Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Gantry Crane Components Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gantry crane components
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing high-quality gantry crane components presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying specifications and standards across regions, navigating this landscape requires strategic insight and detailed knowledge of the industry. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential components of gantry cranes, including types, applications, and the critical factors involved in supplier vetting. By understanding the different types of gantry cranes—ranging from single girder to portable models—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Furthermore, this guide addresses the complexities of pricing, shipping, and compliance with international standards, empowering buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Saudi Arabia. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain efficiency or ensure the safety and reliability of your operations, this resource equips you with actionable insights and expert recommendations. By leveraging the information provided, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement processes, mitigate risks, and ultimately achieve better returns on investment in their gantry crane systems.
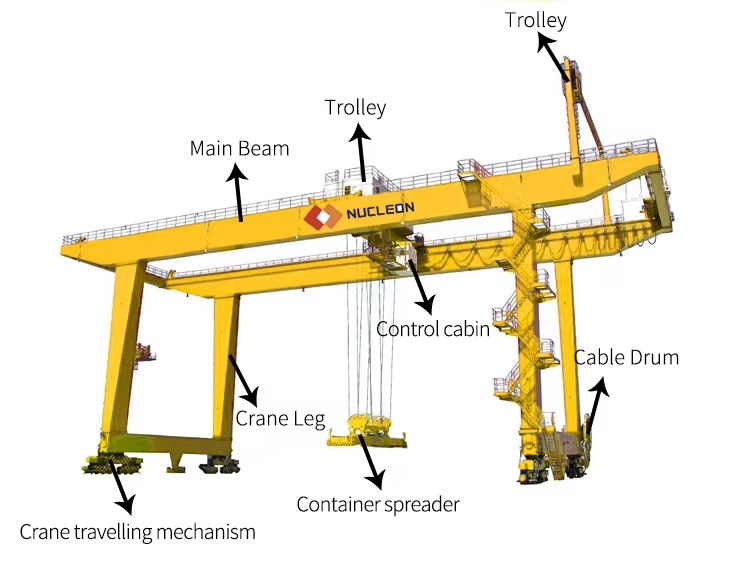
Understanding gantry crane components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Girder Gantry Crane | Lightweight design; single beam structure | Warehousing, light manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install. Cons: Limited lifting capacity compared to double girder. |
| Double Girder Gantry Crane | Robust design; two beams for greater strength | Heavy manufacturing, shipyards | Pros: High lifting capacity, stability. Cons: Higher cost, requires more space. |
| Portable Gantry Crane | Mobile design; adjustable height and width | Construction sites, small workshops | Pros: Versatile and easy to transport. Cons: Lower load capacity compared to fixed cranes. |
| Semi-Gantry Crane | Combines fixed and mobile elements; one side on rails | Construction, maintenance in tight spaces | Pros: Space-efficient, adaptable. Cons: Limited mobility on one side. |
| Truss Gantry Crane | Lightweight truss design; enhanced load distribution | Outdoor applications, heavy lifting | Pros: Good for large spans, reduced weight. Cons: Requires careful engineering for stability. |
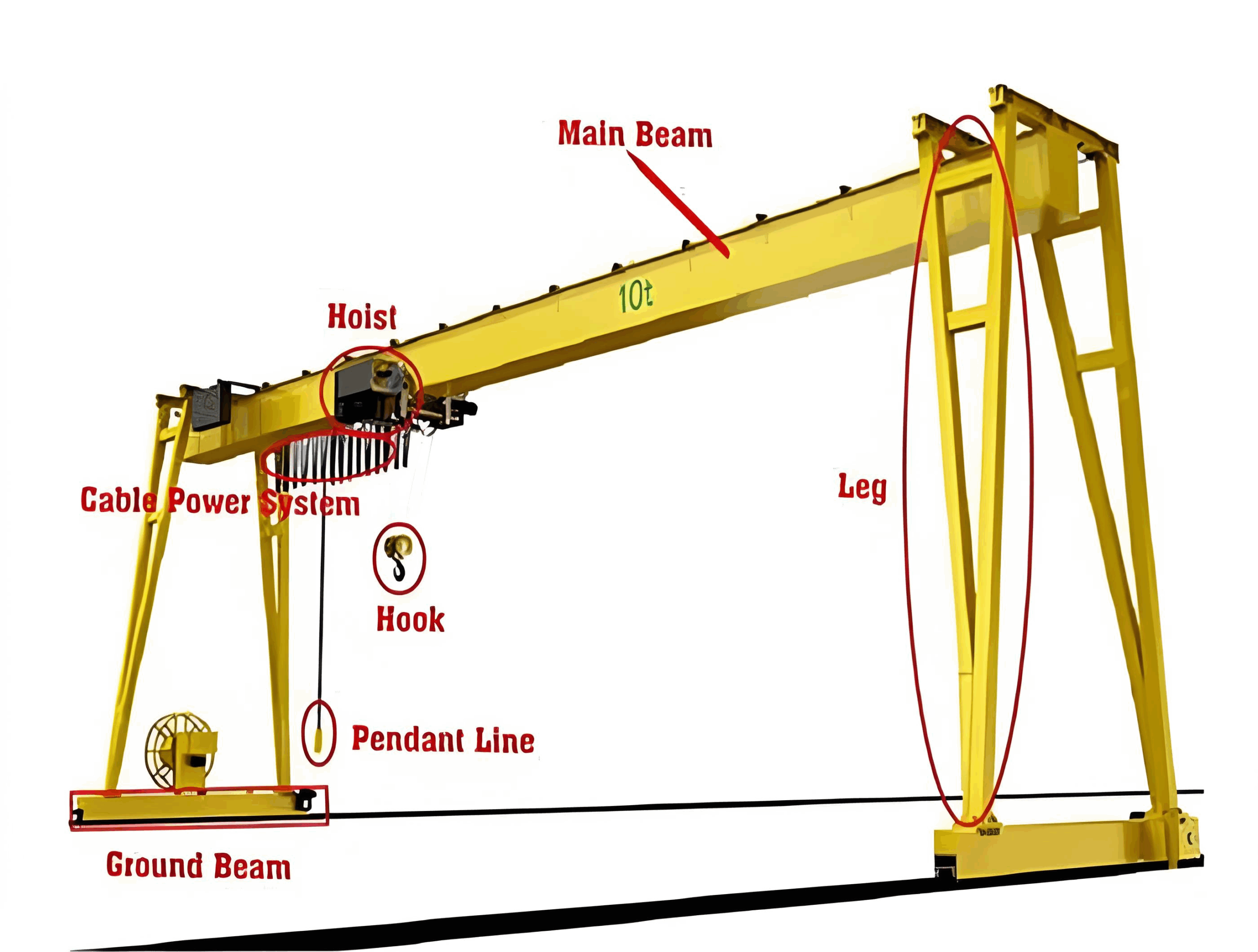
What Are the Key Characteristics of a Single Girder Gantry Crane?
Single girder gantry cranes feature a simple structure with one horizontal beam supported by two vertical legs. This design makes them ideal for lighter loads, typically up to 10 tons. They are particularly suitable for warehouses and light manufacturing facilities where space is limited and cost-effectiveness is a priority. When purchasing, buyers should consider the crane’s height and width adjustments to ensure it fits their operational needs.
Why Choose a Double Girder Gantry Crane for Heavy Lifting?
Double girder gantry cranes are built with two beams, providing superior strength and stability, making them suitable for lifting heavy loads, often exceeding 200 tons. They are commonly used in heavy manufacturing and shipyards where reliability is paramount. Buyers should evaluate the crane’s specifications against the weight of loads they intend to lift and consider the space required for installation, as these cranes typically demand more room than their single girder counterparts.
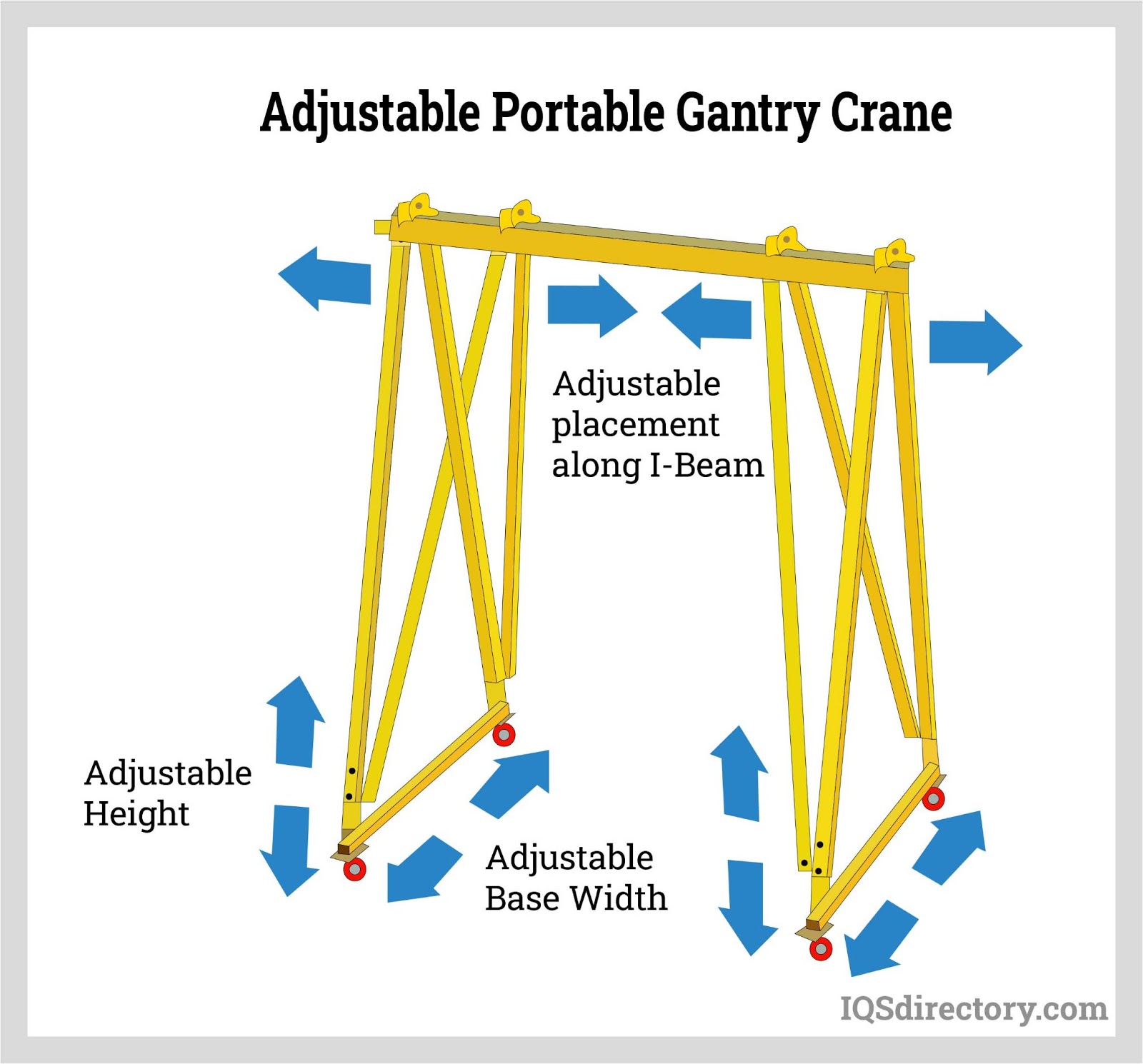
What Makes Portable Gantry Cranes Ideal for Construction Sites?
Portable gantry cranes are designed for mobility, featuring adjustable heights and widths, which makes them exceptionally versatile for various applications, particularly in construction and small workshops. Their lightweight design allows for easy transport and setup. However, buyers should note that while they offer flexibility, their load capacity is generally lower than fixed cranes, making them suitable for lighter lifting tasks.
How Does a Semi-Gantry Crane Maximize Space Efficiency?
Semi-gantry cranes utilize a hybrid design where one side operates on fixed rails while the other is supported by wheels, allowing for efficient use of space in constrained areas. This makes them particularly useful in construction or maintenance tasks where maneuverability is limited. Buyers should consider the operational environment and ensure that the semi-gantry crane meets the specific height and weight requirements of their projects.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Why Are Truss Gantry Cranes Preferred for Outdoor Applications?
Truss gantry cranes are characterized by their lightweight truss design, which allows for larger spans and better load distribution. They are particularly effective in outdoor applications, such as heavy lifting tasks in shipyards or during large construction projects. When considering a truss gantry crane, buyers should assess the environmental conditions it will face, as well as its engineering requirements for stability and safety during operations.
Key Industrial Applications of gantry crane components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gantry crane components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Lifting heavy structural components on-site | Increases efficiency and safety in construction | Ensure compliance with local regulations and load capacities |
| Shipbuilding | Transporting large vessels and components | Enhances workflow and reduces turnaround times | Consider corrosion resistance and marine-grade materials |
| Manufacturing | Assembly line support for heavy machinery | Streamlines production processes and reduces labor | Evaluate customization options for specific machinery needs |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Loading and unloading containers in ports | Improves operational efficiency and reduces delays | Assess compatibility with existing infrastructure |
| Metal Fabrication | Handling and positioning heavy metal sheets | Increases precision and safety in fabrication | Focus on durability and load capacity for heavy materials |
How Are Gantry Crane Components Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, gantry crane components play a crucial role in lifting heavy structural elements such as steel beams, concrete slabs, and prefabricated modules. By utilizing a gantry crane, construction firms can significantly improve their operational efficiency, reduce manual labor, and enhance safety on-site. Buyers in this industry should ensure that the cranes meet local safety standards and are rated for the specific loads they will be handling, particularly in regions with varying regulatory requirements.
What Is the Role of Gantry Crane Components in Shipbuilding?
In shipbuilding, gantry cranes are essential for transporting large vessels and their components, such as hull sections and engines. These cranes streamline the workflow by allowing for simultaneous operations in different areas of the shipyard, thus reducing turnaround times. International buyers, especially in coastal regions, should consider sourcing cranes made from corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh marine environments and ensure long-term reliability.
How Do Gantry Crane Components Enhance Manufacturing Processes?
Manufacturers often employ gantry crane components to support assembly lines, particularly for heavy machinery and equipment. By automating the lifting and positioning of parts, manufacturers can streamline their production processes, reduce the risk of workplace injuries, and improve the overall efficiency of operations. When sourcing, businesses should evaluate options for customization to fit their specific machinery needs, as well as the durability of the components used in high-volume production.
In What Ways Do Gantry Crane Components Benefit Logistics and Warehousing?
In logistics and warehousing, gantry crane components are vital for efficiently loading and unloading containers at ports. They facilitate quick movement of goods, minimizing delays and enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers should assess the compatibility of gantry cranes with existing infrastructure, such as rail systems or container handling equipment, to ensure seamless integration into their logistics operations.
How Are Gantry Crane Components Used in Metal Fabrication?
In metal fabrication, gantry crane components are used for handling and positioning heavy metal sheets and components during the manufacturing process. This application enhances precision and safety, as it allows for accurate placement of materials while reducing the risk of injury to workers. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing cranes with high load capacities and durable designs to accommodate the heavy materials typically handled in fabrication environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gantry crane components’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Gantry Crane Components
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers for gantry crane components that meet their specific requirements. This can lead to delays in project timelines, increased costs, and the risk of purchasing substandard parts. In markets like Africa and South America, where logistics can be complex, the challenge of ensuring timely delivery of high-quality components becomes even more pronounced. Buyers may also face difficulties in verifying the credibility of suppliers, resulting in uncertainty about the quality and performance of the components they are purchasing.
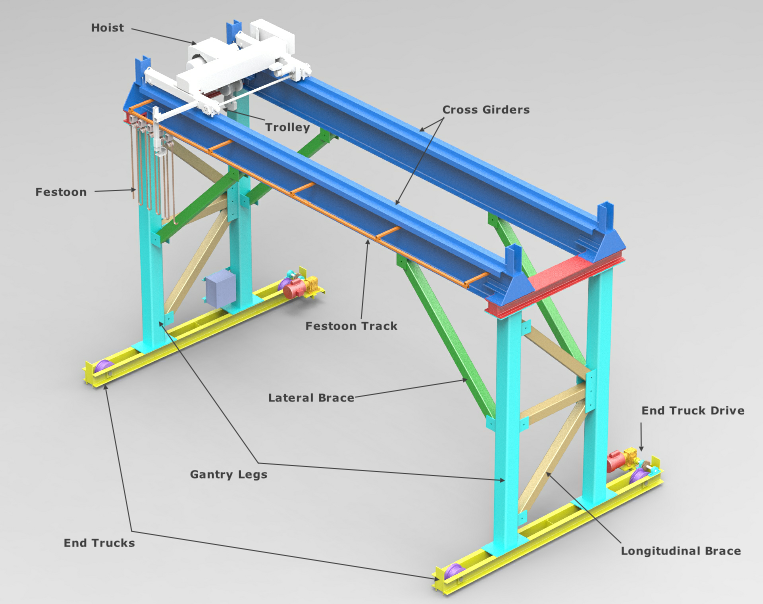
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
The Solution: To effectively source quality gantry crane components, buyers should conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their reputation, certifications, and client reviews. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry is crucial. Consider requesting samples or visiting manufacturing facilities if possible, as this can provide valuable insight into production processes and quality control measures. Additionally, leveraging online platforms and industry-specific trade shows can help establish connections with reputable manufacturers. Building long-term relationships with suppliers who understand the unique challenges of your region can also facilitate better support and responsiveness.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Component Compatibility
The Problem: Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is the compatibility of various gantry crane components. When upgrading or replacing parts, businesses often find that new components do not seamlessly integrate with existing systems. This can lead to operational inefficiencies and additional costs for modifications or replacements. In regions like the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory standards may vary, compatibility issues can also affect compliance with safety regulations.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility challenges, buyers should ensure that all components are sourced from the same manufacturer or verified to meet specific compatibility standards. Before making a purchase, it is essential to review detailed specifications and consult with technical support teams from suppliers. Providing them with information about the existing gantry crane system can lead to tailored recommendations. Utilizing modular components can also help, as they are designed for easier integration with existing systems. Furthermore, implementing a robust inventory management system can help track the specific components used in your cranes, making it easier to identify compatible replacements when necessary.
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Scenario 3: Insufficient Training on Gantry Crane Component Maintenance
The Problem: Many companies overlook the importance of proper training for personnel handling gantry crane components. This can result in improper operation, leading to premature wear and tear or even catastrophic failures. In industries where safety is paramount, such as construction and manufacturing, the lack of trained operators can pose significant risks, not only to equipment but also to employee safety. Buyers often find themselves in a situation where they have invested in high-quality components but are unable to maximize their performance due to inadequate operational knowledge.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is vital for companies to invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff. Collaborating with component suppliers to provide training sessions on proper operation and maintenance can be highly beneficial. These sessions should cover best practices, safety protocols, and troubleshooting techniques. Additionally, developing a user manual or quick-reference guide specific to the gantry crane model and components can aid operators in understanding their equipment better. Regular refresher courses and updates on new technologies or components will ensure that the workforce remains competent and confident in handling the equipment safely and efficiently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gantry crane components
What Are the Key Materials Used in Gantry Crane Components?
When selecting materials for gantry crane components, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis focuses on four common materials: steel, aluminum, composite materials, and cast iron. Each of these materials has unique characteristics that affect performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
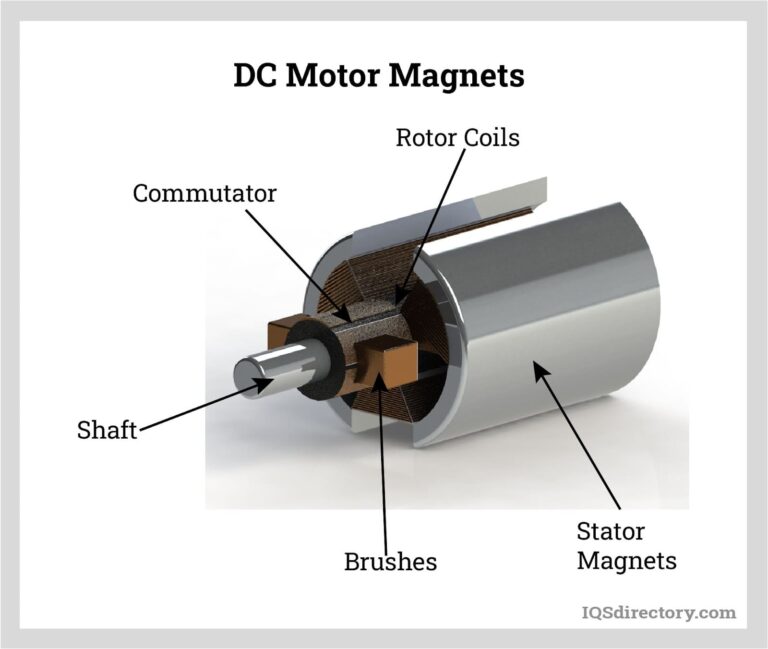
How Does Steel Benefit Gantry Crane Components?
Steel is the most commonly used material for gantry crane components due to its high strength and durability. It typically exhibits excellent tensile strength and can withstand high loads, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Steel components can also be treated for corrosion resistance, enhancing their longevity in harsh environments.
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Pros: Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio allows for the construction of robust crane structures. It is relatively cost-effective and widely available, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
Cons: However, steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to maintenance challenges. Its weight can also pose challenges in terms of transport and installation.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for lifting heavy loads in various environments, including construction sites and shipyards. Its compatibility with standard manufacturing processes ensures compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Gantry Cranes?
Aluminum is increasingly being used in gantry crane components, particularly for portable models. It is lightweight yet strong, making it easier to transport and assemble. Aluminum also has excellent corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in coastal or humid environments.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces transportation costs and allows for easier maneuverability on-site. Its resistance to corrosion minimizes maintenance needs, enhancing operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for applications requiring frequent relocation, such as in warehouses or temporary construction sites. Buyers in regions with high humidity, like parts of South America and the Middle East, may prefer aluminum for its corrosion resistance.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Gantry Crane Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are gaining traction in the manufacturing of gantry crane components. These materials offer a unique combination of strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Pros: Composites are highly resistant to environmental factors and do not corrode, making them ideal for long-term use in various conditions. Their lightweight nature allows for easier handling and installation.
Cons: However, composites can be significantly more expensive than traditional materials like steel and aluminum. Manufacturing processes for composites can also be complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are well-suited for specialized applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace or high-tech manufacturing. Buyers must consider the higher initial investment against long-term savings from reduced maintenance.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Gantry Crane Design?
Cast iron is often used in specific components of gantry cranes, such as wheels and supports, due to its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb shock loads.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Pros: Cast iron’s durability and ability to withstand high pressure make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: The brittleness of cast iron can be a limitation, as it may crack under excessive stress or impact. Additionally, it is heavier than steel, which can complicate transport and installation.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often utilized in fixed installations where heavy loads are consistently handled. International buyers should ensure that cast iron components meet relevant standards for safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gantry Crane Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for gantry crane components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, end carriages | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Portable gantry cranes | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications | Excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight | Higher cost and complex manufacturing processes | High |
| Cast Iron | Wheels and shock-absorbing supports | Durable and wear-resistant | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties and applications of different materials used in gantry crane components, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gantry crane components
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Gantry Crane Components?
The manufacturing of gantry crane components involves several critical stages, ensuring that each part meets the necessary strength, durability, and safety standards. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of their suppliers.
How Are Materials Prepared for Gantry Crane Component Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational stage in the manufacturing process. High-quality steel is often the primary material used due to its strength and durability. The preparation phase includes:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right grade of steel (e.g., S235, S275) based on the load requirements and environmental conditions.
- Cutting and Shaping: Using plasma cutting, laser cutting, or water jet cutting to achieve precise dimensions. This step ensures that the components will fit together correctly during assembly.
- Surface Treatment: Applying processes such as sandblasting or acid pickling to remove impurities and prepare the surface for further treatment, enhancing corrosion resistance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Gantry Crane Components?
Once the materials are prepared, forming techniques are employed to shape the components:
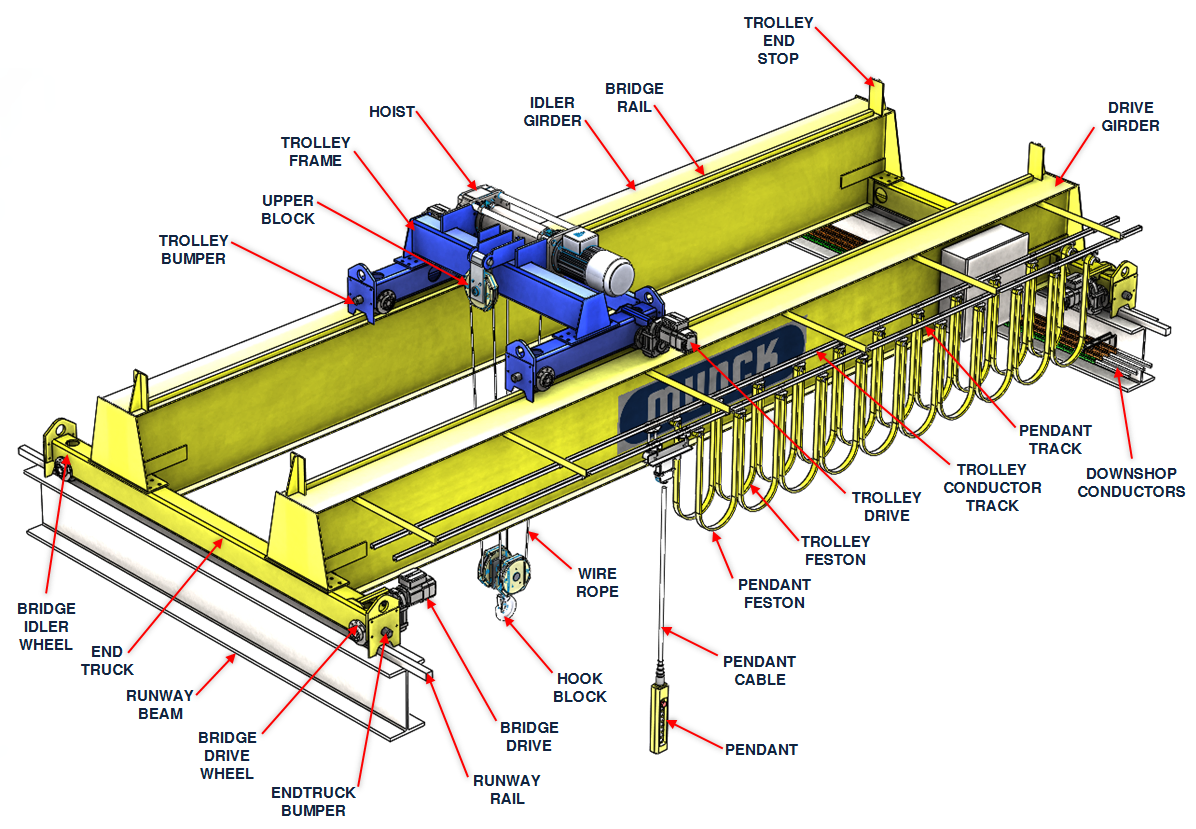
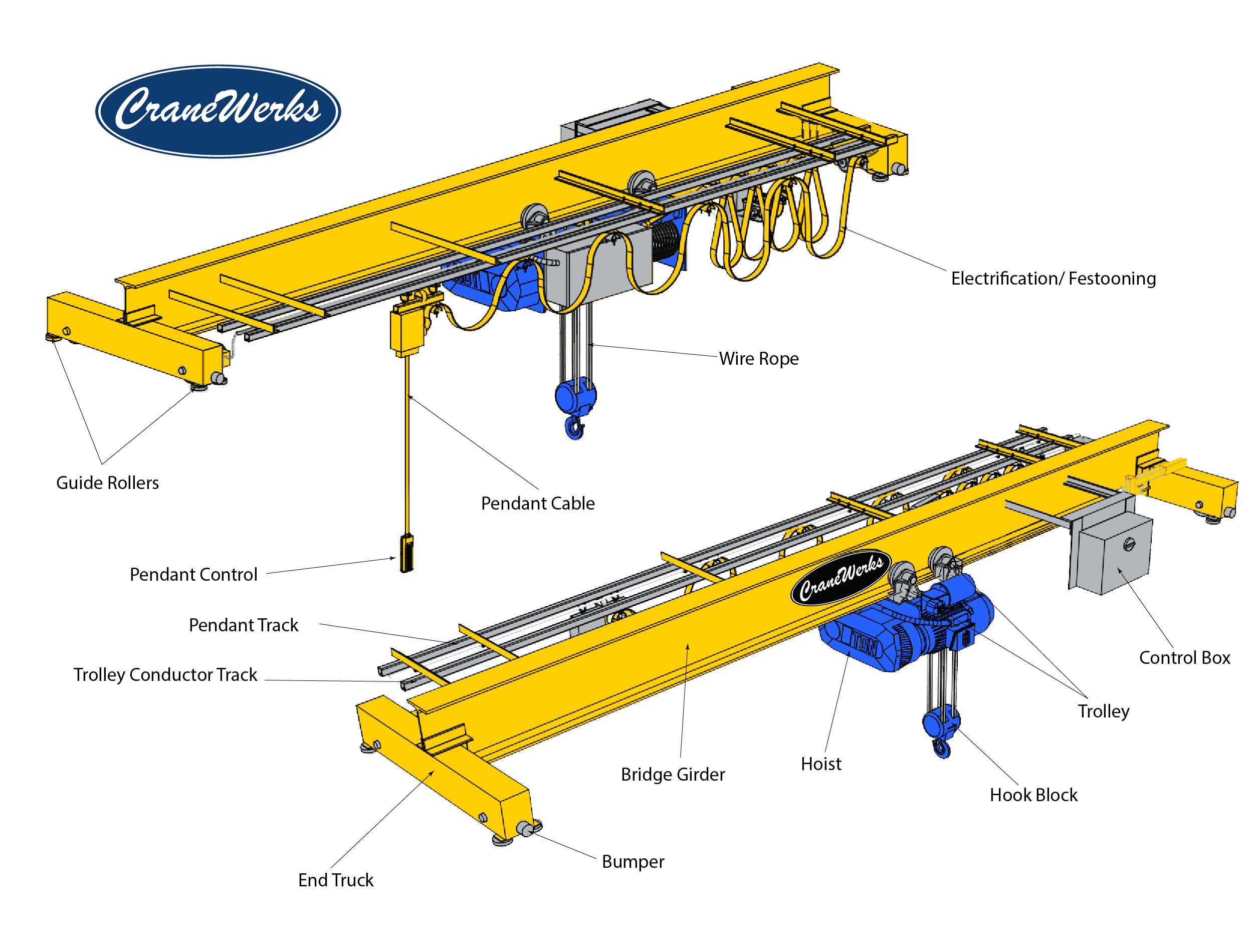
- Welding: Various welding methods, including MIG, TIG, and submerged arc welding, are utilized to join components. This is particularly important for the gantry frame and end carriages, where structural integrity is critical.
- Bending and Forming: Techniques such as roll bending or press braking are used to create the desired shapes for beams and brackets. This process must be precise to maintain the load-bearing capacity of the components.
- Machining: After forming, components may require additional machining to achieve final dimensions. This includes drilling holes for bolts, machining surfaces for fit, and ensuring tolerances are met.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Gantry Crane Components?
The assembly of gantry crane components is a meticulous process that brings all the manufactured parts together:
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller components, such as hoist trolleys and end carriages, are typically assembled first. This allows for easier handling and quality checks before final assembly.
- Main Assembly: The gantry frame is constructed, incorporating the assembled components. This stage often involves the use of jigs to maintain alignment and ensure structural integrity.
- Final Assembly and Integration: All systems, including electrical wiring and control systems, are integrated at this stage. Attention to detail is crucial to ensure that all systems function correctly together.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Gantry Crane Components?
The finishing stage enhances the durability and aesthetic appeal of gantry crane components:
- Coating: Components are often coated with protective finishes such as powder coating or galvanization. These coatings help prevent corrosion and wear, especially in harsh environments.
- Inspection and Testing: Before leaving the factory, components undergo rigorous inspection. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing to identify any structural flaws.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Gantry Crane Components?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing process to ensure that gantry crane components meet international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that manufacturers maintain a quality management system, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For cranes used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in Gantry Crane Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each component meets the required specifications:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Quality checks are conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, such as after welding or before machining, to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed gantry crane components undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet all specifications and standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Gantry Crane Components?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the performance and safety of gantry crane components:
- Load Testing: Components are subjected to load tests to ensure they can handle specified weights without deformation or failure.
- Functional Testing: This involves testing the operational systems, including hoists and electrical controls, to ensure they function as intended.
- Durability Testing: Components may undergo environmental testing to assess their performance under various conditions, including extreme temperatures and humidity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Buyers can request to see their quality management certifications.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including inspection records and test results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality certification is vital:
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements. For example, while CE marking is crucial for Europe, other regions may have their own standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Buyers should be aware of cultural differences that may influence business practices and communication regarding quality assurance.
- Logistical Challenges: When sourcing internationally, consider how transportation and shipping can affect the integrity of the components, necessitating additional inspection upon arrival.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for gantry crane components, ensuring they receive products that meet both quality and safety standards.
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gantry crane components’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring gantry crane components efficiently and effectively. Given the complexity of these systems and their critical role in various industrial applications, following a structured checklist will ensure that you make informed decisions while securing high-quality components tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, establish clear technical specifications for the gantry crane components you require. This includes load capacity, dimensions, and material requirements. Having well-defined specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that you receive components that meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in gantry crane components. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry, particularly those with experience in your geographical market. Assess their online presence, client testimonials, and case studies to gauge their reliability and reputation.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
✅ Verify Supplier Certifications
Certification is crucial in ensuring the quality and safety of the components you purchase. Check for industry-specific certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems, or CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. These certifications demonstrate that the supplier adheres to international quality standards and regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline the components, pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. This step is essential for comparing offers and understanding the total cost of ownership, including any additional fees such as shipping or customs duties. Look for transparency in the quotation to avoid hidden costs later.
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Step 5: Assess Quality Assurance Processes
✅ Inquire About Quality Control Measures
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of gantry crane components. Ask suppliers about their quality control processes, including testing methods and inspection protocols. Understanding these processes will give you confidence in the durability and reliability of the components you are purchasing.
Step 6: Review Warranty and After-Sales Support
Before finalizing your purchase, evaluate the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A robust warranty can protect your investment against defects, while reliable after-sales support can assist you with maintenance and troubleshooting. Ensure you understand the terms and conditions associated with these services.
Step 7: Negotiate Payment and Delivery Terms
✅ Finalize Terms Before Commitment
Once you are satisfied with the supplier’s offerings, negotiate payment and delivery terms that are mutually beneficial. Consider factors such as payment schedules, delivery timelines, and any penalties for delays. Clearly defined terms will help mitigate risks and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for gantry crane components, ensuring they secure high-quality products that meet their operational requirements while fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gantry crane components Sourcing
When sourcing gantry crane components, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will delve into the key cost components, factors influencing pricing, and strategic tips for buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Cost Components in Gantry Crane Components?
The total cost of gantry crane components can be broken down into several critical components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Steel, aluminum, and specialized composites are common, with prices fluctuating based on global market trends. Higher-grade materials, such as corrosion-resistant alloys, can increase costs but provide long-term durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the components being manufactured. Skilled labor for assembly and quality control is essential, and labor costs can be higher in regions with stringent labor laws or higher living expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory rent. Efficient production processes can mitigate overhead costs, making it crucial to assess suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific gantry crane components can lead to significant initial costs. Buyers should consider whether the tooling can be amortized over a larger order volume to reduce per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality assurance processes ensures components meet safety and performance standards. While this may increase upfront costs, it can prevent costly failures and downtime later.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can affect total logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences the Pricing of Gantry Crane Components?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure for gantry crane components:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate favorable terms based on projected volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom components tailored to specific applications often command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary customizations that can inflate costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Components that meet higher quality standards or possess specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may have increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge a premium but provide peace of mind.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) used in transactions is vital. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing gantry crane components, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Strategically: Leverage volume commitments and long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing. Be prepared to walk away if terms do not meet budget constraints.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial purchase prices. Consider factors such as maintenance, expected lifespan, and operational efficiency to determine the true cost of ownership.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of potential tariffs, shipping delays, and currency fluctuations that can affect final costs. Utilizing local suppliers or manufacturers with international experience may mitigate some risks.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly review market trends and competitor pricing to ensure competitiveness. This knowledge can empower negotiations and strategic sourcing decisions.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of cost structures, pricing influencers, and strategic negotiation techniques can significantly enhance the sourcing process for gantry crane components. Buyers should approach sourcing with a clear strategy to optimize costs and ensure long-term operational efficiency. Please note that prices can vary widely based on numerous factors and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate quotes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gantry crane components With Other Solutions
In the industrial lifting landscape, businesses often seek solutions that best fit their operational needs, budget, and efficiency goals. While gantry crane components are a popular choice due to their high lifting capacity and versatility, there are alternative solutions available that can also fulfill similar roles. This section compares gantry crane components with other viable options, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Gantry Crane Components | Forklift Trucks | Overhead Cranes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High lifting capacity, ideal for heavy loads and outdoor use | Suitable for medium loads, flexible movement | Excellent for large spaces, continuous lifting capability |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, potential long-term savings through durability | Lower initial cost, but higher operational costs | Higher initial investment, significant ROI in high-volume operations |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space for setup and rails, installation can be complex | Quick setup and operation, minimal training needed | Installation requires structural support, often complex |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspections and maintenance of moving parts | Regular servicing needed, but simpler than gantries | High maintenance demands due to complexity and wear |
| Best Use Case | Heavy lifting in construction, shipyards, and large warehouses | Material handling in warehouses and distribution centers | Continuous lifting in manufacturing and assembly lines |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Forklift Trucks?
Forklift trucks are a widely used alternative to gantry cranes, particularly in warehouses and distribution centers. They excel in maneuverability, allowing operators to transport materials over shorter distances with ease. The lower initial cost compared to gantry cranes makes them an attractive option for businesses with budget constraints. However, they are limited in lifting capacity and may not be suitable for extremely heavy loads. Additionally, forklifts require ongoing operational costs, including fuel or electricity, maintenance, and potential operator training.
How Do Overhead Cranes Compare to Gantry Crane Components?
Overhead cranes offer a different approach to material handling, particularly in environments with limited floor space but high vertical clearance. They provide continuous lifting capabilities, which can be beneficial in manufacturing settings. The downside is that overhead cranes often require more significant initial investments and structural modifications to the facility. Maintenance can also be more demanding due to their complex systems. However, for businesses engaged in high-volume operations, the return on investment can be substantial, as these systems often enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
When evaluating lifting solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, including load capacity, space constraints, and budget. Gantry crane components shine in heavy-duty applications but may not be the best fit for every scenario. Forklifts are excellent for flexibility and lower upfront costs but come with limitations in load capacity. Overhead cranes offer a robust solution for high-volume operations but require a larger investment. Assessing these factors will enable businesses to select the most effective lifting solution tailored to their operational requirements and financial capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gantry crane components
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gantry Crane Components?
When considering the purchase of gantry crane components, understanding the essential technical specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Here are several critical properties that B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of gantry crane components—such as steel or aluminum—determines their strength, durability, and weight capacity. Common grades include structural steel grades like S235 or S355, which are known for their high tensile strength and resilience. Choosing the right material grade is vital for ensuring that the crane can handle the intended loads without risk of failure, which is particularly important in heavy-duty applications across industries like construction and manufacturing.
2. Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight a gantry crane can safely lift. This specification is often expressed in tons and is crucial for determining the appropriate crane model for specific tasks. Understanding load capacity helps in selecting a crane that can handle the required weight without compromising safety or efficiency, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels specify the allowable deviation in the dimensions and weight of crane components. Precise tolerances are essential for ensuring compatibility among parts and for the overall safety and functionality of the crane. For instance, tighter tolerances may be necessary for components that experience high levels of stress, such as the hoist trolley and gantry frame.
4. Safety Features
Safety features include mechanisms such as limit switches, overload protection, and emergency stop functions. These features are critical for preventing accidents during crane operation and ensuring compliance with industry safety standards. A crane equipped with robust safety features minimizes risks, making it an attractive option for businesses focused on worker safety and regulatory compliance.
5. Operational Speed
Operational speed refers to how quickly the crane can lift, lower, and move loads. This specification can significantly impact operational efficiency in industrial settings. Understanding the operational speed helps buyers choose a crane that aligns with their workflow requirements, allowing for optimized productivity.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
6. Control System Type
The control system type—manual, remote, or automated—affects how operators interact with the crane. Advanced control systems can enhance precision and reduce the likelihood of human error, making them preferable for complex lifting tasks. Selecting the right control system is essential for ensuring ease of use and operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Gantry Crane Industry?
Navigating the gantry crane market involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some common terms that can help facilitate better communication and understanding in B2B transactions:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of gantry cranes, buyers should be aware of OEMs to ensure they are sourcing high-quality, reliable components that meet industry standards.
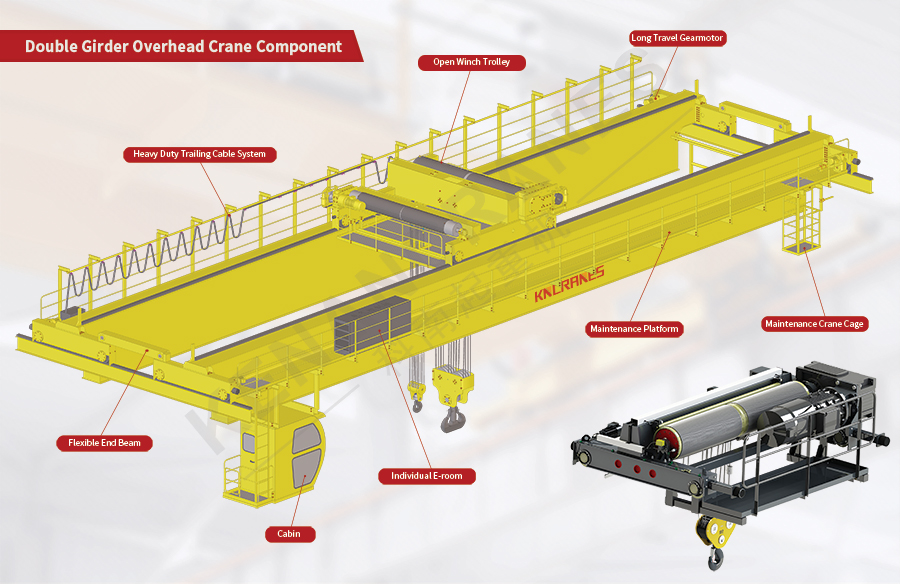
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively, particularly when sourcing multiple components for large-scale projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific products or services. For gantry crane components, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and negotiate terms, ensuring they get the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and liability, particularly for international transactions involving gantry crane components.
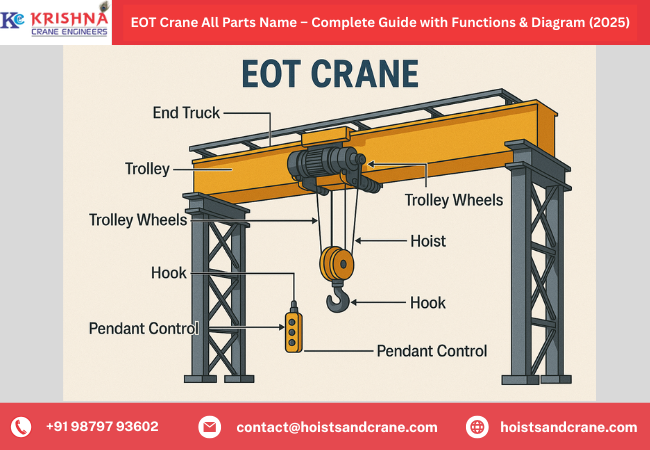
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is crucial for project planning and helps businesses avoid delays in operations, particularly in industries where time-sensitive lifting solutions are essential.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing gantry crane components, ensuring they meet operational needs and safety standards while optimizing their investments.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gantry crane components Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Gantry Crane Components?
The gantry crane components market is experiencing notable growth driven by several global factors. Rapid industrialization, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, is increasing the demand for efficient material handling solutions. In regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, infrastructure development projects are propelling the need for robust lifting equipment, including gantry cranes. Additionally, technological advancements in automation and IoT are reshaping sourcing practices, allowing for smarter, more efficient procurement processes. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide real-time data and insights into equipment performance, leading to a preference for manufacturers that integrate advanced technology into their components.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
Emerging trends in the market include a shift towards modular designs that allow for easy customization and scalability to meet specific operational needs. International buyers are also gravitating towards suppliers that offer comprehensive after-sales support, ensuring maintenance and upgrades are manageable over the crane’s lifecycle. Furthermore, with the rise of e-commerce, there’s a growing emphasis on faster delivery times and flexible payment solutions, compelling suppliers to adapt their logistics strategies accordingly.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Gantry Crane Components Market?
In today’s B2B landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount for businesses in the gantry crane components sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with manufacturing processes and are demanding transparency in supply chains. This shift is leading to a preference for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing carbon emissions during production.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to local environmental regulations are becoming crucial for suppliers looking to establish credibility in the international market. Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of crane components not only enhances the appeal of products but also aligns with the corporate social responsibility goals of many organizations. Ethical sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally-conscious consumers.
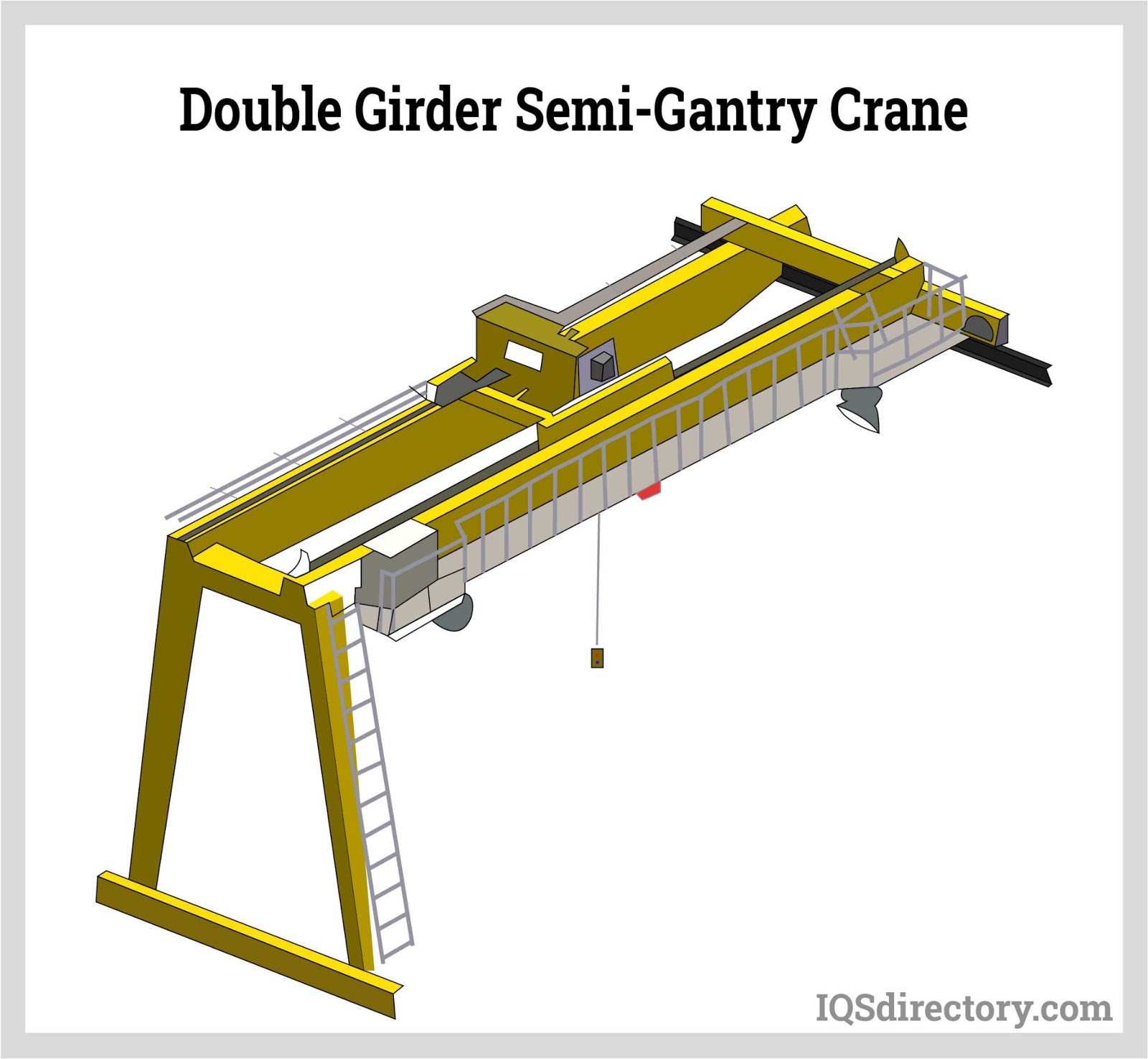
Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
What Is the Historical Context of Gantry Cranes in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of gantry cranes dates back to the early 20th century, initially designed for heavy lifting in shipyards and construction sites. As industries expanded, the demand for efficient lifting solutions grew, prompting innovations in design and technology. The introduction of electric hoists and automated systems in the latter half of the century revolutionized the capabilities of gantry cranes, allowing for greater lifting capacities and improved safety features.
Over the decades, the market has witnessed significant transformations driven by technological advancements and changing industrial needs. Today, gantry cranes are utilized in a variety of sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and construction, reflecting their versatility and adaptability. This historical context highlights the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the evolving demands of international B2B buyers, making it crucial for suppliers to stay ahead of market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gantry crane components
-
How do I ensure the quality of gantry crane components before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of gantry crane components, consider sourcing from reputable manufacturers with a track record in the industry. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 to verify quality management systems. Conduct thorough due diligence by reviewing customer testimonials and case studies. Additionally, consider requesting samples or visiting the supplier’s facility to assess production processes. Establishing a quality assurance agreement can also help ensure compliance with your specifications. -
What is the best gantry crane component for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, a double girder gantry crane is generally the best choice due to its enhanced stability and lifting capacity. It can handle weights ranging from 10 to over 200 tons, making it ideal for heavy industrial environments. The design allows for better load distribution and offers greater rigidity compared to single girder models. When selecting components, ensure they are rated for the specific loads and conditions of your operational environment. -
What are the typical lead times for gantry crane components?
Lead times for gantry crane components can vary significantly based on the complexity of the parts and the manufacturer’s location. Typically, lead times range from 4 to 12 weeks. Custom components may require longer production times due to design and manufacturing processes. When planning your procurement, factor in additional time for shipping and potential customs clearance, especially for international orders from regions like Africa and South America. -
What customization options are available for gantry crane components?
Customization options for gantry crane components include adjustments in size, lifting capacity, and operational features. Buyers can specify hoist types, control systems, and safety features based on their operational needs. Some manufacturers offer bespoke solutions, allowing you to tailor components for specific applications or environments. It’s advisable to communicate your requirements clearly during the sourcing process to ensure that the final products meet your operational demands. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gantry crane components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gantry crane components can vary by manufacturer and the type of component. Generally, MOQs may range from one unit for standard components to several units for custom or specialized items. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are testing a new component or entering a new market. This can help manage initial investment risks. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing gantry crane components internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of gantry crane components often include options like letter of credit, advance payment, or net 30/60 days. Many suppliers may require an upfront deposit, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to establish clear terms before finalizing the contract to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, particularly for large transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers for gantry crane components effectively?
To vet suppliers for gantry crane components, start by checking their industry reputation through online reviews and industry forums. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of service. Conduct background checks to verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. If possible, visit their manufacturing facilities or arrange third-party audits to assess their capabilities firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing gantry crane components?
When importing gantry crane components, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with heavy equipment to ensure proper handling and compliance with local regulations. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may affect your budget. It’s also advisable to plan for potential delays in customs clearance, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Top 7 Gantry Crane Components Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DG Crane – Gantry Cranes
Domain: dgcrane.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Gantry cranes are heavy-duty lifting machines used in various industries to transport and lift heavy loads, typically ranging from 10 to 200 tons. They consist of several components: 1. Gantry Frame – the primary supporting structure with two vertical legs and a horizontal beam. 2. Hoist Trolley – carries the load and moves along the beam, can be fitted with hooks, magnets, or grabs. 3. End Carria…
2. Superior Rigging – Gantry Cranes
Domain: superiorrigging.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: A gantry is an overhead crane with freestanding legs mounted on wheels, allowing it to traverse along a track or rail system. It is adaptable for various environments, suitable for indoor and outdoor applications, and is used for lifting and handling equipment such as art pieces and industrial loads. Key types include: 1) Portable Gantry Crane – for light to medium lifting, mobile and adaptable; 2…
3. AICRANE – Gantry Cranes
Domain: aicraneliftingsolution.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Gantry cranes are essential lifting equipment used in shipbuilding, construction, logistics, and manufacturing. Key components include: 1. Bridge (Girder): Primary horizontal beam, can be single or double girder, made of Q235-B material with a minimum plate thickness of 6mm. 2. Legs: Vertical structures with trapezoidal cross-section for stability. 3. Hoist and Trolley: Lifting mechanism with moto…
4. LinkedIn – Electric Gantry Cranes
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Electric gantry cranes are essential for lifting and transporting heavy materials in various industries such as shipyards, warehouses, manufacturing plants, and construction sites. They operate on tracks or wheels, allowing for mobility and flexibility. Key components include: 1. Gantry Frame – main structure with vertical legs and a horizontal beam, available in single-girder or double-girder con…
5. AG Cranes – Hoist Unit & Crane Beam
Domain: agcranes.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Hoist Unit: Performs lifting and lowering, moves load side to side, typically has steel wire rope or chain, usually 2-speed for accurate positioning. Crane Beam: Single or double beams that span the width of the crane, attached to end carriages, displays SWL and serial number. Electrical Control Panel: Reduces incoming 415v power to 110v or 48v for user safety. End Carriages: Sold in pairs, suppor…
6. JSBWCranes – Gantry Crane Parts
Domain: jsbwcrane.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Gantry Crane Parts: gantry beam, end beam, leg, lifting mechanism, wagon running mechanism, electrical system. Lifting Mechanism: powered by electric motor, connected to reducer, drives drum rotation. Brake System: electromagnetic or hydraulic brakes for load holding. Trolley Mechanism: motor-driven, controls lateral movement, uses frequency conversion for speed regulation. Long Travel: walking wh…
7. IQS Directory – Gantry Cranes
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Gantry cranes are a type of overhead crane with one or two beams supported by upright legs, capable of traversing on wheels, tracks, or rails. They are used in various settings such as workshops, warehouses, freight yards, railroads, and shipyards for both light and heavy-duty lifting tasks. Key types include: 1. Full Gantry Crane: Widely used in heavy industries, customizable for height, span, an…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gantry crane components
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Gantry Crane Components?
As the demand for efficient lifting solutions continues to rise globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of gantry crane components becomes crucial. Buyers should focus on selecting suppliers who not only offer high-quality materials but also provide customizable solutions tailored to specific industry needs. Understanding the critical components—such as the gantry frame, hoist trolley, and electrical systems—enables businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Operations?
Investing in the right gantry crane components through strategic sourcing not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes downtime and maintenance issues. By forging strong relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure a steady supply of quality parts while benefiting from the latest technological advancements in crane design and functionality.

Illustrative image related to gantry crane components
What’s Next for International Buyers?
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to take proactive steps in evaluating their sourcing strategies. Engage with suppliers who understand the regional market dynamics and can offer innovative solutions to meet your lifting challenges. By prioritizing quality and efficiency, you can position your operations for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Start your journey toward optimized sourcing today—your business’s productivity depends on it.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.