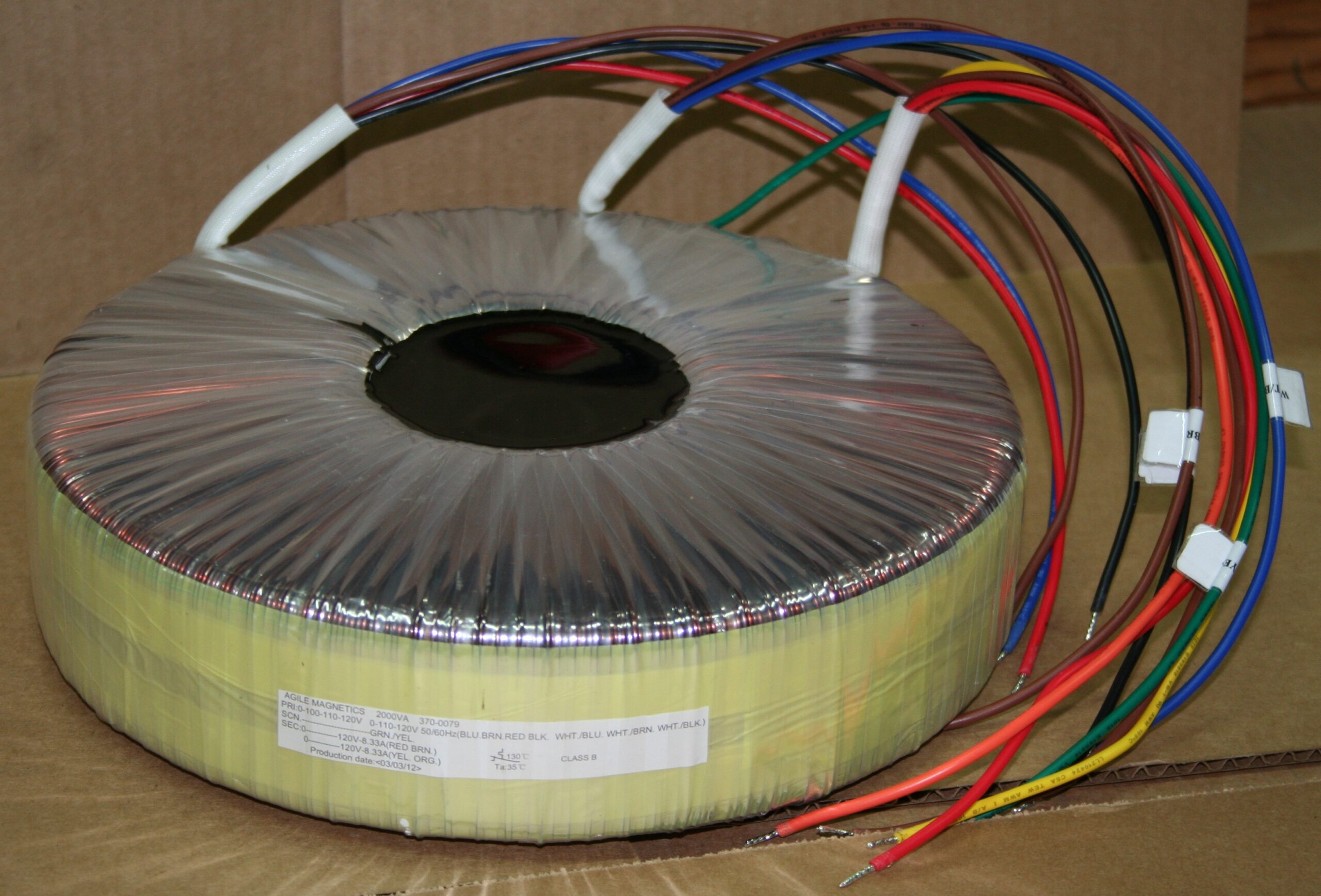
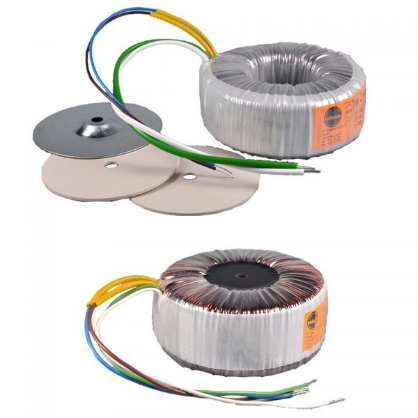
Toroidal Power Transformer: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for toroidal power transformer
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electrical engineering, sourcing the right toroidal power transformer can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you are operating in the dynamic markets of Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of these transformers is crucial. This guide serves as an essential resource, offering insights into the various types of toroidal power transformers, their applications across industries, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
As buyers navigate this complex market, they need to evaluate not only the technical specifications of transformers but also their efficiency, compactness, and suitability for specific applications. The guide delves into the advantages of toroidal transformers, such as reduced stray magnetic fields and improved energy efficiency, making them ideal for sensitive electronic applications, medical equipment, and audio systems. Additionally, it provides a comprehensive overview of cost considerations, ensuring that buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational requirements and budgets.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide helps streamline the sourcing process, ultimately facilitating the acquisition of high-quality toroidal power transformers that meet diverse industry demands. As you explore the content, you will find valuable strategies for selecting reputable suppliers and optimizing your procurement processes, equipping your business for success in the global marketplace.
Understanding toroidal power transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Toroidal Transformers | Designed for low leakage currents and compact size | Medical devices and equipment | Pros: High efficiency, low noise; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Audio Toroidal Transformers | Low electromagnetic interference and reduced hum | Audio amplifiers and high-fidelity systems | Pros: Superior sound quality; Cons: Sensitive to inrush current. |
| General Purpose Toroidal Transformers | Versatile voltage options with dual primary windings | Industrial machinery, consumer electronics | Pros: Flexible applications; Cons: May require additional fusing for inrush. |
| Custom Toroidal Transformers | Tailored specifications for unique applications | Specialized equipment across industries | Pros: Meets specific needs; Cons: Longer lead times. |
| High-Power Toroidal Transformers | Capable of handling higher voltage and current ratings | Power distribution, large machinery | Pros: Efficient power handling; Cons: Larger footprint and weight. |
What are Medical Toroidal Transformers and Their Advantages?
Medical toroidal transformers are specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements of the medical industry. They feature low leakage currents and compact designs, making them ideal for integration into devices where space is limited. These transformers ensure reliable operation and maintain low noise levels, which is critical in sensitive medical environments. Buyers should consider their efficiency ratings and thermal management capabilities, as these factors directly influence device performance and patient safety.
How Do Audio Toroidal Transformers Enhance Sound Quality?
Audio toroidal transformers are renowned for their ability to minimize electromagnetic interference and reduce hum, making them a preferred choice for high-fidelity audio systems and amplifiers. Their design allows for high-quality sound reproduction, which is essential for audio professionals and enthusiasts alike. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the transformer’s inrush current characteristics, as these can affect the performance during startup, potentially requiring soft-start circuits or slow-blow fuses.
What Makes General Purpose Toroidal Transformers Versatile?
General-purpose toroidal transformers are versatile components suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. They often feature dual primary windings, allowing for various voltage configurations, which enhances their adaptability. Buyers should evaluate the specific voltage and current ratings required for their applications, as well as the need for additional protective measures against inrush currents, which can impact the transformer’s longevity and reliability.
Why Opt for Custom Toroidal Transformers?
Custom toroidal transformers are designed to meet unique specifications, making them ideal for specialized equipment across various industries. These transformers provide tailored solutions that can optimize performance in niche applications. While they offer significant advantages in terms of meeting precise needs, buyers should be aware of potentially longer lead times and higher costs associated with custom manufacturing. It’s essential to engage with manufacturers early in the design process to ensure timely delivery and functionality.
What Are the Benefits of High-Power Toroidal Transformers?
High-power toroidal transformers are engineered to handle substantial voltage and current ratings, making them essential for power distribution and large machinery applications. Their efficient design minimizes energy losses, which is crucial in high-demand environments. However, buyers should consider the larger footprint and weight of these transformers compared to standard models. Evaluating the specific power requirements and installation constraints will help in selecting the right high-power transformer for a given application.
Key Industrial Applications of toroidal power transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of toroidal power transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Equipment | Power supply for diagnostic and imaging devices | Ensures low leakage current and reliable operation | Compliance with medical safety standards, compact design |
| Consumer Electronics | Power supply for audio amplifiers and home theater systems | Reduces electromagnetic interference and noise | Low profile and lightweight design, high efficiency |
| Industrial Automation | Control systems for manufacturing processes | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces heat generation | Customization options, voltage and current specifications |
| Renewable Energy | Inverters for solar power systems | Improves overall system efficiency and reduces footprint | Environmental compliance, durability in harsh conditions |
| Telecommunications | Power supply for network equipment | Provides stable power with minimal noise | Voltage compatibility, reliability in continuous operation |
How Are Toroidal Power Transformers Used in Medical Equipment?
In the medical sector, toroidal power transformers are integral to the power supply of diagnostic and imaging devices, such as MRI machines and ultrasound equipment. Their design minimizes leakage currents, ensuring that sensitive medical instruments operate reliably and safely. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, it’s crucial to source transformers that meet stringent medical safety standards and offer compact designs to fit within space-constrained environments.
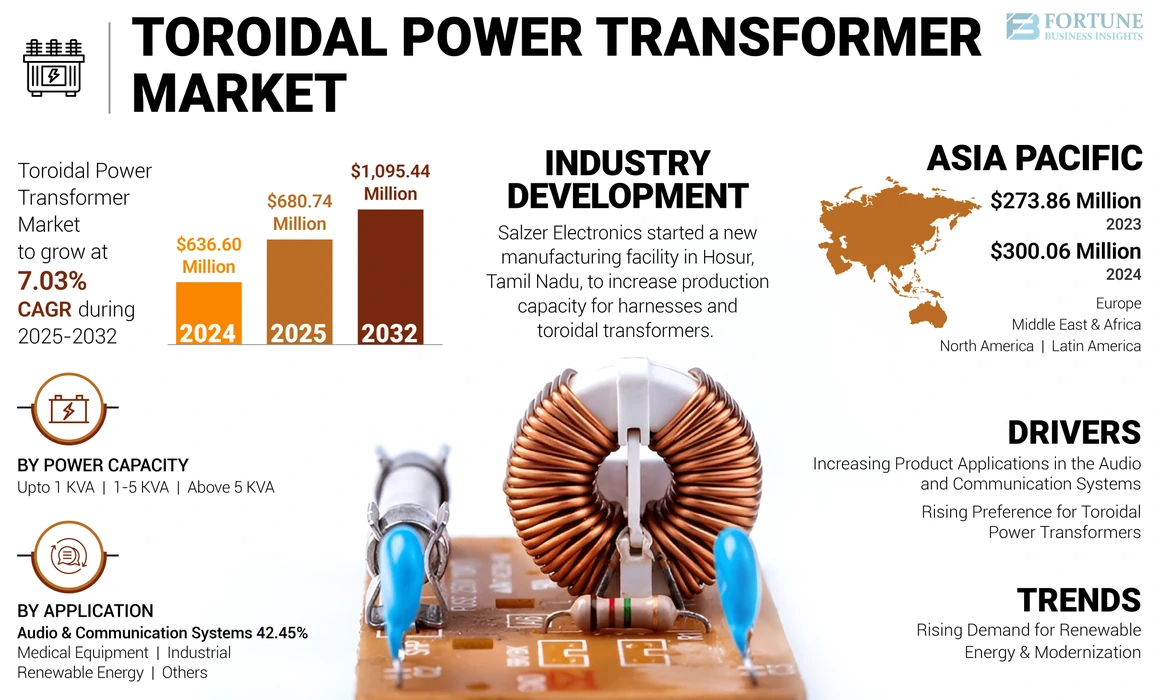
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
What Role Do Toroidal Power Transformers Play in Consumer Electronics?
In consumer electronics, toroidal transformers are commonly used in audio amplifiers and home theater systems. Their ability to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and noise contributes to superior sound quality, making them a preferred choice for high-fidelity audio applications. Buyers from Europe and South America should prioritize lightweight and low-profile designs, as these features enhance the overall aesthetics and functionality of consumer products.
How Do Toroidal Power Transformers Enhance Industrial Automation?
Within industrial automation, toroidal power transformers are used in control systems that manage manufacturing processes. Their high efficiency translates to reduced energy consumption and lower heat generation, which is critical in maintaining optimal operating conditions. For businesses in Africa and South America, sourcing transformers that can be customized to specific voltage and current requirements will ensure compatibility with existing systems and enhance operational efficiency.
What Benefits Do Toroidal Power Transformers Provide in Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, particularly solar power systems, toroidal transformers are essential for inverters that convert DC to AC. Their design allows for improved efficiency and a reduced footprint, which is vital for maximizing space in solar installations. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the durability of these transformers, ensuring they can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining performance.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Why Are Toroidal Power Transformers Important for Telecommunications?
Telecommunications infrastructure relies heavily on stable power supplies for network equipment. Toroidal transformers provide this stability while generating minimal noise, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of communication signals. International buyers should focus on sourcing transformers that offer reliability in continuous operation and compatibility with various voltage levels to ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘toroidal power transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming High Inrush Current Issues in Toroidal Power Transformers
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter the challenge of high inrush current when powering toroidal transformers, which can lead to blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers. This situation is particularly frustrating in critical applications where reliability is paramount, such as medical devices or industrial equipment. The unpredictable nature of inrush current can lead to costly downtime and disruptions, making it crucial for buyers to find a solution that ensures smooth operation from the moment the transformer is energized.
The Solution: To mitigate inrush current issues, B2B buyers should consider implementing a soft-start circuit in their systems. This can involve using a slow-blow fuse or a time-delay circuit breaker that can accommodate the initial surge without tripping. Additionally, selecting a toroidal transformer with an appropriate VA rating for the application is essential; if the transformer is underrated, it may lead to frequent overloads. Buyers should also consult with manufacturers to ensure the chosen transformer is designed with the right specifications for their unique use case, thus ensuring that the system can handle the transient inrush while maintaining overall efficiency.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Scenario 2: Addressing Space Constraints in Electronic Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face space limitations when integrating transformers into their electronic systems, particularly in compact devices like medical equipment or consumer electronics. The traditional power transformers often occupy too much space and generate more heat, leading to design complications. This challenge becomes even more critical when the transformer must coexist with sensitive components that require optimal thermal conditions and minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The Solution: Buyers can leverage the compact design and efficiency of toroidal power transformers to address space constraints effectively. When sourcing toroidal transformers, they should prioritize models that emphasize low-profile designs and reduced footprint. Additionally, it’s vital to work closely with suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific application requirements. Buyers can also benefit from using transformers with enhanced insulation and cooling features to minimize heat generation, ensuring that the overall system remains reliable and efficient. Engaging in thorough discussions with manufacturers can lead to innovative solutions that maximize space utilization without compromising performance.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with International Standards
The Problem: Navigating the complex landscape of international compliance standards can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing toroidal power transformers for use in various regions, including Europe, Africa, and South America. Non-compliance can result in significant delays in product launches, increased costs, and potential legal ramifications. This is particularly concerning for companies involved in highly regulated industries like healthcare and telecommunications.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with relevant international standards, buyers should conduct thorough research on the applicable regulations in their target markets. This includes understanding certifications like UL, CSA, and IEC/EN standards that govern transformer safety and performance. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record of compliance and can provide documentation and certification for their products is essential. Buyers should also consider collaborating with compliance consultants or legal experts to navigate the intricacies of regulations in different regions. By proactively addressing compliance issues, companies can streamline their supply chain processes and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, thus enabling smoother market entry and enhancing their competitive edge.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for toroidal power transformer
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Toroidal Power Transformers?
When selecting materials for toroidal power transformers, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact the performance, efficiency, and suitability of the transformer for specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the construction of toroidal power transformers.
1. Silicon Steel
Key Properties: Silicon steel is characterized by its high magnetic permeability and low core losses. It typically operates efficiently at temperatures up to 130°C and can handle significant magnetic flux densities.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of silicon steel is its excellent magnetic properties, which enhance efficiency and reduce energy losses. However, it can be relatively heavy and may require complex manufacturing processes to achieve optimal performance. Silicon steel is also more susceptible to corrosion unless properly coated.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and low heat generation, such as in audio equipment and medical devices. However, its weight can be a limiting factor in space-constrained designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and ISO, as silicon steel may need specific treatments to meet environmental conditions.
2. Ferrite
Key Properties: Ferrite cores are made from a ceramic material that exhibits high electrical resistance and low eddy current losses. They can operate effectively at high frequencies and temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons: Ferrite is lightweight and compact, making it ideal for applications where space is limited. However, it can be more expensive than silicon steel and is less durable under mechanical stress, which may limit its use in rugged environments.
Impact on Application: Ferrite cores are often used in high-frequency applications such as switch-mode power supplies. Their low weight and size make them suitable for portable devices, but their fragility can be a concern in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is crucial, particularly in Europe, where regulations on electronic components are stringent. Buyers should verify that ferrite materials meet relevant safety and performance standards.
3. Amorphous Steel
Key Properties: Amorphous steel features a non-crystalline structure that provides enhanced magnetic properties and lower energy losses compared to traditional silicon steel. It can operate efficiently at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of amorphous steel is its superior efficiency, which can lead to significant energy savings. However, it is generally more expensive and can be challenging to manufacture, requiring specialized processes.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly beneficial in applications where energy efficiency is paramount, such as renewable energy systems. However, the higher cost may deter some buyers, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the long-term savings from energy efficiency when evaluating the cost of amorphous steel. Compliance with local regulations regarding energy consumption may also be a factor.
4. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is widely used for windings in toroidal transformers due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can handle high currents and operates effectively at temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its high conductivity, which minimizes resistive losses and improves overall efficiency. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum and can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for high-performance transformers, particularly in audio and medical applications where low losses are critical. However, its cost can be a barrier for budget-conscious buyers.
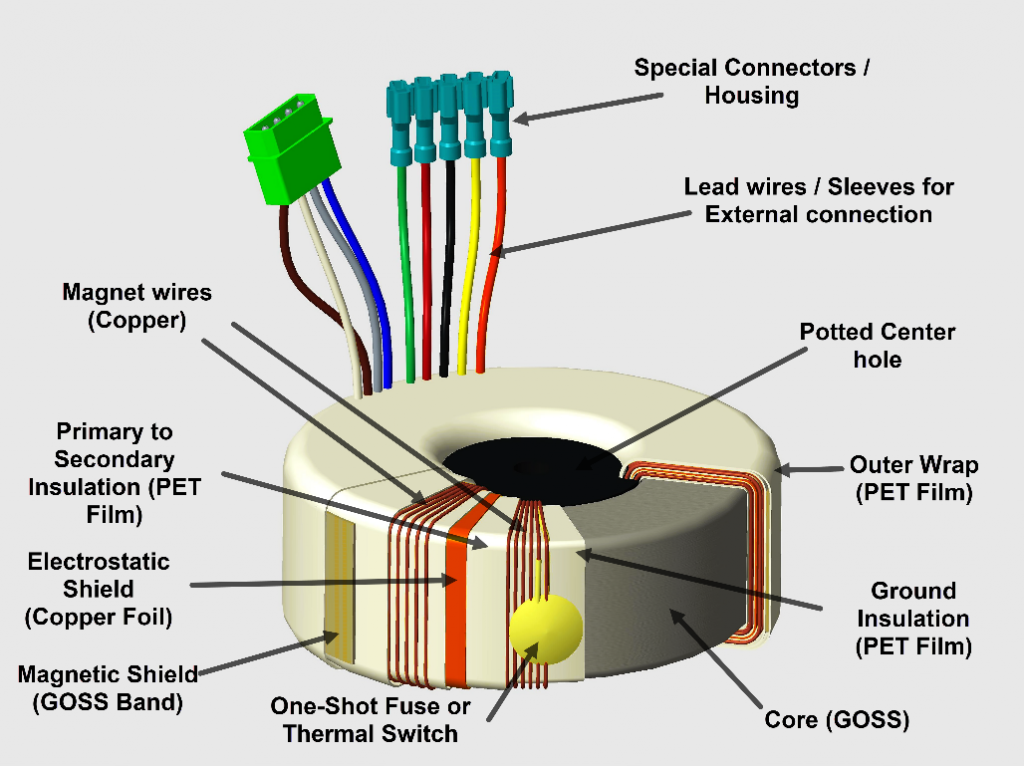
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where environmental conditions may lead to corrosion, buyers should prioritize insulated copper options. Compliance with local electrical standards is also essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for toroidal power transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Audio equipment, medical devices | Excellent magnetic properties | Heavy and corrosion-prone | Medium |
| Ferrite | High-frequency applications | Lightweight and compact | Expensive and fragile | High |
| Amorphous Steel | Renewable energy systems | Superior energy efficiency | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | High-performance transformers | High conductivity and thermal properties | Expensive and corrosion-sensitive | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers considering toroidal power transformers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for toroidal power transformer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Toroidal Power Transformers?
The manufacturing of toroidal power transformers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets high-performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, core forming, assembly, and finishing.
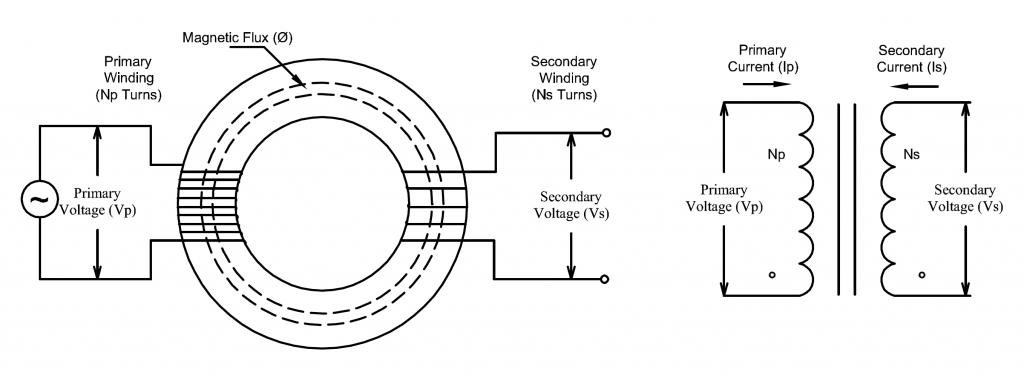
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Material Preparation
The first step is the selection and preparation of materials. High-quality magnetic materials, such as silicon steel or amorphous steel, are essential for the core. These materials are typically processed into thin sheets to reduce eddy current losses. Insulation materials, such as varnishes and insulating papers, are also prepared at this stage to ensure proper electrical isolation between windings.
Core Forming
Once the materials are ready, the next step involves forming the core. The steel sheets are cut into strips and wound into a toroidal shape. This process can be done using automated machines that apply precise tension to ensure uniformity. The toroidal shape minimizes stray magnetic fields and enhances efficiency. Advanced techniques, such as computer-controlled winding machines, are often employed to achieve accurate coil dimensions and reduce the risk of defects.
Assembly
In the assembly stage, the primary and secondary windings are placed onto the toroidal core. This requires careful attention to detail, as improper winding can lead to performance issues. Each winding is insulated and secured to prevent movement during operation. Quality control measures are put in place during assembly to check for short circuits and insulation integrity.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves encapsulating the transformer to protect it from environmental factors and mechanical stress. This often includes applying a protective coating and ensuring all components are securely fastened. Final testing is performed to verify that the transformer meets specified electrical and thermal performance criteria.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Toroidal Power Transformers?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of toroidal power transformers to ensure reliability and compliance with international standards. The quality assurance process typically includes several checkpoints and testing methods.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers must comply with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additional certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards, are also critical. For specific applications, adherence to industry-specific standards like API for the oil and gas industry may be required.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process, including:

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter production. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards is crucial for the overall quality of the transformer.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks are conducted during the manufacturing process to identify defects early. This can include monitoring the winding process and verifying insulation integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the transformer is assembled, it undergoes extensive testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. Common tests include high-voltage tests to check for insulation breakdown and efficiency testing to verify performance against rated specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial in ensuring product reliability. Here are several approaches to consider:
Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. These audits should evaluate compliance with international standards and internal quality management systems.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports from suppliers that outline their quality control procedures, testing results, and any certifications obtained. This documentation provides transparency and helps in assessing the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct random inspections and testing to verify that the products meet specified quality and safety standards before shipment.
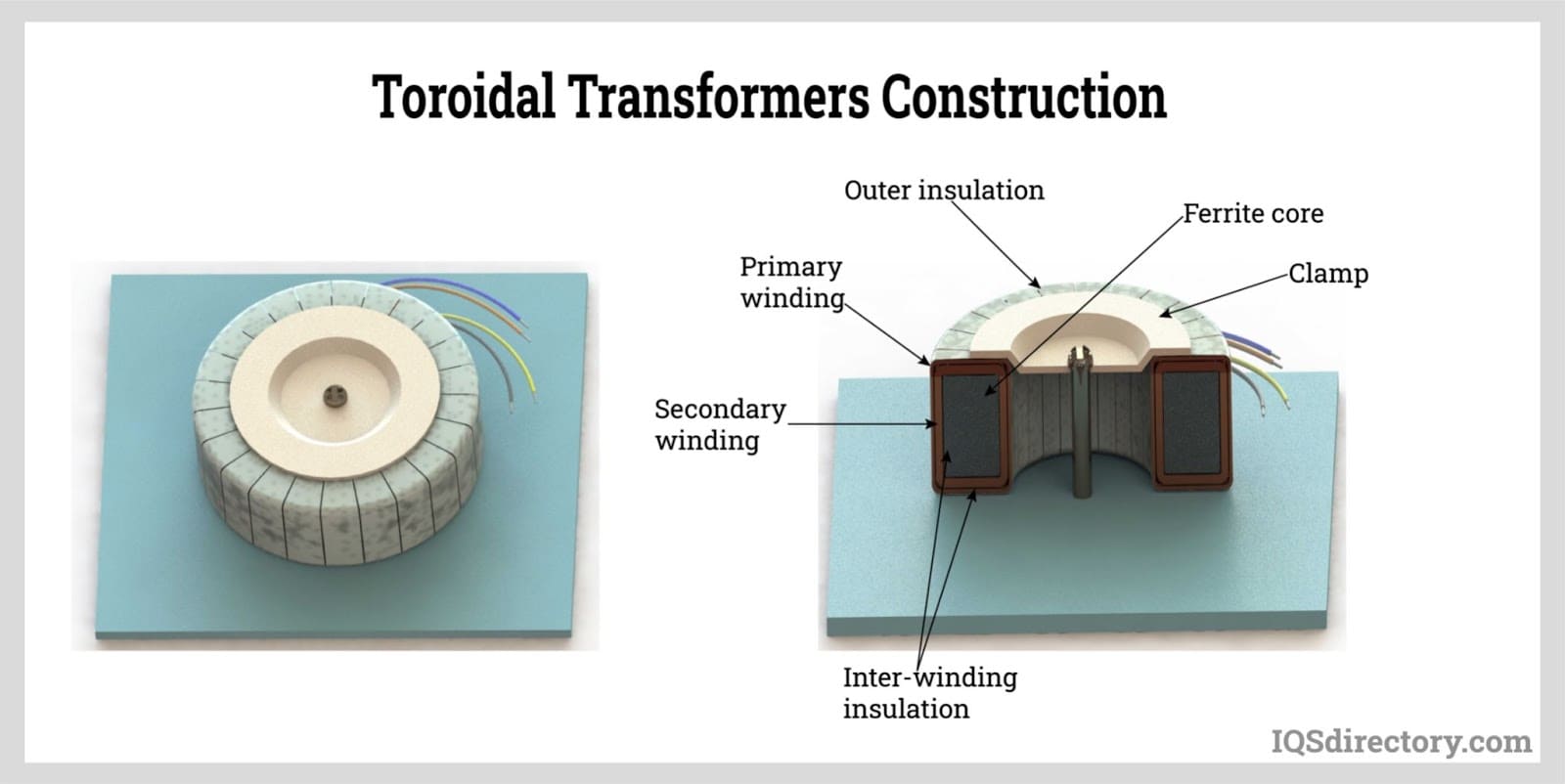
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure the Quality of Toroidal Power Transformers?
Testing methods play a critical role in the quality assurance of toroidal power transformers. Some of the most common methods include:
-
High-Potential (Hi-Pot) Testing: This test applies high voltage to the transformer to ensure insulation integrity and identify any potential breakdowns.
-
Temperature Rise Testing: Assessing how the transformer performs under load conditions helps determine its thermal stability and efficiency. This is particularly crucial for applications where overheating could lead to failure.
-
Efficiency Testing: Measuring the transformer’s efficiency under various loads helps in validating its performance against industry standards.
-
Leakage Current Testing: This involves measuring the amount of current that escapes from the transformer to ensure it remains within acceptable limits, especially for sensitive applications like medical equipment.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Quality Control and Certifications?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly from regions with varying regulatory standards, buyers should be aware of several nuances:
-
Understanding Regional Certifications: Different regions may have specific requirements for certifications. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, while UL certification may be more relevant for North American markets. Buyers should ensure that the supplier’s certifications align with the target market.
-
Language Barriers and Documentation: When dealing with suppliers from diverse regions, language barriers can lead to misunderstandings. Buyers should ensure that all quality documentation is available in a language they can understand and that all specifications are clearly communicated.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Different cultures may have varying perceptions of quality and standards. Buyers should be prepared to navigate these differences and engage in discussions to ensure mutual understanding of quality expectations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for toroidal power transformers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also helps in establishing long-term partnerships based on quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘toroidal power transformer’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing toroidal power transformers, this guide provides a structured checklist that outlines essential steps. By following this step-by-step approach, you can ensure that your procurement process is efficient, informed, and aligned with your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is crucial in the sourcing process. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, power capacity (measured in VA), and application type. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure you receive the right transformer for your needs.
- Voltage Requirements: Specify primary and secondary voltage needs.
- Power Capacity: Determine the VA rating required for your application.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers specializing in toroidal power transformers. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and region. This step is essential for ensuring you partner with a reliable source that can meet your quality and delivery expectations.
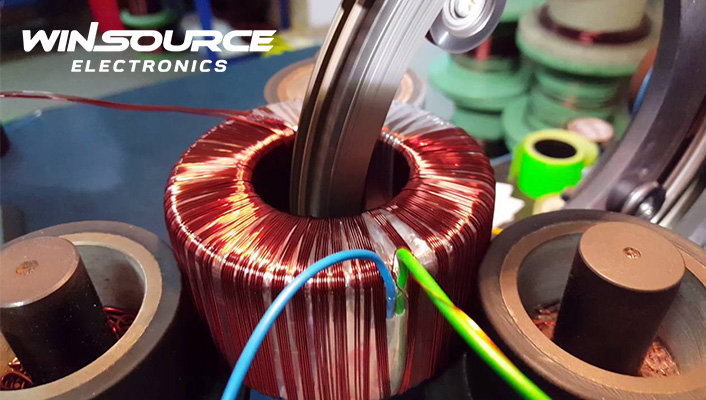
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
- Check Reviews and Ratings: Look for customer testimonials and case studies.
- Assess Industry Experience: Prioritize suppliers with experience in your specific application area.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any purchase, verify the certifications held by your potential suppliers. Certifications such as UL, CSA, and IEC compliance are indicators of quality and safety standards. This ensures that the transformers you procure meet international safety and operational standards.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure suppliers have robust quality management systems in place.
- Safety Standards: Look for compliance with relevant safety standards for your region.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request product samples and detailed specifications. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the transformers with your existing systems. Detailed specifications will also help confirm that the product meets your technical requirements.
- Testing: Use samples for performance testing under your specific conditions.
- Documentation: Ensure you receive complete technical documentation for the products.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with your shortlisted suppliers to negotiate pricing and terms. Be clear about your budget constraints while ensuring you do not compromise on quality. This is also the stage to clarify lead times, payment terms, and warranty conditions.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing for larger orders.
- Warranty and Support: Understand the warranty period and the support offered post-purchase.
Step 6: Finalize the Order and Monitor Delivery
After settling on a supplier and terms, finalize your order. Monitor the delivery process closely to ensure timelines are adhered to, as delays can impact your operations. Establish a communication line with the supplier for updates and any potential issues.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
- Tracking: Use shipment tracking to stay informed about delivery status.
- Inspection: Plan for a quality inspection upon arrival to confirm compliance with specifications.
Step 7: Evaluate Performance Post-Installation
Once the toroidal transformers are installed, monitor their performance closely. Collect data on efficiency, temperature, and reliability during operation. This evaluation will not only confirm the suitability of your choice but also inform future sourcing decisions.
- Performance Metrics: Track efficiency and temperature to ensure optimal operation.
- Feedback Loop: Use this information to refine your future sourcing criteria.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for toroidal power transformers, ensuring they select the right products for their specific needs while building solid relationships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for toroidal power transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Toroidal Power Transformers?
When sourcing toroidal power transformers, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary components of the cost structure include:
-
Materials: The core of a toroidal transformer is typically made from high-quality magnetic materials that enhance efficiency. The choice of materials directly impacts both the cost and performance. For instance, higher-grade silicon steel may lead to increased costs but significantly improves efficiency and reduces losses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for winding the coils and assembling the transformers, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other indirect costs associated with production. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized transformers. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has existing tooling for standard designs or if new tooling is needed for custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that transformers meet required specifications and certifications incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are vital, particularly for applications in sensitive industries like healthcare.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the shipping method and distance. International buyers must factor in customs duties and import taxes, which can significantly affect the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, brand reputation, and customer relationship.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Toroidal Power Transformer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of toroidal power transformers, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it essential for buyers to assess their projected needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom transformers tailored to specific applications or performance requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like UL, CSA) can elevate the price. Buyers should balance the need for quality with budget constraints, especially in competitive markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and service, while emerging suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears the shipping costs and risks, affecting the overall price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
To ensure cost-effective sourcing of toroidal power transformers, buyers should consider the following strategies:
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can encourage suppliers to offer better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifecycle costs. A slightly higher upfront cost for a more efficient transformer can lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying costs due to labor, materials, and shipping. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research local market conditions and potential tariffs that could affect pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from different suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help identify the best value.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to better pricing, faster service, and improved communication, all of which are beneficial in the long run.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this guide are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, specific requirements, and supplier negotiations. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotations tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing toroidal power transformer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Toroidal Power Transformers: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of electrical engineering, the choice of transformers is crucial for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and application suitability. While toroidal power transformers are known for their compact size and high efficiency, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions. This analysis compares toroidal transformers with two viable alternatives: traditional laminated core transformers and ferrite core transformers.
| Comparison Aspect | Toroidal Power Transformer | Traditional Laminated Core Transformer | Ferrite Core Transformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, low noise, compact design | Moderate efficiency, bulkier, higher noise levels | High frequency efficiency, low losses in specific applications |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower initial cost, but potentially higher long-term costs due to inefficiencies | Moderate cost, often cost-effective for specific high-frequency applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise mounting and setup | Easier to install due to standard sizes and configurations | Simple installation for high-frequency applications |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, robust design | Moderate maintenance; prone to wear over time | Low maintenance, but can be sensitive to environmental factors |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for compact, high-efficiency applications like medical devices and audio equipment | Suitable for general-purpose applications where space is not a constraint | Best for high-frequency applications such as RF circuits and switch-mode power supplies |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Laminated Core Transformers?
Traditional laminated core transformers are widely utilized across various industries due to their lower initial costs and simpler installation processes. They are particularly effective in applications where size and weight are not critical factors. However, they have notable downsides, including bulkiness and higher noise levels, which can be problematic in sensitive environments. Additionally, their efficiency may not match that of toroidal transformers, leading to potential long-term operational costs due to energy losses.
How Do Ferrite Core Transformers Compare?
Ferrite core transformers excel in high-frequency applications, making them suitable for RF circuits and switch-mode power supplies. They offer low losses and high efficiency in specific contexts, often at a moderate price point. However, they may not be as robust as toroidal transformers in terms of physical durability and can be sensitive to environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature variations. Their installation is generally straightforward, but the specialized nature of their application may limit their versatility.
How to Choose the Right Transformer for Your Needs?
When selecting a transformer, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, including efficiency, space constraints, and cost. Toroidal transformers may be the best choice for applications demanding high efficiency and compactness, such as in medical devices or high-end audio equipment. Conversely, traditional laminated core transformers can be more economical for general applications where efficiency is less critical. Ferrite core transformers are ideal for high-frequency applications but may not be suitable for all scenarios.
By weighing these factors against each alternative’s pros and cons, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their electrical systems.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for toroidal power transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Toroidal Power Transformers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of toroidal power transformers is crucial for B2B buyers who seek reliable and efficient electrical components. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Core Material Grade
– Definition: The core of a toroidal transformer is usually made from high-quality silicon steel or ferrite materials. These materials enhance magnetic properties and reduce losses.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right core material is vital for efficiency. High-grade materials lead to lower energy losses, which is crucial for applications requiring consistent performance, such as in medical devices or audio systems. -
VA Rating (Volt-Ampere Rating)
– Definition: The VA rating indicates the maximum amount of power the transformer can handle without overheating. This rating is a product of voltage and current.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the VA rating helps buyers determine if a transformer meets their power requirements. Selecting a transformer with an inadequate VA rating can lead to failures and increased operational costs. -
Voltage Regulation
– Definition: This specification refers to the transformer’s ability to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in load current.
– B2B Importance: Good voltage regulation ensures stable operation of sensitive electronic devices. Buyers in sectors such as telecommunications and healthcare need transformers that minimize voltage fluctuations to protect equipment. -
Temperature Rise
– Definition: This refers to the increase in temperature that occurs during operation, typically expressed in degrees Celsius (°C).
– B2B Importance: A low temperature rise indicates better thermal management and efficiency, essential for applications in confined spaces or environments where heat dissipation is challenging. -
Leakage Current
– Definition: This is the unintended flow of electrical current that can occur when insulation fails or is insufficient.
– B2B Importance: Low leakage current is particularly important for medical and safety-critical applications where even minor leaks can lead to hazardous conditions. -
Efficiency Rating
– Definition: Efficiency is the ratio of output power to input power, often expressed as a percentage.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency ratings translate to reduced energy costs and lower operational expenses over time, making them appealing to budget-conscious buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Toroidal Power Transformers?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: OEMs often require custom toroidal transformers to meet specific technical requirements, making it essential for suppliers to understand these needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively, particularly in markets with fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to invite them to bid on providing products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ is critical for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding the capabilities of different suppliers in the toroidal transformer market. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and risks, ensuring smooth international procurement processes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is fulfilled.
– Relevance: Buyers need to consider lead times when planning projects, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Documents that indicate a product meets specific safety, performance, or quality standards (e.g., UL, CE).
– Relevance: Certifications reassure buyers of product reliability and compliance with regional regulations, which is particularly important in markets like Europe and the Middle East.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can significantly enhance the decision-making process for international B2B buyers seeking toroidal power transformers, ensuring they select the right products for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the toroidal power transformer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Toroidal Power Transformers?
The global market for toroidal power transformers is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and compact electrical components. Key trends include a rising focus on miniaturization in electronic devices, which is particularly prominent in industries such as telecommunications and healthcare. Emerging technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, are further propelling the demand for toroidal transformers due to their superior efficiency and reduced electromagnetic interference. This is especially relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where there is a growing emphasis on upgrading electrical infrastructure to support modern applications.

Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
Moreover, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in various sectors is leading to an increased need for reliable power supplies, where toroidal transformers play a crucial role. In markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, local manufacturers are increasingly looking to source these transformers to enhance product performance and meet stringent regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should also be aware of the fluctuating raw material costs and global supply chain challenges, which can impact pricing and availability. Strategic sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide high-quality products with favorable lead times is becoming essential.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing Decisions for Toroidal Power Transformers?
Sustainability is now a critical factor influencing sourcing decisions in the toroidal power transformer sector. As global awareness of environmental issues increases, businesses are compelled to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes selecting suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and manufacturing processes that minimize environmental impact. For example, using recyclable materials and reducing waste during production are practices that resonate well with environmentally conscious buyers.
Moreover, obtaining ‘green’ certifications can enhance a product’s appeal in the marketplace. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) not only ensure compliance with international regulations but also signify a commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers in regions with stringent environmental standards, such as Europe, are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with these certifications. This trend is gaining traction across Africa and South America as well, where companies are beginning to recognize the importance of sustainable sourcing in building a competitive advantage.
What Is the Historical Context of Toroidal Power Transformers for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of toroidal power transformers can be traced back to their introduction in the mid-20th century as a more efficient alternative to traditional laminated transformers. The toroidal shape allows for a compact design with lower electromagnetic interference and improved efficiency, making them particularly suitable for sensitive electronic applications. Over the decades, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have further enhanced their performance, leading to widespread adoption across various sectors, including medical devices, audio equipment, and renewable energy systems.
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to rise, the relevance of toroidal transformers in B2B applications remains strong. Their ability to integrate seamlessly into modern electronic designs while providing reliable performance has positioned them as a staple in the electrical engineering field. Understanding this historical context can help international B2B buyers appreciate the longstanding benefits and innovations associated with toroidal power transformers, guiding them in their procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of toroidal power transformer
-
How do I choose the right toroidal power transformer for my application?
Selecting the appropriate toroidal power transformer involves assessing your specific application requirements. Consider factors such as voltage rating, power rating (in VA), and the type of load (continuous vs. non-continuous). Additionally, evaluate the efficiency levels, size constraints, and noise specifications, especially if the transformer will be used in sensitive environments like medical devices or audio equipment. Consulting with manufacturers about customization options can also help in tailoring a transformer to meet your specific needs. -
What are the key benefits of using toroidal power transformers over traditional transformers?
Toroidal power transformers offer several advantages, including higher efficiency, reduced size, and lower electromagnetic interference (EMI). Their unique design minimizes stray magnetic fields, making them ideal for sensitive applications. They also tend to run cooler than traditional transformers, which can prolong their lifespan and enhance reliability. Moreover, their compact nature allows for easier integration into tight spaces, making them suitable for various electronic and medical applications. -
What customization options are available when sourcing toroidal power transformers?
Customization options for toroidal power transformers can vary by manufacturer but typically include voltage ratings, power ratings, winding configurations, and physical dimensions. Buyers can also request specific insulation materials and thermal ratings to suit their operational environments. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly to suppliers, as many manufacturers offer tailored solutions to meet unique application demands. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for toroidal power transformers?
The MOQ for toroidal power transformers can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the transformer design. Generally, standard models may have lower MOQs, while customized solutions could require higher quantities. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies, which can help in budgeting and planning your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing toroidal power transformers internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can differ based on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to clarify terms like currency, payment methods, and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Establishing trust through clear communication and possibly utilizing escrow services can also help mitigate risks in payment processes. -
How can I ensure the quality of toroidal power transformers from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of toroidal power transformers, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, UL) that indicate compliance with international standards. Request samples and conduct tests to verify performance specifications. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities if possible, or relying on third-party inspection services to assess product quality before large-scale orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing toroidal power transformers?
Logistics for importing toroidal power transformers involve understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Collaborate with logistics providers who specialize in international shipping to ensure compliance with local regulations in your country. Evaluate potential shipping options (air vs. sea) based on urgency and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, be aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply, as these can impact your overall budget. -
What are common applications for toroidal power transformers in various industries?
Toroidal power transformers are utilized across a range of industries due to their efficiency and compact design. Common applications include medical devices where low leakage currents are crucial, audio and video equipment that requires minimal noise, and industrial automation systems needing reliable power transfer. They are also frequently found in consumer electronics, inverters, and renewable energy systems. Identifying the specific needs of your industry can help in selecting the right transformer for optimal performance.
Top 8 Toroidal Power Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HAMMFG – 1182 Series Toroidal Power Transformers
Domain: hammfg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Product Series”: “1182 Series”, “Power Rating”: “15 VA to 1500 VA”, “Transformer Type”: “Toroidal Power Transformers”, “Primary Voltage”: “Dual 117/234 VAC”, “Frequency”: “50/60 Hz”, “Features”: [“Low profile”, “Lightweight”, “Cool running”, “High efficiency”, “Low stray magnetic flux leakage (low EMI)”], “Included Accessories”: [“Two neoprene rubber insulating pads”, “One metal centering washer…
2. Toroidal Power Transformer – Essential Crafting Component
Domain: abioticfactor.wiki.gg
Introduction: {“name”: “Toroidal Power Transformer”, “use”: “Crafting”, “weight”: 0.2, “stack_size”: 64, “research_material”: “Tech”, “sources”: [“Produced by destroying a Transformer box”, “Found by destroying Transformers in Hydroplant, Voussoir, and Reactors”, “Dropped by Defense Robots in Hydroplant”]}
3. Mouser – Toroidal Transformers
Domain: mouser.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Mouser – Toroidal Transformers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. ATO – Toroidal Power Transformers
Domain: ato.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, ATO – Toroidal Power Transformers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Automation Technologies Inc – Unregulated Toroidal Power Supplies
Domain: automationtechnologiesinc.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Unregulated Linear 350W/48DC/7.5A Toroidal PSU (KL-4875) with 5V, 1A – $107.00; Unregulated Power Supply 40VDC 10Amp (KL-4010) with 5V, 1 A – $108.00; Unregulated Linear 38VDC/15A Toroidal PSU (KL-3815) with 5V, 1A – $140.00; Unregulated Linear 50VDC/10AMP Toroidal Power Supply (KL-5010) with 5V, 1A – $159.00; Unregulated Linear 625W/48VDC/13A Toroidal PSU (KL-4813) with 5VDC – $159.00; Unregulate…
6. Talema – Toroidal Transformers
Domain: talema.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Toroidal transformers are electrical transformers with a doughnut-like shape, providing increased design flexibility, efficiency, and compactness compared to traditional transformers. They are suitable for low-KVA applications (up to 15 KVA) in medical, industrial, renewable energy, and audio sectors. Key features include:
– Lightweight and smaller size due to symmetrical winding over the core, al…
7. Newark – Toroidal Power Transformers
Domain: newark.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: {“product_type”:”Toroidal Power Transformers”,”description”:”Toroidal transformers have a doughnut-like shape, composed of a circular magnetic core with wire wrapped around it, used in various AC electronic circuits.”,”total_products_found”:534,”in_stock”:304,”suitable_for_new_designs”:532,”same_day_shipping”:17,”rohs_compliant”:530,”manufacturers”:[{“name”:”HAMMOND”,”count”:137},{“name”:”TRIAD MA…
8. Webb – Toroidal Power Transformers
Domain: webb-transformer.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Toroidal Power Transformers
Description: Low frequency transformers with high efficiency, designed to provide electric power, step-up and step-down voltage, and eliminate high frequency noise.
Advantages:
– High efficiency: 85% at full load compared to 65-75% for EI transformers.
– Small volume and light weight: 40% smaller and lighter than EI transformers.
– Easy installation: Requ…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for toroidal power transformer
As the global demand for efficient and compact power solutions continues to rise, toroidal power transformers stand out as a superior choice for various applications across industries. Their unique design offers distinct advantages, including reduced electromagnetic interference, lower energy losses, and a compact footprint, making them ideal for electronic devices, medical equipment, and audio systems. For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these benefits is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Strategic sourcing of toroidal power transformers not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer customization options and comprehensive support to ensure optimal integration within their systems. As the market evolves, staying abreast of technological advancements and regulatory standards will be essential for leveraging the full potential of toroidal transformers.
Looking ahead, now is the time for international buyers to engage with reputable manufacturers and explore tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. By investing in high-quality toroidal power transformers, businesses can enhance their operational capabilities and future-proof their electrical systems.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
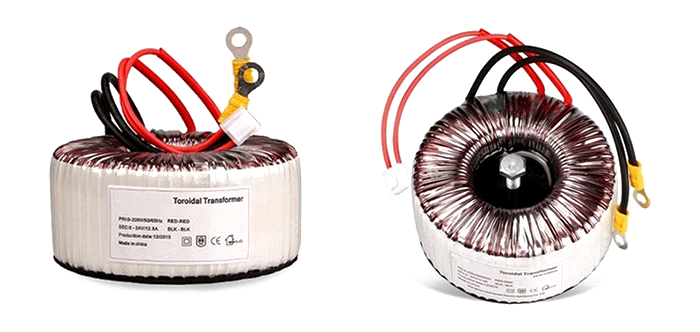
Illustrative image related to toroidal power transformer
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.