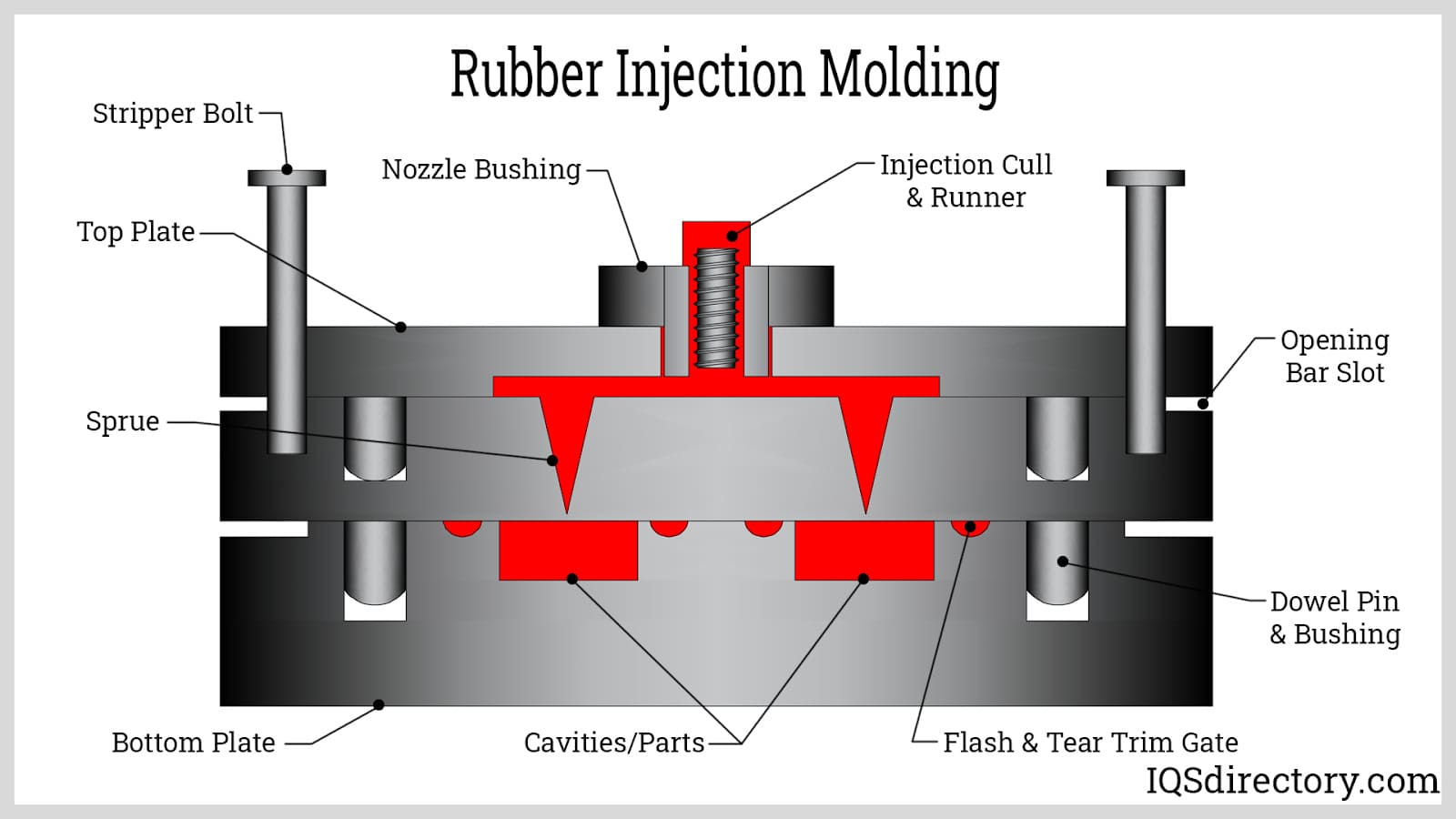
Top 6 Rubber Injection Moulding Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber injection moulding
Navigating the complexities of sourcing high-quality rubber injection moulding components can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on precision-engineered rubber parts for applications ranging from automotive to medical devices, understanding the nuances of rubber injection moulding becomes essential. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the various types of rubber moulding processes, including transfer, compression, and injection moulding, alongside their specific applications and advantages.
In addition to detailing the different moulding techniques, this resource provides insights into effective supplier vetting, cost considerations, and industry best practices. By equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, the guide aims to simplify the procurement process and enhance operational efficiency. Whether you are looking to source customized rubber components or standard products, understanding the intricacies of rubber injection moulding will empower your business to thrive in the competitive global market. With expert insights tailored to the unique needs of buyers in Germany, Saudi Arabia, and beyond, this guide serves as an invaluable tool for navigating the rubber injection moulding landscape.
Understanding rubber injection moulding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Transfer Molding | Uses a closed mold; suitable for intricate designs; multiple cavities | Automotive parts, seals, gaskets | Pros: High precision; reduced cycle times. Cons: More waste; may require complex molds. |
| Rubber Compression Molding | Open mold process; utilizes pre-formed shapes; best for low to medium volumes | O-rings, gaskets, bulkier parts | Pros: Simple setup; strong materials. Cons: Longer curing times; limited to specific shapes. |
| Organic Rubber Injection | Preheats rubber; eliminates pre-forms; efficient for mass production | Consumer goods, automotive components | Pros: Faster cycle times; reduced labor. Cons: Requires precise material preparation. |
| Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection | Utilizes a two-part liquid silicone; closed system reduces contamination | Medical devices, automotive seals | Pros: High purity; quick curing. Cons: Higher initial costs; specialized equipment needed. |
| Thermoplastic Rubber Injection | Similar to plastic injection; recyclable materials; colored options available | Consumer products, automotive applications | Pros: Fast production; easy customization. Cons: Limited to high-temperature applications; not suitable for all rubber needs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Rubber Transfer Molding?
Rubber transfer molding is characterized by its ability to handle intricate designs and multiple cavities within a closed mold system. This process is particularly advantageous for manufacturing parts that require high dimensional tolerances, such as automotive components and seals. B2B buyers should consider the cost of mold creation and the potential for material waste, as leftover rubber must be discarded after the transfer process. However, the precision and efficiency in production make it a popular choice for complex parts.
How Does Rubber Compression Molding Stand Out?
Rubber compression molding is a traditional method that involves placing pre-formed rubber into open molds. It’s ideal for low to medium production volumes, making it suitable for items like O-rings and gaskets. Buyers should weigh the benefits of strong, durable materials against the longer curing times and the necessity for specific mold shapes. This method is often favored for its straightforward setup, but it may not be the best option for high-volume production.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
What Are the Advantages of Organic Rubber Injection?
Organic rubber injection is a modern approach that preheats the rubber before injection, enhancing efficiency and eliminating the need for pre-forms. This method is particularly effective for high-volume production of consumer goods and automotive components. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include the initial setup costs and the need for precise material mixing. The process’s faster cycle times and reduced labor requirements often justify the investment for companies looking to scale.
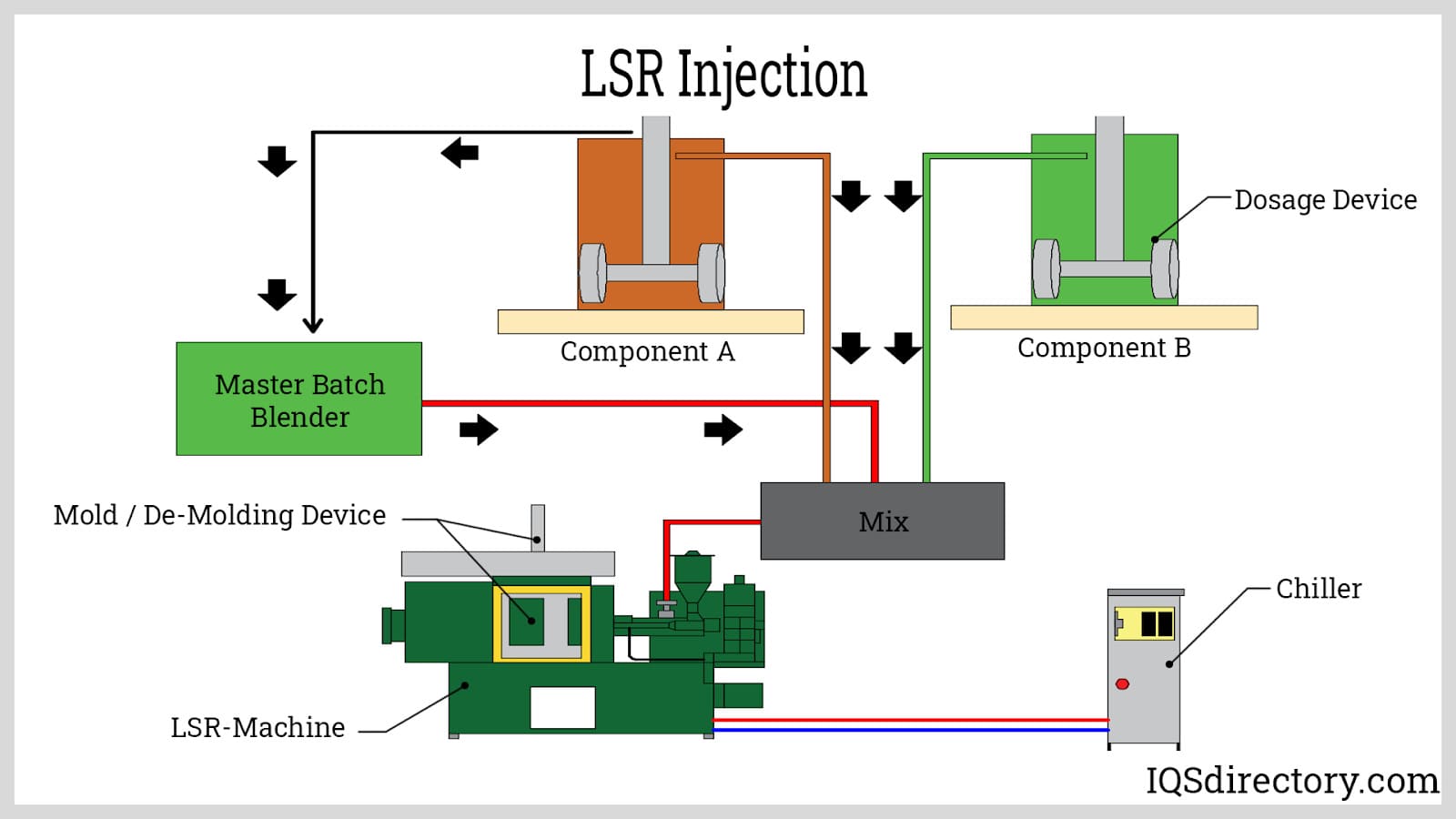
Why Choose Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection?
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection employs a two-part silicone system that minimizes contamination risks through a closed molding environment. This technique is especially beneficial for medical devices and automotive seals, where high purity is essential. B2B buyers must consider the higher initial equipment costs and the specialized nature of LSR systems. However, the quick curing times and high-quality output make it a valuable option for industries requiring reliable and clean components.
What Makes Thermoplastic Rubber Injection Unique?
Thermoplastic rubber injection combines the properties of rubber and plastic, allowing for easy recycling and customization. This method is particularly useful for producing consumer products and automotive applications where color and design flexibility are important. Buyers should be aware that while this process allows for rapid production, it is limited to high-temperature applications. Understanding the specific requirements of their projects will help businesses determine if thermoplastic rubber is the right fit for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber injection moulding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber injection moulding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and gaskets for engine components | Enhanced durability and performance under extreme conditions | Compliance with automotive standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Custom silicone components for surgical instruments | Improved precision and reduced contamination risks | Strict adherence to regulatory requirements (ISO, FDA) |
| Electronics | Insulation and protective casings for components | Increased reliability and safety of electronic devices | Material compatibility with various electronic components |
| Construction | Vibration dampers and expansion joints | Extended lifespan of structures and reduced maintenance costs | Customization for specific structural needs |
| Consumer Products | Non-slip grips and seals for household items | Improved user experience and product longevity | Cost-effective production for high-volume consumer items |
How is Rubber Injection Moulding Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber injection moulding is integral for producing seals and gaskets that prevent leaks in engine components. These parts must withstand high temperatures and corrosive fluids, making durability essential. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with experience in automotive-grade materials that meet industry standards. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers who can guarantee consistent quality and performance will enhance vehicle reliability.
What Role Does Rubber Injection Moulding Play in Medical Devices?
Rubber injection moulding is crucial for creating precise silicone components used in surgical instruments and medical devices. The process allows for the production of intricate shapes that minimize contamination risks, a critical concern in healthcare. International buyers must ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards, such as ISO and FDA certifications, and should seek suppliers who can provide traceability for materials used in their products.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
How is Rubber Injection Moulding Applied in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, rubber injection moulding is used to create insulation and protective casings for various components, enhancing their reliability and safety. The ability to produce parts with complex geometries ensures effective protection against environmental factors. When sourcing, buyers should consider material compatibility with electronic components and the supplier’s ability to produce high-quality parts that meet industry specifications.
What are the Benefits of Rubber Injection Moulding in Construction?
Rubber injection moulding is utilized in construction for producing vibration dampers and expansion joints, which help extend the lifespan of structures. These components mitigate stress caused by movement and vibrations, reducing maintenance costs over time. Buyers should focus on sourcing custom solutions tailored to specific structural requirements and ensure that the materials used can endure the environmental conditions typical in construction applications.
How Does Rubber Injection Moulding Enhance Consumer Products?
In the consumer products sector, rubber injection moulding is essential for creating non-slip grips and seals in household items, enhancing user experience and product durability. The ability to produce these components at scale allows for cost-effective manufacturing. Buyers should seek suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and efficient production processes to meet the demands of high-volume consumer goods.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber injection moulding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality in Rubber Parts Production
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the quality of rubber components produced through injection molding. Inconsistent material properties, such as hardness or elasticity, can lead to parts that do not meet specifications. This inconsistency may arise from variations in raw materials, improper mold design, or errors in the injection process itself. Such quality issues can result in significant production downtime, increased costs, and a tarnished reputation among clients who rely on these components for their machinery or products.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in rubber injection molding, it is crucial to implement a robust quality assurance process. Buyers should begin by partnering with reputable suppliers who use high-quality raw materials and adhere to stringent manufacturing standards. Conducting thorough audits of potential suppliers is essential. Additionally, adopting advanced process controls, such as real-time monitoring of temperature and pressure during injection, can help mitigate variations. Implementing a standardized testing protocol for each batch of produced parts can also verify that they meet the required specifications before they are shipped. Regular feedback loops with suppliers can facilitate continuous improvement and ensure long-term quality consistency.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs for Low Volume Orders
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as automotive or consumer goods encounter high production costs when ordering small quantities of custom rubber parts. Traditional rubber injection molding processes are typically optimized for high-volume production, leading to prohibitive costs for low-volume runs. This creates a dilemma for buyers who need specialized parts without incurring excessive expenses, impacting their overall project budgets and timelines.
The Solution: Buyers should explore alternative molding processes that are better suited for low-volume production, such as compression molding or 3D printing for rubber-like materials. These methods can offer lower initial tooling costs and reduced material waste. Additionally, seeking suppliers who specialize in rapid prototyping and small-batch production can lead to more favorable pricing structures. Collaborating closely with manufacturers during the design phase can also optimize part designs for manufacturing efficiency, thus lowering costs. Finally, leveraging technologies like liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding can provide high-quality results even in smaller quantities, making it a viable option for buyers looking to balance cost and quality.
Scenario 3: Long Lead Times for Custom Rubber Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often experience long lead times when sourcing custom rubber components, which can disrupt their production schedules. These delays may stem from the complexities of mold design, material sourcing, or the injection molding process itself. As businesses strive for agility and responsiveness, any slowdown in acquiring essential components can hinder their ability to meet market demands and fulfill customer orders.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
The Solution: To minimize lead times, buyers should engage in proactive planning and communication with their suppliers. Providing detailed specifications and requirements upfront can streamline the design and prototyping phases. Utilizing a supplier that offers rapid prototyping services can significantly reduce the time from concept to production. Additionally, establishing a clear timeline and milestones with the supplier can help keep the project on track. Buyers may also consider maintaining a small inventory of critical parts or working with suppliers who have a robust inventory management system in place, ensuring that they can quickly respond to orders without compromising on quality or increasing lead times. Regularly reviewing and optimizing the supply chain process can further enhance efficiency and reduce delays in the future.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber injection moulding
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rubber Injection Molding?
When selecting materials for rubber injection molding, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including performance characteristics, cost, and manufacturing complexities. Below, we analyze four common materials used in rubber injection molding, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Properties and Applications of Natural Rubber in Injection Molding?
Natural rubber, derived from latex, is known for its excellent elasticity and resilience. It typically performs well in a temperature range of -50°C to 80°C. Its inherent properties include high tensile strength, good abrasion resistance, and excellent flexibility.
Pros: Natural rubber is highly durable and cost-effective for applications requiring high elasticity, such as seals, gaskets, and vibration dampers. Its manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, making it a popular choice for medium-volume production.
Cons: However, natural rubber has limited resistance to UV light and ozone, which can lead to degradation over time. Its susceptibility to certain chemicals may also restrict its use in specific environments.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is suitable for applications involving water and air, but it may not be compatible with petroleum-based oils or solvents.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D2000 and other international standards is crucial, especially in regulated industries. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should be aware of specific environmental regulations regarding natural rubber sourcing and processing.
How Does Silicone Rubber Perform in Injection Molding Applications?
Silicone rubber is renowned for its high-temperature resistance, typically ranging from -60°C to 200°C, making it ideal for applications in extreme environments. Its chemical stability and flexibility are also notable.
Pros: Silicone rubber is highly resistant to UV light, ozone, and temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for outdoor applications. It is also biocompatible, which is essential for medical device manufacturing.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to natural rubber. Additionally, silicone rubber can be more complex to process, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
Impact on Application: Silicone is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and solvents, and is often used in automotive, aerospace, and medical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that silicone rubber products meet relevant standards such as FDA compliance for medical applications and ISO certifications for industrial uses.
What Advantages and Limitations Does EPDM Rubber Offer in Injection Molding?
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent weather resistance and durability. It typically operates well in temperatures ranging from -50°C to 150°C.
Pros: EPDM is highly resistant to UV light, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as roofing and automotive seals. It also has good electrical insulation properties.
Cons: While EPDM has excellent aging properties, it is less resistant to petroleum-based oils and solvents, which can limit its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: EPDM is suitable for applications involving water and steam but may not be the best choice for environments with exposure to oils.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is essential, particularly for applications in automotive and construction sectors. Buyers should also consider the sourcing of EPDM materials to ensure they meet environmental regulations.
How Does Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) Compare in Injection Molding Applications?
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the properties of rubber and plastic, offering flexibility and ease of processing. It typically operates in a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C.
Pros: TPR is easy to mold and can be recycled, making it a cost-effective option for high-volume production. It also offers good abrasion resistance and is available in various colors.
Cons: The main limitation is its performance in high-temperature applications, where it may not perform as well as other rubber types. Additionally, TPR can be more expensive than traditional rubber options.
Impact on Application: TPR is suitable for consumer products, automotive parts, and toys, where flexibility and aesthetic appeal are important.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with relevant safety and environmental standards, particularly in consumer goods markets in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Rubber Materials for Injection Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber injection moulding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers | High elasticity and cost-effective | Limited UV and chemical resistance | Low |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices, automotive components | Excellent temperature and chemical resistance | Higher cost and complex processing | High |
| EPDM Rubber | Automotive seals, roofing materials | Outstanding weather and UV resistance | Poor resistance to petroleum-based oils | Medium |
| Thermoplastic Rubber | Consumer products, automotive parts | Easy to mold and recyclable | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their rubber injection molding processes. Understanding the properties and applications of these materials will aid in making informed decisions that align with specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber injection moulding
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rubber Injection Moulding?
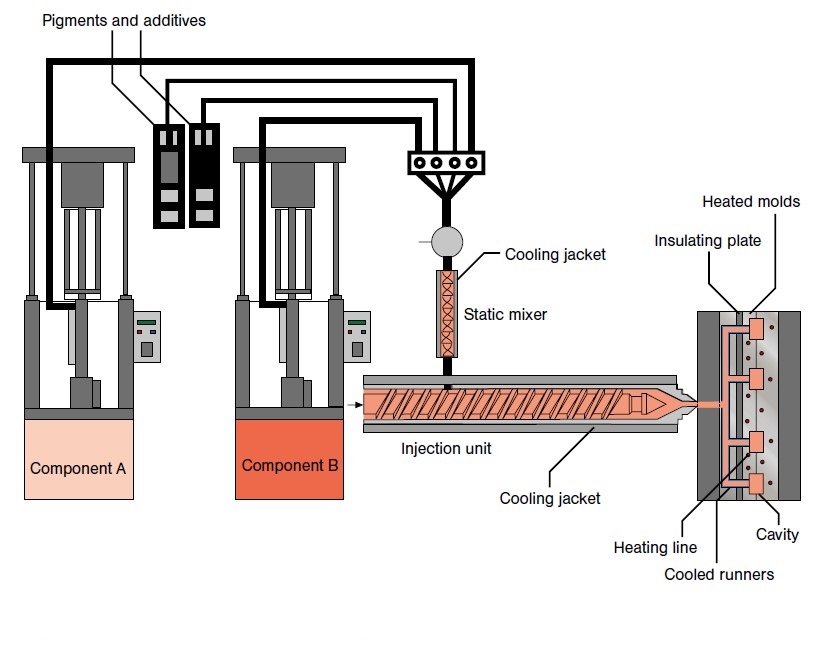
Rubber injection moulding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product meets the necessary quality and performance standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Injection Moulding?
The first stage in the rubber injection moulding process is material preparation. This involves mixing raw rubber compounds to achieve the desired properties. The compounds are typically blended in large quantities and then stripped into continuous strips for efficient feeding into the injection machine.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
Preheating the rubber during this stage reduces its viscosity, allowing for easier flow into the mould cavities. This step is crucial as it eliminates the need for pre-forms, a common requirement in other moulding processes such as compression moulding. By removing this step, manufacturers can significantly reduce labor costs and variability in the final product.
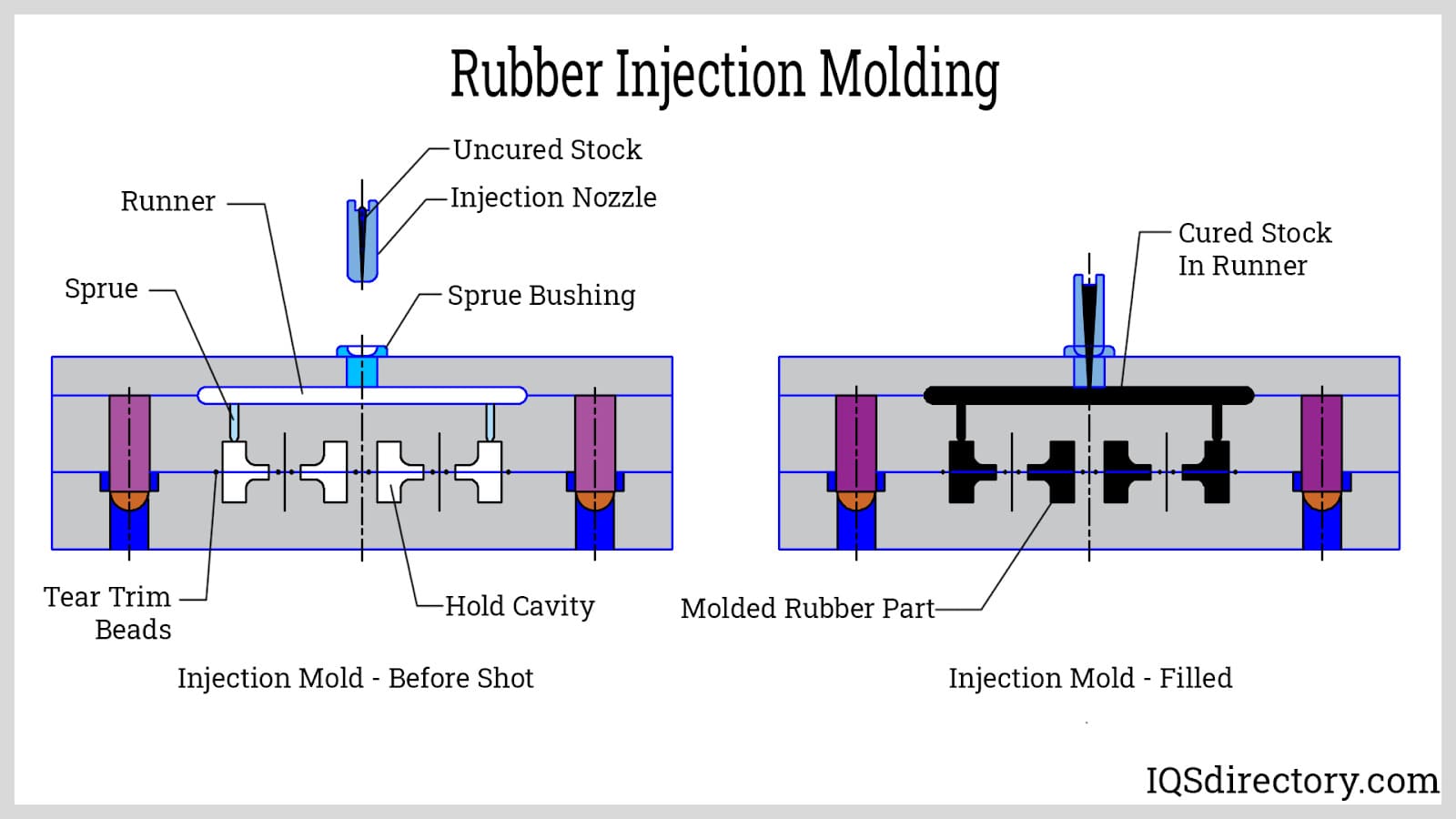
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage is where the actual moulding takes place. In rubber injection moulding, the prepared material is injected into a heated mould under high pressure. This process allows the rubber to fill intricate designs and cavities efficiently, ensuring precise dimensional tolerances.
There are three primary techniques employed in rubber injection moulding:
1. Organic Rubber Injection: Utilizes a screw to inject preheated rubber directly into the mould.
2. Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection: Involves a two-part silicone compound that is mixed, cured, and injected, making it ideal for applications requiring contamination control.
3. Thermoplastic Rubber Injection: Processes elastomers similar to plastics, allowing for recyclability and reduced production time.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
Each method has its unique advantages, making it essential for B2B buyers to choose the right technique based on their specific application requirements.
How Are Components Assembled in Rubber Injection Moulding?
Once the rubber components are formed, they may undergo an assembly process, particularly if they are part of a larger product or system. This stage can involve adding metal parts, fasteners, or other components that enhance the functionality of the rubber parts.
Using advanced techniques such as rubber-to-metal bonding ensures a strong and durable assembly. This method is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where reliability is paramount.
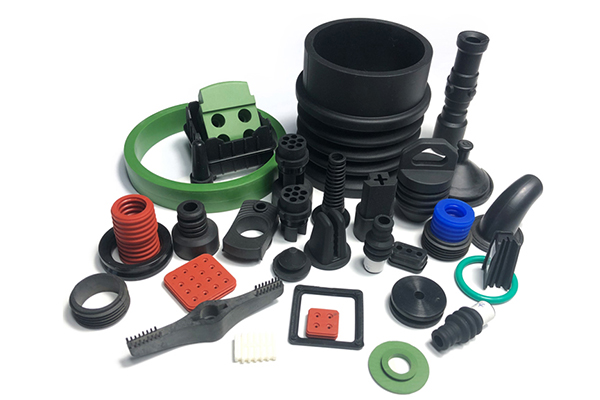

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used?
The finishing stage is essential for enhancing the product’s aesthetics and functionality. This may include trimming excess material, applying surface treatments, or adding color. Quality finishing processes ensure that the rubber parts not only meet functional requirements but also appeal visually to end-users.
Additionally, secondary operations like vulcanization may be employed to improve the rubber’s durability and elasticity.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Rubber Injection Moulding?
Quality assurance is critical in the rubber injection moulding process to ensure that products meet international and industry-specific standards. The most relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization seeking to improve customer satisfaction and product quality.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking ensures that the product complies with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For companies supplying the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products meet specific safety and operational requirements.
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to these standards to mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is implemented throughout the manufacturing process, with several key checkpoints:
Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet specified criteria helps prevent defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is essential. This includes regular checks on temperature, pressure, and material flow to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the production is complete, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet quality standards. Common testing methods include tensile strength testing, hardness testing, and dimensional inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when evaluating suppliers for rubber injection moulding. Here are several effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. This hands-on approach provides valuable insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline the supplier’s QC processes, testing results, and any certifications obtained. This documentation can help buyers assess the reliability and credibility of potential suppliers.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct random checks and audits, ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating quality control can be complex. Key considerations include:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the local business culture can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should be aware of regional practices and standards that may differ from their own.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations concerning product safety and quality. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure market access.
-
Language Barriers: Clear communication is essential for effective quality assurance. Buyers may need to employ translators or bilingual staff to facilitate discussions with suppliers.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can enhance their understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in rubber injection moulding, ultimately leading to better procurement decisions and successful partnerships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber injection moulding’
Introduction
Sourcing rubber injection molding services can be a complex task, particularly for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured checklist to help you navigate the procurement process efficiently. Each step is designed to ensure you find the right supplier and secure high-quality rubber products tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the foundation of successful sourcing. Specify the dimensions, weight, material types, and intended applications of the rubber parts you need.
– Consider volume needs: Determine if your production requires low, medium, or high volumes, as this will influence the molding process and supplier capabilities.
– Identify tolerances: Be explicit about dimensional tolerances and other quality standards to avoid costly mistakes later.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Begin by compiling a list of potential suppliers who specialize in rubber injection molding.
– Check industry directories and trade shows: Utilize resources such as online directories, industry associations, and relevant trade shows to find reputable manufacturers.
– Review supplier capabilities: Look for suppliers with experience in your industry and those who can handle custom designs if necessary.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before making a commitment, ensure that your selected suppliers meet industry standards and regulations.
– Verify certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality management certifications that demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety.
– Assess compliance with local regulations: For international sourcing, ensure suppliers adhere to the specific regulations of your country or region.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you narrow down your list, request samples or prototypes of the rubber parts you need.
– Evaluate quality: Assess the samples for material quality, finish, and adherence to your specifications.
– Test functionality: Conduct functional testing to ensure the parts meet performance requirements in real-world applications.
Step 5: Review Pricing and Terms of Service
Pricing is a critical factor in your sourcing decision, but it should not be the sole determinant.
– Request detailed quotes: Ensure quotes include all costs, such as tooling, production, and shipping, to avoid unexpected expenses.
– Negotiate terms: Discuss payment terms, lead times, and after-sales support to align expectations and reduce risks.
Step 6: Check References and Case Studies
Before finalizing your supplier choice, verify their reliability by checking references and reviewing case studies.
– Contact past clients: Speak with previous customers to gain insights into the supplier’s performance, reliability, and quality of service.
– Analyze case studies: Review documented projects that demonstrate the supplier’s ability to meet specific challenges similar to yours.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership.
– Set clear expectations: Establish regular check-ins and updates throughout the project timeline to ensure alignment.
– Use collaborative tools: Consider using project management software or communication platforms to streamline interactions and documentation.
Following this checklist will empower you to make informed decisions when sourcing rubber injection molding services, ensuring that you find a supplier who meets your specific needs while maintaining quality and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber injection moulding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Injection Moulding?
When sourcing rubber injection moulding, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of rubber used significantly impacts costs. Options include organic rubber, liquid silicone, and thermoplastic elastomers. The quality of the raw material can also influence pricing, with higher-grade materials generally commanding higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the moulding process. Automation in manufacturing can reduce labor costs, but skilled workers may still be necessary for quality control and machine operation.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. These costs are often factored into the overall price per unit.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment. The complexity of the design and the number of cavities in the mould can affect tooling costs. For high-volume production, the initial tooling cost can be amortized over a larger number of parts, reducing the per-unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final products meet specifications requires rigorous quality control processes. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the certifications required (e.g., ISO, TS16949) and the level of testing performed.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms chosen (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Injection Moulding Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of rubber injection moulding services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on volume. Higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts require additional design and tooling efforts, which can increase costs. If a buyer can standardize their requirements, they may benefit from lower prices.
-
Material Selection: The choice of rubber material affects both the performance and cost of the final product. High-performance materials may be necessary for specific applications but can also drive up costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific certifications or rigorous quality testing will typically incur higher costs. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are essential for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Suppliers in regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive prices.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping can significantly affect the overall cost. Understanding responsibilities for shipping and customs can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Rubber Injection Moulding?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing rubber injection moulding, buyers can implement several strategies:
-
Negotiate with Suppliers: Engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to compare prices and services. Building long-term relationships can also lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with the product, including maintenance and disposal, not just the initial purchase price. This holistic view can uncover opportunities for savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fluctuations in currency exchange rates, tariffs, and shipping costs can impact pricing. It’s essential to factor these into your budget.
-
Leverage Local Knowledge: Engage with local experts or consultants who understand the regional market dynamics. They can provide insights into sourcing strategies that may not be immediately apparent.
-
Request Sample Parts: Before committing to large orders, request sample parts to evaluate quality and performance. This can prevent costly mistakes later in the procurement process.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for rubber injection moulding can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber injection moulding With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Rubber Injection Moulding
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly for rubber components, businesses often seek the most efficient and cost-effective methods. While rubber injection moulding stands out for its precision and versatility, it’s crucial to consider viable alternatives that may better suit specific applications or constraints. This analysis compares rubber injection moulding with two prominent alternatives: compression moulding and transfer moulding, providing B2B buyers with valuable insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Injection Moulding | Compression Moulding | Transfer Moulding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; minimal waste | Good for low to medium volumes; slower cycle times | Excellent for intricate designs; moderate waste |
| Cost | Economical for high volumes; initial setup cost | Low initial investment; higher per-unit cost for large runs | Moderate cost; efficient for multi-cavity molds |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment; skilled labor | Simpler setup; less technical expertise needed | Moderate complexity; requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; automated processes | Higher maintenance due to mold wear | Moderate maintenance; potential for more waste |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of complex parts | Low to medium volume production; simple designs | Multi-cavity molds for intricate designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Compression Moulding
Compression moulding is a traditional method that involves placing rubber material in an open mold, which is then closed and heated. This technique is ideal for low to medium production volumes and larger parts. The primary advantage of compression moulding is its low initial investment and simplicity; however, it does come with longer cycle times and potential variability in part quality due to the manual process involved. Businesses looking to produce O-rings, gaskets, or seals may find this method suitable, particularly when initial costs are a concern.
Transfer Moulding
Transfer moulding is a hybrid approach that combines elements of both compression and injection moulding. In this process, pre-heated rubber is placed in a pot and forced into a closed mold, making it effective for producing intricate designs with multiple cavities. The primary benefit of transfer moulding is its ability to produce complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. However, it can generate more waste, as leftover material must be discarded after curing. This method is particularly advantageous for applications requiring precision and multi-part assembly, such as automotive components.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate rubber manufacturing method hinges on various factors, including production volume, part complexity, cost constraints, and desired precision. Rubber injection moulding excels in high-volume scenarios with intricate geometries, while compression moulding offers a cost-effective solution for simpler designs at lower volumes. Transfer moulding strikes a balance between complexity and efficiency but may involve higher material waste. By carefully assessing these alternatives against their specific manufacturing needs, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary considerations.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber injection moulding
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Injection Moulding?
Understanding the essential technical properties of rubber injection moulding is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize production processes and ensure product quality. Here are several critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific type of rubber used in the injection moulding process, such as natural rubber, silicone, or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Each grade has distinct properties like elasticity, thermal stability, and resistance to chemicals. Selecting the right material grade is fundamental, as it directly impacts the performance, durability, and application of the final product.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part. In rubber injection moulding, maintaining tight tolerances is essential for ensuring that components fit correctly within assemblies, especially in sectors like automotive and aerospace. High precision reduces the risk of product failure and enhances overall operational efficiency.
3. Viscosity
Viscosity measures a material’s resistance to flow. In the context of rubber injection moulding, a lower viscosity is desirable as it allows for easier flow into complex mould cavities, ensuring uniform filling and reducing cycle times. Understanding viscosity helps manufacturers optimize the injection process and minimize waste.
4. Cure Time
Cure time is the duration required for the rubber to undergo chemical transformation and achieve its final properties after being injected into the mould. This property affects production speed and overall efficiency. Shorter cure times enable faster turnaround, which is particularly advantageous in high-volume production scenarios.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
5. Shore Hardness
Shore hardness measures the hardness of rubber, impacting its elasticity and resistance to wear. Different applications require varying hardness levels; for instance, softer rubbers are preferred for seals, while harder materials are suitable for structural components. Buyers must specify the desired Shore hardness to ensure the product meets its application needs.
6. Volume
Volume refers to the quantity of rubber products produced in a single injection moulding cycle. Understanding volume requirements helps manufacturers determine the most cost-effective moulding process, whether it be for high-volume production or custom, low-volume orders.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Rubber Injection Moulding Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are several common terms:
Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In rubber injection moulding, OEMs often require custom parts tailored to their specifications. Understanding OEM requirements is vital for ensuring that the supplied components align with the intended application.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost considerations. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and terms of delivery. Using RFQs effectively can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms, making it a critical tool for procurement processes.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They cover aspects such as shipping, risk transfer, and delivery obligations. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global trade, as they help clarify the logistics and costs involved.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the total time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In rubber injection moulding, lead times can vary based on complexity, material availability, and production capacity. Buyers should always factor in lead times when planning their projects to ensure timely delivery.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, improve collaboration with suppliers, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency in the rubber injection moulding sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber injection moulding Sector
What are the Current Trends Shaping the Rubber Injection Molding Market?
The rubber injection molding market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer demands. One of the key global drivers is the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. As industries focus on reducing weight for better fuel efficiency and performance, the adoption of advanced rubber materials, including thermoplastic elastomers, is on the rise.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as automation and Industry 4.0 applications, are also reshaping sourcing strategies. Manufacturers are leveraging smart manufacturing techniques, integrating IoT devices for real-time monitoring, and utilizing predictive analytics to optimize production efficiency. For international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these advancements present opportunities for more efficient sourcing processes, improved product quality, and reduced lead times.
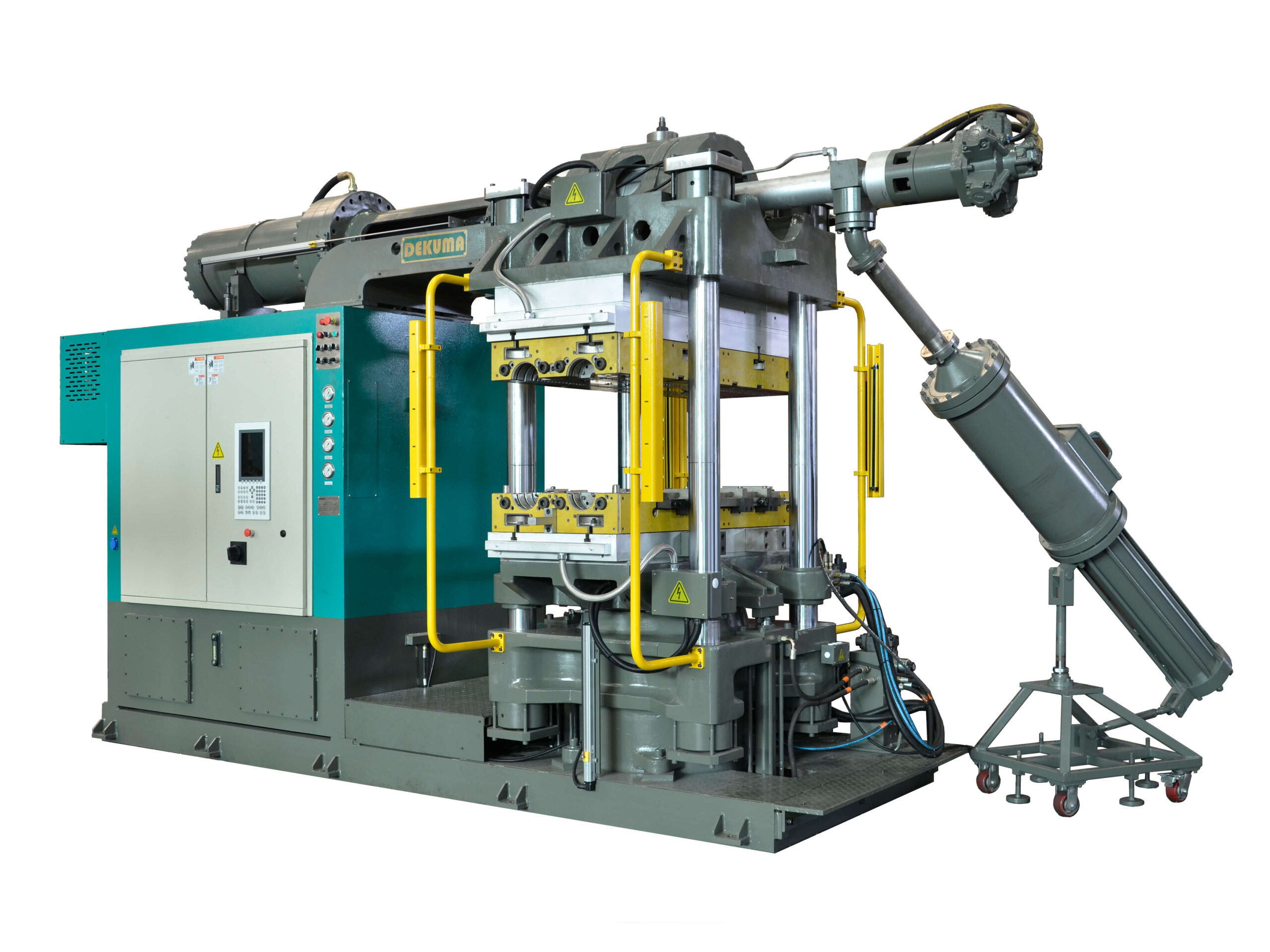

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
Furthermore, as the market grows, competition intensifies, prompting suppliers to innovate and differentiate their offerings. Custom rubber injection molding is gaining traction, allowing businesses to meet specific design requirements and enhance product functionality. Buyers should stay informed about these trends to identify potential suppliers who can deliver tailored solutions that align with their unique operational needs.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Rubber Injection Molding Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the rubber injection molding sector, with increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies for environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of traditional rubber production methods, including deforestation and high energy consumption, has led many companies to seek alternatives that minimize ecological footprints.
Ethical sourcing plays a crucial role in this paradigm shift, as businesses are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled rubber materials are becoming essential criteria for B2B buyers. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
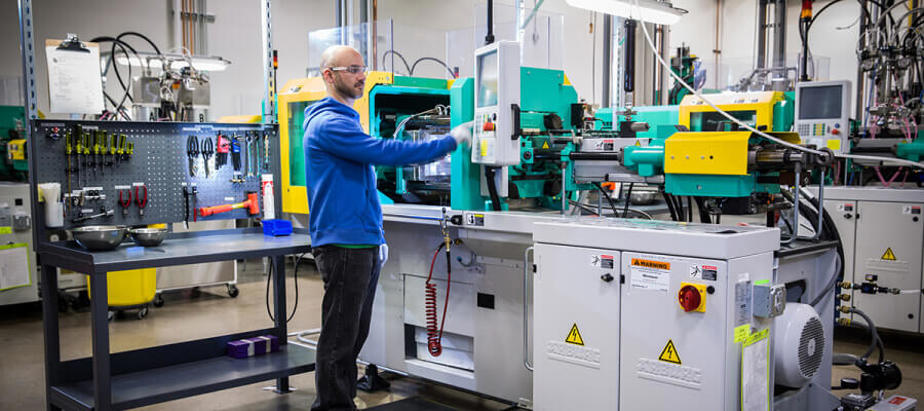

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials, such as bio-based elastomers and eco-friendly additives, is gaining momentum. Suppliers who can provide these materials will have a competitive advantage in the marketplace. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe, where sustainability regulations are stringent, engaging with suppliers committed to ethical practices will be crucial for compliance and market acceptance.
What is the Historical Context of Rubber Injection Molding in B2B?
The rubber injection molding process has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed as a method to improve the efficiency of rubber part production, it drew inspiration from established plastic injection molding techniques. This innovation allowed for higher precision and reduced labor costs, thereby transforming manufacturing practices.
In the decades that followed, the process was refined through advancements in material science and machinery, leading to the introduction of specialized techniques like liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection and thermoplastic rubber injection. These developments enabled manufacturers to create more complex and high-performance rubber components, catering to the diverse needs of modern industries.
As the global market continues to expand, the historical context of rubber injection molding serves as a foundation for understanding current trends and future innovations. For B2B buyers, recognizing this evolution can provide insights into selecting suppliers who are not only rooted in tradition but are also forward-thinking and capable of meeting the demands of an increasingly competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber injection moulding
-
How do I choose the right rubber injection molding process for my needs?
Choosing the right rubber injection molding process depends on several factors including part complexity, production volume, and material requirements. For intricate designs with multiple cavities, rubber transfer molding may be ideal. Conversely, for high-volume production, rubber injection molding offers efficiency and precision. Compression molding is better suited for lower volume runs of larger parts. Assessing your specific application, including size, geometry, and required tolerances, will help determine the most suitable process. -
What are the advantages of custom rubber injection molding?
Custom rubber injection molding provides tailored solutions that meet specific design and performance requirements, ensuring optimal functionality. This method allows for greater design flexibility, enabling manufacturers to create unique parts that fit specialized applications. Additionally, custom molding can lead to cost savings by reducing material waste and improving production efficiency. Businesses can leverage these benefits to enhance their product offerings and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rubber injection molding?
Minimum order quantities for rubber injection molding can vary significantly based on the supplier, the complexity of the part, and the manufacturing process. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to accommodate smaller orders for custom projects, especially if they foresee future business potential. Always clarify MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing rubber injection molding services?
Payment terms in the rubber injection molding industry can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) based on established relationships. It is crucial to discuss and negotiate payment terms before finalizing contracts to ensure they align with your cash flow and budget requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in rubber injection molded parts?
To ensure quality assurance, collaborate closely with your supplier to establish clear specifications and standards for your parts. Request detailed documentation of their quality control processes, including material testing, inspection protocols, and certifications (e.g., ISO). Additionally, consider implementing periodic audits or third-party inspections to validate compliance with your requirements. Establishing a robust communication channel with your supplier will facilitate timely resolution of any quality issues that may arise. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing rubber injection molding?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing rubber injection molding services, especially for international buyers. Key considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure that your supplier can meet your delivery timelines and understand the implications of shipping costs on your overall budget. Additionally, familiarize yourself with any trade agreements or tariffs that may affect pricing and delivery schedules when importing products into your region. -
How do I vet potential suppliers for rubber injection molding?
Vetting potential suppliers involves assessing their experience, capabilities, and reputation in the industry. Request references or case studies from previous clients, and consider their production capacity and technological capabilities. Visiting the facility, if possible, can provide valuable insights into their operations. Additionally, evaluate their customer service responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on custom projects, as these factors can significantly impact your partnership’s success. -
What types of materials are commonly used in rubber injection molding?
Rubber injection molding typically utilizes a variety of elastomers, including natural rubber, synthetic rubber (like nitrile, EPDM, and silicone), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). The choice of material depends on the intended application, performance requirements, and environmental conditions the parts will face. For instance, silicone rubber is often preferred for medical applications due to its biocompatibility, while nitrile rubber is favored for automotive parts due to its oil resistance. Discuss your specific application with suppliers to determine the best material for your needs.
Top 6 Rubber Injection Moulding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Timco Rubber – Rubber Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: timcorubber.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Rubber Injection Molding Process: Developed in the mid 1960s, it involves heating rubber and applying high pressure for molding. Advantages include elimination of pre-forms, reduced cycle time, flashless tooling, and minimal material waste. Transfer Molding: Requires pre-forms placed in a pot, offering high cavity count and tighter dimensional control. Compression Molding: Involves creating pre-fo…
2. Protolabs – Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding produces custom prototypes and end-use production parts in 15 days or less. The process utilizes aluminum molds for cost-efficient tooling and accelerated manufacturing cycles. Various grades and durometers of LSR materials are available. Common applications include low-volume production, bridge tooling, pilot runs, and functional prototyping.
3. Reddit – Silicone Rubber Injection Moulding Resources
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Silicone Rubber Injection Moulding, inquiry about learning resources for injection moulding specific to silicone rubber, noting the difference in material properties compared to plastic moulding.
4. Rubber Group – Key Molding Techniques
Domain: rubber-group.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: The Rubber Group offers three primary rubber molding techniques: Injection Molding, Transfer Molding, and Compression Molding.
1. **Injection Molding**:
– Process: Uncured rubber is fed into a rotating screw, pre-heated, and injected into a mold cavity under high pressure and temperature for curing.
– Advantages: Supports high volumes, medium-to-high precision, shorter cycle times, flash…
5. IQS Directory – Rubber Injection Molding
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Rubber Injection Molding: A process that converts raw rubber into finished products by injecting it into a pre-formed metal mold cavity using pressure and heat. Key types of rubber used include: 1. Natural Rubber: High tensile strength, good friction and abrasion properties, used for seals, O-rings, diaphragms, dampers, and bumpers. 2. Nitrile (Buna-N): Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and …
6. REP – Rubber Molding Machines
Domain: repinjection.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: REP offers a range of machines for rubber molding, including: G10 Performance Range, Multistation Presses (CMX), Horizontal Presses, Vertical Standard Presses, Custom-Built Presses, G10 Lean Range, Entry Range, RT9, G9A India Compression Molding Presses, Composite Molding Presses, and HSR Devulcanizing Machine. Key technologies include Industry 4.0 Automated Solutions, Eco-Design and Energy effici…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber injection moulding
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in rubber injection molding presents a wealth of opportunities for B2B buyers across diverse industries and regions. By understanding the various molding processes—such as transfer, compression, and injection molding—international buyers can select the most suitable methods based on their specific needs, including volume, complexity, and material requirements. Leveraging custom rubber solutions can further enhance operational efficiency and product quality, particularly in sectors like automotive, medical, and manufacturing.
As the global market evolves, it is essential for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to prioritize strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers. This approach not only minimizes costs but also ensures access to innovative technologies and expert support.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality, precision-engineered rubber components will only grow. By embracing strategic sourcing practices now, businesses can position themselves to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. Engage with experienced manufacturers and explore customized solutions that align with your operational goals. The future of rubber injection molding is bright—seize the opportunity to enhance your product offerings today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection moulding
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.