Top 8 Precision Turning Of Steel Parts Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for precision turning of steel parts
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing precision turned steel parts presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. With the demand for high-quality, reliable components growing across industries—from automotive to aerospace—businesses must navigate a complex web of suppliers, materials, and specifications. This guide on precision turning of steel parts is designed to empower buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Within this comprehensive resource, you will find detailed insights into various types of precision turned parts, their specific applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. We will also delve into cost considerations, allowing you to align your budget with your quality requirements. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of precision turning will enable you to select partners who not only meet your operational needs but also enhance your competitive edge.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring that the steel components you source are not only precise but also tailored to your industry’s demanding standards. This guide serves as your roadmap to achieving excellence in procurement, fostering long-lasting partnerships, and driving innovation in your projects.
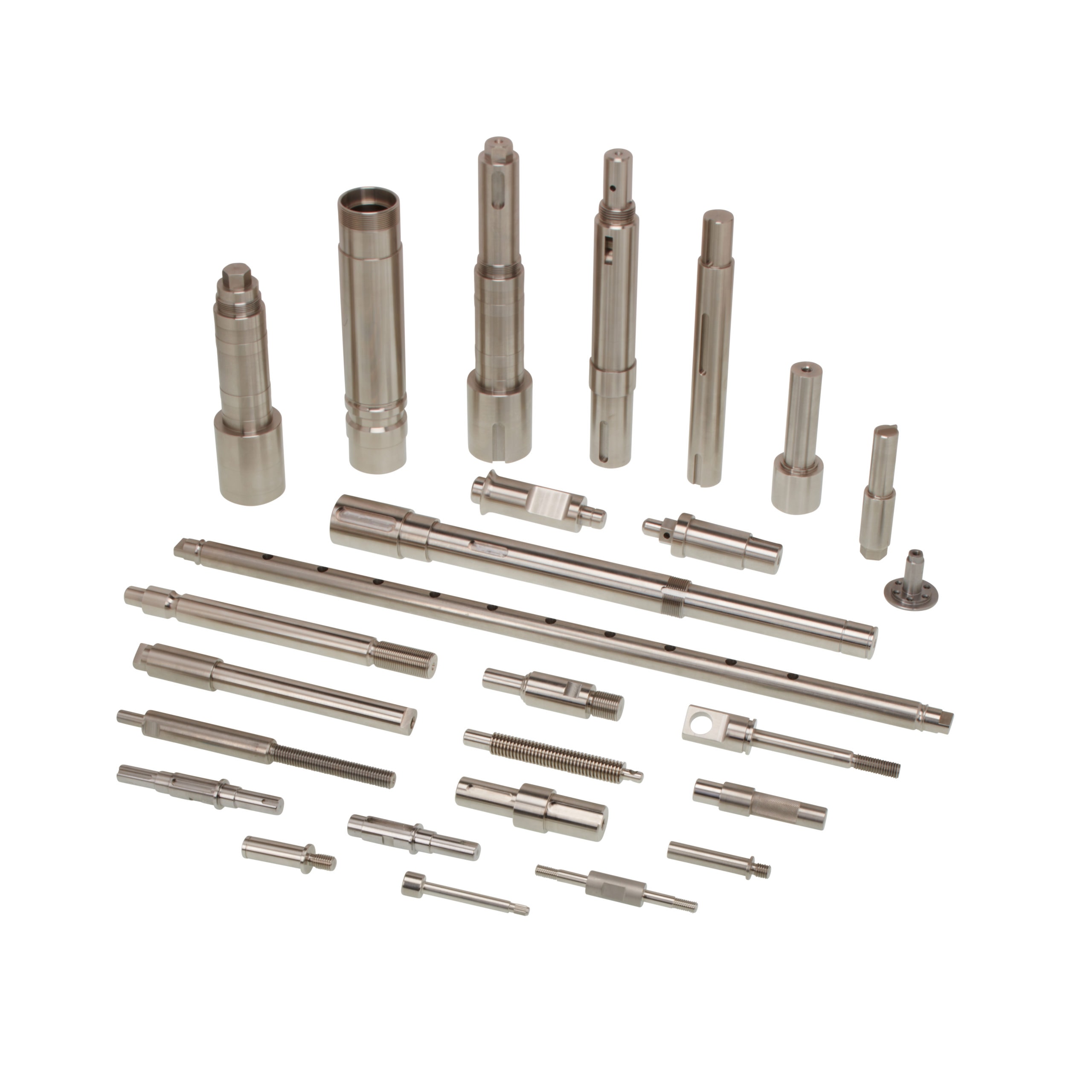
Understanding precision turning of steel parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Turned Parts | High precision, automated process, complex geometries | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical | Pros: Consistent quality, scalability; Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Swiss Screw Machine Parts | Capable of producing intricate components with tight tolerances | Electronics, Telecommunications, Medical | Pros: Superior precision, efficient for small parts; Cons: Limited to smaller diameters. |
| Multi-Spindle Turned Parts | High volume production, efficient for simple designs | Industrial Machinery, Plumbing | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs; Cons: Less flexibility for design changes. |
| Precision Bushings | Designed to reduce friction and ensure alignment | Automotive, Manufacturing, Robotics | Pros: Enhances efficiency, custom designs available; Cons: Requires precise specifications. |
| Fittings | Connectors with precise threads for secure joins | Fluid Control, HVAC, Construction | Pros: Essential for reliable connections; Cons: Variability in material compatibility. |
What Are CNC Turned Parts and Their Key Characteristics?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turned parts are manufactured using automated machinery, allowing for high precision and the ability to produce complex geometries. This method is particularly suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive, where tolerances are critical. When purchasing CNC turned parts, buyers should consider the initial setup costs, which can be higher than traditional machining methods, but the long-term benefits include consistent quality and scalability for large production runs.
How Do Swiss Screw Machine Parts Stand Out?
Swiss screw machine parts are known for their ability to produce intricate components with tight tolerances, making them ideal for applications in electronics and telecommunications. This method excels in creating small, precise parts efficiently. B2B buyers should note that while Swiss machining offers exceptional precision, it is generally limited to smaller diameters, which may not suit all applications.
Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
What Are the Advantages of Multi-Spindle Turned Parts?
Multi-spindle turned parts are designed for high-volume production and are particularly effective for simpler designs. Industries such as industrial machinery and plumbing benefit from this method due to its cost-effectiveness for large runs. Buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and flexibility, as this method may not accommodate design changes as easily as other precision turning techniques.
Why Are Precision Bushings Important for B2B Buyers?
Precision bushings are specialized turned components that reduce friction and ensure proper alignment in rotating and sliding applications. They find extensive use in automotive and robotics sectors. When purchasing bushings, it’s essential for buyers to provide precise specifications to ensure compatibility with their systems. Custom designs can enhance efficiency but may require longer lead times.
What Role Do Fittings Play in Precision Turning?
Fittings are critical components that serve as connectors, allowing for secure joins between different parts in systems such as fluid control and HVAC. Their precision threading is essential for ensuring reliability in connections. Buyers should be aware of the variability in material compatibility, which can impact the performance of fittings in specific applications. Understanding the intended use and environmental factors is crucial when selecting the appropriate fittings.
Key Industrial Applications of precision turning of steel parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Precision Turning of Steel Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of precision-engineered components like fittings and connectors | Ensures reliability and safety in critical systems | Certification standards (e.g., AS9100) and traceability of materials |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of engine components, such as bushings and camshafts | Enhances performance and longevity of vehicles | Tolerances and material specifications for high-stress applications |
| Medical | Creation of surgical instruments and implants | Guarantees precision and biocompatibility | Compliance with medical standards and material certifications |
| Oil & Gas | Development of valves and fittings for pipeline systems | Increases operational efficiency and reduces leaks | Durability and corrosion resistance in challenging environments |
| Telecommunications | Production of connectors and housings for equipment | Supports high performance and reliability in networks | Quality assurance and adherence to industry standards |
How is Precision Turning of Steel Parts Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, precision turning of steel parts is critical for producing components such as fittings and connectors that must withstand extreme conditions. These parts are engineered to meet stringent safety and performance standards, ensuring reliability in flight. Buyers from regions like Europe, where aerospace regulations are rigorous, need to ensure that suppliers hold certifications such as AS9100, which guarantees adherence to quality management systems specifically for aerospace manufacturing.
What Role Does Precision Turning Play in the Automotive Sector?
Precision turning is vital in the automotive sector for manufacturing engine components, including bushings and camshafts. These components require exact tolerances to function correctly and efficiently, directly impacting vehicle performance and durability. Buyers, especially in South America and Africa, should focus on suppliers that can provide materials that meet industry standards for stress resistance and longevity, ensuring that parts can endure the demanding automotive environment.
Why is Precision Turning Important in Medical Applications?
In the medical field, precision turning is used to create surgical instruments and implants that require high levels of accuracy and biocompatibility. This process ensures that each component meets the specific needs of medical applications, including sterility and strength. International buyers must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that comply with medical regulations and hold certifications like ISO 13485, which guarantees the quality management systems for medical devices.
How is Precision Turning Applied in the Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry relies on precision turning for the production of valves and fittings used in pipeline systems. These components are designed to enhance operational efficiency and minimize the risk of leaks in high-pressure environments. Buyers from the Middle East, a region rich in oil resources, should consider suppliers that offer materials resistant to corrosion and wear, as well as those who can demonstrate a history of reliability in harsh conditions.
What Benefits Does Precision Turning Provide in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, precision turning is essential for producing connectors and housings that ensure high performance and reliability in network systems. These components must be manufactured to exact specifications to support the rapid transmission of data. European buyers, in particular, should seek suppliers who adhere to industry standards for quality assurance and can demonstrate their capability in producing high-volume, precision components that meet the demands of modern telecommunications infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘precision turning of steel parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Control Concerns in Precision Turning of Steel Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with quality control when sourcing precision-turned steel parts. The risk of receiving components that do not meet strict specifications can lead to costly production delays and reputational damage. In industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive, where tolerances are critical, the repercussions of poor quality can be severe. Buyers are often left scrambling to find reliable suppliers who can consistently deliver parts that adhere to stringent standards, leading to frustration and uncertainty.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control issues, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers. Look for manufacturers that are ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100:2016 certified, as these certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality management systems. Engage with potential suppliers through initial consultations to discuss their quality assurance processes and request samples to evaluate their capabilities firsthand. It’s also beneficial to establish clear specifications and tolerances upfront, providing suppliers with detailed drawings and requirements. Regular communication and feedback loops can foster a collaborative relationship that prioritizes quality, ultimately ensuring that you receive components that meet or exceed your expectations.
Scenario 2: Lead Time Challenges Affecting Production Schedules
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience delays in lead times when sourcing precision-turned steel parts, which can disrupt their entire production schedule. These delays can stem from various factors, including inadequate inventory management, inefficient production processes, or unexpected machine breakdowns at the supplier’s facility. When lead times are extended, it can result in missed deadlines, dissatisfied customers, and financial losses.
The Solution: To address lead time challenges, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who offer transparent production timelines and have a proven track record of timely deliveries. Consider suppliers that provide customized stocking solutions to ensure that your most critical parts are readily available when needed. Implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory strategy can also be beneficial, allowing you to reduce inventory costs while ensuring that you have access to parts precisely when required. Regularly reviewing and assessing supplier performance based on delivery metrics can help you make informed decisions about which partners to continue working with, ultimately improving your overall supply chain efficiency.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Custom Precision-Turned Steel Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find suppliers capable of producing custom precision-turned steel parts that meet unique design requirements. This challenge is particularly pronounced in specialized industries where standard parts do not suffice. The inability to source these custom components can lead to project delays and increased costs as buyers are forced to settle for off-the-shelf solutions that may not fit their needs.
The Solution: To effectively source custom precision-turned parts, buyers should partner with manufacturers that have a diverse range of machining capabilities and materials expertise. Look for suppliers that utilize advanced CNC machining technology and can accommodate complex geometries and tight tolerances. Engaging in early-stage design discussions with potential suppliers can facilitate the development of prototypes, allowing for adjustments before full-scale production begins. It’s also advantageous to build long-term relationships with manufacturers who demonstrate flexibility and a willingness to collaborate on custom projects. This approach not only streamlines the sourcing process but also enhances innovation, enabling you to develop unique solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for precision turning of steel parts
What Are the Key Materials Used in Precision Turning of Steel Parts?
When selecting materials for precision turning of steel parts, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right choice can significantly impact product performance, manufacturing complexity, and overall costs. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this process: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and brass.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Precision Turning Applications?
Carbon steel is a widely used material in precision turning due to its excellent machinability and strength. It exhibits good wear resistance and can be heat-treated to enhance its hardness, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive, readily available, and offers a good balance of strength and ductility.
Cons: However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in automotive and industrial applications where high strength is required but may not be suitable for corrosive environments without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A36 or equivalent. In regions like Europe, DIN standards may apply, while in South America, local certifications might be necessary.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Precision Turning?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is ideal for applications requiring hygiene and durability, such as in medical and food processing industries.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and staining, which makes it suitable for a wide range of environments.
Cons: Its higher cost compared to carbon steel and more complex machining requirements can be a drawback.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including food and pharmaceuticals, making it a preferred choice for sanitary applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or JIS G4304 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should be aware of local regulations regarding food safety and medical device manufacturing.
How Do Alloy Steels Enhance Precision Turning Performance?
Alloy steels are engineered with specific elements added to enhance performance characteristics. They provide improved strength, toughness, and wear resistance compared to standard carbon steels.
Pros: The tailored properties of alloy steels make them suitable for specialized applications, including aerospace and automotive components.
Cons: The cost can be significantly higher than that of carbon steels, and the complexity of machining can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Alloy steels are often used in high-performance applications where enhanced strength and fatigue resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A304 or equivalent. In Europe, adherence to EN standards is essential, particularly for aerospace applications.
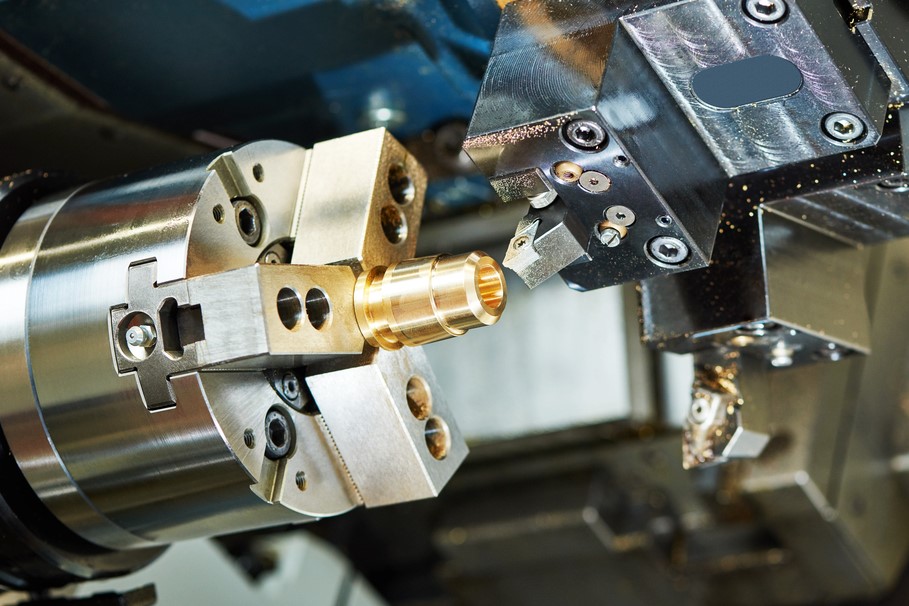
What Role Does Brass Play in Precision Turning?
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used for precision turned parts that require good electrical conductivity.
Pros: Brass is easy to machine, offers good corrosion resistance, and is aesthetically pleasing, making it suitable for decorative applications.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
Cons: However, it is generally less strong than steel and can be more expensive.
Impact on Application: Brass is ideal for fittings, connectors, and other components where electrical conductivity is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 or JIS H3250 is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of brass grades in their region, as it may vary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Precision Turning
| Material | Typical Use Case for precision turning of steel parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive and industrial components | Good strength and machinability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical and food processing applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Alloy Steel | Aerospace and automotive high-performance parts | Enhanced strength and toughness | Higher cost and complex machining | Med |
| Brass | Electrical fittings and decorative components | Excellent machinability and aesthetics | Lower strength compared to steel | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in various international markets, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and compliance requirements.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for precision turning of steel parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Precision Turned Steel Parts?
Manufacturing precision turned steel parts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality components.
How Is Material Prepared for Precision Turning?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which is crucial for achieving the desired precision and quality. Steel is typically sourced in the form of bars or rods that meet specific grade requirements. Before machining, these materials undergo inspection to confirm their properties, such as hardness and tensile strength.
Following inspection, the steel is cut to appropriate lengths for turning. This step may also involve surface cleaning to remove any contaminants that could affect machining accuracy. Proper material preparation not only ensures the reliability of the finished product but also extends the life of the machining tools used in subsequent processes.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Precision Turning?
The forming stage predominantly utilizes CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning machines, which are essential for achieving high precision in the shaping of steel parts. CNC machines allow for complex geometries and tight tolerances, with capabilities to handle various operations, including:
- Turning: The primary operation where the steel is rotated against a cutting tool to shape it into the desired form.
- Boring: Used to enlarge existing holes, ensuring they meet specific diameter and finish requirements.
- Threading: Precision threading ensures that components fit together seamlessly, which is critical for applications in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Additionally, secondary processes such as drilling and milling may be employed to add features like slots or holes that enhance the functionality of the parts.
How Are Steel Parts Assembled and Finished?
Once the turning process is complete, parts may undergo assembly if they are part of a larger component or system. This can involve the integration of multiple turned parts into assemblies that require precise alignment and connection.
Finishing is the final stage and is vital for achieving the required surface quality and aesthetics. Common finishing techniques include:
- Deburring: Removing sharp edges or burrs created during machining.
- Polishing: Enhancing surface smoothness for improved aesthetics and functionality.
- Coating: Applying surface treatments such as anodizing or plating to improve corrosion resistance and wear properties.
These finishing processes not only improve the appearance of the parts but also enhance their performance in demanding environments.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Precision Turned Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for precision turned parts. B2B buyers should be familiar with the various QA practices that ensure the components meet international standards and specific industry requirements.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
For precision turned components, compliance with international standards is paramount. The most recognized standards include:
- ISO 9001: A quality management standard that outlines criteria for an effective quality management system (QMS). It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- AS9100: An extension of ISO 9001, specifically tailored for the aerospace industry, focusing on safety and reliability.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the reliability and quality of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances and quality requirements. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process, including regular inspections of dimensions and surface finishes.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of finished parts before shipment, including functional tests and surface quality assessments.
These checkpoints help in early detection of defects, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the customer.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. Here are several strategies:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should request:

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
- Quality Management System Documentation: Ensure suppliers have robust QMS in place.
- Audit Reports: Review results from previous audits to assess compliance with international standards.
- Certificates of Compliance: Check for relevant certifications that affirm the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence in Supplier Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s capabilities. This can include:
- Pre-shipment Inspections: Ensuring that products meet specified standards before leaving the supplier’s facility.
- Random Sampling Inspections: Verifying the quality of a batch of products to ensure consistency across large orders.
Third-party inspections can significantly reduce risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where quality assurance practices may vary.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding regional nuances in quality assurance is critical. Here are some considerations:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality and standards. Familiarize yourself with the local manufacturing culture to better assess supplier capabilities.
- Logistical Challenges: Ensure that your suppliers can provide consistent quality despite potential logistical issues. This includes understanding how transportation may affect product integrity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different markets may have specific regulations that impact manufacturing processes. Ensure that your suppliers are compliant with all relevant local and international regulations.
By prioritizing these quality assurance practices and understanding the manufacturing processes involved, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing precision turned steel parts, ensuring that they receive reliable, high-quality components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘precision turning of steel parts’
In the competitive landscape of precision manufacturing, sourcing high-quality steel parts through precision turning requires a systematic approach. This checklist aims to guide B2B buyers through the essential steps to ensure they procure reliable, high-performance components that meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first step in the sourcing process. This includes defining tolerances, dimensions, surface finishes, and material properties. Precise specifications help potential suppliers understand your needs and provide accurate quotes, minimizing the risk of miscommunication and subsequent product failures.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong reputation in precision turning. Look for manufacturers that specialize in steel components and have experience in your industry. Utilize platforms such as industry directories, trade shows, and online reviews to gather insights and feedback from other buyers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with any supplier, verify their certifications and quality management systems. Look for ISO 9001:2015 or AS9100:2016 certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Certifications ensure that the supplier maintains rigorous quality control processes, which is critical for precision parts.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their precision-turned steel parts. This allows you to assess the quality of their work firsthand. Evaluate the samples against your specifications, focusing on aspects such as finish, tolerances, and overall craftsmanship.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Delivery Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s lead times and delivery capabilities is essential for effective supply chain management. Discuss their production capacity and how they handle fluctuations in demand. Reliable delivery schedules can significantly impact your project timelines and overall efficiency.
Step 6: Inquire About After-Sales Support and Warranty Policies
Effective communication and support after the sale are critical to a successful partnership. Inquire about the supplier’s after-sales services, including technical support and warranty policies. A supplier committed to customer satisfaction will help resolve issues swiftly and maintain a long-term relationship.
Step 7: Compare Quotes and Negotiate Terms
After gathering all necessary information, compare quotes from different suppliers. While price is an important factor, consider the overall value, including quality, reliability, and service. Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that align with your budget and expectations, ensuring that you receive the best possible deal without compromising quality.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for precision-turned steel parts, ensuring they partner with suppliers that meet their technical and operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for precision turning of steel parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Precision Turning of Steel Parts?
Understanding the cost structure of precision turning of steel parts is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of steel type significantly influences costs. High-strength alloys or stainless steel, for example, are more expensive than standard carbon steel. Bulk purchasing can lower material costs, but quality must be maintained.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial in precision machining. Labor costs vary by region; for instance, skilled labor in Europe may command higher wages compared to regions in South America or Africa. Efficient training and retention strategies can help manage these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Advanced CNC machines may have higher initial costs but can lead to lower per-part costs through increased efficiency.
-
Tooling: The tooling required for precision turning, including custom jigs and fixtures, can be a significant upfront investment. Consideration of tooling longevity and maintenance can impact overall costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential to ensure product consistency. However, these processes can add to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 can also entail additional expenses but can enhance marketability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping can vary widely depending on the origin and destination. International shipping costs can be mitigated by negotiating Incoterms that favor the buyer, such as DDP (Delivered Duty Paid), which can simplify logistics.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically factor in their desired profit margin, which can vary based on the complexity of the parts and market competition. Transparency in pricing can lead to better negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence pricing in the precision turning market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order quantities often lead to lower unit prices. Establishing a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) with suppliers can be beneficial for both parties.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom components require specialized processes that can increase costs. Providing clear specifications can help suppliers offer more accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of material not only affects the cost but also the properties of the finished product. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between material cost and performance.
-
Quality/Certifications: Components that meet specific industry certifications may cost more. Buyers in sectors like aerospace or medical must prioritize quality over cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can significantly affect pricing. Long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers can yield better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international shipping. Choosing terms that minimize risk and clarify responsibilities can help manage costs effectively.
What Are Essential Tips for Negotiating Prices in International B2B Sourcing?
When negotiating pricing for precision turning of steel parts, consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price and consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime costs. This approach can justify paying a slightly higher price for superior quality.
-
Negotiate for Better Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and pricing based on long-term commitments. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that suppliers may have different pricing strategies based on local market conditions. Understanding these nuances can aid in negotiations.
-
Conduct Market Research: Familiarize yourself with market rates for similar components in different regions. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices mentioned in discussions surrounding precision turning of steel parts are indicative and may vary based on specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier capabilities. Always request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and to verify quality standards.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing precision turning of steel parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Precision Turning of Steel Parts
When evaluating manufacturing processes for steel parts, precision turning is a widely adopted method due to its accuracy and efficiency. However, various alternatives can also achieve similar outcomes, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. This section provides a comparative analysis of precision turning against two viable alternatives: CNC machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Precision Turning of Steel Parts | CNC Machining | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and tight tolerances | Very high precision; versatile materials | Moderate precision; suitable for complex geometries |
| Cost | Moderate to high; depends on volume | Can be high; setup costs can be significant | Generally lower for small batches; high for large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup time varies | Requires specialized skills; longer setup times | User-friendly; minimal setup required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance for machines; high reliability | Maintenance-intensive; downtime can be costly | Low maintenance; depends on printer type |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of high-precision components | Custom parts, prototyping, and high-volume production | Prototyping, complex geometries, and low-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machining
CNC machining stands as a robust alternative to precision turning, providing exceptional precision and the ability to work with a diverse range of materials. The process employs computer-controlled machines to create parts from various blocks of material, making it highly versatile for different applications. However, the initial setup costs can be high, and the process can be time-consuming, particularly for complex designs. Additionally, while CNC machining offers high precision, it may not achieve the same level of tight tolerances that precision turning does.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, represents a revolutionary approach to creating parts layer by layer. This method is especially advantageous for producing complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods. The ease of implementation is a significant benefit, as it typically requires less specialized knowledge and has minimal setup time. However, the precision achieved with 3D printing is often lower than that of precision turning, making it less suitable for applications where tight tolerances are critical. Additionally, while costs can be lower for small batch production, larger quantities may not be economically viable.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right manufacturing process for steel parts depends on various factors, including production volume, required precision, and budget. Precision turning is ideal for high-volume production where tight tolerances and surface finishes are paramount. CNC machining is preferable for custom parts and prototypes, offering versatility and high precision, albeit at a higher cost and longer lead times. On the other hand, additive manufacturing shines in scenarios requiring complex designs and rapid prototyping, especially when dealing with small quantities. B2B buyers must assess their specific needs against the strengths and weaknesses of each method to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for precision turning of steel parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Precision Turning of Steel Parts?
In the precision turning of steel parts, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring high-quality outcomes that meet industry standards. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade defines the composition and characteristics of the steel used in production. Common grades include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering different strengths, corrosion resistance, and machinability. B2B buyers must select the appropriate grade to ensure that the final product meets the performance requirements of its intended application, whether in automotive, aerospace, or industrial machinery. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in a part’s dimensions. Precision turned components typically require tight tolerances, often within ±0.001 inches or tighter. This specification is critical for ensuring that parts fit and function correctly in assemblies. Understanding tolerances helps B2B buyers assess manufacturing capabilities and ensures that their components will meet operational standards without costly reworks. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a turned part affects its aesthetic appeal, performance, and durability. Common finishes include rough, polished, and anodized, measured in microinches (µin). A smoother finish can enhance corrosion resistance and reduce friction in moving parts. Buyers need to specify the desired surface finish to align with functional requirements and industry standards. -
Diameter Range
The diameter range indicates the minimum and maximum sizes of parts that can be produced through precision turning. This can vary from small components (e.g., 0.030 inches) to larger ones (e.g., 2.50 inches). Knowing the diameter range helps buyers understand the capabilities of their suppliers and ensures that the parts can be manufactured to their specifications. -
Production Volume
This specification refers to the quantity of parts that can be manufactured in a single run. B2B buyers often seek suppliers that can accommodate varying production volumes, from small batches for prototypes to large-scale orders for mass production. Understanding the production volume helps in planning inventory and managing costs effectively.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Precision Turning?
Navigating the world of precision turning involves familiarizing oneself with essential industry jargon. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding the role of OEMs is vital for buyers looking for custom solutions and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers to know as it impacts budgeting and inventory management. Suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs, material availability, and logistical considerations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of parts. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk, and responsibility, ensuring smoother transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the finished products. Understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management, enabling buyers to plan production schedules and inventory levels accordingly. -
Secondary Operations
These are additional processes applied to a turned part after the primary machining operation, such as drilling, threading, or surface treatment. Knowing about secondary operations helps buyers appreciate the full capabilities of their suppliers and the potential for customization in their components.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in precision turning of steel parts.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the precision turning of steel parts Sector
What Are the Current Trends Shaping the Precision Turning of Steel Parts Market?
The precision turning of steel parts sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. First, the rising demand for high-quality, durable components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical is propelling manufacturers to adopt advanced CNC turning technologies. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only superior quality but also competitive pricing and quick turnaround times. Emerging technologies such as automation and Industry 4.0 are transforming traditional manufacturing processes, enabling companies to improve efficiency and reduce lead times significantly.
Another critical trend is the shift towards customization. International buyers, particularly from emerging markets in Africa and South America, are seeking bespoke solutions that meet their specific requirements. This has led to a surge in demand for precision turned parts that can accommodate complex geometries and tight tolerances. Additionally, the integration of digital tools for supply chain management is enhancing transparency and collaboration among stakeholders, allowing buyers to make more informed decisions.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies, which can affect sourcing strategies. For instance, European buyers may need to navigate tariffs and trade agreements that impact the cost and availability of steel parts sourced from other regions. In this context, understanding local market conditions and establishing strong supplier relationships are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring a steady supply of precision components.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Precision Turning of Steel Parts Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the precision turning of steel parts industry. Environmental concerns related to steel production, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, are driving companies to adopt greener practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, as this can enhance their own brand reputation and comply with regulatory requirements.
One of the ways companies can showcase their commitment to sustainability is through the use of certified materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to sustainable sourcing practices are becoming essential for suppliers. Additionally, using recycled steel or eco-friendly lubricants in the precision turning process can significantly reduce the environmental footprint.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
Ethical sourcing also extends to labor practices and supply chain transparency. Buyers are more inclined to partner with suppliers who uphold fair labor practices and provide visibility into their supply chains. This not only helps in mitigating risks associated with labor exploitation but also aligns with the values of socially conscious consumers and businesses.
How Has the Precision Turning of Steel Parts Evolved Over Time?
The precision turning of steel parts has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, traditional manual turning methods dominated the industry, which limited the complexity and precision of components. However, the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining revolutionized the sector by enabling high-speed production of intricate parts with exceptional accuracy.
As industries have become more reliant on automation and sophisticated manufacturing processes, the precision turning sector has adapted accordingly. The rise of multi-spindle and CNC Swiss machines has expanded production capabilities, allowing manufacturers to produce a wider range of components efficiently. This evolution has not only improved the quality of precision turned parts but has also made it feasible to meet the growing demand for customized solutions across various industries.
Today, the precision turning of steel parts is characterized by a focus on sustainability and ethical practices, alongside continuous innovation in technology. This transformation is essential for meeting the complex demands of modern industries while ensuring responsible production methods.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of precision turning of steel parts
-
1. How do I ensure the precision and quality of turned steel parts?
To ensure high precision and quality in turned steel parts, choose suppliers with ISO certifications like ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100:2016, which indicate adherence to quality management systems. Request detailed specifications, including tolerances and surface finishes, and ask for samples or prototypes to assess quality. Regular audits and quality checks during the manufacturing process can further ensure that your requirements are met consistently. Engaging in direct communication with the supplier’s engineering team can also facilitate understanding of technical requirements and potential issues. -
2. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier for precision turning of steel parts?
When selecting a supplier, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including machinery and technology used, to ensure they can handle your specific requirements. Consider their experience in your industry, customer reviews, and case studies that demonstrate their reliability and quality. Additionally, assess their ability to provide customization options, lead times, and logistical support. Finally, ensure they have robust quality control processes and certifications, which are critical for maintaining the standards you need. -
3. What customization options are typically available for precision turned steel parts?
Customization options for precision turned steel parts often include variations in dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. Suppliers may offer different material grades and types, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel, depending on your application needs. Additional custom features, such as threading, grooves, or specific coatings, can also be incorporated. Discuss your project requirements with the supplier’s engineering team to explore all available customization possibilities and ensure the final product meets your specifications. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for precision turned steel parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for precision turned steel parts can vary significantly by supplier and project specifics. Many manufacturers may set MOQs based on production efficiency and cost-effectiveness, often ranging from 100 to several thousand pieces. For high-volume orders, you may be able to negotiate lower MOQs. Always confirm the MOQ with your supplier upfront to avoid any surprises and ensure your order aligns with your production needs. -
5. How do payment terms typically work in international B2B transactions for precision turned parts?
Payment terms in international B2B transactions often depend on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the order. Common terms include upfront deposits (usually 30% to 50% of the total cost) followed by the balance upon delivery or prior to shipment. Some suppliers may also offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to ensure mutual understanding and avoid disputes. -
6. What quality assurance processes should I expect from a precision turning supplier?
Reputable precision turning suppliers typically implement a series of quality assurance processes, including in-process inspections, final quality checks, and adherence to industry standards. Look for suppliers that utilize statistical process control (SPC) and automated inspection technologies to maintain consistent quality. Additionally, ask for documentation of their quality management system, including how they handle defects and non-conformance issues, to gauge their commitment to quality. -
7. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing precision turned parts internationally?
When sourcing precision turned parts internationally, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to meet your delivery timelines and their experience in handling international logistics. It’s also crucial to understand import duties, taxes, and compliance with local regulations in your country. Establish clear communication regarding shipping terms (like Incoterms) to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth delivery. -
8. How can I build a long-term partnership with a precision turning supplier?
Building a long-term partnership with a precision turning supplier involves open communication, trust, and collaboration. Start by clearly defining your expectations and requirements, and provide constructive feedback on their performance. Regularly engage in discussions about potential improvements, new technologies, and market trends. Establishing mutual goals and maintaining transparency in transactions can help foster a strong working relationship that benefits both parties in the long run.
Top 8 Precision Turning Of Steel Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tuofa – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Precision turned parts are manufactured through the turning process, characterized by tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. Key characteristics include the ability to achieve tight tolerances, ease of machining complex geometries, and suitability for various materials. The precision turning process involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, typically using CNC ma…
2. Makerverse – Custom Steel Turned Parts
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Custom steel turned parts with fast lead times and full quality control. Types include shafts, bushings, and housings. Materials available: Mild steel (1.0038 / S235JR), Alloy steel (42CrMo4), Stainless steel (1.4301 / 304, 1.4404 / 316L). Capabilities include precision turning with diameters up to 300 mm, lengths up to 1000 mm, tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm, and surface finishes down to Ra 0.8 …
3. Groov-Pin – Precision Turned Components
Domain: groov-pin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Precision Turned Components manufactured by Groov-Pin Corp. include high-end, close-tolerance precision machined components for various industries such as Aerospace, Energy, Medical, Defense & Law Enforcement, Farming & Irrigation, and Telecommunications. The components are produced in diameters ranging from 0.030″ to 2.50″ and in quantities from 100 to over 10 million pieces. They are made from m…
4. Screw Machine Products – Precision Turned Components
Domain: screw-machine-products.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Precision turned products are manufactured to meet the highest standards and tolerances required by modern industry. Various turning processes are utilized to produce components that are complex and precise. Key types of precision turned products include:
1. **Fittings**: Used as connectors to join two or more pieces securely, made from materials like copper, cast iron, steel, brass, aluminum, an…
5. Freeway Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: freewaycorp.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components and CNC turned parts manufacturing in the USA. High-quality precision turned parts tailored to specifications. Over 30 multiple spindle automatic screw machines and CNC single-spindle turning centers. Capable of machining up to 2 5/8″ round and 2 5/16″ hex materials. CNC lathes handling up to 2 7/8″ bar stock and chucking up to 7″ blanks. Secondary machining operations …
6. Avantie Engineering – High-Volume Precision Turned Parts
Domain: avantiengineering.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: High-volume precision turned parts are components manufactured using advanced CNC and automatic screw machines for large quantities with tight tolerances. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, carbon and alloy steels, and plastics. Industries served include automotive (fuel system components, fittings, connectors), aerospace (fasteners, bushings, structural components)…
7. Accio – Precision Turned Components
Domain: accio.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Accio – Precision Turned Components, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Protolabs – CNC Turning Service
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Service offers cost-efficient machined parts for rapid prototyping and end-use production with lead times as fast as 1 day. The service utilizes a CNC lathe with live tooling, enabling the machining of features such as axial and radial holes, flats, grooves, and slots. It is suitable for functional prototypes and parts with cylindrical features. Protolabs is certified with ISO 9001:201…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for precision turning of steel parts
As the demand for precision-turned steel parts continues to grow, strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical factor for international buyers. By focusing on suppliers who prioritize quality assurance, such as ISO-certified manufacturers, businesses can ensure that they receive components that meet stringent specifications. Understanding the nuances of CNC machining and the importance of material selection can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the final products.
Moreover, collaboration with reliable partners can lead to innovative solutions that address complex design challenges while reducing overall production costs. The ability to source components in varying quantities—from prototypes to large-scale orders—enhances flexibility and responsiveness in a competitive market.
Looking ahead, the landscape for precision turning will likely evolve with advancements in technology and materials. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging trends and to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to lean manufacturing practices. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can not only secure high-quality components but also foster long-term partnerships that drive mutual growth and success. Seize the opportunity to optimize your supply chain today and ensure your business remains at the forefront of the precision engineering industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to precision turning of steel parts
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.