Top 5 Solenoid Symbol Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid symbol
The global market for solenoid symbols presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations with precision and efficiency. Understanding the various solenoid symbols is crucial for effectively sourcing the right components in industries ranging from manufacturing to automation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of solenoid symbols, exploring their types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the information provided here is tailored to help you navigate the complexities of purchasing solenoid valves and related equipment.
By offering insights into industry standards, symbol interpretations, and practical applications, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. It addresses common pitfalls such as misinterpretations of symbols, ensuring that international buyers can confidently select products that meet their specific operational needs. Additionally, we will cover cost considerations, enabling buyers to evaluate the total value proposition of their investments. As you progress through this guide, you will gain a deeper understanding of how to leverage solenoid symbols to enhance your operational efficiency and reduce downtime, ultimately supporting your business’s growth in a competitive global landscape.
Understanding solenoid symbol Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
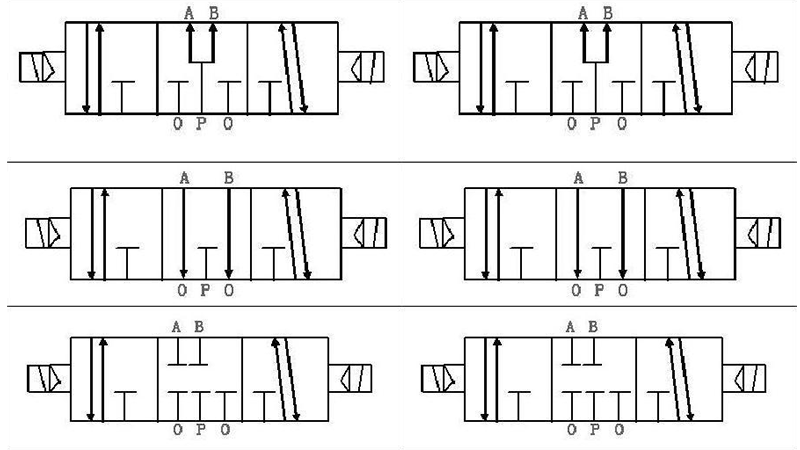
| 2/2 Solenoid Valve | Two ports, two positions; simple operation | Water control, HVAC systems | Pros: Easy to install; Cons: Limited functionality for complex systems. |
| 3/2 Solenoid Valve | Three ports, two positions; versatile operation | Pneumatic controls, automation systems | Pros: Flexible for various applications; Cons: More complex than 2/2 valves. |
| 5/2 Solenoid Valve | Five ports, two positions; commonly used | Industrial machinery, robotics | Pros: Efficient for double-acting cylinders; Cons: Requires careful installation. |
| 4/2 Solenoid Valve | Four ports, two positions; directional control | Fluid power systems, manufacturing | Pros: Good for applications needing direction change; Cons: More expensive than simpler valves. |
| Single Winding | Operates with one coil; simple design | Basic automation tasks | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited in performance under heavy loads. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 2/2 Solenoid Valves?
2/2 solenoid valves feature two ports and two positions, making them ideal for straightforward applications such as controlling water flow in HVAC systems or irrigation. Their simplicity allows for easy installation and maintenance, which is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to minimize downtime. However, their limited functionality means they may not be suitable for more complex systems requiring multiple pathways or functions.
How Do 3/2 Solenoid Valves Enhance Versatility?
The 3/2 solenoid valve introduces a third port, allowing for a wider range of applications, including pneumatic controls and automation systems. This versatility is a significant advantage for industries that require flexible solutions. While they provide greater adaptability than 2/2 valves, the increased complexity can lead to more challenging installations and potential maintenance issues.
Why Are 5/2 Solenoid Valves Common in Industrial Applications?
5/2 solenoid valves are characterized by their five ports and two positions, making them particularly suitable for controlling double-acting cylinders in industrial machinery and robotics. Their efficiency in managing air flow direction is a key benefit, particularly in high-demand environments. However, their installation requires precision and expertise, which can increase initial costs for businesses.
What Makes 4/2 Solenoid Valves Ideal for Fluid Power Systems?
4/2 solenoid valves are designed with four ports and two positions, allowing them to effectively manage the direction of fluid flow. This capability is essential in fluid power systems and manufacturing processes where control over flow direction is critical. While they offer enhanced functionality, the complexity and cost can be a consideration for buyers looking for budget-friendly options.
How Do Single Winding Solenoids Support Basic Automation?
Single winding solenoids operate using a single coil and are designed for basic automation tasks. Their straightforward design makes them a cost-effective option for businesses that require simple actuation solutions. However, their performance may be limited under heavy loads, making them less suitable for high-demand applications where more robust solutions are necessary.
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid symbol
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solenoid symbol | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Automation of packaging machinery | Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs | Compliance with hygiene standards, reliability in high-volume production |
| Oil and Gas | Control of flow in pipelines | Enhanced safety and operational efficiency | Durability in harsh environments, resistance to corrosion |
| Water Treatment | Regulation of water flow in treatment plants | Improved water quality and conservation of resources | Quality certifications, compatibility with various media types |
| Manufacturing | Operation of pneumatic systems in assembly lines | Streamlined operations and reduced downtime | Availability of technical support, ease of integration |
| HVAC Systems | Control of heating and cooling units | Energy efficiency and improved climate control | Compliance with energy regulations, adaptability to local standards |
How is the solenoid symbol utilized in the food and beverage industry?
In the food and beverage sector, the solenoid symbol is crucial for representing the automation of packaging machinery. Solenoid valves control the flow of liquids and gases, ensuring precise filling and sealing processes. This automation not only enhances efficiency but also significantly reduces labor costs. Buyers in this industry must prioritize compliance with hygiene standards, as well as the reliability of components to withstand high-volume production cycles.
What role does the solenoid symbol play in the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas industry, the solenoid symbol is used to signify the control mechanisms for flow regulation in pipelines. These solenoid valves are integral to maintaining safety and operational efficiency, especially in environments where pressure and flow must be meticulously managed. International buyers should focus on sourcing durable components that can withstand harsh conditions and resist corrosion, which is vital for ensuring long-term functionality in this demanding sector.
How is the solenoid symbol applied in water treatment facilities?
Water treatment plants utilize the solenoid symbol to denote the regulation of water flow through various treatment processes. Solenoid valves play a pivotal role in controlling the distribution and treatment of water, leading to improved water quality and resource conservation. Buyers should consider quality certifications and compatibility with different media types to ensure that the solenoid valves meet the specific requirements of their treatment systems.
In what ways does the solenoid symbol facilitate manufacturing processes?
The manufacturing sector leverages the solenoid symbol to depict the operation of pneumatic systems within assembly lines. These systems are crucial for automating tasks such as material handling and assembly, which streamlines operations and minimizes downtime. Buyers should seek components that offer robust technical support and are easy to integrate into existing systems to maximize productivity and efficiency.
How does the solenoid symbol enhance HVAC systems?
In HVAC systems, the solenoid symbol represents the control mechanisms for heating and cooling units. Solenoid valves regulate the flow of refrigerants and air, contributing to energy efficiency and improved climate control within buildings. Sourcing considerations for international buyers include ensuring compliance with local energy regulations and adaptability to various system designs to optimize performance and sustainability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solenoid symbol’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misinterpretation of Solenoid Valve Symbols in Schematics
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter complex schematics that use various solenoid symbols, leading to confusion and misinterpretation. This is especially common in industries like manufacturing and automation, where precise valve operations are critical. A misreading can result in incorrect installations or operations, potentially causing costly downtime or safety issues. Buyers in regions such as Africa or South America, where technical training resources may be limited, face heightened challenges in understanding these symbols accurately.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs that focus on reading and interpreting solenoid valve symbols. Providing visual aids, such as a detailed guide or cheat sheet that explains each symbol and its function, can significantly enhance understanding. Additionally, using software solutions like Siemens’ Capital X Panel Designer can streamline the process. This software offers pre-made solenoid IEC symbols, allowing users to easily integrate them into schematics while ensuring accuracy. By familiarizing staff with these resources, businesses can improve operational efficiency and reduce the risk of errors.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Standardizing Solenoid Symbols Across Teams
The Problem: In multinational companies, differing standards and conventions for solenoid symbols can create inconsistencies in documentation and communication among teams. For instance, teams in Europe might follow one standard (like IEC), while those in the Middle East may adhere to another (like JIC). This lack of standardization can lead to misunderstandings, errors in design, and complications in maintenance, all of which can hinder project progress and escalate costs.
The Solution: Establishing a standardized symbol library is essential for fostering clear communication across all teams. Organizations should adopt a universally accepted standard for solenoid symbols, such as IEC 60617, and ensure that all team members are trained in its use. This can be complemented by creating a centralized digital repository where all schematics and symbols are stored. Additionally, conducting regular workshops to refresh knowledge and address any updates in standards can help maintain consistency. By standardizing these symbols, companies can enhance collaboration and efficiency, reducing the likelihood of costly errors.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Solenoid Symbols for Custom Projects
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find high-quality, accurate solenoid symbols tailored to their specific project needs. This is particularly challenging for companies involved in bespoke automation solutions where generic symbols may not effectively represent their unique systems. The inability to source appropriate symbols can result in delays and increased project costs, particularly for businesses in rapidly developing regions like Brazil or the Middle East, where rapid scaling is essential.
The Solution: To address this sourcing challenge, companies should partner with specialized suppliers who offer customizable solutions. When sourcing solenoid symbols, buyers should look for vendors that provide comprehensive symbol libraries and allow for the customization of symbols based on specific project requirements. Utilizing software tools that facilitate the creation of custom symbols can also be beneficial. Additionally, engaging with local engineering firms or consultants who understand regional practices can help ensure that the sourced symbols are not only accurate but also relevant to local standards. By proactively addressing sourcing issues, companies can keep projects on track and within budget, enhancing overall productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid symbol
What Are the Key Materials Used in Solenoid Symbols?
When selecting materials for solenoid symbols, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific requirements of international markets. Here, we analyze four common materials: brass, stainless steel, plastic, and aluminum.
How Does Brass Perform in Solenoid Applications?
Brass is a popular choice for solenoid components due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically operates well in moderate temperature and pressure environments, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including water and gas systems.
Pros and Cons: Brass is durable and has a good aesthetic appeal, often used in visible applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may not be suitable for highly aggressive media, which can lead to corrosion over time.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with water and air but may struggle with aggressive chemicals. Buyers in regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures and corrosive environments are common, should consider this limitation.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is crucial for applications in industries like oil and gas.
Pros and Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it requires less frequent replacement. However, it is generally more expensive and can be more challenging to machine compared to brass or plastic.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals. For international buyers, compliance with standards like ASTM or DIN is essential, as many regions have strict regulations regarding material use in industrial applications.
How Does Plastic Compare in Solenoid Symbol Applications?
Plastic, particularly engineering-grade plastics like polyamide or polycarbonate, is increasingly used in solenoid applications due to its lightweight and cost-effective nature. These materials can handle moderate pressure and are resistant to many chemicals.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, which can significantly reduce production time. However, plastics typically have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
Illustrative image related to solenoid symbol
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for non-aggressive media, making it ideal for applications in the food and beverage industry. Buyers in Africa and South America may find plastic options appealing due to lower costs and sufficient performance for less demanding applications.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solenoid Symbols?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that is often used in solenoid applications where weight savings are critical. It can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, making it versatile for various uses.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce overall system weight. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications involving air and light oils. Buyers in Europe may prefer aluminum for its compliance with environmental regulations, as it is often more recyclable than other metals.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solenoid Symbols
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid symbol | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Water and gas systems | Good machinability and aesthetics | Corrosion in aggressive media | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas applications | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Plastic | Food and beverage industry | Low cost and easy manufacturing | Limited temperature/pressure ratings | Low |
| Aluminum | Air and light oil applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for solenoid symbols is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with international standards. By understanding the properties and applications of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid symbol
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solenoid Symbols?
The manufacturing process for solenoid symbols encompasses several stages designed to ensure precision and reliability. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who prioritize quality and consistency in their procurement processes.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Solenoid Symbol Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting appropriate materials. Typically, solenoid symbols are made from durable materials such as steel, brass, and various plastics. The choice of material depends on the intended application and environmental conditions. For instance, brass is often used for its resistance to corrosion, while steel offers strength and durability. Materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet required specifications before moving on to the forming stage.
How Are Solenoid Symbols Formed?
Forming is the next critical stage, where raw materials are transformed into components that represent solenoid symbols. This process may involve techniques such as stamping, machining, and injection molding. Stamping is frequently used for creating metal parts, while plastics may be molded using injection techniques to achieve complex shapes. Advanced technologies like CNC machining ensure high precision during this stage, which is vital for the accurate representation of solenoid symbols in diagrams and schematics.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once the individual components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This involves fitting together various parts to create the complete solenoid symbol unit. Automated assembly lines are common in modern manufacturing facilities, enhancing speed and consistency. Skilled technicians often oversee this process to ensure that every symbol is assembled correctly, adhering to stringent standards.
How Is Finishing Achieved for Solenoid Symbols?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the appearance and functionality of solenoid symbols. Techniques such as painting, coating, or plating are employed to provide protection against environmental factors and improve aesthetics. Quality assurance during this stage ensures that the final product meets both functional and visual standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Solenoid Symbols?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of solenoid symbols to ensure that they meet international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA practices is key to making informed purchasing decisions.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of solenoid symbols often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications provide assurance that products meet regulatory and safety requirements.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks are performed to monitor processes and prevent defects.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, final inspections are conducted to ensure the finished product meets all quality criteria.
Each of these checkpoints plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity of the solenoid symbols.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Testing methods for solenoid symbols can vary based on their intended application but often include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that the solenoid operates as intended under various conditions.
- Durability Testing: Assessing how well the solenoid withstands environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
- Electrical Testing: Ensuring that electrical components function correctly and safely.
These tests help guarantee that the solenoid symbols will perform reliably in their respective applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
What Audit Processes Should Be Implemented?
Buyers should consider conducting audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This may involve on-site visits to observe manufacturing practices and review quality assurance documentation.
How Important Are Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting quality control reports from suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing and inspection processes. Additionally, third-party inspections can serve as an independent verification of quality standards. Engaging with accredited inspection agencies can further enhance confidence in supplier capabilities.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing solenoid symbols internationally, buyers should be aware of various nuances that can affect quality assurance. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and industry standards, which can impact product quality. Buyers should communicate their specific requirements clearly to suppliers and ensure that all necessary certifications are in place.
Illustrative image related to solenoid symbol
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for solenoid symbols is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable and high-quality components. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solenoid symbol’
Introduction
When sourcing solenoid symbols for your business, having a structured approach can significantly streamline the process. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure that you select the right symbols that meet your technical requirements while also aligning with industry standards. Following these steps will help you make informed decisions, ensuring that your pneumatic systems operate efficiently and reliably.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before starting your search for solenoid symbols, clearly outline your technical requirements. Understanding the specifics, such as the type of solenoid valve (2/2, 3/2, etc.) and its operational parameters, is critical.
- Consider media type: Different symbols are used for various media (e.g., air, water, steam).
- Identify the application: Determine whether it’s for a specific industry like food production or petrochemical, as this will influence your choices.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards
Familiarize yourself with the relevant industry standards that govern solenoid symbols. Compliance with standards such as ISO, IEC, or local regulations ensures that the symbols you choose will be universally recognized and correctly interpreted.
- Focus on regional standards: Different regions may have specific requirements; for example, symbols used in Europe may differ from those in Africa or South America.
- Check for updates: Standards can evolve; ensure that you are referencing the most current guidelines.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. This includes assessing their reputation, product range, and compliance with industry standards.
- Request documentation: Ask for product catalogs and technical specifications to understand the breadth of their offerings.
- Seek references: Contact other businesses in your industry to get feedback on the supplier’s reliability and product quality.
Step 4: Assess Symbol Compatibility
Ensure that the solenoid symbols you are considering are compatible with your existing systems. This includes checking the electrical specifications and the physical configuration of the symbols.
- Verify software compatibility: If you are using design software, ensure that the symbols can be easily integrated into your schematics.
- Check for custom options: Some suppliers may offer customization to meet your specific needs.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, compare their pricing structures and terms of sale. This includes not only the cost of the symbols but also any additional fees for shipping, handling, or customization.
- Analyze total cost of ownership: Consider long-term costs, including maintenance and potential replacements, rather than just the initial purchase price.
- Look for bulk discounts: If you plan to order large quantities, inquire about volume discounts to optimize your budget.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications that validate their product quality and compliance with industry standards. This step is crucial for ensuring reliability and safety in your operations.
- Check for ISO certifications: These indicate that the supplier adheres to international quality management standards.
- Review safety certifications: Ensure that the products meet safety regulations relevant to your industry.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Establish Communication
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize your order and establish clear communication channels. This ensures that any questions or issues can be addressed promptly.
- Set clear expectations: Discuss lead times, delivery schedules, and any potential challenges upfront.
- Keep lines of communication open: Regular updates can help mitigate any issues during the procurement process.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for solenoid symbols, ensuring that you select the best options for your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid symbol Sourcing
When sourcing solenoid symbols for various applications, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The cost components can be broken down into several key categories: materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Solenoid Symbol Sourcing?
Materials play a significant role in the overall cost, with variations depending on the type of solenoid valve and the materials used (e.g., brass, stainless steel, or plastic). The choice of material impacts both performance and durability, which can be crucial for specific applications in industries such as food production or petrochemicals.
Labor costs include the wages paid to workers involved in the manufacturing process. This can vary significantly depending on the region and the skill level required. For instance, countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but quality and reliability must still be assessed.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and facility maintenance. These costs can differ based on geographical location and the scale of production.
Tooling costs involve the investment in molds and fixtures necessary for manufacturing solenoid symbols. High initial tooling costs can be justified through economies of scale when producing large volumes.
Quality control (QC) is a critical component, ensuring that products meet the required standards and certifications. Enhanced QC processes may increase costs but can lead to higher customer satisfaction and reduced returns.
Logistics costs include shipping, handling, and insurance. Given the international nature of B2B transactions, understanding Incoterms is vital, as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping and risk management.
Margins represent the profit added by suppliers and can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
Illustrative image related to solenoid symbol
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Solenoid Symbols?
Several factors influence the pricing of solenoid symbols, including volume or minimum order quantities (MOQs), specifications, and customization options. Generally, higher volumes lead to reduced per-unit costs, making bulk purchases more economical.
Specifications and customization can significantly impact pricing. Custom solenoid symbols designed for specific applications may involve additional engineering and tooling costs, thus increasing the total price. Buyers must weigh the benefits of customized solutions against the potential cost increases.
Material quality and certifications are also crucial. Products that meet international standards may command higher prices but offer reliability and compliance, particularly important for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food production.
Supplier factors include the reputation and reliability of the manufacturer. Established suppliers often provide better quality assurance and support, which can justify a higher price point.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Solenoid Symbols?
When negotiating prices, it’s essential to approach suppliers with a clear understanding of your needs and budget. Leverage your purchasing power, especially if you can commit to larger volumes or long-term contracts, to negotiate better terms.
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront cost. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with subpar products. Investing in higher-quality solenoid symbols may reduce long-term operational issues.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, be aware of pricing nuances influenced by tariffs, import duties, and local market conditions. Understanding these factors can help in budgeting and forecasting overall expenses.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is crucial to note that prices for solenoid symbols can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and specific buyer requirements. Therefore, always obtain detailed quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate pricing aligned with your project needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solenoid symbol With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Solenoid Symbols: A Comparative Analysis
When selecting a solution for actuating mechanisms in various industrial applications, understanding the alternatives to solenoid symbols is crucial for B2B buyers. Solenoid symbols are widely used in pneumatic and hydraulic schematics to represent solenoid-operated valves and other components. However, there are other technologies and methods that can achieve similar goals, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. This analysis will compare solenoid symbols with two viable alternatives: pneumatic actuators and electric actuators.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Solenoid Symbol | Pneumatic Actuator | Electric Actuator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed operation, precise control | Fast response, but limited by air pressure | High torque and speed, flexible control options |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost | Generally lower cost for large systems | Higher upfront costs, but lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires understanding of symbols | Straightforward installation | More complex due to wiring and configuration |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for air quality | Low maintenance, but may require periodic checks |
| Best Use Case | Compact systems with limited space | Heavy-duty applications with high force needs | Applications requiring precise positioning or variable speed |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators are devices that utilize compressed air to generate mechanical motion. Their primary advantage is speed; they can achieve rapid actuation in a variety of applications, making them ideal for assembly lines and other high-speed environments. However, they often require a compressed air source, which can lead to increased operational costs if not managed properly. Additionally, pneumatic systems can be sensitive to air quality, necessitating regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators operate using electric motors to produce motion. They offer high precision and are easily programmable, making them suitable for applications that require variable speed and position control. While the initial investment can be higher compared to solenoid symbols, electric actuators often result in lower long-term operational costs due to their energy efficiency. Their complexity in installation and setup can be a drawback, particularly for companies with limited technical expertise. However, they excel in environments where precise control is critical.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When considering the best solution for your application, it is essential to evaluate the specific requirements of your project. Solenoid symbols offer a straightforward approach for representing solenoid-operated mechanisms, particularly in compact systems. However, if your application demands rapid actuation or precise control, pneumatic or electric actuators may be more suitable. Assessing factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance will guide B2B buyers in selecting the most appropriate solution to meet their operational goals. Understanding these alternatives will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their unique business needs and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid symbol
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Solenoid Symbols?
Understanding the technical properties of solenoid symbols is crucial for B2B buyers involved in procurement, engineering, or manufacturing. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material used for solenoid components, such as stainless steel, brass, or plastic, significantly affects durability and corrosion resistance. In industries like oil and gas or food production, selecting the right material is essential for compliance with safety standards and operational longevity. -
Voltage Rating
Solenoid symbols indicate the voltage required for operation, typically ranging from 12V to 240V. This specification is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems, preventing equipment failure, and optimizing energy consumption. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating denotes the maximum pressure the solenoid can handle without failure. This property is particularly important in hydraulic and pneumatic applications, where exceeding the rated pressure can lead to system inefficiencies or catastrophic failures. -
Flow Rate
The flow rate specifies the maximum volume of fluid that can pass through the solenoid valve per unit time, usually measured in liters per minute (L/min). Understanding flow rates helps in selecting the appropriate solenoid for specific applications, ensuring that the system can meet operational demands. -
Operating Temperature Range
Solenoid symbols often indicate the temperature range within which the solenoid can function effectively. This property is critical in applications exposed to extreme temperatures, as it influences material selection and overall reliability. -
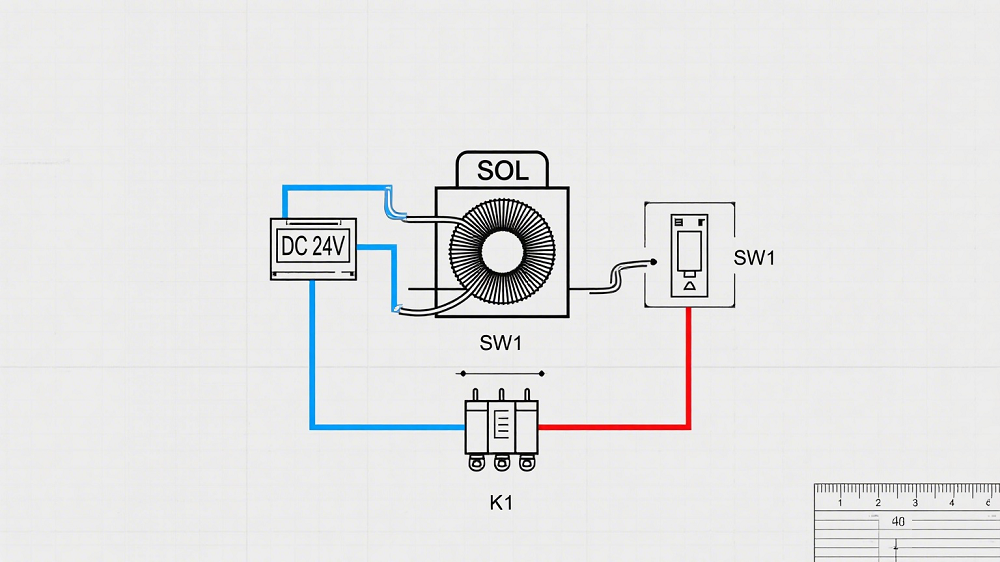
Response Time
This specification indicates how quickly the solenoid can actuate when energized. Fast response times are crucial in automated systems where timing is essential for operational efficiency.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know About Solenoid Symbols?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms relevant to solenoid symbols:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is essential for buyers seeking high-quality components that are compatible with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budgeting and inventory management, as it can affect overall costs and supply chain logistics. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods or services. Knowing how to prepare an effective RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps in understanding shipping, insurance, and liability issues. -
P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram)
P&ID is a schematic illustration of the functional relationship between piping, instrumentation, and system components. Understanding P&ID is essential for engineers and procurement specialists involved in the design and implementation of fluid systems. -
Actuation
Actuation refers to the process of causing a device to operate, often through electrical signals in the case of solenoids. This term is vital for understanding the operational mechanics of solenoids and their integration into automated systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solenoid symbols and related components, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solenoid symbol Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Solenoid Symbol Sector?
The solenoid symbol sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by technological advancements and shifting market demands. As industries increasingly automate processes, the demand for solenoid valves—integral components in pneumatic and hydraulic systems—continues to rise globally. Key trends include the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, with IoT-enabled devices enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. This has led to a growing preference for suppliers who offer smart solenoid solutions that can be seamlessly integrated into existing systems.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate diverse market dynamics. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, the push for infrastructure development and energy efficiency is propelling the adoption of solenoid valves across sectors such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and agriculture. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only high-quality products but also comprehensive technical support and customization options to meet specific operational needs.
Moreover, the emphasis on reducing lead times and optimizing supply chains is reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are leveraging digital procurement platforms to identify reliable suppliers and streamline purchasing processes, thereby enhancing their competitive edge in the global marketplace.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Solenoid Symbol Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the solenoid symbol sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly expected to adopt greener practices, such as utilizing energy-efficient production methods and sourcing raw materials responsibly.
In response to these demands, many manufacturers are obtaining ‘green’ certifications and utilizing environmentally friendly materials in their products. This not only minimizes the ecological footprint but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. Moreover, suppliers that prioritize ethical supply chains—ensuring fair labor practices and transparency—are gaining a competitive advantage. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers, looking for those who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical standards.
For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers that value sustainability can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty, which is essential in today’s market where consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on corporate social responsibility.
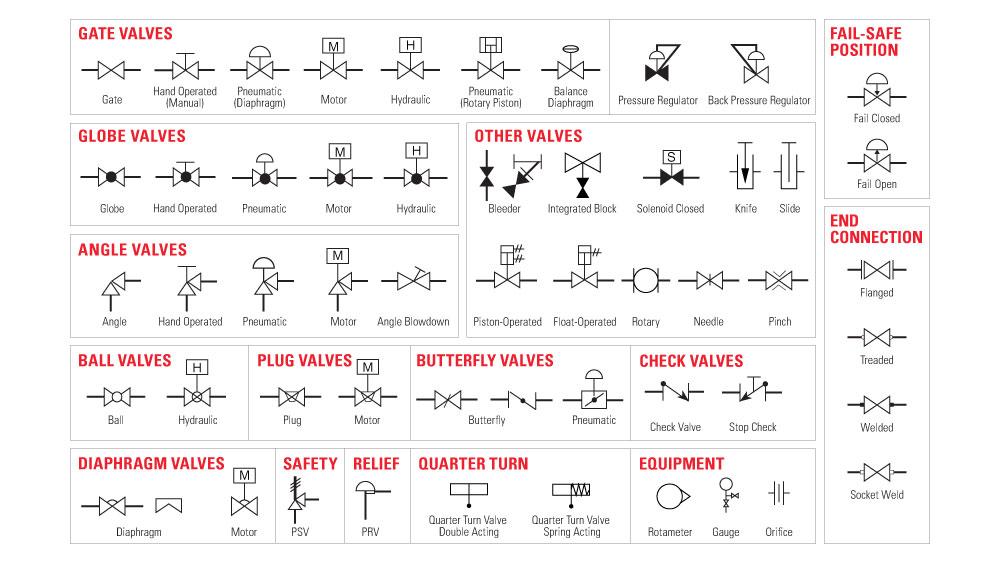
Illustrative image related to solenoid symbol
What Is the Evolution of Solenoid Symbols and Their Relevance Today?
The evolution of solenoid symbols can be traced back to the need for standardized communication in engineering and design. Initially, these symbols were rudimentary, serving basic functions in schematic diagrams. However, as automation and complex systems emerged, the need for more detailed and standardized symbols became apparent.
Standards like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) have played crucial roles in defining solenoid symbols, ensuring consistency across industries. Today, these symbols are vital for engineers and technicians as they facilitate clear communication of system designs, enabling efficient troubleshooting and maintenance.
In a B2B context, the relevance of solenoid symbols extends beyond mere representation; they form the backbone of effective engineering practices. As industries evolve, staying updated with the latest symbol standards is essential for ensuring compliance and operational efficiency, making it a critical consideration for international buyers in the solenoid symbol sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid symbol
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with solenoid symbols in my schematic designs?
To resolve compatibility issues with solenoid symbols in your schematic designs, ensure that you are using standardized symbols recognized in your region or industry, such as IEC or ANSI standards. Utilize schematic design software that supports these standards, allowing for easy integration and modification of symbols. Always consult with your engineering team to verify that the symbols accurately represent the components used in your systems. If needed, consider custom symbols that align with your specific applications while maintaining clarity and compliance. -
What is the best source for purchasing solenoid symbols for international projects?
The best source for purchasing solenoid symbols for international projects includes reputable suppliers with a global reach and strong customer support. Look for manufacturers who provide comprehensive catalogs that include standardized symbols for various applications. Verify their compliance with international standards and their ability to offer customization options. Additionally, consider suppliers who have positive reviews from clients in your region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to ensure reliability and quality. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for solenoid symbols?
When vetting suppliers for solenoid symbols, consider their experience in the industry, product quality, and adherence to international standards. Review their certifications and the range of symbols offered, ensuring they meet your specific project requirements. Assess their customer service, responsiveness, and support for customization. Additionally, check for client testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and performance in past projects, especially those relevant to your geographical market. -
How can I customize solenoid symbols for my specific application?
To customize solenoid symbols for your specific application, start by clearly defining your requirements and the functions that need representation. Work with a supplier or design software that allows for symbol customization, ensuring compliance with industry standards. Provide input on the design elements, such as size, labeling, and connection points, to accurately reflect your system. Collaboration with your engineering team during this process is crucial to ensure that the symbols effectively communicate the intended functionality. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for solenoid symbols?
The typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for solenoid symbols varies by supplier and the complexity of the symbols required. Generally, suppliers may have MOQs ranging from a few dozen to several hundred units, depending on whether the symbols are standard or customized. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller orders if necessary. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial for smaller projects or initial testing phases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing solenoid symbols internationally?
When sourcing solenoid symbols internationally, payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 days after invoice. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or extended terms for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in fulfilling the order. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, credit cards, or letters of credit, to avoid any complications during the transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for solenoid symbols before purchase?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) for solenoid symbols before purchase, request samples or prototypes from potential suppliers. Verify their compliance with relevant industry standards and certifications. Conduct thorough inspections upon receipt, checking for accuracy in design, material quality, and functionality. Establish a clear QA protocol with your supplier that includes criteria for acceptance, return policies for defective items, and measures for continuous improvement. Regular communication with suppliers can also help address any QA concerns proactively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solenoid symbols?
When importing solenoid symbols, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable shipping partner that can handle international logistics efficiently. Be aware of any import duties or taxes applicable in your country, as these can affect the overall cost. Ensure that your supplier provides accurate documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Planning for potential delays and establishing clear communication with your logistics provider can also help in managing the import process effectively.
Top 5 Solenoid Symbol Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Solenoid Symbol in Electrical Schematics
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the symbol used to represent a solenoid in electrical schematics. It mentions that this symbol is commonly used in industrial control schematics and has been in use for over a century. Some users express their opinions on the symbol, with some finding it confusing or resembling a resistor, while others confirm it as an accepted symbol for solenoid valves.
2. Connexion Developments – Solenoid Valve Symbols
Domain: connexion-developments.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valve Symbols UK Free : 0800 808 7799 Int : +44 1454 334 990. Common solenoid valve types include: 2/2 Valve (2 Ports, 2 Positions), 3/2 Valve (3 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/2 Valve (4 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/3 Valve (4 Ports, 3 Positions), 5/2 Valve (5 Ports, 2 Positions), 5/3 Valve (5 Ports, 3 Positions). Media types include: Air and Inert Gases, Light Oil, Natural Gas, Slightly Aggressive Me…
3. Tameson – Solenoid Valves
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Solenoid valves are represented by unique symbols in fluid power diagrams to indicate their functions and connections. Key details include: 1. Types of solenoid valves: 2-Way, 3-Way, Proportional Valves, Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, and Accessories. 2. Valve designations: For example, a 2/2-way valve has two connection ports and two switching states (open and closed). 3. Symbols: A 2/2 valve is repr…
4. Control – Solenoid Valves
Domain: control.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Solenoid valves are on/off valves used in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when energized, attracting a movable ferrous armature to actuate a valve mechanism. Solenoid valves are classified by the number of ports: 2-way valves have two ports for fluid flow, while 3-way valves have three ports, allowing flow to be directed in different pat…
5. Autodesk – Standard Solenoid Valves
Domain: help.autodesk.com
Registered: 1989 (36 years)
Introduction: This company, Autodesk – Standard Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid symbol
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of solenoid symbols is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Understanding the various solenoid valve symbols—such as the distinctions between 2/2, 3/2, and 5/2 configurations—enables companies to streamline their operations and enhance communication in engineering projects. Moreover, leveraging standardized symbols ensures compliance with international standards, facilitating smoother collaboration across borders.
As buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly engage in complex industrial projects, the ability to accurately interpret and utilize solenoid symbols becomes a critical asset. By investing in quality resources and software solutions for schematic design, organizations can significantly improve their workflow and project outcomes.
Looking ahead, the continued evolution of technology and automation will only amplify the importance of precise schematic representations. We encourage B2B buyers to prioritize training and resources that enhance their understanding of solenoid symbols, enabling them to stay competitive and innovative in a rapidly changing marketplace. Explore partnerships with suppliers and software providers to ensure you are equipped for the challenges of tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.