Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Facts About Brass Metal Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for facts about brass metal
Navigating the global market for brass metal can be daunting for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. With the increasing demand for brass in various applications—from plumbing fixtures to musical instruments—understanding the nuances of this versatile alloy is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into essential facts about brass metal, including its types, properties, and various applications, while also addressing key challenges such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and sustainability practices.
Brass, a copper-zinc alloy, offers unique characteristics that make it suitable for a wide range of uses, and its recyclability adds to its appeal in today’s environmentally conscious market. By providing comprehensive insights into the characteristics of different brass alloys, their applications in various industries, and strategic tips for sourcing from reliable suppliers, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate their procurement processes effectively. With actionable strategies and a thorough understanding of the brass market landscape, you can enhance your competitive edge and make decisions that align with your business goals.
Understanding facts about brass metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Brass | Contains less than 40% zinc; highly malleable. | Fasteners, ammunition cartridge cases, decorative items. | Pros: Excellent workability; Cons: Lower strength compared to other brass types. |
| Beta Brass | Contains 40-45% zinc; less malleable but stronger. | Plumbing fixtures, faucet handles, and decorative hardware. | Pros: Greater strength; Cons: More difficult to machine. |
| Lead Brass | Contains lead for improved machinability. | Precision components, fittings, and valves. | Pros: Easy to machine; Cons: Lead content raises health concerns. |
| Admiralty Brass | Contains tin for enhanced corrosion resistance. | Marine applications, such as ship fittings. | Pros: Excellent seawater resistance; Cons: Higher cost due to alloying elements. |
| Aluminum Brass | Contains aluminum for added strength and corrosion resistance. | Industrial applications, heat exchangers. | Pros: Strong and durable; Cons: More complex production process. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Alpha Brass for B2B Buyers?
Alpha brass is characterized by its low zinc content (less than 40%), which grants it remarkable malleability and ductility. This makes it ideal for applications requiring intricate designs, such as fasteners and decorative items. B2B buyers should consider alpha brass for projects where ease of shaping and forming is critical, but they should be aware that its lower strength may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
How Does Beta Brass Differ and What Are Its Key Applications?
Beta brass contains 40-45% zinc, providing increased strength but reduced malleability compared to alpha brass. Its durability makes it suitable for plumbing fixtures, faucet handles, and other components that require a balance of strength and workability. Buyers in industries focused on plumbing and construction should prioritize beta brass for its robustness while considering its machining challenges.
What Are the Advantages of Using Lead Brass in Precision Components?
Lead brass is an alloy that incorporates lead to enhance machinability, making it particularly useful for precision components like fittings and valves. While it allows for easier manufacturing processes, buyers must consider the health implications associated with lead content. This type of brass is optimal for industries where precision and ease of machining are paramount, but companies must ensure compliance with health regulations.
Why Should B2B Buyers Consider Admiralty Brass for Marine Applications?
Admiralty brass is specifically formulated with tin, improving its resistance to corrosion in seawater environments. It is commonly used in marine applications, such as ship fittings and valves. B2B buyers in maritime sectors should recognize the long-term cost benefits of using admirably brass, despite its higher initial expense, due to its durability and reduced maintenance needs.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
What Makes Aluminum Brass a Strong Choice for Industrial Applications?
Aluminum brass combines aluminum with copper and zinc, offering enhanced strength and corrosion resistance. This alloy is particularly suitable for industrial applications like heat exchangers, where durability is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the complexity of the production process and associated costs but can benefit from aluminum brass’s robust performance in demanding environments.
Key Industrial Applications of facts about brass metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of facts about brass metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plumbing and HVAC | Plumbing fixtures and fittings | Excellent corrosion resistance, leading to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. | Ensure compliance with local plumbing standards and regulations; evaluate suppliers for quality certifications. |
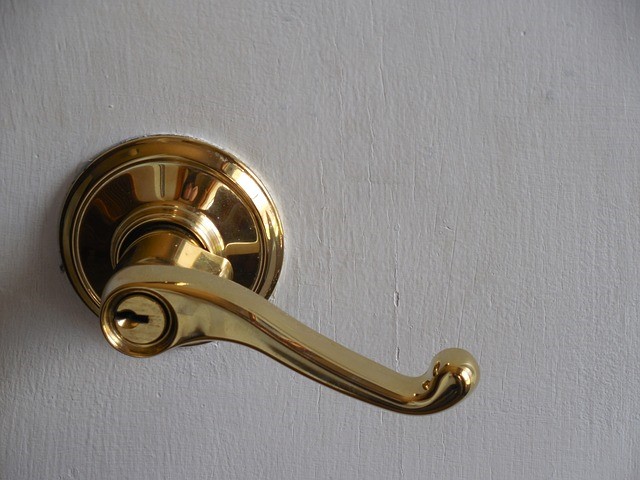
| Musical Instrument Manufacturing | Production of brass instruments | Unique acoustic properties that enhance sound quality, appealing to musicians and educators. | Source from reputable suppliers with experience in musical instrument materials; consider alloy specifications for sound performance. |
| Automotive | Components such as fittings and fasteners | High durability and resistance to wear, contributing to vehicle longevity and safety. | Assess suppliers for metallurgical expertise and ensure they can meet automotive industry standards. |
| Marine Applications | Naval fittings and components | Resistance to seawater corrosion, ensuring reliability in harsh marine environments. | Verify supplier capabilities in producing admiralty brass and other specialized alloys for marine use. |
| Decorative Arts | Ornamental objects and fixtures | Aesthetic appeal with varied color options, enhancing product value and marketability. | Choose suppliers with a strong portfolio in decorative brass items and consider custom design capabilities. |
How is Brass Used in Plumbing and HVAC Applications?
Brass is extensively utilized in plumbing fixtures and fittings due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in environments with high moisture levels, reducing the need for frequent replacements and repairs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing brass that complies with local plumbing standards is crucial. It is important to evaluate suppliers for quality certifications to ensure that the brass products can withstand the rigors of plumbing systems.
What Role Does Brass Play in Musical Instrument Manufacturing?
In the realm of musical instruments, brass is favored for its unique acoustic properties, which contribute to the warm tones produced by instruments such as trumpets and trombones. The malleability of brass allows for intricate designs, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and sound quality. B2B buyers in Europe and South America should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with expertise in musical instrument materials, ensuring that the specific alloy compositions meet the desired sound performance. This focus on quality can significantly impact musicians’ satisfaction and educational outcomes.
Why is Brass Important in the Automotive Industry?
Brass components, such as fittings and fasteners, are vital in the automotive industry due to their high durability and wear resistance. These properties contribute to the overall longevity and safety of vehicles, making brass an essential material for manufacturers. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria should assess suppliers based on their metallurgical expertise and ability to meet stringent automotive industry standards. This diligence ensures that the sourced brass components can perform reliably under various operational conditions.
How Does Brass Benefit Marine Applications?
In marine applications, brass is indispensable for its resistance to seawater corrosion, making it an ideal choice for naval fittings and components. This reliability is crucial for maintaining the integrity of marine vessels and equipment in challenging environments. International buyers should verify supplier capabilities in producing specialized alloys, such as admiralty brass, which are tailored for marine use. Understanding the specific requirements for corrosion resistance can help ensure that the sourced products meet the demands of marine applications effectively.
What Advantages Does Brass Offer in Decorative Arts?
Brass is widely used in decorative arts for creating ornamental objects and fixtures due to its aesthetic appeal and the variety of colors it can achieve. This versatility allows artisans and manufacturers to enhance product value and marketability. B2B buyers should select suppliers with a robust portfolio in decorative brass items and consider those that offer custom design capabilities. By focusing on quality and design, businesses can better cater to the unique demands of the decorative arts market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘facts about brass metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Brass for Industrial Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing high-quality brass that meets their specific requirements for industrial applications. The challenge lies not only in finding suppliers who can provide brass with the right alloy composition but also in ensuring that the material meets international standards for quality and durability. This can lead to delays in production, increased costs due to defective materials, and potential compliance issues that can harm a company’s reputation.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should develop a robust sourcing strategy that includes thorough supplier vetting. Start by identifying suppliers that specialize in brass alloys suitable for your specific applications—whether it’s plumbing, musical instruments, or decorative items. Request material certification that outlines the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the brass. Furthermore, consider engaging in long-term partnerships with suppliers who have proven track records and can offer traceability for their products. Regular audits and quality checks can ensure that the brass you receive consistently meets your specifications, reducing the likelihood of production delays and enhancing your product quality.
Scenario 2: Understanding Brass Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unaware of the varying corrosion resistance properties of different brass alloys, which can lead to inappropriate material selection for specific environments. For example, using standard brass in marine applications can result in rapid deterioration due to saltwater corrosion, ultimately leading to costly repairs and replacements.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should conduct comprehensive research on the corrosion resistance of different brass alloys, particularly admiralty brass and aluminum brass, which are formulated to withstand harsh marine conditions. Engage with metallurgists or material engineers to better understand the implications of alloy compositions on corrosion resistance. Additionally, consider testing small batches of brass in the intended environment to evaluate their performance before making larger orders. Incorporating corrosion-resistant coatings can also provide an extra layer of protection for brass components used in challenging environments.
Scenario 3: Managing Brass Scrap and Recycling Processes Efficiently
The Problem: B2B companies that work with brass often generate scrap metal, which can become a significant management issue. Without an effective recycling strategy, this scrap can lead to increased waste disposal costs and missed opportunities for revenue through recycling. Additionally, companies may lack knowledge about local recycling regulations or the best practices for handling brass scrap, leading to compliance risks.
The Solution: Implementing a structured scrap management and recycling program can help mitigate these issues. Start by identifying local recycling partners who specialize in brass to ensure proper handling and compliance with regulations. Educate your team about the importance of segregating brass scrap from other materials to maximize the recycling value. Establish a regular schedule for scrap collection and engage in negotiations with recyclers to secure competitive pricing. Furthermore, consider investing in training for employees about the benefits of recycling and the environmental impact of waste reduction. By fostering a culture of sustainability, companies can not only reduce costs but also enhance their corporate responsibility profile in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for facts about brass metal
What Are the Key Properties of Brass for B2B Applications?
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, with varying proportions that influence its properties. One of the key characteristics of brass is its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in marine environments and plumbing fixtures. It can withstand exposure to moisture and various chemicals without deteriorating, which is crucial for industries that operate in humid or corrosive conditions. Additionally, brass has a relatively low melting point (around 900-930 degrees Celsius), allowing for ease of fabrication and welding, which is beneficial for manufacturers looking to streamline production processes.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Brass in Manufacturing?
Brass offers several advantages, including its durability and malleability. It is easy to work with, allowing manufacturers to create intricate designs and components, such as musical instruments and decorative items. However, brass is softer than other metals, which can lead to scratching and wear over time, necessitating regular maintenance. From a cost perspective, brass is generally considered a medium-cost material, making it accessible for a wide range of applications. On the downside, the manufacturing complexity can increase with specific brass types, such as those with higher zinc content, which may require specialized processes.
How Does Brass Impact Specific Applications?
Brass is particularly suitable for applications involving water and gas fittings due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to form a tight seal. In plumbing, for instance, brass fixtures are preferred for their longevity and reliability. However, it’s essential to consider the specific media compatibility when selecting brass for particular applications. For example, brass alloys with higher zinc content may not perform well in environments with aggressive chemicals, which could lead to premature failure.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing Brass?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of compliance standards that govern brass products. Common standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) are crucial for ensuring product quality and safety. Additionally, buyers should consider local preferences and regulations regarding the use of brass in their respective markets, as these can vary significantly. For instance, in regions with high humidity, selecting a brass alloy with enhanced corrosion resistance would be prudent.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Summary Table of Brass Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for facts about brass metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Brass | Coins, screws, and ammunition cartridge cases | Excellent malleability and workability | Lower strength compared to other alloys | Medium |
| Beta Brass | Faucet handles and window fittings | Higher strength and durability | Less ductility, requiring hot working | Medium |
| Lead Brass | Precision machining components | Enhanced machinability | Lead content raises health concerns | Medium |
| Naval Brass | Marine applications and plumbing fixtures | Superior corrosion resistance in seawater | Higher cost compared to standard brass | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of brass, highlighting its properties, advantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors can significantly enhance decision-making when sourcing brass for various applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for facts about brass metal
What Are the Main Stages of Brass Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process for brass involves several key stages, ensuring the final product meets the necessary specifications for strength, durability, and appearance. The typical stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Brass Production?
The first step in brass production is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality copper and zinc. The proportions of these metals can vary, allowing for the creation of different brass alloys with unique properties. The raw materials are often melted in a furnace, where they are mixed at controlled temperatures to ensure a uniform composition. This is crucial, as the specific ratios of copper and zinc will determine the mechanical properties of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Brass?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, where the molten brass is shaped into the desired forms. Common techniques include:
- Casting: This involves pouring molten brass into molds. It is suitable for producing complex shapes and large components.
- Extrusion: In this method, heated brass billets are pushed through a die to create long sections of material, such as rods or tubes.
- Rolling: Brass sheets or strips are produced by passing the material through rollers to achieve the desired thickness.
- Forging: This process involves shaping brass through compressive forces, which enhances its strength.
Each technique has its own set of advantages and is selected based on the product’s intended application.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
What Is the Assembly Process for Brass Products?
In the assembly stage, various brass components may be joined together. Techniques such as soldering, brazing, and welding are commonly employed, depending on the product’s requirements and the specific alloy characteristics. This stage is crucial for ensuring the integrity and functionality of the final product, particularly in applications like plumbing fixtures and musical instruments.
How Is the Finishing Stage Conducted in Brass Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves several processes aimed at enhancing the appearance and performance of the brass products. This can include:
- Polishing: To achieve a smooth, shiny surface that is aesthetically pleasing.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to improve corrosion resistance, especially for products used in harsh environments.
- Plating: Sometimes, brass components are plated with other metals to enhance durability or appearance.
Attention to detail in this stage can significantly affect the product’s marketability and longevity.
What Are the Key Quality Control (QC) Measures for Brass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in brass manufacturing to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. The following outlines the key QC measures used in the industry.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Brass Quality Control?
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. In addition, industry-specific standards may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for brass components used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring safety and performance.
These standards help maintain high quality and safety levels, fostering trust among international B2B buyers.
What Are the QC Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials for conformity to specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the production process to catch any deviations early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet all specifications before shipment.
Implementing these checkpoints helps prevent defects and ensures consistent product quality.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Brass Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the properties and performance of brass products, including:
- Mechanical Testing: This may involve tensile tests to measure strength and ductility.
- Chemical Analysis: To verify the composition of the brass alloy, ensuring it meets specified standards.
- Corrosion Testing: Assessing the resistance of brass products to various environmental conditions.
These tests provide valuable data that can be used to refine manufacturing processes and improve product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices. Here are several strategies for verification:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive way to assess the quality management systems in place. Buyers should consider:
- On-Site Visits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes and quality control measures firsthand.
- Documentation Review: Examining quality control records, certifications, and compliance with international standards.
These audits help buyers gauge the reliability and commitment of their suppliers to quality.
How Important Are QC Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting QC reports is essential for transparency in the supply chain. These reports should detail inspection results, testing methodologies, and compliance with standards. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality practices, offering further assurance.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes. Understanding local regulations, certification requirements, and standards can vary significantly by region. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are not only compliant with international standards but also familiar with local regulations that may affect product acceptance in their markets.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough due diligence, B2B buyers can secure high-quality brass products that meet their needs and expectations.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘facts about brass metal’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in understanding and procuring brass metal effectively. Brass is a versatile alloy with applications across various industries, making it essential for international buyers to grasp its properties, standards, and supplier qualifications. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing process is efficient and meets your specific business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the brass you need. This includes understanding the alloy composition, such as the copper and zinc ratios, and specific properties like malleability, corrosion resistance, and tensile strength. Knowing these details helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures that the brass you procure meets your intended application.
- Consider the End Use: Different applications may require different brass grades, such as alpha brass for components like screws and beta brass for plumbing fixtures.
- Determine Required Standards: Familiarize yourself with industry standards relevant to your sector, which can guide your specifications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of brass. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry and positive customer reviews. This step is crucial to ensure reliability and quality in your sourcing.
- Utilize Online Resources: Leverage platforms like LinkedIn, industry-specific directories, and trade shows to gather information on suppliers.
- Check References: Ask for references from other businesses that have sourced brass from these suppliers, especially those in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. This includes ISO certifications, quality management systems, and environmental compliance.
- Request Documentation: Ask suppliers to provide copies of their certifications and any quality assurance processes they have in place.
- Verify Authenticity: Cross-check the validity of certifications through relevant industry bodies to ensure they are up to date.
Step 4: Assess Production Capabilities
Investigate the production capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This includes understanding their manufacturing processes, capacity, and technology used to produce brass.
Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
- Inquire About Quality Control: Assess their quality control measures during production to ensure consistent product quality.
- Evaluate Lead Times: Understand their production timelines and how they align with your project schedules.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the brass to evaluate its quality and suitability for your needs. Testing samples allows you to assess the material’s properties firsthand.
- Conduct Performance Tests: Consider conducting tests for corrosion resistance, malleability, and strength as per your specifications.
- Review Feedback from Technical Teams: Involve your technical team in evaluating the samples to ensure they meet performance requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have verified suppliers and tested samples, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms of sale. Transparency in pricing is crucial to avoid hidden costs later on.
- Discuss Payment Terms: Establish clear payment terms that work for both parties, such as deposits and payment upon delivery.
- Consider Bulk Discounts: Inquire about volume pricing or discounts for larger orders to optimize your procurement budget.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, set up a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Regular communication is key to addressing any issues that may arise during the procurement process.
- Schedule Regular Updates: Agree on a schedule for updates regarding production status and delivery timelines.
- Designate Point of Contact: Ensure there is a designated contact person on both sides to facilitate smooth communication.
By following these steps, you can ensure a comprehensive and effective sourcing process for brass metal that meets your business needs and standards.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for facts about brass metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Brass Metal Sourcing?
When sourcing brass metal for industrial applications, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary components of the cost include:
-
Materials: Brass is primarily an alloy of copper and zinc, with prices fluctuating based on market demand and the purity of the metals involved. The cost of raw materials can constitute a significant portion of the total price, especially in regions where these metals are scarce.
-
Labor: The manufacturing process for brass involves skilled labor for tasks such as casting, machining, and finishing. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region; for instance, wages in South America may differ significantly from those in Europe or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Companies with advanced manufacturing technologies may experience lower overhead costs due to increased efficiency.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling and dies are required to produce custom brass components. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, but it’s amortized over the production run, impacting the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that brass products meet specified standards is vital for quality assurance. QC processes add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity, especially for applications in plumbing and musical instruments.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting brass products can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and the nature of the goods (e.g., bulk vs. packaged). International buyers must consider tariffs and import duties, which can significantly impact total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s position in the market and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Brass Metal Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of brass metal:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to maximize savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom brass alloys or specific dimensions can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The specific copper-zinc ratio can affect price. Higher-quality brass with additional elements (like lead for machinability) may command higher prices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or certifications (like ISO) often come at a premium. Buyers should consider the value of these certifications against their project needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential. Incoterms can dictate who bears the risk and cost at various points in the shipping process, affecting the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Brass Metal Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, optimizing sourcing costs is essential:
-
Negotiate Smartly: Leverage relationships and volume commitments to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for long-term contracts or larger orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial pricing, assess the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential failures. Investing in higher-quality brass may yield lower TCO over time.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Currency fluctuations can affect pricing, especially in international transactions. Buyers should factor in exchange rates and consider locking in prices when feasible.
-
Evaluate Local Suppliers: Sometimes, local suppliers can offer competitive pricing without the added logistics costs associated with international shipping.
-
Request Detailed Quotations: Ensure that quotations include a breakdown of costs to better understand pricing structures and identify areas for negotiation.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always engage with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing facts about brass metal With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Brass Metal
When selecting materials for industrial applications, B2B buyers often face the challenge of evaluating various options that can fulfill their specific needs. Brass metal, known for its durability, malleability, and corrosion resistance, is a popular choice in many sectors. However, alternatives such as stainless steel and aluminum alloys also present viable solutions. This section compares these materials to brass, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Facts About Brass Metal | Alternative 1 Name: Stainless Steel | Alternative 2 Name: Aluminum Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance; malleable | Superior strength and corrosion resistance | Lightweight; good corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate cost; varies by alloy composition | Generally higher initial cost | Lower cost compared to brass and stainless |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to machine and shape | Requires specialized tools for shaping | Easy to work with; can be machined easily |
| Maintenance | Requires regular polishing to avoid tarnish | Low maintenance; resistant to rust | Minimal maintenance; anodizing increases lifespan |
| Best Use Case | Plumbing fixtures, musical instruments | Heavy-duty applications, construction | Aerospace, automotive parts, packaging |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of Stainless Steel Compared to Brass?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as construction and manufacturing. Its high tensile strength allows for the production of thinner and lighter components without compromising durability. However, the initial cost of stainless steel is typically higher than that of brass, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, stainless steel requires specialized machining tools, complicating implementation in some cases. Despite these challenges, its longevity and low maintenance needs make it an attractive option for buyers looking for a robust solution.
How Does Aluminum Alloys Compare to Brass in Terms of Applications?
Aluminum alloys are celebrated for their lightweight properties, which can significantly reduce the overall weight of products, especially in aerospace and automotive applications. They also offer good corrosion resistance and can be easily shaped and machined, making them a practical alternative to brass in many scenarios. The cost of aluminum alloys tends to be lower than that of brass and stainless steel, making them appealing for budget-conscious projects. However, they may not provide the same level of durability as brass, particularly in applications requiring high strength. Thus, while aluminum alloys are versatile, they may not be the best choice for every industrial application.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, selecting the right material involves assessing performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements against the specific demands of the application. Brass remains a strong contender due to its unique blend of properties, especially in plumbing and decorative applications. However, for projects requiring higher strength or lower weight, stainless steel and aluminum alloys may be more suitable. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a thorough analysis of the project’s requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance considerations to ensure optimal outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for facts about brass metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Brass Metal for B2B Buyers?
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its versatility and excellent mechanical properties. Understanding its critical specifications is vital for international buyers looking to source high-quality brass products. Here are some essential technical properties:
-
Material Grade
Material grades for brass are categorized based on the proportion of copper and zinc. Common grades include C26000 (Cartridge Brass), C28000 (Muntz Metal), and C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass). Each grade offers different characteristics like corrosion resistance, workability, and strength, which influence their suitability for specific applications such as plumbing fixtures, electrical components, or decorative items. -
Malleability
Malleability refers to the ability of brass to be shaped or formed without breaking. This property is crucial for applications requiring intricate designs, such as musical instruments or decorative hardware. High malleability allows manufacturers to create detailed components while minimizing waste, making it a cost-effective option for production. -
Corrosion Resistance
Brass exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against moisture and seawater. This characteristic makes it a preferred material in marine applications and plumbing systems. For buyers in humid or coastal regions, sourcing brass with high corrosion resistance can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer-lasting products. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before failure. Brass typically has good tensile strength, making it suitable for applications like fasteners and mechanical parts that must endure stress without breaking. Understanding the tensile strength of specific brass grades helps buyers ensure the material meets the demands of their applications. -
Thermal Conductivity
Brass has high thermal conductivity, which allows it to efficiently transfer heat. This property is essential for applications like cookware and heat exchangers, where effective heat transfer is critical. Buyers must consider thermal conductivity when selecting brass for applications involving heat.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Brass Metal Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common trade terms relevant to the brass metal industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the brass industry, buyers often source components from OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility with their existing systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure reliable sources for their brass needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For brass products, MOQs can vary widely depending on the type and grade of brass. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to effectively plan their inventory and budget, as ordering below the MOQ may result in higher per-unit costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the brass industry, submitting an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and understand the availability of various brass grades. It is a critical step in the procurement process for B2B transactions. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for brass buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with international shipments. -
Alloy Composition
Alloy composition refers to the specific percentages of copper, zinc, and other elements in brass. This specification is vital for buyers to ensure that the brass meets the necessary performance and quality standards for their applications. Knowing the alloy composition helps in sourcing the right material for specific industrial needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and optimize their sourcing strategies for brass metal.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the facts about brass metal Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Brass Metal Market?
The brass metal market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. One primary driver is the increasing demand for brass in diverse applications, ranging from plumbing fixtures to electronics and musical instruments. As urbanization accelerates in regions like Africa and South America, the need for durable and corrosion-resistant materials in construction and infrastructure projects becomes paramount. Additionally, the automotive industry is shifting towards using brass in components due to its advantageous properties, including electrical conductivity and durability.
Emerging technologies are also shaping the sourcing landscape. For instance, advancements in metallurgy and alloy composition are leading to the development of specialty brass alloys tailored for specific applications. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers seeking customized solutions. Digital platforms for procurement and supply chain management are becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing B2B buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and streamline their sourcing processes.
Moreover, geopolitical dynamics and trade agreements play a significant role in the brass market. Buyers in regions such as the Middle East and Europe should stay informed about tariffs, trade policies, and regional partnerships that could impact pricing and availability. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Brass Metal Sourcing and What Are the Ethical Considerations?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the brass metal sector. The environmental impact of metal production, including brass, is under scrutiny as industries strive to reduce their carbon footprints. Brass production can be energy-intensive, and buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate commitment to reducing environmental harm.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, with an emphasis on transparent supply chains. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who comply with environmental regulations and engage in responsible mining and recycling practices. The recycling of brass is particularly noteworthy, as it can be repurposed indefinitely without losing its properties, thus reducing the demand for raw materials.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct are essential for verifying the sustainability and ethical standards of suppliers. Buyers can leverage these certifications to ensure that they are partnering with manufacturers who prioritize environmental stewardship and social responsibility. By integrating sustainability into their sourcing decisions, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Brass Metal and Its Evolution for Modern Applications?
Brass has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was first utilized for tools, decorative items, and armor. Its discovery marked a significant milestone in metallurgy, demonstrating the early understanding of alloy properties. Over the centuries, brass evolved, with its applications expanding into various industries due to its unique characteristics.
In the modern context, brass remains a vital material, particularly in plumbing, electrical components, and musical instruments. Its malleability and resistance to corrosion make it ideal for high-performance applications. The historical evolution of brass has paved the way for innovative uses today, such as in the manufacturing of eco-friendly products and advanced electronic components, reflecting the material’s adaptability to contemporary demands.
Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Understanding the historical significance and evolution of brass can provide B2B buyers with insights into its long-term value and potential applications in their respective industries. By recognizing the heritage and versatility of brass, businesses can make informed decisions regarding its use in their operations and product offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of facts about brass metal
-
How do I ensure the quality of brass metal before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of brass metal, request material certifications from suppliers that verify the alloy composition and mechanical properties. Look for third-party testing reports that confirm the brass meets industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or requesting samples for evaluation. Engaging in a quality assurance agreement can also help set clear expectations regarding the quality and performance of the brass products you intend to purchase. -
What is the best type of brass for marine applications?
For marine applications, admiralty brass is considered the best choice due to its enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly against seawater. This alloy typically contains small amounts of tin, which improves its durability in harsh environments. When sourcing brass for marine use, ensure that the supplier can provide detailed specifications on the alloy’s composition and its resistance to corrosion, as this will significantly impact the longevity of the materials in marine settings. -
What are the common customization options available for brass products?
Customization options for brass products typically include variations in alloy composition, surface finishes (like polished, brushed, or coated), and specific dimensions or shapes tailored to your requirements. Many suppliers also offer engraving or stamping services for branding or identification purposes. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs clearly during initial discussions to ensure that the supplier can meet your customization requests effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for brass metal purchases?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for brass metal can vary widely based on the supplier, the type of brass product, and the complexity of manufacturing. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms for standard items to several tons for specialized or custom orders. Always inquire about MOQs during negotiations, as some suppliers may be flexible, especially for long-term partnerships or repeated orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing brass metal internationally?
Payment terms for international brass metal purchases often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Commonly, suppliers may request a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due prior to shipment or upon receipt of goods. It is crucial to discuss and agree on payment terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I vet suppliers for brass metal sourcing?
Vetting suppliers for brass metal should involve several steps: checking their industry reputation, reviewing customer testimonials, and assessing their financial stability. Requesting references from previous clients and examining their production capabilities can provide insights into their reliability. Additionally, consider conducting a site visit or utilizing third-party verification services to ensure the supplier meets your quality and ethical standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing brass metal?
When importing brass metal, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, customs regulations, and import duties. Work with a logistics partner familiar with international trade to navigate these complexities. Ensure that you have clear agreements regarding incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs clearance to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
What are the environmental considerations when sourcing brass?
When sourcing brass, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of production and recycling. Look for suppliers that practice sustainable sourcing and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. Verify if the brass products are made from recycled materials, as this can reduce the overall carbon footprint. Engaging with suppliers that adhere to international environmental standards can also align your procurement strategy with corporate social responsibility goals.
Top 5 Facts About Brass Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rotax Metals – Brass Sheet Metal
Domain: rotaxmetals.net
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Brass sheet metal is primarily valued for its strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. It is used in various applications beyond decorative purposes, including railings, window frames, door knobs, and home furniture. Brass is a non-ferrous metal made from a combination of copper and zinc, which means it does not rust but may tarnish and develop a protective patina. Not all brass dezincif…
2. Xometry – Brass Alloys
Domain: xometry.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Brass is an antibacterial and seawater-resistant metal alloy primarily made of copper and zinc, with trace amounts of lead, iron, and other elements. It has a golden-yellow color, but can appear reddish if it contains more copper (known as “red brass”). In 2023, the USA was the fourth largest exporter of brass, with an export value of almost $22 billion. Common brass alloys include: Alloy 260 (Car…
3. Baltimore Brassworks – Brass Hardware & Accessories
Domain: baltimorebrassworks.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, used for its beauty, resilience, and durability. It can be cast, forged, spun, wrought, or die-cut, and is commonly used for fine hardware, lighting fixtures, fireplace equipment, and decorative accessories. Brass can have various finishes: highly polished, satin, brushed, hand rubbed, antique, bronze, and verdigris. Solid brass is pure brass, while brass plat…
4. Facebook – Brass Alloys
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, commonly used in musical instruments like horns and trumpets. It has antimicrobial properties, does not lose its shine over time, and is used in various decorative and functional items. Brass tools are safe in explosive situations and are associated with authority in military and music contexts.
5. Rotax Metals – Copper & Copper-Alloy Products
Domain: rotaxmetals.wordpress.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Rotax Metals is a distributor of copper and copper-related metal products, serving various industries including fabricators, industrial arts, jewelry, and hardware. Founded in 1947, they offer a diverse inventory of copper, bronze, and brass materials, including sheet metal, square metal tubing, bronze bars, and brass angles. Their products are processed using advanced equipment and techniques, en…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for facts about brass metal
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Brass Metal Procurement?
In conclusion, understanding the multifaceted nature of brass metal is essential for B2B buyers across diverse industries. Its durability, corrosion resistance, and versatility make it a prime candidate for applications ranging from plumbing fixtures to musical instruments. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, international buyers can ensure they procure high-quality brass that meets specific requirements, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and operational efficiency.
Moreover, as brass continues to be a vital alloy in modern manufacturing, the increasing global focus on sustainability presents new opportunities for sourcing recycled brass. This not only aligns with eco-friendly practices but also supports a circular economy, which is becoming a crucial factor for businesses worldwide.
As you navigate the brass metal marketplace, consider engaging with trusted suppliers who can provide insights into the latest trends and innovations. By fostering strong supplier relationships and staying informed about industry developments, you can position your business for success in an evolving global landscape. Embrace the opportunities that strategic sourcing of brass presents, and drive your business forward in the coming years.

Illustrative image related to facts about brass metal
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.