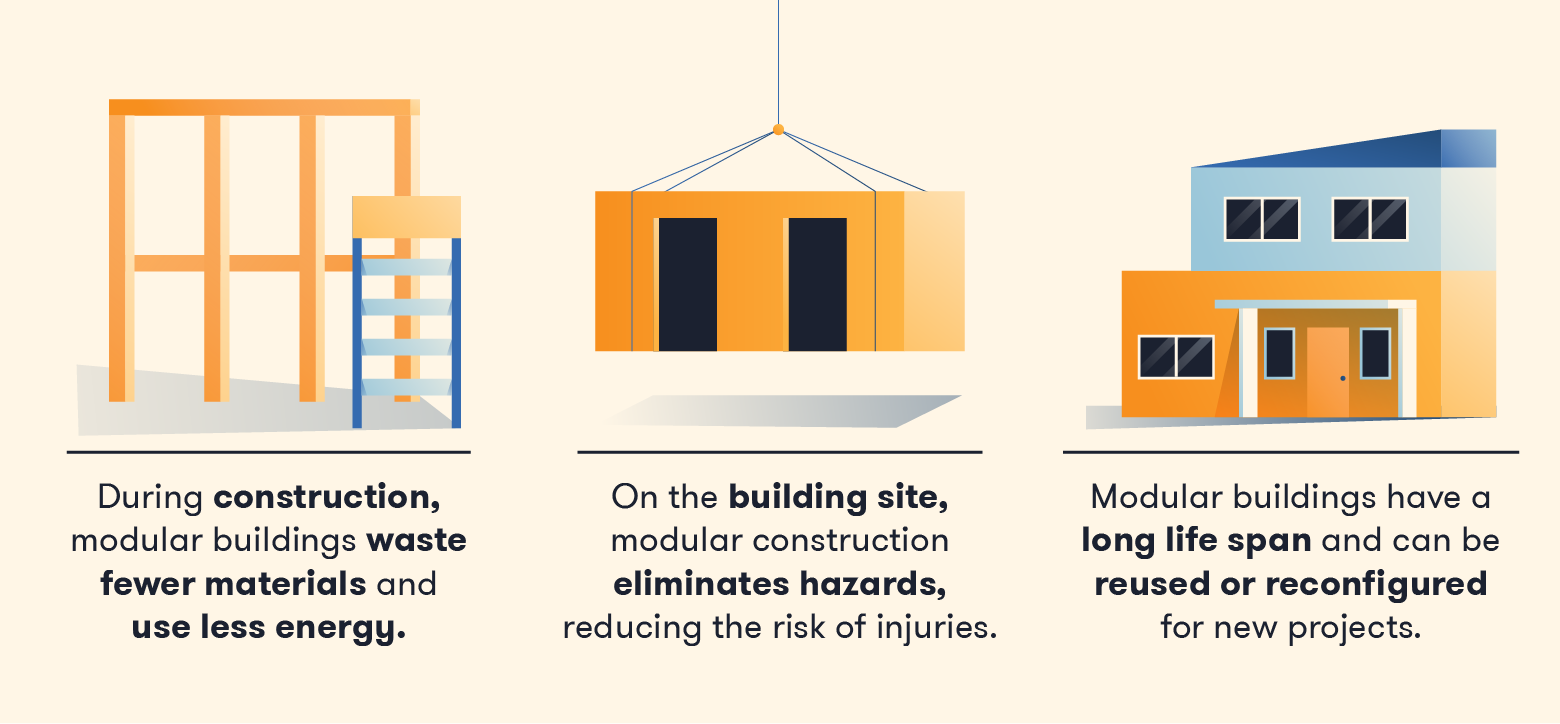
Types Of Modular: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of modular
In today’s fast-paced global economy, sourcing the right types of modular construction can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the increasing demand for efficient, cost-effective building solutions, understanding the various types of modular options available—such as portable offices, prefabricated buildings, and specialized assembly techniques—is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing key areas such as applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, enabling buyers to navigate the complexities of the modular market with confidence.
By delving into the specifics of each modular type, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices tailored to their unique needs. Whether you are a construction firm in Brazil looking to expand your project portfolio or a real estate developer in Nigeria seeking sustainable building solutions, the insights provided here will help you identify the most suitable modular options. With a focus on practical applications and strategic supplier partnerships, this guide is designed to enhance your understanding of the modular landscape, ultimately driving efficiency and innovation in your projects. Equip yourself with the knowledge to leverage modular construction effectively, ensuring your investments yield maximum returns in today’s competitive marketplace.
Understanding types of modular Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Module Assembly | Utilizes wood framing, often in two primary types: Type V and Type III. | Residential buildings, hotels, low-rise apartments | Pros: Cost-effective, sustainable, customizable. Cons: Limited height, moisture vulnerability. |
| Light Gauge Steel Module | Cold-formed steel framing, lightweight and durable. | Commercial structures, retail, industrial facilities | Pros: Strong, non-combustible, longer lifespan. Cons: Higher initial costs, less flexible design. |
| Prefabricated Buildings | Factory-manufactured components assembled on-site. | Temporary structures, classrooms, healthcare facilities | Pros: Quick assembly, reduced labor costs. Cons: Transportation costs, potential design limitations. |
| Portable Offices | Mobile workspaces easily transported and assembled. | Construction sites, remote project locations | Pros: Flexibility, rapid setup. Cons: Limited space, may require additional permits. |
| Modular Mezzanines | Intermediate floors providing extra space within buildings. | Warehouses, manufacturing facilities | Pros: Maximizes vertical space, quick installation. Cons: Structural limitations, potential zoning issues. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Wood Module Assembly?
Wood module assembly is characterized by its use of wood framing, primarily divided into Type V and Type III classifications. Type V involves wood framing throughout, suitable for multi-family residences and hotels up to four stories, while Type III allows for wood framing in interiors with fire-retardant exteriors. This assembly type is ideal for B2B buyers focused on residential construction due to its cost-effectiveness and sustainability. However, buyers must consider its height limitations and susceptibility to moisture, which can lead to increased maintenance costs.
How Does Light Gauge Steel Module Assembly Stand Out?
Light gauge steel module assembly employs cold-formed steel, offering superior strength and durability compared to wood. This type is widely used in commercial applications, such as offices and industrial facilities, where structural integrity is paramount. Its non-combustible nature enhances safety, making it a preferred choice for fire-sensitive environments. While it has a higher initial cost, its longevity and lower maintenance needs can result in long-term savings, making it a valuable investment for B2B buyers.
What Are the Advantages of Prefabricated Buildings?
Prefabricated buildings are constructed from factory-manufactured components, which are then assembled on-site. This method is particularly useful for temporary structures, such as classrooms or healthcare facilities. The primary benefits include rapid assembly and reduced labor costs, appealing to buyers needing quick solutions. However, transportation expenses and potential design restrictions must be factored in, especially for international projects, where logistics can significantly impact overall costs.
Why Choose Portable Offices for Project Sites?
Portable offices provide mobile workspaces that can be quickly set up at construction sites or remote project locations. Their flexibility and ease of transport make them ideal for companies needing temporary office solutions. While they allow for rapid setup, buyers should be aware of space limitations and the necessity for additional permits in certain regions. This type can be particularly beneficial for companies operating in dynamic environments, where adaptability is crucial.
How Do Modular Mezzanines Enhance Warehouse Efficiency?
Modular mezzanines are intermediate floors that create additional storage or office space within existing buildings. They are especially useful in warehouses and manufacturing facilities, where maximizing vertical space is essential for operational efficiency. Quick installation and the ability to customize layouts are significant advantages. However, potential zoning issues and structural limitations may affect their implementation, necessitating careful planning and compliance checks for B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of types of modular
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of modular | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Real Estate | Prefabricated residential units | Reduced construction time and cost, improved quality control | Supplier’s track record, customization options, compliance with local building codes |
| Healthcare | Modular healthcare facilities (clinics, labs) | Rapid deployment for urgent health needs, flexibility in design | Quality certifications, modularity for future expansion, adherence to health regulations |
| Education | Portable classrooms and administrative offices | Quick setup in response to population growth, cost-effective solutions | Durability against weather conditions, ease of relocation, compliance with educational standards |
| Oil & Gas | Modular workforce accommodation | Efficient housing solutions in remote locations, reduced logistical costs | Transport logistics, durability for harsh environments, scalability for workforce needs |
| Retail | Modular retail spaces for pop-up stores | Fast market entry, flexibility to adapt to consumer trends | Location compatibility, design aesthetics, ease of assembly and disassembly |
What Are the Key Applications of Modular Construction in the Construction Industry?
In the construction and real estate sector, prefabricated residential units represent a significant application of modular construction. These units are manufactured off-site, allowing for faster assembly on-site. This method not only reduces construction time and costs but also enhances quality control through factory conditions. For international buyers, it is crucial to consider the supplier’s track record, customization options, and compliance with local building codes to ensure successful project execution.
How Is Modular Construction Transforming Healthcare Facilities?
Modular healthcare facilities, such as clinics and laboratories, are increasingly used to address urgent health needs, especially in remote or underserved areas. These structures can be rapidly deployed and offer design flexibility to accommodate various healthcare services. For B2B buyers in healthcare, sourcing considerations include ensuring quality certifications, the ability to expand modularly in the future, and adherence to local health regulations to maintain safety and compliance.
What Role Does Modular Construction Play in Education?
In the education sector, portable classrooms and administrative offices are vital for accommodating growing student populations. These modular solutions can be set up quickly and are cost-effective, making them ideal for institutions facing budget constraints. Buyers should focus on sourcing durable materials that can withstand various weather conditions, ease of relocation, and compliance with educational standards to ensure a conducive learning environment.
How Does Modular Construction Support the Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas sector often requires workforce accommodation in remote locations. Modular workforce housing provides efficient solutions that minimize logistical challenges and costs associated with transporting workers to and from distant sites. When sourcing these accommodations, businesses must consider transport logistics, the durability of materials in harsh environments, and the scalability of units to meet fluctuating workforce needs.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
In What Ways Are Retail Spaces Adapting Through Modular Solutions?
Modular retail spaces, particularly for pop-up stores, allow businesses to enter markets quickly and adapt to changing consumer trends. These modular units can be easily assembled and disassembled, providing retailers with flexibility in location and design. For international B2B buyers, key considerations include ensuring location compatibility, appealing design aesthetics, and ease of assembly to maximize operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of modular’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Compliance in Modular Construction
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges in ensuring that their modular construction projects comply with local building codes and regulations. This is particularly critical in international markets, such as Africa and South America, where regulations may vary widely and are frequently updated. A buyer may invest in a modular solution only to discover that their project does not meet the necessary safety or structural standards, leading to costly delays, fines, or even project cancellation.
The Solution:
To mitigate compliance issues, buyers should engage with local experts who are well-versed in regional construction regulations. This can be achieved by partnering with a modular construction firm that has a proven track record in the specific market. These firms often have dedicated compliance teams that can assist in navigating the complexities of local laws. Additionally, buyers should request detailed documentation and certifications for all modular components before purchase. Engaging in pre-construction consultation sessions can further clarify requirements and streamline the permitting process. By ensuring that compliance is a priority from the outset, buyers can avoid costly setbacks and maintain project timelines.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem:
Supply chain issues have become increasingly prevalent, affecting the availability and delivery of modular construction components. For B2B buyers, this can result in extended project timelines and increased costs, as delays in receiving critical materials can stall construction. Buyers in regions like the Middle East or Europe may experience additional complications due to varying import regulations and tariffs, which can further disrupt the flow of necessary components.

Illustrative image related to types of modular
The Solution:
To address supply chain disruptions, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers to create a more resilient sourcing strategy. Diversifying the supply base can help mitigate risks associated with delays from any single supplier. Additionally, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can provide real-time insights into inventory levels and delivery timelines, allowing buyers to make proactive adjustments. Implementing just-in-time inventory practices can also help manage costs while ensuring that materials are available as needed. Regular communication with suppliers about potential issues can help anticipate challenges before they impact the project timeline.
Scenario 3: Addressing Customization and Flexibility Needs
The Problem:
In many cases, B2B buyers find that their modular construction needs require a high level of customization that standard modules cannot accommodate. This issue is often exacerbated by the unique architectural requirements or local preferences in regions such as Brazil or Nigeria, where modular solutions may need to integrate traditional design elements or adapt to specific environmental conditions. Buyers may feel constrained by the limited customization options offered by some manufacturers.
The Solution:
To effectively address customization needs, buyers should seek modular construction providers that specialize in bespoke solutions. Engaging manufacturers who have a flexible design process and a robust portfolio of customized projects can ensure that the final product aligns with the buyer’s vision. Before making a commitment, buyers should request case studies or references from previous clients who have undertaken similar custom projects. Collaborating closely with the design team during the early stages of development can facilitate a smoother customization process. Furthermore, leveraging modular components that allow for future expansion or reconfiguration can enhance the flexibility of the project, ensuring that it can adapt to changing needs over time.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of modular
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Modular Construction?
In the realm of modular construction, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring the performance, durability, and suitability of the end product. Here, we analyze four common materials: wood, light gauge steel, red iron steel, and prefabricated concrete. Each material has unique properties that influence its application in modular construction.
How Does Wood Perform in Modular Construction?
Wood is a traditional material in modular building, particularly for residential structures. Its key properties include good insulation, lightweight nature, and ease of customization. However, wood is susceptible to moisture, which can lead to rot and decay, making it less suitable for humid environments.
Pros: Wood is generally more affordable than steel, has a lower carbon footprint, and can be easily modified. It is ideal for low-rise buildings, such as single-family homes and multi-family housing.
Cons: Its limitations in height and span compared to steel alternatives restrict its use in taller structures. Additionally, wood is combustible, presenting a higher fire risk.
Impact on Application: Wood is best suited for residential applications but may not perform well in high-moisture areas or for temporary structures that require durability.
What Advantages Does Light Gauge Steel Offer?
Light gauge steel is increasingly popular in modular construction due to its strength and durability. It features cold-formed steel framing members that are resistant to corrosion and provide excellent structural integrity.
Pros: Light gauge steel is non-combustible, enhancing fire safety. It has a longer lifespan than wood and requires less maintenance, making it suitable for commercial structures like offices and retail outlets.
Cons: The initial cost of light gauge steel can be higher than wood, and its manufacturing process may be more complex.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for environments requiring robust structural performance and fire resistance, making it a preferred choice for commercial and industrial projects.
When is Red Iron Steel the Best Choice?
Red iron steel, or structural steel, is used for larger modular projects, particularly those with stringent engineering requirements. It provides excellent load-bearing capacity and is suitable for high-rise buildings.
Pros: Red iron steel offers exceptional durability and strength, making it ideal for tall structures. Its resistance to fire and pests enhances the longevity of the building.
Cons: The cost of red iron steel is typically higher than wood and light gauge steel. Additionally, its weight can complicate transportation and installation.
Impact on Application: Red iron steel is optimal for high-rise buildings and structures that require significant load-bearing capabilities, particularly in urban settings.
Why Choose Prefabricated Concrete for Modular Construction?
Prefabricated concrete is another material gaining traction in modular construction. Its components are manufactured in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
Pros: Concrete is highly durable, fire-resistant, and requires minimal maintenance. It is also excellent for thermal mass, providing energy efficiency in temperature regulation.
Cons: The weight of concrete can lead to higher transportation costs, and its installation may require specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Prefabricated concrete is suitable for a variety of applications, including commercial and industrial buildings, where durability and energy efficiency are paramount.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
Summary Table of Material Selection for Modular Construction
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of modular | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Residential buildings, low-rise structures | Affordable and customizable | Limited height and fire risk | Low |
| Light Gauge Steel | Commercial structures, offices, retail | Non-combustible and durable | Higher initial cost and complex mfg | Medium |
| Red Iron Steel | High-rise buildings, heavy industrial use | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost and transportation complexity | High |
| Prefabricated Concrete | Commercial and industrial buildings | Highly durable and energy-efficient | Heavy and may require specialized handling | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in modular construction. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed decisions that align with project requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of modular
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Modular Construction?
The manufacturing process of modular construction involves several critical stages that ensure the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of the end product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing modular solutions.
Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality materials such as wood, light gauge steel, or red iron steel. Each material has its own handling requirements and preparation techniques. For instance, wood must be treated for moisture resistance and strength, while steel components are often pre-fabricated and galvanized to prevent corrosion.
In this phase, manufacturers typically conduct inspections to ensure all materials meet specified standards and are free from defects. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials and whether they comply with international sustainability standards.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves cutting, shaping, and assembling the components that will make up the modular units. Advanced technologies such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are often employed to enhance precision in cutting and shaping materials.
For steel structures, cold-forming techniques are commonly used to create lightweight yet strong components. For wooden structures, methods like platform and balloon framing are utilized. Buyers should look for manufacturers who invest in modern machinery and technology, as this often correlates with higher quality outputs.
Assembly
The assembly phase is where the pre-fabricated components come together. This can occur either in a controlled factory environment or on-site, depending on the modular system being used. Factory assembly allows for better quality control, as components are assembled under optimal conditions, reducing exposure to environmental factors that can affect quality.
During this phase, it is vital for manufacturers to adhere to engineering specifications and building codes relevant to the project location. Buyers should verify that suppliers have experience with local regulations and standards.
Finishing
The final stage of the manufacturing process is finishing, which involves adding details such as insulation, electrical wiring, plumbing, and interior finishes. This stage is critical for ensuring the modular units meet both aesthetic and functional requirements.
Quality assurance during finishing includes thorough inspections and testing of all installed systems. Buyers should request detailed documentation on the finishing processes used and any warranties provided for the work completed.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Modular Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an essential aspect of the modular manufacturing process that ensures products meet specified standards and customer expectations. Understanding the QA measures in place can provide B2B buyers with confidence in their purchasing decisions.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 set the benchmark for quality management systems in manufacturing. Compliance with ISO standards signifies that a manufacturer has processes in place to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area and API standards for oil and gas applications, can further assure buyers of quality and safety. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who hold relevant certifications, as this can be a crucial factor in international trade.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Modular Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify defects early and ensure adherence to standards. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet quality specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly and forming stages, random inspections and tests are conducted to monitor the quality of work in progress.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the modular units are complete, a comprehensive inspection is carried out to verify that the finished product meets all specifications and standards.
Buyers should request information about the specific QC measures employed by suppliers, including the frequency of inspections and the criteria used for passing or failing components.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Modular Construction?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the safety and durability of modular units. Common methods include:
- Load Testing: This evaluates the structural integrity of modular units by simulating real-world conditions.
- Thermal Performance Testing: This assesses the energy efficiency of insulation and heating systems.
- Water Infiltration Testing: This ensures that the modular units are sealed correctly and can withstand environmental factors.
Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed reports on testing methods used and the results of any tests conducted.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing modular solutions internationally. Here are some effective strategies:
Conducting Audits
Buyers can perform audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This may involve visiting the production facility and reviewing documentation related to quality management systems.
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports that outline their QC processes, inspection results, and any certifications held. These documents can offer insights into the reliability and trustworthiness of the supplier.
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges in quality control. Key considerations include:
- Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers must be aware of local building codes and regulations that may differ from international standards. Suppliers should demonstrate familiarity with these regulations.
- Navigating Language Barriers: Communication can be challenging when dealing with suppliers in different countries. Clear documentation and regular updates can help mitigate misunderstandings.
- Logistical Challenges: Transportation and shipping can introduce risks to quality. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling processes in place to minimize damage during transit.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure high-quality modular solutions that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of modular’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement of modular construction solutions, this guide outlines essential steps for sourcing various types of modular systems. Understanding the nuances of modular construction can significantly impact project efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall success.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Begin by clearly outlining the specific needs of your project. Consider factors such as the intended use of the modular structure, location, budget, and timeline. This foundational step will guide your decision-making and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
- Types of Modular: Identify whether you need portable offices, prefabricated buildings, or specialized structures like lab workbenches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure your requirements adhere to local building codes and regulations.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the current market landscape for modular construction. This includes understanding trends, technologies, and materials used in modular systems.
- Supplier Landscape: Compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in the types of modular you require.
- Competitive Analysis: Assess competitors’ projects to identify successful strategies and innovations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.

Illustrative image related to types of modular
- Track Record: Look for suppliers with a proven history of delivering quality modular solutions on time.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from previous clients to gauge satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed proposals outlining their offerings. This should include pricing, timelines, and material specifications.
- Customization Options: Inquire about the flexibility of designs and materials to meet your specific project needs.
- Cost Breakdown: Ensure the proposal provides a clear breakdown of costs to avoid hidden charges later.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications and licenses to operate in your region. This step is vital for compliance and quality assurance.
- Quality Standards: Look for certifications such as ISO or other industry-specific standards that demonstrate a commitment to quality.
- Safety Compliance: Confirm that suppliers adhere to safety regulations to mitigate risks during construction.
Step 6: Assess Logistics and Delivery Capabilities
Understanding the logistics involved in delivering modular units is crucial for ensuring timely project completion. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to meet your delivery requirements.
- Transportation: Consider how the modular units will be transported to your site and any associated costs.
- On-Site Assembly: Confirm if the supplier provides on-site assembly services and what that entails.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
After selecting a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms that protect your interests. This includes payment schedules, warranties, and after-sales support.
- Clarity in Agreements: Ensure that all terms are clearly documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings.
- Post-Project Support: Discuss ongoing support for maintenance or any potential issues post-delivery.
Following this structured approach will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when procuring modular construction solutions, ultimately leading to successful project execution and enhanced operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of modular Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Modular Sourcing?
When analyzing the costs associated with modular construction, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. For instance, wood modules tend to be less expensive than steel alternatives. However, the type of finish and treatment (e.g., fire-resistant coatings) can add to costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on location and the complexity of the assembly. Skilled labor is often required for specialized tasks such as installation and finishing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs of running a production facility, including utilities, salaries of support staff, and maintenance of equipment. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is critical, especially for customized modular solutions. Depending on the specifications, tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for unique designs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that modular components meet industry standards and buyer specifications requires a dedicated QC process, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the distance from the manufacturing facility to the construction site. Additionally, the complexity of the modular units can influence logistics expenses, especially if special handling is required.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will incorporate a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
What Influences Pricing in Modular Construction?
Several factors can significantly affect the pricing of modular construction solutions, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) and the volume of the order can lead to discounts. Higher volumes typically result in lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs often come with increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Choices: The selection of materials not only impacts costs but also the durability and maintenance needs of the final structure. Sustainable materials may have a higher initial cost but can offer long-term savings.
-
Quality and Certifications: Materials that meet specific quality standards or certifications may carry a premium. However, these certifications can be essential for compliance and safety in certain markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms defined by Incoterms can help buyers manage costs effectively. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight) will determine who bears the shipping costs and risks.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Modular Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance negotiation leverage. Understanding market trends and being prepared to discuss pricing openly can lead to better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy efficiency, and durability. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of additional costs like tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations. These factors can significantly affect overall project budgets.
-
Research Local Regulations: Understanding local building codes and regulations can prevent costly redesigns or compliance issues later in the project.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Comparing quotes from various suppliers can provide insights into market rates and help identify the best value.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, location, and specific project requirements. It is recommended to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of modular With Other Solutions
In the evolving landscape of construction and infrastructure development, B2B buyers are often confronted with various building solutions. Understanding the alternatives to ‘types of modular’ construction can empower decision-makers to choose the most suitable option based on their specific requirements, budget constraints, and project timelines. This analysis compares modular construction with two prominent alternatives: traditional site-built construction and prefabricated building systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Modular | Traditional Site-Built Construction | Prefabricated Building Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High quality and durability; rapid assembly | Variable quality; longer timelines | Consistent quality; quick assembly |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reduced labor and waste | Higher due to labor intensity and time | Competitive but varies based on customization |
| Ease of Implementation | Streamlined; less site disruption | Complex; reliant on multiple contractors | Moderate; requires logistics planning |
| Maintenance | Low; factory-finished components | Variable; depends on materials used | Low; manufactured for durability |
| Best Use Case | Residential, commercial, and temporary structures | Large, complex projects; custom designs | Quick deployment for various sectors |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional Site-Built Construction?
Traditional site-built construction is the conventional method of erecting structures directly on the construction site. While it allows for complete customization and flexibility, it often involves longer timelines due to weather delays, labor availability, and site-specific challenges. The performance quality can vary significantly based on the skills of the labor force, leading to potential discrepancies in quality. Additionally, this method tends to be more expensive due to higher labor costs and the need for extensive project management.
How Do Prefabricated Building Systems Compare to Types of Modular?
Prefabricated building systems involve the manufacturing of building components in a factory, which are then assembled on-site. This method offers faster construction times and consistent quality, similar to modular construction. However, prefabricated systems may require careful logistical planning to transport components to the site. They can be cost-competitive, but the final price often depends on the level of customization desired. Prefabricated systems are especially advantageous for projects requiring rapid deployment, such as emergency housing or temporary facilities.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
Making the Right Choice for Your Construction Needs
Choosing between types of modular construction, traditional site-built methods, and prefabricated systems ultimately depends on various factors, including project size, budget, timeline, and intended use. B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, such as the desired speed of deployment, quality assurance, and maintenance considerations. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, decision-makers can make informed choices that align with their strategic objectives, ensuring successful project outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of modular
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Modular Construction?
When considering modular construction, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential properties to keep in mind:
-
Material Grade: The material grade refers to the quality and specifications of the materials used in modular construction, such as wood, steel, or concrete. Higher grades typically indicate better strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. For buyers, selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring the longevity and safety of the structure.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance in modular construction pertains to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. It is critical for ensuring that prefabricated components fit together correctly during assembly. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to structural issues and increased costs due to rework. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels helps in evaluating the quality and precision of manufacturing processes.
-
Fire Resistance Rating: This rating indicates how well a material can withstand fire exposure. Different building codes require specific fire resistance ratings based on the type of occupancy and building height. For international buyers, especially in regions prone to wildfires or with stringent safety regulations, this property is essential for compliance and safety assurance.
-
Energy Efficiency Rating: This specification measures how well a building conserves energy, typically through insulation and HVAC systems. High energy efficiency ratings not only reduce operational costs but also enhance the building’s sustainability profile. Buyers looking for eco-friendly solutions will find this property increasingly important in their purchasing decisions.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity: This refers to the maximum load a modular unit can support without failure. It is crucial for determining the suitability of a modular structure for various applications, from residential to commercial. Buyers must evaluate load-bearing capacities to ensure that the modular buildings will meet their specific operational needs.
-
Dimensional Stability: This property indicates how well a material maintains its shape and size under varying environmental conditions. Materials with high dimensional stability reduce the risk of warping or distortion, ensuring the integrity of the modular units over time. For B2B buyers, this is particularly important when selecting materials for projects in areas with extreme weather variations.
What Are Common Trade Terminology Terms in Modular Construction?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the modular construction sector. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In modular construction, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. It is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers need to assess their project needs against the MOQ to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing information from suppliers. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for international B2B transactions, as they clarify risks and costs associated with the delivery of modular units.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. In modular construction, lead times can significantly impact project timelines. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning their construction schedules to avoid delays.
-
Value Engineering: This concept involves analyzing the functions of materials and components to improve quality while reducing costs. For B2B buyers, value engineering can lead to significant savings without compromising the structural integrity of modular buildings.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the modular construction landscape more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their project goals.
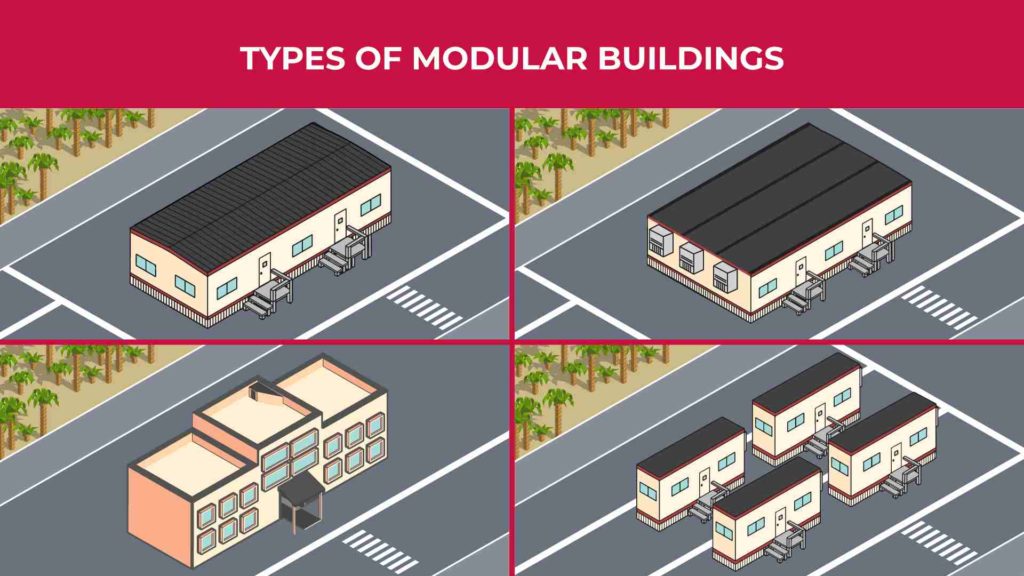
Illustrative image related to types of modular
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of modular Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing Modular Construction?
The global modular construction market is witnessing robust growth driven by several factors, particularly among B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for cost-effective and time-efficient construction solutions. Modular construction significantly reduces project timelines by allowing simultaneous site preparation and module fabrication, which is particularly appealing in fast-paced markets.
Emerging technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and advanced prefabrication techniques, are transforming the modular construction landscape. These technologies enhance collaboration among stakeholders, improve accuracy in project execution, and facilitate better resource management. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing materials and managing supply chains is streamlining procurement processes, making it easier for international buyers to connect with manufacturers.
Market dynamics are also shifting due to urbanization and a growing need for affordable housing solutions. In regions like Brazil and Nigeria, where rapid population growth is straining existing infrastructure, modular construction provides a scalable solution. Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency is driving the adoption of eco-friendly modular designs, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to types of modular
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Modular Construction Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the modular construction industry, with an increasing emphasis on reducing environmental impact. B2B buyers are now prioritizing materials and practices that minimize carbon footprints. This shift is evident in the growing use of sustainable materials like recycled steel, bamboo, and engineered wood, which not only provide structural integrity but also contribute to greener construction practices.
Ethical sourcing has gained traction as companies strive to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible. Buyers are now scrutinizing their suppliers to confirm adherence to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) are becoming crucial in the decision-making process, enabling buyers to identify suppliers committed to sustainability.
Moreover, innovative solutions such as modular buildings designed for disassembly and reuse are emerging, allowing for greater lifecycle management of materials. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates opportunities for cost savings over the long term, making it a compelling proposition for B2B buyers seeking to balance profitability with sustainability.
What is the Historical Context of Modular Construction and Its Relevance Today?
Modular construction has roots that date back to the 19th century, initially gaining traction during the post-war rebuilding efforts. The method evolved through the decades, often associated with temporary structures and affordable housing solutions. In recent years, however, modular construction has experienced a renaissance, driven by technological advancements and a renewed focus on efficiency.
Illustrative image related to types of modular
The evolution of modular construction is significant for B2B buyers as it reflects a shift from traditional building practices towards innovative, sustainable approaches. The ability to produce high-quality, durable structures in a factory setting has expanded the potential applications of modular construction beyond simple housing projects to commercial buildings, healthcare facilities, and even educational institutions.
This historical context underscores the adaptability and resilience of modular construction in meeting contemporary demands, making it a relevant choice for international buyers looking for reliable and innovative construction solutions. As the industry continues to evolve, understanding this history provides valuable insights into future trends and opportunities in the modular sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of modular
-
How do I select the right type of modular construction for my project?
Choosing the right type of modular construction depends on various factors, including project scope, budget, and location. For instance, wooden modular assemblies are ideal for residential projects, while light gauge steel is suited for commercial buildings due to its durability and fire resistance. Assess your project’s specific requirements, including environmental conditions and local building codes, to determine the most suitable option. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights into their product offerings and assist in customizing solutions that meet your needs. -
What are the advantages of modular construction compared to traditional building methods?
Modular construction offers numerous advantages, including reduced construction time, cost savings, and minimal site disruption. As components are prefabricated in a controlled environment, the risk of delays due to weather is significantly lowered. Additionally, modular buildings can be more sustainable, utilizing fewer materials and generating less waste. This approach also allows for greater design flexibility and quicker occupancy, making it an appealing option for businesses seeking rapid deployment. -
What customization options are available for modular buildings?
Customization options for modular buildings are extensive and can include changes in design, layout, materials, and finishes. Many manufacturers offer a range of modular designs that can be tailored to specific client needs, such as office configurations, residential layouts, or specialized facilities. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore their capabilities in customization, ensuring they can deliver a product that aligns with your vision and functional needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for modular units?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for modular units can vary widely among manufacturers. Some may allow single-unit orders, particularly for portable offices or temporary structures, while others might require larger quantities for cost-effective production. It’s essential to communicate with suppliers about your project size and budget to understand their MOQ policies. This discussion will help you determine the feasibility of your project and identify the best suppliers who can accommodate your needs. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by modular construction suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly between modular construction suppliers. Common arrangements include deposits before manufacturing, progress payments during construction, and final payments upon delivery or installation. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timeline. Additionally, inquire about any financing options or discounts for bulk orders, which may help in managing your overall project budget effectively. -
How can I vet suppliers for modular construction projects?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their experience, reputation, and product quality. Start by reviewing their portfolio to see past projects and client testimonials. It’s also beneficial to check for industry certifications and compliance with local building codes. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness. Consider requesting references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and performance on similar projects. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from modular suppliers?
Quality assurance measures from modular suppliers should include rigorous testing of materials, adherence to construction standards, and regular inspections throughout the manufacturing process. Reputable suppliers often have certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality, such as ISO standards. Request information about their quality control processes and any guarantees they provide regarding the durability and safety of their products. Ensuring these measures are in place will help mitigate risks associated with modular construction. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing modular units internationally?
When sourcing modular units internationally, consider logistics such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier has experience in international shipping and can provide detailed timelines for delivery. It’s also essential to account for local regulations that may affect the importation of modular units. Collaborate with logistics experts to navigate these complexities, ensuring a smooth delivery process and compliance with all legal requirements in your destination country.
Top 7 Types Of Modular Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SELO Group – Modular Construction Solutions
Domain: selogroup.co
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: The text discusses three main types of modular construction: 2D panels, 3D modules, and hybrid modular construction.
1. **2D Panels**:
– Flexible design and simple logistics.
– Assembled onsite, can be unfinished or finished, and may include conduits for utilities.
– More cost-effective and easier to transport than 3D modules.
– Ideal for open-concept spaces in high-end residence…
2. IQS Directory – Modular Buildings
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
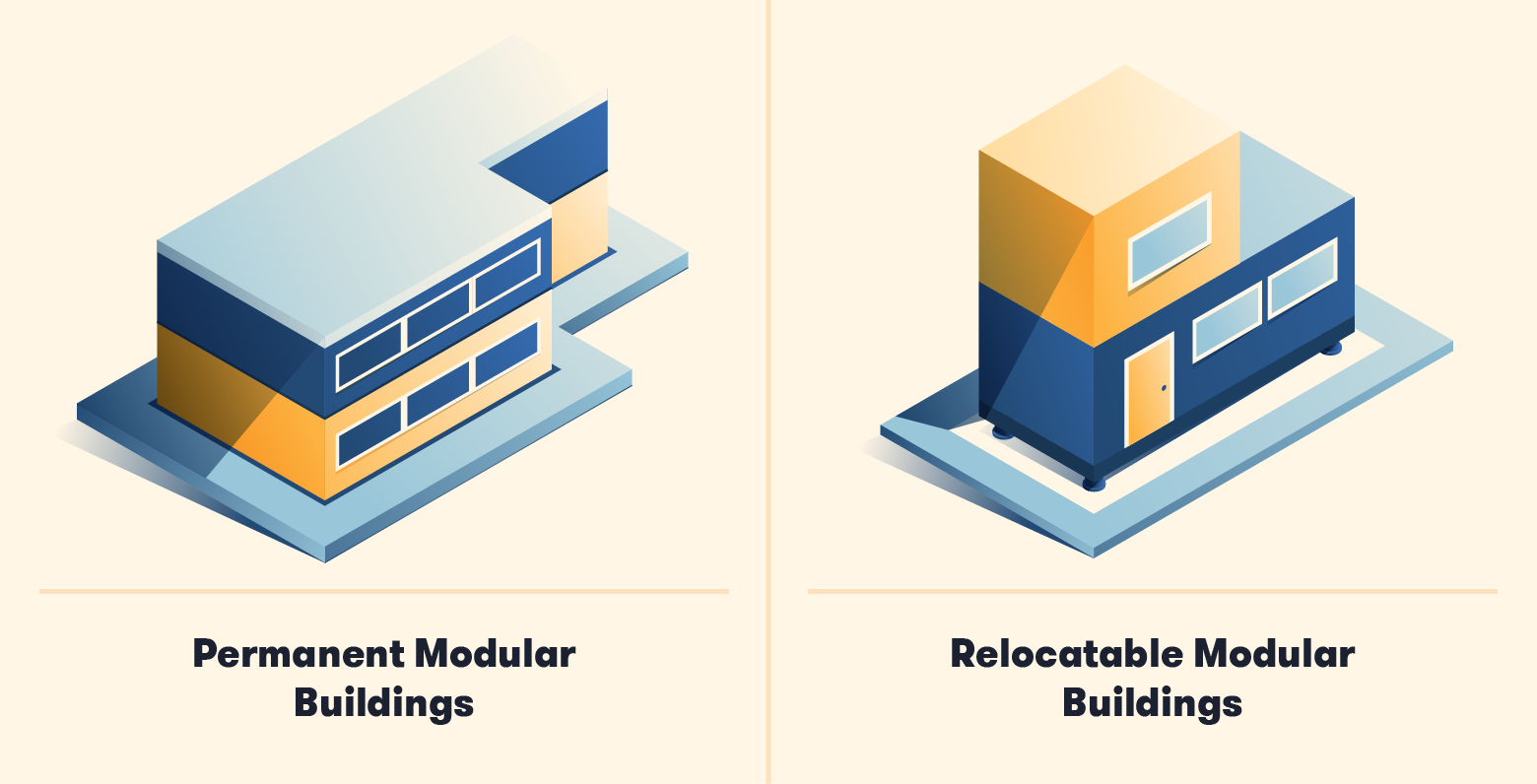
Introduction: Modular buildings are constructed from standardized parts called “modules” produced in a factory. They adhere to building codes and can be permanent or relocatable. Types include Permanent Modular Construction (PMC) for long-term use and Temporary Modular Construction (TMC) for short-term use. PMC buildings are durable, built on concrete foundations, and customizable for various applications like …
3. Modular Homes – Customizable Living Solutions
Domain: modularhomes.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Modular Homes – Customizable Living Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. S3DA Design – Modular Solutions
Domain: s3da-design.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Modular design involves creating individual modules that are built separately to form a complete unit, offering infinite design possibilities. It is used in various applications including building construction (offices, schools, homes), manufacturing (cars, phones, toys), and digital products (websites, ads). Benefits include cost-effectiveness, time-saving, customization, and sustainability throu…
5. iModular – Modular Buildings for Rent or Purchase
Domain: imodular.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Modular buildings are available for rent or purchase in various types, sizes, and configurations, suitable for temporary or permanent use in schools, businesses, healthcare, and more. Common uses include educational facilities, construction site offices, healthcare facilities, office spaces, retail outlets, government and military use, childcare centers, religious and community centers, event faci…
6. Boxx Modular – Prefabricated Building Solutions
Domain: boxxmodular.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Modular buildings are constructed off-site in a factory using assembly line techniques to prefabricate individual sections (modules). They can range from a few hundred to tens of thousands of square feet and are built with standard materials used in traditional construction. Modular construction is suitable for organizations needing additional space, replacing old buildings, or requiring temporary…
7. Futura Modular – Types of Modular Construction
Domain: futuramodular.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Types of Modular Construction include: 1. Volumetric Modular Construction: Entire room modules manufactured in a factory and transported for assembly. 2. Panelized Modular Construction: Walls, floor, and roof panels built in a factory and assembled on-site. 3. Hybrid Modular Construction: A combination of volumetric and panelized methods. 4. Relocatable Buildings: Prefabricated structures designed…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of modular
In summary, the landscape of modular construction presents a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the distinct types of modular buildings—wood, light gauge steel, and red iron steel—enables buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific project needs. Each type offers unique advantages, from the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of wood to the durability and safety of steel structures.
Strategic sourcing remains crucial in navigating this complex market. By establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, buyers can ensure access to high-quality materials that align with their budget and project timelines. As the demand for modular construction continues to rise, especially in developing regions, proactive engagement with suppliers will be essential for staying competitive.
Looking ahead, international buyers should explore innovative sourcing strategies to capitalize on the benefits of modular construction. Embracing this approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions businesses to meet the growing demand for sustainable and adaptable building solutions. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure your place in the future of construction.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.