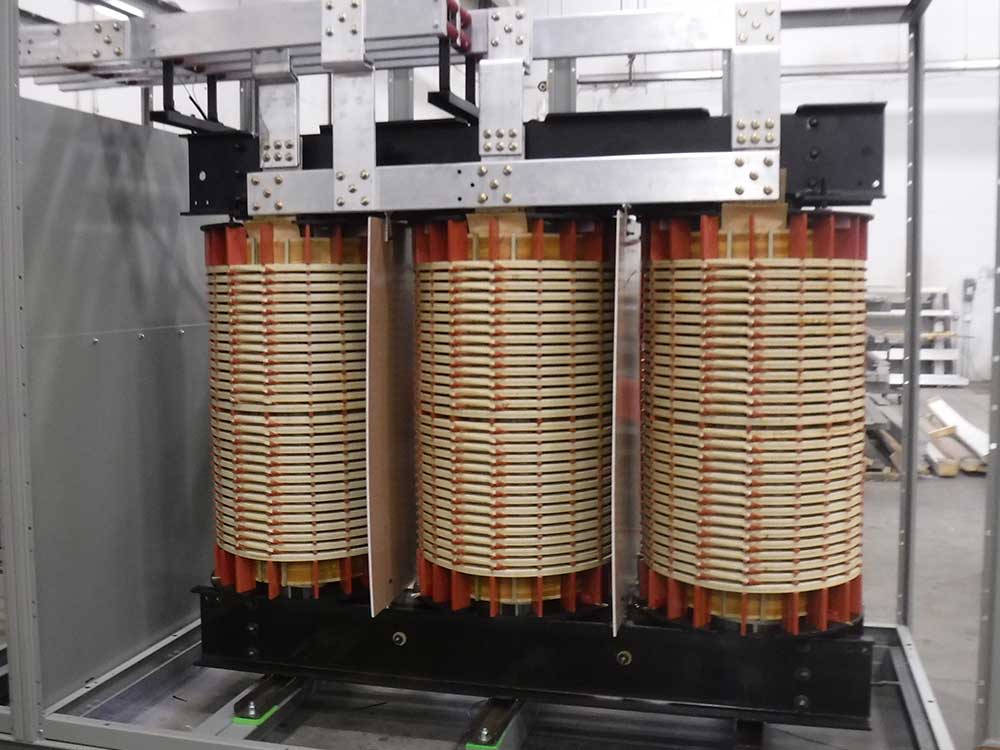
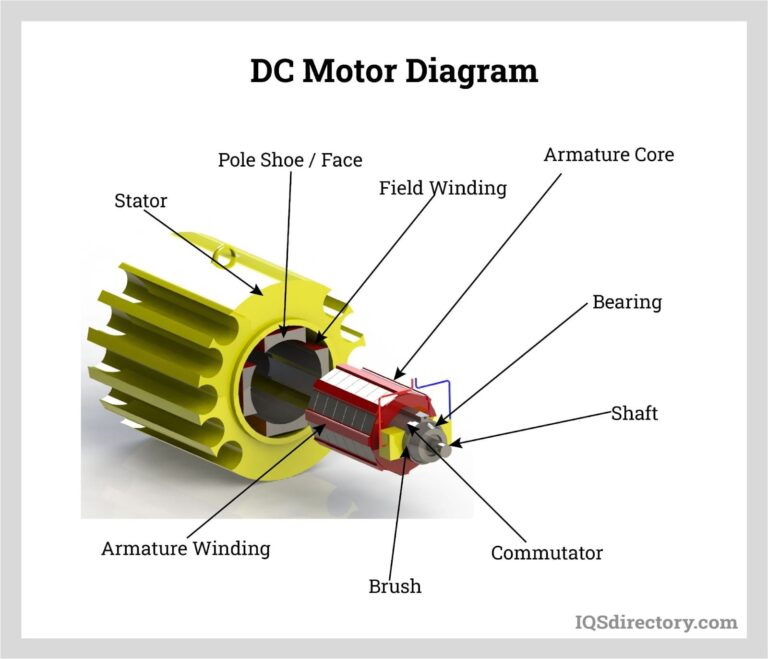
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the High Power Transformer Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high power transformer
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing high power transformers can present a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries strive for efficiency and reliability in electricity transmission and distribution, understanding the intricacies of high power transformers becomes paramount. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower decision-makers by delving into various transformer types, their applications, and the critical factors influencing cost and performance.
From generator transformers to distribution transformers, each variant serves a unique purpose in the energy ecosystem. The guide will also cover essential aspects of supplier vetting, enabling buyers to assess potential partners effectively and ensure they meet rigorous quality standards. Furthermore, it will explore maintenance practices to prolong the lifespan and efficiency of these vital components, ultimately leading to cost savings.
By navigating through this guide, B2B buyers will gain valuable insights that facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right high power transformer for their operational needs. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Vietnam, or any other key market, this resource is tailored to help you understand the complexities of high power transformers, equipping you with the knowledge to make strategic investments in your energy infrastructure.
Understanding high power transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step-Up Transformer | Increases voltage for efficient long-distance transmission | Power plants, transmission substations | Pros: Enhances transmission efficiency; reduces losses. Cons: Higher initial cost; requires careful installation. |
| Step-Down Transformer | Reduces voltage for safe distribution to end-users | Distribution networks, industrial facilities | Pros: Ensures safety for end-users; versatile applications. Cons: Limited to lower voltage applications; potential for energy loss. |
| Auto Transformer | Uses a single winding for both primary and secondary functions | Industrial applications, railway systems | Pros: Compact design; cost-effective for specific applications. Cons: Limited voltage transformation ratio; less isolated than conventional transformers. |
| Generator Transformer | Connects generators to power grids, high voltage output | Renewable energy plants, large industrial setups | Pros: Optimizes power generation; enhances grid stability. Cons: Complex integration; requires skilled technicians for maintenance. |
| Network Transformer | Facilitates interconnection of high-voltage networks | National grids, large-scale energy projects | Pros: Supports high-capacity operations; essential for grid reliability. Cons: High investment; requires extensive infrastructure. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Step-Up Transformers?
Step-up transformers are designed to increase voltage levels, making them essential for efficient long-distance power transmission. They are particularly suited for power plants and transmission substations where high voltage is necessary to minimize energy losses over vast distances. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as the transformer’s capacity, efficiency ratings, and compatibility with existing systems. The initial investment can be significant, but the long-term savings in energy costs often justify the expense.
How Do Step-Down Transformers Ensure Safe Distribution?
Step-down transformers reduce high voltage to safer levels for end-users, playing a crucial role in distribution networks and industrial facilities. Their ability to adapt to varying voltage requirements makes them versatile for different applications. Buyers should focus on the transformer’s voltage rating, load capacity, and thermal performance when making purchasing decisions. While they are generally more affordable than step-up transformers, buyers must also consider potential energy losses that could affect overall efficiency.
Why Choose Auto Transformers for Specific Applications?
Auto transformers are unique as they utilize a single winding to perform both primary and secondary functions. This design results in a more compact and cost-effective solution, making them ideal for specific industrial applications and railway systems. However, B2B buyers should be aware of the limited voltage transformation ratio and the lack of electrical isolation compared to conventional transformers. Evaluating their specific application needs and safety requirements is crucial before proceeding with a purchase.
What Are the Benefits of Generator Transformers?
Generator transformers are specifically engineered to connect generators to power grids, providing high voltage output to stabilize the grid. They are essential in renewable energy plants and large industrial setups where consistent power generation is critical. When purchasing, buyers should assess the generator transformer’s integration capabilities, maintenance requirements, and the technical expertise needed for installation. While they may require a higher upfront investment, the benefits of improved grid stability and optimized power generation can outweigh the costs.
How Do Network Transformers Support High-Capacity Operations?
Network transformers are vital for facilitating the interconnection of high-voltage networks, making them indispensable in national grids and large-scale energy projects. Their design supports high-capacity operations, ensuring reliability and efficiency in power distribution. Buyers should consider the transformer’s capacity, operational efficiency, and the infrastructure required for installation. Although the investment can be substantial, the long-term benefits of enhanced grid reliability and reduced operational risks are significant factors for B2B buyers in energy sectors.
Key Industrial Applications of high power transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high power transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Utilities | Power Generation and Transmission | Enhances efficiency of long-distance electricity transmission | Voltage ratings, transformer capacity, and cooling methods |
| Mining & Minerals | Power Supply for Mining Operations | Ensures consistent energy supply for heavy machinery | Durability, environmental resistance, and maintenance support |
| Manufacturing | Electrical Supply for Industrial Plants | Supports large-scale production with reliable power | Customization options and integration capabilities |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in Wind and Solar Farms | Facilitates efficient energy conversion and grid stability | Compatibility with renewable systems and regulatory compliance |
| Transportation & Logistics | Power for Rail Electrification | Provides reliable energy for electric trains and infrastructure | Voltage requirements, safety features, and installation services |
How is High Power Transformer Utilized in the Energy & Utilities Sector?
High power transformers are pivotal in the energy and utilities sector, particularly for power generation and transmission. They efficiently step up voltage for long-distance electricity transmission, reducing energy losses and ensuring that power reaches consumers effectively. International buyers must consider voltage ratings and transformer capacity to meet specific grid requirements, as well as cooling methods to ensure reliability in varying climates, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
What Role Do High Power Transformers Play in Mining & Minerals?
In the mining and minerals industry, high power transformers provide a stable power supply essential for operating heavy machinery and processing equipment. These transformers are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for remote mining sites. B2B buyers should prioritize transformers with durability and environmental resistance, as well as reliable maintenance support to minimize downtime in operations critical to productivity.
How Do High Power Transformers Benefit Manufacturing Facilities?
Manufacturing plants rely heavily on high power transformers to ensure a consistent electrical supply for their operations. These transformers support large-scale production processes, facilitating the operation of machinery and automation systems. Buyers from this sector should focus on customization options to meet specific power needs and integration capabilities to ensure seamless operation within existing infrastructure, particularly in competitive markets across South America and Europe.
In What Ways Are High Power Transformers Essential for Renewable Energy?
High power transformers are crucial in renewable energy applications, such as wind and solar farms, where they assist in converting and stabilizing the generated electricity for grid integration. By facilitating efficient energy conversion, they enhance overall system performance and reliability. Buyers in this sector must ensure compatibility with renewable systems and adherence to regulatory compliance, which is especially important in regions like Europe, where green energy initiatives are prominent.
What is the Importance of High Power Transformers in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, high power transformers are vital for rail electrification, providing the necessary energy to power electric trains and related infrastructure. This application not only supports efficient transportation but also contributes to reducing carbon emissions. When sourcing transformers for this purpose, buyers should consider voltage requirements, safety features, and installation services to ensure compliance with stringent transportation regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high power transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Power Transformer Sizing Dilemmas in Expanding Operations
The Problem: As businesses expand, they often face the challenge of ensuring that their electrical infrastructure can accommodate increased power demands. A common pain point for B2B buyers in sectors like manufacturing or energy is the uncertainty around selecting the right size of high power transformer. Choosing a transformer that is either too small can lead to overheating and inefficiency, while an oversized transformer may incur unnecessary costs and space issues. Additionally, incorrect sizing can lead to reliability issues, affecting production and operational efficiency.
The Solution: To effectively size a high power transformer, it is essential to conduct a thorough load analysis before making a purchase. Buyers should engage with electrical engineers to evaluate the current and anticipated load requirements, taking into account factors such as peak demand, load diversity, and future expansion plans. This analysis will guide the selection process to ensure that the transformer operates efficiently within its optimal range. Additionally, consider transformers with adjustable tap settings, allowing for flexibility in voltage and load changes without needing a complete replacement as demand fluctuates.
Scenario 2: Maintenance and Downtime Challenges
The Problem: Regular maintenance of high power transformers is critical for reliability, yet many organizations struggle with the associated costs and logistics. Unexpected failures can lead to significant downtime, which translates to lost revenue and operational disruptions. B2B buyers may find it challenging to establish a maintenance routine that balances cost-effectiveness with the need for comprehensive inspections and repairs.
The Solution: Implement a proactive maintenance strategy that includes routine inspections and condition monitoring. Buyers should establish a maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and industry best practices, including thermal imaging, insulation resistance testing, and oil analysis. Partnering with specialized service providers for regular checks can help identify potential issues before they lead to failure. Additionally, consider investing in predictive maintenance technologies that utilize sensors and data analytics to monitor transformer health in real time, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Safety Regulations
The Problem: In regions such as Africa and South America, navigating the compliance landscape for high power transformers can be daunting for B2B buyers. Regulatory requirements concerning safety, environmental impact, and operational standards can vary significantly across countries. This complexity can lead to delays in procurement and installation processes, as well as the risk of non-compliance penalties.
The Solution: To streamline compliance, buyers should conduct thorough research on local regulations and industry standards relevant to high power transformers. Establishing relationships with local regulatory bodies and industry associations can provide valuable insights and updates on compliance requirements. Additionally, when sourcing transformers, work with manufacturers who are familiar with international standards and can provide documentation to support compliance claims. Engaging a local consultant or legal advisor with expertise in electrical standards can also facilitate a smoother procurement process, ensuring that all necessary permits and certifications are in place before installation. This approach not only mitigates compliance risks but also fosters a safer working environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high power transformer
What Materials Are Commonly Used in High Power Transformers?
When selecting materials for high power transformers, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material choice can significantly impact performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in high power transformers: silicon steel, copper, aluminum, and insulating oil.
How Does Silicon Steel Contribute to Transformer Efficiency?
Key Properties: Silicon steel, often used in the core of high power transformers, has excellent magnetic properties and low hysteresis loss. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 150°C and can withstand high pressures without deforming.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its efficiency in reducing energy losses during operation, which enhances overall transformer performance. However, it can be relatively expensive compared to other core materials and may require complex manufacturing processes to achieve optimal magnetic properties.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel’s magnetic characteristics make it suitable for high-frequency applications, which are common in modern power distribution systems. Its compatibility with various media, including air and oil, ensures effective heat dissipation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure that the silicon steel used complies with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Additionally, understanding local sourcing options can help mitigate costs.
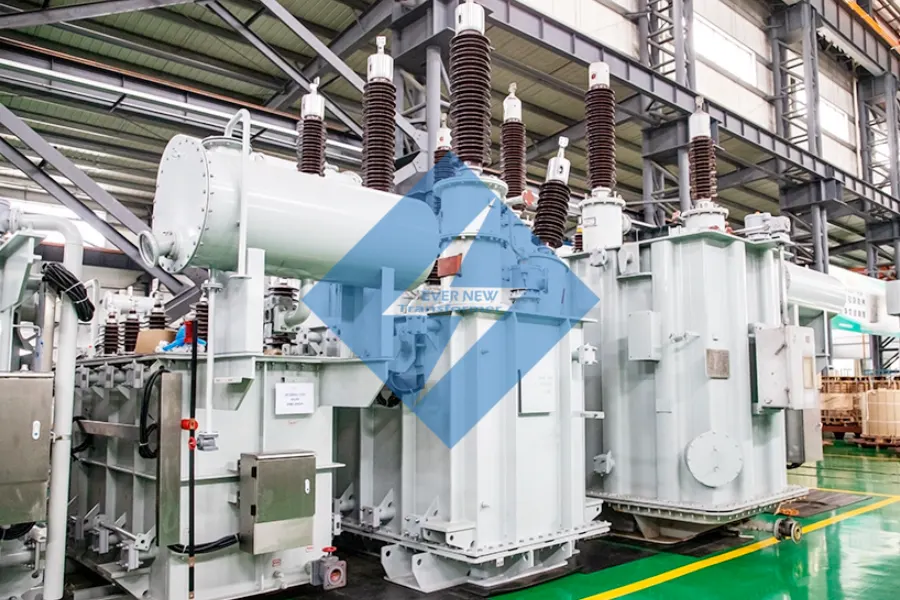
What Role Do Copper and Aluminum Play in Conductivity?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its high electrical conductivity (approximately 59.6 MS/m), while aluminum, with a conductivity of about 37.7 MS/m, is lighter and less expensive. Both materials can withstand significant thermal stress.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Pros & Cons: Copper offers superior conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-load applications. However, it is more costly and heavier than aluminum. Aluminum, while less conductive, is more affordable and easier to work with, but it may require larger cross-sectional areas to achieve the same conductivity as copper.
Impact on Application: The choice between copper and aluminum can affect the transformer’s weight and efficiency. For instance, copper is often preferred in applications requiring high performance, while aluminum is suitable for cost-sensitive projects.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local electrical standards is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of materials and local manufacturing capabilities, especially in regions where copper may be more scarce.
How Does Insulating Oil Affect Transformer Performance?
Key Properties: Insulating oil is crucial for cooling and insulation in transformers, with a high dielectric strength and a boiling point typically above 250°C. It also provides excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of insulating oil is its ability to dissipate heat effectively, which prolongs transformer life. However, it requires careful handling and storage to prevent contamination and degradation over time.
Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Impact on Application: Insulating oil is compatible with various transformer designs and is essential for maintaining operational efficiency. Its thermal properties are vital for high power applications, ensuring that transformers operate within safe temperature limits.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the insulating oil meets international standards such as IEC 60296. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding oil disposal and environmental impact is crucial for compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for High Power Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for high power transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Transformer core | Reduces energy losses | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Windings | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher weight and cost | High |
| Aluminum | Windings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Excellent thermal management | Requires careful handling and storage | Medium |
This material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions when sourcing components for high power transformers, ensuring compliance with local standards while balancing performance and cost.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high power transformer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Power Transformers?
The manufacturing process of high power transformers is intricate and requires precision at every stage. This process typically comprises four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for High Power Transformers?
Material preparation is the foundation of transformer manufacturing. High-quality materials, such as electrical steel for the core and copper or aluminum for the windings, are selected based on their electrical and thermal properties. The materials undergo rigorous quality checks before entering production. Each batch of materials is inspected for compliance with international standards, including ISO 9001, to ensure reliability and performance.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, the core and windings are shaped and configured. The core is usually constructed from stacked laminations of electrical steel to minimize energy losses. Advanced techniques like laser cutting and precision punching are employed to achieve high accuracy in the core components. The winding process involves the careful layering of copper or aluminum wire, utilizing automatic winding machines for consistency and precision. These machines are programmed to create the exact number of turns required for the specified voltage transformation.
How is the Assembly of High Power Transformers Conducted?
The assembly stage involves integrating the core and windings into a complete unit. This process is meticulous, as the alignment of components is critical for optimal performance. The transformer is typically assembled within a controlled environment to prevent contamination from dust and moisture. During this phase, the transformer tank is also prepared, often made from high-grade steel to withstand the operational pressures.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to High Power Transformers?
Finishing processes include insulating, sealing, and painting the transformer. Insulation is crucial for safety and efficiency; hence, high-quality insulating materials are applied to all electrical components. The transformer is then filled with insulating oil, which serves both as a coolant and an insulator. Finally, the unit is painted with weather-resistant coatings to protect against environmental factors, especially important for transformers deployed in outdoor settings.
What Are the Quality Assurance Protocols in High Power Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of high power transformers to ensure they meet safety and performance standards. Manufacturers adhere to both international and industry-specific standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European safety regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are systematically implemented throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first checkpoint where raw materials are inspected upon arrival. Certifications and test reports from suppliers are reviewed to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to ensure that each stage meets the required quality standards. This includes monitoring the precision of machining processes and the integrity of windings.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the transformer is assembled, it undergoes comprehensive testing, which includes electrical testing, thermal performance checks, and mechanical integrity assessments. This stage ensures that the transformer operates within its specified parameters.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for High Power Transformers?
Testing methods for high power transformers vary based on the intended application and operational environment. Common tests include:
-
Power Factor Testing: This assesses the insulation quality and helps identify any potential issues.
-
Transformer Turns Ratio (TTR) Testing: This ensures that the turns ratio is within specified limits, confirming the transformer’s voltage transformation capabilities.
-
Short-Circuit and Open-Circuit Tests: These tests evaluate the transformer’s performance under different electrical conditions.
-
Temperature Rise Testing: Conducted to ensure that the transformer can operate efficiently without overheating under load.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. This documentation should outline testing methodologies and results.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an objective assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must consider the nuances of quality control that may vary by region. For instance, certain countries may have specific regulatory requirements that must be met for transformers. Understanding these regulations can help buyers ensure compliance and avoid potential issues during shipping and installation.
Additionally, cultural differences can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear agreements and understanding the local market practices will facilitate smoother transactions and ensure that both parties are aligned in their quality expectations.
In summary, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for high power transformers are complex and require a meticulous approach to ensure safety and reliability. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with manufacturers who uphold the highest standards in transformer production.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high power transformer’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing high power transformers effectively, this guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline the procurement process. This checklist will ensure that buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical requirements is crucial for sourcing the right transformer. Consider factors such as voltage levels, power ratings, and application types.
– Voltage Class: Determine if you need a high voltage (HV), medium voltage (MV), or low voltage (LV) transformer based on your distribution network.
– Power Rating: Specify the required megavolt-amperes (MVA) capacity to meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on manufacturers and suppliers that specialize in high power transformers.
– Industry Experience: Look for companies with a proven track record in producing transformers that match your specifications.
– Reputation: Check reviews, ratings, and testimonials from previous customers to gauge reliability and service quality.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify that suppliers hold relevant industry certifications and quality standards.
– ISO Certifications: Ensure that the supplier adheres to international quality management standards, indicating reliability and quality assurance.
– Safety Standards: Confirm compliance with safety standards applicable in your region, especially if your operations are in regions with stringent regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Obtain comprehensive quotations from shortlisted suppliers to compare offerings effectively.
– Breakdown of Costs: Look for a detailed cost breakdown that includes manufacturing, shipping, installation, and maintenance.
– Lead Times: Inquire about production and delivery timelines to ensure they align with your project schedules.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Inspections
If feasible, conduct site visits to the manufacturing facilities or request virtual inspections.
– Manufacturing Processes: Assess the manufacturing processes to ensure they meet your quality expectations.
– Quality Control Measures: Observe quality control practices in place to minimize defects and ensure reliability.
Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the level of after-sales support and warranty options provided by the supplier.
– Technical Support: Ensure that the supplier offers robust technical support for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
– Warranty Terms: Understand warranty coverage and conditions to protect your investment against defects and performance issues.
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize the contract terms.
– Payment Terms: Agree on payment schedules that align with your cash flow requirements.
– Delivery and Installation: Clearly outline delivery timelines and responsibilities for installation to avoid future disputes.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing high power transformers with confidence, ensuring they select the right equipment to meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high power transformer Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances associated with high power transformers is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and buyer tips to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components of High Power Transformers?
When sourcing high power transformers, buyers should consider several cost components that contribute to the overall price:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-grade electrical steel, copper or aluminum windings, and insulation materials are essential for optimal performance. Suppliers often source these materials globally, which can affect pricing based on market fluctuations.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for manufacturing high power transformers, particularly for assembly, quality control, and maintenance. Labor costs can vary depending on the region and the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs down, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized machinery and tools for transformer production can be substantial. These costs are amortized over production runs, influencing unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that transformers meet international standards necessitates rigorous testing and certification processes, which add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs vary based on distance and shipping methods. Incoterms also play a crucial role, as they dictate the responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s business model.
What Influences the Pricing of High Power Transformers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of high power transformers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often dictate pricing. Bulk orders typically attract discounts, making it essential for buyers to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized transformers designed for specific applications or operating conditions may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Transformers that meet higher quality standards or possess specific certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC) often come at a premium. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications based on their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their perceived quality and service levels.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total cost of ownership, as they define the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in terms of shipping and insurance.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Sourcing High Power Transformers?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, here are actionable tips to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, especially on large orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or better payment terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also long-term costs, including installation, maintenance, and energy efficiency. A lower initial price may lead to higher operational costs over time.
-
Research Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations and standards is essential to ensure compliance and avoid costly modifications post-purchase.
-
Evaluate Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and preferential treatment on future orders.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help identify the best value for your investment.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing dynamics of high power transformers allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By considering the various cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic sourcing tips, buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies and ensure a successful procurement process.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high power transformer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to High Power Transformers in Electricity Distribution
In the realm of electricity distribution, high power transformers are pivotal for efficient energy transmission. However, businesses exploring energy solutions should consider viable alternatives that can also meet their operational needs. This section delves into the comparative aspects of high power transformers against other technologies, offering insights that help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | High Power Transformer | Voltage Regulators | Static Frequency Converters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in long-distance transmission; handles massive loads. | Regulates voltage levels but limited to lower power applications. | Converts power frequency and maintains stability in varying loads. |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs; long-term investment. | Generally lower initial costs; cost-effective for small-scale applications. | Moderate costs; varies based on complexity and application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant infrastructure and skilled personnel for installation. | Easier to implement; can be installed quickly in existing systems. | Complex setup; requires specialized knowledge for installation and integration. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; can be costly and time-consuming. | Low maintenance; requires periodic checks but less intensive than transformers. | Maintenance varies; can be complex depending on system design. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industrial applications and large-scale power distribution. | Suitable for residential and small commercial use where voltage stability is needed. | Best for applications requiring frequency conversion and dynamic load management. |
Analyzing Alternative Solutions: Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators serve as an alternative to high power transformers, especially in scenarios where voltage stability is a priority. They maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. The advantages of voltage regulators include lower initial costs and simpler implementation, making them ideal for smaller systems or residential applications. However, they cannot handle the high load capacities that transformers can manage, making them less suitable for large-scale industrial applications.
Examining Static Frequency Converters
Static frequency converters (SFCs) offer a different approach by converting power from one frequency to another, which is especially useful in applications involving variable speed drives or when connecting systems operating on different frequencies. SFCs can help stabilize power supply under fluctuating load conditions, providing a unique advantage over traditional transformers. However, the complexity of installation and the need for specialized technical knowledge can present challenges, making them less accessible for some businesses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating whether to invest in a high power transformer or consider alternatives like voltage regulators or static frequency converters, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and future scalability. High power transformers are unparalleled for large-scale energy distribution, while alternatives may offer more cost-effective and simpler solutions for smaller applications. By carefully weighing these factors, businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their long-term energy goals and operational efficiencies.
Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high power transformer
High power transformers are crucial components in the electrical distribution and transmission landscape. Understanding their essential technical properties and trade terminology can significantly impact procurement decisions for businesses operating in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below are key specifications and industry terms that every B2B buyer should be familiar with.
What Are the Critical Technical Specifications for High Power Transformers?
1. Material Grade
The core and winding materials used in high power transformers directly influence efficiency and longevity. Common materials include silicon steel for the core, which reduces energy losses, and copper or aluminum for windings. Selecting high-grade materials minimizes maintenance costs and enhances performance, making it a vital consideration for B2B buyers.
2. Voltage Rating
High power transformers operate at various voltage levels, typically ranging from 69 kV to 1,500 kV. Understanding the voltage rating is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure. For international buyers, it’s crucial to consider local regulations and standards when selecting transformers to avoid compliance issues.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
3. Power Capacity (MVA Rating)
The power capacity, measured in megavolt-amperes (MVA), indicates the maximum load a transformer can handle. High power transformers can exceed 1,000 MVA, making this specification vital for applications in large industrial settings or power plants. Buyers must match the MVA rating with their operational requirements to ensure reliable performance.
4. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings determine how well a transformer converts input power to output power, usually expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency reduces energy losses, which can lead to significant cost savings over time. B2B buyers should prioritize transformers with high-efficiency ratings to optimize operational costs and sustainability efforts.
5. Cooling Method
High power transformers require effective cooling mechanisms to maintain performance and prevent overheating. Common methods include oil immersion and air cooling. Understanding the cooling method is crucial for installation considerations and long-term operational reliability, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of high power transformers, working with OEMs ensures that buyers receive products that meet specific technical standards and quality controls.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For high power transformers, understanding the MOQ can help businesses plan their procurement budgets and inventory levels. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their project timelines and capital constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In the high power transformer market, providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate pricing and better supplier responses, ultimately aiding in cost-effective decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and costs involved in the procurement process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For high power transformers, lead times can vary significantly based on customization and production schedules. Awareness of lead times helps businesses effectively plan their projects and manage expectations.
In summary, grasping the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to high power transformers enables B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding specifications such as material grade, voltage rating, and terms like OEM and MOQ, companies can better navigate the complexities of international procurement.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high power transformer Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Global High Power Transformer Market?
The high power transformer market is witnessing robust growth, primarily driven by the increasing demand for electricity due to urbanization and industrialization in developing regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As countries invest in infrastructure and renewable energy projects, the need for efficient power transmission and distribution systems has become paramount. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as smart grid solutions, are enhancing operational efficiency and reliability, making high power transformers essential for modern energy systems.
Emerging trends include the integration of digital technologies in transformer design and management. Internet of Things (IoT) applications allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and enhancing safety. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on modular and scalable solutions that can be customized to meet specific regional requirements, particularly in markets like Nigeria and Vietnam where energy demands are rapidly evolving.
B2B buyers are also increasingly focused on sourcing transformers from manufacturers who offer comprehensive service packages, including installation, maintenance, and after-sales support. This trend is particularly relevant in regions with limited local expertise in transformer technology, where international partnerships can provide essential support.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the High Power Transformer Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for international B2B buyers of high power transformers. The environmental impact of transformer production and operation is significant, and companies are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints. As such, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and offer environmentally friendly products.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
Ethical sourcing is essential in this context, as it ensures that materials are obtained responsibly and that manufacturing processes minimize waste and emissions. Buyers should look for manufacturers who utilize “green” certifications and materials, such as recyclable components and low-emission insulating oils. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and others related to sustainable production practices can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
Moreover, the trend towards renewable energy sources is pushing the high power transformer sector to innovate. Transformers that can efficiently integrate with solar, wind, and other renewable sources are not only attractive from a performance perspective but also align with global sustainability goals.
What Has Been the Evolution of High Power Transformers in the B2B Market?
High power transformers have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the late 19th century. Initially designed for basic voltage transformation, advancements in materials and technology have led to the development of highly efficient and reliable transformers capable of handling voltages exceeding 1000 kV. The introduction of digital monitoring systems in the 21st century has further revolutionized the sector, allowing for enhanced operational oversight and maintenance.
In recent decades, the shift towards renewable energy sources has prompted manufacturers to innovate, creating transformers that can operate efficiently in variable conditions, such as those found in solar or wind applications. This evolution reflects a broader trend within the energy sector, where adaptability and efficiency are becoming essential to meet growing demands and sustainability targets.

Illustrative image related to high power transformer
As international B2B buyers navigate the high power transformer market, understanding these trends and historical developments will be crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both their operational needs and sustainability commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high power transformer
-
How do I ensure the quality of a high power transformer before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of a high power transformer, request detailed technical specifications and certifications from the manufacturer. Look for compliance with international standards such as IEC or ANSI, and inquire about the materials used in construction. It’s beneficial to visit the factory or request third-party inspections. Additionally, reviewing customer testimonials and case studies can provide insight into the manufacturer’s reliability and product performance in similar applications. -
What is the best type of high power transformer for long-distance transmission?
The best type of high power transformer for long-distance transmission is the step-up transformer. This transformer increases the voltage from the generator before transmission, minimizing energy loss over long distances. For applications requiring over 1000 MVA, consider ultra-high voltage transformers, which can handle voltages exceeding 1000 kV. These transformers are essential in large-scale power plants and substations to ensure efficient energy distribution. -
How can I customize a high power transformer for my specific needs?
Customization of a high power transformer can include adjustments in voltage ratings, physical dimensions, and specific features such as insulation materials or cooling systems. Discuss your requirements with the manufacturer to explore options like tailored designs, branding, and unique specifications. Ensure that the supplier has a solid track record in delivering custom solutions and can provide prototypes or simulations to validate your specifications before production. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for high power transformers?
Minimum order quantities for high power transformers can vary significantly between manufacturers. Typically, MOQs can range from one unit for custom orders to several units for standard models. It’s essential to discuss your project scope and budget with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility on MOQs based on your specific needs or long-term partnership potential. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing high power transformers?
Payment terms for high power transformers can vary based on the supplier and order size. Common terms include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, including letters of credit or wire transfers, and ensure that all terms are documented in a contract to avoid disputes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing transformers?
When importing high power transformers, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and customs clearance procedures. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary shipping documentation, including bills of lading and certificates of origin. It’s also vital to assess the transport and handling requirements due to the transformers’ size and weight. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in heavy equipment can streamline the process and minimize delays. -
How do I vet suppliers of high power transformers effectively?
To vet suppliers effectively, conduct thorough research on their background, including years in business, production capacity, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and check their compliance with international quality standards. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn or industry-specific forums to gather insights about their performance. Engaging in initial discussions to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs can also provide clarity on their customer service. -
What maintenance practices are essential for high power transformers?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of high power transformers. Essential practices include routine inspections of insulation integrity, thermal monitoring, and cleaning of cooling systems. It’s recommended to engage professional technicians for periodic assessments and preventive maintenance. Establishing a maintenance schedule based on operational hours and environmental factors can help mitigate unexpected failures and extend the operational lifespan of the transformer.
Top 7 High Power Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Daelim – Electrical Transformers
Domain: daelimtransformer.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: 1,000+ Electrical Transformers (7.2–34.5 kV, 25–3000 kVA) — UL Evaluated, Certificate of Compliance Available — In Stock & Ready to Ship from Houston, CA & Florida. High voltage power transformers operate at high voltage levels, typically ranging from 115-230kV, with maximum transmission voltages of 1000kV in China and 500kV in the U.S. They are used for long-distance transmission of electrical en…
2. Velatron – High Voltage Transformers
Domain: velatron.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: A high voltage transformer is designed to step up or step down the voltage level of an alternating current power supply, operating at high voltage levels typically above 600 volts. It is used in applications requiring high voltage for efficient power transmission over long distances with minimal losses. High voltage transformers are utilized in power generation plants to increase voltage before tr…
3. Hammond Manufacturing – Power Transformers
Domain: hammfg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Power Transformers from Hammond Manufacturing include a variety of low voltage and high voltage options. Key details include: Low Voltage PC Board Mount transformers ranging from 0.5 VA to 24 VA, with series such as 160-161 (1.1 VA to 36 VA), 162-164 (2.5 VA to 56 VA), and 183 (2 VA to 48 VA). Other low voltage options include 229 Series (1 VA to 40 VA), 226-227-228 Series (2.4 VA to 102 VA), and …
4. Mitsubishi Electric – Power Transformers
Domain: meppi.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Power Transformers by Mitsubishi Electric are designed for energy transmission and distribution systems, with over 95 years of experience. They offer both shell-form and core-form designs, with shell-form transformers preferred for high voltage (275 kV) and large capacity (200 MVA) applications. Shell-form transformers provide advantages such as high short-circuit withstand capability, mechanical …
5. GE Vernova – Transformer Solutions
Domain: gevernova.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: GE Vernova offers a wide range of transformer solutions for utility, industrial, commercial, residential, and energy markets. These transformers feature flexible, reliable, and robust designs to support various applications. Key product categories include: Power Transformers, Conventional Power Transformers, Green Transformers, Special Power Transformers, Distribution Transformers, Pole-mount & Pa…
6. Lightbulb Wholesaler – High Voltage Transformers
Domain: lightbulbwholesaler.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: High Voltage Transformers are designed for industrial-grade power conversion, suitable for high-output fixtures and applications requiring higher electrical loads, such as signage. They ensure safe power distribution over long distances and are built for durability and performance in demanding conditions. Available configurations include various wattages: 375W, 250W, 150W, and 70W, with input volt…
7. WE – WE-PoEH Power over Ethernet Transformer
Domain: we-online.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “WE-PoEH Power over Ethernet High Power Transformer”, “product_group”: “Passive Components”, “product_family”: “Transformers for DC/DC Converter”, “dimensions”: {“length_mm”: 14, “width_mm”: 17.65, “height_mm”: 14.5}, “mount”: “EPQ13”, “characteristics”: {“type”: [“Flyback”, “Forward”], “input_voltage”: [“9 V”, “33 V to 57 V”], “switching_frequencies_kHz”: “200-400”, “operating_te…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high power transformer
In navigating the complex landscape of high power transformers, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of transformer specifications—ranging from voltage levels to construction materials—can significantly influence procurement decisions. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, businesses can ensure optimal performance in power transmission and distribution, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency.
Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on establishing robust partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer customizable solutions tailored to their unique needs. Emphasizing local supplier relationships can also facilitate smoother logistics and support sustainable development initiatives.
Looking ahead, the demand for high power transformers is set to rise, driven by the growing need for efficient energy solutions and infrastructure expansion. As industries evolve, embracing innovative technologies and maintaining a proactive approach to sourcing will be critical. We encourage buyers to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation, ensuring they are well-positioned to meet future energy demands and contribute to a more sustainable global economy.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.