Types Of Centrifuge: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of centrifuge
In the dynamic landscape of laboratory equipment, sourcing the right types of centrifuge can be a pivotal challenge for B2B buyers. With a multitude of options available, each designed for specific applications—ranging from benchtop and high-speed centrifuges to specialized models for blood analysis—making an informed decision is crucial. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the various types of centrifuges, their operational principles, and their applications across different industries.
Additionally, we delve into key considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including markets like Vietnam and Germany) can navigate the complexities of sourcing with confidence. By addressing critical factors such as pricing, quality assurance, and the latest technological advancements, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding the nuances of centrifuge types and their respective applications not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures compliance with industry standards. Equip yourself with the insights necessary to choose the right centrifuge for your laboratory, ultimately contributing to your organization’s success in a competitive global market.
Understanding types of centrifuge Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchtop Centrifuge | Compact, electric motor-driven, versatile rotor options | Clinical labs, research facilities | Pros: Space-efficient, user-friendly; Cons: Limited capacity for large samples. |
| Continuous Flow Centrifuge | High throughput, continuous operation, designed for large volumes | Industrial applications, bioprocessing | Pros: Saves time, handles large volumes; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| High-Speed Centrifuge | Operates at 15,000-30,000 RPM, precise speed control | Biochemical research, pharmaceutical labs | Pros: Fast separation, accommodates various sample sizes; Cons: More complex and costly. |
| Microcentrifuge | Designed for small volumes (0.5-2 ml), high-speed operation | Molecular biology, genetic research | Pros: Ideal for small samples, compact; Cons: Limited to smaller volumes. |
| Refrigerated Centrifuge | Temperature control (-20°C to -30°C), suitable for sensitive samples | Clinical diagnostics, biochemistry | Pros: Maintains sample integrity; Cons: Requires more maintenance. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Benchtop Centrifuges?
Benchtop centrifuges are compact units commonly found in clinical and research laboratories. They operate on an electric motor, providing a reliable and consistent means of separating components based on density. Their versatility in rotor design allows for a range of applications, from blood sample analysis to cell culture. Buyers should consider the limited capacity of benchtop centrifuges, which may not be ideal for larger batch processing.
How Do Continuous Flow Centrifuges Enhance Operational Efficiency?
Continuous flow centrifuges are engineered for high-volume processing, enabling the separation of large sample volumes without the need for frequent loading and unloading. This design significantly reduces processing time, making it ideal for industrial applications and bioprocessing. However, the initial investment is higher compared to traditional centrifuges, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Choose a High-Speed Centrifuge for Advanced Applications?
High-speed centrifuges can achieve speeds of 15,000 to 30,000 RPM, making them suitable for sophisticated laboratory applications, including biochemical and pharmaceutical research. The precision in speed control allows for optimal separation of sensitive biological molecules. While they offer high efficiency, the complexity and cost may deter smaller laboratories from investing in this technology.
What Advantages Do Microcentrifuges Offer for Molecular Research?
Microcentrifuges are specialized for handling small sample volumes, typically ranging from 0.5 to 2 ml. They are ideal for molecular biology applications, such as DNA extraction and protein purification, where precision is critical. Their compact design is advantageous for laboratories with limited space. However, potential buyers should note that microcentrifuges are limited to small sample sizes, which may not meet the needs of all applications.
How Do Refrigerated Centrifuges Support Sensitive Sample Handling?
Refrigerated centrifuges provide temperature control, crucial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive samples during centrifugation. Operating at temperatures between -20°C and -30°C, these centrifuges are essential in clinical diagnostics and biochemical applications where sample degradation is a concern. While they ensure optimal results, the need for regular maintenance and the higher operational costs may be factors for buyers to consider.
Key Industrial Applications of types of centrifuge
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of centrifuge | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug formulation and purification | Enhanced purity and yield of active pharmaceutical ingredients | Compliance with regulatory standards; energy efficiency |
| Food and Beverage | Separation of fats and oils from food products | Improved product quality and shelf life | Food-grade materials; ease of cleaning and maintenance |
| Biotechnology and Research | Isolation of biomolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins) | Critical for research accuracy and reproducibility | High-speed capabilities; temperature control features |
| Wastewater Treatment | Sludge separation and dewatering | Reduced disposal costs and improved treatment efficiency | Durability; capacity for large volumes; energy consumption |
| Oil and Gas | Separation of drilling fluids and solids | Enhanced recovery rates and operational efficiency | Material compatibility; rugged design for harsh environments |
How Are Centrifuges Utilized in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
In the pharmaceutical industry, centrifuges play a vital role in drug formulation and purification processes. High-speed and refrigerated centrifuges are employed to isolate active pharmaceutical ingredients from crude extracts, ensuring high purity levels essential for compliance with stringent regulatory standards. For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing centrifuges that meet local regulations while also being energy-efficient can significantly reduce operational costs and improve product quality.
What Role Do Centrifuges Play in Food and Beverage Production?
Centrifuges are extensively used in the food and beverage industry for the separation of fats and oils from various products. This process enhances the quality and shelf life of food items, making them more appealing to consumers. Buyers should consider centrifuges constructed from food-grade materials that facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance, particularly important in regions with diverse food safety regulations, such as Europe and the Middle East.
How Are Centrifuges Applied in Biotechnology and Research?
In biotechnology and research laboratories, centrifuges are essential for isolating biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. High-speed centrifuges enable researchers to achieve precise results that are crucial for experiments and clinical trials. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe, it’s important to prioritize centrifuges that offer temperature control features to preserve the integrity of sensitive samples, ensuring reproducibility and accuracy in research outcomes.
What Benefits Do Centrifuges Provide in Wastewater Treatment?
Centrifuges are employed in wastewater treatment facilities for effective sludge separation and dewatering. This application not only reduces disposal costs but also enhances overall treatment efficiency. Buyers from regions with growing urban populations, such as Africa and the Middle East, should focus on sourcing durable centrifuges capable of handling large volumes while maintaining low energy consumption to meet increasing demand for sustainable wastewater management solutions.
How Do Centrifuges Enhance Operations in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, centrifuges are crucial for separating drilling fluids from solids, which enhances recovery rates and operational efficiency. The rugged design of these centrifuges is essential to withstand harsh environments, making them ideal for offshore and remote operations. International buyers should prioritize material compatibility to ensure longevity and reliability, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions, such as South America and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of centrifuge’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Selecting the Right Centrifuge Type for Specific Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate type of centrifuge that meets the specific requirements of their laboratory or production environment. With various types available, such as benchtop, high-speed, and continuous flow centrifuges, it can be overwhelming to determine which model will deliver optimal performance for particular tasks. This confusion may lead to purchasing equipment that is either underperforming or overly complex for their needs, resulting in wasted resources and inefficient workflows.
The Solution:
To effectively choose the right centrifuge, buyers should start by clearly defining their specific applications. They need to assess factors such as sample volume, desired separation speed, and the type of materials being processed. For instance, if the goal is to separate large volumes of liquid without frequent loading and unloading, a continuous flow centrifuge might be the best choice. Consulting with manufacturers or distributors who specialize in centrifuge technology can provide valuable insights. Additionally, requesting demonstrations or trials can help buyers evaluate the equipment in real-world scenarios before making a significant investment.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Equipment Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem:
Maintaining centrifuge equipment can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where uptime is crucial. Issues like rotor wear and tear, imbalance, or unexpected breakdowns can lead to costly downtime, affecting productivity and project timelines. Buyers may not have the in-house expertise to perform regular maintenance, leading to increased reliance on external service providers, which can further exacerbate operational delays.
The Solution:
To mitigate maintenance challenges, buyers should prioritize purchasing centrifuges that come with comprehensive service agreements and support packages. Choosing equipment from reputable manufacturers that offer training on routine maintenance can empower laboratory staff to handle minor issues internally, reducing downtime. Implementing a preventative maintenance schedule, including regular inspections and rotor checks, can also help identify potential problems before they escalate. Investing in centrifuges equipped with advanced diagnostic features can provide real-time monitoring, alerting operators to any anomalies that could lead to failures.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Scenario 3: Compliance with Regulatory Standards and Quality Assurance
The Problem:
In many industries, particularly pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, adhering to regulatory standards is essential. Buyers may face difficulties ensuring that their centrifuge operations meet stringent quality assurance protocols. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, product recalls, or compromised research results, placing immense pressure on procurement teams to select equipment that meets these rigorous standards.
The Solution:
To ensure compliance, buyers should conduct thorough research on the regulatory requirements specific to their industry and region. They should look for centrifuges that are certified or validated for use in regulated environments, such as those meeting ISO or FDA standards. It’s also crucial to work closely with suppliers who understand these regulations and can provide documentation proving compliance. Establishing a quality management system that includes regular audits and documentation of centrifuge performance can help maintain compliance and enhance overall quality assurance practices. Engaging with third-party consultants for guidance on best practices can further solidify compliance efforts and protect the organization’s interests.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of centrifuge
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Centrifuge Manufacturing?
When selecting a centrifuge, the choice of materials can significantly impact performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of centrifuges: stainless steel, aluminum, plastic, and glass. Each material has unique properties that can influence the centrifuge’s application and effectiveness.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Centrifuge Applications?
Stainless steel is widely regarded for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for centrifuge components that must withstand high pressures and temperatures. Its ability to resist oxidation and staining ensures longevity, especially in harsh laboratory environments.
Pros: Stainless steel offers high durability and is suitable for a wide range of applications, including those involving aggressive chemicals. Its robust nature allows for high-speed operations without compromising structural integrity.
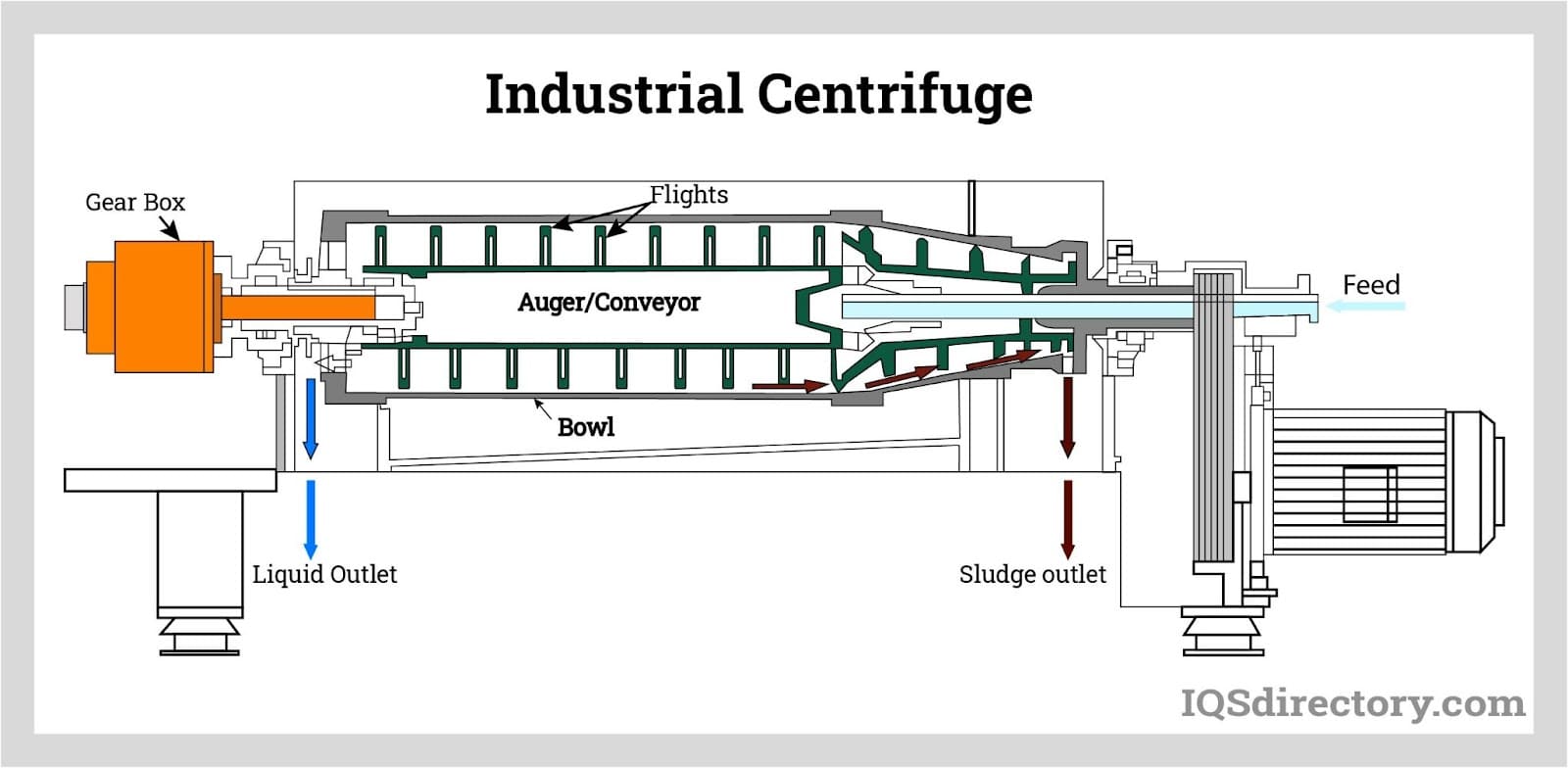
Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to other materials, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including biological samples and corrosive chemicals, making it versatile for laboratory use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for stainless steel grades, which can vary significantly.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Centrifuge Components?
Aluminum is another popular material, particularly for rotors and other components that require lightweight yet strong construction. Its excellent thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial in high-speed centrifugation.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, making it easier to handle and reducing wear on the centrifuge’s motor. It also has a lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it an attractive option for many laboratories.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it may not withstand highly acidic or alkaline environments as effectively as stainless steel. Additionally, it may have a shorter lifespan under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications involving non-corrosive media, but users must be cautious with aggressive solvents or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet relevant international standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory environments, such as Germany.
How Do Plastics Fit into Centrifuge Design?
Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, are increasingly used in centrifuge manufacturing due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are often used in lower-speed centrifuges or for specific components like tubes and rotors.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They also resist a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for various applications.
Cons: Plastics may not withstand high temperatures or pressures as effectively as metals, which can limit their use in high-performance centrifuges. Additionally, they can be less durable over time compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are ideal for applications involving biological samples where contamination risk must be minimized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with health and safety regulations, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where standards may vary.
What Role Does Glass Play in Centrifuge Applications?
Glass is traditionally used for centrifuge tubes and vials due to its chemical resistance and inertness. It is particularly favored in applications requiring high purity and minimal contamination risk.
Pros: Glass provides excellent clarity for visual inspection and is chemically inert, making it suitable for a wide range of substances.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Cons: The fragility of glass can be a significant drawback, as it is prone to breakage during handling or operation. Additionally, glass components can be heavier, affecting the centrifuge’s overall performance.
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for applications involving sensitive biological samples or when visual monitoring is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the shipping and handling requirements for glass components, especially in regions with less reliable transport infrastructure.
Summary of Material Selection for Centrifuge Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of centrifuge | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-speed and high-pressure applications | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight rotors and components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited chemical resistance | Medium |
| Plastic | Tubes and low-speed centrifuges | Cost-effective and flexible design | Limited temperature and pressure resistance | Low |
| Glass | Tubes for sensitive biological samples | Chemically inert and high clarity | Fragility and weight | Medium |
This guide provides crucial insights for international B2B buyers in selecting the appropriate materials for centrifuge applications, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of centrifuge
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Centrifuges?
The manufacturing process of centrifuges is a complex and multi-stage operation, which requires precision engineering and adherence to international standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Centrifuge Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. Commonly used materials include high-grade stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and specialized plastics that can withstand high rotational forces and corrosive environments.
Material preparation includes sourcing raw materials from certified suppliers, verifying their quality through inspection, and preparing them for subsequent processing. This step may involve cutting, machining, or treating materials to ensure they meet specific performance criteria, such as strength and resistance to fatigue.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Centrifuge Production?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes that shape them into the required components of the centrifuge. Techniques such as CNC machining, stamping, and injection molding are commonly employed.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
CNC machining is particularly critical for creating rotors and housing components with high precision. This ensures that the dimensions are exact and that the rotor can achieve the desired rotational speeds without failure. For plastic parts, injection molding is often used, allowing for complex shapes and high-volume production.
How Are Centrifuges Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form a complete centrifuge. This stage involves several sub-processes, including the installation of rotors, motors, and electronic control systems.
Quality control during assembly is crucial; components must fit correctly, and operational testing must be performed to ensure that all parts function together harmoniously. Assembly may involve both manual labor and automated systems to enhance efficiency and precision.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Centrifuge Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and aesthetics of the centrifuge. These may include surface treatments like anodizing, powder coating, or passivation, which improve corrosion resistance and durability.
Additionally, finishing processes may involve cleaning the assembled units to remove any contaminants that could affect performance or safety. After finishing, centrifuges are typically subjected to rigorous testing to confirm that they meet performance specifications before they are packaged for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Centrifuge Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral aspect of centrifuge manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both internal standards and external regulatory requirements.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Centrifuge Quality Control?
B2B buyers should be familiar with key international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system, and ISO 13485, specific to medical devices. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality and safety in their processes.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications may also apply. These certifications demonstrate compliance with relevant safety and efficacy standards, which can be crucial for B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Centrifuge Manufacturing?
Quality control in centrifuge manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to catch any deviations from quality standards early. This can include real-time monitoring of machining processes or assembly line inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, a thorough inspection is conducted to verify that the final product meets all operational and safety specifications. This may include performance testing, safety checks, and compliance verification.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing environment, processes, and adherence to quality standards. Audits can reveal insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including test results and compliance certificates, can provide assurance that products meet necessary standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an additional layer of verification, providing unbiased assessments of the manufacturer’s quality control processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in ensuring quality.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Understanding regional regulations and standards is crucial; for example, products exported to Europe must comply with CE marking requirements. Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication about quality standards and expectations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide documentation in a language they understand and that all communications are clear and precise.
Additionally, logistics and transportation can impact product quality. It’s vital to discuss packaging and shipping methods with suppliers to prevent damage during transit. B2B buyers should also consider the supplier’s ability to provide after-sales support and service, as this is essential for maintaining quality over the product lifecycle.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for centrifuges are intricate and critical for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality centrifuges that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of centrifuge’
Introduction
When sourcing centrifuges for your business, it’s essential to approach the process methodically to ensure you select the right equipment for your specific needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of centrifuge procurement, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical specifications. Determine the type of centrifuge required based on your application, such as benchtop, high-speed, or refrigerated models. Understand the necessary features, such as rotor types, capacity, and temperature control, to ensure compatibility with your laboratory processes.
- Application Needs: Identify whether you need the centrifuge for biological, chemical, or industrial applications.
- Volume and Sample Size: Consider the volumes you will be processing regularly to select a centrifuge that can handle your workload efficiently.
Step 2: Assess Budget Constraints
Establish a budget that encompasses not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational costs. This includes maintenance, consumables, and potential upgrades. A well-planned budget helps avoid overspending and ensures you can sustain the equipment in the long run.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Calculate all associated costs over the equipment’s lifespan.
- Return on Investment: Consider how the centrifuge will impact productivity and efficiency to justify the investment.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, detailed product catalogs, and customer references to gauge their reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers that specialize in the type of centrifuge you require, as they will be more familiar with your specific needs.
- Check Certifications: Verify any industry certifications that indicate quality standards, such as ISO or CE markings.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Seek feedback from other clients, especially those in similar sectors or geographic regions.
Step 4: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, request a demonstration or a trial period for the centrifuge. This hands-on experience allows you to assess its performance and compatibility with your existing processes. Pay attention to user interface, ease of operation, and any specific features that may be critical for your applications.
- Test for Usability: Ensure that your laboratory staff can operate the centrifuge effectively.
- Assess Performance Metrics: Evaluate speed, efficiency, and reliability during the demonstration.
Step 5: Inquire About Warranty and Support
Understand the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A robust warranty can safeguard your investment against defects and unexpected failures. Additionally, confirm the availability of technical support, spare parts, and service agreements.
- Duration and Coverage: Check how long the warranty lasts and what it covers.
- Response Times: Ensure that the supplier can provide timely support in case of equipment issues.
Step 6: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Options
Discuss logistics with your chosen supplier, including delivery timelines, installation services, and training for your staff. Effective logistics planning ensures that the centrifuge arrives on schedule and is set up correctly, minimizing downtime.
- Installation Services: Determine whether the supplier provides installation and operational training.
- Shipping Costs: Clarify any additional shipping fees and customs duties, especially for international purchases.
Step 7: Plan for Maintenance and Compliance
Establish a maintenance schedule to ensure the longevity and proper functioning of your centrifuge. Regular maintenance not only prevents breakdowns but also ensures compliance with safety and operational standards.
- Routine Checks: Schedule regular inspections and maintenance based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Compliance Requirements: Be aware of any regulatory requirements in your region regarding centrifuge operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing centrifuges, ensuring they choose equipment that meets their specific needs and supports their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of centrifuge Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Centrifuge Manufacturing?
When analyzing the cost structure of centrifuge sourcing, several critical components come into play. The primary cost drivers include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality stainless steel, specialized plastics, and electronic components can increase expenses but ensure durability and performance. For instance, a benchtop centrifuge may use less expensive materials compared to a high-speed or refrigerated centrifuge, which require more advanced materials to withstand higher forces and temperatures.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for assembling high-precision instruments, which can drive up costs in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the facilities, utilities, and equipment used in production. Companies in countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities may have higher overhead costs due to investment in technology and automation.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specialized centrifuge designs, contributing to upfront costs. This is particularly relevant for manufacturers producing customized or high-specification models.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the centrifuge meets international standards requires rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with testing and certification can add significantly to the price, especially for models used in critical applications like medical laboratories.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on distance, shipping method, and the complexity of customs regulations in international trade. Buyers should account for these factors in their total cost calculations.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competition.
What Influences Pricing for Centrifuge Types?
Several factors influence the pricing of centrifuges, making it essential for buyers to understand these nuances.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to significant discounts. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing, especially when sourcing from manufacturers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as specialized rotors or temperature controls can elevate costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Centrifuges that meet specific quality certifications (ISO, CE marking) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total landed cost. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and customs duties is crucial for accurate budgeting.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Centrifuge Sourcing Costs?
To effectively manage centrifuge sourcing costs, international buyers should adopt several strategic approaches:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing structures, payment terms, and potential discounts for larger orders. Building a strong relationship can lead to better terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive solutions, including maintenance services and spare parts, which can reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with owning a centrifuge, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower initial purchase price may not equate to lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions that may impact pricing. Understanding these factors can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for centrifuges can vary widely based on specifications, supplier agreements, and market conditions. As such, the figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers for accurate quotations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to ensure the best sourcing decisions.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of centrifuge With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Centrifuges
In laboratory and industrial settings, centrifuges are widely used for separating components of mixtures based on their densities. However, various alternative technologies can achieve similar separation goals, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. This section evaluates types of centrifuges against alternative methods like membrane filtration and sedimentation, providing B2B buyers with insights into which solution best fits their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Centrifuge | Membrane Filtration | Sedimentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High separation efficiency; RCF varies by type | Moderate to high separation efficiency; depends on membrane type | Low separation efficiency; relies on gravity |
| Cost | Generally high initial investment; operational costs vary | Moderate initial cost; ongoing costs for membrane replacement | Low initial cost; minimal operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training; setup may be complex | Relatively easy to set up; can be integrated into existing systems | Simple setup; minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and maintenance; rotor wear | Regular membrane replacement needed; low maintenance otherwise | Minimal maintenance; periodic cleaning may be required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for precise molecular separations and large volumes | Best for continuous processing and filtration of fluids | Suitable for large-scale separations over extended periods |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration employs semi-permeable membranes to separate particles from liquids. It is particularly effective for processes requiring the filtration of bacteria, viruses, or larger particles from solutions. The primary advantages of membrane filtration include lower operational costs over time and the ability to integrate seamlessly into existing processing lines. However, the efficiency of separation can vary significantly based on the type of membrane used and the nature of the fluid being processed. Additionally, membranes require regular replacement, which can lead to increased long-term costs.
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is a traditional method of separation that relies on gravity to settle particles out of a liquid. It is a cost-effective solution, particularly for large-scale operations, as it requires minimal investment in equipment and infrastructure. While sedimentation is straightforward to implement and requires little maintenance, its efficiency is significantly lower than that of centrifuges and membrane filtration. This method is best suited for applications where high precision is not critical, and the separation of large particles is sufficient.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate separation technology depends on various factors, including specific application requirements, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. B2B buyers should evaluate their needs carefully, considering factors such as the desired efficiency of separation, available space for equipment, and the necessary skill level for operation and maintenance. By weighing these considerations against the strengths and weaknesses of centrifuges, membrane filtration, and sedimentation, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of centrifuge
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Centrifuges Important for B2B Buyers?
When selecting a centrifuge, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring it meets specific operational needs. Here are several critical properties to consider:
-
Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF): RCF is a measure of the acceleration exerted on the samples in the centrifuge, expressed in multiples of gravity (g). It is pivotal for comparing centrifuges and their performance. Higher RCF values indicate greater separation efficiency, making this a key factor for buyers aiming for optimal results in sample processing.
-
Rotor Speed (RPM): The speed at which the rotor spins, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), directly influences the separation efficiency and time. Different applications require specific RPMs for optimal performance. Understanding the RPM capabilities of a centrifuge helps buyers match the equipment to their operational requirements.
-
Capacity: This refers to the volume of samples that can be processed simultaneously, often measured in liters. Centrifuges with larger capacities can significantly increase throughput, reducing operational time and costs. Buyers must assess their volume needs to select a centrifuge that enhances productivity.
-
Temperature Control: Some centrifuges offer temperature control features, maintaining samples at specific temperatures during operation. This is crucial for sensitive biological materials that can degrade or alter under temperature fluctuations. Buyers in sectors such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology should prioritize this feature to ensure sample integrity.
-
Rotor Type Compatibility: Centrifuges can accommodate different rotor types—fixed angle, swinging bucket, and vertical rotors—each serving specific applications. Understanding rotor compatibility is essential for buyers to ensure they can conduct a range of experiments or processes effectively.
-
Material Grade: The materials used in the centrifuge construction (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel, or plastic) impact durability, maintenance needs, and chemical resistance. Buyers should consider the intended use and environment to choose a centrifuge made from appropriate materials, ensuring longevity and reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Centrifuge Purchases?
Navigating the procurement process for centrifuges involves understanding industry terminology. Here are several essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that manufacture products that may be marketed by another company. In centrifuge procurement, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can assure buyers of the quality and authenticity of the equipment.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in regions with diverse market demands, as it affects budgeting and inventory management.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request price quotes for specific products or services. For buyers looking to procure centrifuges, issuing an RFQ allows them to compare pricing, lead times, and terms from multiple vendors.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the time taken from placing an order until the product is delivered. For centrifuges, understanding lead times is essential for planning and ensuring that operational timelines are met.
-
Calibration and Validation: Calibration refers to the process of adjusting the centrifuge to ensure accurate performance, while validation is confirming that it meets required specifications. Both processes are critical for buyers in regulated industries, ensuring compliance and quality assurance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right centrifuge that meets their specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of centrifuge Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Types of Centrifuge Sector?
The centrifuge market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and clinical diagnostics. Global trends indicate a shift towards automation and digitalization, with advanced centrifuge models integrating IoT capabilities for remote monitoring and data analysis. This technological evolution is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where operational efficiency and real-time data access can significantly enhance productivity.
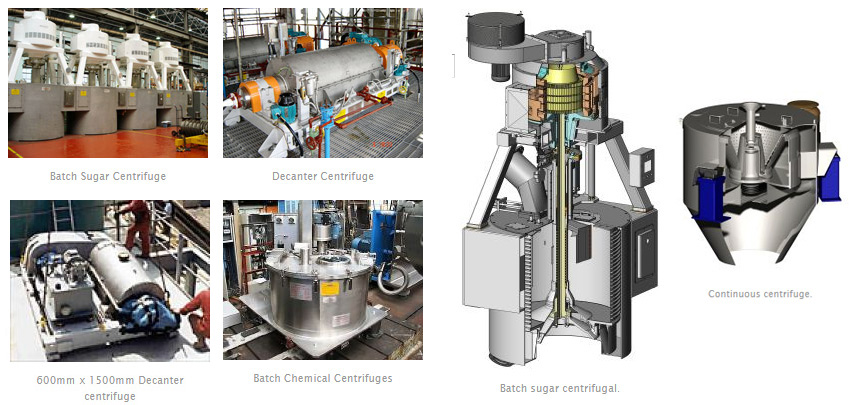
Illustrative image related to types of centrifuge
Emerging markets are increasingly adopting high-speed and continuous flow centrifuges to meet the needs of large-scale operations, reflecting a broader trend towards efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the rise of personalized medicine and biotechnology innovations is driving the demand for specialized centrifuge types, such as microcentrifuges and refrigerated centrifuges. Buyers in these markets should prioritize suppliers who not only offer cutting-edge technology but also provide comprehensive customer support and training to ensure optimal equipment utilization.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing Trends for Centrifuges?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the procurement of centrifuge equipment. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of centrifuge products are under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and can provide transparent supply chain information. The emphasis on ethical sourcing is pushing manufacturers to adopt ‘green’ certifications and materials, which can improve brand reputation and compliance with international regulations.
Buyers should look for centrifuge models that are designed with energy efficiency in mind, as these can significantly reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. Furthermore, suppliers that utilize recyclable materials or that can demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste in their production processes are becoming more attractive to conscientious buyers. By prioritizing sustainability, companies can align their procurement strategies with broader corporate social responsibility goals while enhancing their competitive edge in a growing market.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Centrifuge Technology?
The evolution of centrifuge technology dates back to the late 19th century when the first mechanical centrifuge was developed for the separation of cream from milk. Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have led to the diversification of centrifuge types, each tailored for specific applications ranging from laboratory research to industrial processes. The introduction of high-speed and ultra-centrifuges in the mid-20th century revolutionized the field, allowing for the separation of biomolecules and cells at unprecedented speeds.
Today, centrifuges are equipped with sophisticated features such as temperature control, automated processes, and digital interfaces, catering to the diverse needs of modern laboratories and industrial facilities. As industries continue to innovate and evolve, the centrifuge market is expected to adapt further, focusing on efficiency, precision, and sustainability—key factors that international B2B buyers must consider in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of centrifuge
-
How do I choose the right type of centrifuge for my laboratory needs?
Choosing the right centrifuge involves understanding the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the sample volume, type of materials, desired speed (RPM), and whether temperature control is necessary. For routine applications, a low-speed or benchtop centrifuge may suffice, while high-speed centrifuges are ideal for more complex biochemical separations. Additionally, assess the rotor types available and ensure compatibility with your sample tubes. Consulting with suppliers about your needs can further help narrow down your options. -
What is the best centrifuge for separating biological samples?
The best centrifuge for separating biological samples often depends on the specific type of sample and the desired outcome. For routine blood analysis, a hematocrit or low-speed centrifuge is commonly used. If working with sensitive biological molecules, a high-speed or refrigerated centrifuge might be necessary. Consider also the need for rotor adaptability and temperature control to maintain sample integrity during the separation process. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in biological applications can provide valuable insights for selecting the right model. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for centrifuges when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for centrifuges can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Generally, manufacturers may set MOQs based on production costs, shipping logistics, and demand forecasts. In the B2B space, MOQs can range from a single unit for specialized models to several dozen for standard units. To optimize procurement, engage directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs. Be sure to clarify any additional costs associated with lower MOQs, such as shipping or customization fees. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing centrifuges internationally?
When sourcing centrifuges internationally, payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common terms include advance payments, net 30-90 days, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide you with financial flexibility while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in the transaction. Always review the terms in the context of international trade regulations and currency exchange rates to avoid unforeseen costs. -
How can I ensure the quality and reliability of centrifuges from suppliers?
Ensuring quality and reliability starts with thorough supplier vetting. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and a proven track record in producing centrifuges. Request samples or demonstrations to assess performance and durability. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, including maintenance services. Reading reviews and testimonials from other customers can also provide insight into a supplier’s reputation. Establishing a good relationship with the supplier can lead to better transparency regarding quality assurance practices. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing centrifuges?
When importing centrifuges, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Evaluate whether air freight or sea freight is more cost-effective based on your urgency and budget. Be aware of import duties, taxes, and any specific regulations regarding laboratory equipment in your country. Collaborating with logistics partners who specialize in international trade can streamline the process, ensuring compliance with all regulations and minimizing delays. -
Can I customize centrifuges to meet specific laboratory requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for centrifuges to better suit specific laboratory needs. Customizations may include rotor types, speed settings, and additional features like temperature control or specialized interfaces. When discussing your requirements with suppliers, provide detailed specifications to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Keep in mind that custom orders may involve longer lead times and potentially higher costs, so plan accordingly to align with your project timelines. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering centrifuges from international suppliers?
Lead times for ordering centrifuges can vary based on several factors, including the supplier’s production capacity, the complexity of the centrifuge, and shipping logistics. Standard centrifuges may have lead times of 4-6 weeks, while customized units can take longer, sometimes 8-12 weeks or more. To minimize delays, place orders well in advance and maintain open communication with your supplier regarding production schedules. Understanding the factors that affect lead time can help you plan your laboratory operations more effectively.
Top 7 Types Of Centrifuge Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Microbenotes – Centrifuge Solutions
Domain: microbenotes.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Benchtop Centrifuge: Compact, used in clinical and research labs, driven by electric motor, suitable for smaller spaces, various variations available. 2. Continuous Flow Centrifuge: Rapid, allows centrifugation of large volumes, maintains sedimentation rates, larger capacities, can process up to 1 liter in 4 hours or less. 3. Gas Centrifuge: Separates gases based on isotopes, used for uranium s…
2. Trucent – Types of Centrifuges
Domain: trucent.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Types of Centrifuges: 1. Laboratory Centrifuges: – Benchtop devices including hematocrit centrifuges, microcentrifuges, vacuum concentrators, slide-spinners, ultracentrifuges. – Used for separating solids from liquids in samples. – Rotor types: fixed angle and swing-bucket. 2. Industrial Centrifuges: – High-speed, high-throughput devices for continuous processing. – Types: Two-phase (solid and liq…
3. IQS Directory – Centrifuges
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Centrifuges are essential scientific tools used to separate fluids, gases, or liquids based on varying densities through rapid spinning, creating centrifugal forces. Key features include:
– **Construction**: Comprises main structure, rotors (angular and horizontal), drive mechanism, control interface, cooling system, and safety features.
– **Operational Principle**: Utilizes sedimentation, combi…
4. Pipette – Types of Laboratory Centrifuges
Domain: blog.pipette.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 8 Types of Laboratory Centrifuges: Clinical Centrifuges, Microcentrifuges / Mini Centrifuges, Hematocrit Centrifuges, Refurbished Centrifuges.
5. Separators Inc – Centrifuges
Domain: separatorsinc.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Centrifuges are essential in many industrial plants for separating components in fluids using centrifugal force. There are two main types of centrifuges: high-speed vertical centrifuges and low-speed horizontal decanter centrifuges. High-speed centrifuges can run up to 26,000 RPM and handle solid loads of up to 0.5% for solid bowl centrifuges and up to 10% for discharging centrifuges. Discharging …
6. Centrifuge Types – Key Features and Applications
Domain: slideshare.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The document describes different types of centrifuges based on their design features and intended applications. Key details include: 1. Small benchtop centrifuges: Used in clinical labs for blood separation, can hold around 100 tubes. 2. Microcentrifuges: Common in biology labs, hold small tube volumes, generate forces up to 15,000g. 3. High-speed centrifuges: Spin at 15,000-20,000 RPM, used for r…
7. DSC Balances – Centrifuge Solutions
Domain: dscbalances.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: This company, DSC Balances – Centrifuge Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of centrifuge
In summary, the diverse range of centrifuges available today—ranging from benchtop to high-speed and specialized models—offers significant advantages for various applications in laboratory and industrial settings. Strategic sourcing of centrifuges involves understanding the specific requirements of your operations, including rotor types, speed capabilities, and temperature control features. By aligning your procurement strategies with the unique needs of your business, you can optimize efficiency, enhance productivity, and ultimately drive innovation.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of selecting the right centrifuge cannot be overstated. It is crucial to assess suppliers based on their reliability, support services, and the technological advancements they offer. As you navigate the complexities of sourcing, consider leveraging partnerships with trusted manufacturers who can provide customized solutions tailored to your operational challenges.
Looking ahead, the centrifuge market is poised for growth, fueled by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors. Embrace this opportunity to invest in high-quality centrifuges that will propel your business forward. Start your sourcing journey today and unlock the full potential of your laboratory or production capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.