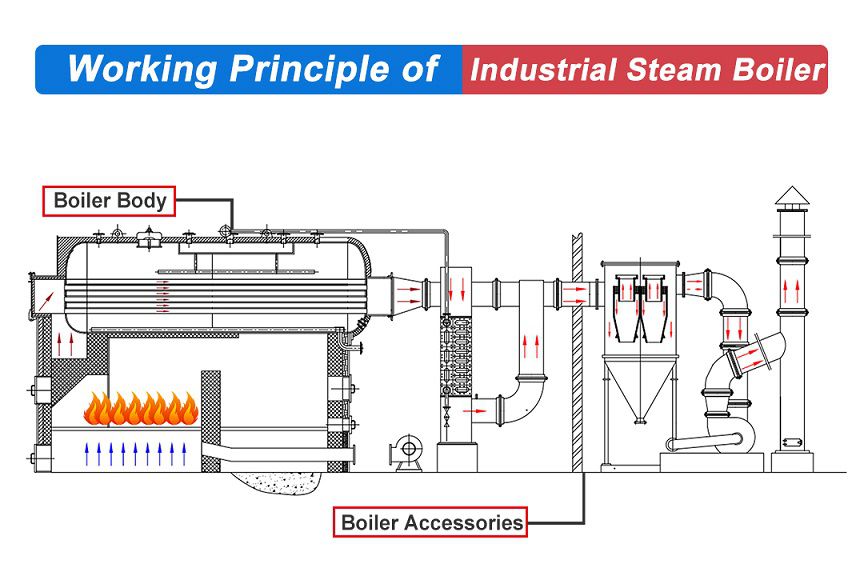
Top 6 How The Steam Boiler Works Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how the steam boiler works
In the complex landscape of industrial operations, understanding how steam boilers work is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable heating solutions. The challenge often lies in selecting the right boiler that aligns with specific operational needs while ensuring efficiency and safety. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the intricacies of steam boilers, covering essential topics such as types (firetube vs. watertube), applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By demystifying the workings of steam boilers, this guide empowers international B2B buyers—particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia)—to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance operational efficiency in manufacturing, streamline processes in food production, or ensure compliance with environmental regulations, understanding the nuances of steam boiler technology can significantly impact your bottom line.
Our aim is to equip you with actionable insights and a clear understanding of boiler systems, enabling you to navigate the global market with confidence and select the most suitable steam boiler for your business needs. With this knowledge, buyers can optimize performance, enhance safety protocols, and ultimately drive sustainable growth in their respective markets.
Understanding how the steam boiler works Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firetube Boiler | Flame passes through tubes, heating water externally. | Commercial heating, small-scale industries. | Pros: Lower initial cost; simpler design. Cons: Lower efficiency; limited steam pressure. |
| Watertube Boiler | Water flows through tubes heated by external gases. | Heavy industries, power generation. | Pros: Higher efficiency; capable of high pressures. Cons: Higher initial investment; more complex maintenance. |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electric resistance to heat water. | Hospitals, laboratories, small facilities. | Pros: Clean energy; low emissions. Cons: Higher operational costs; limited capacity. |
| Biomass Boiler | Burns organic materials for heat. | Eco-friendly industries, agricultural sectors. | Pros: Renewable energy source; reduces waste. Cons: Variable fuel quality; requires more space. |
| Condensing Boiler | Recovers heat from exhaust gases to improve efficiency. | Commercial and industrial applications. | Pros: High efficiency; lower fuel costs. Cons: More complex installation; higher upfront costs. |
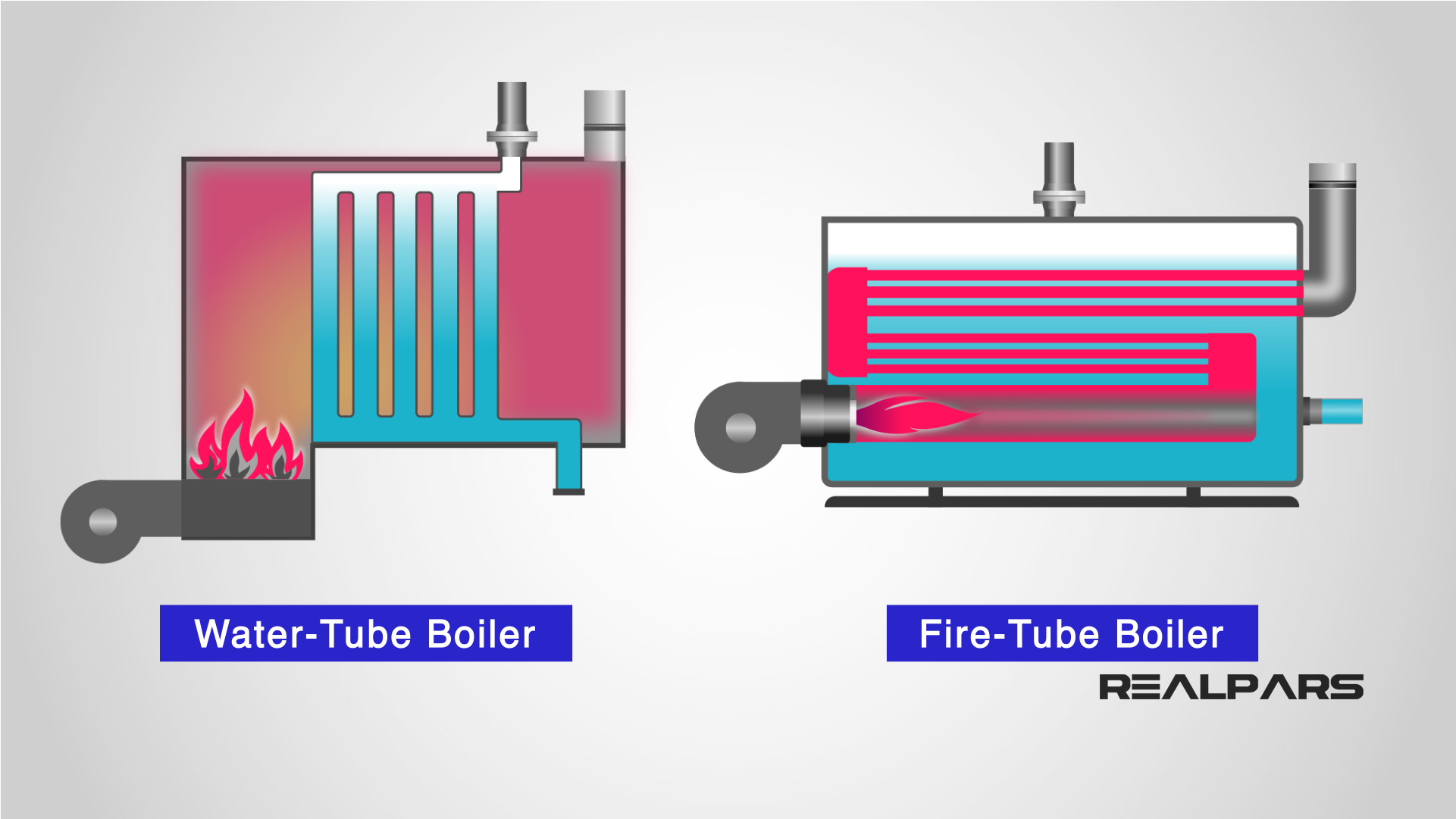
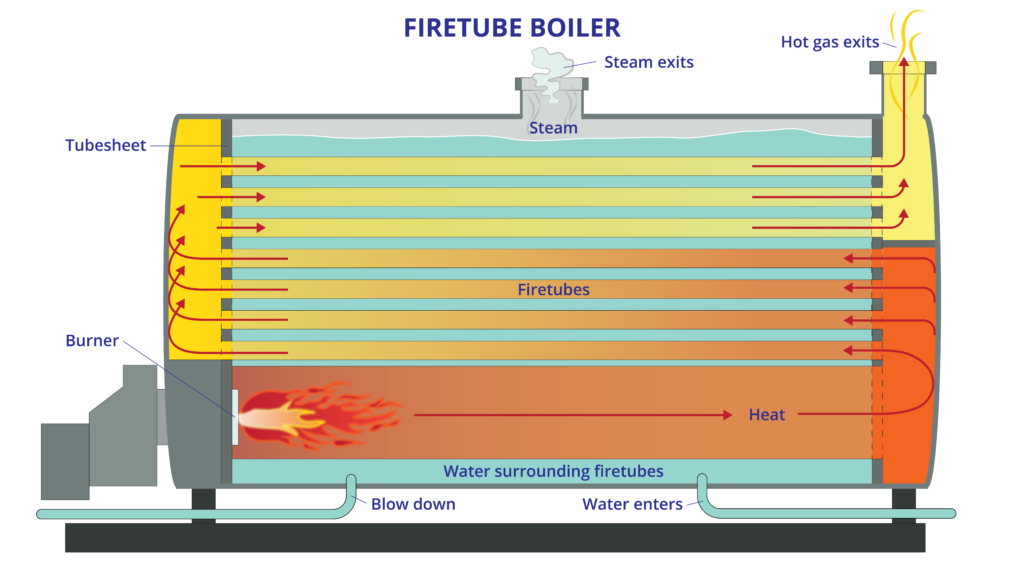
What are the Characteristics of Firetube Boilers?
Firetube boilers are characterized by their design, where hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. They are typically used in commercial heating applications and smaller industrial processes due to their lower initial costs. B2B buyers should consider that while firetube boilers are simpler to operate and maintain, they have limitations in terms of steam pressure and efficiency compared to other types.
How Do Watertube Boilers Compare in Efficiency?
Watertube boilers feature a design where water circulates through tubes that are heated externally. This allows them to generate higher pressures and efficiencies, making them suitable for heavy industrial applications and power generation. B2B buyers should evaluate the higher initial investment and maintenance complexity against the benefits of greater efficiency and performance in demanding environments.
When Should You Consider Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers utilize electric resistance to heat water and are ideal for settings like hospitals or laboratories where emissions must be minimized. They are compact and can be installed in areas with limited space. However, B2B buyers should be aware of the higher operational costs associated with electricity and the limited capacity for larger scale operations.
What are the Benefits of Biomass Boilers?
Biomass boilers burn organic materials, providing a renewable energy source that can be advantageous for eco-friendly industries and agricultural sectors. They help reduce waste and are often incentivized by government policies. However, B2B buyers must consider the variability in fuel quality and the requirement for more space to store biomass materials.
How Do Condensing Boilers Enhance Efficiency?
Condensing boilers are designed to recover heat from exhaust gases, significantly improving efficiency. They are commonly used in commercial and industrial settings where fuel costs are a major concern. While they offer substantial long-term savings, B2B buyers should factor in the more complex installation requirements and higher upfront costs associated with these systems.
Key Industrial Applications of how the steam boiler works
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how the steam boiler works | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Steam generation for pasteurization and sterilization | Ensures food safety and extends shelf life | Compliance with food safety regulations and efficiency ratings |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Providing heat for chemical reactions and distillation | Enhances production efficiency and consistency | Material compatibility and safety standards |
| Textile Industry | Steam for dyeing and finishing processes | Improves product quality and reduces processing time | Temperature control and energy efficiency |
| Healthcare | Steam for sterilizing surgical instruments | Guarantees hygienic conditions and patient safety | Reliability and compliance with health regulations |
| Power Generation | Steam generation for turbine operation | Maximizes energy output and operational efficiency | Fuel type adaptability and maintenance support |
How Do Steam Boilers Enhance Food Safety in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, steam boilers are critical for processes like pasteurization and sterilization. By generating high-temperature steam, these boilers ensure that harmful pathogens are eliminated, thereby guaranteeing food safety and extending the shelf life of products. Buyers in this industry must consider compliance with strict food safety regulations, as well as the boiler’s efficiency ratings, to minimize operating costs while maintaining high safety standards.
What Role Do Steam Boilers Play in Chemical Manufacturing Efficiency?
In chemical manufacturing, steam boilers are utilized to provide the necessary heat for various chemical reactions and distillation processes. The consistent and controlled steam supply enhances production efficiency and ensures product quality. International buyers should focus on the compatibility of boiler materials with the chemicals used, as well as adherence to safety standards to mitigate risks associated with high-pressure steam systems.
How Do Steam Boilers Improve Product Quality in the Textile Industry?
The textile industry relies on steam boilers for dyeing and finishing processes, where precise temperature control is essential. The use of steam improves the quality of the finished products by ensuring even dye application and reducing processing times. Buyers in this sector should prioritize energy efficiency and the ability to maintain consistent steam pressure to optimize production workflows and reduce operational costs.
Why Are Steam Boilers Essential for Sterilization in Healthcare?
In healthcare settings, steam boilers are indispensable for sterilizing surgical instruments and medical equipment. The high-pressure steam ensures that all contaminants are eliminated, thus maintaining hygienic conditions critical for patient safety. When sourcing steam boilers for healthcare applications, buyers must ensure reliability and compliance with health regulations, focusing on systems that provide consistent performance under stringent requirements.
How Do Steam Boilers Contribute to Efficiency in Power Generation?
In power generation, steam boilers are used to produce steam that drives turbines, converting thermal energy into electrical energy. This process is vital for maximizing energy output and operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should consider the adaptability of the boiler to different fuel types and the availability of maintenance support to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how the steam boiler works’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Boiler Efficiency Metrics
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to steam boiler systems, struggle to grasp the various efficiency metrics associated with these machines. Buyers often encounter terms like fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency, leading to confusion over which metric is most relevant for their operational needs. Without a clear understanding of how these efficiency ratings impact overall costs and performance, businesses risk investing in systems that do not meet their energy efficiency goals, ultimately leading to increased operational expenses.
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
The Solution: To effectively navigate efficiency metrics, B2B buyers should engage in comprehensive training or consult with industry experts to understand the significance of fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency. When evaluating steam boilers, buyers should look for models with high Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings, as these indicate better performance at full capacity. However, it is equally important to assess in-service efficiency, which reflects the boiler’s performance under typical operating conditions. Buyers can request operational data from manufacturers or suppliers to compare these metrics across different models. Additionally, utilizing a boiler with a high turndown ratio allows for more flexible operations, matching steam production to actual demand and improving efficiency.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Proper Water Treatment
The Problem: A common challenge for B2B buyers is the maintenance of water quality for steam boilers. Poor water treatment can lead to scale buildup, corrosion, and ultimately, equipment failure. Buyers in industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, where steam quality is critical, may find themselves facing costly downtime due to inadequate water treatment practices. This not only impacts productivity but also raises safety and compliance concerns.
The Solution: To mitigate water quality issues, buyers should prioritize investing in comprehensive water treatment systems tailored to their specific boiler needs. This includes implementing reverse osmosis systems to remove dissolved impurities and using chemical monitoring systems to ensure optimal water chemistry. Establishing regular water testing protocols will help monitor water quality and detect any potential issues before they escalate. Collaborating with water treatment specialists can also provide insights into selecting the right chemicals and treatment methods, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the steam boiler. Furthermore, buyers should develop a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of the feedwater system to identify and address any emerging concerns promptly.
Scenario 3: Navigating Boiler Safety Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the daunting task of ensuring compliance with safety regulations governing steam boiler operations. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory standards are stringent, failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in severe penalties or even shutdowns. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the complexities of safety certifications, inspections, and the necessary documentation required to operate steam boilers legally and safely.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with safety regulations, buyers should begin by familiarizing themselves with the relevant local and international standards applicable to their industry. Engaging with industry associations or regulatory bodies can provide valuable resources and guidance on compliance requirements. It is crucial to maintain detailed records of all safety inspections, maintenance activities, and operational changes to demonstrate adherence to regulations. Collaborating with certified boiler manufacturers or service providers can also streamline the compliance process, as they often have the expertise to navigate regulatory landscapes. Additionally, establishing an internal safety committee dedicated to regular training and updates on safety practices will foster a culture of safety and compliance within the organization, further mitigating risks associated with boiler operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how the steam boiler works
What Are the Key Materials Used in Steam Boiler Construction?
When selecting materials for steam boilers, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in steam boiler construction: carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and copper. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly influence the boiler’s efficiency, durability, and overall operational effectiveness.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Steam Boiler Applications?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and excellent weldability, making it a popular choice for pressure vessels. It typically has a temperature rating up to 600°F (316°C) and can withstand high pressures, which is crucial for steam generation.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and availability. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in high-temperature environments, which can lead to premature failure. This necessitates regular maintenance and protective coatings to extend its lifespan.
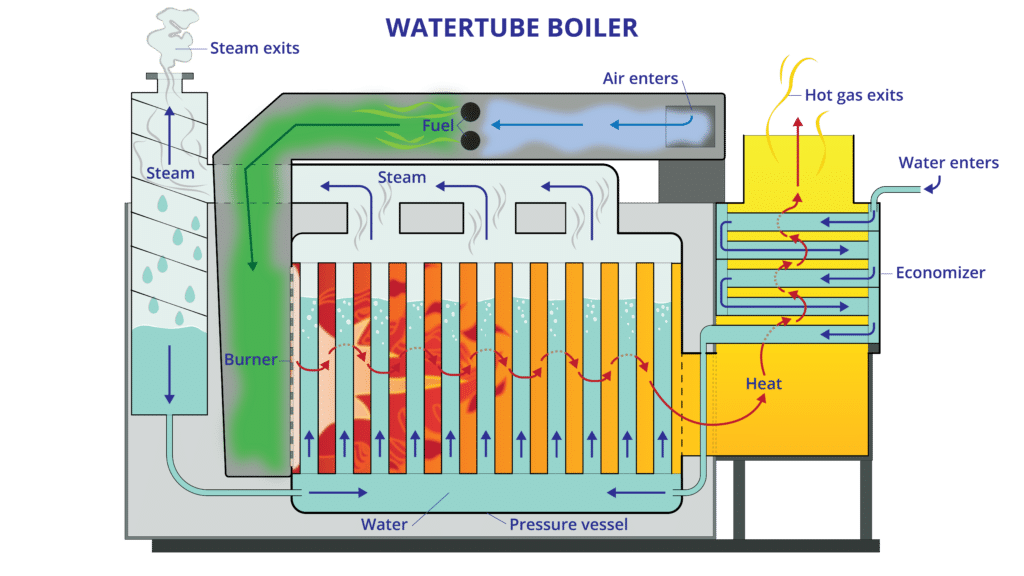
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with a wide range of steam applications, including industrial and commercial boilers. However, its susceptibility to corrosion means that water treatment is critical to prevent damage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM A106 for seamless carbon steel pipes. Understanding the specific environmental conditions that may accelerate corrosion is also vital.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and can handle temperatures up to 1,200°F (649°C) and high pressures. Its alloying elements, such as chromium and nickel, enhance its durability and resistance to oxidation.
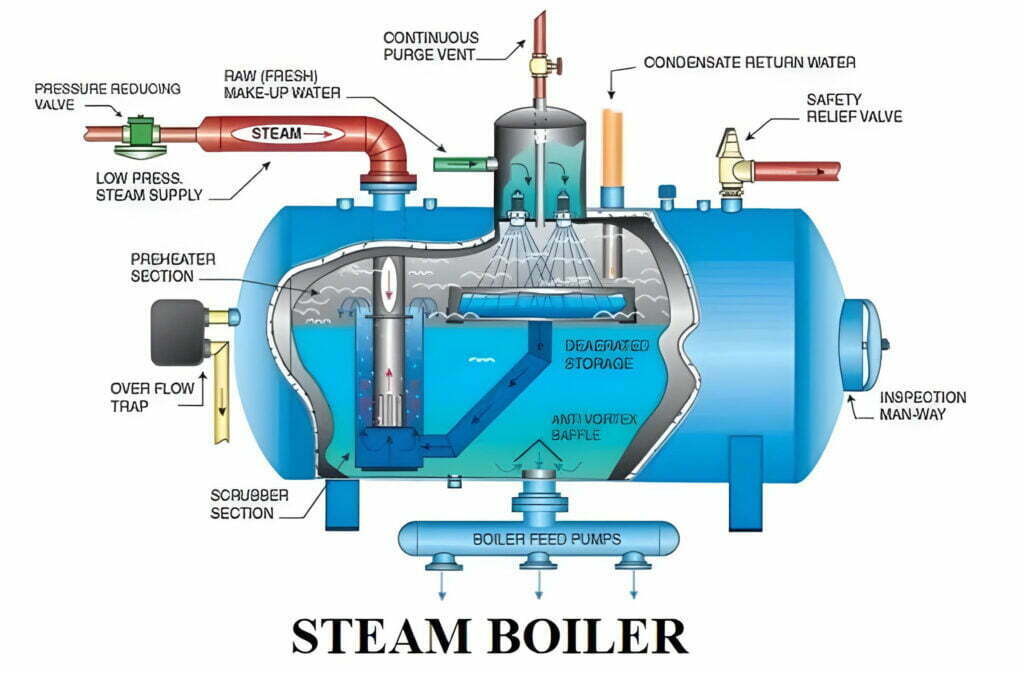
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and reduced maintenance requirements due to its corrosion resistance. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel, which may impact budget considerations for some buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, making it ideal for industries like petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. Its compatibility with various media further enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes is crucial. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, may also consider the DIN standards for quality assurance.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Steam Boiler Design?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically operates well in environments up to 1,000°F (538°C).
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to retain heat, which enhances energy efficiency. However, it is brittle and can crack under extreme stress, limiting its use in high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in residential and low-capacity commercial boilers. Its thermal properties are beneficial in applications requiring steady heat output, such as heating systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards like ASTM A48 for cast iron. Understanding the local market’s preferences for boiler types can also guide material selection.
How Does Copper Compare in Steam Boiler Applications?
Key Properties: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for heat exchangers and low-pressure applications. It can handle temperatures up to 400°F (204°C).
Pros & Cons: The advantage of copper lies in its efficient heat transfer capabilities, which can enhance boiler performance. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be less effective in high-pressure environments.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for smaller-scale applications, such as residential heating systems and hot water boilers, where efficiency and quick heating are priorities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B280 for copper tubing is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of copper in their region, as it may vary significantly.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Boilers
| Material | Typical Use Case for how the steam boiler works | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Industrial and commercial boilers | Cost-effective and widely available | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure and high-temperature applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Cast Iron | Residential and low-capacity commercial boilers | Excellent thermal conductivity | Brittle and can crack | Medium |
| Copper | Residential heating systems and hot water boilers | Efficient heat transfer | Less effective in high pressure | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the material selection process for steam boilers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how the steam boiler works
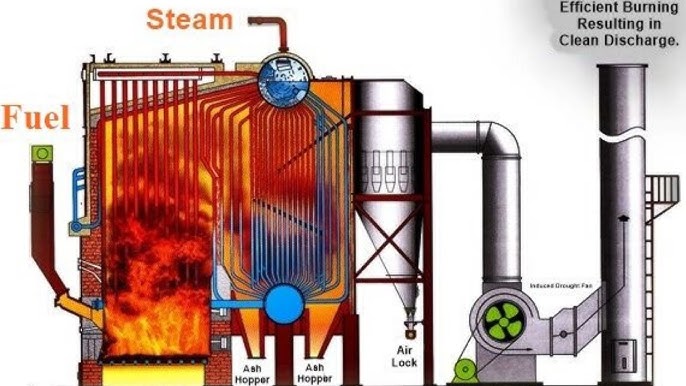
What Are the Main Stages of Steam Boiler Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process for steam boilers involves several critical stages to ensure that the final product meets safety, efficiency, and performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers identify quality suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Prepared?
The first stage in the manufacturing of steam boilers is the selection and preparation of raw materials. High-strength steel is typically the primary material used due to its ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. Quality assurance begins here, as suppliers must adhere to international standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) for material quality.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes processes like cutting, machining, and surface treatment to prepare it for forming. This may involve using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines to ensure precision in dimensions, which is critical for the boiler’s performance and safety.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Steam Boilers?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the various components of the boiler. Common techniques include:
- Welding: This is a crucial process for joining metal parts, especially in pressure vessels. Techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are often employed to ensure strong, leak-proof joints.
- Pressing and Bending: These techniques are used to create the boiler’s shell and other structural components. Hydraulic presses are often utilized to achieve the required shapes.
- Casting: Some components, like the burner or specific fittings, may be cast from molten metal to achieve complex shapes.
Each of these techniques requires skilled labor and advanced machinery to maintain high-quality standards.
How Is Assembly Performed in Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly stage begins. This is where the various parts of the boiler, such as the pressure vessel, burner, economizer, and control panel, are brought together.
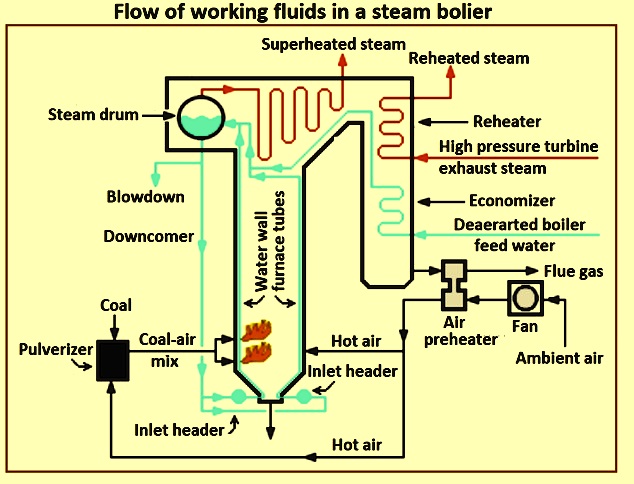
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
- Sub-Assembly: Components may first be assembled into sub-units before being integrated into the final boiler unit. This can enhance efficiency and quality control.
- Final Assembly: During this stage, all sub-assemblies are combined. Attention to detail is critical, as any misalignment or improper fitting can lead to inefficiencies or safety hazards.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Steam Boilers?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and performance of steam boilers. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Coating: Applying protective coatings can prevent corrosion and extend the boiler’s lifespan. This is particularly important for boilers operating in harsh environments.
- Testing and Calibration: Before leaving the factory, boilers undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. This includes pressure testing, leak testing, and calibration of control systems.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of steam boilers. It ensures that the products meet both international standards and customer requirements.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Steam Boiler Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be familiar with several international standards that govern boiler manufacturing:
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines quality management principles, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality and efficiency.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. It is essential for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, including certain boiler components.
Each of these standards helps ensure that boilers are safe and reliable for industrial applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is monitored at various stages of the manufacturing process through specific checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Materials must meet specified quality criteria before use.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, inspections are conducted to ensure that components are fabricated correctly. This may include dimensional checks and visual inspections for defects.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a final inspection is performed to verify that the boiler meets all performance and safety standards. This stage often includes testing under actual operating conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Boiler Quality?
Testing methods play a crucial role in quality assurance. Common techniques include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This test involves filling the boiler with water and pressurizing it to check for leaks and structural integrity.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to examine welds and material integrity without damaging the components.
- Performance Testing: Boilers are evaluated for efficiency, output, and emissions during this stage to ensure they meet industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is critical to ensure the reliability of their products.
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier Quality Control?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to evaluate compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation, interviewing staff, and inspecting equipment.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including testing results and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly valuable for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
What Quality Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
When dealing with international suppliers, buyers should be aware of certification nuances, such as:
- Local Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations regarding boiler manufacturing and safety. Understanding these can help buyers ensure compliance.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across regions. Being aware of these differences can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in steam boiler production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and choose suppliers that align with their operational needs and safety standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how the steam boiler works’
Introduction
When considering the procurement of steam boilers, it is essential to understand how they function and the various factors that influence their efficiency and safety. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
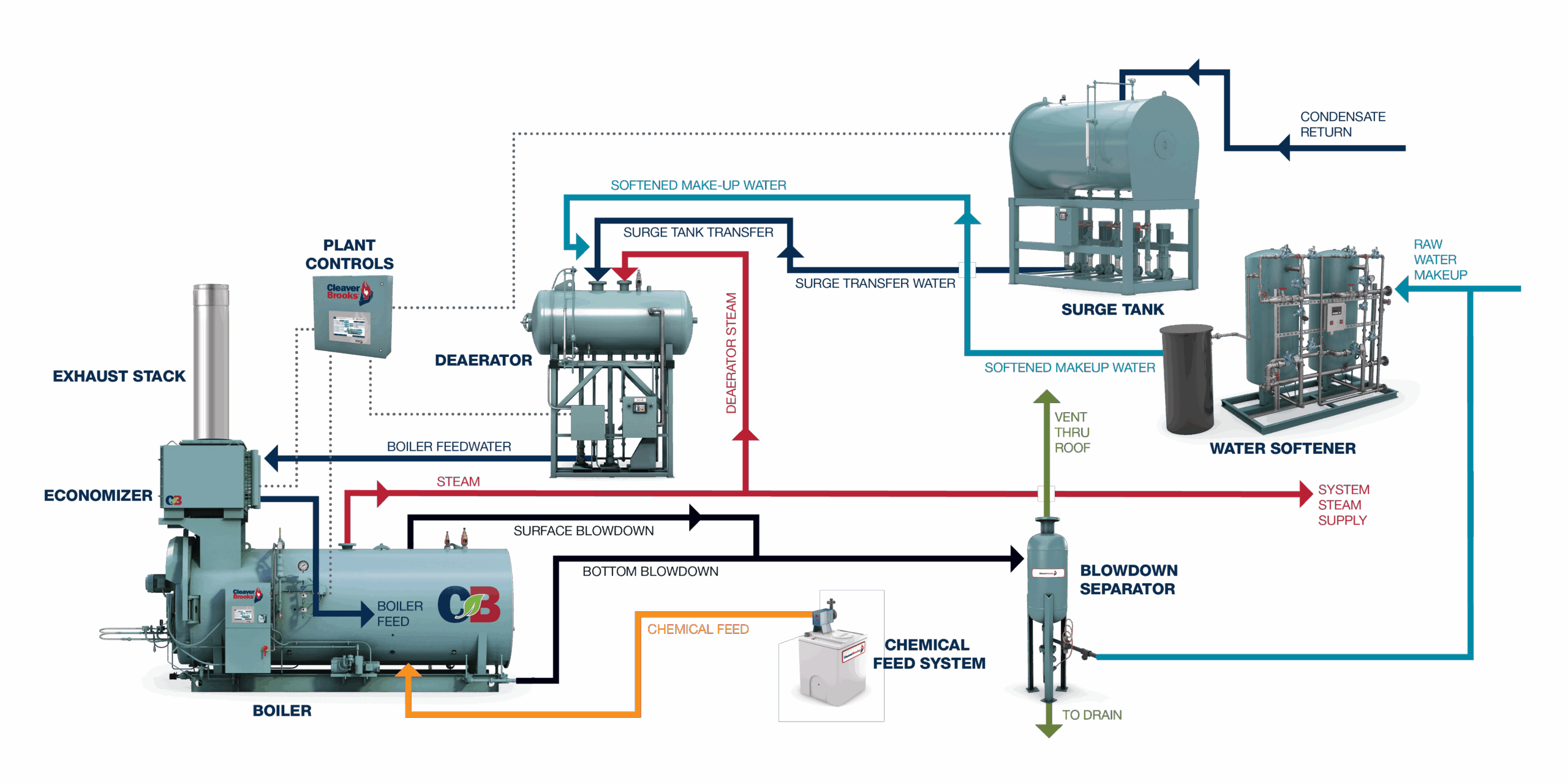
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements for your steam boiler. Consider factors such as steam capacity, pressure requirements, and fuel type. Specific specifications help streamline the selection process and ensure that the boiler can meet your operational demands.
- Capacity Requirements: Determine how much steam is needed for your applications.
- Operating Pressure: Identify the pressure levels that the steam system will require.
Step 2: Research Boiler Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of steam boilers available in the market, primarily firetube and watertube boilers. Understanding their operational differences can help you select the most suitable option for your business needs.
- Firetube Boilers: Generally easier to maintain but less efficient at higher pressures.
- Watertube Boilers: More suitable for large-scale operations requiring high pressure and efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses within your industry. A well-established supplier can provide insights into reliability and performance.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from other clients.
- Experience in Your Industry: Ensure the supplier has relevant experience with similar applications.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Safety Standards
Ensure that the boilers you are considering comply with local and international safety standards. This step is critical to avoid potential hazards that could arise from non-compliant equipment.
- Certifications: Check for ISO certifications or local safety regulations.
- Safety Features: Inquire about built-in safety mechanisms such as pressure relief valves.
Step 5: Assess Boiler Efficiency Ratings
Evaluate the efficiency ratings of the boilers you are considering. Look for metrics such as Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) and in-service efficiency. Higher efficiency ratings typically lead to lower operational costs over time.
- Fuel-to-Steam Efficiency: Understand how well the boiler converts fuel into steam.
- Turndown Ratio: A higher turndown ratio allows for better operational flexibility.
Step 6: Consider Maintenance and Support Services
Inquire about the maintenance and support services offered by the supplier. Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and efficiency of steam boilers.
- Service Agreements: Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive service contracts.
- Emergency Support: Ensure that the supplier provides 24/7 support for urgent issues.
Step 7: Request Detailed Quotations
Finally, request detailed quotations from shortlisted suppliers. Ensure that the quotations include all costs, such as installation, maintenance, and any potential additional fees. A transparent pricing structure will help you make an informed decision.
- Cost Breakdown: Review the itemized costs for clarity.
- Warranty Information: Understand the warranty terms offered for the boiler and its components.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for steam boilers, ensuring a selection that meets their operational requirements and enhances efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how the steam boiler works Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Steam Boiler Sourcing?
When sourcing steam boilers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in the construction of the boiler significantly impact costs. High-strength steel, specialized alloys for corrosion resistance, and insulation materials are common examples. Selecting materials that balance cost and durability is essential.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both skilled and unskilled workforce expenses. Skilled labor is required for welding, assembly, and quality inspections. Depending on the region, labor costs can vary significantly, affecting the overall pricing structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and maintenance. A higher manufacturing overhead often leads to increased boiler prices, particularly in regions with higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the investment in specialized equipment and molds necessary for production. This is particularly relevant for custom or high-volume orders, where specific tooling may need to be developed.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance processes ensure the boiler meets safety and efficiency standards. Implementing stringent QC measures can increase costs but is crucial for long-term reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary greatly based on distance, shipping method, and current fuel prices. International buyers should consider these costs, especially when importing boilers from other continents.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and risks. Understanding the margin can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Steam Boiler Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of steam boilers, particularly for B2B buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often results in lower per-unit costs. Manufacturers may offer discounts for bulk orders, which can be advantageous for companies planning extensive installations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom boilers designed to meet specific operational needs or regulatory requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against standard options.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and any applicable certifications (such as ASME, ISO) can influence pricing. High-quality materials and certified products typically carry a premium but offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge higher prices but can provide assurances regarding quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is critical for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Steam Boiler Prices?
To navigate the complexities of steam boiler sourcing effectively, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you can commit to larger orders or longer-term contracts. Building a relationship can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes installation, maintenance, and energy costs over the boiler’s lifespan.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, tariffs and import duties may apply when sourcing from outside the region, impacting total costs.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Collecting quotes from various suppliers can provide a better understanding of market rates and help identify the best deal.
-
Leverage Local Expertise: When sourcing from regions like Africa or South America, consider engaging local consultants who can provide insights into supplier reliability and market conditions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for steam boilers can vary widely based on numerous factors, including specification, location, and market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how the steam boiler works With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Steam Boilers
In the industrial landscape, steam boilers have long been a reliable solution for generating heat and power through steam. However, as businesses seek efficiency and sustainability, exploring alternative technologies becomes crucial. This section compares steam boilers with other viable methods, such as electric boilers and thermal fluid heaters, to help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How The Steam Boiler Works | Electric Boiler | Thermal Fluid Heater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High steam output; suitable for large-scale applications. | Lower output; ideal for small to medium applications. | Consistent heat transfer; flexible temperature control. |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational costs due to fuel and maintenance. | Lower installation costs; electricity may be cheaper in some regions. | Moderate costs; efficiency can offset initial investment. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant infrastructure; installation can be complex. | Simple installation; often plug-and-play. | Moderate complexity; requires proper piping and insulation. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; potential for corrosion and scaling. | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts. | Requires periodic maintenance; risk of overheating. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for heavy industrial processes needing high steam volumes. | Best for facilities with limited space and lower steam needs. | Suitable for processes requiring precise temperature control, like chemical processing. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Electric Boilers and Their Advantages?
Electric boilers utilize electricity to heat water and produce steam. They are particularly advantageous in settings where natural gas or other fuel sources are limited or expensive. Their installation is relatively straightforward, often requiring less infrastructure than steam boilers. Additionally, electric boilers have lower maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts and the absence of combustion processes. However, they may not provide the high output needed for larger industrial applications and can lead to higher operational costs in regions with expensive electricity.
How Do Thermal Fluid Heaters Work and What Are Their Benefits?
Thermal fluid heaters circulate a heat transfer fluid, which is heated in a furnace and then circulated through a closed loop to transfer heat to various processes. These systems offer flexibility in temperature control and are particularly effective for applications requiring consistent heating, such as in chemical processing or food production. While they can be more efficient than steam boilers at lower temperatures, they may come with moderate installation costs and require careful management to prevent overheating.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate heating solution involves evaluating multiple factors, including the specific needs of your operations, budget constraints, and long-term goals for efficiency and sustainability. While steam boilers remain a robust choice for high-demand scenarios, electric boilers and thermal fluid heaters present viable alternatives for businesses seeking flexibility, lower maintenance, or reduced space requirements. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower B2B buyers to make decisions that align with their operational objectives and financial strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how the steam boiler works
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steam Boilers?
When considering a steam boiler for industrial applications, several critical specifications are essential for ensuring performance, safety, and efficiency. Understanding these properties can significantly impact purchasing decisions and operational success.
What Material Grades Are Commonly Used in Steam Boilers?
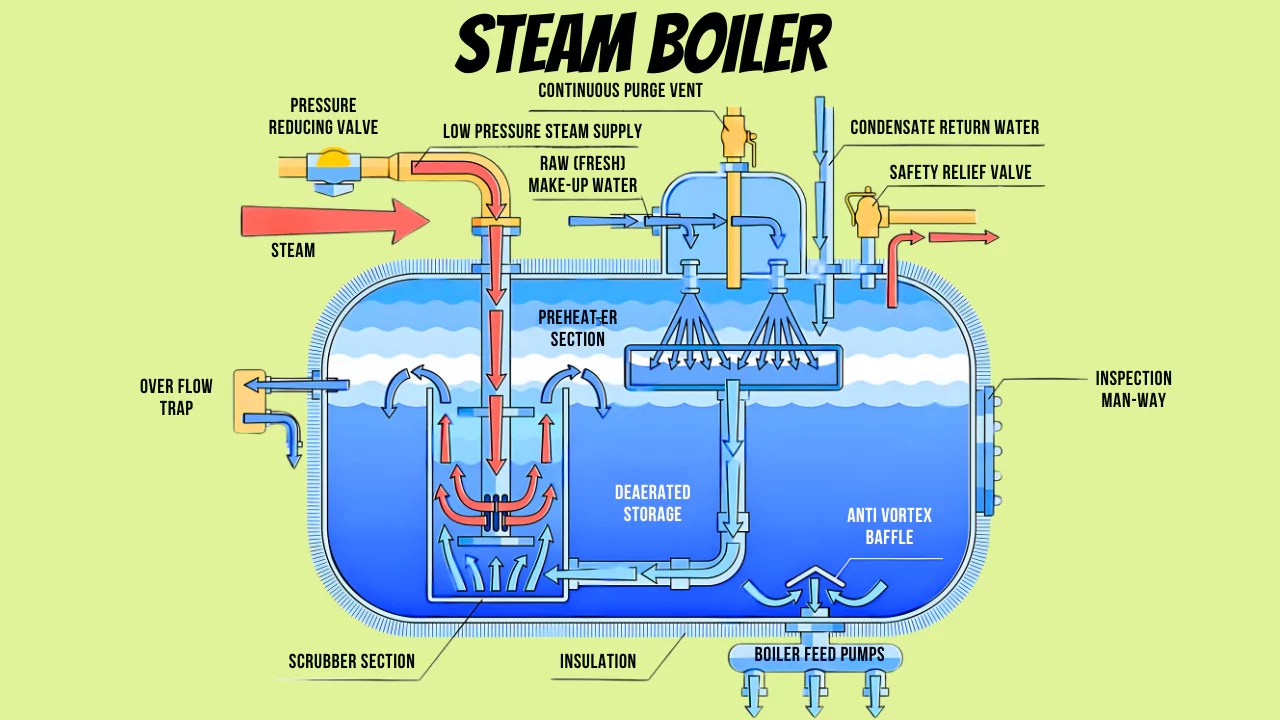
The construction of steam boilers typically employs high-strength materials like carbon steel or stainless steel. Carbon steel is favored for its strength and cost-effectiveness, while stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for high-pressure environments. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for durability and compliance with safety standards, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions, such as the humid climates in parts of Africa or the desert conditions in the Middle East.
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
How Do Tolerances Affect Boiler Performance?
Tolerances refer to the allowable deviations in the dimensions and properties of boiler components. Precise tolerances are vital for ensuring that all parts fit together correctly, which is critical for safe operation. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, and premature failure of the boiler system. Understanding tolerances is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that they are investing in quality products that meet operational specifications.
Why Is Boiler Efficiency Important in the B2B Market?
Boiler efficiency directly influences operational costs. Key metrics include fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency. Fuel-to-steam efficiency measures how effectively the boiler converts fuel into steam, while in-service efficiency reflects the boiler’s performance during actual operation. For businesses, higher efficiency translates to lower fuel costs and reduced environmental impact, making it a significant consideration in procurement decisions.
What Is a Boiler Turndown Ratio and Its Significance?
The boiler turndown ratio indicates the flexibility of a boiler to operate at varying capacities. A high turndown ratio allows the boiler to adjust steam output based on demand, which can lead to significant energy savings. For industries with fluctuating steam requirements, such as food processing or chemical manufacturing, understanding this ratio is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and cost management.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Steam Boiler Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace.
What Does OEM Mean in Boiler Procurement?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. In the context of steam boilers, an OEM produces the original components and systems. Engaging with OEMs often ensures quality and reliability, as these manufacturers adhere to specific standards and provide warranties for their products.
How Does MOQ Influence Purchasing Decisions?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for businesses to manage inventory costs and avoid overstocking, particularly in regions with variable demand patterns.
What Is an RFQ and Its Role in Boiler Acquisition?
An RFQ, or Request for Quotation, is a document that businesses send to suppliers to obtain price quotes for specific products. In the steam boiler market, issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare costs, specifications, and delivery timelines, facilitating informed decision-making.
How Do Incoterms Affect International Boiler Transactions?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are predefined rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is critical for B2B buyers to manage logistics, shipping costs, and risks associated with transporting steam boilers across borders.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful boiler procurement and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how the steam boiler works Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Impacting the Steam Boiler Sector?
The global steam boiler market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving customer demands. Key trends include the increasing adoption of smart boiler technologies, which integrate IoT for enhanced monitoring and control, enabling operators to optimize performance and reduce operational costs. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, there is a strong push towards energy efficiency and sustainability, propelling the demand for high-efficiency steam boilers that can lower fuel consumption and emissions.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America are also experiencing growth as industries expand and modernize their processes. With a focus on reducing operational costs, companies are increasingly seeking boilers with high turndown ratios, allowing for better adaptability to fluctuating steam demands. Additionally, regulatory frameworks are becoming stricter, particularly concerning emissions, prompting manufacturers to innovate towards cleaner combustion technologies and alternative fuel sources, such as biomass and hydrogen.
International buyers should also be aware of the competitive landscape, where both established players and new entrants are vying for market share. Understanding local market dynamics, including regulations and procurement practices, is crucial for successfully navigating the steam boiler sourcing process.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Steam Boiler Sourcing?
Sustainability is now a pivotal factor in the steam boiler sector, compelling manufacturers and buyers alike to prioritize environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of steam boiler operations, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, has led to a heightened focus on sustainable solutions. Buyers are increasingly seeking steam boilers that not only meet efficiency standards but also contribute to their corporate social responsibility goals.
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Ethical sourcing practices are becoming vital, with businesses emphasizing transparency in their supply chains. This includes ensuring that materials used in boiler manufacturing are sourced from suppliers who adhere to environmental regulations and labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 50001 for energy management are becoming essential benchmarks for buyers assessing the sustainability of their suppliers.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled steel in boiler construction and low-emission fuel options, is gaining traction. As organizations strive to reduce their carbon footprints, the integration of these sustainable practices into the procurement process will likely become a key differentiator in the marketplace.
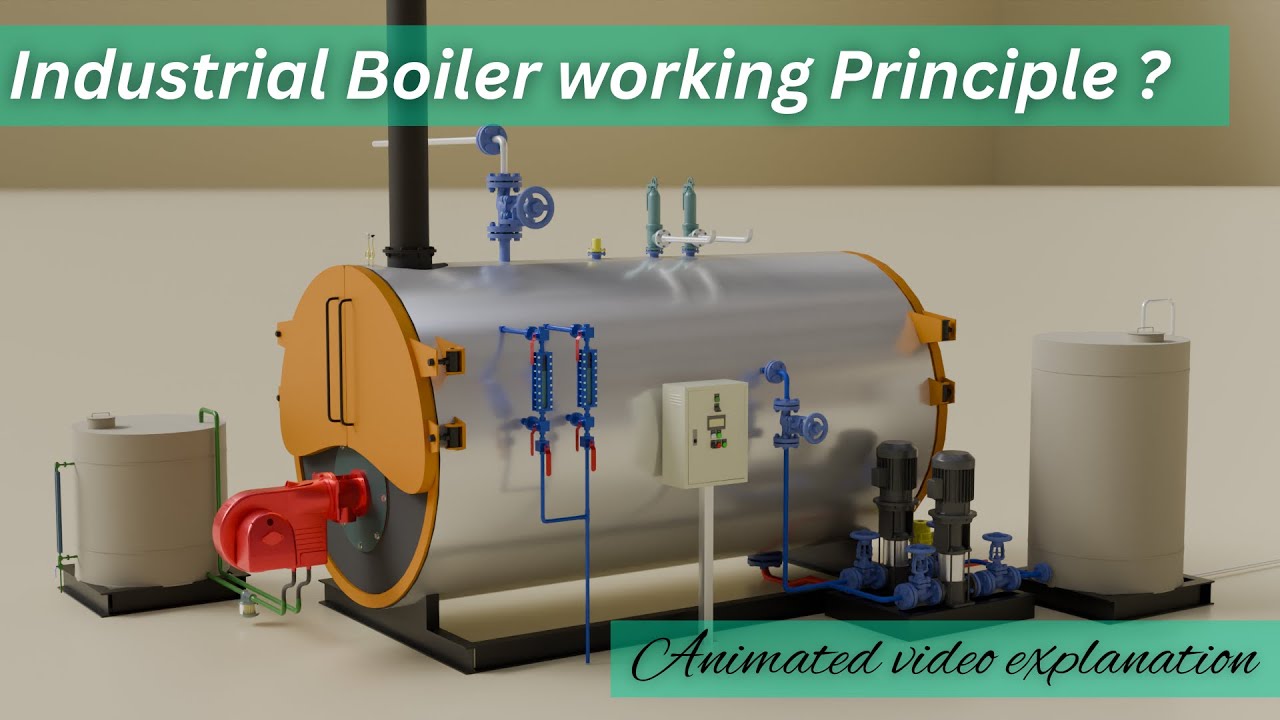
What Is the Historical Context of Steam Boilers in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of steam boilers dates back to the early industrial era, where they played a crucial role in powering factories and locomotives. Initially, firetube boilers dominated the market due to their simplicity and reliability. However, as industrial processes grew more complex and the demand for higher efficiency and safety increased, watertube boilers emerged as the preferred choice, capable of generating higher pressures and offering better operational flexibility.
The introduction of regulations and efficiency standards over the decades has further shaped the development of steam boilers. Technological innovations, such as advanced control systems and eco-friendly combustion techniques, have continuously improved their performance and reduced their environmental impact. This historical context highlights the ongoing transformation of the steam boiler sector, driven by both technological advancements and the growing emphasis on sustainability, which continues to influence sourcing decisions for international B2B buyers today.
Illustrative image related to how the steam boiler works
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how the steam boiler works
-
How do I determine the right steam boiler for my industrial application?
Choosing the right steam boiler requires evaluating several factors, including the specific steam requirements of your processes, the type of fuel available, and the desired efficiency ratings. Start by assessing your facility’s steam demand in terms of pressure and volume. Next, consider the type of boiler—firetube or watertube—based on your operational needs. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customizations that may enhance efficiency or meet local regulations. A thorough analysis will ensure the selected boiler aligns with your operational goals and budget. -
What are the critical safety features to look for in a steam boiler?
When sourcing a steam boiler, prioritize safety features such as pressure relief valves, water level controls, and automatic shut-off systems. Inspect the boiler’s construction materials for high-strength steel to withstand high pressures. Additionally, inquire about safety certifications and compliance with international standards. Regular maintenance and monitoring systems, including chemical monitoring, also contribute to operational safety. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive safety training and documentation can further enhance your operational security. -
How can I ensure the steam boiler is efficient for my operations?
To ensure your steam boiler operates efficiently, consider both fuel-to-steam and in-service efficiency ratings. Opt for boilers with high turndown ratios, which allow for better modulation of steam output according to demand, reducing energy waste. Regular maintenance, including water treatment processes to prevent scaling and corrosion, is essential for sustaining efficiency. Collaborating with suppliers who offer energy audits can also help identify areas for improvement, ensuring your boiler operates at peak performance. -
What factors should I consider when vetting steam boiler suppliers?
Vetting steam boiler suppliers involves assessing their experience, product range, and customer service. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and a solid reputation for reliability. Evaluate their responsiveness to inquiries and their ability to provide technical support and documentation. Certifications and compliance with international quality standards are also crucial. Request references from previous clients to gauge their satisfaction levels and ensure the supplier can meet your specific needs. -
What customization options are available for steam boilers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for steam boilers to suit specific operational requirements. Customizations can include modifications to the boiler’s size, pressure settings, and fuel type compatibility. You might also explore additional features like enhanced automation systems, economizers for improved efficiency, or specific safety enhancements. Discuss your unique needs with potential suppliers to identify feasible custom solutions that align with your operational goals. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steam boilers?
Minimum order quantities for steam boilers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of boiler. Some suppliers may have strict MOQs, particularly for custom or specialized units, while others may accommodate smaller orders for standard models. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly during negotiations to ensure you receive a flexible solution that meets your operational demands without excess inventory costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a steam boiler?
Payment terms for steam boiler purchases typically depend on the supplier’s policies and the size of the order. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront, followed by the balance upon delivery or after installation. For large orders, some suppliers may offer financing options or staggered payment plans. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing a purchase to ensure they align with your budget and cash flow requirements, and consider negotiating favorable terms based on your relationship with the supplier. -
How is logistics managed for international steam boiler shipments?
Logistics for international steam boiler shipments involves multiple considerations, including compliance with export regulations, shipping methods, and delivery timelines. Discuss logistics with your supplier to understand their shipping processes and any associated costs. Ensure they have experience in handling large industrial equipment and can provide tracking information. Additionally, factor in customs clearance procedures and potential duties or tariffs that may apply in your region. A reliable logistics partner can streamline the process, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing disruptions.
Top 6 How The Steam Boiler Works Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CN Control Valve – Steam Boiler Solutions
Domain: cncontrolvalve.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: A steam boiler is a heating system that generates steam by boiling water. It converts thermal energy from various fuels (gas, coal, biomass, fuel oil) into steam for industrial and domestic purposes. Key types of steam boilers include:
1. **Electric Boilers**: Utilize electric components for heating, environmentally friendly, durable, and require less maintenance.
2. **Hot Water Boilers**: Compos…
2. The Engineering Mindset – Steam Heating Systems
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Steam heating systems are used in residential, commercial, and industrial sites, particularly in large campuses and older buildings. They do not require pumps, using steam itself to distribute heat. A typical two-pipe steam heating system includes a boiler that heats water to create steam, which is then pushed through pipes to radiators. The system relies on pressure to move steam and return conde…
3. EPCB – Industrial Steam Boilers
Domain: epcbboiler.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: EPCB Boiler offers various types of industrial steam boilers, including coal-fired, oil/gas-fired, biomass-fired, and electric boilers. Key features include:
1. **Coal Fired Steam Boiler**:
– New design with large heating surface.
– Advanced steam-water separation technology.
– Thermal efficiency up to 84.61%.
2. **Oil/Gas Fired Steam Boiler**:
– 3-pass wet back structure.
– Aut…
4. Cleaver-Brooks – Steam Boilers
Domain: cleaverbrooks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Steam Boilers: Advanced solutions for industrial and commercial use, designed for efficiency and reliability. Types include Firetube Boilers (used in commercial/small industrial applications), Watertube Boilers (ideal for high pressures), Electric and Electrode Boilers (efficient and emission-free). Key components: Pressure Vessel (ASME standards), Burner System (precision combustion), Control Sys…
5. Reddit – Boiler Inputs and Outputs Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Boilers have 2 inputs and 2 outputs. The first input is for water, which can be pumped in normally. The second input is for hot water, which is created by pumping water and coal into a firebox. Using natural gas is recommended for the hot water input, requiring 45L of water and 30L of refined gas, and a water pump 2 is suggested for efficiency. The first output is steam, which can be used to power…
6. IQS Directory – Steam Boilers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are apparatuses designed to produce steam by heating water, functioning as heat exchangers. They come in various sizes and types, including hot water boilers, electric boilers, gas boilers, low pressure boilers, high pressure boilers, and oil boilers. Hot water boilers transfer thermal energy to water for heating and are constructed from materials like stainless steel and cast iron. …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how the steam boiler works
In conclusion, understanding how steam boilers operate is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their industrial processes. The choice between firetube and watertube boilers can significantly impact efficiency, safety, and operational costs. Key factors such as boiler efficiency, fuel type, and the implementation of advanced water treatment systems can enhance performance and longevity.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in acquiring high-quality, reliable steam boilers tailored to specific operational needs. By partnering with reputable suppliers, businesses can ensure they receive equipment that meets industry standards and supports sustainable practices, particularly vital in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where energy efficiency is increasingly prioritized.
As the demand for efficient steam solutions grows, investing in cutting-edge technology and maintaining a proactive approach to sourcing can position your business for long-term success. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations and reduce costs by making informed decisions today. Your path to efficient steam generation starts with understanding your needs and leveraging strategic partnerships for optimal boiler solutions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.