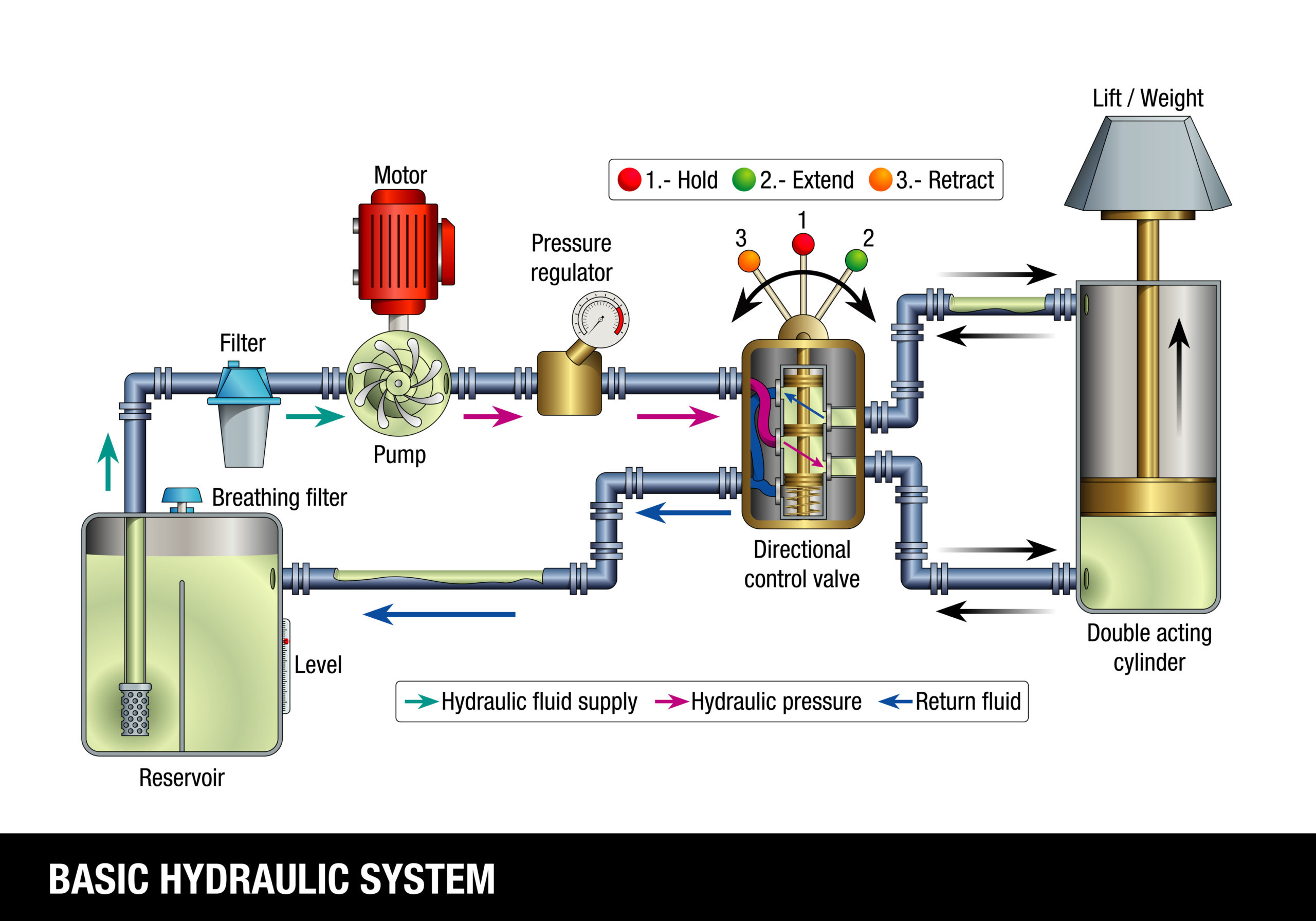
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Hydraulic Pump Diagram Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic pump diagram
In the intricate world of industrial machinery, sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly those from emerging markets such as Brazil, Nigeria, and other regions in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. These diagrams are crucial for understanding the functionality and maintenance of hydraulic systems, which are pivotal in various applications, from construction to agriculture. However, the challenge lies in navigating the plethora of options available while ensuring compliance with local standards and operational needs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted landscape of hydraulic pump diagrams, offering insights into different types, their applications, and critical considerations for supplier vetting. We will explore how to interpret various diagram formats, understand their components, and utilize them effectively for troubleshooting and system optimization. Additionally, we will provide actionable strategies for assessing costs and value, empowering international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
By equipping you with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate this global market, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process, mitigate risks, and enhance operational efficiency in your hydraulic systems. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, understanding hydraulic pump diagrams is essential for maximizing productivity and ensuring the longevity of your equipment.
Understanding hydraulic pump diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open-Center Circuit Diagram | Fluid flows continuously; pressure drops when actuators are inactive. | Construction machinery, agricultural equipment | Pros: Simple design, easy to troubleshoot. Cons: Less efficient under low load. |
| Closed-Center Circuit Diagram | Fluid flow is directed only when actuators are engaged; holds pressure. | Industrial machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Efficient use of energy, better control. Cons: More complex, higher initial cost. |
| Pictorial Diagram | Visual representation of components and flow paths. | Training and maintenance manuals | Pros: Intuitive understanding, useful for training. Cons: May oversimplify system intricacies. |
| Schematic Diagram | Symbolic representation of system components and connections. | Engineering design, system analysis | Pros: Precise technical details, standardized symbols. Cons: Requires knowledge to interpret effectively. |
| Functional Diagram | Shows the operational relationships and functions of components. | System design and troubleshooting | Pros: Clarifies system operation, aids in diagnostics. Cons: Can be complex, may require expert interpretation. |
What are Open-Center Circuit Diagrams and Their Applications?
Open-center circuit diagrams are characterized by a continuous flow of hydraulic fluid, allowing for quick transitions between operations. Commonly used in construction machinery and agricultural equipment, these diagrams are valued for their simplicity and ease of troubleshooting. When considering an open-center system, buyers should evaluate the specific operational needs, as these systems can be less efficient under low load conditions.
How Do Closed-Center Circuit Diagrams Differ?
Closed-center circuit diagrams direct fluid flow only when actuators are engaged, maintaining pressure when inactive. This design is prevalent in industrial machinery and automotive applications due to its energy efficiency and enhanced control. Buyers should consider the complexity and initial costs associated with closed-center systems, as they may require more sophisticated maintenance and installation.
Why Choose Pictorial Diagrams for Training?
Pictorial diagrams provide a visual representation of hydraulic systems, illustrating components and flow paths in an intuitive manner. These diagrams are particularly useful in training and maintenance manuals, offering a straightforward way for technicians to understand system operations. However, while they simplify comprehension, they may not capture all system intricacies, making them less suitable for detailed engineering work.
What are the Benefits of Schematic Diagrams?
Schematic diagrams utilize standardized symbols to represent hydraulic system components and their interconnections. Widely used in engineering design and system analysis, they offer precise technical details essential for effective communication among engineers. Buyers should be aware that interpreting schematic diagrams requires a certain level of expertise, as the symbols may not be immediately recognizable to all users.
How Do Functional Diagrams Enhance System Understanding?
Functional diagrams illustrate the operational relationships and functions of hydraulic system components, making them invaluable for system design and troubleshooting. By clarifying how different parts interact, these diagrams aid in diagnosing issues and optimizing performance. However, their complexity may pose challenges for interpretation, necessitating a knowledgeable approach to ensure accurate application.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic pump diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic pump diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Hydraulic Excavators | Enhanced operational efficiency and productivity | Quality of components, local availability, compliance with international standards |
| Agriculture | Tractors and Agricultural Implements | Improved crop yield through efficient machinery use | Durability in harsh conditions, compatibility with existing systems, maintenance support |
| Mining | Hydraulic Drilling and Excavation Equipment | Increased safety and reduced downtime | Supplier reliability, availability of spare parts, adherence to safety regulations |
| Oil & Gas | Hydraulic Fracking Equipment | Maximized extraction efficiency and reduced costs | Technical specifications, environmental compliance, logistical support |
| Manufacturing | Hydraulic Presses for Metal Forming | Enhanced precision and reduced material waste | Customization options, supplier certifications, after-sales service availability |
How is the Hydraulic Pump Diagram Used in Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, hydraulic pump diagrams are essential for understanding the operational mechanisms of hydraulic excavators and loaders. These diagrams help technicians visualize the flow of hydraulic fluid and the interaction between various components, such as pumps, valves, and actuators. By accurately interpreting these diagrams, businesses can troubleshoot issues effectively, ensuring minimal downtime and maintaining productivity on job sites. Key considerations for sourcing include ensuring that components meet durability standards and are readily available in local markets to avoid delays.
What Role Does Hydraulic Pump Diagram Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, hydraulic pump diagrams are critical for the operation of tractors and various implements such as plows and seeders. These diagrams illustrate how hydraulic systems power attachments, enabling farmers to perform tasks efficiently. The use of hydraulic systems allows for precise control over machinery, which can lead to improved crop yields. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing durable components that can withstand challenging conditions, ensuring compatibility with existing equipment, and obtaining reliable maintenance support to minimize operational disruptions.
How are Hydraulic Pump Diagrams Applied in Mining Operations?
Mining operations heavily rely on hydraulic drilling and excavation equipment, where hydraulic pump diagrams are used to optimize the performance of these machines. These diagrams provide insights into the hydraulic circuits, helping operators understand how to manage fluid power effectively for drilling and material handling. The application of these diagrams can enhance safety measures and reduce the risk of equipment failure. When sourcing hydraulic systems for mining, businesses must consider supplier reliability and the availability of spare parts to ensure continuous operation in demanding environments.
In What Ways are Hydraulic Pump Diagrams Important in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas sector, hydraulic pump diagrams are crucial for the operation of hydraulic fracking equipment. These diagrams help engineers and technicians comprehend the flow paths and pressure requirements needed for efficient extraction processes. By leveraging hydraulic pump diagrams, companies can maximize extraction efficiency while minimizing operational costs. Key sourcing considerations include ensuring that equipment meets technical specifications and environmental compliance, as well as having logistical support for timely delivery and installation.
How Do Hydraulic Pump Diagrams Enhance Manufacturing Processes?
In manufacturing, hydraulic pump diagrams are vital for the functioning of hydraulic presses used in metal forming. These diagrams allow engineers to visualize the hydraulic system, leading to enhanced precision in production and reduced material waste. Understanding these diagrams aids in troubleshooting and maintenance, critical for maintaining production schedules. When sourcing hydraulic presses, businesses should focus on customization options, supplier certifications, and the availability of after-sales services to ensure optimal performance and support throughout the equipment’s lifecycle.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hydraulic pump diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Complex Diagrams
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter hydraulic pump diagrams that are overly complex, filled with technical jargon, and lack clear annotations. This can lead to confusion, misinterpretation of the system’s layout, and ultimately, costly mistakes during installation or maintenance. For instance, a technician may struggle to identify the correct flow paths or pressure settings, resulting in inefficient operation or even equipment failure. This challenge is particularly acute for companies in regions with limited access to technical training resources, such as parts of Africa or South America.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams that come with comprehensive legends and annotations. Look for diagrams that use standardized symbols as outlined by organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). These symbols help in recognizing the components and their functions quickly. Additionally, investing in training sessions or workshops focused on reading and interpreting hydraulic diagrams can significantly enhance your team’s understanding. Online platforms and webinars can provide targeted education tailored to your specific industry needs, ensuring your team feels confident in their ability to utilize these diagrams effectively.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of Diagrams Across Suppliers
The Problem: Another common pain point is the inconsistency in the quality and format of hydraulic pump diagrams provided by different suppliers. This variability can lead to confusion when integrating components from multiple vendors, as each may have their own representation of the same systems. For example, a hydraulic system designed for a construction vehicle may use different symbols or layouts depending on the supplier, complicating assembly and maintenance tasks. This inconsistency can also prolong project timelines, especially in sectors where time is critical, such as construction or oil extraction.
The Solution: To address this, B2B buyers should establish clear communication with their suppliers about the standards and formats expected for hydraulic pump diagrams. Request that suppliers adhere to established industry standards like ISO 1219, which provides guidelines for fluid power diagrams. Additionally, create a centralized repository for all hydraulic pump diagrams used within your organization. This repository should include a standardized template that all suppliers can follow, ensuring uniformity. Regular audits of the diagrams can help in identifying discrepancies early on, fostering smoother collaboration between different vendors.
Scenario 3: Lack of Integration with Digital Tools
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves limited by traditional hydraulic pump diagrams that do not integrate well with digital tools and software. As industries increasingly move towards digital transformation, the inability to easily incorporate diagrams into CAD systems or maintenance software can hinder efficiency. For instance, an engineering team might struggle to import diagrams into their design software, resulting in duplicated efforts and potential errors when designing new systems based on outdated representations.
The Solution: To overcome this barrier, buyers should seek hydraulic pump diagrams that are available in digital formats compatible with common engineering software. Request diagrams in vector formats (like SVG or DWG) that can be easily manipulated within CAD programs. Furthermore, investing in software that allows for the import and editing of hydraulic diagrams can streamline the design process. Encourage your team to use digital tools that facilitate real-time collaboration, allowing engineers and technicians to update and annotate diagrams as needed. This approach not only enhances productivity but also ensures that all team members are working from the most current and accurate representations of hydraulic systems.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic pump diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Hydraulic Pump Diagrams?
When selecting materials for hydraulic pump diagrams, it is essential to consider their properties, suitability for specific applications, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials: steel, aluminum, plastic, and composite materials. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly influence the performance and longevity of hydraulic systems.
How Does Steel Perform in Hydraulic Pump Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in hydraulic pump diagrams due to its high strength and durability. It typically exhibits excellent temperature and pressure ratings, making it suitable for high-demand applications. Steel also offers good corrosion resistance when treated or coated appropriately.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can withstand extreme conditions, which makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, particularly in large quantities.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its weight, which can complicate installation and increase transportation costs. Additionally, untreated steel is susceptible to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, but it is vital to ensure that the chosen coating does not react negatively with the fluid.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that steel components comply with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. Additionally, understanding the availability of corrosion-resistant coatings in specific markets can impact procurement strategies.
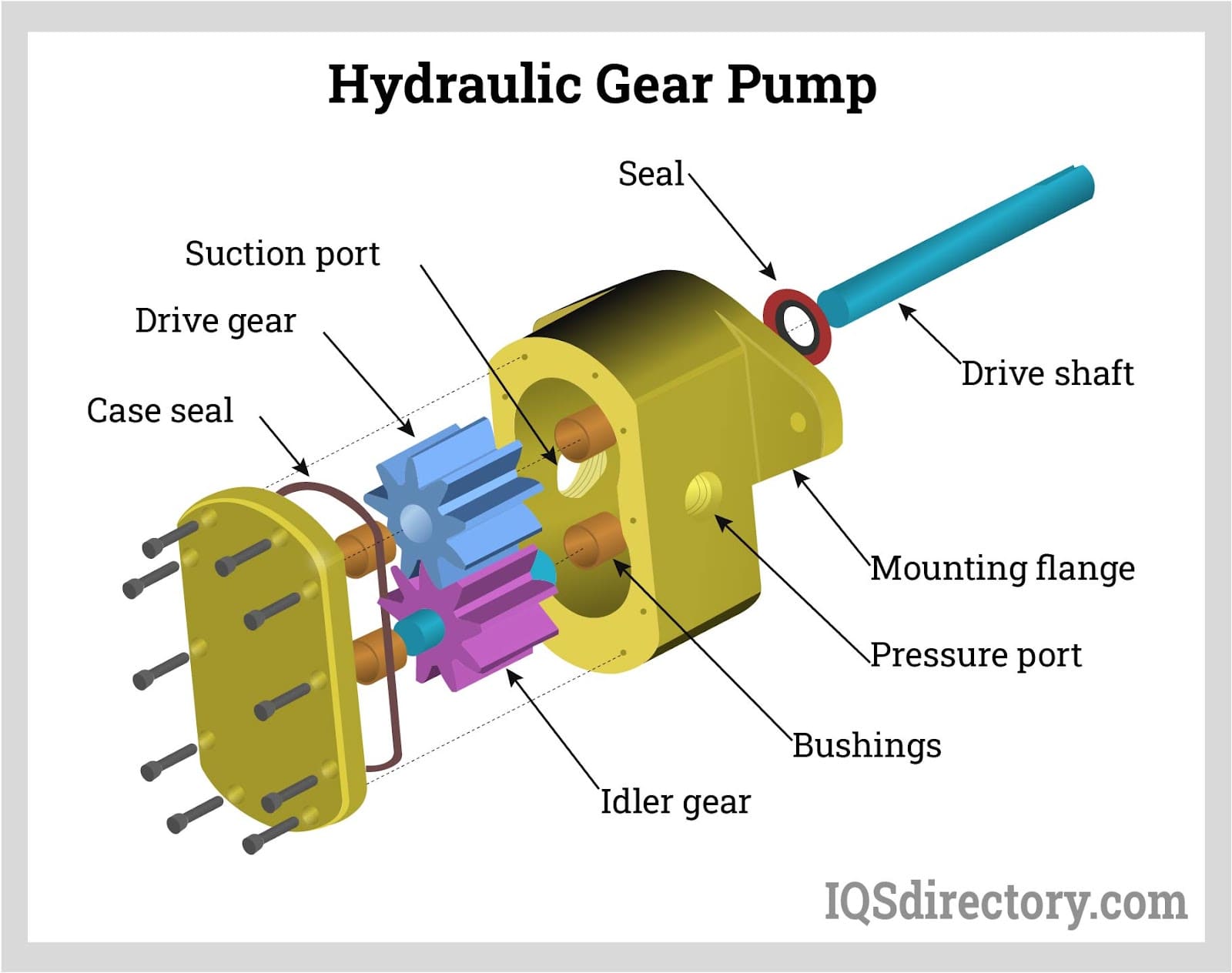
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in Hydraulic Pump Systems?
Aluminum is another popular choice for hydraulic pump diagrams, especially in applications where weight reduction is critical. It has a lower density than steel, which makes it easier to handle and install.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature allows for easier transport and installation. It also offers good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized or treated.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as durable as steel under extreme conditions. It may also be more expensive than steel, depending on the market.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for hydraulic fluids but may not be ideal for high-temperature applications due to its lower melting point compared to steel.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet relevant international standards. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, understanding the thermal properties of aluminum in specific applications is crucial.
How Do Plastics Compare in Hydraulic Pump Applications?
Plastics, particularly engineered thermoplastics, are increasingly being used in hydraulic pump diagrams due to their versatility and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for various hydraulic fluids. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastics is their lower strength compared to metals, which may restrict their use in high-pressure applications. They can also be more sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Impact on Application: Plastics are generally compatible with a wide range of fluids, but it is essential to choose the right type of plastic to avoid degradation over time.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastics comply with local regulations and standards, especially in regions with stringent safety requirements. Understanding the specific chemical compatibility of plastics with hydraulic fluids is also vital.
What Role Do Composites Play in Hydraulic Pump Design?
Composite materials combine the best properties of metals and plastics, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Cons: The manufacturing complexity of composites can lead to higher costs, and they may not be as widely available as traditional materials.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
Impact on Application: Composites can be tailored for specific media compatibility, making them versatile in various hydraulic applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should investigate the availability and cost of composite materials in their regions. Compliance with international standards is also critical, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Pump Diagrams
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic pump diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty hydraulic pumps | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight hydraulic systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Plastic | Low-pressure hydraulic applications | Lightweight and versatile | Lower strength and temperature sensitivity | Low |
| Composite | Specialized hydraulic applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for hydraulic pump diagrams, ensuring they can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic pump diagram
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Hydraulic Pumps?
The manufacturing process for hydraulic pumps involves several key stages, each essential for ensuring the performance and reliability of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
The first step in hydraulic pump manufacturing is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include high-grade steels, aluminum alloys, and composite materials, chosen for their strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. The preparation process involves cutting, machining, and sometimes heat treating the materials to achieve desired physical properties. This stage is crucial, as the quality of the raw materials directly influences the pump’s efficiency and durability.
How Are Hydraulic Pump Components Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which involves shaping the components using various techniques such as casting, forging, and machining.
- Casting: This method is often used for complex shapes and large components, where molten metal is poured into molds.
- Forging: This technique enhances material strength and is often applied to critical components like housings and shafts.
- Machining: Precision machining is essential for achieving tight tolerances, especially for components like gears and valves that require high accuracy for proper functioning.
These techniques ensure that each component meets the necessary specifications for pressure, flow, and durability.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve for Hydraulic Pumps?
After forming, components undergo assembly, which is a critical phase where individual parts are put together to create the hydraulic pump. This process may involve:
- Joining: Techniques such as welding, bolting, or adhesives are used to join components securely.
- Integration: Components such as motors, valves, and control systems are integrated into the assembly.
- Alignment: Proper alignment is crucial for operational efficiency, and this is often achieved using precision tools and fixtures.
Quality control is essential during this stage to ensure that the assembly meets design specifications and functions correctly.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Hydraulic Pumps?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and aesthetics of hydraulic pumps. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing or coating are applied to improve corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
- Polishing: This step ensures that surfaces are smooth, reducing friction and improving the efficiency of moving parts.
- Testing and Inspection: Final inspections and testing are conducted to ensure that the pump meets all operational and safety standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Hydraulic Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that hydraulic pumps meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 serve as a framework for quality management systems across various industries, including hydraulic pump manufacturing. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that manufacturers have established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) further enhance product credibility. These certifications indicate that products have been tested for safety and performance, making them more appealing to international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, components are monitored for adherence to specifications. This may involve dimensional checks and performance tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed hydraulic pumps undergo comprehensive testing, including pressure tests and performance evaluations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Testing methods vary based on the type of hydraulic pump being manufactured, but common techniques include:
- Pressure Testing: Pumps are subjected to pressures higher than their operational limits to ensure they can withstand extreme conditions.
- Flow Testing: This evaluates the pump’s flow rate and efficiency under various load conditions.
- Vibration Testing: Ensures that the pump operates smoothly without excessive vibrations, which can indicate imbalances or defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for ensuring product reliability.
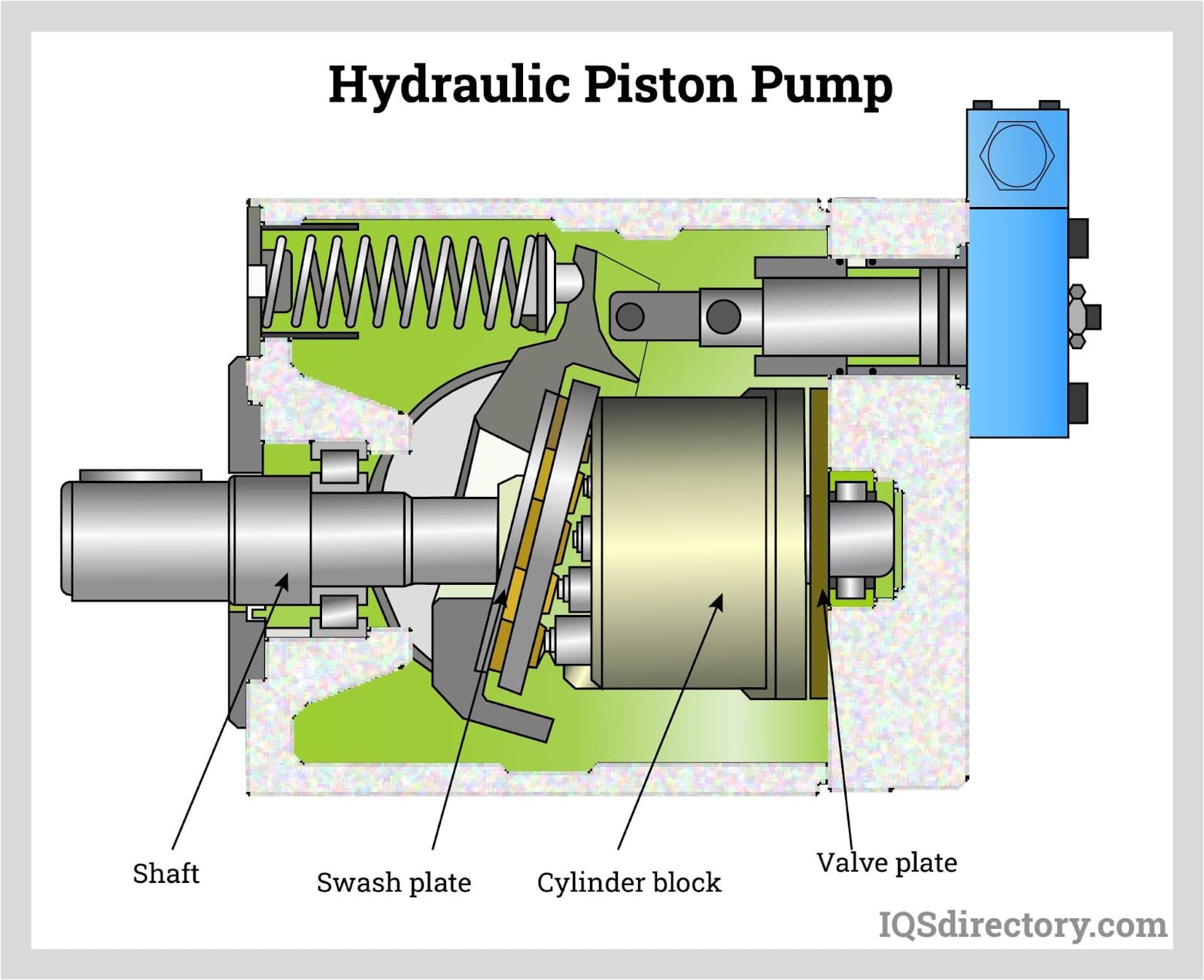
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Verify Supplier Quality?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place. This firsthand observation can reveal a lot about a supplier’s operational integrity.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control measures, including testing results and compliance with international standards, provides transparency into the supplier’s processes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, including:
- Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations, which can affect product compliance. For example, European buyers should be particularly aware of CE marking requirements.
- Language Barriers: Communication can pose challenges, so it is advisable to have clear documentation and, if necessary, translators during discussions.
- Cultural Differences: Recognizing and respecting cultural differences can enhance negotiations and foster better supplier relationships.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for hydraulic pumps is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on quality at every stage of production and utilizing effective verification methods, buyers can ensure they receive reliable and high-performance hydraulic pumps that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hydraulic pump diagram’
Introduction
Procuring hydraulic pump diagrams is essential for businesses aiming to understand and optimize their hydraulic systems. This guide outlines a systematic approach to sourcing these diagrams, ensuring that B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements for the hydraulic pump diagram. Consider factors such as the type of hydraulic system, components involved, and specific features needed, like directional control valves or safety mechanisms. This clarity helps suppliers provide tailored solutions that meet your operational needs.
2. Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers specializing in hydraulic pump diagrams. Look for companies with a strong track record in the industry and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize online platforms, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of potential partners who can fulfill your requirements.
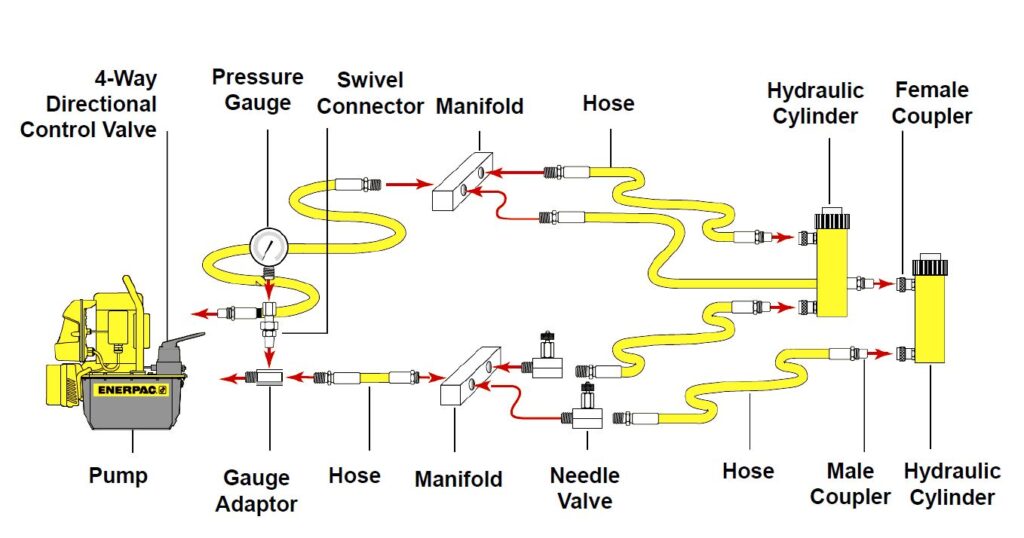
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
3. Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to ensure that suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Check for ISO certifications or other quality assurance credentials that signify adherence to best practices. Such certifications not only validate the supplier’s credibility but also ensure that the diagrams produced meet safety and operational standards.
4. Request Sample Diagrams
Before finalizing a supplier, request sample hydraulic pump diagrams to assess their quality and detail. Evaluate whether the diagrams are clear, accurate, and comply with industry standards. This step is vital to ensure that the diagrams will effectively aid in troubleshooting and maintaining your hydraulic systems.
5. Evaluate Technical Support and Documentation
Assess the level of technical support and accompanying documentation offered by the supplier. Reliable suppliers should provide user manuals, troubleshooting guides, and ongoing support for their diagrams. This additional information can be invaluable for training staff and ensuring the effective use of the hydraulic systems.
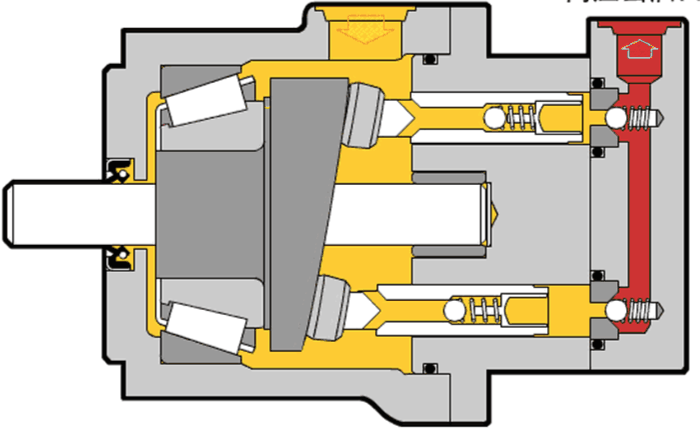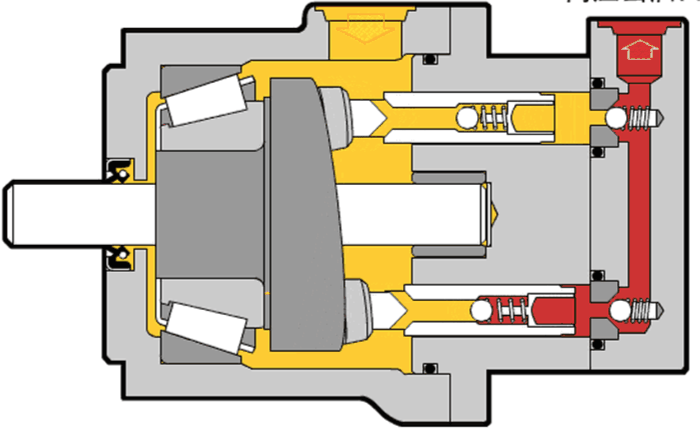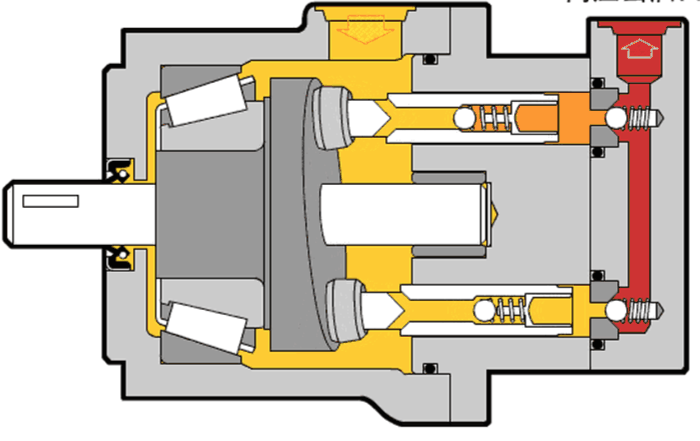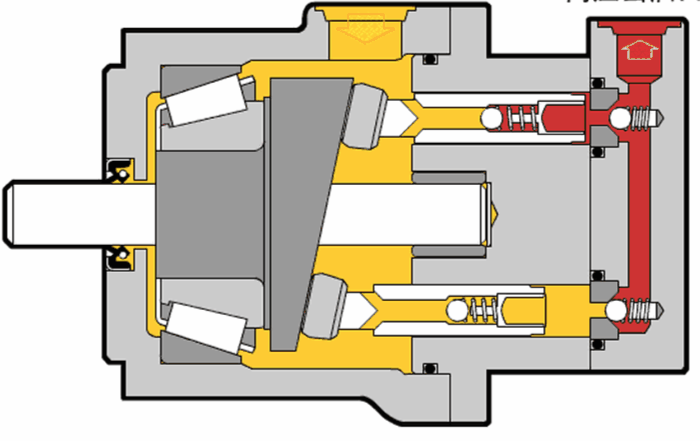
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
6. Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their pricing and terms of service. Look for transparency in pricing structures, including any potential additional costs for revisions or updates to diagrams. Make sure to consider the long-term value rather than just the initial cost, as investing in quality diagrams can lead to significant operational savings.
7. Finalize the Agreement with Clear Terms
After selecting a supplier, ensure that the agreement includes clear terms regarding deliverables, timelines, and payment structures. Establish a communication plan for regular updates and feedback during the diagram development process. A well-defined agreement minimizes misunderstandings and fosters a productive partnership.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source hydraulic pump diagrams that meet their specific needs, ultimately enhancing the performance and reliability of their hydraulic systems.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic pump diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Hydraulic Pump Diagrams?
When sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly influences the cost. High-quality hydraulic components, such as those made from durable metals or specialized polymers, may come at a premium but ensure longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are affected by the complexity of the hydraulic pump design and the expertise required. Skilled labor, particularly for custom designs or intricate systems, tends to be more expensive.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of non-production staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized hydraulic pump diagrams. This cost is typically amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability of hydraulic systems requires rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with testing and certification, particularly for products intended for critical applications, can be significant.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary greatly based on distance, shipping methods, and customs duties. These factors are particularly important for international buyers who need to factor in the complexities of global supply chains.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on market competition and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Hydraulic Pump Diagrams?
Several key factors influence pricing in the hydraulic pump diagram market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating for a lower MOQ can be beneficial for smaller operations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against the benefits it provides.
-
Materials: The selection of raw materials not only affects durability but also the overall cost. Suppliers often provide a range of options, and buyers should consider the long-term implications of their material choices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications may incur higher costs. However, these certifications can enhance marketability and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge more but offer greater assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale can greatly affect the total cost. Understanding whether costs are inclusive of shipping and duties (e.g., CIF vs. FOB) is critical for accurate budgeting.
What Buyer Tips Can Optimize Hydraulic Pump Diagram Sourcing?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Building relationships can often lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Sometimes, a higher initial investment can lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional market conditions that can affect pricing.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers. Assess their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and after-sales support to avoid hidden costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for hydraulic pump diagrams can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is crucial for buyers to obtain quotes tailored to their specific needs and circumstances, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of all associated costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hydraulic pump diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Hydraulic Pump Diagrams for Fluid Power Systems
In the realm of fluid power systems, hydraulic pump diagrams serve as a critical tool for understanding and troubleshooting hydraulic systems. However, there are alternative solutions and methodologies that can also achieve similar objectives. This section explores viable alternatives, providing a comprehensive comparison to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Hydraulic Pump Diagram | Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) | 3D CAD Modeling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High | High | Very High |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to High | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively Easy | Moderate | Complex |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | High |
| Best Use Case | Basic troubleshooting | Complex system design and operation | Detailed visualization and simulation |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs)?
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs) are widely used in industrial settings to illustrate the relationship between various components in a system, including piping, valves, and instrumentation.
Pros: P&IDs provide a comprehensive view of the entire system, allowing for better understanding and communication among engineers and technicians. They are essential for regulatory compliance and safety audits.
Cons: While P&IDs are beneficial for complex systems, they can be more challenging to create and interpret than hydraulic pump diagrams. The initial setup cost may also be higher due to the need for specialized software and training.
How Do 3D CAD Models Compare as an Alternative?
3D CAD modeling offers a modern approach to visualizing hydraulic systems, enabling detailed representations that can be manipulated in a virtual space.
Pros: The primary advantage of 3D CAD models is their ability to provide an interactive experience, allowing users to visualize and simulate the hydraulic systems dynamically. This can facilitate better design decisions and troubleshooting.
Cons: However, 3D CAD modeling is typically more expensive and requires specialized skills and software. Additionally, the complexity of creating accurate models can lead to longer implementation times compared to simpler diagrams.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between hydraulic pump diagrams and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects. For basic troubleshooting and straightforward systems, hydraulic pump diagrams remain effective and cost-efficient. Conversely, for more complex operations requiring extensive detail and compliance, P&IDs or 3D CAD models may be more appropriate despite their higher costs and complexity. Ultimately, understanding the specific use case and operational needs will guide buyers toward the most effective solution for their hydraulic system designs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic pump diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Pump Diagrams?
Understanding the technical specifications of hydraulic pump diagrams is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting components that will perform reliably in various industrial applications. Here are some essential technical properties:
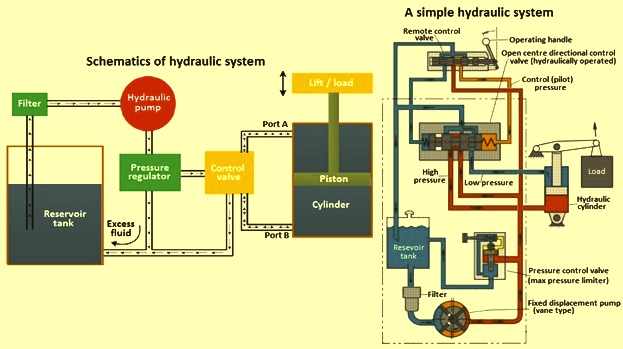
Illustrative image related to hydraulic pump diagram
-
Material Grade
The material used in hydraulic pumps and components typically includes various grades of steel, aluminum, or composite materials. The material grade affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For instance, high-grade steel may be preferred for heavy-duty applications, while lighter materials might be more suitable for portable machinery. Selecting the right material is vital for ensuring longevity and minimizing maintenance costs. -
Flow Rate (GPM or LPM)
Flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), indicates how much fluid a hydraulic pump can move within a specific timeframe. This property is critical for determining the efficiency of the hydraulic system and ensuring it meets the operational demands of machinery. B2B buyers must evaluate flow rates to ensure compatibility with existing systems and to achieve desired performance outcomes. -
Pressure Rating (PSI or Bar)
The pressure rating signifies the maximum pressure the hydraulic pump can handle, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. This specification is crucial for safety and operational efficiency. A pump operating beyond its pressure rating can lead to catastrophic failures, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. Understanding pressure ratings helps buyers select pumps that align with their application’s pressure requirements. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and specifications of hydraulic components. Precise tolerances are essential for ensuring proper fit and function, especially in systems where multiple components interact closely. Poor tolerance can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, and increased wear. For B2B buyers, specifying the correct tolerances can significantly affect the performance and reliability of hydraulic systems. -
Operating Temperature Range
Hydraulic systems often operate under varying temperatures, which can affect fluid viscosity and system performance. Knowing the operating temperature range of a hydraulic pump helps buyers ensure that the components chosen can withstand the thermal conditions of their environment. This property is especially important in regions with extreme temperatures, as it directly influences the longevity and efficiency of the hydraulic system.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Hydraulic Pump Procurement?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement of hydraulic pumps. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For hydraulic pumps, working with OEMs ensures that the components are designed to fit specific machinery and meet quality standards. Buyers often prefer OEM parts for reliability and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and minimize costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing needs while ensuring they do not overstock or understock critical components. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ allows B2B buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. It is a critical step in ensuring competitive pricing and securing the best possible terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to comprehend shipping costs, risks, and obligations. Clear knowledge of Incoterms can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smoother transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. It is a crucial consideration for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where timely delivery is essential for maintaining production schedules. Being aware of lead times helps buyers plan their operations and manage expectations effectively.
By understanding these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring hydraulic pumps and components, ultimately contributing to the efficiency and reliability of their hydraulic systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hydraulic pump diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting the Hydraulic Pump Diagram Sector?
The hydraulic pump diagram sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by several global factors. As industries increasingly prioritize automation and efficiency, the demand for sophisticated hydraulic systems is surging. Key trends include the rise of digital twin technology, which allows for real-time monitoring and simulation of hydraulic systems, enabling better maintenance and performance optimization. Additionally, the shift towards Industry 4.0 has prompted manufacturers to invest in IoT-enabled hydraulic components, enhancing connectivity and data analytics capabilities.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer customized solutions to meet their specific operational needs. For instance, Brazil and Nigeria are witnessing significant infrastructure development, necessitating reliable hydraulic systems for construction and agriculture. Moreover, sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration, with buyers preferring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to eco-friendly practices and materials.
Emerging markets are also showing a growing preference for modular hydraulic systems that allow for easier upgrades and maintenance, thus reducing downtime. As competition intensifies, suppliers who can offer comprehensive support, including training and troubleshooting based on hydraulic pump diagrams, will likely secure a competitive advantage.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Hydraulic Pump Diagram Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the hydraulic pump diagram sector, as environmental awareness grows among consumers and businesses alike. The hydraulic systems industry is under pressure to minimize its environmental impact, prompting manufacturers to adopt greener practices. This includes using biodegradable hydraulic fluids and ensuring that components are recyclable at the end of their life cycle.
For B2B buyers, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Suppliers that demonstrate transparency and social responsibility not only enhance their brand reputation but also build trust with clients. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the Responsible Business Alliance standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices.
Moreover, the demand for “green” hydraulic pump diagrams that incorporate eco-friendly materials is on the rise. Buyers are increasingly looking for components that meet stringent environmental regulations, which can often lead to reduced operational costs in the long run. This shift towards sustainability not only aligns with global trends but also provides an opportunity for B2B buyers to differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
How Has the Hydraulic Pump Diagram Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of hydraulic pump diagrams reflects significant advancements in technology and engineering practices. Historically, hydraulic systems relied heavily on manual calculations and basic schematics, which often led to inefficiencies and operational risks. As technology progressed, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) revolutionized the way hydraulic diagrams are created and utilized, allowing for greater precision and adaptability.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies such as 3D modeling and simulation software has further enhanced the design and analysis of hydraulic systems. These tools enable engineers to visualize complex interactions within systems, leading to improved troubleshooting and maintenance strategies. Furthermore, the adoption of standardized symbols and notations in hydraulic pump diagrams has facilitated clearer communication among engineers and technicians across diverse industries.
This historical progression underscores the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements for B2B buyers. As the hydraulic pump diagram sector continues to innovate, understanding these changes will be critical for making informed sourcing decisions and optimizing operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic pump diagram
-
How do I troubleshoot issues with hydraulic pump diagrams?
To troubleshoot issues effectively, start by reviewing the hydraulic pump diagram to understand the flow paths and component interrelationships. Check for any discrepancies between the diagram and the physical system, such as misrouted hoses or improperly installed components. Utilize diagnostic tools like pressure gauges and flow meters to assess performance against the expected outputs indicated in the diagram. Regular maintenance and familiarity with the system will also help in identifying and resolving potential issues promptly. -
What is the best hydraulic pump diagram for a specific application?
The best hydraulic pump diagram depends on your specific application requirements, such as flow rate, pressure, and type of actuation. For instance, a front-end loader may require a diagram showcasing a PTO-driven pump with a 2-spool directional control valve, while a winch might necessitate a design focusing on hydraulic motors and flow control. Consult with suppliers to ensure the diagram aligns with your operational needs, and consider customizing it to optimize efficiency and functionality for your particular machinery. -
What should I consider when sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams from international suppliers?
When sourcing hydraulic pump diagrams internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, expertise, and familiarity with local regulations. Verify their compliance with international standards, such as ANSI or ISO, to ensure quality and reliability. Assess their ability to provide customization options and support for local conditions, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. Additionally, inquire about their experience in shipping logistics and any potential tariffs or trade barriers that may affect delivery timelines. -
What are common customization options for hydraulic pump diagrams?
Customization options for hydraulic pump diagrams often include modifications in flow paths, component specifications, and integration with existing systems. Buyers can request diagrams that reflect specific requirements such as pressure ratings, tank sizes, and control mechanisms tailored to their operational needs. It’s advisable to communicate clearly with suppliers about your unique requirements and expectations to ensure the final diagram accurately represents the intended design and functionality. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when purchasing hydraulic pump diagrams?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for hydraulic pump diagrams can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the diagrams. Some suppliers may offer individual diagrams with no MOQ, while others may require bulk orders if they are providing a complete set of documentation for a larger project. Always clarify MOQs before placing an order, and consider negotiating terms that align with your purchasing capabilities and project timelines. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of hydraulic pump diagrams?
Payment terms for hydraulic pump diagrams can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established businesses or bulk orders. It’s essential to discuss payment terms upfront and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the implications of currency fluctuations when dealing with international suppliers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for hydraulic pump diagrams?
To ensure quality assurance for hydraulic pump diagrams, request samples or previous work portfolios from potential suppliers to gauge their expertise and attention to detail. Establish clear specifications and standards that the diagrams must meet, and inquire about the supplier’s QA processes, including testing and validation methods. Regular communication during the production phase can also help identify any issues early on, ensuring that the final product meets your expectations and operational requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when ordering hydraulic pump diagrams from abroad?
When ordering hydraulic pump diagrams from abroad, logistics considerations include shipping methods, delivery timelines, and customs regulations. Determine the most efficient shipping option that balances cost and speed, and be aware of any potential delays due to customs clearance processes. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes that may apply to your order. Maintaining open communication with your supplier regarding shipping updates can help mitigate any logistical challenges that may arise.
Top 4 Hydraulic Pump Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cross Manufacturing – Hydraulic Cylinders & Valves
Domain: crossmfg.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Hydraulics Cylinders, Valves, Gear Pumps & Motors, Accumulators, Filters, Custom Products, Custom Hydraulic Cylinders, Custom Hydraulic Fittings and Manifolds. Applications include Agriculture, Construction, and Mobile/Light Industrial. Key components include a 2-spool directional control valve with built-in relief for loaders, hydraulic motors for winches, and directional control valves with opti…
2. SKS HYDRAULIC TECHNOLOGY – Hydraulic Pumps & Actuators
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Pump Technical Drawing; Self Actuated Valve; Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators; Fluoroplastic Centrifugal Pump; SKS HYDRAULIC TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.; K5V200 Hydraulic Pump; K5V200DTH Hydraulic Pump; Payment Methods: T/T, Western Union, Paypal; Delivery: DHL, UPS, TNT, Fedex, or By sea; Hydraulic System Technical Manual; Water Pump Technical Specifications; Hydraulic Pump Spare Parts; Commer…
3. Hidraoil – Hydraulic Products
Domain: hidraoil.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Hidraoil Fluid Power offers a range of hydraulic products including hydraulic pumps, hydraulic motors, hydraulic systems, hydraulic valves, actuators, accessories, and OEM spare parts. The company provides technical resources such as hydraulic symbols, fluid circuit diagrams, and detailed information on various hydraulic components including unidirectional and bidirectional fixed and variable disp…
4. Hydraulic Supermarket – Load Sensing Pump Schematic
Domain: hydraulicsupermarket.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic pump schematic diagram for load sensing and pressure limiting control; includes a variant with power limiter for hydraulic power unit.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic pump diagram
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers in Hydraulic Pump Sourcing?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of hydraulic pump diagrams is pivotal for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring long-term success. By understanding the intricate relationships among system components, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance performance while minimizing costs. Emphasizing quality and compatibility when selecting hydraulic pumps and associated components will not only mitigate risks but also improve system reliability.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Strategic Sourcing?
For international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing can unlock significant advantages in procurement processes. Engaging with reputable suppliers and leveraging detailed hydraulic pump diagrams will empower businesses to troubleshoot effectively and maintain robust systems.
What Are the Next Steps for Buyers in the Hydraulic Pump Market?
As you look ahead, consider deepening your partnerships with established manufacturers and suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet your specific needs. Invest in training and resources that enhance your team’s understanding of hydraulic systems to further capitalize on these insights. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you position your business for growth and resilience in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.