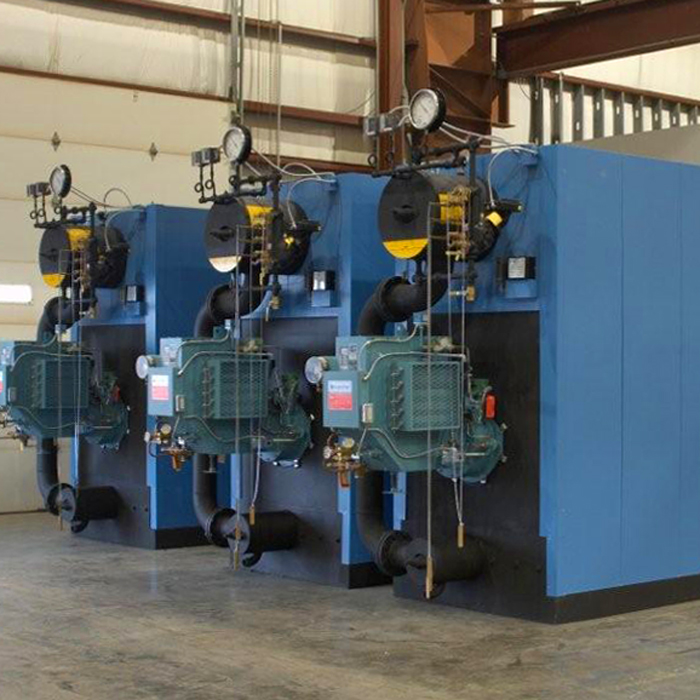
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the High Pressure Boilers Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high pressure boilers
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing high-pressure boilers presents unique challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These industrial systems are critical for various applications, from energy generation to manufacturing processes, and navigating the complexities of procurement can be daunting. Factors such as compliance with local regulations, technological advancements, and supplier reliability are pivotal in making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of high-pressure boilers, covering essential aspects such as types, operational efficiencies, maintenance requirements, and the latest innovations in combustion technology. Buyers will gain insights into the diverse applications of high-pressure boilers, including their role in enhancing operational efficiency and meeting stringent environmental standards.
Moreover, we provide practical strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and assessing the total cost of ownership. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and best practices, this guide empowers them to make strategic decisions that enhance productivity and ensure compliance with industry standards. Whether you’re in Vietnam, Saudi Arabia, or any other global market, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for successful procurement of high-pressure boilers tailored to your specific operational needs.
Understanding high pressure boilers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Tube Boilers | Water circulates in tubes heated by combustion gases; high efficiency. | Power generation, chemical processing, food production. | Pros: Efficient heat transfer, high pressure capacity. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex maintenance. |
| Fire Tube Boilers | Hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water; simpler design. | Heating, food processing, and general industrial use. | Pros: Lower upfront cost, easier to operate. Cons: Limited steam output at high pressures. |
| Electric Boilers | Use electric elements for heating; no combustion emissions. | Hospitals, schools, and facilities with limited space. | Pros: Environmentally friendly, compact design. Cons: Higher operational costs, limited capacity for large-scale applications. |
| Biomass Boilers | Utilize organic materials for fuel; renewable energy source. | Agriculture, food processing, and sustainable industries. | Pros: Eco-friendly, reduces carbon footprint. Cons: Variable fuel supply, higher maintenance needs. |
| Modular Boilers | Composed of several smaller units; scalable and flexible. | Temporary heating solutions, industrial applications. | Pros: Quick installation, adaptable to changing needs. Cons: Potentially higher cost per unit, requires careful management. |
What Are Water Tube Boilers and Their Key Benefits for B2B Buyers?
Water tube boilers are recognized for their efficient heat transfer and ability to generate high-pressure steam. In these systems, water circulates through tubes that are heated by combustion gases, allowing for rapid steam production. This design is particularly suitable for power generation and industries requiring consistent steam supply, such as chemical processing and food production. Buyers should consider initial costs and the complexity of maintenance, as water tube boilers typically require skilled personnel for operation.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
How Do Fire Tube Boilers Compare in Terms of Applications and Costs?
Fire tube boilers are characterized by hot gases passing through tubes surrounded by water. They are simpler in design, making them easier to operate and maintain. These boilers are commonly used in heating applications, food processing, and various industrial settings. While they present a lower upfront cost, they may not be as efficient at producing high-pressure steam compared to water tube options. Buyers should weigh the operational needs against the steam output requirements when considering fire tube boilers.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Boilers for Specific Industries?
Electric boilers utilize electric heating elements, producing steam without combustion emissions. Their compact design makes them ideal for facilities with limited space, such as hospitals and educational institutions. While they are environmentally friendly and easy to operate, buyers must consider the higher operational costs, especially for large-scale applications. Additionally, electric boilers may not be the best fit for industries requiring extensive steam production.
How Do Biomass Boilers Contribute to Sustainability in B2B Operations?
Biomass boilers use organic materials as fuel, making them a renewable energy source. They are particularly beneficial for industries like agriculture and food processing, where sustainability is a priority. While they significantly reduce carbon footprints, buyers should be aware of the variability in fuel supply and the potential for increased maintenance needs. These factors can impact the overall cost-effectiveness of biomass boilers in the long term.
What Are Modular Boilers and Their Unique Selling Points for Buyers?
Modular boilers consist of several smaller units, offering scalability and flexibility for various applications. They are ideal for temporary heating solutions and can adapt to changing industrial needs. While modular systems allow for quick installation and customization, buyers should consider the potentially higher cost per unit and the need for careful management to optimize performance.
Key Industrial Applications of high pressure boilers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of High Pressure Boilers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Steam generation for cooking, sterilization, and drying processes | Ensures consistent product quality and safety standards | Compliance with food safety regulations and energy efficiency |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Providing heat for chemical reactions and process heating | Increases production efficiency and reduces operational costs | Material compatibility and safety features in high-pressure systems |
| Textile Industry | Dyeing and finishing processes requiring high-temperature steam | Improves fabric quality and reduces processing time | Availability of quick-start capabilities and reliability |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization and cleaning processes in drug manufacturing | Ensures compliance with stringent health regulations | Certifications and adherence to industry standards |
| Power Generation | Steam generation for turbines in electric power plants | Enhances energy output and operational efficiency | Consideration of fuel types and emissions control technologies |
How Are High Pressure Boilers Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, high pressure boilers are crucial for generating steam used in cooking, sterilization, and drying processes. The consistent and high-quality steam produced ensures that food products meet safety standards and maintain flavor integrity. International buyers must consider sourcing boilers that comply with local food safety regulations and are energy-efficient to reduce operational costs, particularly in regions like Africa and South America where energy prices can be volatile.
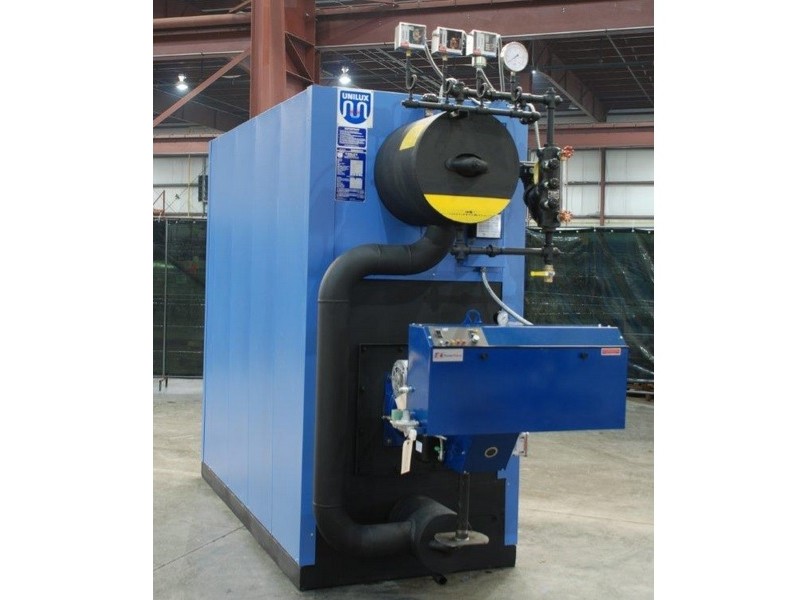

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
What Role Do High Pressure Boilers Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
High pressure boilers are employed in chemical manufacturing to provide the necessary heat for various chemical reactions and process heating. This application is vital for enhancing production efficiency, as it allows for faster reaction times and improved energy transfer. Buyers in this sector should focus on the compatibility of boiler materials with specific chemicals and the safety features of the systems to handle high-pressure environments, particularly in the Middle East where chemical production is a key industry.
Why Are High Pressure Boilers Important for the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, high pressure boilers facilitate dyeing and finishing processes that require high-temperature steam. This application leads to better fabric quality and significantly reduces processing time, allowing manufacturers to meet demand more effectively. B2B buyers should prioritize boilers that offer rapid start-up capabilities and reliability, especially in European markets where production timelines are often tight.
How Are High Pressure Boilers Used in Pharmaceuticals?
High pressure boilers are integral to sterilization and cleaning processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The steam generated must meet stringent health regulations to ensure product safety and efficacy. Buyers in this industry should seek boilers that are certified and adhere to industry standards, particularly in regions like South America and Europe where regulatory compliance is heavily monitored.
What Is the Role of High Pressure Boilers in Power Generation?
In power generation, high pressure boilers are essential for steam generation that drives turbines in electric power plants. This application enhances energy output and operational efficiency, making it a key component in energy production. Buyers must consider the type of fuel used and the emissions control technologies available to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, which is particularly relevant in developing regions seeking sustainable energy solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high pressure boilers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Steam Pressure Affecting Production Quality
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with high pressure boilers when the steam pressure fluctuates unexpectedly. This inconsistency can lead to production bottlenecks, reduced efficiency, and compromised product quality, particularly in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where precise conditions are critical. For example, a manufacturer may find that their high pressure steam boiler fails to maintain the necessary pressure for cooking or sterilization processes, resulting in undercooked products or ineffective sterilization, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
The Solution: To mitigate issues with inconsistent steam pressure, it is essential to invest in high-quality boiler controls and instrumentation. Implementing advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time data on pressure levels can help operators respond quickly to fluctuations. Additionally, consider selecting boilers that feature low water content designs, which allow for rapid adjustments and more stable pressure maintenance. Regular maintenance checks and investing in a skilled boiler operator training program can further enhance operational efficiency. By ensuring that your team is knowledgeable about troubleshooting common issues and understanding the boiler’s control systems, you can significantly reduce the risk of pressure inconsistencies.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Boiler Systems
The Problem: Many businesses utilizing high pressure boilers experience high operational costs, primarily stemming from inefficient fuel usage and maintenance. This is particularly problematic for companies in regions with rising energy costs or strict environmental regulations. For instance, a textile manufacturer may find that their outdated boiler technology leads to excessive fuel consumption, making it increasingly difficult to maintain profit margins while adhering to environmental standards.
The Solution: Transitioning to modern, high-efficiency high pressure boilers can yield significant savings. Look for units that are designed for low NOx emissions and have advanced combustion technology to optimize fuel usage. Additionally, consider the implementation of boiler rental services during peak operational times or when transitioning to new equipment. This approach allows for flexibility without the burden of permanent investments in outdated systems. Conducting a thorough analysis of your current boiler’s performance and collaborating with a reputable manufacturer or supplier to identify the best solutions tailored to your operational needs will help reduce costs and improve environmental compliance.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Safety Concerns
The Problem: Navigating regulatory compliance for high pressure boilers can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially in regions with stringent safety and environmental regulations. Companies may struggle with ensuring that their equipment meets local codes, which can lead to costly penalties or operational shutdowns. For example, a chemical processing facility might find itself in violation of emissions standards due to outdated boiler technology that does not meet current regulations, risking both financial loss and damage to its reputation.
The Solution: To ensure compliance, it is crucial to partner with manufacturers who prioritize safety and regulatory standards in their designs. Invest in high pressure boilers that are equipped with the latest safety features, such as automatic shut-off valves and pressure relief systems. Regular training for your staff on compliance regulations and safety protocols is also vital. Conducting regular audits and maintenance checks can help identify potential compliance issues before they escalate. Furthermore, staying informed about changes in regulations by subscribing to industry publications or joining relevant associations can provide timely insights that help your business remain compliant and avoid penalties.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high pressure boilers
What Are the Key Materials Used in High Pressure Boilers?
High pressure boilers require materials that can withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and pressures, while also being resistant to corrosion and wear. Here, we analyze four common materials used in high pressure boiler construction, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and toughness. It can withstand temperatures up to 450°C (842°F) and pressures exceeding 20 bar.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for high pressure applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance, which can lead to premature failure in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for water and steam applications but may not be ideal for corrosive media without additional protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A106 or DIN 17175. The availability of carbon steel can vary by region, impacting lead times and costs.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
2. Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steels, particularly those containing chromium and molybdenum, offer enhanced strength and corrosion resistance. They can operate at temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F) and pressures of 40 bar or more.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of alloy steel is its ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and requires more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Alloy steels are ideal for applications involving high-temperature steam and corrosive environments, making them suitable for industries such as petrochemical and power generation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM A335 and JIS G3461 is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of alloy steel in their region, as it may not be as widely stocked as carbon steel.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C or 1472°F) and pressures (up to 50 bar).

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Pros & Cons: Its durability and low maintenance requirements make stainless steel an attractive choice for high pressure boilers. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon and alloy steels, which can impact project budgets.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suited for applications involving water treatment and steam generation in corrosive environments, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 and EN 10216. The cost implications of stainless steel may necessitate careful budgeting and planning.
4. Copper-Nickel Alloys
Key Properties: Copper-nickel alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in seawater and other harsh environments. They can handle temperatures up to 300°C (572°F) and moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is their superior resistance to corrosion and biofouling, making them ideal for marine applications. However, they are more expensive and less commonly used in high pressure boiler applications compared to other materials.
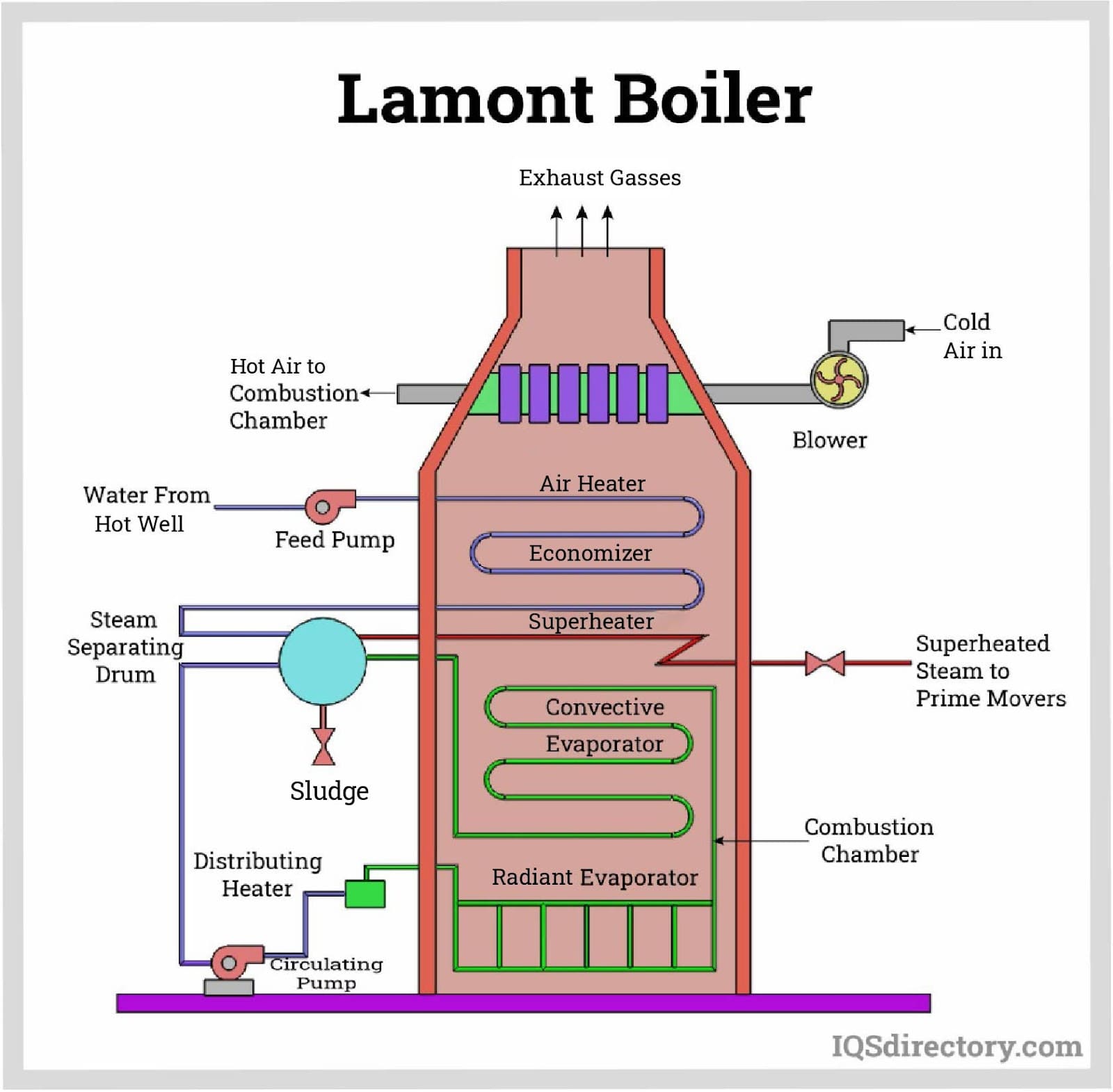
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Impact on Application: These alloys are particularly effective in applications where seawater or other corrosive fluids are present, such as in offshore platforms.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with ASTM B171 and similar standards. The availability of copper-nickel alloys can vary significantly by region, which may affect procurement strategies.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for high pressure boilers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General steam and water applications | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Alloy Steel | High-temperature and pressure applications | Enhanced strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments like food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost | High |
| Copper-Nickel Alloys | Marine and harsh environments | Superior corrosion resistance | More expensive and less common | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the materials commonly used in high pressure boilers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high pressure boilers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Pressure Boilers?
The manufacturing process of high pressure boilers is intricate and requires precision at every stage to ensure efficiency, safety, and compliance with international standards. The key stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
How is Material Prepared for High Pressure Boilers?
The first step in manufacturing high pressure boilers involves selecting high-grade materials that can withstand extreme pressure and temperature. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, which are chosen for their strength and durability.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a rigorous quality check to ensure they meet specified standards. Material testing often includes chemical composition analysis and mechanical property tests, which verify that the materials can withstand high pressures and temperatures.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in High Pressure Boiler Manufacturing?
Forming is the next crucial stage, where the raw materials are shaped into the required components. This process can involve several techniques such as:
- Hot and Cold Rolling: Used to create sheets and plates from bulk material.
- Bending and Forming: Essential for shaping tubes and other structural components.
- Welding: A critical technique for joining various components together. High-quality welding is vital, as weld integrity directly impacts the boiler’s performance under pressure.
Advanced technologies such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining may also be employed to ensure precision and reduce waste, enhancing the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
How Are High Pressure Boilers Assembled?
The assembly stage involves putting together all the formed components, including the boiler shell, heat exchanger tubes, and combustion systems. This phase requires skilled technicians who follow strict engineering guidelines to ensure that every part is correctly positioned and securely attached.
Quality assurance is integrated into this stage through thorough inspections. Each assembly line may include checkpoints where components are tested for fit and function before moving on to the next stage. This approach minimizes the risk of defects and ensures that the final product meets performance specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to High Pressure Boilers?
Once assembled, high pressure boilers undergo finishing processes that enhance their durability and efficiency. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like shot blasting or sandblasting are used to prepare surfaces for coating, which protects against corrosion.
- Coating: High-quality protective coatings are applied to enhance the boiler’s lifespan and efficiency.
- Final Inspection: Before shipping, each boiler undergoes a comprehensive inspection, ensuring that it meets all design specifications and quality standards.
What Are the International Standards for Quality Assurance in High Pressure Boilers?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of high pressure boilers, particularly for B2B buyers operating in international markets. Compliance with recognized standards not only assures product quality but also builds trust with clients.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Key international standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards specifically for the oil and gas industry, which are critical for boilers used in these sectors.
These standards guide manufacturers in implementing effective quality control systems and processes, thus ensuring the reliability of their products.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Critical in High Pressure Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality control in the manufacturing of high pressure boilers is a multi-tiered process involving several checkpoints, each designed to catch potential issues before they escalate.
What Are the Main Quality Control Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint assesses raw materials as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Rigorous testing ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections are conducted at different stages. This can include checking the accuracy of machining processes, the integrity of welds, and the overall assembly quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the boiler is dispatched, a final inspection is conducted. This includes pressure testing, operational testing, and a thorough review of compliance with all applicable standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing high pressure boilers, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers.
What Actions Can Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier Quality?
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing practices. Buyers can request to observe the manufacturing process and quality control measures in place.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation that outlines the quality control processes used by the supplier, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspectors to review the manufacturing process can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances that could affect their procurement process.
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Quality Control?
Different regions may have unique regulations and standards that impact the manufacturing and testing of high pressure boilers. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local regulations in their respective markets, which may involve additional certifications or testing.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Additionally, cultural factors can influence quality assurance practices. Understanding the local manufacturing landscape and establishing clear communication channels with suppliers will help mitigate risks and ensure that the desired quality standards are met.
By taking these factors into account, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing high pressure boilers, leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high pressure boilers’
Introduction
Sourcing high pressure boilers is a critical decision for any business requiring efficient steam generation. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, ensuring they select the right boiler for their operational needs while considering safety, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it is essential to clearly define the technical specifications of the high pressure boiler you require. Consider factors such as steam output capacity, pressure requirements, fuel type, and efficiency ratings. This ensures that you select a boiler that meets the specific demands of your industrial applications and complies with local regulations.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Step 2: Research and Understand Boiler Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of high pressure boilers available on the market, such as water tube and fire tube boilers. Each type has distinct advantages and operational characteristics. Understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions based on your operational requirements, including efficiency and space constraints.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold necessary certifications and adhere to industry standards. Look for certifications such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). These certifications ensure that the manufacturer meets safety and quality benchmarks, which is crucial for reliable operation and compliance with regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Solicit detailed proposals from shortlisted suppliers, including technical specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. Ensure that each proposal addresses your defined specifications and includes terms related to warranties and maintenance support. A comprehensive proposal allows for easier comparison and evaluation of the offerings.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
After-sales support is a crucial factor in the long-term performance of your boiler. Inquire about the availability of maintenance services, spare parts, and customer support. A supplier that offers robust after-sales service can significantly reduce downtime and operational disruptions, enhancing the overall value of your investment.
Step 6: Consider Environmental Impact and Efficiency
Evaluate the environmental performance and energy efficiency of the boilers you are considering. Look for features that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, such as low NOx burners or advanced combustion technologies. Selecting a boiler with a lower environmental impact not only meets regulatory requirements but can also improve your company’s sustainability profile.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Step 7: Check References and Case Studies
Before finalizing your choice, request references and case studies from the supplier. Speak to existing customers in similar industries to gain insights into their experiences regarding performance, reliability, and service quality. This feedback can provide invaluable information that may influence your decision and help mitigate risks associated with your purchase.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a systematic and informed approach to sourcing high pressure boilers, ultimately leading to a successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high pressure boilers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of High Pressure Boilers?
The cost structure for high pressure boilers consists of several critical components that contribute to the final pricing. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in high pressure boilers include steel, insulation, and various alloys designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The quality and source of these materials significantly affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the manufacturing and assembly of high pressure boilers. Labor costs vary by region, with countries that offer skilled labor at competitive rates often providing a cost advantage.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs low.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds are required for producing high pressure boilers. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, but it is amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are necessary to ensure that boilers meet safety standards and operational efficiency. These QC measures are crucial, especially in industries where boiler failure could have catastrophic consequences.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering boilers to international markets can vary significantly based on distance and transport mode. Understanding Incoterms is vital to managing these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a margin to cover their operational risks and profit expectations. This margin can fluctuate based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect High Pressure Boiler Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of high pressure boilers, making it essential for buyers to understand these variables:

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders generally reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider negotiating for better pricing based on their purchasing volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built boilers tailored to specific operational requirements can incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of materials and the certifications (e.g., ASME, ISO) can significantly influence pricing. Higher-quality materials and certifications usually come at a premium but ensure reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and financial stability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better warranties and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms determine who bears the costs and risks during shipping, which can affect the total landed cost of the boiler.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers of High Pressure Boilers?
When sourcing high pressure boilers, buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your organization anticipates a substantial order, use this to negotiate lower prices. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs when evaluating a boiler’s overall value. A slightly higher upfront cost may yield long-term savings.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide a benchmark for negotiation. It enables buyers to understand market rates and leverage this information to negotiate better terms.
-
Prioritize Quality and Compliance: While price is crucial, ensure that the selected boiler meets all regulatory requirements and quality standards. Compromising on quality to save costs can lead to expensive failures in the future.
-
Be Informed About Local Market Conditions: Understanding the economic landscape and supply chain dynamics in your region can provide insights into pricing trends and negotiation leverage.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing High Pressure Boilers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are additional considerations:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Currency volatility can impact the total cost of acquisition. It’s wise to negotiate prices in a stable currency to mitigate risks.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Be aware of any tariffs or taxes that may apply to importing high pressure boilers, as these can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Lead Times and Delivery Schedules: International shipping can result in longer lead times. Ensure that the supplier can meet your deadlines, especially if the boiler is critical to your operations.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is essential when negotiating with suppliers from different regions. Understanding cultural nuances can facilitate smoother negotiations.
Conclusion: What Are the Implications of Pricing Nuances for High Pressure Boilers?
While indicative prices for high pressure boilers can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors, understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers allows buyers to make informed decisions. By applying strategic negotiation tactics and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing process and achieve better value in their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high pressure boilers With Other Solutions
Understanding the Need for Alternatives to High Pressure Boilers
In the industrial landscape, high pressure boilers serve a vital role in generating steam for various processes. However, as businesses seek more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solutions, it is essential to consider alternatives that may offer similar benefits. This analysis compares high pressure boilers with other viable solutions, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table of High Pressure Boilers and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | High Pressure Boilers | Low Pressure Boilers | Electric Boilers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High steam output, suitable for large-scale operations | Lower steam output, ideal for smaller applications | Instant heat, precise temperature control |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, but long-term savings through efficiency | Lower upfront costs, but potentially higher operational costs | Moderate initial costs, depending on capacity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and regulatory compliance | Simpler to install and operate, fewer regulations | Easy installation, minimal space requirements |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and maintenance due to high pressures | Generally lower maintenance requirements | Minimal maintenance, as fewer moving parts are involved |
| Best Use Case | Industrial processes needing high energy transfer | Small-scale heating for buildings and facilities | Situations where energy efficiency and space are critical |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Low Pressure Boilers
Low pressure boilers operate at pressures below 15 psi, making them suitable for applications that do not require the high energy output of their high-pressure counterparts. The primary advantage of low pressure boilers is their lower operational costs, as they consume less energy and require less rigorous maintenance. However, they are limited in their output capacity, making them less suitable for large industrial applications that demand high steam production.
Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are another alternative, utilizing electricity to generate steam or hot water. They offer precise temperature control and are particularly beneficial in settings where space is at a premium. Their installation is generally straightforward, and they require minimal maintenance due to fewer mechanical components. However, they may have higher operational costs depending on local electricity rates and can be less efficient in large-scale applications compared to high pressure boilers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a boiler solution, B2B buyers must consider factors such as the scale of operations, energy efficiency, and specific heating requirements. High pressure boilers excel in large industrial settings where high steam output is crucial, while low pressure boilers may be more economical for smaller applications. Electric boilers can be advantageous for their ease of use and space-saving design. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals, budget constraints, and regulatory requirements specific to the industry and region. This thoughtful approach will ensure that businesses invest in the most effective and sustainable solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high pressure boilers
High-pressure boilers are critical components in various industrial applications, and understanding their technical properties and associated trade terminology can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers. Below are essential specifications and industry terms that are relevant to high-pressure boilers.
What are the Key Technical Properties of High-Pressure Boilers?
1. Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP)
MAWP refers to the maximum pressure at which a boiler is designed to operate safely. It is a crucial specification as it determines the operational limits of the boiler and its suitability for specific applications. For B2B buyers, understanding the MAWP is vital for ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations, which can vary by region and industry.
2. Material Grade
High-pressure boilers are typically constructed from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, each offering different strengths and resistance to corrosion and heat. The material grade influences the boiler’s durability, efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Buyers must consider the material grade to ensure that the boiler meets their operational needs and environmental conditions, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures or corrosive environments.
3. Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating of a high-pressure boiler indicates how effectively it converts fuel into usable energy, often expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency ratings translate to lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact. For international buyers, understanding efficiency is crucial for evaluating potential cost savings and compliance with environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
4. Heat Transfer Surface Area
This specification refers to the total area within the boiler where heat is exchanged between the flue gas and the water/steam. A larger heat transfer surface area typically allows for more efficient heat exchange, leading to higher steam output and reduced fuel consumption. B2B buyers should assess this property to optimize energy use and operational efficiency in their facilities.
5. Safety Features
Modern high-pressure boilers are equipped with safety features like pressure relief valves, low-water cutoffs, and automatic shut-off systems. These features are critical for preventing accidents and ensuring safe operation. Buyers should prioritize safety features when selecting a boiler, as they are essential for compliance with local safety regulations and for protecting personnel and equipment.
What are Common Trade Terms Used in the High-Pressure Boiler Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of high-pressure boilers, understanding OEM relationships is important for ensuring the quality and compatibility of replacement parts and services.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the boiler industry, MOQs can affect procurement strategies, especially for international buyers who must balance inventory costs with supply chain efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. For B2B buyers in the high-pressure boiler market, submitting RFQs can help obtain competitive pricing and facilitate negotiations, ultimately leading to better purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers as they dictate aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For high-pressure boilers, lead time can vary based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the order. Buyers should consider lead times in their project planning and inventory management to avoid operational disruptions.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing high-pressure boilers, ensuring that their investments align with operational requirements and regulatory standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high pressure boilers Sector
What are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the High Pressure Boilers Market?
The high pressure boilers market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for energy-efficient steam generation across various industries, including manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions such as Africa and South America, where industrial growth is accelerating. Additionally, the push for sustainable practices is prompting businesses to invest in advanced boiler technologies that reduce emissions and enhance efficiency.
Emerging technologies, such as smart boiler systems equipped with IoT capabilities, are gaining traction. These systems allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of boiler operations, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and maintenance costs. Moreover, the integration of automation in boiler controls is becoming a key trend, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher operational efficiencies and safety standards.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regulatory changes aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, stricter emissions regulations in Europe and the Middle East are compelling companies to upgrade their boiler systems to meet compliance standards. This trend offers international B2B buyers an opportunity to source advanced high pressure boilers that not only comply with regulations but also contribute to operational sustainability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers in the High Pressure Boilers Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of business strategy for many organizations, particularly in the high pressure boilers sector. The environmental impact of boiler operations is significant, and buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly and adopting manufacturing processes that minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses seek to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible. This means selecting suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the incorporation of ‘green’ materials and technologies—such as low NOx burners and energy-efficient designs—can enhance a company’s market position. By prioritizing sustainability, B2B buyers not only contribute to environmental preservation but also align with consumer expectations for corporate responsibility, potentially leading to increased brand loyalty and market competitiveness.
Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
What is the Historical Evolution of High Pressure Boilers Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
The evolution of high pressure boilers dates back to the industrial revolution when steam power became a dominant force in manufacturing and transportation. Initially, these boilers were simple designs that prioritized function over safety. Over the years, technological advancements have transformed high pressure boilers into sophisticated systems that offer enhanced safety, efficiency, and environmental performance.
In the mid-20th century, innovations in materials and combustion technology led to the development of more reliable and efficient boilers. The introduction of automated controls and monitoring systems further revolutionized boiler operations, allowing for precise management of steam generation processes.
Today, the focus is on sustainability and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. This historical context underscores the importance of innovation and adaptability in the high pressure boilers market, providing B2B buyers with insights into the evolution of technology that can influence their sourcing decisions. Understanding this history helps buyers appreciate the advancements that contribute to safer and more efficient operations, ultimately guiding them in making informed purchasing choices.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high pressure boilers
-
How do I choose the right high pressure boiler for my industrial needs?
Choosing the right high pressure boiler involves assessing your specific operational requirements, including steam demand, pressure levels, and fuel type. Consider factors such as the intended application (e.g., food processing, manufacturing) and efficiency ratings. Additionally, evaluate the boiler’s design features, such as its ability to minimize emissions and energy consumption. Collaborate with suppliers who can offer tailored solutions, ensuring that the boiler meets both local regulations and international standards. -
What are the key differences between water tube and fire tube high pressure boilers?
Water tube boilers circulate water through tubes heated by combustion gases, allowing them to handle higher pressures and temperatures efficiently. They are typically more compact and offer quicker response times. In contrast, fire tube boilers contain hot gases within tubes surrounded by water, making them simpler but less efficient at high pressures. The choice between the two depends on your specific requirements, such as space constraints, steam output, and operational efficiency. -
What customization options are available for high pressure boilers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for high pressure boilers to meet specific industrial needs. Customizations may include adjusting the boiler size, pressure ratings, fuel type (natural gas, oil, etc.), and control systems. Additionally, options for advanced features like automatic blowdown controls and enhanced safety systems can be integrated. When engaging with suppliers, discuss your requirements upfront to ensure that the proposed solutions align with your operational goals. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when purchasing high pressure boilers?
The MOQ for high pressure boilers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the boiler system. Typically, manufacturers may set a MOQ of one unit for standard models, while custom units may require higher quantities to justify production costs. It’s advisable to communicate your needs clearly with suppliers, as some may offer flexible options or financing plans that allow for smaller initial purchases. -
How can I vet suppliers of high pressure boilers effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by assessing their industry reputation and experience, particularly in your region. Look for certifications such as ISO and ASME, which indicate compliance with international safety and quality standards. Request references and case studies from previous clients to evaluate their reliability and service quality. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or attending industry trade shows to gain insights into their manufacturing processes and capabilities. -
What payment terms are typical in international transactions for high pressure boilers?
Payment terms for international purchases of high pressure boilers vary, but common practices include advance payment, letters of credit, or staggered payments based on production milestones. It’s essential to establish clear terms that protect both parties, particularly concerning currency fluctuations and delivery timelines. Discuss these terms with suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure transparency and mutual agreement. -
How do logistics and shipping work for high pressure boilers?
Logistics for high pressure boiler shipments involve careful planning due to their size and weight. Discuss with your supplier the best shipping methods, which may include sea freight or air freight, depending on urgency and budget. Ensure that all shipping documents, including customs clearance paperwork, are in order to avoid delays. Additionally, consider working with logistics partners experienced in handling heavy industrial equipment to streamline the process. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from high pressure boiler manufacturers?
Reputable manufacturers of high pressure boilers should have robust quality assurance (QA) protocols in place. This includes thorough testing during various production stages, compliance with international safety standards, and post-manufacture inspections. Ask potential suppliers about their QA processes, including certifications and testing methodologies. Additionally, consider requesting third-party inspection reports to verify the quality and safety of the boilers before purchase.
Top 6 High Pressure Boilers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – High Pressure Boilers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Boilers operate at pressures of 80 bars or more, primarily used in thermal power plants for electricity generation. They convert water into steam using thermal energy within tubes filled with water. Key characteristics include:
– Ability to produce significant pressure, distinguishing them from other boiler types.
– Utilization of fuels like coal, natural gas, or oil for steam genera…
2. Reddit – High Pressure Steam Overview
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High pressure steam is generally considered to be steam over 15 psi. Additionally, anything over 5 psi is technically classified as pressure equipment and requires certifications, welding procedure specifications (WPS), and quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC). In the context of the discussion, a steam line operating at 125 psi is deemed high pressure, and welding on such a line should only b…
3. Boiler Specialists – High Pressure Boilers
Domain: boilerspecialists.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High pressure boiler is defined as having a max allowable working pressure (MAWP) above 15 PSI. Low pressure steam typically runs at a pressure no higher than 2 PSI. Cast iron sectional boilers have an MAWP of 15 PSI steam, making them low pressure boilers. It is important to check that the manufacturer’s MAWP stamp matches or exceeds the safety valve ratings for safety and compliance.
4. Chardon Labs – Low & High-Pressure Boilers
Domain: chardonlabs.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Low-pressure boilers have a MAWP (max allowable working pressure) of 15 PSI or less, while high-pressure boilers have a MAWP higher than 15 PSI. Low-pressure boilers are commonly used in apartments, schools, hospitals, churches, and offices, whereas high-pressure boilers are found in commercial laundromats, processing plants, drill rig sites, rubber vulcanizing facilities, and utilities. High-pres…
5. High Pressure Boilers Study Guide – Brand New
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Boilers products for sale on eBay include various editions and conditions of books related to high pressure boilers, primarily authored by Frederick M. Steingress and Harold J. Frost. Key products include:
1. High Pressure Boilers Study Guide 6th Edition – Brand New – $28.99 (Trending at $46.20)
2. High Pressure Boilers – Paperback by Steingress Frederick M. – Very Good – Pre-Owned -…
6. Wood Boilers – High Pressure Steam Solutions
Domain: wood-boilers.net
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: High pressure boilers create steam by heating water at over 15 psi and have water pressure over 160 psig. They are extremely efficient with combustion efficiency converting all fuel to thermal energy. High pressure boilers achieve up to 95% thermal efficiency and have an 85% fuel-to-steam efficiency. Stack temperature loss is minimized by controlling the amount of air, typically requiring 15-20% e…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high pressure boilers
In today’s competitive landscape, effective strategic sourcing for high-pressure boilers is not just a necessity; it’s a catalyst for operational excellence. By prioritizing quality, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations, businesses can optimize their boiler systems, significantly reducing operational costs while enhancing productivity. Understanding the diverse types of high-pressure boilers—such as water tube and fire tube options—enables buyers to select the best fit for their specific applications, whether for industrial processes or energy generation.
As the global demand for sustainable and efficient energy solutions grows, investing in advanced boiler technologies becomes imperative. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must leverage strategic partnerships with reputable manufacturers to ensure they receive cutting-edge equipment that meets both performance and environmental standards.
Looking ahead, the boiler market is poised for innovation, driven by technological advancements and increasing regulatory pressures. International buyers should stay informed and proactive in their sourcing strategies, seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability. Embrace the opportunity to future-proof your operations—partner with leading boiler manufacturers today and ensure your business remains at the forefront of the industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to high pressure boilers
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.