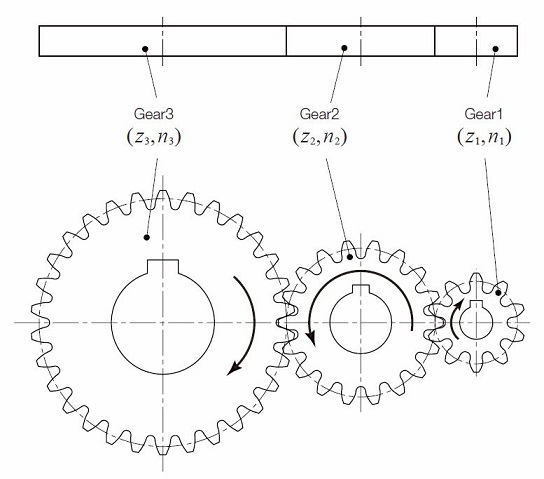
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Idler Gear Diagram Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for idler gear diagram
In the complex landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right idler gear diagram can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. These diagrams serve as essential blueprints for understanding the intricate mechanics of idler gears, which play a crucial role in various machinery applications. This guide aims to demystify the procurement process by providing comprehensive insights into different types of idler gears, their applications across industries, and effective strategies for supplier vetting.
With an emphasis on actionable information, this resource empowers international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Brazil—to make informed purchasing decisions. We delve into critical factors such as cost analysis, quality assurance, and the importance of compatibility with existing machinery. By equipping buyers with knowledge about the idler gear market, this guide not only enhances procurement efficiency but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Navigating the global market for idler gears need not be a daunting task. With the right information at your fingertips, you can streamline your sourcing process, reduce downtime, and ultimately drive your business’s operational success. Whether you are looking for specific part numbers or exploring new suppliers, this guide serves as a vital resource in your journey towards effective gear procurement.
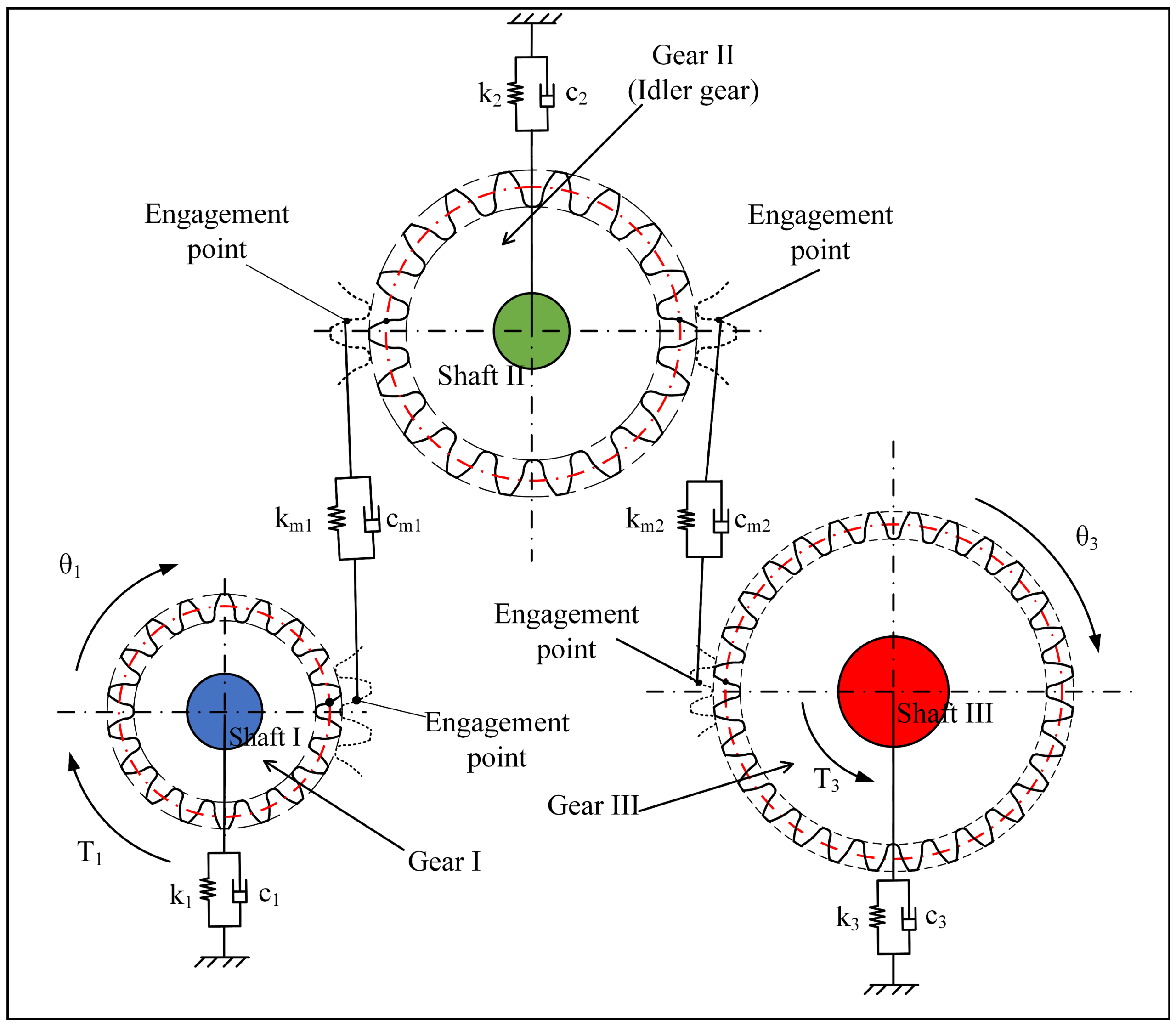
Understanding idler gear diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Idler Gear Diagram | Basic representation with minimal components, often 2D. | Small machinery, basic automotive designs | Pros: Easy to understand; Cons: Limited detail. |
| Exploded View Diagram | Components shown separately, providing a 3D perspective. | Complex machinery, automotive assembly | Pros: Comprehensive; Cons: Can be overwhelming. |
| Schematic Idler Gear Diagram | Focus on functional relationships rather than physical layout. | Electrical systems, robotics | Pros: Highlights interactions; Cons: Less intuitive. |
| Assembly Diagram | Step-by-step assembly process with labeled parts. | Manufacturing, repair services | Pros: Clear instructions; Cons: Requires prior knowledge. |
| Comparative Idler Gear Diagram | Side-by-side comparison of different gear types. | Engineering design, product development | Pros: Facilitates selection; Cons: May lack depth. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Simple Idler Gear Diagrams?
The Simple Idler Gear Diagram is characterized by its straightforward representation of idler gears, often depicted in two dimensions. This type is particularly useful for basic machinery and automotive designs, where the focus is on clarity and ease of understanding. For B2B buyers, these diagrams are beneficial due to their simplicity, making them an excellent choice for initial design discussions. However, they may lack the detail required for more complex applications, which could limit their utility in advanced engineering contexts.
How Do Exploded View Diagrams Enhance Understanding of Idler Gears?
Exploded View Diagrams provide a three-dimensional perspective, showing how components fit together. This type is essential for complex machinery and automotive assembly, as it allows engineers to visualize the spatial relationships between parts. For B2B buyers, these diagrams facilitate a deeper understanding of assembly processes and maintenance requirements. However, the complexity of these diagrams can sometimes overwhelm users unfamiliar with the specific machinery, necessitating careful interpretation.
In What Scenarios Are Schematic Idler Gear Diagrams Most Useful?
Schematic Idler Gear Diagrams emphasize the functional relationships between components rather than their physical arrangement. This type is prevalent in electrical systems and robotics, where understanding the interactions is crucial for troubleshooting and design. B2B buyers can benefit from these diagrams when developing or repairing systems where gear functionality is key. However, their abstract nature may be less intuitive for those accustomed to more traditional representations.
Why Are Assembly Diagrams Important for B2B Buyers?
Assembly Diagrams offer a detailed, step-by-step process for assembling idler gear systems, complete with labeled parts. These diagrams are invaluable in manufacturing and repair services, where precision and clarity are critical. For B2B buyers, these diagrams serve as clear instructions that can streamline assembly processes and reduce errors. However, they may require users to have some prior knowledge of the components involved, which could be a barrier for those new to the field.
Illustrative image related to idler gear diagram
How Do Comparative Idler Gear Diagrams Aid in Decision-Making?
Comparative Idler Gear Diagrams present different gear types side by side, allowing for easy comparison of features and specifications. This type is particularly useful in engineering design and product development, where selecting the right gear can significantly impact performance. For B2B buyers, these diagrams simplify the decision-making process by highlighting the pros and cons of each option. However, they may lack the depth of information needed for a thorough analysis, making it essential for buyers to supplement their research with additional data.
Key Industrial Applications of idler gear diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of idler gear diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine assembly and timing systems | Improved engine efficiency and performance | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems |
| Marine Equipment | Trolling motors for fishing boats | Enhanced maneuverability and control | Durability against corrosion, fitment with various motor models |
| Heavy Machinery | Gearboxes in construction equipment | Increased reliability and reduced downtime | Material specifications, load capacity, and operational environment |
| Agricultural Equipment | Idler gears in tractors and harvesters | Optimized power transmission and fuel efficiency | Availability of replacement parts, support for diverse models |
| Aerospace | Auxiliary power units in aircraft | Critical for operational reliability and safety | Compliance with aviation standards, precise engineering specifications |
How is the Idler Gear Diagram Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, idler gears are integral to engine assembly and timing systems. The idler gear diagram provides a visual representation of gear relationships, helping engineers design and assemble components that optimize engine performance. This application addresses challenges related to engine timing and synchronization, which are crucial for efficiency and performance. Buyers in this sector must consider quality certifications and ensure compatibility with existing systems to avoid costly modifications.
What is the Role of Idler Gears in Marine Equipment?
In the marine sector, idler gears are commonly used in trolling motors for fishing boats. The idler gear diagram is essential for understanding the gear arrangement and ensuring proper installation, which enhances maneuverability and control of the vessel. This application is particularly beneficial for businesses seeking to improve the operational efficiency of their marine equipment. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable materials resistant to corrosion, as marine environments can be harsh on mechanical components.
How Do Idler Gears Benefit Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery relies on idler gears for effective power transmission within gearboxes. The idler gear diagram assists in the design and maintenance of these systems, ultimately increasing reliability and reducing downtime. For businesses in construction and mining, this is critical, as equipment failure can lead to significant operational delays. When sourcing idler gears for heavy machinery, companies should focus on material specifications and load capacities to ensure the components can withstand demanding conditions.
Why Are Idler Gears Important in Agricultural Equipment?
In the agricultural sector, idler gears play a vital role in tractors and harvesters, where they help optimize power transmission and improve fuel efficiency. The idler gear diagram aids manufacturers in understanding the mechanical interactions within these machines, leading to better design and maintenance practices. Buyers need to ensure that replacement parts are readily available and compatible with various models, as agricultural machinery often requires specific configurations to function effectively.
How Does the Aerospace Industry Utilize Idler Gears?
In aerospace applications, idler gears are found in auxiliary power units, where they are critical for operational reliability and safety. The idler gear diagram serves as a crucial tool for engineers to visualize and analyze the gear setup, ensuring that all components function harmoniously. For international buyers in the aerospace sector, compliance with stringent aviation standards and precise engineering specifications is essential. This ensures that all components meet safety and performance requirements, which is paramount in this industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘idler gear diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying Correct Idler Gear Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when trying to identify the correct idler gear parts for their machinery. This difficulty often stems from the vast array of options available, each with specific part numbers and compatibility requirements. For instance, a manufacturer might be searching for an idler gear that fits a particular model of a trolling motor, yet they struggle to match the right part number to their existing equipment. This confusion can lead to delays in production, increased costs, and frustration as they navigate through complex specifications and diagrams.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should invest time in familiarizing themselves with detailed parts diagrams and specifications specific to their machinery. Start by gathering all relevant documentation, including user manuals and maintenance guides, which often contain exploded diagrams of the assembly. Additionally, utilize online resources and manufacturer databases to cross-reference part numbers. Websites that offer comprehensive parts lookup tools can significantly streamline this process. Engaging directly with suppliers or manufacturers for clarification can also ensure that the right parts are sourced. Finally, consider creating a systematic inventory management process that includes part numbers and their corresponding diagrams for future reference, thus reducing the likelihood of errors.
Scenario 2: Misalignment Issues in Gear Assemblies
The Problem: Another common pain point is the misalignment of idler gears during installation, which can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased wear on machinery. Buyers may find that despite having the right parts, the installation does not yield the expected performance. This misalignment can stem from incorrect assembly procedures or a lack of understanding of how the idler gear interacts with other components in the system.
The Solution: To ensure proper alignment, it’s essential to follow a step-by-step assembly guide that emphasizes the importance of each component’s position. Buyers should consult detailed idler gear diagrams that illustrate the precise placement and orientation of each gear within the assembly. Implementing a checklist during installation can help verify that all components are positioned correctly before finalizing assembly. Additionally, utilizing alignment tools or fixtures can enhance accuracy during the installation process. If issues persist, engaging with technical support teams can provide insights into common alignment problems and offer tailored solutions.
Scenario 3: Limited Access to High-Quality Diagrams and Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with limited access to high-quality idler gear diagrams and specifications, particularly when dealing with older or less common machinery. This scarcity can result in reliance on outdated or inaccurate diagrams, leading to incorrect part selection and assembly errors. For buyers in regions with less comprehensive supplier networks, this issue can be particularly pronounced, affecting their ability to maintain equipment effectively.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should proactively seek out reputable online platforms that specialize in parts catalogs and technical documentation. Joining industry forums and professional networks can provide valuable insights and access to shared resources, including high-quality diagrams. Collaborating with suppliers who offer robust technical support and can provide updated diagrams is crucial. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can also enhance access to rare parts and documentation. Furthermore, investing in training for staff on how to interpret and utilize these diagrams effectively can lead to more informed decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for idler gear diagram
What Are the Common Materials Used for Idler Gears in Diagrams?
When selecting materials for idler gears, it’s crucial to consider various factors such as performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of idler gears, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as an Idler Gear Material?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials for idler gears due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Steel gears can be treated through processes like hardening to enhance their durability further.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can handle significant loads, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other high-performance materials.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in humid or saline environments. This necessitates protective coatings or surface treatments, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel idler gears are compatible with a wide range of media, but they may require protective measures in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and the cost of protective coatings.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum for Idler Gears?
Aluminum is another popular choice for idler gears, particularly where weight reduction is a priority. It has good corrosion resistance and is lightweight, making it easier to handle and install.
Pros: Aluminum gears are less dense than steel, which can lead to reduced overall system weight. They also exhibit good thermal conductivity, which helps in heat dissipation during operation.
Cons: Although aluminum has decent strength, it is not as strong as steel, making it less suitable for high-load applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive to produce due to the complexity of machining.
Illustrative image related to idler gear diagram
Impact on Application: Aluminum gears can be used in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. However, they may not be suitable for high-torque environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with JIS standards for aluminum components and consider the availability of aluminum alloys in their region.
Why Choose Plastic for Idler Gears?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like nylon or acetal, are increasingly popular for idler gears due to their self-lubricating properties and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Plastic gears are lightweight, resistant to chemicals, and can operate quietly. They also require less maintenance compared to metal gears.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic gears is their lower load-bearing capacity compared to metals. They can also be sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which may affect their performance.
Impact on Application: Plastic idler gears are ideal for applications that require low friction and noise, such as in consumer electronics or small machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with specific material standards and consider the implications of temperature variations in their operational environments.
How Does Bronze Compare as an Idler Gear Material?
Bronze is often used in applications requiring excellent wear resistance and low friction. It is particularly suitable for marine applications due to its corrosion resistance.
Pros: Bronze gears are durable and can withstand harsh environments, making them ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Cons: The major downside is the higher cost of bronze compared to steel or plastic. Additionally, bronze can be more challenging to machine, leading to increased manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Bronze idler gears are highly suitable for marine and industrial applications where corrosion resistance is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with relevant standards is crucial, especially in regions with strict regulations regarding material properties.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Idler Gears
| Material | Typical Use Case for idler gear diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery | High durability and load capacity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics | Self-lubricating and low maintenance | Lower load-bearing capacity | Medium |
| Bronze | Marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for idler gears, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for idler gear diagram
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Idler Gears?
The manufacturing process of idler gears involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications for performance and durability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used for Idler Gears?
The first step in manufacturing idler gears is selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials include high-carbon steel, alloy steel, and sometimes plastic composites for lighter applications. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and wear resistance. Suppliers typically source raw materials from certified vendors, ensuring they meet international standards.
Before forming, the materials undergo several preparatory processes. These include cutting to size, heat treatment, and surface cleaning to remove any contaminants that could affect the final product’s performance.
2. Forming: How Are Idler Gears Shaped and Sized?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the desired gear configuration. Key techniques used in this stage include:
Illustrative image related to idler gear diagram
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is widely used for precision shaping. It allows for high accuracy in dimensions and surface finishes, essential for ensuring the gear meshes correctly with other components.
- Hobbing: This is a specific method for creating gear teeth profiles. The process is efficient for producing large quantities and maintains consistency in tooth shape and size.
- Forging: In some cases, forging is employed to enhance the material’s structural integrity. This technique involves deforming the material under high pressure, which can improve its mechanical properties.
Once shaped, the gears are sized to exact specifications, ensuring they fit seamlessly into the intended application.
3. Assembly: What Are the Key Considerations in Gear Assembly?
In the assembly stage, various components, such as the idler gear and its associated plates or housings, are brought together. This process may involve:
- Alignment Checks: Proper alignment is crucial to prevent premature wear or failure. Techniques such as laser alignment can be employed to ensure precision.
- Fastening: Using screws, bolts, or other fastening methods, the components are secured. The choice of fastening method depends on the specific application requirements, including vibration resistance and thermal expansion considerations.
4. Finishing: How Do Finishing Techniques Affect Gear Performance?
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality of idler gears, improving their performance and longevity. Common finishing techniques include:
- Grinding: This process is used to achieve tight tolerances and superior surface finishes. Grinding can eliminate any imperfections left from the machining processes.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings, such as nitriding or phosphate, can significantly enhance corrosion resistance and reduce friction during operation.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Idler Gear Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that idler gears meet international standards and customer expectations. Effective QA involves several checkpoints and testing methods.
1. What Are the Relevant International Standards for Idler Gear Quality?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the quality standards applicable to idler gears is essential. Relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality processes and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: This indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: For gears used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be required.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step ensures that all raw materials meet specified standards before they enter the production process. Suppliers often conduct material certifications to validate quality.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are performed to catch any deviations from quality standards early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, finished products undergo rigorous testing, including dimensional checks, material hardness tests, and functionality assessments.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Idler Gears?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of idler gears:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers, manufacturers check that the dimensions of the gears meet specified tolerances.
- Load Testing: Gears may be subjected to simulated operational conditions to assess their performance under stress.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection help identify internal flaws without damaging the product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
1. Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. These audits should focus on:
- Compliance with international standards.
- The effectiveness of their quality management systems.
- Staff training and competency levels.
2. Request Quality Assurance Documentation
Buyers should ask for documentation that demonstrates the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. This includes:
- Certificates of compliance with ISO and other relevant standards.
- Reports from quality control checkpoints.
- Records of any third-party inspections.
3. Leverage Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These agencies can conduct independent assessments of the supplier’s facilities and processes, ensuring that they adhere to industry standards and best practices.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Idler Gear Manufacturing
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for idler gears is vital for B2B buyers aiming to secure high-quality components. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers. Implementing thorough verification processes further ensures that the products meet the necessary standards for performance and reliability, ultimately contributing to the success of their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘idler gear diagram’
In the world of mechanical engineering, sourcing the right idler gear diagram is essential for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility in various machinery applications. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process and select the best suppliers for their needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific requirements for the idler gear you need. This includes dimensions, material specifications, and load capacity. Clearly defined specifications help prevent costly mistakes and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
- Considerations:
- What type of machinery will the idler gear be used in?
- Are there industry standards or certifications that must be met?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in idler gears and related components. Look for companies with a strong track record in your industry and positive customer reviews.
- Actions:
- Check online marketplaces, industry forums, and trade directories.
- Compile a list of suppliers and their offerings to compare later.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a decision, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. This ensures that their products meet international quality standards and regulatory requirements.
- Key Certifications:
- ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
- Specific industry-related certifications based on your region or application.
Step 4: Request Technical Documentation
Always ask for technical documentation, including detailed idler gear diagrams and installation guides. This documentation provides insights into the product’s specifications and compatibility.
- What to Look For:
- Clear and detailed diagrams that illustrate dimensions and parts.
- Maintenance guidelines that indicate the longevity and reliability of the gear.
Step 5: Inquire About Customization Options
If your machinery requires specific adaptations, inquire whether the supplier can customize the idler gear. Customization may be necessary to ensure optimal performance and fit.
Illustrative image related to idler gear diagram
- Questions to Ask:
- What is the minimum order quantity for custom parts?
- What is the typical lead time for customized products?
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among shortlisted suppliers. While it’s important to consider cost, don’t compromise on quality for a lower price. Also, clarify payment terms to avoid misunderstandings.
- Considerations:
- Are there volume discounts available?
- What payment methods are accepted, and are there any financing options?
Step 7: Check After-Sales Support
After you’ve made your purchase, reliable after-sales support is crucial. Ensure the supplier offers assistance with installation, troubleshooting, and warranty claims.
- What to Confirm:
- Is technical support available post-purchase?
- What is the warranty period, and what does it cover?
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the process of sourcing idler gear diagrams and ensure they select the right suppliers for their needs. Proper due diligence not only saves time and money but also enhances operational efficiency in the long run.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for idler gear diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Idler Gear Diagrams?
When sourcing idler gear diagrams, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Common materials for idler gears include high-strength steel, plastic composites, or aluminum, each varying in price based on quality and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with skilled technicians and machinists involved in the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to increased pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs related to production facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. This includes the cost of molds, dies, and specialized machinery required for production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the idler gears meet specified standards. This process adds to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and the volume of the order. International shipping may involve additional tariffs and customs fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. This margin can vary based on market conditions and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Idler Gear Diagram Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of idler gear diagrams, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often qualify for bulk discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized gears to meet specific engineering requirements can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes.
-
Materials: The quality and type of material directly impact the price. High-performance materials will command higher prices but may offer better longevity and performance.
-
Quality Certifications: Gears that meet international standards (e.g., ISO, CE) may be priced higher due to the rigorous testing and quality assurance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for pricing. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the total cost of acquisition.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Idler Gear Diagrams Internationally?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals and discounts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, durability, and performance over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market conditions that may affect pricing, such as currency fluctuations and regional demand for idler gears.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Assess potential suppliers for quality, reliability, and production capabilities. This can help mitigate risks associated with poor-quality products.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: Consider sourcing from local manufacturers to reduce logistics costs and lead times, especially for smaller, less complex orders.
Final Thoughts
While indicative prices for idler gear diagrams vary widely based on the above factors, understanding the cost components and price influencers can empower buyers to make informed decisions. Conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to ensure optimal sourcing outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing idler gear diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Idler Gear Diagrams in Mechanical Applications
When considering mechanical solutions for power transmission and gear alignment, idler gear diagrams serve as a critical tool. However, there are alternative methods and technologies that can also fulfill similar objectives. This analysis will compare the idler gear diagram against two viable alternatives: Chain Drives and Belt Drives. Understanding the nuances of these options will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Idler Gear Diagram | Chain Drives | Belt Drives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for precise gear alignment and minimal backlash. | High efficiency and torque transmission, suitable for heavy loads. | Moderate efficiency, but quieter and smoother operation. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for maintenance. | Generally lower upfront costs; maintenance can be higher due to wear. | Higher initial costs; less frequent replacements lead to lower long-term costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires detailed diagrams and skilled labor for installation. | Easier to install with fewer components; requires proper tensioning. | Simple installation process; requires alignment but less precision than gears. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspections and adjustments; parts can be expensive. | Needs regular lubrication and tension checks; susceptible to wear. | Minimal maintenance; periodic inspections needed, but generally more durable. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications needing precise gear ratios and minimal space. | Best for high-torque applications, such as automotive or heavy machinery. | Suitable for applications requiring flexibility and vibration absorption, like conveyor systems. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Chain Drives?
Chain drives are a robust alternative to idler gears, especially in scenarios demanding high torque and efficiency. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications where power transmission over a significant distance is required. The primary advantage of chain drives is their ability to handle heavy loads without slippage, making them ideal for high-torque environments. However, they do require regular maintenance, including lubrication and tension adjustments, which can increase operational costs over time.
How Do Belt Drives Compare to Idler Gear Diagrams?
Belt drives offer a flexible and quieter alternative to idler gear systems. They are particularly advantageous in applications where noise reduction and vibration absorption are critical, such as in conveyor systems. The installation process for belt drives is straightforward, and they generally require less maintenance compared to chain drives or idler gears. However, they may not achieve the same level of efficiency in power transmission as gear systems, particularly in high-torque applications, which could limit their effectiveness in some industrial settings.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between idler gear diagrams and alternative solutions like chain or belt drives, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Each solution offers unique benefits and potential drawbacks; thus, understanding these distinctions is vital for making an informed decision. By carefully evaluating the trade-offs, businesses can optimize their mechanical systems to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for idler gear diagram
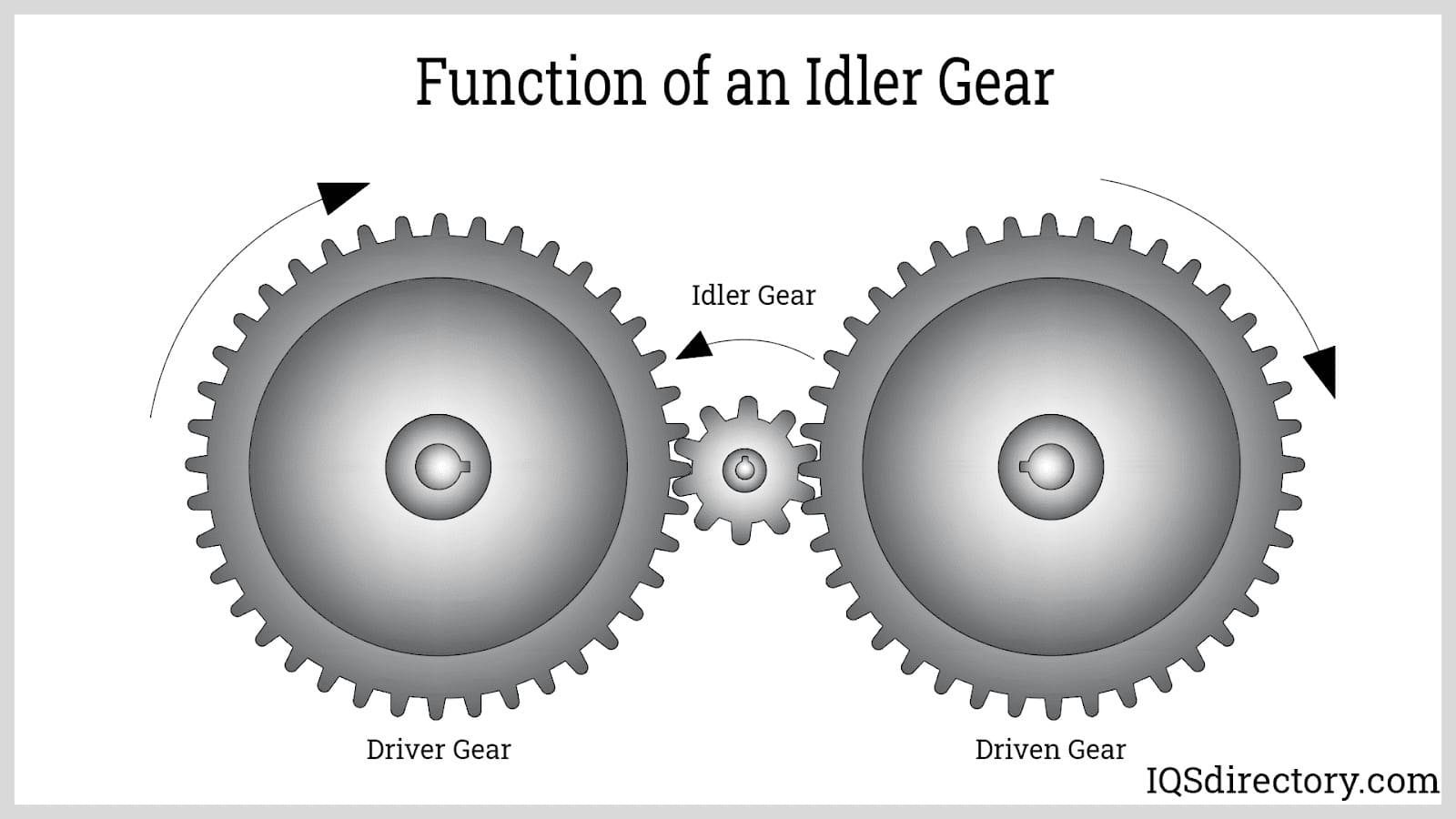
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Idler Gears?
When dealing with idler gears, particularly in a B2B context, understanding key technical specifications is critical for ensuring compatibility, performance, and longevity. Here are some essential properties that buyers should consider:
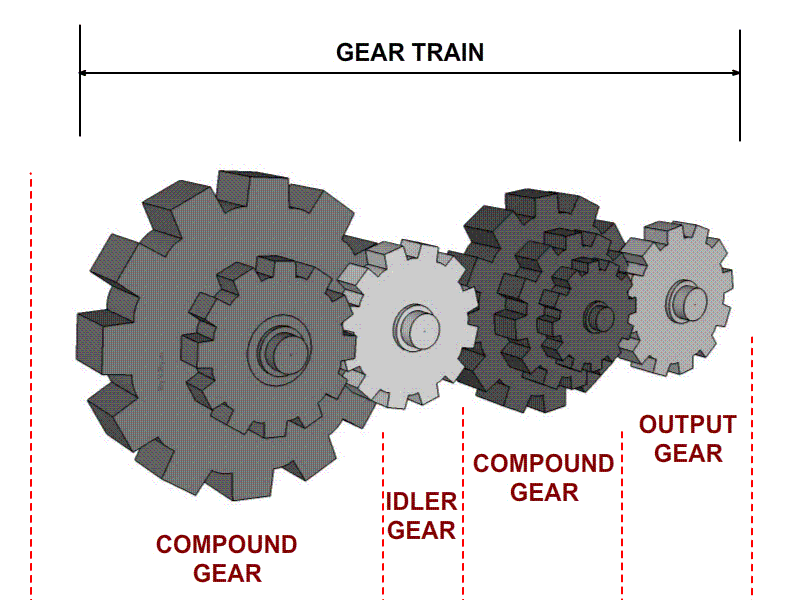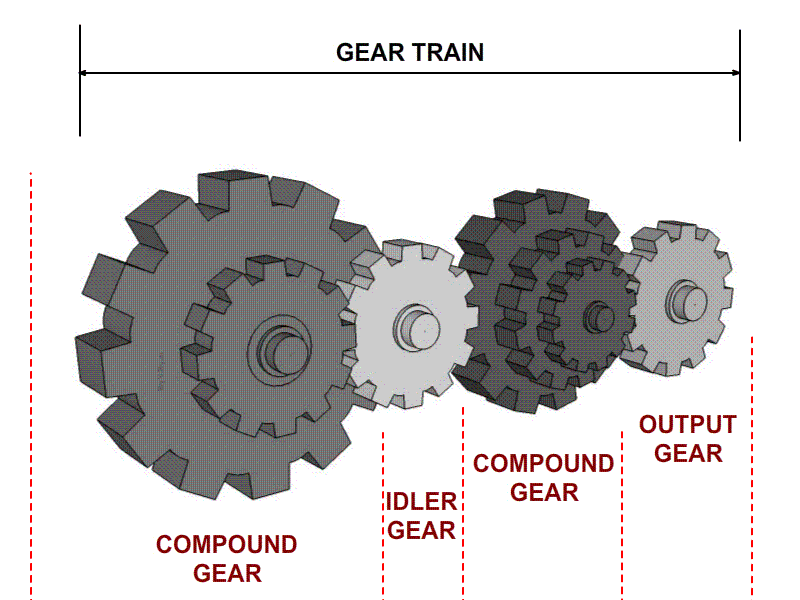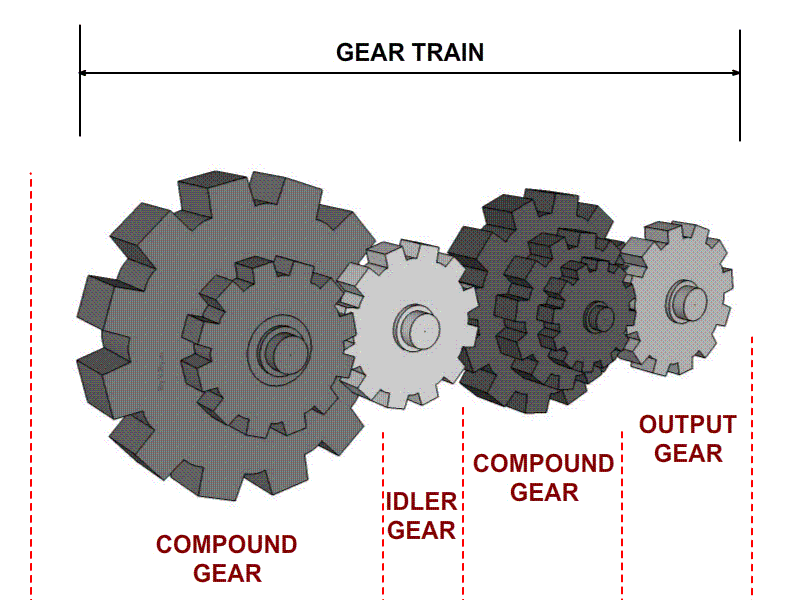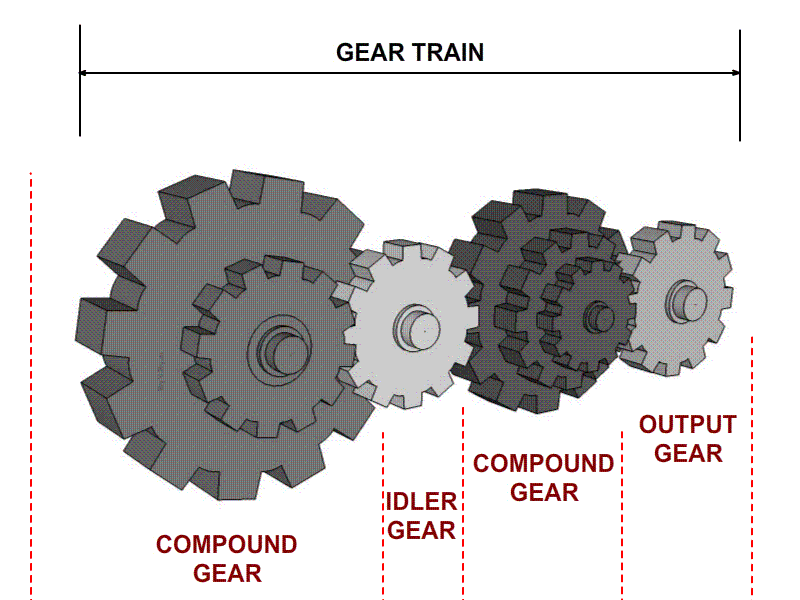
Illustrative image related to idler gear diagram
-
Material Grade
Idler gears are typically made from various materials such as steel, aluminum, or plastic composites. The choice of material affects durability, weight, and cost. For instance, steel gears offer high strength and wear resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, while plastic gears might be used for lighter loads due to their lower cost and weight. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For idler gears, precise tolerances are crucial to ensure smooth operation and minimize wear. A tighter tolerance generally results in better performance and longer life, which is particularly important in high-speed applications. -
Pitch Diameter
The pitch diameter is the diameter of the circle on which the teeth of the gears effectively engage. It is a fundamental measurement for ensuring that gears mesh correctly. Selecting the right pitch diameter is vital for preventing mechanical failure and ensuring optimal transmission of power. -
Tooth Profile
The shape and design of the gear teeth, such as involute or cycloidal profiles, can significantly impact efficiency and noise levels. Understanding the tooth profile helps buyers select gears that meet their application’s specific requirements for smooth operation and load distribution. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of an idler gear affects friction, wear resistance, and overall performance. A smoother finish can reduce friction, leading to improved efficiency and extended lifespan. Buyers should consider the intended application and operating conditions when evaluating surface finish specifications. -
Load Rating
Load rating indicates the maximum load that an idler gear can handle before failure. This specification is essential for ensuring that the gear can withstand operational stresses without risk of damage. Selecting a gear with an appropriate load rating is crucial for maintaining equipment reliability and performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Idler Gears?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms related to idler gears:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of idler gears, buyers often seek OEM parts for guaranteed compatibility and quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for international buyers as it can affect inventory levels and overall costs. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and manage cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. For idler gears, an RFQ can ensure that buyers receive accurate pricing based on their specific needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They cover aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which are crucial for businesses importing or exporting idler gears. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for planning and inventory management, especially in industries where idler gears are critical for ongoing operations. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components produced by third-party manufacturers that are not made by the original equipment manufacturer. These parts can offer cost-effective alternatives for idler gears but may vary in quality and compatibility.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right idler gears for their applications while optimizing procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the idler gear diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing the Idler Gear Diagram Sector?
The global idler gear diagram market is experiencing a notable evolution driven by various factors. Key among these is the increasing demand for precision engineering across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. As manufacturers strive for enhanced efficiency and performance, the need for reliable idler gears has intensified. Additionally, the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles is propelling innovation in gear design, creating new opportunities for B2B buyers seeking cutting-edge solutions.
Emerging technologies such as 3D printing and advanced materials are reshaping sourcing trends. 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and customization of idler gears, which can be particularly appealing for businesses in Africa and South America, where the ability to adapt quickly to market needs is crucial. Furthermore, the integration of IoT in manufacturing processes is enhancing the monitoring and maintenance of idler gear systems, ensuring longer lifespans and reduced downtime.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of regional dynamics that influence sourcing decisions. In Europe, strict regulations around safety and sustainability are prompting manufacturers to prioritize compliance, while in the Middle East, the focus is on leveraging local resources to reduce import dependency. Understanding these dynamics can help buyers navigate the market effectively, ensuring they source the right products that meet both performance and regulatory standards.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Idler Gear Diagram Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the idler gear diagram sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, compelling companies to adopt greener practices. For B2B buyers, this means prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 can serve as indicators of a supplier’s environmental management practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, especially in regions where labor practices may vary significantly. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor standards and ethical sourcing principles. This not only mitigates reputational risks but also fosters a more sustainable supply chain. As a result, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking partnerships with manufacturers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and who can provide documentation of their supply chain sustainability efforts.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials—such as biodegradable or recyclable components—is on the rise. Buyers who invest in sustainable idler gear solutions not only contribute to environmental preservation but also meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products, enhancing their brand reputation in the process.
What Is the Evolution of the Idler Gear Diagram Sector and Its Implications for B2B Buyers?
The idler gear diagram sector has evolved significantly over the years, transitioning from rudimentary designs to highly sophisticated components integral to modern machinery. Initially, idler gears were primarily mechanical components with limited functionality. However, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of gears that not only improve efficiency but also reduce noise and wear.
The historical context of idler gears highlights the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the demands of various industries. For instance, the automotive sector’s shift towards electric vehicles has necessitated a rethinking of gear design to accommodate different powertrains. This evolution presents B2B buyers with opportunities to invest in cutting-edge products that can enhance their operational capabilities.
Understanding the historical development of idler gears also provides insights into future trends. As industries continue to prioritize automation and efficiency, the demand for advanced idler gear solutions is expected to grow. Buyers who remain attuned to these trends will be better positioned to leverage emerging technologies and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of idler gear diagram
-
How do I choose the right idler gear diagram for my application?
Selecting the appropriate idler gear diagram involves understanding your specific machinery needs. Start by identifying the type of machinery you are working with and the specifications required for the idler gear, such as size, material, and load capacity. Consult with suppliers to obtain detailed diagrams that match your equipment. It’s also beneficial to compare diagrams across multiple suppliers to ensure compatibility and functionality. Always request samples or prototypes when possible to validate your choice before making a bulk order. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing idler gear diagrams internationally?
When sourcing idler gear diagrams from international suppliers, consider factors such as supplier reliability, production capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Verify the supplier’s credentials and experience in manufacturing idler gears specific to your industry. Additionally, assess the quality assurance processes they have in place. Look for suppliers who offer detailed diagrams and technical support to help you understand the components and their applications effectively. -
What customization options are available for idler gear diagrams?
Many suppliers offer customization options for idler gear diagrams to meet specific operational requirements. You can request modifications to dimensions, materials, or gear ratios based on your machinery’s specifications. Some suppliers may also provide design support to help you create a diagram that optimally fits your application. Ensure you discuss your customization needs upfront and inquire about any additional costs or lead times associated with these modifications. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for idler gear diagrams?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for idler gear diagrams can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from a few pieces to hundreds, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and your specific requirements. It’s important to communicate your needs clearly to potential suppliers and negotiate MOQs that align with your business model. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time orders or trials, so don’t hesitate to ask. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering idler gear diagrams?
Payment terms for ordering idler gear diagrams can vary by supplier and region. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments before shipment, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify payment terms during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. In international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in your contract. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing idler gear diagrams?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing idler gear diagrams, request detailed quality control procedures from your suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or requesting third-party inspections before shipment. It’s also beneficial to request samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality before placing larger orders. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract can help safeguard against discrepancies. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing idler gear diagrams?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of idler gear diagrams. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines when placing your order. Collaborate with suppliers to determine the best shipping options based on your location and urgency. Ensure that all documentation is in order to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to international shipping, and plan accordingly to avoid disruptions in your operations. -
How can I vet suppliers for idler gear diagrams effectively?
Effective supplier vetting involves a comprehensive assessment of their capabilities, reputation, and reliability. Start by researching potential suppliers online, checking reviews, and seeking references from other businesses. Request documentation of their certifications and quality assurance processes. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their responsiveness and customer service. If feasible, visit the supplier’s facility or request a video tour to assess their operations firsthand, ensuring they meet your standards for quality and production.
Top 3 Idler Gear Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Minn Kota – Idler Gear and Plate Assembly
Domain: northlandmarine.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Minn Kota Idler Gear and Plate Assembly”, “part_number”: “2772215”, “old_part_numbers”: [“2071900”, “2072215”, “2882215”], “price”: “$9.00”, “description”: “Fits Minn Kota trolling motor models with 3X steering.”, “included_parts”: [{“quantity”: 1, “part_number”: “2071900”, “part_description”: “Idler Plate”}, {“quantity”: 1, “part_number”: “2072215”, “part_description”: “Idler Ge…
2. Hydra Glide – Idler Gear #25775-36
Domain: hydra-glide.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Idler gear part # 25775-36 used from 1941 to 1968; 1969 Idler gear may be different; Jarhead’s gear has 51 teeth; questioned gear has 46 teeth; diameter of 45 WL gears is almost 3 inches and has 46 teeth; potential identification as a sportster gear.
3. S&S – CR-35384 Idler Gear
Domain: corrugatedreplacements.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “CR-35384 S&S S&S Idler Gear”, “SKU”: “CR-35384”, “category”: “S&S Pusher Shifter Gear Box Assembly”, “OEM_number”: “ZLG-1420”, “compatible_machine”: “S&S ZLR-10308 (Pusher Shift Gear Box Assembly)”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for idler gear diagram
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Idler Gear Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of idler gear procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality and compatibility in your sourcing process, you not only ensure the longevity and efficiency of your machinery but also foster strong supplier relationships that can lead to better pricing and service terms.
Understanding the intricacies of idler gear diagrams is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The details encapsulated in these diagrams provide insights into part compatibility, assembly processes, and maintenance requirements, which can significantly reduce operational downtime and enhance productivity. Additionally, leveraging local suppliers can mitigate shipping costs and lead times, creating a more agile supply chain.
As you look to the future, consider the potential of emerging technologies and innovations in the idler gear sector. Engaging with suppliers who are at the forefront of these advancements will position your business for success. Now is the time to take proactive steps in your sourcing strategy—evaluate your current suppliers, explore new partnerships, and invest in quality components that will drive your operational success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.