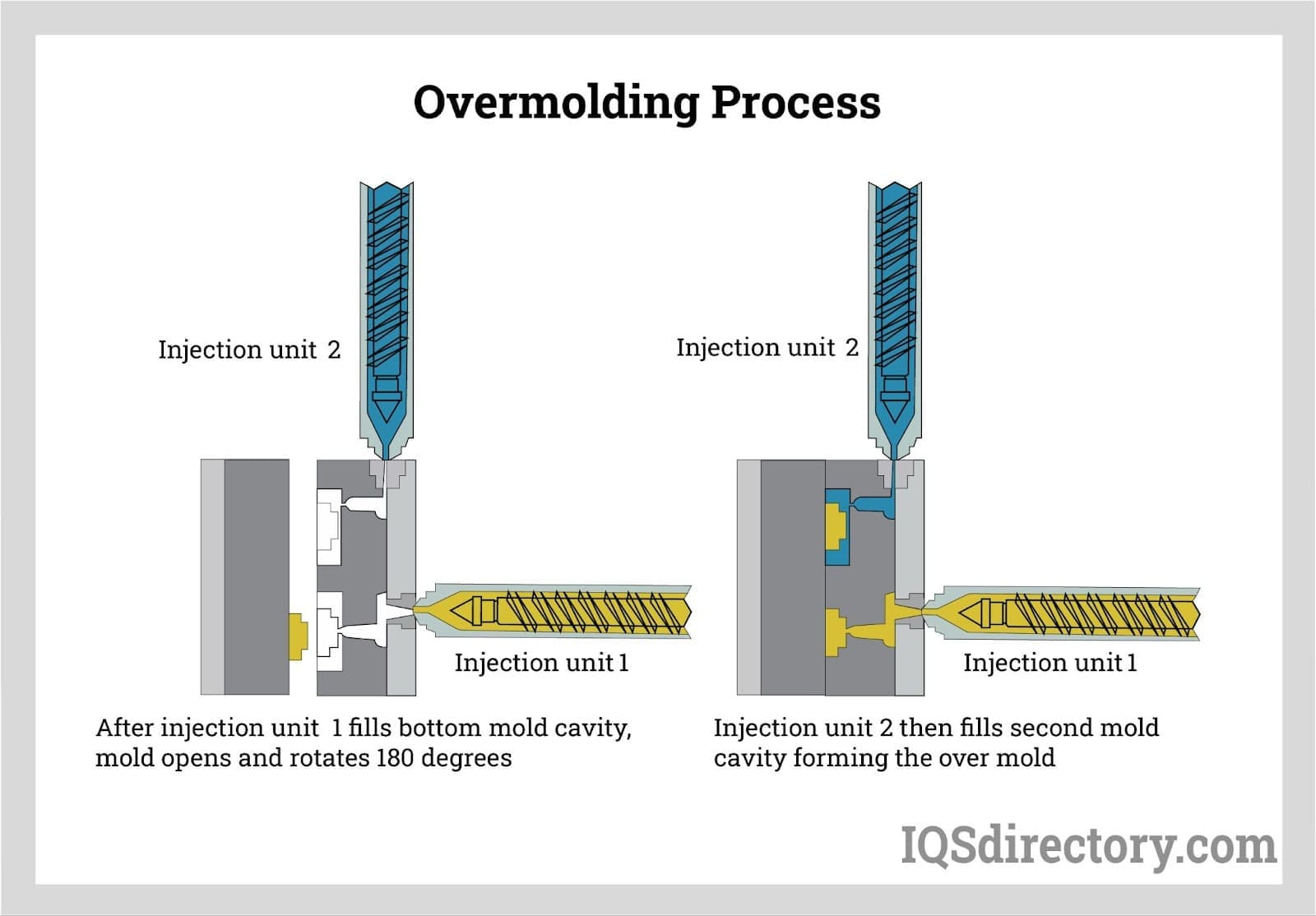
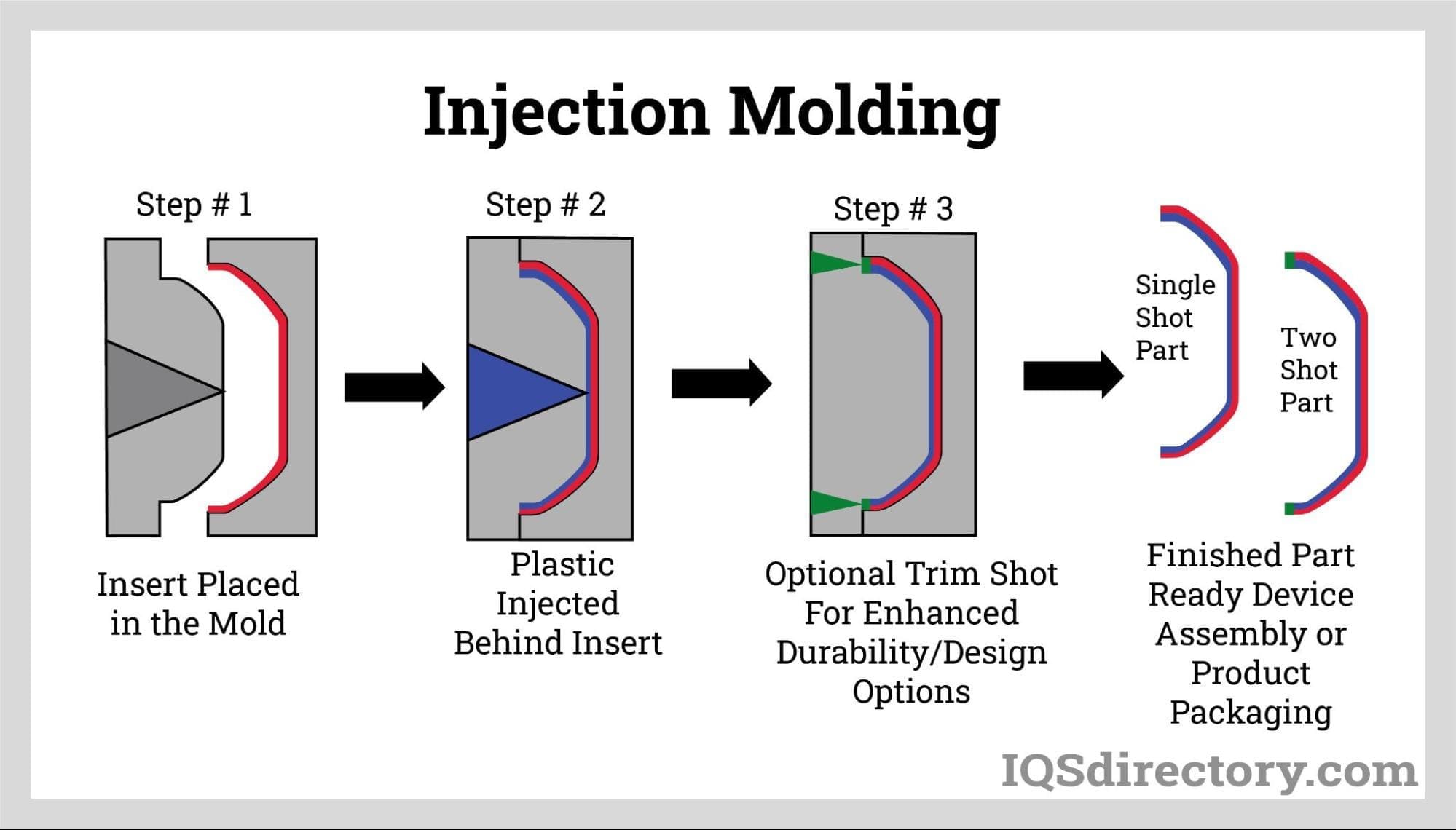
Top 6 Rubber Overmolding Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber overmolding
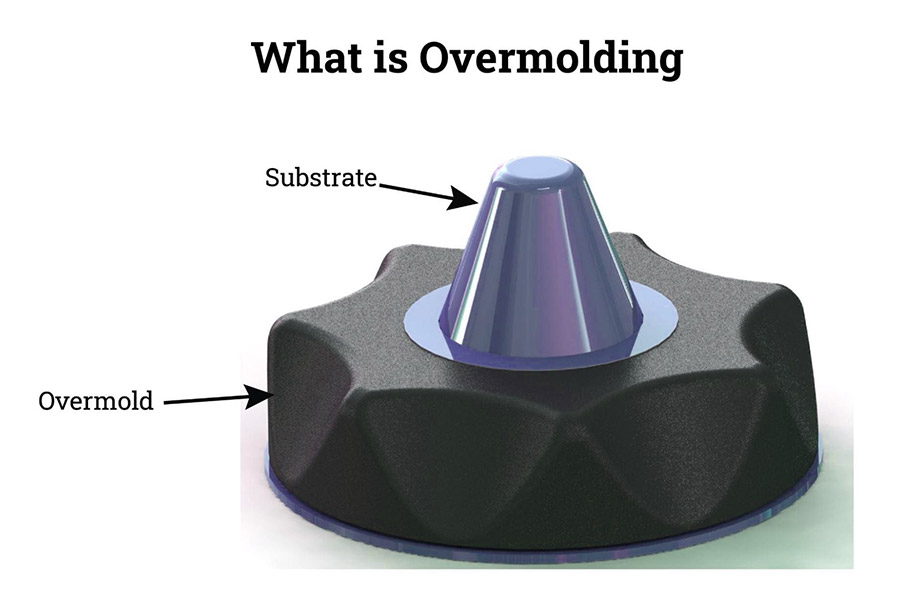
Navigating the complexities of sourcing rubber overmolding solutions can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially when seeking to enhance product functionality and performance. This guide delves into the intricate world of rubber overmolding, a process that merges the durability of various substrates with the adaptability of rubber, catering to diverse applications across industries. Whether you’re involved in manufacturing automotive components, medical devices, or consumer electronics, understanding the nuances of rubber overmolding is crucial for optimizing product design and cost-efficiency.
In this comprehensive resource, we will explore key aspects of rubber overmolding, including various types of materials, molding processes, and applications. Additionally, we will provide insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for achieving high-quality results. By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Brazil and Germany—with actionable information, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Buyers will learn how to identify the right partners and technologies to meet their specific needs, ensuring that their products stand out in a competitive global market.
Understanding rubber overmolding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Overmolding | Uses uncured rubber injected around a substrate | Automotive, electronics, medical devices | Pros: Strong bond, complex shapes; Cons: Higher tooling costs |
| Transfer Overmolding | Premeasured rubber is forced into the mold | Industrial seals, consumer products | Pros: Good for intricate designs; Cons: Longer cycle times |
| Compression Overmolding | Preformed rubber blank is used with heat and pressure | Hand tools, ergonomic grips, seals | Pros: Ideal for rigid materials; Cons: Limited design flexibility |
| Dual-Durometer Overmolding | Combines different rubber hardnesses for varied properties | Medical devices, automotive interiors | Pros: Customizable softness; Cons: More complex production |
| Insert Overmolding | Incorporates metal or plastic inserts for added strength | Aerospace components, high-performance seals | Pros: Enhanced durability; Cons: Requires precise insert design |
What is Injection Overmolding and Its Applications?
Injection overmolding is a process where uncured rubber is injected into a mold containing a substrate, forming a strong bond as the rubber cures. This method is particularly suitable for producing complex shapes and designs, making it ideal for automotive components, electronics, and medical devices. Buyers should consider the higher tooling costs associated with this method, but the benefits of achieving intricate designs and robust bonding often justify the investment.
How Does Transfer Overmolding Work and Where is it Used?
In transfer overmolding, a premeasured amount of rubber is heated and forced into the mold cavity, encapsulating the substrate. This technique is beneficial for applications that require intricate designs, such as industrial seals and consumer products. While it offers good design flexibility, buyers must be aware of potentially longer cycle times, which can affect production schedules.
What Makes Compression Overmolding Unique?
Compression overmolding involves placing a preformed rubber blank into the mold with the substrate and applying heat and pressure. This method is particularly effective for hard or difficult-to-flow rubber materials, making it a popular choice for hand tools, ergonomic grips, and seals. Although it may limit design flexibility, its ability to work with rigid materials makes it a valuable option for manufacturers looking for durability.
What are the Advantages of Dual-Durometer Overmolding?
Dual-durometer overmolding allows for the combination of rubber materials with different hardness levels, providing products with varied tactile properties. This method is highly customizable, making it suitable for applications in medical devices and automotive interiors where comfort and grip are essential. However, the complexity of production can be a drawback, requiring careful design and planning.
Why Choose Insert Overmolding for Strength?
Insert overmolding incorporates metal or plastic inserts into the rubber component, enhancing strength and durability. This process is commonly used in aerospace components and high-performance seals, where precision and reliability are crucial. While the need for precise insert design can complicate the manufacturing process, the resulting robust components offer significant advantages in demanding applications.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber overmolding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber overmolding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Overmolded grips and seals for vehicle components | Enhanced comfort, improved ergonomics, and reduced noise | Compatibility with existing designs, durability standards, and regulatory compliance. |
| Electronics | Rubber overmolded housings for consumer devices | Improved grip, shock absorption, and aesthetic appeal | Material certification, resistance to environmental factors, and design flexibility. |
| Medical Devices | Overmolded handles and seals for surgical instruments | Enhanced user safety, improved ergonomics, and compliance with medical standards | Biocompatibility, sterilization requirements, and precision engineering. |
| Industrial Equipment | Seals and gaskets for machinery and tools | Improved durability, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced performance | Material selection for chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and custom design capabilities. |
| Aerospace | Overmolded seals and components for aircraft systems | Increased reliability, weight reduction, and improved safety features | Compliance with aerospace standards, precision manufacturing, and testing for performance under extreme conditions. |
How is Rubber Overmolding Beneficial in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber overmolding is frequently applied to create grips and seals for various vehicle components such as shifter grips and steering wheels. This process not only enhances user comfort but also contributes to noise reduction and improved ergonomics. For international buyers, especially in regions like Brazil and Germany, sourcing partners must ensure compatibility with existing designs and adherence to durability standards while considering regulatory compliance to meet local automotive industry requirements.
What Applications Exist for Rubber Overmolding in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, rubber overmolding is commonly utilized for device housings, keypads, and buttons, providing improved grip and shock absorption. This enhances the user experience and adds aesthetic value to consumer products. B2B buyers from South America and Europe should prioritize sourcing materials that are certified for environmental resistance and ensure design flexibility to accommodate varying product specifications.
Why is Rubber Overmolding Critical for Medical Devices?
Rubber overmolding plays a vital role in the medical device industry by enhancing the ergonomics of surgical instruments through overmolded handles and seals. This application not only improves user safety but also ensures compliance with stringent medical standards. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa must focus on biocompatibility and sterilization requirements while seeking precision engineering to guarantee the reliability and safety of medical applications.
How Does Rubber Overmolding Enhance Industrial Equipment?
In industrial settings, rubber overmolding is essential for producing durable seals and gaskets for machinery and tools. These components enhance performance and reduce maintenance costs by providing superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance. B2B buyers should consider sourcing partners who offer custom design capabilities and material selection tailored to specific industrial applications, ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding environments.
What Role Does Rubber Overmolding Play in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, rubber overmolding is used for seals and components that require high reliability and performance under extreme conditions. This application helps reduce weight while enhancing safety features. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with rigorous aerospace standards, prioritize precision manufacturing, and conduct thorough testing to guarantee that overmolded components can withstand the demanding operational environments of aviation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber overmolding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Adhesion Issues in Rubber Overmolding
The Problem: One common challenge faced by B2B buyers involved in rubber overmolding is ensuring strong adhesion between the rubber and the substrate. When producing components such as grips for hand tools or seals for machinery, poor bonding can lead to delamination or failure during use. This not only compromises product performance but can also lead to costly recalls and damage to brand reputation. Buyers must navigate complex material properties and processing conditions, making it essential to achieve optimal adhesion.
Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
The Solution: To overcome adhesion issues, it’s crucial to start with a thorough understanding of both the rubber and substrate materials. Buyers should prioritize working closely with suppliers to select the appropriate elastomer that matches the performance requirements of their application. For metal substrates, consider incorporating mechanical bonding features like holes or grooves, which enhance the surface area for the rubber to grip onto. For plastic substrates, applying a chemical bonding agent before molding can significantly improve adhesion. Additionally, conducting comprehensive pre-production tests will ensure that the final product meets durability standards, thereby minimizing the risk of failure in the field.
Scenario 2: Managing Production Costs in Rubber Overmolding
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges related to production costs when implementing rubber overmolding processes. The combination of materials, the complexity of designs, and the need for precision can lead to unexpectedly high expenses. This is particularly true for companies in regions like Africa and South America, where budget constraints are prevalent. Without effective cost management strategies, businesses risk reduced profit margins and may struggle to compete in the market.
The Solution: To effectively manage production costs, buyers should engage in value engineering during the design phase. Collaborating with suppliers early in the process allows for identifying cost-saving opportunities without compromising quality. For instance, optimizing part designs to reduce material waste, simplifying mold designs, or choosing alternative rubber compounds that still meet performance criteria can significantly lower costs. Additionally, investing in advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation can enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve overall production output. By strategically evaluating each aspect of the production process, businesses can achieve a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness.
Scenario 3: Navigating Material Selection for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is selecting the right elastomer for specific applications in rubber overmolding. With a wide array of materials available, each offering different mechanical properties, chemical resistances, and temperature tolerances, making the wrong choice can lead to product failures or performance issues. This is especially critical in industries such as automotive and medical devices, where safety and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of material selection, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment for each application. This involves identifying the specific environmental conditions the end product will face, such as exposure to chemicals, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress. Collaborating with material scientists or suppliers who specialize in elastomers can provide valuable insights into which materials will perform best under these conditions. Furthermore, considering dual-material solutions that combine the strengths of two different elastomers may offer enhanced performance for demanding applications. Regularly reviewing and updating material choices based on the latest advancements in elastomer technology can also ensure that products remain competitive and reliable.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber overmolding
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Rubber Overmolding?
When selecting materials for rubber overmolding, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance in specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in rubber overmolding, highlighting their suitability for various industries and regions.
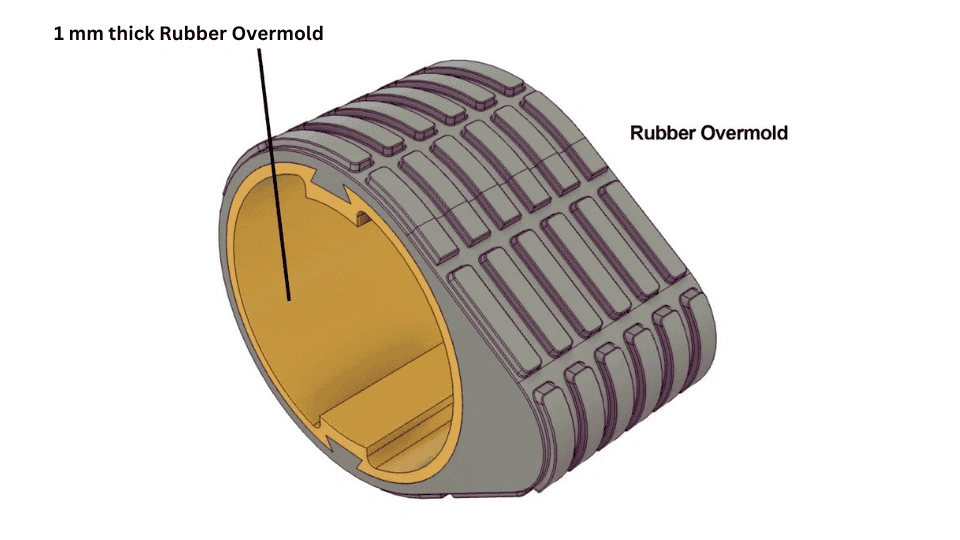
1. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Key Properties: Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other petroleum-based products, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. It has a temperature range of -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 120°C) and is known for its durability under mechanical stress.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of NBR is its high resilience against abrasion and wear. However, it can be less effective in extreme temperatures and is not suitable for applications involving ozone exposure. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it can be processed using standard molding techniques.
Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Impact on Application: NBR is particularly compatible with automotive components, seals, and gaskets that require oil resistance. In regions like Brazil, where oil and gas industries are prevalent, NBR is a preferred choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D2000 standards is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should also consider local certifications for automotive applications.
2. Silicone Rubber
Key Properties: Silicone rubber is known for its exceptional temperature stability, with a range from -100°F to 500°F (-73°C to 260°C). It is also highly resistant to UV light, ozone, and extreme weather conditions.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of silicone rubber is its versatility and ability to maintain flexibility at high temperatures. However, it tends to be more expensive than other elastomers and may not provide the same level of mechanical strength as NBR. The manufacturing process can be complex, particularly for intricate designs.
Impact on Application: Silicone is ideal for medical devices, food processing equipment, and applications requiring high-temperature resistance. In Europe, where stringent health and safety regulations apply, silicone’s compliance with FDA standards makes it an attractive option.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the silicone rubber meets relevant certifications, such as FDA or EU food safety regulations, particularly for applications in the food and beverage industry.
3. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
Key Properties: EPDM is highly resistant to heat, oxidation, and ozone, with a temperature range of -60°F to 300°F (-51°C to 149°C). It also exhibits good resistance to water and steam.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of EPDM is its durability in outdoor applications and resistance to environmental factors. However, it has limited compatibility with petroleum-based products, which can restrict its use in certain industrial applications. Manufacturing complexity is relatively low, making it a cost-effective option.
Impact on Application: EPDM is widely used in roofing, automotive weather seals, and electrical insulation. In regions with high UV exposure, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, EPDM’s weather resistance is particularly beneficial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D1418 and other regional standards is essential for ensuring product quality. Buyers should also consider the specific environmental conditions of their applications.
4. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Key Properties: TPEs combine the properties of rubber and plastic, offering excellent elasticity, flexibility, and chemical resistance. They can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40°F to 212°F (-40°C to 100°C).

Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Pros & Cons: TPEs are favored for their ease of processing and recyclability, making them a sustainable choice. However, they may not provide the same level of high-temperature resistance as silicone or EPDM. The manufacturing process is generally straightforward, allowing for rapid production.
Impact on Application: TPEs are commonly used in consumer products, automotive interiors, and medical devices. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across different markets, including Europe and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that TPEs comply with relevant safety and environmental regulations, especially in the medical and food sectors.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rubber Overmolding
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber overmolding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Automotive seals and gaskets | Excellent oil resistance | Limited temperature range | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices and food processing | High-temperature stability | Higher cost | High |
| Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) | Automotive weather seals | Superior weather resistance | Not oil-resistant | Medium |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Consumer products and automotive interiors | Ease of processing and recyclability | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview to help international B2B buyers make informed decisions about rubber overmolding materials, considering both performance and regional compliance factors.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber overmolding
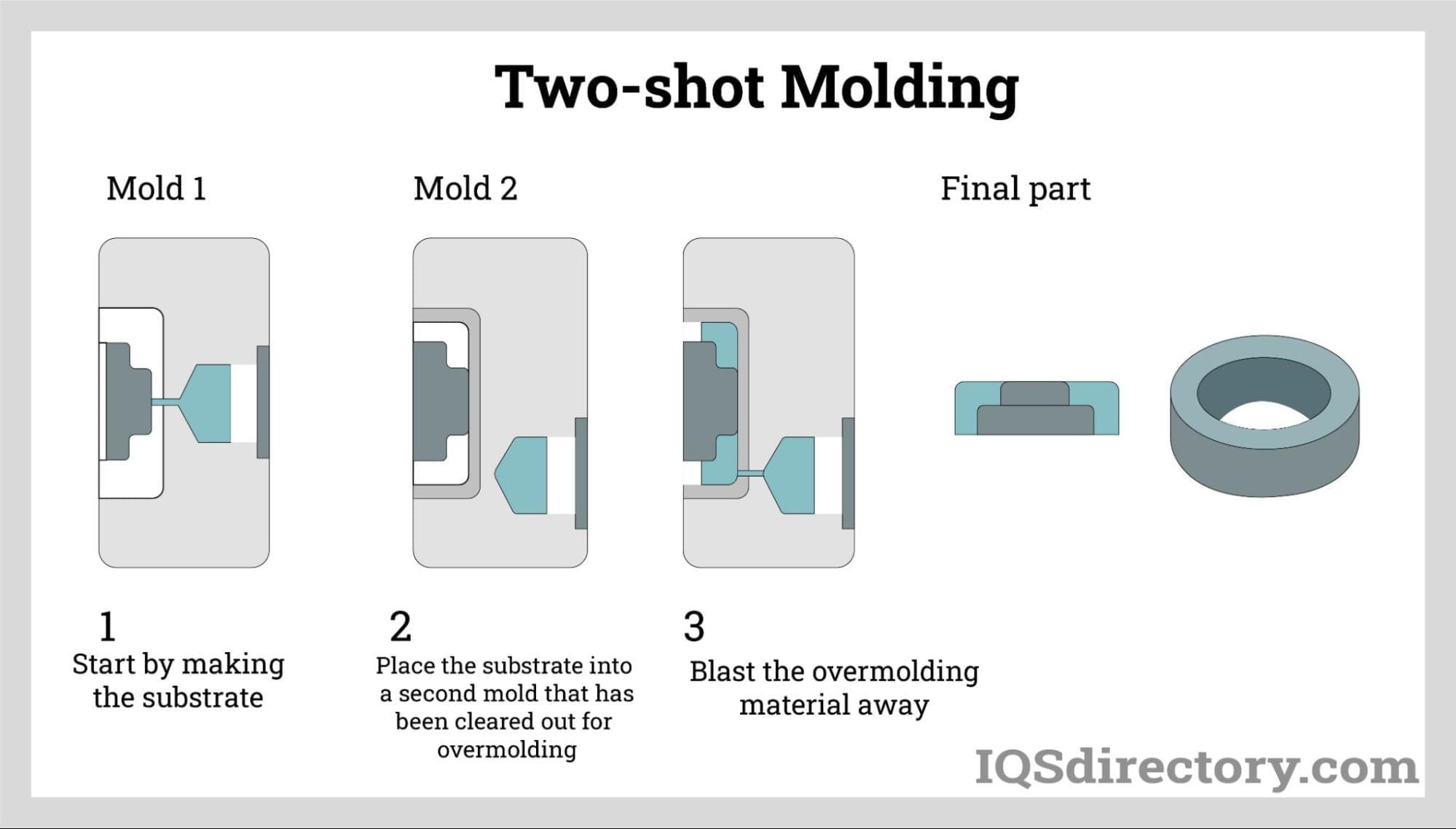
What Are the Main Stages of the Rubber Overmolding Manufacturing Process?
Rubber overmolding is a sophisticated manufacturing process that combines rubber with various substrates to create durable, multi-functional components. The process typically involves four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Overmolding?
Material preparation is crucial in ensuring the quality of the final product. This stage includes selecting the appropriate elastomeric materials based on the application requirements, such as temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and mechanical properties.
Common materials used in rubber overmolding include nitrile, silicone, and polyurethane, each offering unique characteristics suitable for specific applications. For instance, silicone is often selected for medical devices due to its biocompatibility, while nitrile is preferred in automotive applications for its oil resistance.
Before molding, substrates—typically metal or plastic—undergo surface treatment processes such as cleaning and etching. These treatments enhance bonding by improving surface roughness and removing contaminants. Additionally, inserts may be coated with adhesives to facilitate a strong chemical bond with the rubber.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Rubber Overmolding?
The forming stage is where the actual molding of rubber over the substrate takes place. There are three primary techniques employed: injection molding, transfer molding, and compression molding.
-
Injection Molding: This method involves placing the substrate into the mold cavity, followed by injecting uncured rubber into the mold. As the rubber heats and cures, it bonds with the substrate, creating a robust and seamless product.
-
Transfer Molding: In this technique, a premeasured amount of rubber is heated and then forced into the mold around the substrate. This method is particularly effective for intricate designs or when precise control over the rubber flow is necessary.
-
Compression Molding: This technique utilizes a pre-formed rubber blank that is placed into the mold cavity alongside the substrate. Heat and pressure are applied to ensure the rubber conforms to the mold shape, making it ideal for hard or viscous rubber materials.
Each of these methods has distinct advantages, and the choice often depends on the specific application, the complexity of the part, and cost considerations.
What Are the Key Steps in the Assembly and Finishing Processes?
After the molding process, the assembly stage involves integrating the overmolded parts with other components, if applicable. This can include fastening, aligning, or combining with additional parts to create a final assembly. Effective design minimizes the need for additional hardware, reducing assembly time and costs.
Finishing processes, such as deflashing, surface treatment, and quality checks, follow assembly. Deflashing involves removing excess rubber that may have formed during the molding process. Surface treatments, such as polishing or coating, can enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the product, ensuring it meets customer specifications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Rubber Overmolding?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the rubber overmolding process to ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Implementing a robust QA program involves adhering to various industry standards and conducting thorough inspections at multiple checkpoints.

Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Certification to ISO 9001 demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may be relevant. For example, the CE mark is essential for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. In the medical field, certifications from organizations like the FDA or ISO 13485 are critical to ensure safety and efficacy.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Rubber Overmolding?
Quality control (QC) should be integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established for Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular inspections should be conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and curing times. This helps identify any deviations from the process that could affect product quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet design specifications and performance criteria. Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, elongation tests, and hardness tests, which evaluate the mechanical properties of the rubber.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should conduct due diligence to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can include requesting documentation of their QA processes, certifications, and test reports.
Auditing suppliers is another effective method to assess their quality management systems. An audit can help verify compliance with international standards and assess the effectiveness of their QC processes. Additionally, buyers may consider third-party inspections to ensure that the products meet specified requirements before shipment.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances that can impact procurement. Different countries may have varying regulatory requirements, which can influence product specifications and certifications.
For example, products intended for the European market must comply with CE marking requirements, while those for the U.S. market may require FDA approval. Understanding these regulations is essential to ensure that products meet market entry requirements.
Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices and communication styles can affect supplier relationships. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can help mitigate these challenges and foster successful partnerships.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Rubber Overmolding for Global Markets
The rubber overmolding process combines advanced manufacturing techniques with stringent quality assurance measures to produce high-performance components. By understanding the manufacturing stages and quality control practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately enhancing their product offerings in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber overmolding’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing rubber overmolding services effectively, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist to navigate the procurement process. It ensures that your final products meet quality standards while optimizing performance and cost.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for successful rubber overmolding projects. This includes determining the required elastomer material, hardness, and performance characteristics needed for your application. Consider factors such as environmental resistance, mechanical properties, and compliance with industry standards to ensure that the final product meets your operational needs.
Step 2: Identify Suitable Materials
Choosing the right elastomer is essential for the performance and durability of the overmolded component. Evaluate different rubber materials such as silicone, nitrile, or EPDM, based on their specific properties. Consider the application requirements, such as temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, to select the most suitable material.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. Request detailed company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies relevant to your industry. This step helps confirm their capabilities, reliability, and experience in rubber overmolding, which is vital for maintaining quality in your final products.
Step 4: Request Prototypes
Always request prototypes before finalizing your order. Prototyping allows you to assess the fit, functionality, and overall quality of the overmolded components. It’s also an opportunity to test the bonding between the rubber and the substrate, ensuring that the performance meets your expectations and the design specifications.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s important to ensure that your selected supplier has relevant certifications that guarantee compliance with international quality standards. Look for ISO certifications, FDA approvals (if applicable), and other industry-specific certifications. These credentials demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality and safety, which is critical for maintaining your brand’s reputation.
Step 6: Understand the Molding Process
Familiarize yourself with the different rubber overmolding processes—such as injection, transfer, and compression molding. Each method has distinct advantages and is suited for specific applications. Understanding these processes will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and make informed decisions about which method best meets your project requirements.
Step 7: Discuss Production Timelines and Costs
Finally, engage in detailed discussions regarding production timelines and costs. Ask for a breakdown of pricing structures, including tooling, material costs, and any potential additional charges. Understanding the lead times for production will help you align your supply chain effectively and ensure timely delivery of your components.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for rubber overmolding and ensure they are making informed decisions that align with their business goals and product requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber overmolding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Overmolding Sourcing?
When sourcing rubber overmolding, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of elastomeric materials significantly influences costs. Common materials include silicone, nitrile, and polyurethane, each varying in price based on properties such as hardness, temperature resistance, and certifications. Specialty compounds for specific applications, like FDA-approved materials for food-related products, can further increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in molding, assembly, and quality assurance. Skilled labor is often required for precision tasks, particularly when dealing with complex designs or custom specifications, which can drive up labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operation, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, impacting the overall cost.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are significant in rubber overmolding, as custom molds can be expensive. The complexity of the mold design and the materials used also affect pricing. Buyers should consider the longevity and reusability of the molds to maximize their investment.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet required specifications is critical, particularly in regulated industries. The costs associated with QC processes, such as testing and inspection, can vary based on the level of scrutiny required by the buyer.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must be factored into the total cost. Depending on the geographical location of the supplier and the buyer, logistics can vary significantly. Incoterms also play a role in determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s business model, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Overmolding Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in rubber overmolding, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals.

Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) and order volume can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized parts or complex designs typically incur higher costs due to the additional resources required for development and production. Buyers should clarify their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also pricing. High-performance materials may come at a premium, so aligning material choice with application needs is essential.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (e.g., medical or food-grade) generally involve higher costs due to additional testing and compliance measures.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can affect the total landed cost.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Rubber Overmolding?
To navigate the complexities of rubber overmolding sourcing effectively, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions regarding pricing, MOQs, and payment terms. Suppliers often have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and replacement frequency to make a cost-effective decision.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may face unique challenges such as currency fluctuations and customs regulations. Building relationships with local suppliers or freight forwarders can mitigate these issues.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs by component. This transparency can help identify areas for negotiation and potential savings.
-
Be Aware of Indicative Prices: Market conditions can affect pricing, so remain informed about industry trends and fluctuations. Prices provided by suppliers may be indicative and subject to change based on raw material costs and market demand.
By leveraging these insights and strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing rubber overmolding, ensuring they achieve the best value for their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber overmolding With Other Solutions
When considering manufacturing solutions for components that require a combination of durability and flexibility, rubber overmolding stands out as a popular choice. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore viable alternatives that may also meet their specific requirements. This analysis compares rubber overmolding against two other manufacturing methods: plastic overmolding and traditional assembly.
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Overmolding | Plastic Overmolding | Traditional Assembly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent bond strength; superior shock absorption; ergonomic benefits. | Good for lightweight applications; less shock absorption than rubber. | Varies widely; relies on quality of assembly and materials used. |
| Cost | Moderate; higher initial tooling costs but lower assembly costs. | Generally lower; simpler tooling and materials. | Can be lower or higher depending on complexity; labor-intensive. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized molds and equipment; longer lead times. | Easier to implement; often compatible with existing processes. | Can be straightforward but may involve complex logistics. |
| Maintenance | Low; rubber components require minimal upkeep. | Low; generally durable but dependent on material selection. | Varies; may require regular maintenance depending on the assembly method. |
| Best Use Case | High-performance applications needing durability, grip, and shock resistance. | Consumer products where weight savings are important. | General applications where component integration is straightforward. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Plastic Overmolding?
Plastic overmolding involves molding plastic over a substrate, typically to enhance aesthetics and reduce weight. One of its primary advantages is cost-effectiveness due to lower material costs and simpler tooling requirements. Additionally, the process is often easier to implement, allowing for quicker production cycles. However, plastic overmolding may not provide the same level of shock absorption or grip that rubber offers, making it less suitable for applications where these properties are critical.
How Does Traditional Assembly Compare?
Traditional assembly involves joining components using fasteners or adhesives. This method can be highly flexible, allowing for a wide variety of materials and designs. Its cost can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the assembly and the labor involved. While it can be a more straightforward solution, traditional assembly may lead to inconsistencies in quality and performance, particularly if not executed properly. Furthermore, maintenance requirements can be higher, as assembled components may require regular checks and repairs.
Making the Right Choice: Which Solution Is Best for Your Needs?
When selecting the right manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs and constraints. Rubber overmolding is ideal for applications requiring durability, impact resistance, and ergonomic features. Conversely, plastic overmolding may be more suitable for lightweight consumer products, while traditional assembly offers flexibility for simpler applications. Ultimately, the decision should be based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and the desired longevity of the product, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with the strategic goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber overmolding
What Are the Key Technical Properties Essential for Rubber Overmolding?
Understanding the technical specifications of rubber overmolding is crucial for B2B buyers looking to integrate these components into their products. Here are several critical properties:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the elastomer used in rubber overmolding, which impacts performance attributes such as durability, temperature resistance, and flexibility. Common materials include silicone, nitrile, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Selecting the right material grade ensures the final product meets industry standards and functional requirements, which can lead to enhanced product longevity and customer satisfaction.
2. Shore Hardness
Shore hardness measures the hardness of rubber using a durometer scale. This specification is crucial because it determines the rubber’s flexibility and resistance to deformation under stress. For instance, softer grades (e.g., 30 Shore A) are often chosen for ergonomic grips, while harder grades (e.g., 70 Shore A) may be selected for industrial seals. Understanding this property helps buyers select the appropriate rubber for their application, balancing comfort and performance.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the molding process. Tight tolerances are essential for components that must fit precisely, such as seals and gaskets. Specifying the right tolerances ensures compatibility with mating parts and reduces the risk of assembly issues, which can lead to costly production delays and rework.
4. Bonding Strength
Bonding strength is the measure of adhesion between the rubber overmold and the underlying substrate, whether metal or plastic. A high bonding strength is critical for ensuring durability, especially in applications subjected to mechanical stress or environmental exposure. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers who can guarantee strong bonds through proper surface treatment and molding techniques.
5. Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance indicates how well the rubber can withstand exposure to various substances, such as oils, solvents, and detergents. This property is particularly important in industries like automotive and medical, where components may encounter harsh environments. Understanding the chemical compatibility of the selected elastomer can prevent premature failure and enhance product reliability.
6. Temperature Range
The temperature range specifies the operational limits within which the rubber maintains its performance characteristics. Buyers should consider this property, especially for applications exposed to extreme heat or cold. Selecting a rubber that can withstand the intended temperature range ensures that the product performs reliably throughout its lifecycle.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in Rubber Overmolding?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms commonly encountered in rubber overmolding:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in another company’s end product. In rubber overmolding, an OEM may require custom solutions to meet specific functional requirements. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential suppliers capable of delivering tailored products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cost-efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning orders and understanding pricing structures.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate pricing and timelines from potential vendors.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, risks, and insurance, ensuring smoother international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. It is a critical factor in supply chain management, affecting production schedules and inventory levels. Buyers should clarify lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of components.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring rubber overmolding solutions, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber overmolding Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Rubber Overmolding?
The rubber overmolding sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for multi-material components across various industries, including automotive, electronics, and medical devices. Key market drivers include the push for enhanced product performance, where the combination of rigid substrates with flexible rubber enhances durability and user comfort. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide innovative solutions that meet specific functional requirements, such as shock absorption and ergonomic designs.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in the rubber overmolding market. Automation and advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and sophisticated molding processes, are enhancing production efficiency and reducing lead times. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is enabling buyers to connect with global suppliers more easily, fostering competition and driving down costs. The focus on customization is also notable, with clients seeking tailored solutions that fit unique specifications, further fueling the growth of the sector.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Rubber Overmolding Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical focus for B2B buyers in the rubber overmolding sector. The environmental impact of traditional rubber production methods has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and eco-friendly materials. This includes the use of recycled rubber, bio-based elastomers, and adherence to stringent environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Ethical supply chains are essential not only for compliance but also for enhancing brand reputation and customer loyalty. Companies are now seeking certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for ‘green’ materials, which indicate a reduced environmental footprint. By choosing suppliers with these credentials, international buyers can ensure that their sourcing practices align with global sustainability goals, which is becoming a decisive factor in purchasing decisions.
What Is the Historical Context of Rubber Overmolding in B2B Applications?
The evolution of rubber overmolding can be traced back to advancements in polymer science and molding technologies. Initially, the process was limited to simple applications; however, as industries evolved, so did the complexity of rubber overmolding techniques. The introduction of improved bonding methods, such as mechanical and chemical bonding, has expanded the range of applications significantly.
From its early uses in consumer products to its current applications in high-performance industrial components, rubber overmolding has transformed into a critical process for creating durable, multifunctional products. This historical context not only highlights the adaptability of rubber overmolding but also underscores the importance of innovation in meeting the demands of modern B2B buyers. As the sector continues to evolve, understanding its history can provide valuable insights into future trends and opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber overmolding
-
How do I ensure the quality of rubber overmolding components?
To ensure quality, establish a robust supplier vetting process that includes evaluating their certifications, manufacturing capabilities, and previous client feedback. Request samples of their rubber overmolding products to assess the material properties, bonding strength, and overall finish. Additionally, implement a quality assurance protocol that includes inspections at various stages of production, as well as final product testing to verify compliance with industry standards and specific requirements. -
What is the best material for rubber overmolding in high-performance applications?
For high-performance applications, selecting elastomers like silicone or fluorocarbon is often optimal due to their superior temperature resistance, chemical stability, and durability. Silicone rubber is ideal for applications requiring flexibility and resilience, while fluorocarbon offers excellent resistance to aggressive chemicals. Consult with your supplier to understand the specific requirements of your application, including environmental conditions and mechanical stresses, to choose the most suitable material. -
What factors should I consider when customizing rubber overmolding designs?
When customizing designs, consider the functional requirements, such as the desired grip, impact absorption, and environmental exposure. Additionally, pay attention to the geometry of the inserts, ensuring they allow for effective bonding without compromising structural integrity. Discuss potential challenges with your supplier, including mold design, elastomer selection, and production methods, to ensure that the final product meets your specifications and performance standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rubber overmolding?
Minimum order quantities for rubber overmolding can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the project. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. When negotiating with suppliers, consider your production schedule and volume needs. Communicate your requirements clearly to find a supplier that can accommodate your needs without compromising cost-effectiveness. -
How do I handle payment terms when sourcing rubber overmolding products internationally?
When sourcing internationally, discuss payment terms early in the negotiation process. Common terms include a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after passing quality inspections. Consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Ensure that payment terms align with your cash flow and production timelines to maintain smooth operations. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind for importing rubber overmolding products?
Logistics is critical when importing rubber overmolding products. Consider shipping costs, customs duties, and potential delays at borders. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling your specific goods to navigate international regulations and ensure compliance with customs requirements. Additionally, establish a clear timeline for delivery, factoring in production lead times and transit times, to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
How can I verify the capabilities of a rubber overmolding supplier?
To verify a supplier’s capabilities, request detailed information about their manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality control measures. Ask for case studies or references from previous clients in your industry. Conduct a factory visit, if feasible, to assess their operations firsthand. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards, and ensure they can meet your specific production requirements. -
What are the common applications for rubber overmolding in various industries?
Rubber overmolding is widely used across multiple industries, including automotive for interior components and seals, medical for device housings and ergonomic features, and electronics for keypads and grips. Its versatility allows it to enhance product functionality, improve user comfort, and provide protective features. Discuss your application needs with suppliers to explore tailored solutions that leverage the benefits of rubber overmolding for your specific market segment.
Top 6 Rubber Overmolding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Panova – Custom Rubber Overmolding Services
Domain: panova.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Panova offers custom rubber overmolding services that bond rubber onto metal or plastic substrates, enhancing product performance by combining the strength of the substrate with the softness and impact absorption of rubber. Key product applications include: 1. Rubber overmolded handles for tools and devices for improved grip and comfort. 2. High-performance seals that combine metal durability with…
2. IQS Directory – Rubber Overmolding Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Rubber overmolding involves various processes including Injection Molding, Compression Molding, Transfer Molding, Liquid Injection Molding (LIM), and Two-Shot Molding. Key design considerations include material compatibility (with options like TPE, silicone rubber, EPDM, and natural rubber), surface finish (importance of smooth, clean surfaces), tolerances (precise dimensions to ensure proper fit)…
3. Lake Erie Rubber – Custom Rubber Overmolding Solutions
Domain: lakeerierubber.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Lake Erie Rubber specializes in rubber overmolding and rubber to metal bonding, offering custom manufacturing solutions with over 60 years of experience. They utilize injection molding, transfer molding, and compression molding techniques. The rubber overmolding process encapsulates a substrate (often metal) with rubber, creating a bonded part that combines the properties of both materials. They o…
4. Basilius – Overmolding Solutions
Domain: basilius.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Overmolding is an injection molding process that involves molding one plastic (often TPE, a rubber-like plastic) over another component (substrate). Applications include: 1. Grip enhancement for handles, improving safety and grip in wet conditions. 2. Vibration dampening for electronics using rubber bumpers or mounts. 3. Ergonomic comfort through customizable grip shapes. 4. Water-resistant seals …
5. Plasti Dip – Textured Rubber Coating Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The user is looking to add an overmolded rubber coating onto cosplay gun grips and hobby tools. They have previously used Plasti Dip but are seeking a textured surface similar to knurling. They are considering pouring Plasti Dip into a mold but are unsure if it’s suitable. They want a 2-part rubber that is soft enough for comfort but not squishy, with a desired hardness of shore 30. They are also …
6. SIMTEC – LSR Overmolding Solutions
Domain: simtec-silicone.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: SIMTEC offers Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) overmolding solutions with over 20 years of expertise. The LSR overmolding process involves two steps: placing a finished plastic or metal substrate into a specialized mold and injecting LSR material to create an integrated component. Key applications include medical devices (biocompatible and hypoallergenic), automotive seals, consumer goods (water-resis…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber overmolding
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Rubber Overmolding?
In the competitive landscape of rubber overmolding, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial factor for B2B buyers seeking to enhance product performance and reduce costs. By collaborating with reputable suppliers who understand the intricacies of rubber and substrate materials, businesses can ensure high-quality, durable components that meet specific functional requirements. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of selecting the right elastomers and molding processes, as well as integrating design principles that maximize bonding and performance.
As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to evolve, businesses must remain agile in their sourcing strategies. Leveraging the benefits of rubber overmolding can lead to innovative solutions, such as improved ergonomics and enhanced protection for various applications—from automotive to medical devices.
Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies and engage with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions. By prioritizing strategic partnerships in rubber overmolding, businesses can not only meet current market demands but also position themselves for future growth and success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to rubber overmolding
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.