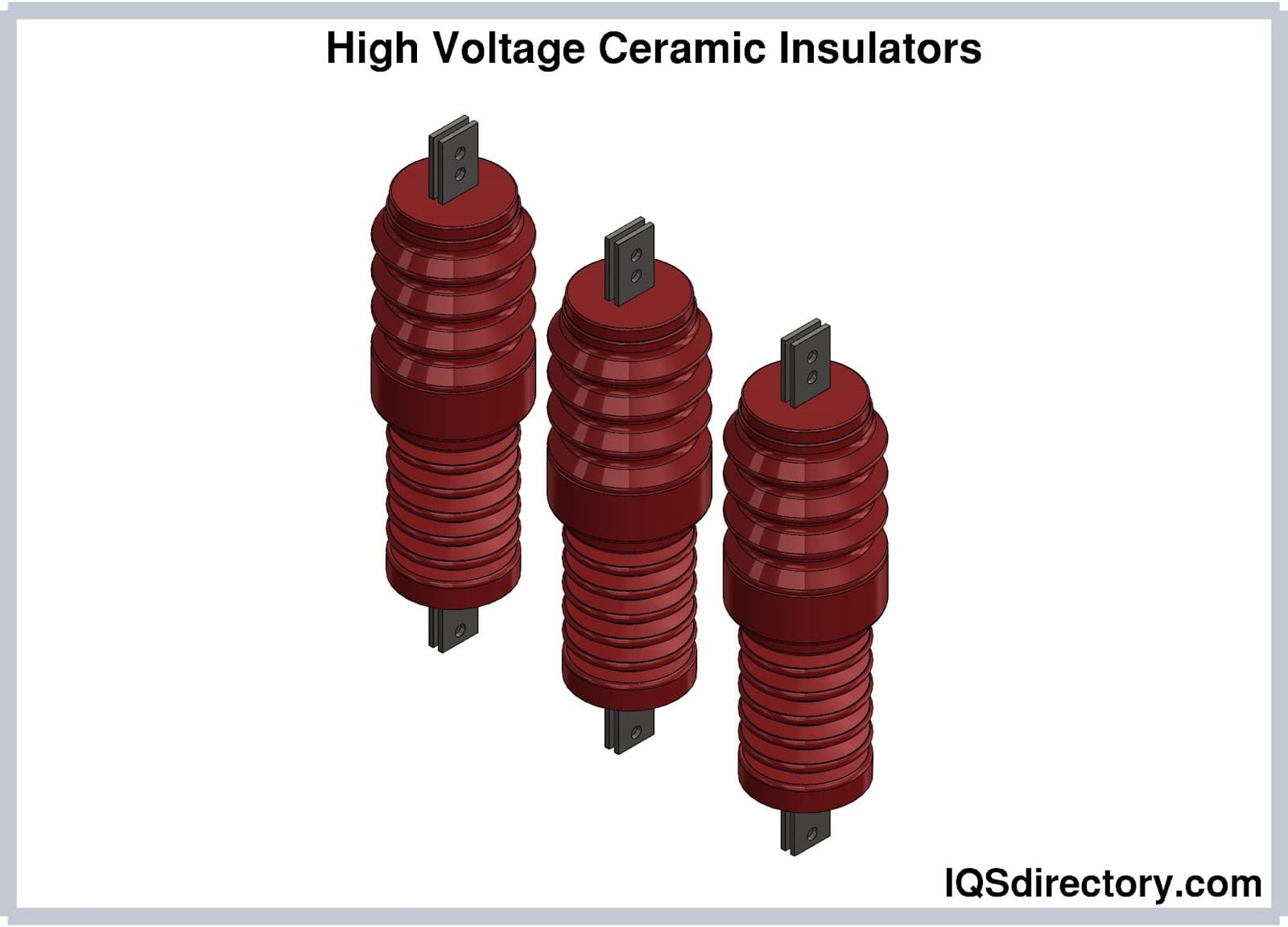
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Insulating Ceramics Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for insulating ceramics
Navigating the global market for insulating ceramics presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers seeking reliable solutions for thermal and electrical insulation needs. As industries worldwide increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and high-performance materials, sourcing the right insulating ceramics becomes critical. This guide delves into the diverse types of insulating ceramics—such as alumina and zirconia—highlighting their applications across various sectors including manufacturing, aerospace, and energy.
Buyers will benefit from a comprehensive overview that not only examines the specifications and performance characteristics of these materials but also discusses key factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and market trends. By understanding the nuances of insulating ceramics, international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—especially in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia—will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
This guide aims to equip buyers with actionable insights, enabling them to navigate the complexities of sourcing insulating ceramics effectively. From understanding thermal conductivity to evaluating supplier capabilities, readers will gain the knowledge necessary to select materials that not only meet their technical requirements but also provide long-term value and performance reliability.
Understanding insulating ceramics Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | High hardness, excellent wear resistance, and thermal stability | Electrical insulators, furnace components | Pros: Durable, versatile; Cons: Brittle, can be expensive. |
| Zirconia Ceramics | Superior strength, toughness, and low thermal conductivity | Thermal barriers, cutting tools | Pros: High resistance to thermal shock; Cons: More costly than alumina. |
| Refractory Ceramics | High thermal shock resistance, lower strength compared to dense types | Kiln linings, furnace components | Pros: Excellent for extreme temperatures; Cons: Weaker under mechanical stress. |
| Fully Dense Ceramics | High strength and density, lower thermal shock resistance | Aerospace components, high-performance engines | Pros: Strong and durable; Cons: Prone to fracture under rapid temperature changes. |
| Ceramic Fibers | Lightweight, low thermal mass, and customizable shapes | Insulation in industrial furnaces | Pros: Reduces weight and costs; Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid damage. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Alumina Ceramics for B2B Buyers?
Alumina ceramics are widely recognized for their high hardness and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring wear resistance, such as electrical insulators and components within high-temperature furnaces. Their ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions is a key consideration for B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing and energy. However, buyers should be aware that while alumina ceramics are versatile, they tend to be brittle, which can pose challenges in environments subject to mechanical stress.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Why Choose Zirconia Ceramics for High-Performance Applications?
Zirconia ceramics, known for their exceptional strength and toughness, are particularly suitable for applications that demand low thermal conductivity and high resistance to thermal shock. Industries such as aerospace and automotive benefit from zirconia’s properties, as it can withstand extreme conditions without degrading. However, the higher cost associated with zirconia compared to alumina ceramics may require buyers to evaluate their budget against performance needs.
How Do Refractory Ceramics Perform Under High-Temperature Conditions?
Refractory ceramics are specifically designed to endure extreme temperatures and thermal shock, making them essential for kiln linings and furnace components. They excel in applications where thermal stability is crucial, but their lower mechanical strength may limit their use in high-stress environments. B2B buyers should consider the balance between thermal performance and mechanical requirements when selecting refractory ceramics for their operations.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Fully Dense Ceramics?
Fully dense ceramics offer high strength and durability, making them suitable for demanding applications such as aerospace components and high-performance engines. Their ability to withstand mechanical stress is a significant advantage; however, they are less resistant to thermal shock, which can lead to fractures if subjected to rapid temperature changes. Buyers should assess their specific application requirements to determine if the benefits of fully dense ceramics outweigh the potential for thermal-related issues.
How Do Ceramic Fibers Enhance Industrial Insulation Solutions?
Ceramic fibers are lightweight and offer low thermal mass, making them an ideal choice for insulation in industrial furnaces. Their flexibility allows for the creation of customized shapes, enhancing design versatility. While ceramic fibers can significantly reduce weight and manufacturing costs, they require careful handling to prevent damage. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of cost savings and efficiency against the need for proper installation and maintenance practices.
Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Key Industrial Applications of insulating ceramics
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Insulating Ceramics | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Thermal insulation for engine components | Enhanced thermal protection and weight reduction in critical parts | Ensure high-temperature resistance and compliance with aerospace standards |
| Manufacturing | Insulation in kilns and furnaces | Improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Look for custom shapes and high durability under thermal stress |
| Electronics | Insulating substrates for circuit boards | Enhanced electrical performance and reliability | Consider dielectric strength and thermal conductivity specifications |
| Oil & Gas | Insulation for pipelines and drilling equipment | Reduction in heat loss and improved operational efficiency | Focus on corrosion resistance and high-temperature capabilities |
| Renewable Energy | Insulation in solar thermal collectors | Increased energy capture and efficiency | Evaluate environmental resistance and thermal stability over time |
How Are Insulating Ceramics Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, insulating ceramics serve as crucial thermal barriers for engine components. They help manage extreme temperatures, ensuring that vital parts remain operational under high-stress conditions. This application addresses the challenge of weight reduction while maintaining thermal protection, which is essential for fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing materials that meet stringent aerospace standards, ensuring high-temperature resistance and reliability.
What Role Do Insulating Ceramics Play in Manufacturing?
Insulating ceramics are extensively used in kilns and furnaces across various manufacturing processes. Their role is to improve energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss, thus reducing operational costs. These materials can withstand high thermal stress, making them ideal for environments where temperature fluctuations occur frequently. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who can provide custom shapes and formulations tailored to their specific operational requirements, ensuring durability and performance.
How Are Insulating Ceramics Essential in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, insulating ceramics are utilized as substrates for circuit boards, providing essential electrical insulation. They enhance the performance and reliability of electronic components by preventing electrical leakage and thermal interference. Buyers in this market must consider specifications such as dielectric strength and thermal conductivity to ensure optimal performance in their applications, particularly in high-frequency and high-temperature environments.
Why Are Insulating Ceramics Important for the Oil & Gas Industry?
Insulating ceramics are vital for the oil and gas sector, particularly in insulating pipelines and drilling equipment. They help reduce heat loss, improving the overall efficiency of operations and maintaining the integrity of materials under extreme conditions. For international buyers, sourcing ceramics that offer high corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures is crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh environments.
How Do Insulating Ceramics Benefit Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy, particularly in solar thermal collectors, insulating ceramics contribute to increased energy capture and efficiency. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures, thus enhancing the overall performance of solar energy systems. When sourcing these materials, buyers should evaluate their environmental resistance and thermal stability over time, ensuring that they can withstand the rigors of outdoor applications while providing consistent performance.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘insulating ceramics’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty with Thermal Shock Resistance in High-Temperature Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as ceramics manufacturing or metal processing often face challenges when selecting insulating ceramics that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations. For instance, in furnace applications, materials may experience thermal shock due to rapid temperature changes, leading to cracks or complete failure of the insulator. This not only impacts operational efficiency but can also result in costly downtime and repairs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing refractory ceramics that exhibit high thermal shock resistance. Products like Ceramco’s refractory alumina formulations (e.g., A9468 and A9968) are specifically designed for high-temperature applications while maintaining structural integrity under thermal stress. When specifying materials, buyers should conduct thorough thermal shock testing data comparisons among suppliers to ensure the chosen ceramics meet operational demands. Additionally, incorporating a gradual heating and cooling protocol during the operation can help mitigate thermal stress and prolong the life of insulating ceramics.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Electrical Insulation Properties
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the electrical equipment manufacturing sector encounter difficulties when their insulating ceramics fail to provide the necessary electrical insulation properties, especially in environments with high voltages or corrosive conditions. This can lead to short circuits, equipment failures, and even safety hazards, ultimately impacting productivity and increasing liability concerns.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, it’s crucial for buyers to select insulating ceramics with proven electrical insulation capabilities. Materials like zirconia ceramics are known for their excellent electrical resistance and stability in harsh environments. Buyers should also collaborate closely with suppliers to understand the specific electrical requirements of their applications and request detailed technical data sheets that highlight dielectric strength, resistivity, and thermal conductivity. In addition, conducting on-site evaluations and pilot tests with prospective materials can provide insights into their performance before making large-scale purchases.
Scenario 3: Cost Management and Sourcing Complex Geometries
The Problem: Sourcing insulating ceramics that meet complex geometrical requirements while staying within budget can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers. Industries such as aerospace and automotive often need custom components that not only fit specific designs but also perform under demanding conditions. The challenge lies in balancing the need for precision with cost-effectiveness, as custom manufacturing can lead to inflated prices and extended lead times.
Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
The Solution: Buyers should leverage advanced manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) or precision machining to create custom insulating ceramic components. Companies like Ceramco offer a variety of forming processes, including low-pressure injection molding and CNC machining, which can be tailored to the specific geometries required. To manage costs effectively, buyers should engage in early discussions with manufacturers to outline design specifications and volume needs, enabling the supplier to provide cost estimates and lead times upfront. Additionally, exploring bulk purchasing agreements for high-volume orders can help lower per-unit costs and streamline supply chain logistics.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for insulating ceramics
What Are the Key Properties of Alumina Ceramics for Insulating Applications?
Alumina ceramics, primarily composed of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), are renowned for their high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and thermal stability. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 1,600°C and are resistant to corrosion from various chemicals, making them suitable for harsh industrial environments. The ability to be formed through various methods, including injection molding and slip casting, enhances their versatility in manufacturing.
Pros & Cons: The durability of alumina ceramics is a significant advantage, especially in applications requiring long-lasting performance. However, their high brittleness can lead to challenges in machining and handling. Additionally, while the cost of alumina ceramics is moderate, the complexity of manufacturing processes can increase overall production expenses.
Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Impact on Application: Alumina ceramics are particularly effective in electrical insulation applications due to their high dielectric strength. They are also compatible with a range of media, including oils and solvents, which makes them suitable for diverse industrial uses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and JIS, particularly for electrical applications. In Europe, especially in Germany, adherence to DIN standards is critical for quality assurance.
How Do Zirconia Ceramics Compare in Terms of Insulation and Strength?
Zirconia ceramics (ZrO₂) are characterized by their exceptional toughness, high strength, and resistance to thermal shock. They can operate effectively at temperatures around 1,200°C and exhibit low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for insulating applications where heat retention is crucial.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of zirconia ceramics is their ability to withstand thermal shock without fracturing, which is vital in high-temperature environments. However, they are generally more expensive than alumina ceramics, and their manufacturing processes can be more complex, potentially leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is particularly beneficial in applications requiring thermal insulation in furnaces and kilns, where maintaining temperature is essential. Its compatibility with various aggressive media further enhances its appeal in demanding industrial settings.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific thermal and mechanical properties required by their applications and ensure that suppliers can meet these specifications. Compliance with international standards is essential, particularly in regions like Europe where stringent regulations are in place.
What Are the Benefits of Refractory Ceramics in High-Temperature Insulation?
Refractory ceramics, often composed of alumina and silica, are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, typically above 1,600°C. They exhibit high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for insulating applications in furnaces and kilns.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of refractory ceramics is their ability to endure high temperatures without degrading, which is crucial for industrial processes. However, they may have lower mechanical strength compared to fully dense ceramics, which can limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Refractory ceramics are particularly effective in applications involving direct contact with molten metals or glass, where high thermal resistance is required. Their performance in such environments makes them indispensable in the metalworking and glass industries.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that refractory materials meet local and international standards for thermal performance. In regions like South America and the Middle East, understanding the specific thermal requirements of local industries is critical for successful procurement.
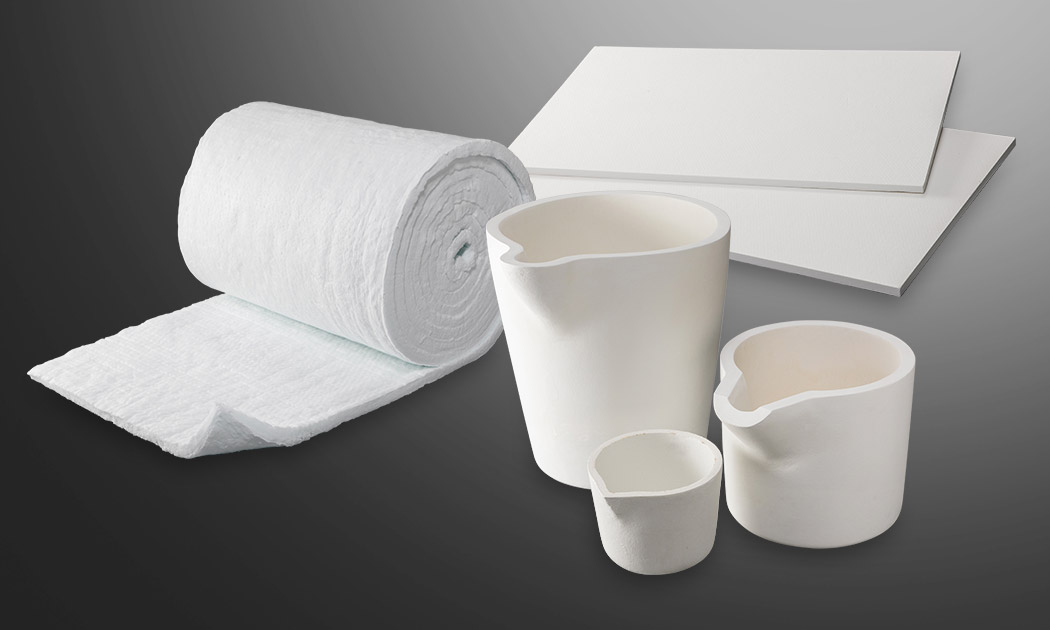
How Do Ceramic Fibers Enhance Insulation Performance?
Ceramic fibers, made from alumina or silica, provide lightweight and flexible insulation solutions. They are engineered to withstand temperatures up to 1,200°C and are often used in applications requiring low thermal mass.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of ceramic fibers allows for easier handling and installation, which can reduce overall project costs. However, their lower mechanical strength compared to solid ceramics may limit their use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application: Ceramic fibers are ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. Their flexibility allows for custom configurations, enhancing their suitability for various designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific thermal and mechanical requirements of their applications and ensure that suppliers can provide fibers that meet these needs. Compliance with international safety and performance standards is also crucial.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
| Material | Typical Use Case for insulating ceramics | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | Electrical insulation, wear-resistant components | High hardness and durability | Brittle, complex manufacturing processes | Medium |
| Zirconia Ceramics | Thermal insulation in kilns and furnaces | Exceptional toughness and thermal shock resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Refractory Ceramics | Insulation in high-temperature applications | High thermal stability | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
| Ceramic Fibers | Lightweight insulation in aerospace and automotive | Low thermal mass and flexibility | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for insulating ceramics
The manufacturing processes for insulating ceramics are intricate and require precision at every stage to ensure product performance and reliability. For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is crucial for selecting the right supplier and ensuring the longevity of their applications.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Insulating Ceramics?
How Is Material Prepared for Insulating Ceramics?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality raw materials such as alumina, zirconia, or silica. The choice of material significantly affects the thermal and mechanical properties of the final product. For example, alumina ceramics are known for their hardness and wear resistance, while zirconia ceramics offer superior toughness and thermal stability.
Once the raw materials are selected, they undergo processing steps such as grinding, mixing, and milling to achieve the desired particle size and homogeneity. This is a critical phase, as the uniformity of the material influences the consistency of the final product’s properties. Advanced techniques like chemical vapor deposition may also be employed to create specialized materials with specific characteristics.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of Insulating Ceramics?
The next stage is forming, which shapes the prepared materials into usable forms. Several techniques can be employed, including:
-
Injection Molding: This method is suitable for high-volume production and allows for complex geometries. It involves injecting a mixture of ceramic powder and binder into a mold.
-
Isostatic Pressing: This technique applies uniform pressure to the ceramic powder, ensuring density and strength across the entire component.
-
Slip Casting: A slurry of ceramic materials is poured into a mold, where it hardens into the desired shape. This method is often used for larger components.
-
Extrusion: This method forces the material through a die to create long shapes, which are then cut to the desired length.
Each of these methods has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, including the size, complexity, and performance characteristics of the final product.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Insulating Ceramics?
In some cases, multiple components may need to be assembled to create a final product. This can involve techniques such as bonding, welding, or the use of mechanical fasteners. For insulating ceramics used in high-temperature environments, it is essential that the assembly methods maintain the integrity and thermal performance of the materials.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Quality of Insulating Ceramics?
Finishing processes are crucial for achieving the desired surface characteristics and tolerances. Common techniques include:
-
Sintering: This process involves heating the formed ceramic to a temperature below its melting point, allowing particles to fuse and densify. Sintering enhances the mechanical strength and thermal stability of the ceramics.
-
Machining: After sintering, components may require precision machining to achieve tight tolerances and specific surface finishes. Techniques such as grinding, lapping, or diamond machining can be used.
-
Coating: In some applications, coatings may be applied to enhance thermal resistance or reduce wear. This could include ceramic coatings or other materials that provide additional protective layers.
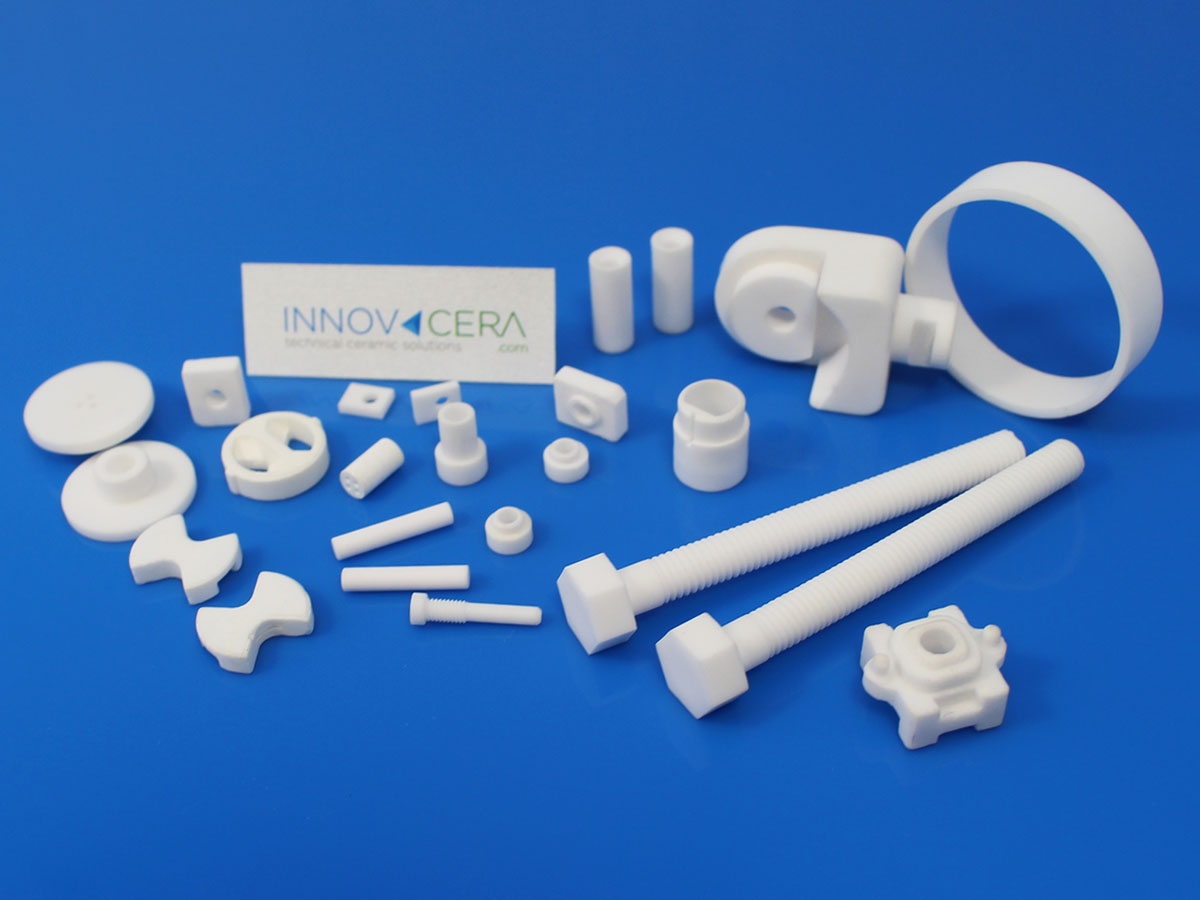
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in the Production of Insulating Ceramics?
Which International Standards Govern Quality Assurance for Insulating Ceramics?
Quality control is paramount in the production of insulating ceramics to ensure they meet international standards and customer specifications. Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications may be required.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves the inspection of raw materials to ensure they meet specified requirements before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various tests and measurements are conducted to ensure that the production remains within acceptable limits.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are completed, they undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance characteristics, including thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal shock resistance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can ensure the quality of insulating ceramics by conducting thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. This may include:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices and manufacturing capabilities.
-
Review of Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control processes, test results, and certifications can help verify compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance regarding product quality and adherence to specifications.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional standards and compliance requirements is critical. Suppliers may need to navigate different regulations and certifications depending on the destination market.
Buyers should be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication regarding quality standards. Establishing a clear line of communication and setting explicit expectations can mitigate these challenges.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for insulating ceramics are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘insulating ceramics’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure insulating ceramics. Insulating ceramics are essential for various industrial applications, including thermal insulation in furnaces and kilns. This step-by-step checklist will help you navigate the sourcing process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical requirements is crucial. Consider the specific properties you need, such as thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock. For instance, refractory ceramics may be suitable for high-temperature environments, while fully dense ceramics could be better for applications requiring strength.
Step 2: Identify Relevant Suppliers
Research and compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in insulating ceramics. Focus on manufacturers with experience in your industry and geographical region. For example, if you are sourcing from Europe, look for companies that have a strong presence in the DACH region or have successfully served similar markets.
Step 3: Evaluate Material Options
Different types of insulating ceramics, such as alumina and zirconia, offer varied benefits. Assess the performance characteristics of each material, including thermal insulation properties and mechanical stability at high temperatures. This evaluation will help you choose the right material that aligns with your application needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications for quality and safety standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific accreditations indicate a commitment to maintaining high-quality manufacturing processes. This step is vital to mitigate risks associated with product failures or non-compliance.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the insulating ceramics to assess their performance in your specific application. Conduct thorough testing to evaluate their thermal conductivity, durability, and compatibility with your processes. This hands-on approach will provide valuable insights into the material’s suitability.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Terms of Supply
Once you have shortlisted suppliers and tested samples, compare pricing and terms of supply. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Be wary of prices that seem too low, as they may indicate compromised quality or service.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Finally, establish clear lines of communication with your chosen supplier. Ensure that they provide dedicated support for any inquiries or issues that may arise during the procurement process. Good communication can significantly enhance the collaboration and ensure that your project stays on track.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing insulating ceramics, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for insulating ceramics Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Insulating Ceramics?
When sourcing insulating ceramics, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts pricing. Alumina and zirconia ceramics, known for their thermal stability, generally have higher costs due to their manufacturing processes and raw material availability. Refractory ceramics tend to be less expensive compared to fully dense ceramics, which exhibit higher strength and thermal shock resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can affect quality. Skilled labor is essential for processes like ceramic machining and custom formulation, which can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Advanced manufacturing processes, such as chemical vapor deposition or precision machining, can lead to higher overhead costs, which are typically passed on to the buyer.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom parts. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating total expenditure, as they may be amortized over larger production runs, lowering per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high standards of quality through rigorous testing and certification processes can add to costs. International buyers often require specific certifications, which may necessitate additional investments in quality assurance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the distance, mode of transport, and any tariffs or customs fees. For international transactions, understanding Incoterms is essential to clarify who bears the logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product. High-quality materials or specialized formulations often come with higher margins.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Insulating Ceramics Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of insulating ceramics:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to cost savings due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, which can be beneficial for businesses looking to stock inventory.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs. Tailoring materials to meet specific thermal or mechanical properties requires additional research and development, which should be factored into pricing.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used play a critical role. High-purity materials or specialized formulations will typically command higher prices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific international standards or certifications may be priced higher due to the additional costs incurred in achieving and maintaining these certifications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge premium prices.
-
Incoterms: These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risks. Understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation is key to achieving cost-efficiency:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Whenever possible, commit to larger orders to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to lower prices for guaranteed bulk purchases.
-
Explore Long-Term Contracts: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can yield more favorable pricing structures and ensure consistent quality.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, evaluate the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime. This broader view can help justify higher upfront costs for superior products.
-
Be Informed About Market Trends: Understanding market trends and fluctuations can empower buyers during negotiations. Staying informed about raw material costs and supplier capabilities can enhance leverage.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Engaging with several suppliers and requesting quotes can create competitive pressure, often resulting in better pricing and terms.
Conclusion
While sourcing insulating ceramics involves various cost components and influencing factors, a strategic approach can enhance cost-efficiency and value. International buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, focusing on total cost, quality, and supplier reliability to make informed purchasing decisions. Prices may vary significantly based on specifications and market conditions, so it is essential to approach negotiations with a clear understanding of the underlying cost structure. Always remember that indicative prices may fluctuate based on market dynamics and should be treated as a guideline rather than a fixed rate.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing insulating ceramics With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Insulation Solutions
In the realm of industrial insulation, selecting the right material can significantly impact performance, efficiency, and cost. While insulating ceramics have established themselves as a robust option due to their superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, several alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or budget constraints. This analysis explores these alternatives, providing actionable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their insulation solutions.
Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Comparison of Insulating Ceramics with Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Insulating Ceramics | Aerogel | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength; withstands high temperatures (up to 1200°C). | Outstanding thermal insulation with very low thermal conductivity; can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 650°C). | Good thermal insulation but less effective at high temperatures; can degrade at elevated temperatures (around 300°C). |
| Cost | Generally high initial cost due to manufacturing processes and material properties. | High cost per unit; production is complex and energy-intensive. | Cost-effective; lower upfront investment compared to ceramics and aerogels. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise manufacturing techniques and may need custom solutions for specific applications. | Lightweight and easy to install, but handling requires care due to fragility. | Simple installation with standard procedures; can be cut and shaped easily. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable and long-lasting under proper conditions. | Low maintenance; however, can be damaged easily if not handled properly. | Moderate maintenance; can accumulate dust and moisture, affecting insulation properties over time. |
| Best Use Case | High-temperature industrial applications, such as furnaces and kilns. | Applications requiring lightweight, high-performance insulation, such as aerospace and cryogenics. | General construction and insulation of buildings, HVAC systems, and low-temperature applications. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Aerogel
Aerogel is known for its exceptional insulating properties, boasting the lowest thermal conductivity of any solid material. This lightweight material is ideal for applications where space and weight are critical, such as in aerospace or advanced thermal insulation in buildings. However, aerogel’s high production costs and fragility can limit its use in demanding industrial environments. While its performance is unmatched, the investment may not be justifiable for all applications.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass insulation is a well-established solution, particularly in the construction industry. It offers a favorable cost-to-performance ratio, making it an attractive option for many projects. Fiberglass is relatively easy to install and can be adapted to various shapes and sizes. However, its performance diminishes at higher temperatures, making it unsuitable for high-heat applications. Additionally, fiberglass can absorb moisture, which may compromise its insulating effectiveness over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation Solution
When selecting an insulation material, B2B buyers must consider their specific application requirements, including temperature tolerances, cost constraints, and installation capabilities. Insulating ceramics excel in high-temperature scenarios, providing durability and performance, while alternatives like aerogel and fiberglass present unique advantages for different contexts. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing these factors to meet operational needs and budgetary limitations effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for insulating ceramics
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Insulating Ceramics?
Understanding the essential technical properties of insulating ceramics is crucial for B2B buyers looking to select the most suitable materials for their applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the composition and quality of the ceramic. Common grades include alumina (Al2O3) and zirconia (ZrO2). Higher grades typically offer enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance. For instance, 99.8% alumina ceramics are favored for their superior thermal insulation properties, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Selecting the right grade can significantly impact the longevity and performance of components in demanding environments.
2. Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material conducts heat. Lower thermal conductivity is desirable for insulating ceramics, as it minimizes heat loss in applications such as furnaces and kilns. For example, zirconia ceramics have lower thermal conductivity than alumina ceramics, making them preferable in situations where heat retention is critical. Understanding this property helps businesses optimize energy efficiency and operational costs.
3. Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength refers to a material’s ability to withstand applied forces without failure. It is essential for ensuring the reliability of components under load and thermal stress. Fully dense ceramics generally exhibit higher mechanical strength compared to refractory ceramics, which may be more susceptible to fracture under thermal shock. B2B buyers must assess the mechanical requirements of their applications to avoid premature failures.
4. Density
Density affects both the weight and strength of ceramic materials. Fully dense ceramics, while heavier, provide better structural integrity and thermal resistance. Conversely, refractory ceramics are lighter but may compromise strength under extreme conditions. Understanding the trade-offs between density and performance can guide manufacturers in selecting materials that align with their production and operational needs.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a material’s dimensions. In the context of insulating ceramics, precise tolerances are critical for ensuring that components fit correctly in their applications. Tighter tolerances often translate to higher manufacturing costs, so it is important for buyers to balance performance requirements with budget constraints.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Insulating Ceramics Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of insulating ceramics, OEMs often produce custom components tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their unique specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it can impact inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms, facilitating informed decision-making. Crafting a detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and service agreements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers negotiate favorable shipping conditions and avoid misunderstandings.
5. Thermal Shock Resistance
This term refers to a material’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing. Insulating ceramics with high thermal shock resistance are vital for applications involving fluctuating temperatures, such as kilns and furnaces. Buyers should prioritize this property when selecting materials for environments prone to thermal cycling.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their applications and enhance operational efficiency in the field of insulating ceramics.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the insulating ceramics Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Insulating Ceramics?
The insulating ceramics market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. Key drivers include the push for energy efficiency and thermal management solutions, as companies seek to reduce operational costs and enhance performance. Emerging technologies such as advanced manufacturing techniques and the integration of IoT in thermal applications are reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay attuned to these trends, as they dictate shifts in product offerings and supplier capabilities.
In particular, the rise of refractory ceramics—capable of withstanding extreme temperatures—has gained traction in industrial applications. Buyers should be aware of the differences between fully dense and refractory ceramics, as each serves distinct roles in thermal insulation and shock resistance. Furthermore, the push for lightweight materials has led to innovations in ceramic fiber technology, offering substantial benefits in terms of cost efficiency and performance.
The global insulating ceramics market is also witnessing regional dynamics, with Europe leading in technological advancements while Africa and South America present opportunities for growth due to expanding industrial bases. Understanding these market shifts is crucial for international buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies and leverage competitive advantages.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers of Insulating Ceramics?
Sustainability has become a focal point for businesses globally, prompting B2B buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing in their procurement strategies. The environmental impact of ceramic production—particularly in terms of raw material extraction and energy consumption—necessitates a shift toward more sustainable practices. Buyers should seek suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, such as recycled content and low-energy manufacturing methods, to minimize their carbon footprint.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing suppliers for compliance with environmental regulations and labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the introduction of ‘green’ materials, including bio-based ceramics and those with lower thermal conductivity, can enhance energy efficiency in applications, aligning with the broader goals of corporate responsibility and environmental stewardship. As the demand for sustainable products grows, international buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that align with these values, ensuring their sourcing strategies reflect a commitment to sustainability.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Insulating Ceramics Industry?
The insulating ceramics industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional materials to advanced engineered solutions. Initially, ceramic insulators were primarily used in electrical applications due to their excellent dielectric properties. Over time, the focus shifted towards high-performance ceramics that could withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments, leading to the development of refractory ceramics and insulating fibers.
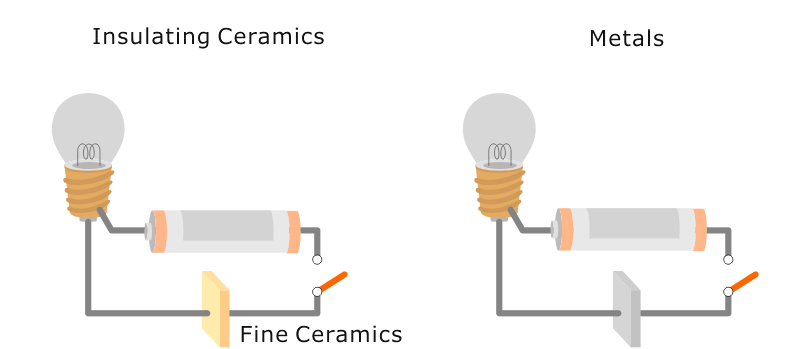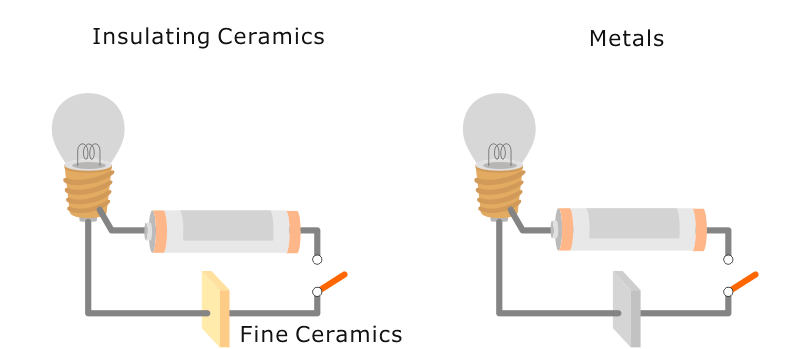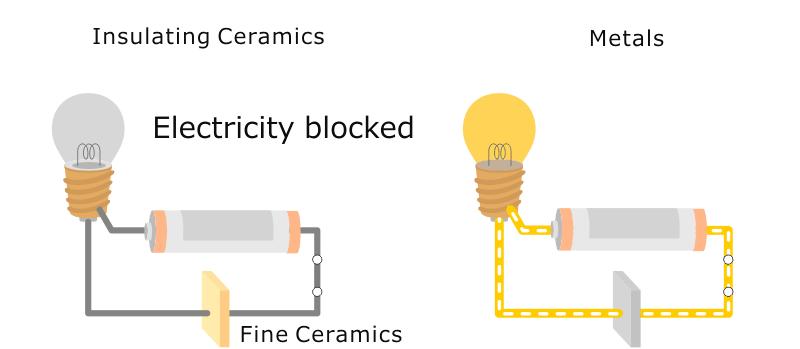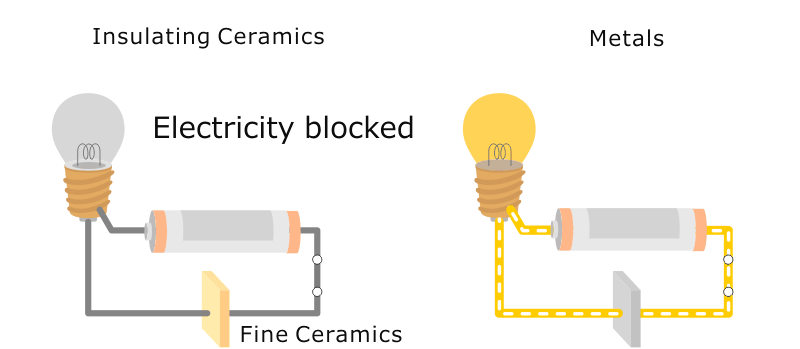
Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
The 1980s and 1990s marked a period of innovation, with advancements in manufacturing techniques such as injection molding and chemical vapor deposition, enabling the production of complex geometries and customized solutions. Today, the integration of digital technologies and additive manufacturing is further revolutionizing the industry, allowing for rapid prototyping and tailored applications.
As the demand for energy-efficient materials continues to rise, the insulating ceramics sector is well-positioned to meet the challenges of modern industrial applications, making it a crucial area for international B2B buyers to explore for sourcing opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of insulating ceramics
-
How do I choose the right insulating ceramic material for my application?
Choosing the right insulating ceramic material involves understanding the specific thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties required for your application. Consider factors such as operating temperature, thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shock, and mechanical strength. For high-temperature applications, refractory ceramics like alumina or zirconia may be preferable. It’s also crucial to evaluate the environment in which the material will be used, including exposure to chemicals or physical wear. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide tailored advice based on your needs can greatly enhance your selection process. -
What is the best insulating ceramic for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, refractory ceramics such as alumina and zirconia are among the best options. Alumina ceramics can withstand temperatures exceeding 1000°C, while zirconia offers exceptional toughness and thermal shock resistance. When selecting a ceramic, consider its density and thermal conductivity as well; fully dense zirconia typically has lower thermal conductivity than alumina, making it ideal for applications requiring thermal insulation. Consulting with manufacturers about specific formulations that meet your temperature and performance requirements is advisable. -
What customization options are available for insulating ceramics?
Many suppliers offer customization options for insulating ceramics, including tailored shapes, sizes, and material formulations. Customization may involve adjusting the composition to enhance specific properties like thermal resistance or mechanical strength. Manufacturers often utilize various forming techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, or 3D printing to meet unique design specifications. It’s beneficial to discuss your project requirements with suppliers early in the process to ensure the final product aligns with your application needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for insulating ceramics?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for insulating ceramics can vary significantly among suppliers and depend on the type of product and customization level. Generally, standard products may have lower MOQs, while customized solutions might require larger orders to justify production costs. When sourcing internationally, be sure to clarify MOQs upfront and consider how these numbers align with your project requirements. Additionally, some manufacturers may offer flexibility in MOQs for repeat orders or long-term contracts. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing insulating ceramics internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing insulating ceramics, it’s essential to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request product samples to evaluate their performance against your specifications. Additionally, establish clear quality control processes, including inspection protocols and testing procedures, before placing large orders. Maintaining open communication with your supplier throughout the production process can also help address any potential issues early. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing insulating ceramics?
Payment terms for insulating ceramics can vary by supplier and region. Common terms include upfront deposits ranging from 30% to 50%, with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60) for established relationships. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement. Understanding the currency fluctuations and potential import duties for international transactions is also important. -
How does logistics affect the sourcing of insulating ceramics?
Logistics plays a crucial role in sourcing insulating ceramics, especially for international buyers. Factors to consider include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Discuss with your supplier about their shipping options, including air freight for quicker delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Understanding the delivery timeline is essential for project planning. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides proper documentation for customs clearance to avoid delays and extra costs upon arrival. -
What are the key properties to consider for thermal insulation in ceramics?
When evaluating ceramics for thermal insulation, key properties to consider include thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistance, and mechanical strength. Low thermal conductivity is vital for effective insulation, while high thermal shock resistance ensures durability under fluctuating temperatures. Mechanical strength is also important for structural integrity in demanding applications. Additionally, consider factors such as chemical resistance and weight, which can impact the overall performance of the insulating material in your specific application.
Top 10 Insulating Ceramics Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic insulators are insulating materials made from clay, available in red, brown, or white, characterized by a porous texture. They offer outstanding dielectric properties, exceptional resistance to electrical currents, low energy dissipation, and are easy to maintain with high resistance to staining and residue buildup. They are used in high-voltage power transmission systems, coaxial cables, …
2. Ceramco – Thermal Insulation Ceramics
Domain: ceramcoceramics.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Ceramco offers two categories of thermal insulation ceramics: refractory and fully dense.
1. **Refractory Ceramics**:
– Higher resistance to thermal shock but lower strength.
– Material formulations include:
– A9468 (94% refractory alumina)
– A9968 (99% refractory alumina)
– MUL6 (refractory Mullite)
– Applications:
– Kiln and furnace components (roof anchors,…
3. Precision Ceramics – Thermal Conductivity Solutions
Domain: precision-ceramics.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Ceramic materials discussed for thermal conductivity and insulation include: Alumina, Zirconia family, Cordierite, Steatite, Porcelain, Macor, Aluminium Nitride, and Beryllium Oxide (Beryllia). Thermal conductivity values: Macor – 1.5 W/mK, Silicate ceramics – 2 to 4 W/mK, Zirconia-based ceramics – around 3 W/mK, Alumina toughened zirconia – approximately 6 W/mK, Alumina-based ceramics – 25 to 40 …
4. Thermcraft Inc – Ceramic Insulation Solutions
Domain: thermcraftinc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Ceramic insulation is made from refractory ceramic fibers, typically generated from oxide ceramics like alumina (Al2O3) or silica (Si3O4). These fibers are produced using processes such as chemical vapor deposition, extrusion, melt drawing, and spinning. The insulation products can withstand working temperatures up to 1200°C (2192°F) and are designed with grooved surfaces embedded with helically-w…
5. Kyocera – Fine Ceramics
Domain: global.kyocera.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Fine Ceramics, also known as advanced ceramics, are engineered materials that provide electrical insulation, inhibiting electricity from passing through. They are used in products such as packages for surface-mounted electronic components, including quartz crystal oscillators and surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters, which are common in mobile phones, automotive navigation systems, and portable mus…
6. Reddit – Understanding Ceramic Thermal Insulation
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Ceramic materials are generally good thermal insulators due to their structure, which allows heat transfer primarily through atomic-scale vibrations (phonons) rather than through free-moving electrons, as seen in metals. However, not all ceramics are good thermal insulators; some have high thermal conductivity. Factors affecting thermal conductivity in ceramics include crystal structure, atomic ma…
7. Hy-Tech – Ceramic Insulating Additive
Domain: hytechsales.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Hy-Tech Insulating Additive is a ceramic insulating paint additive designed to create a radiant heat reflecting, insulating thermal barrier coating. It consists of high strength ceramic microspheres that have compressive strengths up to 6,000 psi and a softening point of about 1800° C. The microspheres are vacuum-sealed, which minimizes thermal conductivity and sound transfer. When mixed into pain…
8. MGlaser – Fast Delivery & Easy Returns
Domain: mglaser.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, MGlaser – Fast Delivery & Easy Returns, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
9. Zareba Systems – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: zarebasystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulators: Made of red, brown, or white porous clay, fired at 2,100° to 2,300° F. Less expensive, can chip or break in cold weather, excellent insulation quality, better durability than plastic insulators. Available varieties include multi-groove with nails, single groove, large insulator with lag screw, and corner post insulator. Standard return policy.
Porcelain Insulators: Made from …
10. Zircar Ceramics – Alumina Type AL-25/1700
Domain: zircarceramics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Alumina Type AL-25/1700″,”description”:”Cost-effective medium duty 1700°C rated hot face insulation.”,”temperature_rating”:”1700°C”},{“name”:”Alumina Type AL-28/1800″,”description”:”Cost effective, utility-grade hot face insulation for use in kilns, furnaces and other thermal process systems operating to temperatures of 1800°C (3272°F).”,”temperature_rating”:”1800°C”},{“name”…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for insulating ceramics
In the rapidly evolving landscape of insulating ceramics, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. Understanding the diverse types of ceramics, such as alumina and zirconia, along with their unique properties—such as thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock—can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer tailored solutions, whether through custom formulations or specialized manufacturing processes like additive manufacturing or chemical milling.
Moreover, as industries worldwide increasingly emphasize sustainability and efficiency, sourcing high-performance insulating ceramics can lead to enhanced operational efficiencies and reduced costs. This is particularly relevant for sectors in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where demand for innovative thermal management solutions is on the rise.
Looking ahead, the global market for insulating ceramics is poised for growth, driven by technological advancements and a focus on energy efficiency. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers, leveraging partnerships that foster innovation and adaptability. As you consider your next procurement strategy, evaluate your sourcing practices and explore opportunities that align with future trends in the insulating ceramics industry. Your next strategic move could redefine your operational success.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to insulating ceramics