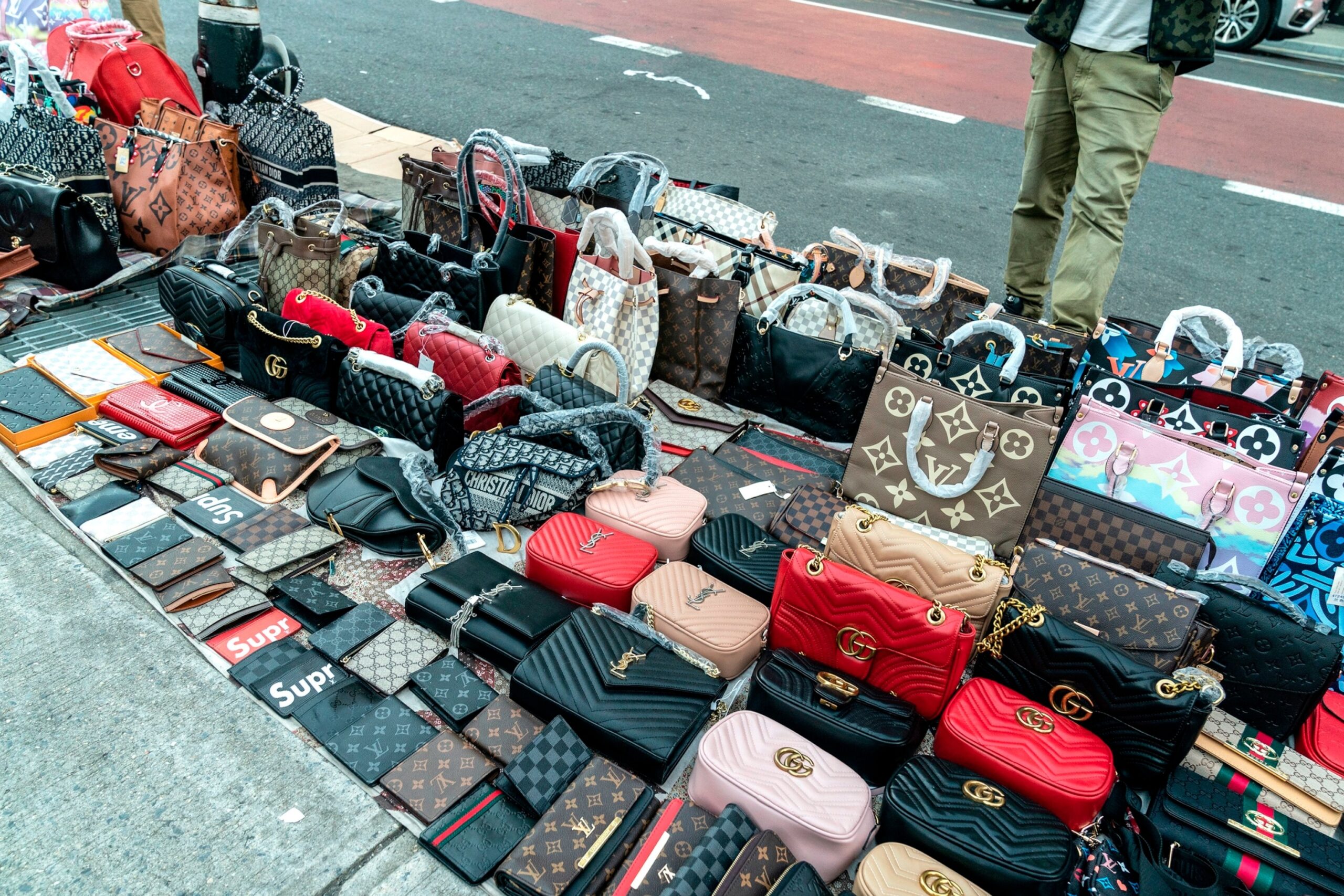
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Fake Designer Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fake designer
In an increasingly interconnected global market, the challenge of sourcing authentic yet affordable products remains a critical concern for B2B buyers, particularly when navigating the realm of fake designer goods. As businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—seek to enhance their offerings without inflating costs, understanding the nuances of fake designer products becomes essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of fake designer items available, their applications across different industries, and vital insights into effective supplier vetting processes.
By exploring the cost implications and the quality spectrum of fake designer goods, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re looking to stock your retail space with trendy replicas or seeking unique items for promotional purposes, our detailed analysis will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex market. Moreover, we will delve into the ethical considerations and potential risks associated with fake designer products, ensuring that your procurement strategies align with both market demands and regulatory frameworks.
As you progress through this guide, you will gain valuable insights that not only streamline your sourcing efforts but also enhance your competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace. With the right information at your fingertips, your business can successfully tap into the lucrative market for fake designer goods while mitigating risks and maximizing profitability.
Understanding fake designer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replica Designers | Exact copies of original designs, often with lower quality materials | Retail and e-commerce | Pros: Lower cost; Cons: Legal risks and brand dilution |
| Inspired Designs | Designs that take inspiration from originals but are distinctly different | Fashion and accessory markets | Pros: Unique offerings; Cons: Potential for brand backlash |
| Unauthorized Copies | Products made without permission from the original designer, often of inferior quality | Bulk purchasing for discount retail | Pros: High profit margins; Cons: Ethical concerns and legality issues |
| High-Quality Fakes | Well-crafted replicas that closely mimic high-end products | Luxury resale and boutique markets | Pros: Appealing to budget-conscious consumers; Cons: Risk of counterfeit claims |
| Custom Counterfeits | Tailored designs that mimic high-end brands, often personalized for buyers | Niche markets and special events | Pros: Unique appeal; Cons: Legal ramifications and potential market confusion |
What Are Replica Designers and How Do They Serve B2B Buyers?
Replica designers produce exact copies of original designs, typically using lower-quality materials. These products are popular in retail and e-commerce, where businesses seek to offer consumers affordable alternatives to high-end brands. However, buyers must weigh the legal risks and potential for brand dilution against the lower costs. Ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws is crucial for businesses considering this option.
How Do Inspired Designs Differ and What Are Their Benefits?
Inspired designs take cues from original creations but maintain distinct differences in style and execution. These designs are suitable for fashion and accessory markets, allowing businesses to offer unique products that stand out in a competitive landscape. While they provide a creative edge, buyers should be cautious of potential backlash from consumers who may perceive them as knock-offs, impacting brand reputation.
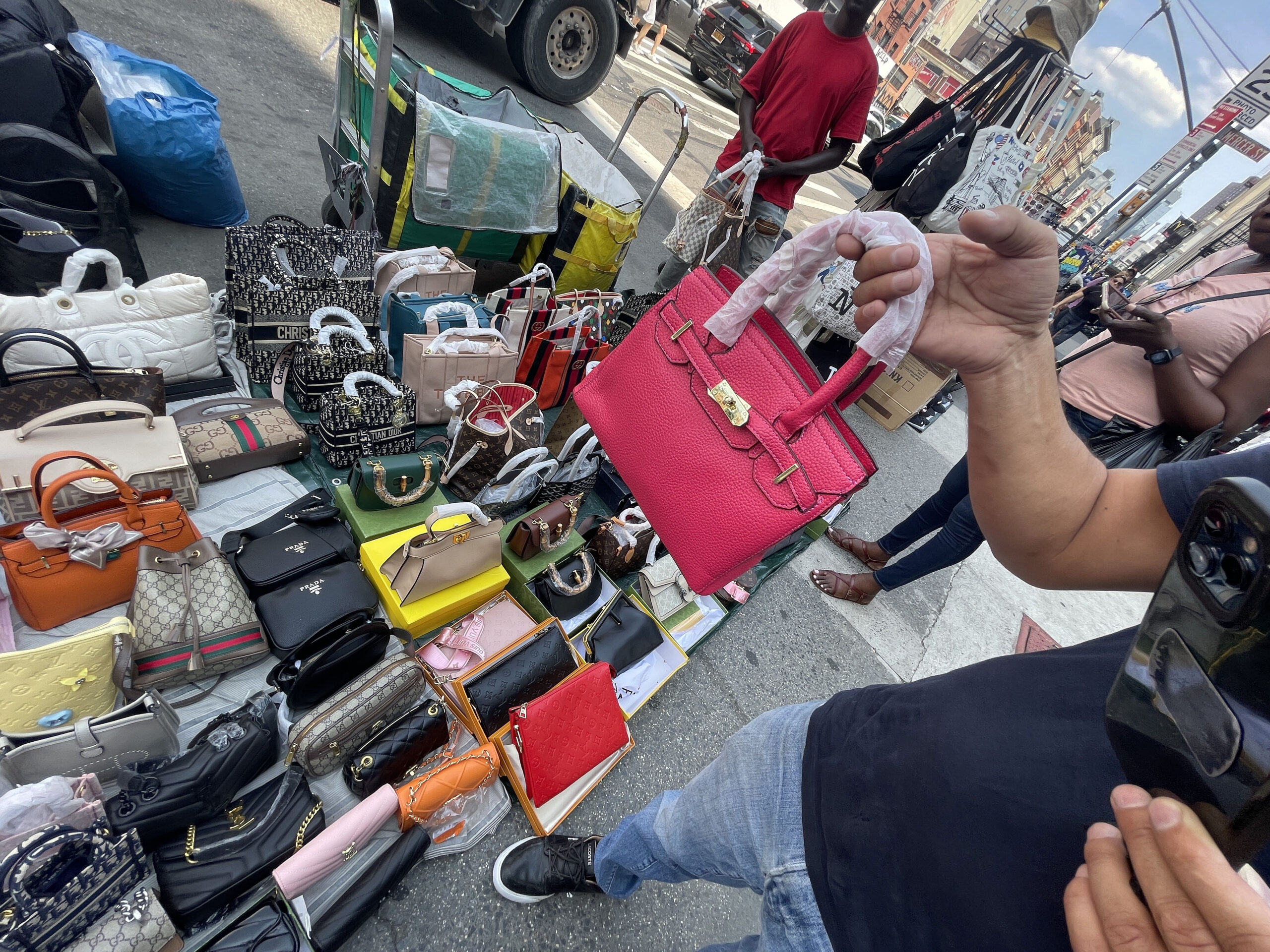
What Risks Are Associated with Unauthorized Copies?
Unauthorized copies are products made without the original designer’s permission, often resulting in inferior quality. They are commonly used in bulk purchasing for discount retail outlets. Although they can yield high profit margins, buyers face significant ethical concerns and legal implications. Businesses must navigate these challenges carefully to avoid damaging their reputation or facing lawsuits.
What Makes High-Quality Fakes Attractive to B2B Buyers?
High-quality fakes are well-crafted replicas that closely mimic luxury products, appealing to budget-conscious consumers. They find their place in luxury resale and boutique markets, where buyers seek affordable luxury options. While they can attract a strong customer base, businesses must remain vigilant against counterfeit claims, which can lead to legal disputes and customer trust issues.
How Do Custom Counterfeits Cater to Specific Market Needs?
Custom counterfeits are tailored designs that imitate high-end brands, often personalized for specific buyers. This niche market appeals to businesses looking to provide unique offerings for special events or targeted audiences. However, the legal ramifications of selling such products can be severe, and businesses should consider the potential for market confusion and brand integrity when exploring this avenue.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Key Industrial Applications of fake designer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fake designer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion Retail | Trend Analysis and Design Prototyping | Enables quick adaptation to market trends, reducing time-to-market for new collections. | Verify the authenticity of designs and ensure compliance with intellectual property laws. |
| Advertising & Marketing | Brand Promotion and Campaign Development | Helps create compelling visuals that resonate with target audiences, enhancing brand appeal. | Assess the quality of design and alignment with brand identity. |
| Interior Design | Space Planning and Conceptual Design | Provides innovative design solutions that can elevate client projects, increasing customer satisfaction. | Ensure designers understand local cultural nuances and preferences. |
| E-commerce Platforms | Product Listing and Visual Merchandising | Enhances online presence through attractive product representations, leading to increased sales. | Prioritize high-resolution images and accurate representations of products. |
| Event Planning | Thematic Event Design and Branding | Facilitates cohesive branding and visual storytelling for events, improving attendee experience. | Consider logistics and timely delivery of design materials to meet event timelines. |
How is ‘fake designer’ used in the Fashion Retail sector?
In the fashion retail industry, ‘fake designer’ applications primarily revolve around trend analysis and design prototyping. Retailers leverage these designs to quickly adapt to emerging fashion trends, allowing them to reduce their time-to-market for new collections. This is particularly valuable in fast-paced markets, where consumer preferences shift rapidly. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to ensure that the designs comply with local regulations and respect intellectual property laws to avoid legal complications.
What role does ‘fake designer’ play in Advertising & Marketing?
In advertising and marketing, ‘fake designer’ applications are vital for brand promotion and campaign development. Businesses utilize these designs to create visually compelling marketing materials that resonate with their target audiences, enhancing brand appeal and engagement. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, understanding the specific cultural nuances of their markets is essential to ensure that the designs align with local tastes and preferences, thereby maximizing the impact of their marketing efforts.
How does ‘fake designer’ contribute to Interior Design?
In the interior design sector, ‘fake designer’ applications are used for space planning and conceptual design. Designers can access innovative design solutions that elevate client projects, leading to increased customer satisfaction and repeat business. For international buyers, particularly in diverse regions like Africa, it is important to source designers who understand local cultural contexts and preferences, ensuring that the designs not only meet aesthetic goals but also resonate with the intended audience.
What is the significance of ‘fake designer’ in E-commerce Platforms?
For e-commerce platforms, ‘fake designer’ applications are crucial for product listing and visual merchandising. Attractive product representations, created through skilled design, significantly enhance a brand’s online presence and can lead to increased sales. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-resolution images and accurate representations of products to ensure that they meet customer expectations and reduce return rates, which is particularly important in competitive online markets.
How does ‘fake designer’ enhance Event Planning?
In event planning, ‘fake designer’ applications facilitate thematic event design and branding. They enable planners to create cohesive branding and visual storytelling that enhances the attendee experience. For international buyers, especially in regions with unique cultural traditions, it is essential to consider logistics and the timely delivery of design materials to meet event timelines. This ensures that the visual elements align with the event’s theme and objectives, ultimately leading to a successful outcome.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fake designer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Risk of Brand Dilution from Poor-Quality Fake Designers
The Problem: For B2B buyers, particularly in markets like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, investing in fake designer products can lead to significant brand dilution. When a company sources items that are poorly made or that don’t align with their brand values, they risk tarnishing their reputation. This can result in a loss of customer trust and loyalty, especially when the quality of these products fails to meet customer expectations. Buyers might find themselves in a precarious position where they need to balance cost savings against the potential long-term impacts on their brand image.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should establish strict quality control protocols before engaging with any fake designer. This includes conducting comprehensive due diligence on suppliers, requesting samples, and ensuring that the materials used in the products meet the required standards. Additionally, consider implementing a trial phase where a limited quantity of products is tested in the market. Gathering feedback from customers can provide invaluable insights that help refine future orders. Building a strong relationship with reliable suppliers who understand your brand’s ethos can also enhance quality assurance.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Legal and Ethical Implications of Fake Designers
The Problem: In regions such as South America and Europe, the legal landscape surrounding counterfeit goods is complex and stringent. B2B buyers often face dilemmas when sourcing fake designer products, as these can sometimes infringe on intellectual property rights. This not only exposes companies to potential legal action but can also harm their business relationships and reputations in the marketplace. The fear of legal ramifications can create a significant barrier to sourcing products that may otherwise be appealing.
The Solution: To navigate these legal waters effectively, B2B buyers should prioritize transparency in their sourcing practices. This means thoroughly researching the legalities surrounding the use of fake designers in their respective markets. Engage legal experts familiar with intellectual property law to review contracts and product specifications. Furthermore, opt for suppliers who provide clear documentation that their products do not violate copyright or trademark laws. Creating a clear sourcing policy that outlines acceptable practices and the importance of ethical sourcing can serve as a guideline for your purchasing team, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of legal issues.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Scenario 3: The Challenge of Ensuring Consistent Supply Chains with Fake Designers
The Problem: For businesses operating in diverse regions like Africa and the Middle East, maintaining a reliable supply chain for fake designer products can be a significant challenge. Fluctuations in quality, delivery delays, and inconsistent communication from suppliers can lead to operational disruptions. B2B buyers often find themselves in a position where they cannot meet customer demand due to supply chain inefficiencies, which can result in lost sales and eroded customer relationships.
The Solution: To enhance supply chain reliability, B2B buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base. Relying on multiple suppliers can reduce the risk associated with dependency on a single source. Implementing a robust supplier management system that tracks performance metrics, such as delivery times and product quality, can provide insights into which suppliers are most reliable. Regular communication and establishing clear expectations can also foster better relationships. Additionally, consider integrating technology such as supply chain management software to streamline operations and improve visibility into inventory levels, allowing for proactive adjustments to meet customer needs effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fake designer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Fake Designer Products?
In the realm of fake designer products, the choice of materials significantly affects the overall quality, durability, and marketability of the end product. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here, we analyze four common materials used in fake designer items, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse markets.
How Does PVC Influence the Quality of Fake Designer Products?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used synthetic plastic polymer known for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. PVC is lightweight, resistant to moisture, and can be produced in various colors and finishes, making it suitable for items like bags, wallets, and accessories.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Pros: PVC is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for high-volume production. It also exhibits good resistance to weathering, which is beneficial for outdoor applications.
Cons: However, PVC can be less durable than other materials, particularly under extreme temperatures. It may also have a lower aesthetic appeal compared to leather or high-end synthetics.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with various media, but it may not perform well under high heat or pressure conditions. This limits its use in products that require structural integrity.
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding PVC use, particularly in regions with stringent environmental standards. Compliance with ASTM or DIN standards can enhance product credibility.
What Role Does PU Leather Play in Fake Designer Items?
Polyurethane (PU) leather is a synthetic alternative to genuine leather that offers a similar look and feel at a lower cost. It is often used in fashion items, such as shoes, handbags, and jackets.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Pros: PU leather is more environmentally friendly than PVC and is easier to clean and maintain. It also offers good breathability and flexibility, enhancing comfort for wearables.
Cons: On the downside, PU leather may not be as durable as genuine leather, especially in high-wear applications. It can also be prone to cracking over time.
Impact on Application: PU leather is suitable for a wide range of products but may not withstand extreme conditions, such as high humidity or direct sunlight, as effectively as natural leather.
Considerations for Buyers: B2B buyers should ensure that PU leather products comply with local regulations, especially in terms of chemical safety. Standards such as REACH in Europe may apply.
How Does Canvas Compare for Fake Designer Goods?
Canvas is a durable fabric made from cotton or a blend of cotton and synthetic fibers. It is commonly used for bags, shoes, and casual wear in the fake designer market.
Pros: Canvas is highly durable and can withstand heavy use, making it ideal for everyday items. It is also relatively inexpensive and can be printed on easily, allowing for creative designs.
Cons: While canvas is robust, it is less water-resistant than synthetic alternatives unless treated. This can limit its application in wet environments.
Impact on Application: Canvas is compatible with various media, including paint and print, but may require additional treatment for waterproofing in certain applications.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider the local climate when selecting canvas products. In regions with high humidity, treated canvas may be preferable to ensure longevity.
What Advantages Does Nylon Offer in Fake Designer Products?
Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its strength and elasticity. It is commonly used in fashion accessories, bags, and outerwear.
Pros: Nylon is highly durable, resistant to abrasion, and has excellent tensile strength. It is also lightweight, making it suitable for travel-related products.
Cons: However, nylon can be less breathable than natural materials, which may affect comfort in clothing. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other synthetic options.
Impact on Application: Nylon is suitable for a variety of applications, including those exposed to moisture or wear. Its compatibility with different dyes allows for vibrant color options.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should be aware of the varying quality of nylon products. Compliance with international standards, such as ISO and ASTM, can help ensure product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Fake Designer Products
| Material | Typical Use Case for fake designer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Bags, wallets | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable under extreme temps | Low |
| PU Leather | Handbags, shoes | Eco-friendly and easy to maintain | Prone to cracking over time | Medium |
| Canvas | Casual bags, shoes | Highly durable and inexpensive | Less water-resistant | Low |
| Nylon | Travel bags, outerwear | Strong and lightweight | Less breathable | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in fake designer products, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fake designer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Fake Designer Products?
The manufacturing process for fake designer products typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage requires careful consideration to ensure that the final product meets the desired aesthetic and quality standards while remaining cost-effective.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
Material preparation is the first step, where manufacturers select appropriate materials that mimic the original designs. Common materials include synthetic leathers, textiles, and plastics. The choice of materials is crucial for achieving the desired look and feel of the product. Suppliers often source these materials from local or international markets, ensuring they comply with relevant safety and quality standards.
During this stage, materials undergo initial testing to check for durability, colorfastness, and resistance to wear and tear. This testing is vital to ensure that the final product can withstand consumer use while maintaining its appearance.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Fake Designer Products?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves cutting, molding, or weaving the selected materials into the desired shapes. Techniques vary depending on the product type. For instance, handbags may require cutting and sewing, while shoes might involve molding and stitching processes.
Advanced technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and laser cutting, are increasingly utilized to enhance precision and reduce waste. This stage is critical for ensuring that the dimensions and proportions of the product align closely with the original designs.
Assembly: How Are Components Brought Together?
The assembly stage is where the individual components are brought together to create the final product. This may involve sewing, gluing, or using other fastening methods. Quality craftsmanship is essential at this stage, as it directly impacts the durability and visual appeal of the product.
Manufacturers often employ skilled labor to ensure that the assembly process meets high standards. Additionally, some companies may use automated systems to streamline production, especially for larger orders. This combination of skilled labor and technology helps maintain consistency and quality across production runs.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure a Polished End Product?
Finishing involves adding final touches to the product, such as applying coatings, polishing surfaces, and ensuring all components are securely attached. This stage is crucial for achieving a high-quality appearance that closely resembles genuine designer products. Common finishing techniques include embossing logos, adding hardware, and applying protective coatings.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Quality control checks are integrated into the finishing process to ensure that any defects are identified and corrected before the products are shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Fake Designer Products?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of fake designer products. B2B buyers should be aware of several international and industry-specific standards that can help ensure product quality.
How Does ISO 9001 Certification Impact Quality Assurance?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems. Manufacturers who are ISO 9001 certified demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. This certification requires companies to implement a structured approach to quality management, including documentation, process control, and continuous improvement.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification, as this provides assurance that the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality management practices.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
What Other Industry-Specific Certifications Should Buyers Consider?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for specific materials can further enhance quality assurance. These certifications indicate compliance with regulatory requirements and safety standards, which are particularly important for buyers from regions with stringent import regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to ensuring that products meet the required standards throughout the manufacturing process. The most common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. The goal is to verify that the materials meet predefined specifications before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to identify any deviations from quality standards. This ensures that issues can be addressed promptly, minimizing defects in the final product.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs once the product is fully assembled and finished. This stage includes a thorough review of the product’s appearance, functionality, and adherence to specifications before it is shipped to buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers looking to ensure the quality of their products should adopt a proactive approach to verifying supplier QC practices. Here are several strategies:
What Role Do Audits Play in Supplier Quality Assurance?
Conducting regular audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control practices. These audits can be performed by the buyer or a third-party inspection agency. During an audit, the buyer can evaluate the manufacturing processes, QC checkpoints, and overall compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Why Are Quality Control Reports Important?
Requesting quality control reports from suppliers is another key step in verifying quality assurance. These reports should detail the results of inspections conducted at various stages of production, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC. Analyzing these reports can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in the supplier’s quality control practices. These independent agencies conduct thorough evaluations of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet the required standards before shipment. This additional layer of scrutiny can be particularly beneficial for buyers in regions with strict import regulations.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various nuances when it comes to quality control and certification. Differences in regulatory standards, import laws, and consumer expectations can complicate the sourcing process.
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Sourcing Decisions?
For instance, buyers in Europe may face stricter regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact compared to those in other regions. It is crucial for buyers to familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply accordingly.
What Should Buyers Know About Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations?
Cultural differences can also play a role in quality expectations. For example, buyers from the Middle East may prioritize luxury finishes, while those from South America may focus more on functionality. Understanding these differences can help buyers communicate their quality expectations effectively and ensure that suppliers deliver products that meet their needs.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for fake designer products is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of production, relevant standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the quality and success of their sourcing endeavors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fake designer’
This guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers with a structured approach for sourcing ‘fake designer’ products. As the demand for unique and cost-effective designs rises, understanding how to navigate the market is essential. This checklist will help you identify reliable suppliers, ensure quality, and make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Identify Your Design Needs
Before diving into the sourcing process, clarify what you specifically need from fake designers. This includes the type of products, design styles, and target audience.
– Key Considerations: Think about the market trends in your region and how these designs will appeal to your customers. This will help you communicate your requirements effectively to potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in fake designer products. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and social media channels.
– Where to Look: Explore platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and dedicated fashion forums where suppliers showcase their work. Pay attention to reviews and customer feedback to gauge reliability.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Credentials
Before engaging with a supplier, it’s crucial to validate their credentials and experience in the industry.
– What to Check: Request their business registration documents, certifications, and references from previous clients. This step ensures you are dealing with a legitimate supplier who adheres to industry standards.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always ask for product samples before making bulk purchases. This allows you to evaluate the quality of the designs and materials used.
– Quality Indicators: Assess the craftsmanship, durability, and overall aesthetic appeal of the samples. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure the products meet your standards.
Step 5: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in transparent discussions regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Understanding these factors upfront can save you from unexpected costs later.
– Negotiation Tips: Be open about your budget constraints and negotiate terms that work for both parties. Also, inquire about potential discounts for bulk orders.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Establish how you will communicate throughout the sourcing process.
– Preferred Methods: Choose a reliable method of communication, whether it’s email, messaging apps, or video calls. Regular updates will help keep both parties aligned on expectations and timelines.
Step 7: Finalize Agreements and Contracts
Once you’ve vetted your supplier and are satisfied with the terms, draft a formal agreement to protect both parties.
– Contract Essentials: Ensure the contract includes product specifications, delivery timelines, payment terms, and quality assurance policies. A well-drafted contract minimizes risks and clarifies responsibilities.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for fake designer products, ensuring they find reliable suppliers while meeting their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fake designer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Fake Designers?
When engaging in the sourcing of fake designer goods, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and pricing strategy. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used significantly influence the overall cost. Sourcing from regions with cheaper raw materials can reduce costs, but may also affect the perceived quality of the final product.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on geographic location. In countries with lower wages, such as certain regions in Africa and South America, production costs may be minimized. However, the skill level of labor can impact the craftsmanship and quality of the items produced.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Factoring these into your pricing strategy is essential to ensure that all operational costs are covered.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery can be significant, especially for customized designs. This cost should be amortized over the expected production volume to determine its impact on per-unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process incurs additional costs but is necessary to maintain product standards and avoid returns. Consider these expenses as part of your total cost structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the shipping method and distance. Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who bears the cost and risk at each stage of the supply chain.
-
Margin: Establishing a competitive profit margin is essential. This margin should reflect market conditions and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence pricing when sourcing fake designer goods, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically attract lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. B2B buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their sales projections to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to suppliers to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., compliance with safety standards) can raise costs but may also enhance marketability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certifications against the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their reliability can reduce risks associated with delays and quality issues.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, impacting overall cost and risk.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to ensure cost-efficiency in sourcing fake designer goods:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should prepare by researching market rates and being ready to discuss volume discounts or payment terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with logistics, warehousing, and potential returns. This holistic view helps in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that may affect overall costs. Understanding local regulations can prevent unexpected expenses.
-
Supplier Diversification: Relying on multiple suppliers can mitigate risks associated with price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. It also fosters competitive pricing among suppliers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for fake designer goods can vary significantly based on multiple factors. The insights provided in this analysis are indicative and should be used as a guideline. Actual costs may fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and buyer specifications. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to establish a reliable pricing strategy.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fake designer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to ‘Fake Designer’ Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of design, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance their brand presence and streamline operations. The ‘fake designer’ concept has gained traction for its unique approach, but it is essential for B2B buyers to explore viable alternatives that may better suit their specific needs. This section compares ‘fake designer’ with two notable alternatives: Custom Design Services and AI-Powered Design Tools.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | ‘Fake Designer’ | Custom Design Services | AI-Powered Design Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High creativity, variable quality | Tailored to brand identity | Consistent output, variable creativity |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to expertise | Moderate to low |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick setup | Longer onboarding process | User-friendly, quick setup |
| Maintenance | Minimal upkeep | Requires ongoing collaboration | Low, automatic updates |
| Best Use Case | Trendy, casual branding | Professional, bespoke needs | Rapid prototyping, cost-effective projects |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Custom Design Services?
Custom design services provide tailored solutions that align closely with a brand’s identity and objectives. These services typically involve collaboration with skilled designers who understand the nuances of a company’s vision. The primary advantage is the high level of personalization and quality assurance. However, the cost can be prohibitive for smaller businesses, and the onboarding process may take longer, delaying project launches.
How Do AI-Powered Design Tools Compare to ‘Fake Designer’?
AI-powered design tools offer a blend of efficiency and innovation, providing users with the ability to generate design concepts quickly. These tools often feature templates and automated suggestions that can help in creating visually appealing content at a fraction of the cost of traditional design services. The downside is that the creativity may sometimes feel limited, as the outputs are based on existing patterns and algorithms. Nonetheless, they are ideal for businesses needing rapid prototyping or cost-effective solutions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When evaluating the best solution for your design requirements, consider the specific goals of your project. If you seek a trendy and informal branding approach, ‘fake designer’ may provide the necessary creativity at a lower cost. However, for businesses that prioritize a polished and professional image, custom design services could be more appropriate, albeit at a higher investment. Alternatively, if speed and cost-effectiveness are your primary concerns, AI-powered design tools can deliver satisfactory results with less financial commitment.
Ultimately, the choice between ‘fake designer’ and its alternatives should align with your brand’s identity, budget constraints, and the specific outcomes you aim to achieve. By thoroughly assessing each option, you can make an informed decision that propels your business forward in a competitive marketplace.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fake designer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fake Designer Products?
Understanding the essential technical properties of fake designer products is crucial for B2B buyers. These properties not only dictate the quality and appeal of the items but also influence procurement decisions. Here are the critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in the production of fake designer goods. Common materials include high-quality synthetic leathers, metals, and textiles. Higher-grade materials tend to be more durable and visually appealing, which can impact customer satisfaction and brand reputation. For buyers, assessing material grade helps ensure that products meet their quality standards.
2. Construction Tolerance
Construction tolerance indicates the permissible limits of variation in product dimensions and features. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5 mm in stitching or cutting can significantly affect the overall appearance and fit of an item. In B2B transactions, understanding construction tolerances is vital for ensuring that products will meet the expectations of end customers, especially in industries where precision is crucial.
3. Finish Quality
Finish quality encompasses the final treatment and appearance of the product, including aspects like stitching, polishing, and surface treatments. High-quality finishes not only enhance aesthetics but also affect durability and user experience. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who maintain stringent quality control processes for finishes, as this can directly impact product lifecycle and customer retention.
4. Weight Specifications
Weight specifications play a significant role in the perception of quality for fake designer products. Heavier items often feel more substantial and luxurious, while lighter options may be preferred for practicality and ease of use. Buyers must consider the weight specifications to align product offerings with market expectations and consumer preferences.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Fake Designer Industry?
Navigating the B2B landscape of fake designer products requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are several key terms that are essential for effective communication and negotiation:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce goods based on the designs and specifications provided by another company. In the fake designer sector, OEM partnerships can allow buyers to offer customized products without investing in manufacturing infrastructure. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers leverage existing expertise and streamline their supply chains.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it influences inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and avoid overstocking or stockouts, ensuring a smooth sales process.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price and product information for specific orders. This process is essential for comparing offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring that buyers can make informed purchasing decisions. Crafting a well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand their obligations and costs, allowing for smoother international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the products. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and meeting customer demands. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers about expected lead times to avoid delays that could impact sales.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions in the competitive landscape of fake designer products, ensuring they secure quality merchandise that meets market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fake designer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Fake Designer Sector?
The fake designer market has seen significant growth, driven by several global factors. In recent years, the rise of social media and e-commerce platforms has accelerated demand, particularly among younger consumers who seek affordable luxury alternatives. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore this market, they must be aware of emerging trends such as digital marketing tactics that leverage platforms like TikTok and Instagram for brand visibility. These platforms not only enhance engagement but also offer insights into consumer preferences, allowing businesses to tailor their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Technological advancements are also shaping the landscape. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in trend forecasting and inventory management is becoming more prevalent. By harnessing these technologies, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions, ensuring they stay ahead of the competition. Additionally, the growth of online marketplaces dedicated to fake designer goods presents new opportunities for international buyers to connect with suppliers, streamlining the procurement process. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses looking to tap into this lucrative sector.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Fake Designer Industry?
As awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, sustainability has become a critical factor in the sourcing of fake designer goods. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical practices, recognizing that consumers are more inclined to support brands that demonstrate social responsibility. The environmental impact of production processes, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing, cannot be overlooked. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers that utilize sustainable materials, such as recycled textiles or eco-friendly production methods, to minimize their carbon footprint.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
Moreover, ‘green’ certifications are gaining traction in the fake designer sector. Certifications like Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX Standard 100 can serve as benchmarks for assessing the sustainability of suppliers. By choosing partners who are committed to ethical sourcing, businesses not only align with consumer values but also mitigate risks associated with potential backlash from unethical practices. This focus on sustainability is not just a trend; it’s becoming a foundational aspect of competitive differentiation in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of the Fake Designer Market for B2B Buyers?
The fake designer market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially perceived as a niche segment catering to a limited audience, it has transformed into a global phenomenon fueled by consumer desire for luxury goods at accessible price points. The advent of the internet and globalization has further facilitated this shift, allowing counterfeit products to reach international markets more efficiently.
In the early 2000s, the rise of online auction sites and later social media platforms democratized access to these goods, making it easier for consumers worldwide to purchase fake designer items. As a result, B2B buyers must now navigate a complex landscape where quality, branding, and ethical considerations play a crucial role in supplier selection. Understanding this evolution is essential for businesses seeking to capitalize on the opportunities within the fake designer sector while maintaining a commitment to responsible sourcing practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fake designer
-
How do I ensure the quality of fake designer products before placing a large order?
To ensure quality, it’s crucial to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Start by requesting samples to evaluate craftsmanship, materials, and overall design. Additionally, establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols with your supplier, detailing standards and inspection methods. Engage with suppliers who have a proven track record in your target market and can provide customer references. Regular communication and factory visits, if feasible, can further enhance your confidence in their quality. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for sourcing fake designer items?
MOQs vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the type of product and customization options. Some manufacturers may have a low MOQ of 50-100 units, while others may require higher quantities. It’s essential to discuss your needs upfront and negotiate terms that align with your business model. Be aware that lower MOQs can lead to higher per-unit costs, so weigh your options carefully to find the best balance between quantity and pricing. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing fake designer products?
Common payment terms include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer payment upon delivery or a letter of credit for larger orders, which can provide additional security. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, PayPal, or escrow services. Ensure that your payment terms are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and protect your interests. -
How can I customize fake designer products to fit my brand?
Customization options often depend on the supplier’s capabilities. Discuss specific design elements, such as logos, color schemes, and materials, during initial negotiations. Many manufacturers are open to customization, especially for larger orders. It’s advisable to provide clear design specifications and prototypes to guide the production process. Additionally, be prepared for potential minimums on custom orders and ensure that timelines accommodate your marketing needs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing fake designer items?
Logistics play a vital role in the sourcing process. Consider shipping methods (air freight vs. sea freight), transit times, and customs regulations in your target market. Work with a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international trade and can navigate customs clearance effectively. Additionally, factor in shipping costs and insurance to protect your investment during transit. -
Are there legal implications for importing fake designer products?
Yes, importing counterfeit goods can lead to severe legal consequences, including fines and confiscation of products. It’s crucial to understand the laws in your target market regarding counterfeit goods. Consult with legal experts familiar with international trade laws and intellectual property rights to mitigate risks. Additionally, consider sourcing products that closely resemble high-end designs without infringing on trademarks to avoid legal challenges. -
How do I evaluate potential suppliers for reliability and trustworthiness?
Start by researching suppliers through online platforms, trade shows, and industry networks. Look for manufacturers with positive reviews and a solid reputation in the market. Request references and reach out to previous clients to gauge their experiences. Conduct background checks to confirm the supplier’s legitimacy and production capabilities. Building a relationship with suppliers through open communication can also enhance trust and reliability. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing fake designer products internationally?
Common challenges include navigating complex customs regulations, ensuring product quality, and managing shipping logistics. Cultural differences and language barriers can complicate communication with suppliers. Additionally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates may impact pricing. To overcome these challenges, establish strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, stay informed about trade policies, and utilize local expertise to streamline the sourcing process.
Top 3 Fake Designer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Etsy – Fake Designer Purse Inserts
Domain: etsy.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Etsy – Fake Designer Purse Inserts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Designer Replicas – Luxury Brand Alternatives
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Designer fakes, specifically high-quality replicas of luxury brands like Chanel and Louis Vuitton, are discussed. Users express interest in the quality and indistinguishability of these replicas from authentic items. Some mention that they prefer buying replicas due to cost-effectiveness and perceived quality. There are references to underground marketplaces for buying and selling these replicas, …
3. Faire – Wholesale Replica Designer Products
Domain: faire.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Wholesale replica designer products including frames, decorative objects, and a variety of categories such as home decor, food & drink, women, beauty & wellness, jewelry, paper & novelty, kids & baby, pets, and men.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fake designer
In the evolving landscape of the fashion industry, the strategic sourcing of fake designer products offers a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers. By understanding market trends and consumer preferences, businesses can align their sourcing strategies to capitalize on the demand for high-quality replicas that appeal to various demographics, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to fake designer
The importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers ensures not only the quality of products but also the sustainability of supply chains. Buyers must prioritize due diligence in supplier selection to mitigate risks associated with counterfeit goods and uphold brand integrity.
Looking ahead, the market for fake designer products is poised for growth, driven by a combination of increasing consumer awareness and the desire for luxury at accessible price points. B2B buyers are encouraged to adopt innovative sourcing strategies that leverage digital platforms and social media insights, as seen on channels like TikTok. By staying ahead of trends and consumer demands, businesses can enhance their competitive edge.
To seize these opportunities, it is vital for international buyers to engage actively with suppliers, share insights, and adapt to shifting market dynamics. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing today to foster long-term success in the fashion industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.