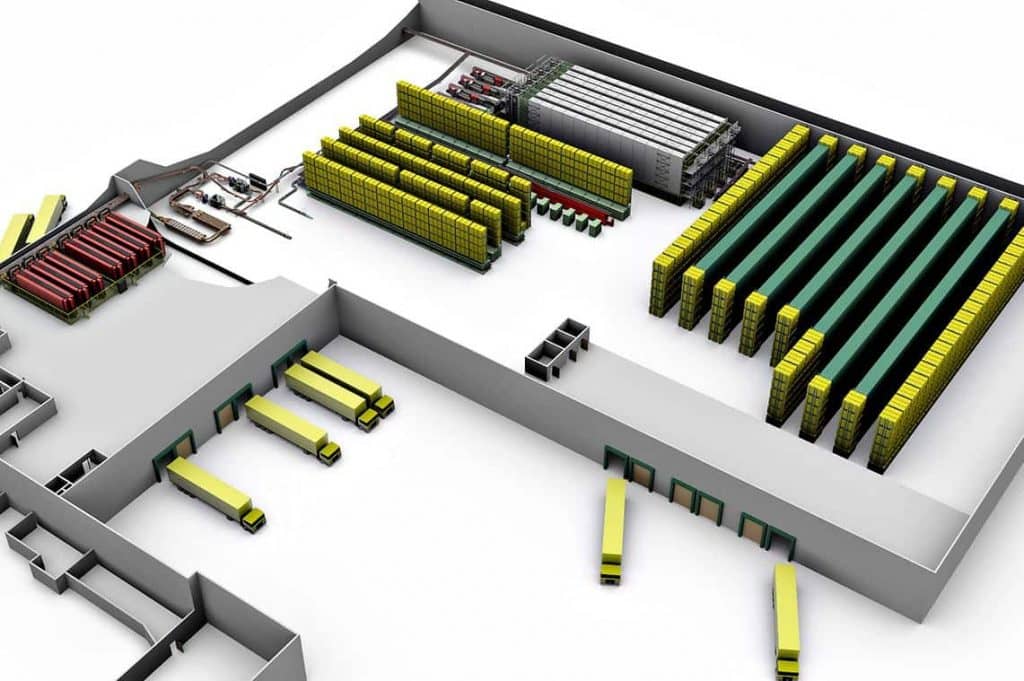
Top 4 Cold Storage Design Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold storage design
The global market for cold storage design presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers aiming to maintain the quality and integrity of perishable goods. As businesses across diverse sectors—from pharmaceuticals to food services—seek reliable cold storage solutions, the complexities of sourcing effective designs that comply with local regulations and international standards can be daunting. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of cold storage design, detailing various types of facilities, their specific applications, and the critical factors influencing cost and efficiency.
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Vietnam and Brazil—will find valuable insights tailored to their unique needs. The guide empowers readers to navigate supplier vetting processes, ensuring they select partners who not only provide cutting-edge technology but also understand the regional nuances that affect cold storage operations. By addressing key considerations such as temperature control, regulatory compliance, and logistical coordination, this resource equips businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product preservation. Whether you’re exploring refrigerated or frozen storage options, our guide is your go-to resource for optimizing cold storage design in a rapidly evolving market.
Understanding cold storage design Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerated Storage | Maintains temperatures between 33°F and 55°F; ideal for perishables | Food service, supermarkets, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Cost-effective, suitable for many products. Cons: Limited to non-frozen items. |
| Frozen Storage | Operates at temperatures below 32°F; designed for frozen goods | Meat processing, seafood distribution, frozen foods | Pros: Extends shelf life of products. Cons: Higher energy costs and infrastructure requirements. |
| Climate-Controlled Storage | Regulates both temperature and humidity; more precise control | Pharmaceuticals, high-value art, and archival storage | Pros: Protects sensitive items; reduces spoilage. Cons: More expensive due to advanced systems. |
| Private Cold Storage | Owned by the same entity that produces the goods stored | Large manufacturers, food producers | Pros: Tailored to specific needs; greater control. Cons: High initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| Public Cold Storage | Available for lease to multiple users; shared facilities | Small businesses, seasonal producers | Pros: Flexible leasing options; lower upfront costs. Cons: Less control over storage conditions. |
What Are the Characteristics of Refrigerated Storage?
Refrigerated storage is designed to maintain a temperature range of 33°F to 55°F, making it suitable for a wide variety of perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and pharmaceuticals. Businesses in the food service and supermarket sectors often utilize this type of storage to preserve the freshness of their products. When considering refrigerated storage, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific temperature requirements of their goods, the potential for energy efficiency, and the ease of access for inventory management.
How Does Frozen Storage Operate?
Frozen storage facilities operate at temperatures below 32°F, making them essential for products that require freezing, such as meat, fish, and frozen meals. This type of storage is crucial for businesses involved in meat processing and seafood distribution, where maintaining product integrity is paramount. Buyers should consider the facility’s energy costs, the technology used for refrigeration, and the potential for expansion as demand grows. Additionally, understanding the logistics of transporting goods in and out of frozen storage can help streamline operations.
What Benefits Does Climate-Controlled Storage Offer?
Climate-controlled storage goes beyond temperature regulation by also managing humidity levels, making it ideal for sensitive items such as pharmaceuticals and high-value artwork. This type of storage is essential for businesses that deal with products sensitive to environmental changes. B2B buyers should assess the specific climate control technologies available, the facility’s compliance with industry regulations, and the associated costs. The investment in climate-controlled storage can lead to significant reductions in spoilage and damage.
What Are the Advantages of Private Cold Storage?
Private cold storage facilities are owned by the same company that produces or uses the goods stored within, providing tailored solutions for specific needs. This type of storage is commonly found in large manufacturing environments, where logistics and efficiency are critical. Buyers considering private cold storage should evaluate the initial investment costs, the potential for customization, and ongoing maintenance requirements. While this option can provide greater control and efficiency, it may also come with higher operational costs.
How Does Public Cold Storage Serve Businesses?
Public cold storage facilities are available for lease to multiple users, offering a cost-effective solution for businesses that may not need dedicated cold storage space. This model is particularly beneficial for small businesses and seasonal producers who require flexibility without the burden of high upfront costs. When choosing public cold storage, buyers should consider the facility’s location, the terms of the lease, and the shared resources available. While this option offers lower costs, it may limit control over storage conditions and access times.
Key Industrial Applications of cold storage design
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cold storage design | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Refrigerated storage for fresh produce | Extends shelf life, reduces spoilage | Temperature control technology, energy efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Cold storage for vaccines and biologics | Ensures product integrity and compliance | Regulatory compliance, monitoring systems |
| Agriculture | Cold storage for harvested crops | Preserves quality and market value | Scalability, humidity control, transportation logistics |
| E-commerce | Cold chain logistics for perishable goods | Enhances customer satisfaction, reduces waste | Inventory management systems, real-time tracking |
| Cosmetics | Storage for temperature-sensitive beauty products | Maintains product effectiveness and safety | Packaging solutions, temperature monitoring |
How Is Cold Storage Design Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, cold storage design is crucial for managing the supply of fresh produce. Facilities are engineered to maintain optimal temperatures, minimizing spoilage and extending shelf life. International buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating temperatures, must prioritize energy-efficient systems and robust insulation to ensure product integrity. Additionally, compliance with food safety regulations is critical, making temperature monitoring systems an essential consideration for sourcing.
What Role Does Cold Storage Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Cold storage design is vital in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for vaccines and biologics that require stringent temperature control. Facilities must adhere to regulatory standards to prevent degradation of sensitive products. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, it’s essential to invest in advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time data on temperature and humidity levels. This ensures compliance and mitigates the risk of financial losses due to compromised inventory.
How Does Cold Storage Benefit the Agriculture Sector?
In agriculture, cold storage plays a pivotal role in preserving harvested crops, allowing them to reach markets while maintaining quality. Facilities designed for this purpose help manage temperature and humidity, which are critical for preventing spoilage. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should consider scalability options, as well as logistics for transporting goods from farms to storage facilities. Effective cold storage solutions can significantly enhance the market value of agricultural products.
Why Is Cold Storage Important for E-commerce?
The rise of e-commerce has made cold chain logistics increasingly important for perishable goods. Cold storage design ensures that products remain at the required temperatures throughout the supply chain, enhancing customer satisfaction by delivering fresh goods. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing sophisticated inventory management systems that facilitate real-time tracking of perishable items. This minimizes waste and optimizes delivery times, which are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
How Does Cold Storage Impact the Cosmetics Industry?
In the cosmetics sector, cold storage design is essential for products that are sensitive to temperature changes, such as skincare and makeup items. Proper storage conditions help maintain the effectiveness and safety of these products. Buyers should seek out solutions that include innovative packaging and temperature monitoring technologies to ensure product integrity. Given the global nature of the cosmetics market, understanding local climate conditions and regulatory requirements is also vital for successful sourcing.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold storage design’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Fluctuating Temperature Control in Cold Storage Facilities
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers encounter in cold storage design is maintaining consistent temperature control. Fluctuations can lead to spoilage of perishable goods, which is particularly problematic for industries dealing with food, pharmaceuticals, or sensitive biological materials. For instance, a food distributor may invest heavily in a state-of-the-art cold storage facility, but if the cooling system fails or is improperly calibrated, products can spoil, leading to financial losses and damaged reputation. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the technical specifications and the potential for costly mistakes.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should prioritize the selection of advanced temperature monitoring systems integrated with real-time analytics. These systems can provide alerts for any deviations from the set temperature range, allowing for immediate corrective actions. Additionally, sourcing equipment from reputable manufacturers who offer warranties and robust support services is crucial. When specifying cold storage designs, include redundancy in cooling systems, such as backup generators and dual-cooling units, to prevent failures. Regular maintenance schedules and training staff on emergency protocols can further ensure that temperature control remains stable.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Space Utilization in Cold Storage Design
The Problem: Efficient space utilization is a common pain point for businesses operating cold storage facilities. Many B2B buyers find that their storage designs do not maximize available space, resulting in increased operational costs and reduced inventory turnover. For instance, a pharmaceutical company may struggle to store a wide variety of temperature-sensitive products without an organized layout, leading to wasted time and potential errors in order fulfillment.
The Solution: To address space inefficiencies, buyers should consider implementing a modular racking system that allows for adjustable storage configurations. This flexibility can accommodate varying product sizes and quantities while maximizing vertical space, which is often underutilized. Additionally, employing advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) can optimize inventory tracking and facilitate better organization. Using software that integrates with cold storage design can help track stock levels, manage expiration dates, and ensure that the most perishable items are accessed first. Investing in automated retrieval systems can also enhance efficiency by reducing the time staff spends locating products.
Scenario 3: Compliance with Regulatory Standards in Cold Storage
The Problem: Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory compliance presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers involved in cold storage design. Regulations vary widely across regions and industries, particularly for those handling food and pharmaceuticals. A buyer in South America, for example, may face stringent local health regulations that require specific temperature controls and documentation for all stored products. Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties, including fines and product recalls.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
The Solution: To ensure compliance, buyers should work closely with legal experts familiar with local and international regulations regarding cold storage. Developing a compliance checklist specific to their products and operational regions can streamline the process. Incorporating technology solutions like electronic logging systems can automate record-keeping and ensure that temperature and humidity data are accurately documented. Furthermore, conducting regular audits and staff training sessions on compliance standards will reinforce the importance of adherence and prepare the team to address potential regulatory challenges proactively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold storage design
What Are the Key Materials for Cold Storage Design?
Selecting the right materials for cold storage design is critical for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in cold storage facilities, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Insulated Panels Perform in Cold Storage Applications?
Insulated panels, typically made of polyurethane or polystyrene, are widely used in cold storage construction due to their excellent thermal insulation properties. These panels can maintain a temperature range of -40°F to 70°F, making them suitable for both refrigerated and frozen storage applications.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Pros: Insulated panels offer high durability and energy efficiency, which can significantly reduce operational costs. They are lightweight, making installation easier and quicker.
Cons: The initial investment can be higher compared to traditional materials. Additionally, if not properly sealed, they may be susceptible to moisture infiltration, leading to potential degradation.
Impact on Application: Insulated panels are compatible with various media, including food products and pharmaceuticals, due to their non-toxic properties.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different regions may have specific building codes and standards, such as ASTM in the U.S. or DIN in Europe. Buyers should ensure that panels meet local regulations regarding fire safety and insulation performance.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Cold Storage Design?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for cold storage environments, particularly for shelving, racks, and equipment. It is known for its corrosion resistance and ability to withstand low temperatures without compromising structural integrity.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and easy to clean, making it ideal for maintaining hygiene in food storage. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of equipment.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to other metals, such as aluminum. Additionally, stainless steel can be heavier, which may complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with food and pharmaceutical products, ensuring no leaching of harmful substances occurs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the stainless steel grades used comply with international standards like JIS for Japan or EN for Europe, ensuring quality and safety.
How Does Polyethylene Compare in Cold Storage Design?
Polyethylene is often used for containers and pallets in cold storage due to its flexibility and resistance to moisture. It can handle temperatures as low as -40°F, making it suitable for various cold storage applications.
Pros: Polyethylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it an excellent choice for cold storage solutions.
Cons: While durable, polyethylene can become brittle at extremely low temperatures, which may limit its lifespan under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Polyethylene containers are compatible with a wide range of products, from food items to pharmaceuticals, due to their inert nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polyethylene products meet local food safety standards and regulations, which can vary significantly across regions.
What Advantages Does Glass-Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GRP) Offer for Cold Storage?
Glass-fiber reinforced plastic (GRP) is gaining traction in cold storage design, particularly for its structural applications. GRP can withstand a wide temperature range and offers excellent insulation properties.
Pros: GRP is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into various shapes, allowing for customized solutions in cold storage design.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and may lead to higher costs. Additionally, GRP may not be as widely accepted in some regions compared to traditional materials.
Impact on Application: GRP is suitable for use in environments where corrosion from moisture is a concern, making it ideal for food and pharmaceutical storage.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations and standards is crucial, as GRP products may need to meet specific fire safety and insulation performance criteria.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cold Storage Design
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold storage design | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulated Panels | Wall and ceiling construction | Excellent thermal insulation | Higher initial investment | High |
| Stainless Steel | Shelving and equipment | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Polyethylene | Containers and pallets | Cost-effective and moisture-resistant | Can become brittle at low temperatures | Med |
| Glass-Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GRP) | Structural applications | Lightweight and customizable | Complex manufacturing process | Med |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific cold storage needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold storage design
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cold Storage Design?
The manufacturing process for cold storage design encompasses several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the facility meets the required specifications for temperature control and product safety. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Cold Storage Design?
Material preparation is the first stage, involving the selection and treatment of raw materials. High-quality insulation materials, such as polyurethane or polystyrene, are crucial for maintaining temperature stability. Additionally, metal components, often made from stainless steel or galvanized steel, are treated to resist corrosion and enhance durability.
During this stage, suppliers must ensure that all materials comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Buyers should inquire about the material certifications and specifications, as these directly impact the cold storage unit’s efficiency and longevity.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Components in Cold Storage?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components for cold storage. Key techniques include:
-
CNC Machining: This precision technique is used for cutting and shaping metal parts. It ensures high accuracy and repeatability, which is essential for components like doors, frames, and structural supports.
-
Foam Injection Molding: For insulation panels, foam injection molding is commonly employed. This process creates seamless panels that provide superior thermal resistance, crucial for maintaining the desired internal temperatures.
The choice of forming technique can affect the thermal efficiency of the cold storage facility. B2B buyers should assess the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers to ensure they utilize modern and efficient techniques.
How Is Assembly Performed in Cold Storage Design?
The assembly stage integrates all individual components into a cohesive cold storage unit. This process includes the installation of refrigeration systems, shelving, and temperature monitoring equipment. It is critical that assembly is carried out in a controlled environment to prevent contamination and ensure that all parts fit correctly.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Buyers should request detailed assembly protocols from suppliers, including diagrams and assembly instructions. This documentation can aid in understanding the quality and thoroughness of the assembly process.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance Cold Storage Performance?
Finishing involves applying protective coatings and seals to components. This stage is vital for enhancing durability and ensuring that the cold storage unit meets hygiene standards. Techniques such as powder coating for metal surfaces provide a robust, corrosion-resistant finish.
Additionally, sealing joints and connections properly can prevent air leaks, which could compromise temperature control. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to finishing standards that ensure longevity and compliance with health regulations.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Practices for Cold Storage Design?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of cold storage facilities, ensuring that products meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements. The QA process involves several checkpoints and methodologies.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Cold Storage Design?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems that manufacturers must adhere to. In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for components used in the pharmaceutical cold storage sector, ensuring that materials and processes meet stringent safety and efficacy requirements.
Understanding these standards is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing products internationally, as they assure compliance with local and global regulations.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Cold Storage Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each component meets quality standards. Common checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process at various stages to identify and rectify issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive inspections and tests on the finished product before delivery.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC processes employed by suppliers, as this directly impacts the reliability and performance of the cold storage unit.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can employ several verification methods:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s facilities and processes can provide insights into their compliance with quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports that outline testing results, non-conformance issues, and corrective actions taken can help buyers assess supplier reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing process and finished products can offer an unbiased assessment of quality.
These practices are particularly important for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance may differ.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several unique QC nuances when sourcing cold storage solutions. Understanding local regulations and standards in the supplier’s country is essential, as compliance may vary significantly.
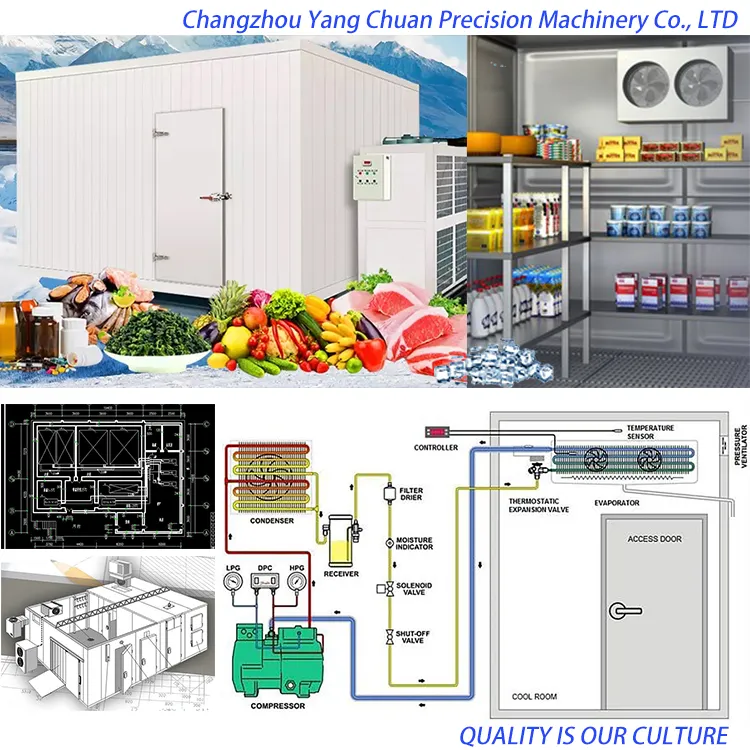
Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can affect communication and quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear quality agreements and expectations upfront to mitigate misunderstandings.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the logistics of transporting cold storage units across borders, as variations in climate and handling can impact product integrity. Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics and quality assurance measures in place can help safeguard the investment.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in cold storage design, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold storage design’
To ensure a successful procurement process for cold storage design, follow this practical step-by-step checklist. Each step is designed to guide you through critical considerations that will enhance your decision-making and ultimately optimize your cold storage operations.
Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the foundation of effective cold storage design. This includes determining the temperature ranges necessary for your products—whether they require refrigerated or frozen storage. Consider the size of the facility, the types of goods stored, and any specific regulatory requirements that may impact your design.
- Temperature Range: Specify whether you need a chilled environment (33° to 55° F) or a frozen one (down to -20° F or lower).
- Storage Capacity: Calculate the cubic footage required based on your inventory turnover and growth projections.
Step 2: Assess Regulatory Compliance Needs
Understanding local and international regulations is crucial for maintaining food safety and product integrity. Different regions may have specific guidelines governing the storage of perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
- Food Safety Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local health codes and food safety standards applicable in your operating regions.
- Pharmaceutical Guidelines: If storing medical supplies, ensure compliance with regulations set by health authorities, such as the FDA or EMA.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence. Evaluate their capabilities, experience, and reputation in the cold storage industry.
- Request Documentation: Ask for company profiles, case studies, and references from similar businesses to gauge their reliability and performance.
- Site Visits: If possible, conduct site visits to their existing facilities to assess their technology and operational standards firsthand.
Step 4: Consider Energy Efficiency Options
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in cold storage operations due to high operational costs. Choosing energy-efficient systems not only reduces expenses but also supports sustainability initiatives.
- Look for Certifications: Check if the cooling systems meet energy efficiency standards such as LEED or ENERGY STAR.
- Evaluate Insulation: High-quality insulation can significantly reduce energy consumption by maintaining stable temperatures with less energy input.
Step 5: Plan for Scalable Solutions
As your business grows, your cold storage needs may change. Selecting a design that allows for scalability will help you adapt to future requirements without extensive overhauls.
- Modular Design: Consider facilities that can be expanded easily or modified to accommodate new technologies and storage methods.
- Flexible Layouts: A design that allows for reconfiguration can help optimize space utilization as product lines evolve.
Step 6: Incorporate Advanced Technology
Investing in modern technology can enhance efficiency and monitoring capabilities in your cold storage facility. Implementing smart technology provides real-time data and alerts, improving operational responsiveness.
- Temperature Monitoring Systems: Use IoT-based solutions for continuous temperature monitoring and automatic alerts for deviations.
- Automated Inventory Management: Explore software solutions that integrate with your storage systems to streamline inventory tracking and reduce waste.
Step 7: Finalize Logistics and Transportation Planning
The effectiveness of your cold storage design is not just about the facility itself but also how products are transported to and from it. Develop a comprehensive logistics plan that ensures timely deliveries while maintaining temperature integrity.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
- Refrigerated Transport: Ensure that your logistics partners have the capability to use temperature-controlled vehicles.
- Delivery Scheduling: Implement efficient scheduling practices to minimize the time products spend in transit and reduce the risk of spoilage.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can systematically approach the sourcing of cold storage design, ensuring that all critical factors are considered for optimal operational performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold storage design Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Storage Design?
When sourcing cold storage design, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and investment. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses insulation, refrigeration units, shelving, and flooring materials. High-quality materials that meet specific regulatory standards can significantly impact costs. For instance, durable and efficient insulation not only affects the initial outlay but also contributes to long-term energy savings.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the installation and maintenance of cold storage facilities. Costs can vary based on the complexity of the design and the local labor market. In regions such as Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but expertise in cold storage technology might be limited.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Understanding overhead is vital for suppliers when pricing their services, especially in different geographic regions.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment needed for the construction and maintenance of cold storage facilities can add to initial costs. Investing in the right tooling can enhance efficiency but requires careful consideration.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the cold storage design meets industry standards and regulations incurs additional costs. Implementing robust QC measures can prevent costly mistakes and ensure compliance with safety standards, particularly for pharmaceuticals and food storage.
-
Logistics: Transportation of materials and equipment to the site can be a significant cost factor, especially for remote locations. Efficient logistics planning can help mitigate these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the design services.
What Influences Pricing in Cold Storage Design?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cold storage design, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for bulk pricing when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs that meet specific requirements may incur higher costs. Standardized solutions can be more cost-effective but may not meet all operational needs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can have a direct impact on both upfront and long-term costs. Higher-quality materials may be more expensive initially but can lead to lower energy costs and longer lifespan.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with certifications (e.g., ISO, HACCP) may charge a premium for their services, but this can also assure buyers of compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better support and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities can influence total costs. Buyers should be clear on who bears the risk and cost during transportation.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Ensure Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize value in sourcing cold storage design, buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and seek to understand their cost drivers. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but the long-term operational costs, including energy consumption, maintenance, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment in quality materials may yield significant savings over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, currency fluctuations, import duties, and shipping costs can significantly affect the final price. It’s crucial to factor these into the overall budget.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of trends in cold storage technology and pricing can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best suppliers.
Conclusion
Investing in cold storage design requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influences, and negotiation strategies. By focusing on these elements, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always consult multiple suppliers and consider the total cost of ownership to ensure the best value for your investment.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold storage design With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Cold Storage Design
As businesses increasingly prioritize the preservation of perishable goods, the need for effective cold storage solutions has never been more critical. However, cold storage design is not the only option available. There are alternative methods that can also meet the demands of temperature-sensitive products. This analysis explores cold storage design alongside two viable alternatives: temperature-controlled packaging and cryogenic storage systems.
Comparison of Cold Storage Design and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Storage Design | Temperature-Controlled Packaging | Cryogenic Storage Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Maintains consistent temperatures; ideal for large volumes | Provides localized temperature control; suitable for smaller shipments | Extremely low temperatures; preserves integrity of sensitive materials |
| Cost | High initial setup and operational costs | Moderate costs; varies by packaging type | Very high due to specialized equipment and operation |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires significant infrastructure | Simple; can be implemented quickly | Complex; requires specialized handling and facilities |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and monitoring | Low maintenance; typically single-use | High maintenance; requires monitoring of cryogenic systems |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale storage for food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals | Distribution of smaller batches; e-commerce deliveries | Long-term preservation of biological samples, vaccines, and sensitive materials |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Temperature-Controlled Packaging
Temperature-controlled packaging, often referred to as insulated shipping containers, is an alternative that focuses on maintaining specific temperatures during transportation. This method is particularly effective for small to medium-sized shipments that require temperature regulation, such as pharmaceuticals or perishables.
Pros: It is cost-effective, as it eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure. Furthermore, these solutions can be implemented quickly and are highly flexible, adapting to various product needs.
Cons: However, temperature-controlled packaging may not provide the same level of consistency as dedicated cold storage facilities. The risk of temperature fluctuations during transportation can compromise product quality if not managed carefully.
Cryogenic Storage Systems
Cryogenic storage employs extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C, to preserve biological samples, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items. This technology is essential for long-term storage of items like stem cells or certain vaccines.
Pros: The primary advantage is its ability to maintain the integrity of sensitive materials for extended periods, effectively halting biological degradation.
Cons: The significant drawback is the high cost associated with the required infrastructure and ongoing operational expenses. Additionally, the complexity of handling cryogenic materials necessitates specialized training and equipment, making it less accessible for many businesses.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate storage solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the volume of goods, budget constraints, and the specific requirements of the products being stored or transported. Cold storage design is ideal for large-scale operations requiring consistent temperature control, while temperature-controlled packaging offers flexibility for smaller shipments. Conversely, businesses needing long-term preservation of sensitive materials may find cryogenic storage systems to be the best choice despite the higher costs. Ultimately, aligning the chosen solution with operational needs and budget will lead to optimal efficiency and product integrity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold storage design
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Cold Storage Design?
When designing a cold storage facility, several technical properties are critical to ensure optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Here are some of the most important specifications:
1. Insulation Value (R-Value)
The R-value measures the thermal resistance of insulation materials. A higher R-value indicates better insulating properties, which is crucial for maintaining desired temperatures and energy efficiency. For B2B buyers, selecting high R-value insulation not only reduces energy costs but also enhances product quality by minimizing temperature fluctuations.
2. Temperature Range
Cold storage facilities must be designed to maintain specific temperature ranges based on the type of goods stored. For instance, refrigerated storage typically operates between 33°F and 55°F, while frozen storage can go as low as -20°F. Understanding the required temperature range is essential for ensuring the integrity and shelf life of sensitive products, thereby preventing spoilage and financial losses.
3. Humidity Control
While not all cold storage facilities require humidity control, maintaining appropriate humidity levels can be vital for specific products, such as pharmaceuticals and fresh produce. Facilities designed with humidity control systems help preserve product quality, making it essential for industries where moisture levels can impact the integrity of goods.
4. Load-Bearing Capacity
Cold storage structures must support heavy loads, including racking systems and the products stored within. The load-bearing capacity is a critical specification that affects design and construction materials. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the facility can handle the necessary weight without compromising structural integrity is vital for long-term operational success.
5. Energy Efficiency (kWh/m²/year)
Energy efficiency metrics, often expressed in kilowatt-hours per square meter per year (kWh/m²/year), are essential for assessing the operational costs of a cold storage facility. High energy efficiency translates to lower operational costs, which is a significant consideration for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain and reduce overhead.
6. Material Grade
The choice of materials used in the construction of cold storage facilities can significantly impact durability and maintenance. Material grades, such as stainless steel for refrigeration units, are selected based on their resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand low temperatures. B2B buyers should prioritize high-quality materials to enhance longevity and reduce maintenance costs.

Illustrative image related to cold storage design
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Storage Design?
Understanding industry terminology is essential for navigating the procurement process effectively. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In cold storage design, OEMs provide specialized refrigeration units and cooling systems tailored to specific operational needs. For buyers, working with reputable OEMs ensures access to quality equipment and reliable support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost per unit. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan purchases and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ is a strategic move for buyers looking to compare options and secure the best pricing for cold storage solutions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping contracts. For cold storage design, understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics and ensuring that both parties are clear on shipping responsibilities, which can affect delivery timelines and costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. In cold storage design, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and ensuring that facilities are operational when needed, thereby avoiding delays in supply chain processes.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their cold storage design projects, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and product integrity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold storage design Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Cold Storage Design?
The cold storage design sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the rising demand for perishable goods, fueled by population growth and changing consumer preferences toward fresh and healthy foods. Additionally, the rapid expansion of e-commerce has intensified the need for efficient cold chain logistics, pushing businesses to invest in advanced cold storage solutions to meet customer expectations for quality and delivery speed.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the cold storage landscape. Automation and IoT (Internet of Things) are increasingly being integrated into cold storage facilities, allowing for real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels. This technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces waste by ensuring that products are stored under optimal conditions. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, investing in automated cold storage solutions can provide a competitive edge by improving supply chain resilience and reducing operational costs.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a shift towards modular cold storage designs that can be easily scaled to meet growing demands. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses in rapidly developing markets, enabling them to adapt to fluctuating consumer demands without significant capital investment.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Cold Storage Design?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the cold storage design sector, as businesses are increasingly aware of their environmental impact. The refrigeration process is energy-intensive, and with rising energy costs and regulatory pressures, companies are seeking more sustainable solutions. Utilizing energy-efficient systems, such as natural refrigerants and advanced insulation materials, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of cold storage facilities.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is essential for maintaining a responsible supply chain. This involves selecting materials and suppliers that adhere to environmental standards and fair labor practices. Certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 for environmental management can help buyers identify sustainable options in cold storage design. Implementing such practices not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Investing in sustainable cold storage solutions can also lead to cost savings over time, as energy-efficient systems lower operational costs. For B2B buyers, prioritizing sustainability in sourcing decisions is not just a trend; it’s a strategic approach that supports long-term profitability and compliance with global sustainability goals.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Cold Storage Design?
The evolution of cold storage design has significantly influenced its current state. Initially, cold storage facilities were rudimentary, utilizing ice and natural refrigeration methods. The introduction of mechanical refrigeration in the early 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for more reliable and controlled temperature environments.
As globalization expanded in the late 20th century, the demand for cold storage surged, driven by international trade in perishable goods. Advances in technology, such as the development of better insulation materials and refrigeration systems, further enhanced the efficiency and capacity of cold storage facilities. Today, the focus has shifted towards integrating smart technology and sustainability into cold storage design, reflecting the industry’s adaptation to modern market demands and consumer expectations.
This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of innovation and adaptability in sourcing cold storage solutions. Understanding these dynamics can help businesses make informed decisions that align with both current trends and future developments in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold storage design
1. How do I solve the challenges of temperature control in cold storage design?
To effectively manage temperature control in cold storage, invest in advanced HVAC systems tailored for your specific goods. Ensure proper insulation to minimize heat transfer and regularly maintain refrigeration units to avoid breakdowns. Implement real-time monitoring systems that alert you to temperature fluctuations. Additionally, train staff on best practices for loading and unloading to reduce exposure to ambient temperatures, ensuring the integrity of perishable items.
2. What is the best cold storage solution for perishable goods?
The best cold storage solution for perishable goods typically combines refrigerated and frozen storage options, depending on the types of products you handle. For fresh produce, a refrigerated environment (33°F to 55°F) is ideal, while frozen goods require temperatures below 32°F. Selecting a facility with customizable zones allows for flexibility in managing various products while maintaining their quality. Consider energy efficiency and compliance with local regulations when choosing your solution.
3. What factors should I consider when selecting a cold storage supplier?
When selecting a cold storage supplier, evaluate their reputation, compliance with industry standards, and experience with your specific product types. Check for certifications related to food safety and pharmaceuticals, as applicable. Assess their facility’s technology and capacity, as well as their logistics capabilities, including transportation options. Finally, ensure they can provide tailored solutions to meet your unique needs, and ask for references from similar businesses to validate their performance.
4. How can I customize my cold storage design to meet specific needs?
Customization of cold storage design can be achieved by working closely with a supplier to assess your operational requirements. Factors such as temperature zones, shelving configurations, and loading/unloading areas can be tailored to optimize efficiency. Additionally, consider implementing technology like automated inventory management systems that align with your business processes. Collaborate with engineers and architects who specialize in cold storage to ensure that your design adheres to industry standards while meeting your specific operational needs.
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold storage systems?
Minimum order quantities for cold storage systems vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Typically, MOQs can range from a few units for modular systems to larger quantities for custom-built solutions. It’s essential to communicate your project scope and requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your budget and timeline. Some suppliers may also offer flexible options for smaller businesses or pilot projects.
6. What payment terms are standard for cold storage equipment purchases?
Payment terms for cold storage equipment purchases often include an upfront deposit (usually 20-50% of the total cost) followed by progress payments throughout the project. Upon completion, the final payment is typically required before the equipment is delivered or installed. Always clarify terms with the supplier and consider negotiating for favorable conditions, such as extended payment periods or financing options, especially for large-scale projects.
7. How do I ensure quality assurance in cold storage design and construction?
To ensure quality assurance in cold storage design and construction, work with suppliers who have a proven track record and relevant certifications. Implement a comprehensive quality management plan that includes regular inspections during the construction phase. Establish clear specifications and performance metrics in your contract to hold suppliers accountable. Post-installation, conduct thorough testing of temperature control systems and overall functionality to confirm compliance with your standards.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for cold storage operations?
Logistics in cold storage operations require careful planning to ensure timely transportation and delivery of goods. Consider the routes and modes of transport that maintain temperature integrity, utilizing refrigerated trucks for perishable items. Coordinate with suppliers and distributors to streamline inventory management and minimize delays. Additionally, stay informed about local regulations regarding food safety and transportation to ensure compliance and avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
Top 4 Cold Storage Design Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. APX Construction Group – Cold Storage Warehouse Design
Domain: apxconstructiongroup.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Cold Storage Warehouse Design: 5 Factors To Consider
1. The Total Area of the Cold Storage Facility: Critical for functionality, efficiency, and cost. Includes storage capacity, handling and processing area, cold storage rooms, loading docks and parking, administrative spaces, equipment and machinery space, utility room, and insulation.
2. The Type of Cold Storage Warehousing: Different types acco…
2. Frigosys – Cold Storage Solutions
Domain: frigosys.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Cold Storage Design – Industrial Cold Room & Equipments: 1. Cold Room: Customizable cold rooms for various storage needs. 2. Cold Room Doors: High-speed PVC doors, hinged doors, sliding doors. 3. Industrial Doors: Designed for durability and efficiency. 4. Cold Room Panels: Available in discontinuous and continuous production lines. 5. Floor Panel: Specialized panels for cold storage floors. 6. Co…
3. FCL Builders – Cold Storage Solutions
Domain: fclbuilders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: FCL Builders specializes in cold storage construction, focusing on precise, investment-grade temperature-controlled facilities. They address the aging cold storage infrastructure and the industry’s need for expansion. Their cold storage projects are innovative and efficient, utilizing sound engineering principles and time-tested construction strategies, including thermal and vapor envelope design….
4. Eng-Tips – Cold Storage Design Insights
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cold storage facility design considerations include unique building codes, material properties of concrete and steel, shrinkage of concrete, and potential effects on steel strength. Specific design features mentioned include: 1) Use of double columns for thermal separation, 2) Hardwood insulation pads under column baseplates, 3) Insulation and heat recycling under slabs to prevent frost heave, 4) …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold storage design
As the demand for cold storage solutions continues to rise globally, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor in optimizing supply chains. By investing in the right cold storage design, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure the integrity of perishable goods. Key considerations include understanding the specific temperature requirements for various products, selecting the appropriate type of cold storage, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers must prioritize partnerships with suppliers who can provide innovative and sustainable cold storage solutions. The increasing consumer preference for fresh and safe products, coupled with population growth and e-commerce expansion, underscores the urgency for companies to adopt advanced cold storage technologies.
Looking ahead, businesses that leverage strategic sourcing in their cold storage designs will not only meet current market demands but also position themselves for future growth. Engage with suppliers who understand your regional challenges and can offer tailored solutions that enhance your competitive edge. Embrace this opportunity to revolutionize your cold chain logistics and secure your place in an evolving marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.