Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Examples Of Lead Screws Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for examples of lead screws
In the quest for efficient and reliable mechanical power transmission, sourcing examples of lead screws can often pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These essential components, which convert rotational motion into linear movement, are crucial in various applications ranging from precision machinery to everyday consumer products. As global markets expand, understanding the diverse types of lead screws, their unique applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting becomes imperative for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of lead screws, exploring various types, including square, Acme, and buttress threads, along with their specific applications in industries such as manufacturing, robotics, and medical technology. Furthermore, we will address critical factors such as cost considerations, quality assurance, and best practices for supplier evaluation, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing with confidence.
By empowering B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Vietnam and Germany—this guide aims to streamline the decision-making process. With a focus on actionable insights and practical advice, it serves as an essential resource for businesses looking to optimize their procurement strategies and enhance their operational efficiency in a competitive global market.
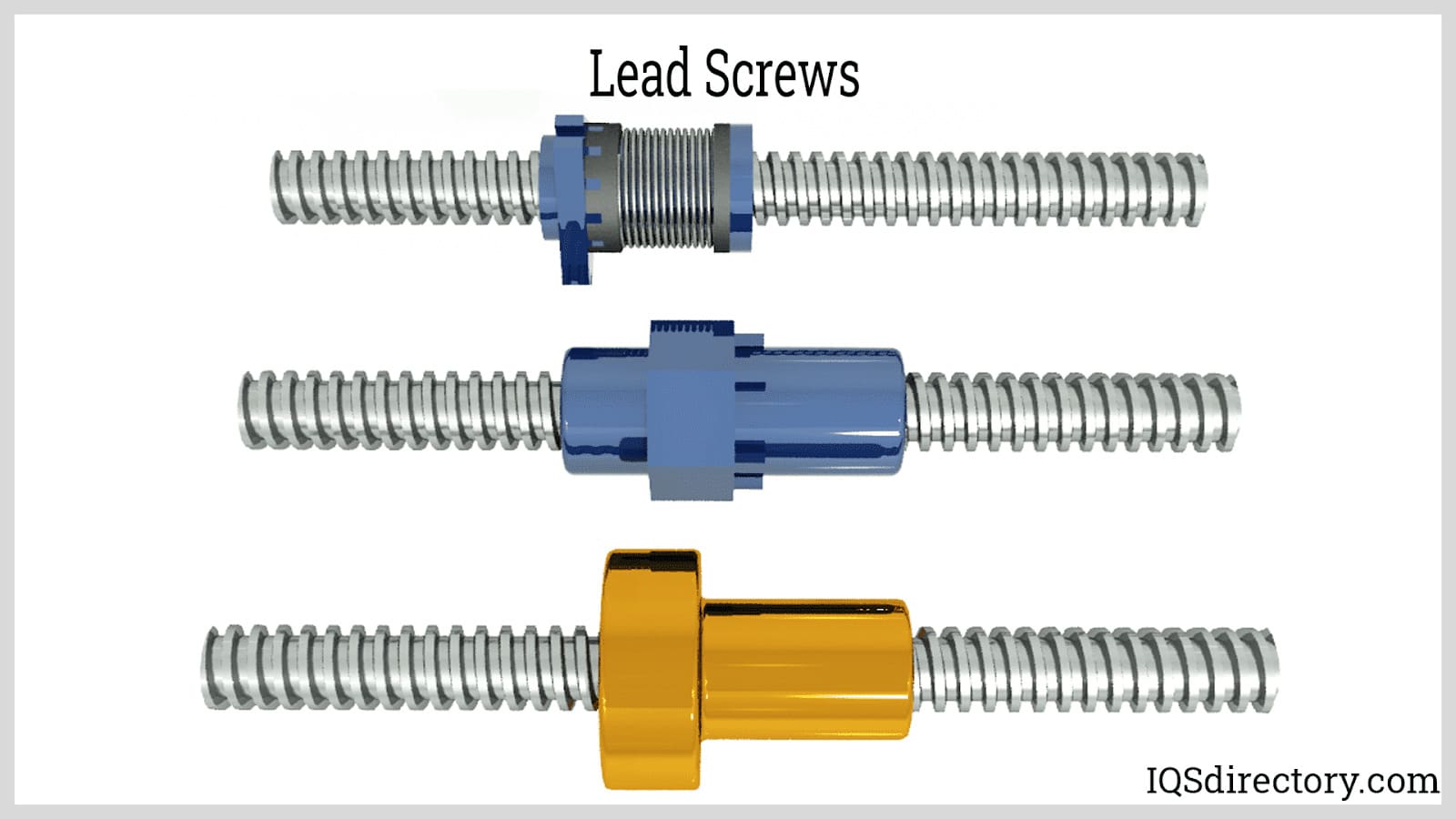
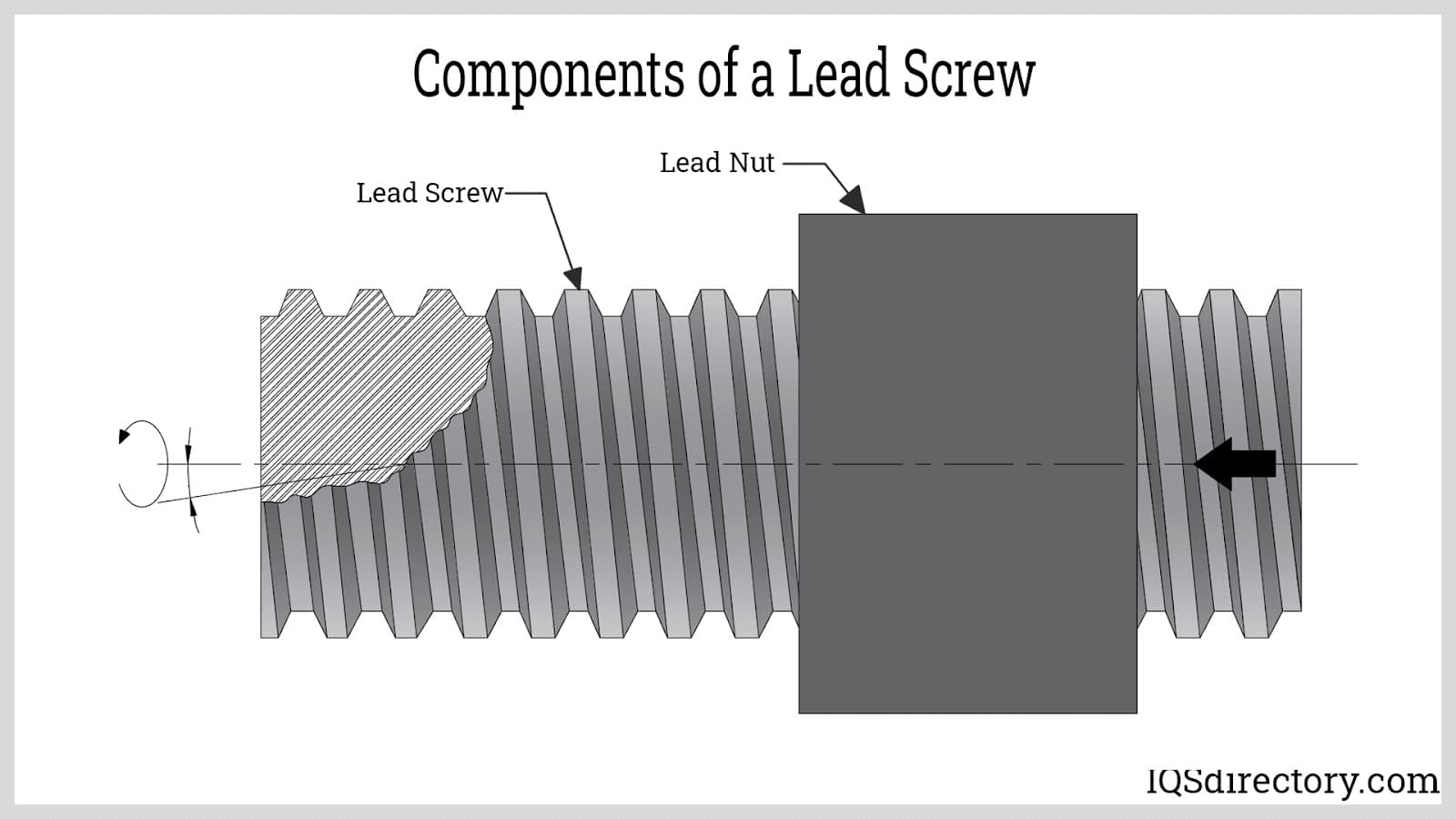
Understanding examples of lead screws Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square Thread | Square-shaped threads, low friction, high efficiency | Heavy machinery, aerospace, robotics | Pros: High load capacity, compact design; Cons: Difficult to manufacture, higher cost. |
| Acme Thread | Trapezoidal shape, easier to machine | CNC machines, industrial machinery, automotive | Pros: Stronger than square threads, versatile; Cons: Moderate friction, less efficient than square threads. |
| Buttress Thread | Triangular shape, unidirectional load transmission | Lifting equipment, precision tools, jacks | Pros: Efficient under load, precise movement; Cons: Poor performance under reverse loads. |
| Lead Screw with PTFE Coating | Enhanced durability, reduced lubrication needs | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Pros: Corrosion resistance, less maintenance; Cons: Higher upfront cost, limited temperature range. |
| Multi-Start Lead Screw | Multiple threads for faster movement | Automation, robotics, linear actuators | Pros: Increased speed, reduced torque; Cons: More complex design, potential for increased wear. |
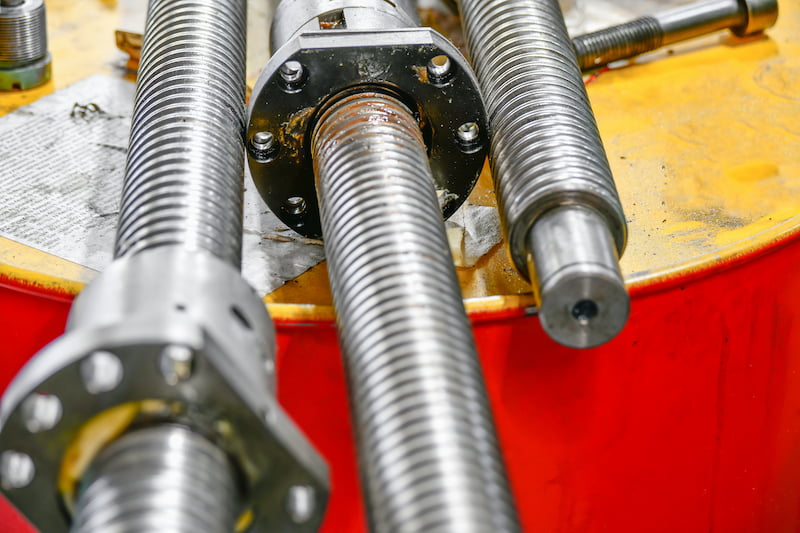
What Are the Characteristics of Square Thread Lead Screws?
Square thread lead screws feature threads shaped like squares, which minimize friction and enhance efficiency. These screws are particularly suitable for applications requiring high load capacity and compact design, such as in heavy machinery and aerospace. When purchasing square thread lead screws, B2B buyers should consider the complexity of manufacturing, as these screws are more challenging to produce, leading to higher costs. However, their performance in demanding environments often justifies the investment.
How Do Acme Thread Lead Screws Differ from Others?
Acme thread lead screws have a trapezoidal shape that allows for easier machining compared to square threads. They are widely used in CNC machines and industrial applications due to their strength and versatility. Buyers should note that while Acme threads offer a good balance between performance and manufacturability, they may experience higher friction compared to square threads, which can impact efficiency in high-speed applications.
Why Choose Buttress Thread Lead Screws for Specific Applications?
Buttress thread lead screws are designed with a triangular thread profile optimized for unidirectional load transmission. They are ideal for applications such as lifting equipment and precision tools, where accurate movement is crucial. B2B buyers should consider that while buttress threads perform exceptionally well under load, they are not suitable for applications requiring bidirectional movement due to their design limitations.
Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
What Are the Benefits of Lead Screws with PTFE Coating?
Lead screws with PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) coatings offer enhanced durability and reduced lubrication needs, making them suitable for sensitive environments like medical devices and food processing. These screws resist corrosion and minimize maintenance requirements, which can be a significant advantage for manufacturers. However, buyers should be aware of the higher upfront costs and potential limitations in temperature ranges when opting for PTFE-coated lead screws.
How Do Multi-Start Lead Screws Enhance Performance?
Multi-start lead screws feature multiple threads that allow for faster linear movement and reduced torque requirements. These screws are commonly used in automation and robotics, where speed and efficiency are paramount. When considering multi-start lead screws, B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of the design and the potential for increased wear, which may necessitate more frequent maintenance compared to single-start options.
Key Industrial Applications of examples of lead screws
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of examples of lead screws | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machines | High precision and repeatability in machining processes | Material quality, thread type, and precision standards |
| Medical Devices | Automated Surgery Equipment | Enhanced accuracy and reliability in surgical procedures | Compliance with medical standards, precision engineering |
| Robotics | Linear Actuators in Robotic Arms | Improved control and efficiency in robotic movements | Load capacity, thread design, and durability under stress |
| 3D Printing | Motion Control Systems | Consistent layer precision and speed in additive manufacturing | Thread type, backlash control, and material compatibility |
| Lifting Equipment | Screw Jacks for Elevation | Safe and efficient lifting mechanisms | Load rating, environmental resistance, and installation ease |
How Are Lead Screws Used in Manufacturing CNC Machines?
In the manufacturing sector, lead screws are integral to CNC machines, where they convert rotational motion into precise linear movement. This mechanism allows for the accurate positioning of cutting tools, ensuring high-quality finishes on machined parts. B2B buyers in this sector must consider factors such as the material quality of the screws, the specific thread type suited for their machinery, and adherence to precision standards to minimize downtime and enhance production efficiency.
What Role Do Lead Screws Play in Medical Devices?
Lead screws are critical in automated surgical equipment, where precision is paramount. They facilitate controlled movements of instruments, ensuring accuracy during procedures. For international buyers in the medical sector, sourcing lead screws requires a focus on compliance with stringent medical standards, as well as precision engineering to ensure reliability and safety in high-stakes environments.
How Are Lead Screws Essential for Robotics?
In robotics, lead screws serve as linear actuators that enable smooth and accurate movements in robotic arms. This application is vital for tasks requiring fine control, such as assembly or material handling. Buyers should prioritize lead screws with high load capacities and robust thread designs to withstand repeated use and stress, ensuring the longevity and reliability of robotic systems.
Why Are Lead Screws Important in 3D Printing?
Lead screws are crucial in 3D printing for controlling the vertical and horizontal movements of the print head or build platform. Their precision ensures consistent layer thickness, which is essential for the quality of the final product. Buyers from the 3D printing industry should focus on sourcing lead screws with specific thread designs that minimize backlash and ensure compatibility with various printing materials.
How Do Lead Screws Contribute to Lifting Equipment?
In lifting equipment, lead screws are employed in screw jacks, providing a mechanical advantage for raising and lowering loads. This application is vital for ensuring safety and efficiency in lifting operations. B2B buyers must consider the load rating of lead screws, their resistance to environmental factors, and ease of installation to ensure optimal performance in demanding conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘examples of lead screws’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Selecting the Right Lead Screw Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate type of lead screw for their applications. Given the variety of lead screw threads available—such as square, Acme, and buttress—determining which thread geometry will provide the best performance under specific load and motion requirements can be daunting. This often leads to either over-engineering solutions, which increases costs, or under-engineering, resulting in mechanical failure and costly downtime.
The Solution: To effectively select the right lead screw, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements, focusing on load capacity, speed, and precision. Start by defining the maximum load the lead screw will need to handle and the required speed of movement. If high load capacity and minimal friction are essential, square threads may be ideal, despite their higher manufacturing costs. For applications requiring a balance of strength and ease of machining, Acme threads are often a suitable choice. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and performance data for each lead screw type will facilitate informed decisions. Leveraging simulation tools or consulting with an engineering expert can also provide insights into the best lead screw design for specific scenarios.
Scenario 2: Issues with Backlash and Precision Control
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is backlash, which can severely affect the precision of machinery using lead screws. Backlash occurs when there is a gap between the screw and nut, leading to a delay or deviation in motion when the direction changes. This can be particularly problematic in high-precision applications such as CNC machining or automated assembly systems, resulting in reduced quality and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate backlash, buyers should consider using precision lead screws that incorporate features such as pre-loaded nuts or anti-backlash designs. These innovations help to maintain constant pressure between the nut and screw, eliminating gaps that contribute to backlash. Additionally, proper installation and alignment of lead screws are crucial; misalignment can exacerbate backlash issues. Regular maintenance, including lubrication and wear inspection, can prolong the life of lead screws and ensure consistent performance. Engaging with manufacturers that offer customizable solutions or technical support can provide buyers with the right tools to address and eliminate backlash in their systems effectively.
Scenario 3: High Wear Rates and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience high wear rates in lead screws, particularly in heavy-duty applications or environments where contaminants are prevalent. This wear can lead to frequent replacements, increased operational costs, and unplanned downtime. The challenge is exacerbated in regions with limited access to quality components or maintenance services, making it difficult for companies to sustain productivity.
The Solution: To combat wear issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing lead screws made from high-quality materials, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys, which offer better resistance to wear and corrosion. Implementing PTFE-based coatings can also enhance durability, especially in harsh environments. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspections can significantly extend the lifespan of lead screws. Buyers should also consider working with suppliers who provide comprehensive warranties and support services, ensuring they have access to replacement parts and technical assistance when needed. Investing in training for maintenance personnel can further improve the reliability of lead screw systems, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for examples of lead screws
What Are the Key Materials for Lead Screws in B2B Applications?
Selecting the right material for lead screws is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in lead screw manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Material Selection Impact Lead Screw Performance?
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand significant loads and has a temperature rating that typically exceeds 200°C. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated.

Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, its susceptibility to rust can limit its use in corrosive environments unless coated or treated, which adds to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel lead screws are ideal for applications involving high loads and moderate speeds, such as in machinery and construction equipment. Buyers should consider environmental factors, as exposure to moisture can lead to premature failure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for carbon steel is essential. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that suppliers can provide certifications for material quality.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can maintain its strength at elevated temperatures. It typically performs well in environments where cleanliness is critical, such as in the food and medical industries.

Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel, which can impact budget considerations.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel lead screws are preferred in applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as in food processing equipment and medical devices. They are compatible with various media, including water and chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 for stainless steel. In regions like South America and Africa, ensuring local availability and support for stainless steel products can be crucial.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and is easy to machine. It typically has a lower tensile strength compared to steel but is suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, making it ideal for portable and mobile applications. However, its lower strength limits its use in heavy-duty applications, and it may require additional support structures.
Impact on Application: Aluminum lead screws are often used in lightweight machinery, robotics, and aerospace applications. They are compatible with low to moderate loads and can operate effectively at lower speeds.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum. In Europe, specific grades may be preferred, so understanding local specifications is essential.
4. Bronze
Key Properties: Bronze is known for its excellent wear resistance and self-lubricating properties. It performs well in high-load applications and can withstand corrosive environments, particularly in marine applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of bronze is its durability and ability to reduce friction, which can extend the life of lead screws. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials, which can affect budget constraints.
Impact on Application: Bronze lead screws are commonly used in applications requiring high precision and low friction, such as in aerospace and marine industries. They are particularly effective in environments where lubrication is challenging.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B150 for bronze is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of bronze lead screws in their region, as they may not be as widely stocked as steel or aluminum.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lead Screws
| Material | Typical Use Case for examples of lead screws | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Aluminum | Robotics, lightweight machinery | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower strength | Medium |
| Bronze | Aerospace, marine applications | Wear resistance and self-lubricating | Higher cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions about lead screw materials, taking into account both performance and compliance factors relevant to their specific markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for examples of lead screws
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Lead Screws?
The manufacturing process of lead screws involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers gauge the reliability of their suppliers.
Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Material Preparation: What Types of Materials Are Commonly Used?
The manufacturing of lead screws typically begins with the selection of appropriate materials. Common choices include carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. These materials are chosen for their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and suitability for various applications. For instance, stainless steel is often preferred for environments where corrosion resistance is paramount, such as in medical devices.
Once materials are selected, they undergo processes like cutting and shaping to meet specified dimensions. This initial preparation is crucial as it affects the subsequent forming and machining processes.
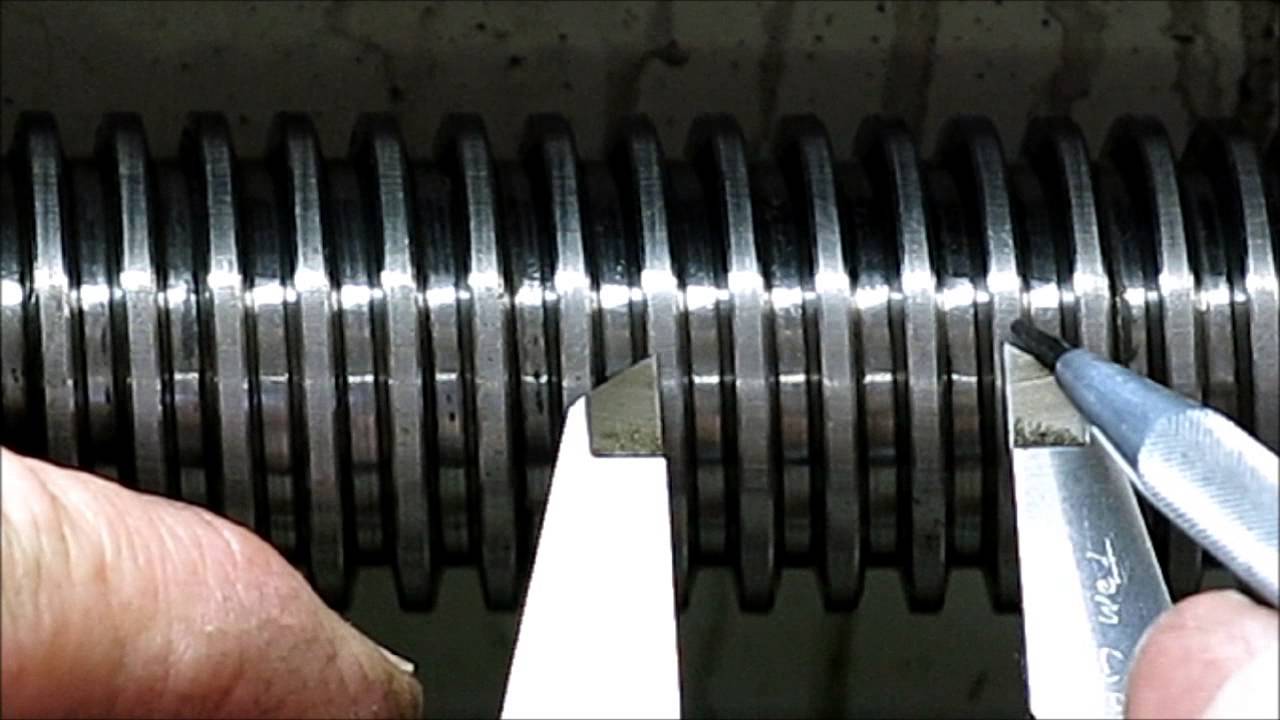
How Are Lead Screws Formed?
The forming stage is where the raw materials are transformed into lead screws. This can involve several techniques, including:
-
Turning: A CNC lathe is commonly used to create the cylindrical shape of the screw shaft. This process also involves cutting the threads onto the screw, which can be done using single-point cutting tools for square threads or multi-point tools for Acme threads.
-
Thread Rolling: For mass production, thread rolling is often employed. This cold-forming process enhances the strength of the threads and improves surface finish, leading to better performance in applications requiring high load capacities.
-
Grinding: After the primary shaping processes, grinding may be used to achieve the required tolerances and surface finishes. This is particularly important for applications demanding high precision.
What Is Involved in Assembly and Finishing?
Once the lead screws are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This involves attaching nuts, which may be made from materials like bronze or plastic, and ensuring that they fit perfectly with the screw shaft.
The finishing stage includes processes such as coating or anodizing to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce friction. PTFE-based coatings are frequently used for applications in harsh environments, allowing for lubrication-free operation.
Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Lead Screws?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in lead screw manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on consistent quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications can provide further assurance of quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in lead screw manufacturing typically involves several critical checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of the screws being produced. This includes dimensional checks, thread inspections, and surface finish evaluations.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a final inspection is performed. This includes functional testing of the lead screws to ensure they meet performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should actively engage in verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can help buyers assess compliance with quality standards. This includes evaluating the processes, equipment, and staff qualifications.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These documents should outline testing methods and any deviations from specifications.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These inspectors can validate that the products meet both the buyer’s requirements and international standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Lead Screws?
Understanding common testing methods can help buyers evaluate the quality of lead screws effectively.
Which Testing Methods Are Most Relevant?
-
Dimensional Inspection: This involves measuring the critical dimensions of the lead screw, such as diameter, thread pitch, and lead. This ensures that the components will fit correctly in their intended applications.
-
Load Testing: Lead screws may be subjected to load testing to assess their performance under various conditions. This is especially important for applications involving significant forces.
-
Surface Roughness Testing: The surface finish of lead screws is crucial for performance. Testing for surface roughness can help ensure that friction losses are minimized, enhancing the efficiency of the screw.
What Are the Specific QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider several nuances in quality control when sourcing lead screws internationally.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations concerning quality assurance. Buyers should be aware of local compliance requirements and ensure that their suppliers can meet these standards. This may involve additional certifications or testing methods specific to certain markets.
What Should Buyers Consider About Supplier Communication?
Effective communication with suppliers about quality expectations is essential. B2B buyers should establish clear quality requirements upfront and maintain ongoing dialogue to address any potential issues promptly.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in lead screw production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select suppliers that meet their stringent quality standards. This not only ensures the integrity of their products but also strengthens the overall supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘examples of lead screws’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing lead screws effectively, this guide provides a practical checklist that highlights essential steps. Lead screws are critical components in various industrial applications, and ensuring you select the right type and supplier can significantly impact your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s crucial to clearly outline your technical requirements. Identify the necessary dimensions, load capacities, and thread types (such as Acme, square, or buttress) that fit your application. A well-defined specification helps streamline the sourcing process and reduces the risk of acquiring unsuitable products.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in lead screws. Look for companies with a strong presence in your target markets—Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Evaluate their expertise in lead screw manufacturing and their ability to cater to your specific needs.
- Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews, testimonials, and industry references.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Ensure they can produce the required specifications consistently.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate their compliance with industry standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management systems are crucial indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability.
- Quality Assurance: Ask for documentation that outlines their quality control processes.
- Material Certifications: Ensure that materials used in lead screw production meet necessary standards (e.g., ASTM or ANSI).
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples of their lead screws for evaluation. Testing samples helps ensure that the products meet your performance and quality standards in real-world conditions.
- Performance Testing: Assess factors such as load capacity, friction, and wear resistance.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure that the samples are compatible with your existing systems.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have narrowed down your options, compare pricing structures and payment terms among the shortlisted suppliers. While cost is an important factor, consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping, duties, and any potential import taxes.
- Transparency in Pricing: Ensure that quotes include all costs to avoid surprises later.
- Flexible Payment Options: Look for suppliers who offer favorable payment terms that suit your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Review Delivery Timelines
Discuss and confirm delivery timelines with your selected supplier to ensure they align with your production schedule. Timeliness is critical in maintaining efficient operations, especially in industries where downtime can be costly.
- Lead Times: Ask for estimated lead times and any factors that might influence them.
- Logistics Capabilities: Evaluate their ability to handle international shipping if applicable.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Effective communication is vital for addressing any issues that may arise during the procurement process or after delivery.
- Regular Updates: Set up regular check-ins to discuss progress and any potential challenges.
- Point of Contact: Ensure you have a dedicated contact person for streamlined communication.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing lead screws more effectively, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for examples of lead screws Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lead Screws Sourcing?
When sourcing lead screws, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum vary in price based on market conditions and availability. Specialty materials or coatings, such as PTFE for harsh environments, will further increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location and the complexity of the lead screw design. Skilled labor is often required for precision machining, particularly for intricate thread geometries like square or buttress threads.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. A higher level of automation can reduce these costs, but initial investments may be significant.
-
Tooling: The production of lead screws often requires specialized tooling, which can be a considerable upfront expense. For example, creating square threads may necessitate single-point cutting tools that are more expensive and time-consuming to set up.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the precision and reliability of lead screws is critical, particularly in high-stakes applications like medical devices or CNC machinery. Quality control processes add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically depending on the origin, destination, and mode of transport. For international buyers, understanding the implications of logistics is essential for total cost calculations.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a margin in their pricing to cover their operational costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on competition, demand, and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lead Screws Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of lead screws, and understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically attract lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to secure the best pricing structure.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom lead screws tailored to specific applications will usually command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate whether standard options can meet their needs to reduce costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) often lead to increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certified products against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can significantly impact pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may offer better guarantees of quality but can also come with higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) is vital, as these can affect the total landed cost of lead screws. Buyers should clarify these terms with suppliers to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Lead Screws Pricing?
Effective negotiation strategies can help buyers achieve more favorable pricing for lead screws:
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate orders to increase volume. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate on price with larger orders.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to understand the typical pricing landscape. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. Presenting a TCO analysis can provide compelling arguments for negotiating lower prices.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Long-term relationships often result in loyalty discounts and more favorable negotiations.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and regional market conditions that can affect pricing.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for lead screws can vary widely based on the factors discussed above, and it is advisable for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. The figures provided are indicative and should be validated with suppliers for precise cost assessments.
Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing examples of lead screws With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Lead Screws: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, lead screws are a popular choice for converting rotational motion into linear movement. However, there are several alternative technologies that may better suit specific applications or requirements. This analysis compares lead screws with two viable alternatives: ball screws and linear actuators, providing insights for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Examples of Lead Screws | Ball Screws | Linear Actuators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for light to medium loads; high precision | Excellent for high load capacities; lower friction | Varies widely; can offer high force and speed |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment due to complexity | Moderate, varies by type and application |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; minimal adjustments | Requires precise alignment and setup | Easy to integrate with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Moderate; may require lubrication | Low; sealed systems reduce maintenance needs | Varies; electric versions need less maintenance than pneumatic |
| Best Use Case | CNC machines, 3D printers | Industrial machinery, robotics | Automation systems, medical devices |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball Screws?
Ball screws utilize ball bearings to reduce friction, allowing for smoother and more efficient operation, especially under heavy loads. Their design enables high load capacities and precise movements, making them ideal for applications requiring accuracy and speed, such as CNC machines and robotic arms. However, ball screws are generally more expensive than lead screws and may require more complex installation and alignment. Additionally, they can be sensitive to misalignment, which can affect performance and longevity.
How Do Linear Actuators Compare to Lead Screws?
Linear actuators offer another alternative for applications requiring linear motion. These devices can be powered by electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic systems, providing flexibility in terms of force and speed. They are particularly useful in automation and medical devices where precise control is crucial. While electric linear actuators tend to require less maintenance than lead screws, their complexity can lead to higher costs. Moreover, the performance of linear actuators can vary significantly based on the type selected, making it essential to choose the right model for specific applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between lead screws and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, ease of integration, and maintenance needs. Lead screws are often a cost-effective solution for applications requiring moderate loads and high precision. Conversely, ball screws may be more suitable for high-load environments, while linear actuators provide versatility across various applications. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific operational demands of the business, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in their mechanical systems.

Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for examples of lead screws
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lead Screws That B2B Buyers Should Consider?
Understanding the technical properties of lead screws is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several essential specifications that impact performance and compatibility with various applications:
1. Material Grade
Lead screws can be constructed from a variety of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. The choice of material affects strength, corrosion resistance, and weight. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in environments prone to moisture or chemicals, while aluminum is lighter and ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor. Buyers should assess the material grade based on the intended application to ensure durability and performance.
2. Thread Type
The type of thread—be it square, Acme, or buttress—affects load capacity, efficiency, and ease of machining. Square threads minimize friction and maximize load-bearing capabilities, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Acme threads, with their trapezoidal shape, offer a balance between strength and ease of manufacturing. Understanding the implications of each thread type helps buyers select the most suitable option for their operational needs.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in dimensions and can significantly influence the lead screw’s precision and fit within a mechanical assembly. Higher precision tolerances are essential in applications requiring tight control, such as CNC machines or medical devices. B2B buyers should consider tolerance specifications to avoid performance issues and ensure seamless integration into their systems.
4. Lead and Pitch
Lead is the linear distance the nut moves with one complete revolution of the screw, while pitch is the distance between two adjacent thread crests. These parameters affect the speed and accuracy of linear motion. A smaller lead results in finer adjustments, whereas a larger lead allows for quicker movement. Buyers must evaluate these specifications based on the required operational speed and precision of their applications.

Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
5. Load Capacity
The load capacity of a lead screw determines its suitability for specific applications. It is essential to assess the maximum load that a lead screw can handle without failure. This information is critical for applications involving heavy machinery or high-stress environments. Buyers should consult with manufacturers to ensure the selected lead screw meets the load demands of their projects.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Lead Screws in B2B Transactions?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and transactions. Here are some essential trade terms that buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding the role of OEMs is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers for lead screws, as OEMs typically adhere to strict quality standards and specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For lead screws, MOQs can impact inventory management and cash flow for businesses. Buyers should consider their project requirements and negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products, including lead screws. This process allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and delivery schedules, aiding in informed decision-making.

Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and delivery. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they clarify logistical obligations and costs associated with lead screw purchases.
5. Backlash
Backlash refers to the clearance or lost motion in a mechanical system, often caused by gaps between components. For lead screws, minimizing backlash is crucial for maintaining precision in applications like CNC machining. Buyers should inquire about backlash specifications to ensure optimal performance in their machinery.
By understanding these key technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that the lead screws they procure meet their specific operational requirements and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the examples of lead screws Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Lead Screws Sector?
The global lead screws market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, robotics, and medical technology. Factors such as the demand for high-precision motion control systems and the rise of smart manufacturing technologies are propelling the adoption of lead screws. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly sourcing lead screws to enhance their machinery’s efficiency and performance.
Emerging trends include the integration of advanced materials and manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing, which allows for the production of complex lead screw designs tailored to specific applications. Additionally, the shift towards electric actuation systems over traditional pneumatic and hydraulic systems is driving innovation in lead screw applications. As companies globally focus on improving operational efficiency, the versatility of lead screws in various applications, from CNC machines to medical devices, positions them as a critical component in modern engineering solutions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Lead Screws?
Sustainability has become a paramount concern for international B2B buyers, influencing sourcing decisions in the lead screw sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in lead screws cannot be overlooked. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through ethical sourcing practices and the use of eco-friendly materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains is underscored by the growing consumer demand for transparency and accountability. Buyers are now looking for manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled metals or biodegradable materials in their lead screw production. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to green standards can significantly enhance a supplier’s credibility. Furthermore, incorporating sustainable practices not only reduces environmental footprints but can also lead to cost savings in the long run, making it a win-win for both suppliers and buyers.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Lead Screws in B2B Applications?
The evolution of lead screws dates back to ancient times, with early applications found in devices like Archimedes’ screw for lifting water. Over the centuries, the design and functionality of lead screws have advanced significantly. The industrial revolution marked a pivotal point where lead screws became integral to machinery, providing a reliable means of converting rotational motion into linear motion.
In the 20th century, the introduction of new materials and manufacturing techniques enhanced the performance and durability of lead screws. Innovations such as the Acme and square thread designs provided greater load-bearing capabilities and efficiency. Today, lead screws are not only fundamental in traditional machinery but have also found applications in cutting-edge technologies, including robotics and medical equipment. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers to appreciate the ongoing advancements and the potential applications of lead screws in modern industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of examples of lead screws
-
How do I select the right lead screw for my application?
Selecting the right lead screw involves evaluating your specific application needs, such as load capacity, precision requirements, and operating environment. Consider the thread type (square, acme, or buttress) based on your load and efficiency needs. Additionally, assess the lead and pitch to ensure compatibility with your required movement speed and accuracy. Consulting with suppliers about your application can help you narrow down options and ensure that you choose a lead screw that meets your operational demands. -
What are the differences between lead screws and ball screws?
Lead screws and ball screws serve similar functions, but they differ significantly in design and performance. Lead screws convert rotational motion into linear motion through sliding contact, which can lead to higher friction and wear. In contrast, ball screws utilize recirculating ball bearings to minimize friction, allowing for higher efficiency and load capacities. If your application requires high precision and efficiency, ball screws may be preferable, whereas lead screws are suitable for simpler, lower-load applications. -
What should I consider when sourcing lead screws internationally?
When sourcing lead screws internationally, consider factors like supplier reliability, lead times, and compliance with international quality standards. Evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and experience in your specific industry. Additionally, assess any tariffs or trade regulations that may impact costs and delivery times. Establishing clear communication regarding specifications and delivery expectations is vital to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process. -
How can I ensure the quality of lead screws from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of lead screws from suppliers, request certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 9001). Conducting a factory audit can provide insight into the manufacturer’s processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider requesting samples for testing before placing a bulk order. Establishing a strong relationship with the supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and any potential issues. -
What customization options are available for lead screws?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for lead screws, including thread type, length, material, and coatings. Discussing your specific requirements with potential suppliers can yield tailored solutions that meet your operational needs. Customizations may also include modifications for specific environmental conditions, such as corrosion resistance or enhanced lubrication features. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your needs within your project timeline and budget. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lead screws?
Minimum order quantities for lead screws can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on factors such as material type, customization, and production capabilities. Some manufacturers may have flexible MOQs for standard products, while custom lead screws may require higher quantities to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with suppliers upfront to determine their MOQs and negotiate terms that suit your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms are typically offered by lead screw suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits, or net payment terms after delivery. International buyers should also consider factors like currency fluctuations and transaction fees. Establishing clear payment terms in advance can help prevent disputes and facilitate smoother transactions. Always ensure that the payment method is secure and provides adequate protection against fraud. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing lead screws?
When importing lead screws, consider the logistics of shipping, including freight options, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Assess the supplier’s ability to manage international shipping and whether they can provide documentation required for customs. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs inspections or local regulations. Working with a freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process and ensure that your lead screws arrive on time and in good condition.
Top 6 Examples Of Lead Screws Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fractory – Lead Screws
Domain: fractory.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Lead screws are mechanical power transmission devices used for high-precision actuation, converting rotational motion into linear motion. They are also known as power screws or translation screws. Key components include the screw shaft, threads, and nut. The screw shaft is typically made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, and may have PTFE-based coatings for durability. Lead screws a…
2. igus – Lead Screws
Domain: blog.igus.ca
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: A lead screw is a component that converts rotary motion into linear motion, typically consisting of a screw shaft and a nut for power transmission. It is different from threaded rods as it is designed for power transmission rather than fastening. Common applications include linear actuators, machine tools, screw jacks, and biomedical devices. Lead screws come in various thread types, including squ…
3. Heason – Lead Screws
Domain: heason.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Lead screws are part of Heason’s motion control products, translating rotary motion into linear motion. They are threaded metal bars with a nut that moves along the screw, generating sliding friction. Lead screws can be made of stainless steel, with nuts available in metal or molded plastic depending on the application. Applications include laboratory equipment, fluid handling devices, paper proce…
4. Noll Inc – Lead Screws
Domain: nollinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Lead screws, also known as power screws or translation screws, are used to convert turning motion into linear motion. They can be manufactured through rolling, cutting, or grinding the threads. Lead screws require a large area of sliding contact, resulting in higher frictional energy loss compared to other linkages. Historically, they were used in devices like olive and grape presses. Today, they …
5. Haydon Kerk Pittman – Lead Screws
Domain: haydonkerkpittman.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Lead Screws offer the latest technology in material science and tribology for motion control with distinct advantages: 1. Zero maintenance; 2. No lubrication required; 3. Lower particulate generation (clean option); 4. Longer life with non-catastrophic failure; 5. Quieter operation (no re-circulating ball noise); 6. High helix/Fast leads (greater than 100mm/rev); 7. Fine threads (as small as 0.3mm…
6. ScienceDirect – Lead Screws
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Lead screws are mechanical components that convert motor rotation into linear translation. They offer good axial stiffness and smooth small displacements, making them suitable for low-duty applications. Key features include:
– Self-locking capabilities in vertical configurations.
– Generally preloaded with an axial load to maintain contact between the nut and screw filets, minimizing hysteresis….
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for examples of lead screws
In navigating the complexities of lead screw applications, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the distinct types of lead screws—such as square, acme, and buttress threads—empowers businesses to select the right component tailored to their operational needs. This knowledge not only enhances efficiency but also optimizes manufacturing processes, providing a competitive edge in various industries, from automation to medical technology.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable suppliers, it is essential to prioritize partnerships that emphasize quality and precision in lead screw manufacturing. The ability to access high-quality lead screws can significantly impact production timelines and cost-effectiveness, ultimately driving profitability.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative solutions in linear motion will only grow. Buyers should actively engage with manufacturers who leverage advanced technologies and materials to meet evolving market needs. By fostering these strategic relationships, businesses can ensure they remain at the forefront of their industries, equipped to tackle the challenges of tomorrow. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategy—your success hinges on it.
Illustrative image related to examples of lead screws
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.