Top 3 Household Transformer Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for household transformer
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing household transformers can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With diverse voltage requirements and safety standards across regions—such as the high voltage specifications in Nigeria or the stringent efficiency regulations in Germany—making informed purchasing decisions is crucial. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of household transformers, providing insights into various types, applications, and the critical aspects of supplier vetting.
Navigating the intricacies of transformer specifications, such as single-phase versus three-phase options, and understanding their roles in residential and commercial settings, is essential for ensuring reliable energy distribution. Additionally, this guide will delve into the financial considerations, offering a detailed breakdown of costs and potential return on investment for different transformer models.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this comprehensive resource is designed to empower you with the knowledge needed to select the right products and partners. By addressing key challenges and equipping you with actionable insights, this guide will enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring that your household transformer needs are met with efficiency and compliance.
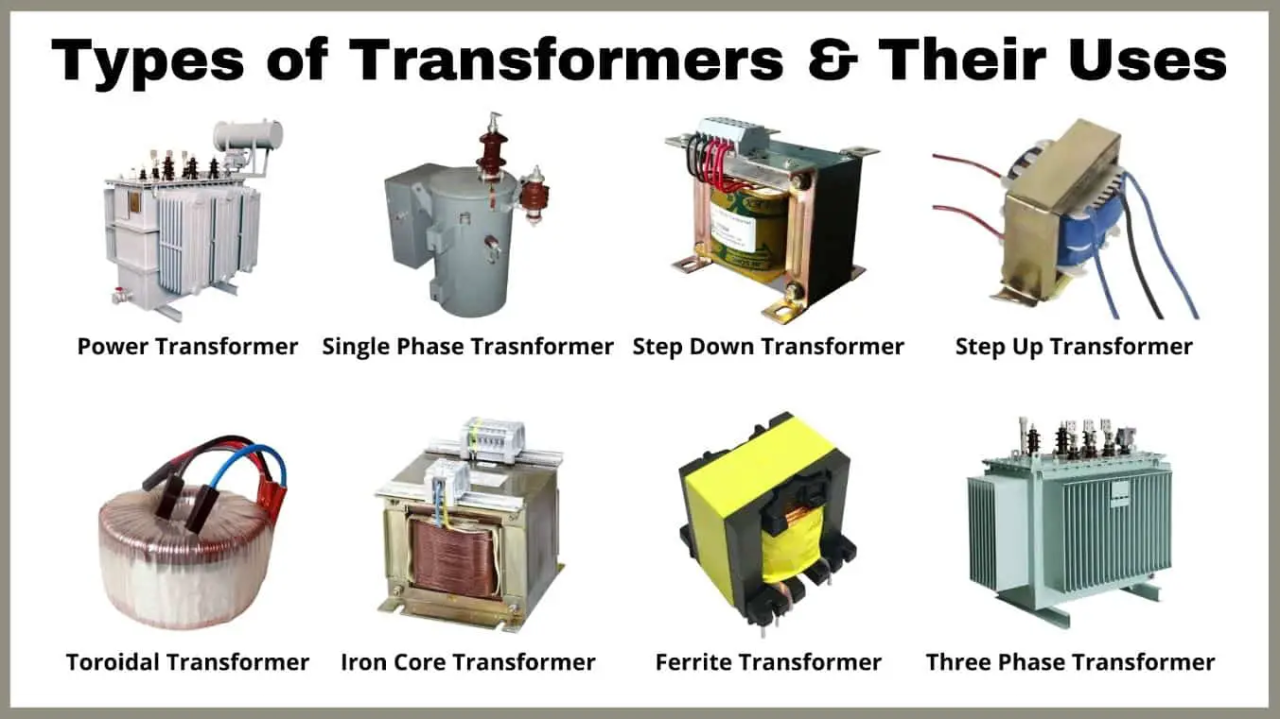
Understanding household transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step-Up Transformer | Increases voltage from low to high levels | Industrial equipment, renewable energy | Pros: Efficient for high voltage needs. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Step-Down Transformer | Reduces voltage from high to low levels | Residential appliances, machinery | Pros: Safe for household use. Cons: Limited to lower power applications. |
| Isolation Transformer | Provides electrical isolation between circuits | Sensitive equipment, medical devices | Pros: Enhances safety and reduces noise. Cons: Can be more expensive. |
| Auto Transformer | Combines step-up and step-down capabilities | Electrical distribution, HVAC systems | Pros: Compact and lightweight. Cons: Less isolation compared to other types. |
| Three-Phase Transformer | Handles three-phase power supply for larger applications | Manufacturing, large commercial setups | Pros: Efficient for high-load applications. Cons: Requires more complex installation. |
What are the characteristics of a Step-Up Transformer?
Step-up transformers are designed to increase voltage levels from a lower input to a higher output, making them ideal for applications in industrial settings and renewable energy systems. They are commonly used to improve transmission efficiency over long distances, minimizing energy loss. B2B buyers should consider the specific voltage requirements and the transformer’s capacity to handle peak loads when selecting this type.
How does a Step-Down Transformer function in residential applications?
Step-down transformers are essential for reducing high voltage levels to safe, usable voltages for residential appliances and machinery. They play a crucial role in ensuring that electrical devices operate safely and efficiently. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate the transformer’s wattage capacity and its compatibility with existing electrical systems to ensure optimal performance.
Why choose an Isolation Transformer for sensitive equipment?
Isolation transformers provide a vital layer of safety by electrically isolating circuits, which is particularly important for sensitive equipment and medical devices. They help reduce electrical noise and protect against surges. Buyers in sectors such as healthcare and technology should prioritize certifications and reliability when selecting isolation transformers to ensure compliance with safety standards.
What advantages does an Auto Transformer offer for electrical distribution?
Auto transformers are unique in that they can both step up and step down voltages, making them versatile for various electrical distribution needs. Their compact design is beneficial for space-constrained installations. However, B2B buyers should be aware that while they are cost-effective, they offer less electrical isolation, which may not be suitable for all applications.
When is a Three-Phase Transformer necessary for commercial setups?
Three-phase transformers are essential for managing three-phase power supply, which is commonly used in manufacturing and large commercial operations. They efficiently handle high-load applications, ensuring stable power delivery. Buyers should assess the transformer’s capacity to meet their specific load demands and consider installation complexities when making a purchasing decision.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
Key Industrial Applications of household transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Household Transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Construction | Voltage regulation for home electrical systems | Ensures stable power supply, enhancing appliance longevity and safety | Compliance with local electrical standards and safety regulations |
| Renewable Energy | Integration with solar energy systems | Facilitates efficient energy conversion and distribution | Compatibility with existing solar equipment and energy storage |
| Telecommunications | Power supply for communication equipment | Maintains uninterrupted service, reducing downtime and operational costs | Reliability and capacity to handle peak loads |
| Hospitality and Retail | Power management in hotels and retail outlets | Improves energy efficiency and customer experience | Energy efficiency ratings and scalability for future expansion |
| Manufacturing | Power supply for machinery and equipment | Optimizes operational efficiency and reduces equipment failure risks | Voltage ratings and compatibility with industrial machinery |
How is a Household Transformer Used in Residential Construction?
In residential construction, household transformers are integral for voltage regulation within home electrical systems. They step down high voltage from power lines to a safe level suitable for household appliances, ensuring stable power supply. This reduces the risk of electrical surges that can damage sensitive electronics. For international buyers, especially in regions like Nigeria or Germany, sourcing transformers that comply with local electrical standards and safety regulations is crucial to avoid installation issues and ensure safety.
What Role Do Household Transformers Play in Renewable Energy Systems?
Household transformers are essential in renewable energy applications, particularly in solar energy systems. They convert and regulate the voltage generated by solar panels, allowing it to be compatible with home electrical systems. This ensures efficient energy conversion and distribution, maximizing the use of renewable resources. Buyers in South America and the Middle East should consider transformers that are compatible with existing solar infrastructure and energy storage solutions to enhance overall system performance.
How Do Household Transformers Support Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications sector, household transformers power communication equipment, ensuring reliable service delivery. They help maintain a steady power supply, crucial for minimizing downtime and operational costs. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing transformers that offer high reliability and capacity to handle peak loads is essential, particularly in regions with fluctuating power supply.
Why Are Household Transformers Important in Hospitality and Retail?
In the hospitality and retail industries, household transformers manage power distribution for various electrical systems, enhancing energy efficiency and customer experience. By ensuring stable power supply, they help prevent outages that could disrupt services. B2B buyers in these sectors should prioritize transformers with high energy efficiency ratings and scalability options, allowing for future expansion as business needs grow.
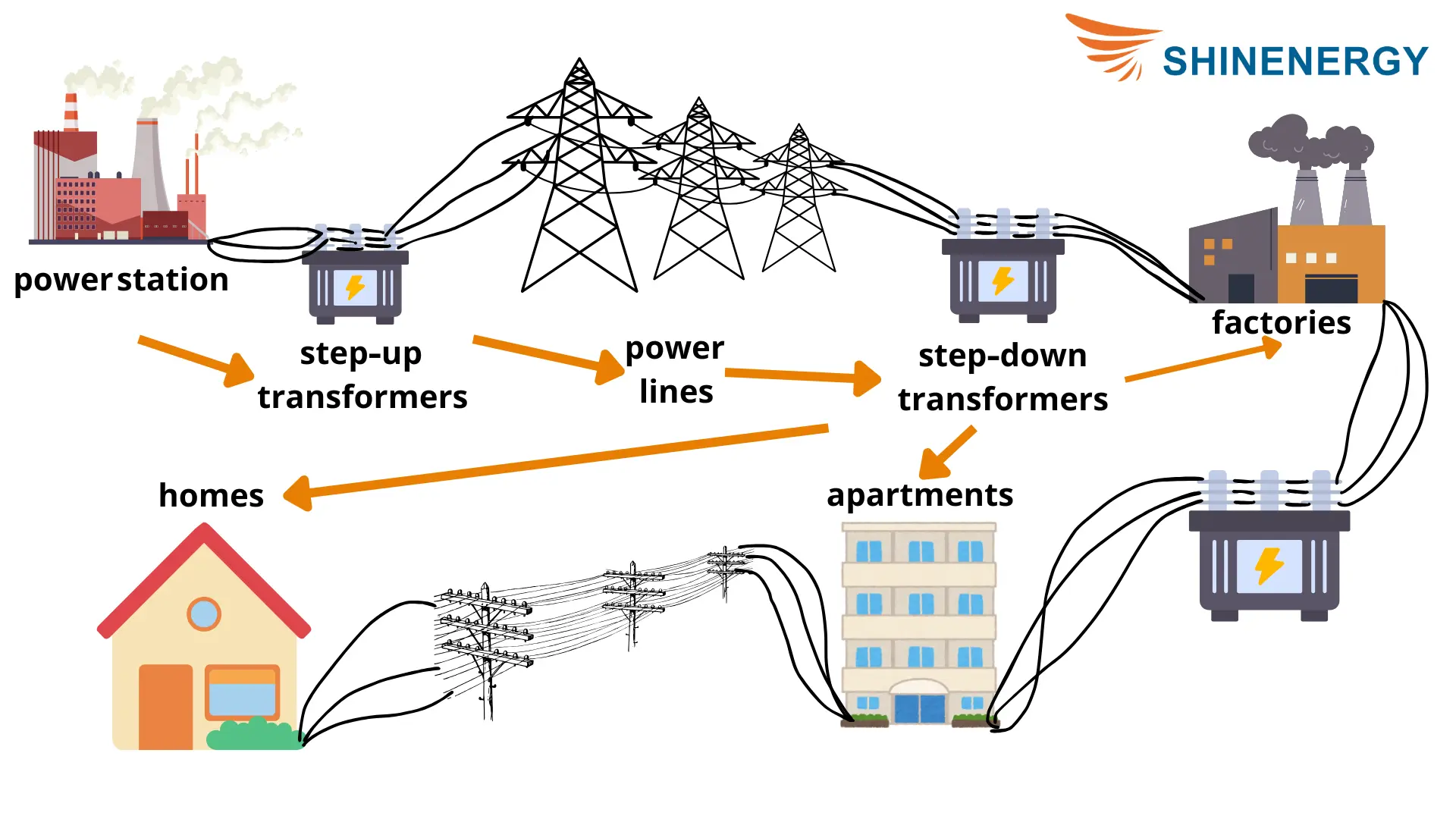
Illustrative image related to household transformer
How Do Household Transformers Enhance Manufacturing Operations?
Manufacturers rely on household transformers to supply power to machinery and equipment, optimizing operational efficiency. By providing the correct voltage levels, they reduce the risk of equipment failure, which can lead to costly downtimes. Buyers in the manufacturing sector must consider voltage ratings and compatibility with their specific machinery to ensure seamless integration and operation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘household transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sizing Challenges for Diverse Voltage Requirements
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the right size of household transformer to meet varying voltage requirements in their operations. For instance, a company in Nigeria may need to step down voltage from a 220V supply to 110V for specific machinery while also needing to support devices that require 240V. Incorrect sizing can lead to inefficiencies, potential equipment damage, or even safety hazards, creating a daunting task for procurement teams.
The Solution: To accurately determine the appropriate transformer size, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their equipment’s voltage and wattage requirements. It is essential to compile a list of all devices that will be powered, noting their individual voltage and power specifications. Based on this data, buyers can calculate the total wattage needed and select a transformer with a capacity exceeding this total to ensure reliable performance. Consulting with suppliers who provide transformers specifically designed for the local market can also help, as they will have insights into common voltage specifications and can recommend models that meet safety standards and efficiency requirements.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with International Equipment
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers face compatibility issues when integrating household transformers with imported equipment. A company in South America may purchase machinery from Europe that operates on different voltage levels, leading to concerns about potential damage to their new equipment or inefficiencies in operation. This situation can be particularly frustrating when there are multiple voltage standards to navigate.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing transformers that offer dual or multiple voltage outputs. When purchasing equipment, it is critical to verify the voltage and frequency specifications of the machinery. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who specialize in transformers that accommodate varying international standards can be beneficial. It is advisable to look for transformers with adjustable settings or converters that can adapt to different voltage levels seamlessly. Furthermore, investing in surge protection features will safeguard sensitive equipment from voltage spikes, enhancing operational safety.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Safety Concerns
The Problem: In regions such as the Middle East and Africa, buyers often encounter complex regulatory requirements related to electrical installations, including household transformers. Ensuring compliance with local safety standards can be a daunting task, especially for businesses unfamiliar with the regulations. Non-compliance not only poses legal risks but also endangers personnel and equipment, leading to costly downtime and repairs.
The Solution: B2B buyers should proactively research and understand the regulatory landscape in their respective countries before purchasing household transformers. Engaging with local electrical engineers or consultants who specialize in compliance can provide invaluable insights into the necessary certifications and standards required for transformers. Additionally, buyers should ensure that the transformers they consider are certified by recognized bodies, such as UL or CE, which can help assure compliance with local regulations. Implementing regular safety audits and training for staff on the operational protocols of transformers will further enhance workplace safety and ensure adherence to legal requirements, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents and liabilities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for household transformer
When selecting materials for household transformers, it is crucial to consider the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications of various materials. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in the manufacturing of household transformers: copper, aluminum, steel, and plastic. Each of these materials has distinct characteristics that can influence performance, durability, and cost, making them suitable for different applications.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Household Transformers?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for transformer windings. It can handle high temperatures, typically rated up to 200°C, and offers good corrosion resistance. The high tensile strength of copper ensures durability under mechanical stress, which is essential for maintaining performance over time.
Pros and Cons of Copper:
The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which leads to higher efficiency in transformers. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase the overall cost of the transformer. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex due to the need for precise handling and processing.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s compatibility with various media and its ability to perform well in high-load situations make it suitable for residential transformers that require reliable performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Europe and Germany, compliance with standards such as DIN and IEC is crucial. Buyers should ensure that copper transformers meet these regulations to avoid issues with installation and operation.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Transformers?
Aluminum is another popular choice for transformer windings, primarily due to its lightweight nature and lower cost compared to copper. Aluminum can withstand temperatures up to 150°C and has a decent resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
The key advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper means that larger wire gauges are necessary to achieve similar performance levels, which can lead to increased material usage and weight.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for transformers in residential applications where weight and cost are significant factors. However, its lower conductivity may limit its use in high-power applications.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum transformers must comply with local standards, such as ASTM in the U.S. and JIS in Japan. Buyers in Africa and South America should consider the availability of aluminum and its compliance with local electrical codes.
What Role Does Steel Play in Transformer Construction?
Steel is often used in the core of transformers due to its magnetic properties, which enhance efficiency. It can withstand high pressures and has good mechanical strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel cores typically operate at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros and Cons of Steel:
The main advantage of steel is its ability to provide excellent magnetic permeability, which improves transformer efficiency. However, it is heavier than other materials and can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application:
Steel is essential for transformers that require robust magnetic cores, especially in high-load residential applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the steel used meets international standards for magnetic properties and corrosion resistance, particularly in humid climates found in parts of Africa and South America.
How Is Plastic Used in Household Transformers?
Plastic is primarily used for insulating components within transformers. It is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 100°C.
Pros and Cons of Plastic:
The advantage of plastic is its low cost and versatility in design. However, it has limited thermal stability compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastic is ideal for insulation in residential transformers where electrical safety and lightweight design are priorities.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Ensure that the plastic materials comply with safety standards relevant to electrical components, such as UL certification in the U.S. and CE marking in Europe.
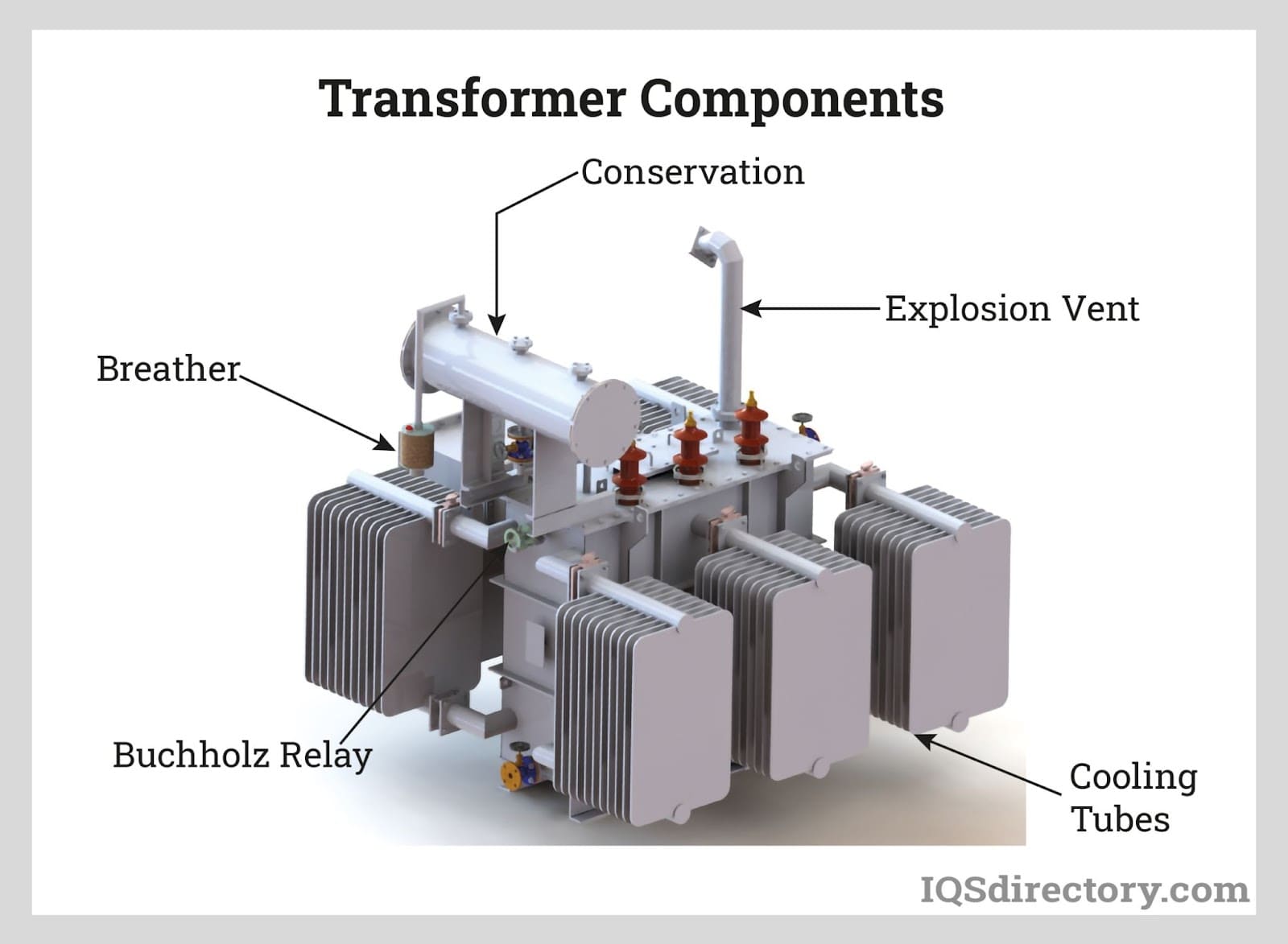
Illustrative image related to household transformer
Summary Table of Material Selection for Household Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for household transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in high-efficiency transformers | Superior electrical conductivity | High cost and complex processing | High |
| Aluminum | Windings in budget-friendly transformers | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity requires larger gauges | Medium |
| Steel | Magnetic cores in heavy-duty transformers | Excellent magnetic permeability | Heavier and corrosion-prone | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation components in transformers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited thermal stability | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for household transformers, focusing on the properties and considerations relevant to international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for household transformer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Household Transformers?
The manufacturing process for household transformers is a multi-faceted operation that encompasses several key stages, each critical to ensuring the product meets performance standards and safety regulations.
How Is Material Prepared for Household Transformers?
The first stage involves material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are sourced. Common materials include copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for cores, and various insulating materials. The selection of materials is crucial as it affects the efficiency and longevity of the transformer. Suppliers often utilize automated systems for cutting and shaping materials to precise specifications, ensuring uniformity across production batches.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Household Transformers?
During the forming stage, raw materials are transformed into functional components. This includes winding the copper or aluminum wire into coils, which are then assembled onto the core. Techniques such as CNC machining and automated winding machines are commonly employed to enhance precision and reduce labor costs. The windings are typically insulated to prevent electrical shorts, and manufacturers may use techniques like vacuum impregnation to enhance insulation quality.
How Is Assembly Executed for Household Transformers?
The assembly stage involves combining the core, windings, and other components into a complete transformer unit. Quality control measures are integrated into this stage, where components are inspected for defects before assembly. This can include visual inspections and electronic testing to ensure that all parts conform to design specifications. Workers often follow standardized assembly protocols to minimize errors, and advanced technologies such as robotics are increasingly being adopted to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
What Finishing Processes Are Used in Household Transformer Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for ensuring that transformers are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and durable. This stage may involve painting, coating, or applying protective finishes to enhance corrosion resistance and overall durability. Manufacturers often utilize automated painting systems to ensure a consistent application. Additionally, final inspections are conducted to check for any cosmetic defects or functional issues before the product is packaged and shipped.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Household Transformers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of transformer manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It ensures that manufacturers adhere to a systematic approach to managing their processes, which can lead to improved efficiency and customer satisfaction. In addition to ISO 9001, compliance with CE (Conformité Européenne) marking indicates that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. For electrical transformers, adherence to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards is also crucial, ensuring that products are safe and reliable.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process, categorized into three main types:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers should provide documentation demonstrating compliance with quality standards, such as test certificates for materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various tests are conducted at different stages to ensure that components meet specifications. This can include electrical testing of windings and visual inspections for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished transformers undergo rigorous testing, including performance tests and safety checks. This stage often verifies compliance with international standards and ensures that transformers operate efficiently under load conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Transformer Quality?
Testing methods play a pivotal role in quality assurance for household transformers. Key methods include:
- Insulation Resistance Testing: This checks the insulation quality of windings, ensuring that there are no leaks or shorts.
- Winding Resistance Testing: This measures the resistance of the windings to ensure they meet design specifications.
- Temperature Rise Testing: Conducted to ensure the transformer can operate within its specified temperature limits under load.
- Short-Circuit Testing: This evaluates the transformer’s ability to withstand short-circuit conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control processes is crucial for mitigating risks.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request documentation of quality control processes, including audit reports and quality certifications. Regular audits by third-party organizations can provide independent verification of a supplier’s compliance with international standards. Additionally, buyers should inquire about the supplier’s history of quality-related issues and how they were addressed.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
How Do Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Third-party inspections add an extra layer of assurance by providing unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing process and finished products. Engaging a reputable inspection agency can help identify potential quality issues before the products are shipped, ensuring that they meet the required standards. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with varying regulatory standards, as it helps to ensure compliance across different markets.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing household transformers from international suppliers, buyers must navigate various quality certification nuances. For instance, while CE marking may be sufficient for European markets, additional certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) may be required for the North American market. Understanding these nuances ensures that buyers are equipped to meet the regulatory requirements of their target markets.
By grasping the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who prioritize safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance in their household transformers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘household transformer’
Introduction
Sourcing household transformers can be a complex process, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a practical, step-by-step checklist to ensure you make informed procurement decisions. By following these steps, you can identify the right transformer that meets your operational needs while ensuring compliance and reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of the transformer you need. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, phase type (single-phase or three-phase), wattage capacity, and efficiency ratings. These specifications will guide your search and ensure the transformer aligns with your operational demands.
- Voltage Requirements: Determine the input and output voltage levels necessary for your applications.
- Power Capacity: Assess the wattage or kVA ratings that match your equipment’s needs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Understanding the market landscape and current standards is crucial. Familiarize yourself with the certifications that transformers should hold, such as UL, CE, or FCC certifications. This ensures compliance with safety regulations in your region, particularly if you are sourcing from international suppliers.
- Local Regulations: Be aware of any specific regulations or standards in your target market that may affect your procurement.
- Efficiency Standards: Look for products that meet energy efficiency guidelines to save on operational costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and customer testimonials. This step is vital to ensure you are partnering with a reputable supplier who can deliver quality products.
- References: Ask for references from other businesses in similar industries or regions to gauge supplier reliability.
- Production Capacity: Confirm that the supplier can meet your volume requirements and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Before making a large purchase, request samples of the transformers along with technical documentation. This will allow you to assess the quality and suitability of the products firsthand.
- Documentation: Review installation guides, operational manuals, and maintenance recommendations to ensure compatibility with your systems.
- Testing: If possible, conduct performance tests on the samples to validate their functionality.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential import duties, is essential for budgeting.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk purchases to optimize your procurement costs.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure that warranty terms and after-sales support are clearly defined in the contract.
Step 6: Finalize the Order and Plan for Logistics
After agreeing on terms, finalize your order and plan for logistics. Coordinate with the supplier on shipping methods, insurance, and tracking. Proper logistics management ensures timely delivery and reduces the risk of disruptions.
- Shipping Options: Choose a reliable shipping method that aligns with your timeline and budget.
- Customs Clearance: Prepare necessary documentation for customs to avoid delays at the border.
Step 7: Monitor Installation and Performance
Once the transformers arrive, oversee the installation process to ensure compliance with safety standards. Regularly monitor their performance to identify any issues early, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Installation Checks: Verify that the installation adheres to manufacturer guidelines and local regulations.
- Performance Monitoring: Implement a routine inspection and maintenance schedule to ensure long-term reliability.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing household transformers effectively, ensuring they meet their operational needs while adhering to regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for household transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Household Transformer Sourcing?
When considering the cost structure of household transformers, several components must be taken into account:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing transformers include copper or aluminum for windings, steel for the core, and various insulating materials. The choice of material significantly impacts both performance and cost, with copper generally being more expensive but offering superior conductivity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, the overall manufacturing expenses will be higher. Conversely, countries in Africa or South America may offer more competitive labor rates, potentially lowering costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory maintenance, utilities, and salaries of administrative staff. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom transformer designs can be significant. Depending on the complexity and specifications required, the tooling investment may vary, impacting the final pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes are essential to ensure compliance with international standards (e.g., UL, CE certifications). Enhanced QC protocols may increase costs but are critical for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can fluctuate based on the shipping method (air, sea, or land), distance, and local tariffs or taxes. International buyers should factor in these logistics expenses when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Household Transformer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of household transformers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Buyers purchasing larger volumes often benefit from reduced pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing, where the unit cost decreases with higher order quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom transformers designed for specific applications or unique specifications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect pricing. High-quality, durable materials may increase initial costs but can lead to lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Transformers that meet stringent international certifications (e.g., UL, CE) may be priced higher due to the added value of compliance and reliability. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on their markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon shipping terms (Incoterms) can impact total costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears shipping and insurance costs, influencing the final price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Household Transformers?
B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can employ several strategies to optimize their purchasing process:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, volume discounts, and payment terms can lead to more favorable agreements. Buyers should be prepared to negotiate based on competitive quotes.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assessing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial. This includes not only the purchase price but also installation, operation, maintenance, and potential replacement costs over the product’s lifespan.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understanding regional market dynamics, including currency fluctuations, local demand, and supplier capabilities, can empower buyers to make informed decisions. This awareness can also aid in negotiating terms that accommodate international shipping and customs considerations.
In conclusion, while the pricing of household transformers is influenced by multiple factors, informed B2B buyers can strategically navigate these components to achieve cost-effective sourcing solutions. Remember, prices can vary widely based on market conditions, and potential buyers should always seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing household transformer With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Household Power Management
In the realm of electrical distribution for residential settings, household transformers play a critical role in stepping down high voltage electricity to usable levels for home appliances. However, various alternative solutions exist that can serve similar purposes, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This analysis provides a comparative overview of household transformers against other viable solutions, including power converters and voltage regulators.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Household Transformer | Power Converter | Voltage Regulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in voltage conversion; supports multiple appliances simultaneously. | Good for limited applications; ideal for converting specific voltages. | Maintains steady voltage levels; effective for sensitive equipment. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment; costs vary by capacity and brand. | Typically lower cost; prices vary based on wattage. | Moderate cost; varies with specifications and brand reputation. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; may need upgrades to existing wiring. | Easy to install; often plug-and-play for small devices. | Simple installation; can be integrated into existing systems with minimal modifications. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; long lifespan with proper usage. | Minimal maintenance; dependent on usage frequency. | Requires occasional checks; wear and tear can affect performance. |
| Best Use Case | Best for whole-home power distribution; necessary for high-demand appliances. | Ideal for specific devices needing voltage adjustments; useful for travel. | Best for protecting sensitive electronics; suitable for devices with fluctuating power needs. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Power Converter
Power converters are compact devices designed to convert one voltage level to another, typically used for specific appliances that require a different voltage than what is available. They are particularly useful for travelers who need to power devices in regions with different electrical standards. While their installation is straightforward, they typically support limited wattage and may not be suitable for high-demand applications. Their lower cost makes them an attractive option for individual device use, but they lack the capacity to manage entire home systems effectively.
Voltage Regulator
Voltage regulators function by maintaining a constant voltage level to protect sensitive electronics from fluctuations in the power supply. These devices are crucial for environments where electrical stability is paramount, such as in IT and telecommunications sectors. While they can be more affordable than transformers, they serve a different purpose and are not designed for high-capacity applications. Their ease of integration and minimal maintenance requirements make them a reliable choice for specific uses, but they do not replace the comprehensive power distribution capabilities of a household transformer.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a power management solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including the scale of power distribution needed, the types of devices to be supported, and budget constraints. Household transformers are best suited for comprehensive residential power needs, especially in larger installations or where multiple high-demand appliances are in use. In contrast, power converters and voltage regulators offer effective solutions for specific applications, providing flexibility and cost savings for smaller-scale needs. Ultimately, the decision should align with the buyer’s operational requirements and future growth plans, ensuring that the chosen solution provides both reliability and efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for household transformer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Household Transformers?
When considering household transformers, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Here are key specifications that B2B buyers should focus on:
1. Voltage Rating
Voltage ratings indicate the maximum voltage the transformer can handle. For household transformers, this typically ranges from 110V to 240V. Understanding the voltage rating is essential for compatibility with local electrical systems. Buyers must ensure that the transformer matches the voltage requirements of their applications to prevent damage and ensure safety.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
2. Power Rating (kVA or Watts)
The power rating, expressed in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or watts (W), indicates the transformer’s capacity to handle electrical load. Common household transformers range from 0.03 kVA for small applications to 10 kVA for larger systems. Selecting the appropriate power rating is critical to avoid overloading the transformer, which can lead to overheating and failure.
3. Winding Material
Transformers can utilize copper or aluminum windings, with copper being the preferred choice due to its superior conductivity and durability. While aluminum is lighter and often less expensive, it may not perform as efficiently in high-demand scenarios. B2B buyers should consider the material based on the intended use, cost, and long-term performance expectations.
4. Temperature Rise Rating
The temperature rise rating indicates how much the transformer’s temperature can increase above ambient levels during operation. Common ratings are 80°C, 115°C, and 150°C. This specification is vital for assessing the transformer’s ability to dissipate heat and maintain safe operating conditions. A lower temperature rise rating can enhance reliability and lifespan, making it an important consideration for B2B procurement.
5. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings reflect how effectively a transformer converts input power to output power, typically expressed as a percentage. High-efficiency transformers reduce energy loss, translating to lower operational costs. For businesses focusing on sustainability and cost-effectiveness, selecting a transformer with a high-efficiency rating is essential.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
6. Certification and Compliance
Transformers often come with certifications such as UL, CE, or RoHS, which indicate compliance with international safety and environmental standards. These certifications are crucial for B2B buyers, ensuring that the products meet regulatory requirements and are safe for use in their respective markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Household Transformers?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms used in the transformer industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of transformers, working with OEMs can ensure that buyers receive high-quality products tailored to specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand, as it impacts inventory management and cost-efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses gauge their purchasing strategy and budget.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. For transformers, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare options, negotiate prices, and establish relationships with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for ensuring clarity in shipping, insurance, and risk management when importing transformers from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from the placement of an order to the delivery of the product. In the transformer industry, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the product and supplier capabilities. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and project management.
6. Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the performance and durability of the transformer. It outlines the terms under which repairs or replacements will occur. For B2B buyers, a solid warranty can provide peace of mind and reduce long-term costs associated with maintenance and replacements.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring household transformers, ultimately ensuring reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the household transformer Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Household Transformer Market?
The household transformer market is experiencing notable growth driven by several global factors. As urbanization accelerates in regions such as Africa and South America, there is a rising demand for reliable power distribution systems. Additionally, the global push towards renewable energy sources has increased the need for efficient voltage regulation and management, particularly in developing countries where infrastructure is still evolving. B2B buyers must also consider the impact of technological advancements in smart grids and IoT, which facilitate better energy management and enhance the functionality of household transformers.

Illustrative image related to household transformer
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technology into transformers, enabling real-time monitoring and maintenance, which helps reduce downtime and operational costs. This is particularly relevant for buyers in the Middle East, where investment in smart city initiatives is surging. Furthermore, the availability of online platforms has transformed sourcing practices, allowing international buyers to compare products and suppliers easily. Countries like Germany are witnessing a shift towards modular transformers that offer flexibility in installation and scalability, catering to the diverse needs of residential consumers.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Household Transformers?
In today’s environmentally conscious market, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers. The production of household transformers can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and material waste. Therefore, selecting suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices is essential. This includes using sustainable materials, minimizing carbon footprints during manufacturing, and ensuring responsible disposal or recycling of old transformers.
B2B buyers should look for certifications such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management, and other green certifications that signify compliance with sustainability standards. Additionally, transparency in the supply chain is vital; buyers should inquire about a supplier’s sourcing practices, labor conditions, and the use of hazardous materials. By choosing manufacturers that adhere to ethical practices, companies can not only reduce their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements, which are increasingly important in markets across Europe and beyond.
What Is the Historical Context of Household Transformers in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of household transformers can be traced back to the late 19th century when the first electrical systems were being developed. Initially, transformers were large, cumbersome devices primarily used in industrial settings. However, as the demand for electricity surged in residential areas, particularly post-World War II, the design and functionality of transformers underwent significant advancements. Innovations led to the development of compact and efficient models that could be easily installed in residential settings, allowing for safer and more reliable power distribution.
Illustrative image related to household transformer
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards enhancing energy efficiency and integrating advanced technology into transformers. This evolution has been largely driven by the increasing awareness of energy conservation and the need for sustainable practices. Today, household transformers are not only vital components in residential electrical systems but also play a crucial role in the broader context of energy management and distribution, making them a key consideration for international B2B buyers looking to invest in reliable power solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of household transformer
-
How do I choose the right transformer for my residential project?
Selecting the appropriate transformer involves understanding your power requirements, including voltage and wattage. Assess the total load of the devices to be powered and consider whether you need a step-up or step-down transformer. Additionally, ensure that the transformer meets local electrical standards and certifications, such as UL or CE. For large projects, consulting with a qualified electrical engineer can help ensure optimal performance and safety. -
What is the best transformer type for residential use?
The best transformer for residential applications is typically a pad-mounted or pole-mounted transformer, depending on space availability and local regulations. Pad-mounted transformers are often preferred for their safety and accessibility, while pole-mounted transformers are suitable for overhead power lines. The choice also depends on the load requirements and whether a single-phase or three-phase transformer is needed. Evaluate the installation site and power needs to make an informed decision. -
What are the common voltage ratings for household transformers?
Household transformers commonly operate at voltage ratings of 120V, 240V, and can step down from higher voltages like 7.2kV or 14.4kV. When sourcing transformers, confirm that the voltage output matches the requirements of your residential electrical system. Understanding local voltage standards is crucial, especially when importing equipment from different regions, to ensure compatibility and safety. -
What factors should I consider when vetting a transformer supplier?
When evaluating a transformer supplier, consider their certifications, manufacturing capabilities, and reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers with international certifications like ISO, UL, or CE, which indicate compliance with quality and safety standards. Additionally, assess their production capacity, lead times, and customer service responsiveness. Requesting references and reviewing case studies can also provide insight into their reliability and performance history. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for household transformers?
Minimum order quantities for household transformers can vary widely based on the supplier and the product specifications. Generally, MOQs may range from 10 to 100 units for standard models. For custom transformers, the MOQ may be higher due to the increased manufacturing complexity. Discussing your specific needs with the supplier can lead to more flexible arrangements, especially for larger or ongoing projects. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by international suppliers?
International suppliers typically offer a range of payment terms, including upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment on delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or discounts for early payments. Understanding the payment structure can help mitigate risks and improve cash flow management for your project. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for transformers sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing transformers, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Conduct factory audits if possible, or hire third-party inspection services to verify compliance with quality standards. Additionally, consider requesting samples for testing before placing a large order. Establishing clear quality expectations and maintaining open communication with the supplier can help ensure that the final products meet your requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing transformers?
When importing transformers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. It’s also crucial to select a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling electrical equipment to avoid delays and damage during transit. Planning for contingencies, such as unexpected shipping costs or customs inspections, can help ensure a smooth delivery process.
Top 3 Household Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. ACUPWR – Whole-Home Voltage Transformers
Domain: acupwr.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Whole-home voltage transformers convert electricity for entire homes or offices from 110-120 volts to 220-240 volts and vice-versa. They are designed for high power consumption needs, with ACUPWR models ranging from 3000 to 6000 watts. These transformers are typically hand-wired to a circuit breaker and provide power to all wall outlets in a home or building. ACUPWR transformers are made in the US…
2. HNK Parts – Power Transformers
Domain: hnkparts.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Transformer for Home Appliance – Power Transformer. Types include HV transformers, power transformers, and LED transformers. HV transformers are used in appliances like microwaves and refrigerators to step up voltage. Power transformers step down voltage for high-power appliances. LED transformers convert AC voltage to low DC voltage for LED lights in appliances. Special prices range from $35.44 t…
3. Thomas Edison Electric – Home Transformers
Domain: thomasedisonelectric.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Home transformers are electrical devices that adjust voltage levels between circuits, stepping down voltage for household use or stepping up for specific applications. Common uses include: 1. Powering low-voltage lighting systems (landscape lighting, under-cabinet kitchen lighting, LED accent lighting). 2. Charging electronic devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops, gaming consoles, wireless router…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for household transformer
In the evolving landscape of household transformers, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for B2B buyers aiming to optimize both cost and efficiency. By carefully selecting suppliers who demonstrate reliability and compliance with international standards, businesses can ensure the seamless integration of transformers into their operations. It is essential to consider not only the technical specifications and certifications but also the supplier’s production capacity and delivery capabilities, especially for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing in high-quality transformers is crucial for enhancing electrical safety and performance in residential settings. As global energy demands rise, the importance of efficient voltage management cannot be overstated. By leveraging strategic sourcing, buyers can position themselves to capitalize on emerging trends, such as the growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in transformer design.
Looking ahead, international buyers should engage proactively with manufacturers and suppliers to explore innovative solutions that meet their unique requirements. This approach will not only streamline procurement processes but also foster long-term partnerships that drive growth and sustainability in the household transformer market. Embrace the future of electrical infrastructure by making informed sourcing decisions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
Illustrative image related to household transformer
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.