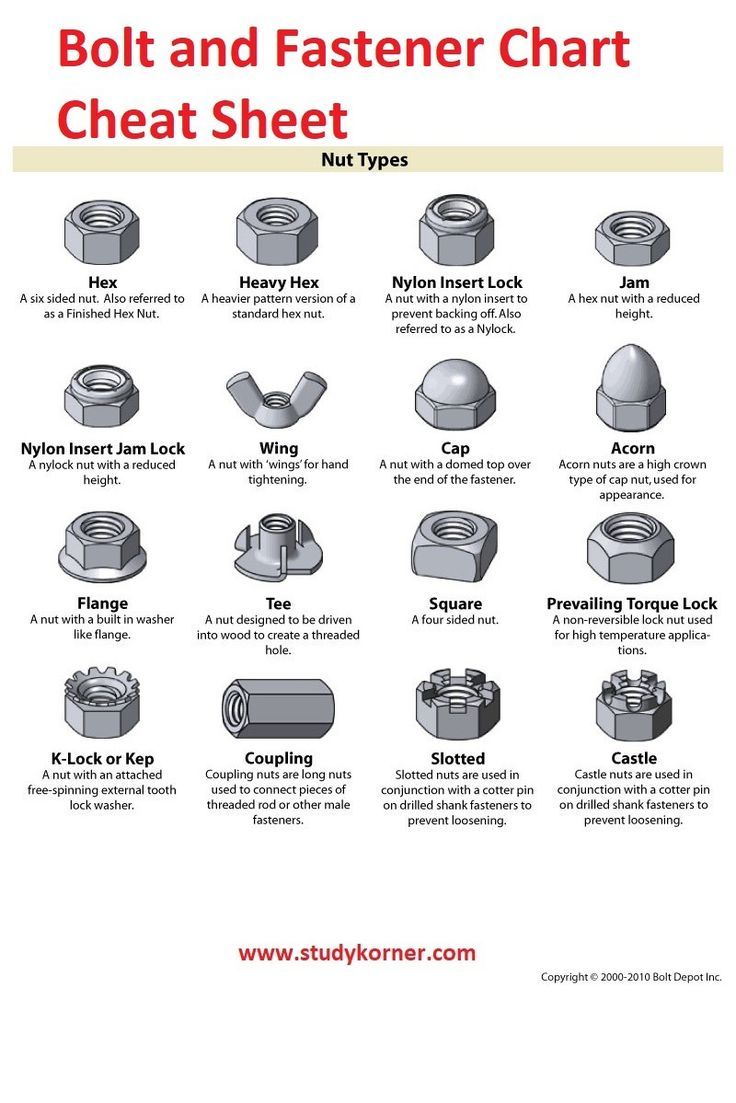
Top 3 Polyglycol Foam Properties Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polyglycol foam properties
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing polyglycol foam properties poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the multifaceted benefits and applications of polyglycol foams is crucial for industries ranging from textiles to food production. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing key aspects such as types of polyglycol foams, their unique properties, various industrial applications, and strategies for supplier vetting.
Navigating this intricate market requires a clear understanding of the specific requirements for each application, whether it’s for enhancing foam control in emulsions or leveraging biodegradable properties for sustainable practices. The guide also delves into cost considerations, helping buyers make informed decisions that align with their budget and operational needs. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this resource empowers them to confidently select the right polyglycol foam solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
Whether you are based in bustling economies like Vietnam or established markets like Germany, this guide facilitates a streamlined sourcing process, ensuring you remain competitive and compliant in a global marketplace.
Understanding polyglycol foam properties Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Polyglycol Foam | Excellent lubricity, low pour points, biodegradable | Textile processing, food production, wastewater treatment | Pros: Versatile, eco-friendly; Cons: Limited shelf life in some formulations. |
| Crosslinked Polyglycol Foam | Enhanced durability, chemical resistance | Gasketing, insulation, packaging | Pros: Stronger structure, moisture-resistant; Cons: Higher cost due to complex manufacturing. |
| Expanded Polyglycol Foam | Lightweight, good thermal insulation | Packaging, cushioning, marine applications | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to mold; Cons: Lower durability compared to crosslinked types. |
| Extruded Polyglycol Foam | High insulation properties, customizable density | Construction, automotive, HVAC systems | Pros: Tailored density options, high thermal efficiency; Cons: Requires specialized processing. |
| Low-Density Polyglycol Foam | Soft, compressible, buoyant | Protective packaging, marine applications | Pros: Ideal for delicate items, moisture-resistant; Cons: Less structural integrity. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Liquid Polyglycol Foam?
Liquid polyglycol foam is particularly noted for its excellent lubricity and low pour points, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including textile processing, food production, and wastewater treatment. Its biodegradable nature is a significant advantage for companies looking to enhance their sustainability profile. However, buyers should be aware that some formulations may have a limited shelf life, which can affect inventory management.
How Does Crosslinked Polyglycol Foam Differ from Other Types?
Crosslinked polyglycol foam stands out due to its enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications such as gasketing and insulation. This type is manufactured through a chemical process that creates a stronger structure, providing superior moisture resistance. While the benefits include increased longevity and performance, the cost may be higher compared to non-crosslinked options, which could impact budget considerations for B2B buyers.
What Advantages Does Expanded Polyglycol Foam Offer?
Expanded polyglycol foam is lightweight and provides good thermal insulation, making it widely used in packaging and cushioning applications. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of molding are attractive to manufacturers looking for efficient solutions. However, it may not be as durable as crosslinked varieties, which is a critical factor for buyers who prioritize long-lasting materials in their products.
Why Choose Extruded Polyglycol Foam for Your Business Needs?
Extruded polyglycol foam is characterized by its high insulation properties and the ability to customize density, making it suitable for construction, automotive, and HVAC applications. Its tailored options allow businesses to optimize performance for specific requirements. However, the need for specialized processing can increase production time and costs, which buyers must factor into their decision-making process.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Low-Density Polyglycol Foam?
Low-density polyglycol foam is soft, compressible, and buoyant, making it an excellent choice for protective packaging and marine applications. Its moisture resistance and suitability for delicate items are significant benefits for businesses in these sectors. However, its lower structural integrity compared to other foams may limit its use in applications requiring higher strength, which buyers should consider when evaluating potential uses.
Key Industrial Applications of polyglycol foam properties
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of polyglycol foam properties | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Textile and Fiber Processing | Antifoam agent in dyeing and finishing processes | Reduces foam formation, improving process efficiency and quality | Ensure compatibility with specific dye and chemical formulations |
| Food and Beverage | Foam control in fermentation and food processing | Enhances product consistency and quality, ensuring compliance with safety standards | Look for certifications (e.g., Kosher, FDA) and biodegradability |
| Paper and Pulp Industry | Foam control in pulp processing and paper production | Minimizes waste and improves product yield | Consider sourcing biodegradable options to meet sustainability goals |
| Water and Wastewater Treatment | Antifoaming agent in treatment processes | Increases treatment efficiency and reduces operational costs | Assess local regulations on chemical usage and environmental impact |
| Personal Care and Cosmetics | Foam control in emulsions and formulations | Improves product texture and stability, enhancing consumer satisfaction | Prioritize sourcing biodegradable and skin-friendly options |
How are Polyglycol Foam Properties Applied in Textile and Fiber Processing?
In the textile and fiber processing industry, polyglycol foam properties serve as an effective antifoam agent during dyeing and finishing processes. This application addresses the common issue of foam formation, which can lead to inconsistencies in dye uptake and fabric quality. By minimizing foam, manufacturers can enhance overall process efficiency and product quality. B2B buyers should ensure that the polyglycol foam is compatible with specific dyes and chemicals used in their formulations to achieve optimal results.
What Role Does Polyglycol Foam Play in Food and Beverage Production?
In the food and beverage sector, polyglycol foam properties are utilized as a foam control agent during fermentation and processing. This application is crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of products, which is essential for consumer safety and satisfaction. B2B buyers should look for polyglycol foams that meet safety standards, such as Kosher and FDA certifications, while also being readily biodegradable to align with sustainability initiatives.
How is Polyglycol Foam Beneficial in the Paper and Pulp Industry?
The paper and pulp industry leverages polyglycol foam properties for effective foam control during pulp processing and paper production. This application helps minimize waste and enhances product yield, directly impacting profitability. When sourcing polyglycol foam for this industry, buyers should consider options that are biodegradable to meet increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable practices.
Why is Polyglycol Foam Important for Water and Wastewater Treatment?
In water and wastewater treatment, polyglycol foam properties are used as an antifoaming agent to improve treatment efficiency. By controlling foam formation, these agents help reduce operational costs associated with maintenance and equipment wear. International B2B buyers should assess local regulations regarding chemical usage and environmental impact when sourcing polyglycol foams to ensure compliance and sustainability.
How is Polyglycol Foam Used in Personal Care and Cosmetics?
Polyglycol foam properties find application in the personal care and cosmetics industry as a foam control agent in emulsions and formulations. This use enhances the texture and stability of products, leading to higher consumer satisfaction. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing biodegradable and skin-friendly options to align with consumer preferences for natural ingredients and sustainability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyglycol foam properties’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Foam Performance During Production
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers in industries such as food production and latex formulation is the inconsistency in foam performance during production processes. Variations in polyglycol foam properties can lead to unpredictable foaming behavior, which may compromise product quality. For instance, excessive foaming can disrupt production lines, while insufficient foam can lead to inadequate product characteristics. This inconsistency not only affects operational efficiency but can also result in increased waste and higher production costs.
The Solution: To address these challenges, it is crucial to establish a consistent formulation process. Buyers should source high-quality polyglycol foam products with known and reliable properties, such as Dow’s Polyglycol P 400 E, which is recognized for its excellent lubricity and solvency. Implementing a comprehensive testing regime during initial product trials can also help identify the optimal balance of polyglycol properties for specific applications. Documenting the results will allow for fine-tuning and scaling up the process with confidence. Additionally, maintaining a consistent temperature and pH level during the mixing process can help mitigate performance variability, ensuring a more predictable foaming outcome.
Illustrative image related to polyglycol foam properties
Scenario 2: Environmental Compliance Challenges in Foam Use
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in regions with strict environmental regulations, face challenges in ensuring their materials are compliant with sustainability standards. The use of non-biodegradable foams can lead to significant regulatory hurdles and reputational risks. This is especially pertinent for companies operating in sectors such as personal care and food processing, where sustainable practices are increasingly demanded by consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing polyglycol foams that are readily biodegradable and meet international sustainability standards. Products like Polyglycol P 400 E not only fulfill performance needs but also support compliance with environmental regulations due to their biodegradable nature. When selecting suppliers, it is vital to request certifications that verify the product’s environmental claims. Additionally, integrating a lifecycle assessment into the procurement process can help identify and mitigate potential environmental impacts associated with foam use, ensuring that companies remain compliant while also enhancing their sustainability profile.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Achieving Desired Product Characteristics
The Problem: In industries such as textiles and personal care, achieving specific product characteristics—like the right hydrophile-lipophile balance (HLB) or foam stability—can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers. The complexity of formulating with polyglycol foams can lead to trial-and-error approaches that are time-consuming and costly. Without a clear understanding of how different properties interact, achieving the desired end-product can become a frustrating and inefficient process.
The Solution: To streamline the formulation process, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their product development teams focused on the properties of polyglycol foams. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support and formulation expertise can provide invaluable insights into optimizing foam properties for specific applications. For instance, leveraging the diverse range of molecular weights and HLB values offered by polyglycol products can help tailor formulations to meet precise performance criteria. Additionally, conducting small-scale tests to evaluate different combinations of polyglycols can lead to more efficient and effective product development, ultimately saving time and resources while achieving the desired characteristics.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyglycol foam properties
What Are the Key Properties of Polyglycol Foam?
Polyglycol foams, particularly those based on polyglycol P 400 E, exhibit a range of properties that make them suitable for diverse applications across various industries. Key properties include low pour points, excellent lubricity, and a wide range of hydrophile-lipophile balances. These attributes enhance the foam’s performance in applications such as foam control, heat transfer fluids, and as industrial surfactants. The material’s water solubility and biodegradability further bolster its appeal, especially in environmentally conscious markets.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Polyglycol Foam in B2B Applications?
When considering polyglycol foam, it’s essential to weigh its advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
– Durability and Performance: Polyglycol foam demonstrates excellent lubricity and solvency, making it a reliable choice for applications requiring consistent performance under varying conditions.
– Sustainability: The biodegradable nature of polyglycol foam aligns with global sustainability trends, appealing to companies focused on reducing their environmental footprint.
– Versatility: Its compatibility with a wide range of formulations allows for flexibility in product development.
Cons:
– Cost Considerations: While polyglycol foam offers numerous benefits, it may be more expensive than other foam options, which can impact budget-sensitive projects.
– Manufacturing Complexity: The formulation process can be intricate, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment, which may complicate production for some manufacturers.
How Does Polyglycol Foam Impact Specific Applications?
The impact of polyglycol foam on specific applications is substantial. For instance, in the food production industry, its biodegradable properties make it an ideal choice for formulations that require compliance with stringent safety and environmental regulations. Additionally, in textile processing, the foam’s lubricity enhances the quality of fiber treatment, leading to improved product performance. However, buyers must consider the specific media compatibility, as certain formulations may not be suitable for all applications.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Polyglycol Foam?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several considerations are paramount. Compliance with local and international standards, such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS, is crucial to ensure product safety and effectiveness. Additionally, buyers should be aware of regional preferences regarding sustainability, as markets increasingly favor biodegradable materials. Understanding the logistics of sourcing and distribution, including potential tariffs and import regulations, is also essential for smooth transactions.
Summary Table of Polyglycol Foam Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for polyglycol foam properties | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyglycol P 400 E | Food production, textile processing | Biodegradable and environmentally friendly | Higher cost compared to traditional foams | High |
| Polyethylene Foam | Packaging, cushioning | Excellent shock absorption and durability | Limited temperature resistance | Medium |
| Crosslinked Polyethylene Foam | Gasketing, insulation | Strong moisture and gas resistance | More complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Expanded Polyethylene Foam | Marine applications, thermal insulation | Lightweight and buoyant | Lower durability compared to crosslinked types | Low |
This structured guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations of polyglycol foam, enabling informed decision-making in material selection.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyglycol foam properties
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Polyglycol Foam?
The manufacturing process of polyglycol foam involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets specific performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: What Are the Initial Steps in Manufacturing Polyglycol Foam?
The first stage in the manufacturing of polyglycol foam is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality polyalkylene glycols, which serve as the primary ingredient. The selection of raw materials is crucial; suppliers should ensure that the glycols meet industry standards for purity and performance.
Once sourced, the materials undergo a series of pre-treatment processes, such as filtration and mixing, to remove impurities and achieve the desired viscosity and molecular weight. This step is vital for ensuring the final foam exhibits the expected properties, such as lubricity and biodegradability.
Forming: How Is Polyglycol Foam Shaped and Cured?
Following material preparation, the next stage is forming. This typically involves the use of specialized machinery to blend the polyalkylene glycols with any necessary additives, such as surfactants or stabilizers. The mixture is then subjected to controlled temperature and pressure conditions to initiate the foaming process.
There are several techniques for forming polyglycol foam, including batch processing and continuous extrusion. Batch processing allows for precise control over the foam characteristics, while continuous processes can enhance efficiency and scalability. The choice of technique can influence the foam’s density, cell structure, and overall performance.
Assembly: What Role Does Assembly Play in Foam Production?
In some cases, additional assembly processes may be required, especially if the foam is intended for specific applications. This could involve cutting, shaping, or laminating the foam to meet customer specifications. For instance, foams used in industrial surfactants or heat transfer fluids may require precise dimensions and surface finishes.
Finishing: How Is Quality Finalized in Polyglycol Foam Production?
The finishing stage involves several post-production treatments to enhance the foam’s properties. This can include drying, surface treatment, or coating to improve chemical resistance or aesthetic appeal. Proper finishing ensures that the foam meets the stringent performance criteria required for various applications, such as food processing or personal care products.
What Are the Quality Control Measures for Polyglycol Foam?
Quality assurance is critical in the production of polyglycol foam, especially for B2B buyers who demand consistency and reliability.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of polyglycol foam often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which sets criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that processes are consistently monitored and improved, leading to higher product quality.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific standards may apply. For example, products intended for food contact must meet regulations set by the FDA or EFSA in Europe. Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers assess supplier credibility and product safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) in polyglycol foam production typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase assesses raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages ensures adherence to process parameters. This can involve real-time testing of viscosity, foam density, and other critical properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the foam is produced, it undergoes thorough testing to verify that it meets the established quality standards. This includes mechanical testing, biodegradability assessments, and performance evaluations based on the intended application.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Polyglycol Foam?
Several testing methods are utilized to ensure the quality and performance of polyglycol foam:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile strength, elongation, and compression tests to assess the foam’s durability and resilience.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluates how the foam interacts with various chemicals, particularly if it’s used in industrial applications.
-
Biodegradability Testing: Essential for products marketed as environmentally friendly, this testing determines the foam’s degradation rate in natural environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are several strategies:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control practices. During an audit, buyers should evaluate the supplier’s adherence to ISO standards, review documentation related to quality procedures, and inspect the production facility. Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports and Certifications?
Buyers should request quality reports and certifications from suppliers. These documents should detail the results of various quality tests and confirm compliance with international standards. Reviewing these reports helps buyers understand the reliability of the foam and the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:

Illustrative image related to polyglycol foam properties
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations governing product safety and environmental impact. Buyers must ensure that suppliers can meet these requirements.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: The complexity of international shipping can affect product quality. Buyers should inquire about how suppliers manage logistics to minimize risks associated with transportation and storage.
-
Cultural and Communication Factors: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers, ensuring that quality expectations are clearly conveyed and met.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with polyglycol foam, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyglycol foam properties’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to source polyglycol foam properties effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that your procurement process is thorough, aligned with your technical needs, and compliant with industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Consider the specific properties required for your applications, such as molecular weight, hydrophile-lipophile balance, and biodegradability. This clarity helps in communicating your needs to potential suppliers and assessing their offerings effectively.
Step 2: Research Application Areas
Understanding the various applications of polyglycol foam is crucial for making an informed decision. This material is used in diverse industries, including food production, textiles, and water treatment. By identifying which specific applications are relevant to your business, you can narrow down your supplier options and focus on those that align with your industry requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, product samples, and case studies from previous clients in similar sectors. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability, as this will minimize risks associated with sourcing.
- Check certifications: Ensure that suppliers adhere to international quality standards and environmental regulations.
- Assess production capabilities: Evaluate whether they can meet your volume requirements and timeline.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Obtaining product samples is a critical step in verifying the quality of polyglycol foam properties. Analyze the samples for performance characteristics such as lubricity, solubility, and foam control capabilities. This hands-on evaluation allows you to assess whether the material meets your specific technical requirements before making a larger investment.
Step 5: Verify Sustainability Claims
Sustainability is increasingly important for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Europe and South America. Confirm that the polyglycol foam is readily biodegradable and check for any relevant sustainability certifications. This not only supports your corporate social responsibility goals but also aligns with customer expectations in environmentally conscious markets.
Illustrative image related to polyglycol foam properties
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate terms and pricing. Discuss minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Make sure to clarify any additional costs related to shipping, handling, or customs, especially for international transactions, to avoid unexpected expenses.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to ensure that the polyglycol foam meets your standards consistently. This could involve setting up regular inspections, testing batches upon arrival, and maintaining open lines of communication with your supplier. Establishing these protocols will help in building a long-term relationship and ensuring product reliability.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing polyglycol foam properties confidently, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyglycol foam properties Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Polyglycol Foam Properties?
When sourcing polyglycol foam properties, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.

Illustrative image related to polyglycol foam properties
-
Materials: The raw materials for polyglycol foam, such as polyalkylene glycol, play a significant role in pricing. Prices can fluctuate based on global oil prices, as these materials are petroleum-derived. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs or exploring alternative suppliers.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the production location. Regions with lower wage rates may offer cost advantages, but buyers should also consider the skill level of the workforce. High-quality production often requires skilled labor, which can increase costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize these overheads, impacting the overall price of the foam.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which adds to initial costs. However, investing in the right tools can lead to long-term savings through increased efficiency and reduced waste.
-
Quality Control (QC): High-quality standards, especially for applications in the food and personal care industries, necessitate rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with these practices can influence pricing but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are vital to consider, particularly for international buyers. Incoterms will dictate who bears these costs and can significantly impact total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary widely depending on the supplier’s market positioning and the perceived value of their product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Polyglycol Foam Pricing?
Several factors influence the final pricing of polyglycol foam properties, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should explore minimum order quantities (MOQ) to leverage volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom formulations or specific properties can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected surcharges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) can drive up costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these certifications based on their application to balance quality and budget.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and historical performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect who pays for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Understanding these terms helps buyers accurately calculate total costs.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize value, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Research and Comparison: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to understand market rates. This information can serve as leverage during negotiations.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers may offer discounts for repeat business.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assessing the TCO, which includes purchase price, logistics, and maintenance, can uncover hidden costs. This broader view can justify higher upfront costs if they lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: Be open to alternative materials or formulations that meet your needs but may be more cost-effective.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding the cultural nuances in negotiation styles can enhance communication with suppliers, particularly in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers should be aware of potential pricing nuances that can impact their sourcing strategy. Currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and regional economic conditions can all affect pricing. Additionally, local demand and supply dynamics in regions such as Africa and South America can lead to price variations.
Buyers should also consider the implications of shipping times and costs, especially when sourcing from suppliers in Europe or the Middle East. Timing can be critical, particularly for industries with tight deadlines.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing for their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyglycol foam properties With Other Solutions
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses often seek effective solutions that can meet their specific needs in various applications. When evaluating polyglycol foam properties, it’s crucial to consider viable alternatives that may offer different benefits, costs, or performance metrics. Below, we compare polyglycol foam properties with two notable alternatives: polyethylene foam and polyethylene glycol/melamine foam composites.
| Comparison Aspect | Polyglycol Foam Properties | Polyethylene Foam | Polyethylene Glycol/Melamine Foam Composite |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent lubricity, solvency, and foam control | High chemical resistance, shock absorption | High thermal conductivity and photothermal conversion |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on formulation | Generally lower; cost-effective options available | Higher due to complex manufacturing processes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific formulation expertise | Easy to fabricate and process | More complex due to advanced composites |
| Maintenance | Low; biodegradable with minimal environmental impact | Low; durable and long-lasting | Moderate; may require specific handling |
| Best Use Case | Chemical processing, food production, textiles | Packaging, cushioning, marine applications | Advanced thermal applications and energy efficiency |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight and versatile material, making it ideal for applications such as packaging and cushioning. It boasts high chemical and moisture resistance, good tear resistance, and excellent shock absorption properties. However, while it is cost-effective and easy to implement, it may not provide the same level of lubricity and foam control as polyglycol foam. Its applications are generally limited to less complex environments where high-performance lubrication is not critical.
How Does Polyethylene Glycol/Melamine Foam Composite Compare?
Polyethylene glycol/melamine foam composites represent an advanced option that excels in thermal management and energy efficiency. With exceptional thermal conductivity and photothermal conversion capabilities, this composite is suited for innovative applications such as energy storage and thermal regulation. However, its cost is higher due to the complex manufacturing process involved in creating these composites. Additionally, the implementation may require specialized expertise, which can complicate the adoption process.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate foam solution, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific requirements, including performance metrics, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. For applications requiring high lubricity and foam control, polyglycol foam may be the best choice. Conversely, for cost-sensitive projects or those needing basic cushioning and insulation, polyethylene foam could be more suitable. Lastly, for cutting-edge applications demanding advanced thermal properties, polyethylene glycol/melamine foam composites may offer the most significant benefits. By understanding the unique properties and best-use cases of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyglycol foam properties
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Polyglycol Foam?
When evaluating polyglycol foam for various industrial applications, several critical technical properties must be considered. Understanding these specifications can significantly influence purchasing decisions and product performance.
1. Molecular Weight
Molecular weight is a crucial property of polyglycol foam, affecting its viscosity, solubility, and overall performance in applications. Higher molecular weights generally enhance the foam’s mechanical properties and stability, making it suitable for demanding industrial uses. Buyers should assess the molecular weight to ensure it aligns with their specific application requirements, such as lubrication or foam control.
2. Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance (HLB)
The HLB value indicates the balance between hydrophilic (water-attracting) and lipophilic (oil-attracting) properties. This balance is vital for applications in emulsification and stabilization in various industries, including personal care and food processing. Buyers need to consider the HLB to ensure optimal performance in their formulations, particularly in creating stable emulsions.
3. Pour Point
The pour point is the lowest temperature at which the foam remains pourable. This property is particularly important in applications exposed to low temperatures, such as in refrigeration or outdoor environments. A low pour point ensures that the foam maintains its flow characteristics and performance under various temperature conditions, which is essential for reliability in industrial processes.
4. Biodegradability
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in global markets, the biodegradability of polyglycol foam represents a significant advantage. Products classified as readily biodegradable can help companies meet environmental regulations and consumer demands for sustainable materials. Buyers should prioritize biodegradable options to enhance their brand’s eco-friendliness and compliance with international environmental standards.
5. Solubility
Polyglycol foam’s solubility, particularly in water, is a critical property that influences its application in industries such as textiles, food processing, and wastewater treatment. Understanding solubility helps buyers select the right formulation for their specific needs, ensuring that the foam integrates well with other components in their processes.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Polyglycol Foam?
Navigating the world of polyglycol foam purchasing requires familiarity with industry-specific jargon. Understanding these terms can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance communication between buyers and suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the context of polyglycol foam, OEMs may provide custom formulations tailored to specific applications. Buyers should seek OEM partners who can offer quality assurance and compliance with their unique requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. High MOQs may not be feasible for smaller operations, so negotiating favorable terms is crucial for maximizing efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting pricing and terms from suppliers. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different manufacturers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms. This process is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping agreements. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international B2B transactions involving polyglycol foam, as they clarify costs, risks, and the point at which ownership transfers. This understanding helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures smooth logistics.
5. SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
An SDS provides detailed information about the properties, hazards, handling, and safe use of a chemical product. Buyers should always request an SDS for polyglycol foam to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to inform employees about proper handling procedures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality in the global market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyglycol foam properties Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Polyglycol Foam Properties Sector?
The global market for polyglycol foam properties is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across diverse industries such as food production, textiles, personal care, and wastewater treatment. The versatility of polyglycol P 400 E, for instance, as an antifoam agent and its biodegradable nature align well with the rising consumer preference for sustainable products. Emerging technologies, such as advanced formulations and the incorporation of nanomaterials, are enhancing the performance attributes of polyglycol-based products, making them more appealing to B2B buyers.
In regions like Africa and South America, there is a burgeoning interest in sustainable materials, particularly in sectors such as food and beverage, where compliance with health and safety standards is paramount. Conversely, European markets, especially Germany, are leading the way in adopting stringent regulations that favor environmentally friendly materials. This creates an opportunity for suppliers to differentiate themselves by offering polyglycol products that not only meet these regulations but also enhance operational efficiency.
Moreover, with the rise of Industry 4.0, digital transformation in sourcing and procurement processes is becoming a norm. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI-driven insights to optimize their supply chains, ensuring timely delivery and better inventory management. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who need reliable sourcing solutions across different geographical regions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Polyglycol Foam Properties?
Sustainability is a critical consideration in the sourcing of polyglycol foam properties. As global awareness of environmental impacts grows, companies are prioritizing ethical sourcing practices. Polyglycol P 400 E is noted for its readily biodegradable properties, making it a favorable choice for organizations aiming to reduce their ecological footprint. The push towards ‘green’ certifications and materials is not just a trend but a necessity for companies looking to maintain competitiveness in the global market.
For B2B buyers, the importance of establishing ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing suppliers for their sustainability practices, including waste management, energy use, and resource sourcing. Engaging with suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards can enhance a company’s reputation and consumer trust.
Additionally, companies are looking for products with certifications that validate their sustainability claims, such as the OECD 301F testing results for biodegradability. This not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also meets regulatory compliance in various markets, particularly in Europe and North America, where environmental regulations are stringent.
What Is the Historical Context of Polyglycol Foam Properties in B2B Applications?
The development of polyglycol foam properties dates back several decades, beginning with the introduction of polyalkylene glycols in industrial applications. Initially utilized primarily in lubrication and surfactant roles, polyglycols have evolved significantly due to advancements in chemical processing technologies and a growing understanding of their versatile properties.
Illustrative image related to polyglycol foam properties
As industries faced increasing regulatory pressures regarding environmental sustainability, polyglycols emerged as viable alternatives to traditional materials, thanks to their biodegradable nature and multifunctional capabilities. This evolution has positioned polyglycol products not only as functional materials but also as integral components in sustainable manufacturing practices.
With ongoing innovations and a focus on sustainability, the future of polyglycol foam properties looks promising, offering B2B buyers a range of options that meet both performance requirements and environmental standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyglycol foam properties
-
How do I choose the right polyglycol foam for my application?
Choosing the right polyglycol foam depends on your specific application needs. Consider factors such as the foam’s chemical resistance, biodegradability, and thermal stability. For instance, if you are in the food production industry, opt for polyglycol foams that meet safety and regulatory standards. Additionally, evaluate the molecular weight and hydrophile-lipophile balance, as these properties can significantly impact performance in various formulations. Collaborating with suppliers who offer samples can aid in making an informed decision tailored to your requirements. -
What are the key properties of polyglycol foam that impact its performance?
Polyglycol foam properties include low pour points, excellent lubricity, and a range of hydrophile-lipophile balances. These attributes enable effective foam control in applications like latex formulations and paper processing. Additionally, its biodegradability is a crucial factor for companies prioritizing sustainability. Understanding these properties helps in assessing how the foam will perform in specific environments, thus ensuring optimal functionality in your processes. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing polyglycol foam?
When sourcing polyglycol foam, look for certifications that confirm product quality and safety, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, for food-related applications, ensure the product is FDA-compliant and meets specific food safety standards. If your operations involve sensitive environments, check for certifications that validate biodegradability and non-toxicity, which can enhance your brand’s sustainability profile. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for polyglycol foam?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for polyglycol foam can vary significantly by supplier and specific product type. Typically, MOQs range from 100 kilograms to several tons, depending on the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and inventory policies. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production requirements while considering potential cost savings on larger orders. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for polyglycol foam?
Payment terms in international B2B transactions for polyglycol foam often include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or net 30 to net 90 days after invoice. Suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom formulations or larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate clear terms that safeguard both parties and ensure timely delivery. Familiarize yourself with international payment methods to avoid currency exchange issues and transaction fees. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my polyglycol foam supplies?
To ensure quality assurance for polyglycol foam, request detailed product specifications and safety data sheets from your suppliers. Establish a QA protocol that includes regular testing of foam properties such as viscosity, biodegradability, and chemical resistance. Consider third-party certifications and audits to validate supplier claims. Building a strong relationship with your suppliers can also facilitate better communication and quicker resolutions for any quality concerns. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing polyglycol foam?
Logistical considerations for importing polyglycol foam include understanding shipping regulations, customs duties, and import taxes specific to your region. Work with logistics providers who specialize in chemical transportation to ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Additionally, factor in lead times, storage conditions, and potential disruptions in the supply chain that may affect delivery schedules. Proper planning can help mitigate risks and streamline the import process. -
What are the best practices for vetting suppliers of polyglycol foam?
When vetting suppliers of polyglycol foam, conduct thorough background checks to assess their reputation and reliability. Look for established companies with proven experience in the industry and positive customer reviews. Request references and case studies to gauge their performance in similar applications. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities if possible, and verify compliance with relevant standards and certifications to ensure they meet your quality requirements.
Top 3 Polyglycol Foam Properties Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dow – Polyglycol P 400 E
Domain: dow.com
Registered: 1992 (33 years)
Introduction: Polyglycol P 400 E is a liquid polyalkylene glycol used as an antifoam agent in various industries, including latex formulations, paper and pulp processing, emulsion paints, and food production. It is considered readily biodegradable based on OECD 301F testing. Key uses include fiber and textile processing, food and fermentation (Kosher applications), paper processing, personal care, plastics, wat…
2. Amcon Foam – Polyethylene Foam
Domain: amconfoam.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Polyethylene foam is a versatile, durable, lightweight, and resilient foam ideal for packaging, cushioning, gasketing, and various healthcare and marine applications. It is a closed-cell material with high chemical and moisture resistance, good tear resistance, shock absorption, non-abrasive, vibration dampening, resistance to mold and mildew, odorless, buoyant, thermally insulating, flexible, and…
3. PDF Coffee – Polyglycol Foam Control Agents
Domain: pdfcoffee.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Polyglycol Foam Control Agents Reference Chart provides information on foam control solutions used in various industries including agrochemical production, bioethanol production, chemical manufacturing, household cleaners, construction products, food and beverage, personal care, metal working fluids, oil and gas production, paint, coatings and ink formulations, pulp and paper, textiles, and water …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyglycol foam properties
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Use of Polyglycol Foams?
In summary, polyglycol foams, particularly variants like Polyglycol P 400 E, offer diverse applications across industries such as food production, textile processing, and wastewater treatment. Their unique properties—such as biodegradability, excellent lubricity, and solubilization capabilities—provide significant advantages for manufacturers seeking to enhance product formulations while maintaining environmental compliance.
Strategic sourcing of these materials can lead to cost efficiencies, improved supply chain resilience, and access to innovative formulations tailored to specific market needs. As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing, understanding the properties and benefits of polyglycol foams will be critical in making informed decisions.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and high-performance materials is set to rise. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability, ensuring they stay competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace. By leveraging strategic sourcing, you can enhance your product offerings and meet the growing expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. Connect with industry experts today to explore how polyglycol foams can transform your business solutions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.