Top 3 4 Terminal Solenoid Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 4 terminal solenoid
As global industries increasingly rely on advanced electrical components, sourcing a reliable 4 terminal solenoid has become a pivotal challenge for B2B buyers. This critical component plays a significant role in various applications, from automotive systems to industrial machinery, making its procurement crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. However, navigating the complexities of supplier options, performance standards, and pricing can overwhelm even the most seasoned professionals.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower international B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Vietnam and Nigeria—by detailing essential aspects of 4 terminal solenoids. We will explore the diverse types available, their specific applications, and the vital factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, the guide will provide insights into pricing structures, shipping considerations, and best practices for ensuring quality and reliability.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the market landscape, this guide facilitates informed purchasing decisions. With the right knowledge, businesses can streamline their procurement processes, enhance product performance, and ultimately drive growth in an increasingly competitive global market. The goal is to transform the sourcing experience from a daunting task into a strategic advantage.
Understanding 4 terminal solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Starter Solenoid | 4 terminals, typically 12V, high amperage | Automotive starter systems | Pros: Reliable performance, widely available. Cons: May require specific mounting solutions. |
| Heavy-Duty Starter Solenoid | Higher amp ratings (up to 300A), rugged design | Commercial vehicles, heavy machinery | Pros: Durable, handles high load requirements. Cons: Bulkier, higher initial cost. |
| HVAC Solenoid | Designed for heating and cooling systems | HVAC systems, refrigeration units | Pros: Efficient operation, compact design. Cons: Limited to HVAC applications. |
| Marine Solenoid | Corrosion-resistant materials, waterproof design | Marine engines, boats | Pros: Built for harsh environments, reliable. Cons: Higher price due to specialized materials. |
| Automotive Relay Solenoid | Smaller, lightweight, with multiple configurations | Automotive electrical systems | Pros: Versatile, easy to install. Cons: Lower amperage, not suitable for heavy-duty use. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Starter Solenoids?
Standard starter solenoids are commonly used in automotive applications, featuring a robust design that supports high amperage, typically around 12V. They are characterized by their four terminals, which facilitate easy connections to the starter motor and battery. When considering procurement, buyers should focus on compatibility with existing systems and the reliability of the manufacturer. Availability in the market is generally high, making these solenoids a convenient option for automotive repair shops and parts distributors.
How Do Heavy-Duty Starter Solenoids Differ from Standard Models?
Heavy-duty starter solenoids are engineered to handle significantly higher electrical loads, often rated up to 300A. This makes them ideal for commercial vehicles and heavy machinery that demand robust performance under strenuous conditions. Buyers should assess the durability and construction quality, as these solenoids often feature enhanced materials to withstand harsh environments. While they may come at a higher price point, their longevity and reliability can lead to reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
What Applications Benefit from HVAC Solenoids?
HVAC solenoids are specifically designed for regulating electrical flow in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. They are typically compact and efficient, ensuring optimal performance in temperature control applications. B2B buyers in the HVAC sector should prioritize solenoids that meet specific voltage and amperage requirements for their systems. While they offer excellent efficiency, their specialized nature may limit cross-application use.
Why Choose Marine Solenoids for Marine Applications?
Marine solenoids are built with corrosion-resistant materials and waterproof designs, making them essential for marine engines and boats operating in challenging environments. Their durability ensures reliable operation, even in saltwater conditions. When purchasing marine solenoids, B2B buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions and ensure compatibility with marine electrical systems. Although they are typically more expensive, their longevity in harsh conditions can justify the investment.
What Are the Advantages of Automotive Relay Solenoids?
Automotive relay solenoids are smaller and lighter than traditional starter solenoids, making them suitable for various automotive electrical applications. They offer multiple configurations to accommodate different vehicle systems. Buyers should evaluate the solenoid’s amperage rating and installation requirements, as these relays are often easier to integrate into existing systems. While they may not support heavy-duty operations, their versatility and ease of installation make them a popular choice among automotive suppliers.
Key Industrial Applications of 4 terminal solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 4 terminal solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Starter systems in vehicles | Reliable starting performance and reduced downtime | Voltage ratings, amperage capacity, and compatibility with vehicle models |
| Industrial Equipment | Control systems in heavy machinery | Enhanced efficiency and safety in operations | Durability, environmental resistance, and ease of integration with existing systems |
| Agricultural Machinery | Engine ignition systems in tractors and harvesters | Improved reliability during critical farming operations | Resistance to corrosion and vibration, as well as operational temperature ranges |
| HVAC Systems | Control of heating and cooling systems | Energy efficiency and reliable temperature control | Voltage specifications, response time, and compatibility with HVAC controls |
| Marine Applications | Engine start/stop mechanisms in boats | Dependable operation in harsh marine environments | Saltwater resistance, size constraints, and compliance with marine standards |
How Are 4 Terminal Solenoids Used in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, 4 terminal solenoids are primarily used in starter systems to initiate the engine’s operation. They serve as an essential link between the battery and the starter motor, facilitating the flow of electricity required to start the vehicle. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing solenoids with the appropriate voltage and amperage ratings is crucial to ensure compatibility with various vehicle models. Additionally, the solenoids must be durable to withstand harsh environmental conditions, reducing the risk of failure during operation.
What Role Do 4 Terminal Solenoids Play in Industrial Equipment?
In industrial settings, 4 terminal solenoids are integral to control systems in heavy machinery, such as cranes and conveyor belts. These solenoids help manage the flow of electricity to various components, ensuring smooth operation and enhancing safety measures during industrial processes. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing solenoids that can operate under high loads and are resistant to dust and moisture is vital. Buyers should also consider the ease of integration into existing machinery to minimize downtime during installation.
Why Are 4 Terminal Solenoids Important for Agricultural Machinery?
Agricultural machinery, including tractors and harvesters, relies on 4 terminal solenoids for engine ignition systems. These solenoids ensure reliable starting, which is critical during planting and harvesting seasons when delays can result in significant financial losses. Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam need to prioritize solenoids that can withstand vibrations and exposure to agricultural chemicals. Furthermore, understanding the operational temperature ranges is essential to ensure that solenoids function effectively in diverse climatic conditions.
How Do 4 Terminal Solenoids Enhance HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, 4 terminal solenoids control the operation of heating and cooling units, ensuring efficient temperature regulation in residential and commercial buildings. They help manage the electrical flow to the compressor and fan motors, contributing to energy efficiency and operational reliability. For buyers in the Middle East, where temperature extremes are common, it is crucial to source solenoids that can handle high voltages and provide quick response times. Compatibility with various HVAC control systems is another key consideration to ensure seamless integration.
What Are the Advantages of Using 4 Terminal Solenoids in Marine Applications?
In marine applications, 4 terminal solenoids are used for engine start/stop mechanisms, which are vital for the operation of boats and ships. These solenoids must be highly reliable and capable of performing in harsh marine environments, where exposure to saltwater can lead to corrosion. Buyers in this sector should prioritize solenoids that meet marine standards for durability and resistance to environmental factors. Size constraints are also a consideration, as space on vessels can be limited, necessitating compact solenoid designs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘4 terminal solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying the Right Specifications for 4 Terminal Solenoids
The Problem: When sourcing 4 terminal solenoids, B2B buyers often face the challenge of identifying the correct specifications that fit their unique applications. This can lead to confusion over voltage ratings, amperage requirements, and compatibility with existing systems. For instance, a buyer may mistakenly order a solenoid rated for 24 volts when their system operates at 12 volts, resulting in wasted time and resources. This misalignment can also cause operational failures, increased downtime, and ultimately impact business efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their specific applications before purchasing. This involves reviewing system manuals, consulting with engineers, and understanding the operational requirements of the machinery in which the solenoid will be installed. It is also crucial to cross-reference product specifications against trusted manufacturers’ guidelines. Creating a checklist of essential parameters—such as voltage, amperage, terminal types, and physical dimensions—can help streamline the selection process. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive product documentation and technical support can also facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Scenario 2: Quality and Reliability Concerns with Imported Solenoids
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, express concerns regarding the quality and reliability of imported 4 terminal solenoids. Poor quality components can lead to premature failures, resulting in costly repairs and replacements, as well as disruptions in operations. Buyers may find themselves stuck in a cycle of purchasing cheap alternatives that do not meet quality standards, causing frustration and potential reputational damage.
The Solution: To address quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers known for their rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. Investigating the manufacturer’s certifications, such as ISO or UL ratings, can provide insights into their commitment to quality. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who offer warranties and guarantees can further ensure reliability. Implementing a quality control process upon receiving shipments—such as visual inspections and functional testing—can help catch defective units before they are installed. Investing in higher-quality solenoids may incur higher upfront costs but will save money in the long run through enhanced durability and reduced maintenance needs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter integration challenges when replacing or upgrading existing solenoids in their systems. Compatibility issues can arise due to differences in terminal configurations or wiring setups, leading to installation delays and additional costs. For example, a company may find that the new 4 terminal solenoid does not match the existing harness, necessitating custom wiring or adapters, which can complicate the installation process.
The Solution: To facilitate seamless integration, buyers should conduct a comprehensive review of the existing system architecture before making a purchase. This includes documenting current wiring setups and terminal configurations. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can also be beneficial, as they may provide tailored solutions that align with specific installation requirements. Additionally, investing in modular solenoid designs can ease future upgrades and replacements by maintaining compatibility across different models. Providing detailed installation guides and support from the manufacturer can also ensure that the integration process goes smoothly, minimizing operational disruptions.
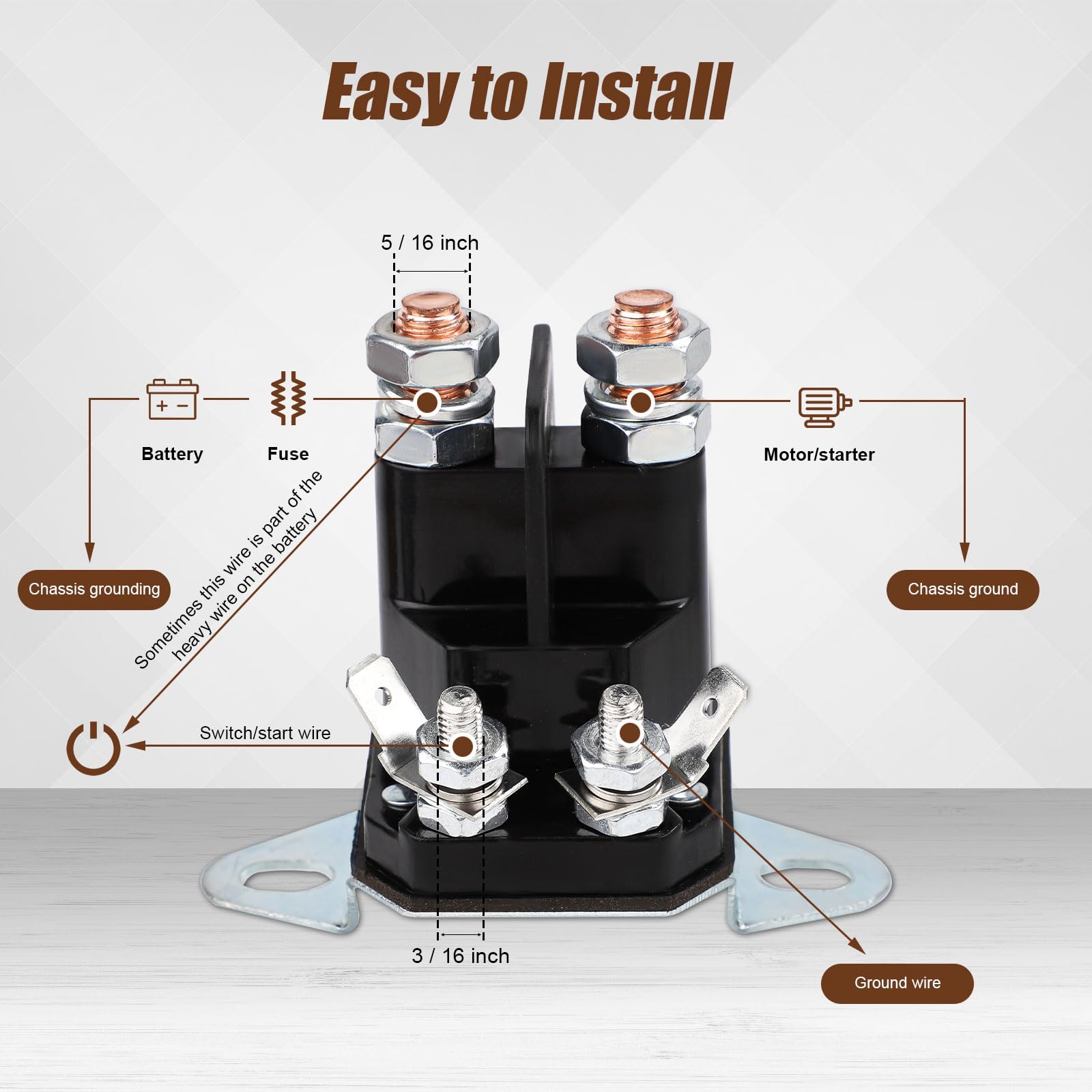
Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 4 terminal solenoid
What Are the Key Materials Used in 4 Terminal Solenoids?
When selecting materials for 4 terminal solenoids, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these components: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic.
How Does Copper Benefit 4 Terminal Solenoids?
Copper is a widely used material in electrical components, including 4 terminal solenoids, due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can handle high currents and dissipate heat effectively, making it suitable for applications that require rapid switching and high power.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, which is crucial for efficiency. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be easily formed into various shapes.
Cons: However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments. This susceptibility can lead to reduced lifespan and performance in harsh conditions.
Impact on Application: In applications where moisture or corrosive substances are present, using copper may necessitate additional protective coatings or treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B75 for copper tubing and consider the local environmental conditions that could affect copper’s longevity.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in 4 Terminal Solenoids?
Aluminum is another popular choice for solenoid construction, particularly in applications where weight is a concern. It offers a good balance between strength and weight, making it ideal for portable or mobile applications.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has good thermal conductivity. Its lower cost compared to copper makes it attractive for budget-sensitive projects.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum has lower electrical conductivity than copper, which can lead to higher energy losses in some applications. Additionally, its mechanical strength is less than that of copper.
Impact on Application: Aluminum solenoids may be suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, but they may not perform as well in high-current scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the relevant standards, such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions, and ensure that the solenoids meet local regulations regarding material properties and environmental impact.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for 4 Terminal Solenoids?
Stainless steel is often selected for its durability and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It is an excellent choice for solenoids used in outdoor or industrial settings.
Pros: Stainless steel offers superior strength and resistance to rust and corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan in challenging conditions. Its robustness makes it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Cons: However, stainless steel is heavier than both copper and aluminum, which can be a drawback in applications where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, it is more expensive to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel solenoids are ideal for applications exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, ensuring reliable operation over time.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A276 for stainless steel bars is crucial. Buyers should also consider the additional costs associated with stainless steel components.
How Does Plastic Factor into 4 Terminal Solenoid Design?
Plastic components are increasingly being used in solenoid construction, particularly for housings and insulators. They provide electrical insulation and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be produced at a lower cost than metals. They also offer excellent electrical insulation properties.
Cons: The main limitation of plastic is its lower mechanical strength compared to metals, making it unsuitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, plastics can degrade over time when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic solenoids are best suited for low-power applications where insulation is essential, but they may not be appropriate for high-current or high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for plastic materials and consider the environmental impact of plastic usage in their applications.
Summary of Material Selection for 4 Terminal Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for 4 terminal solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-power applications | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Portable or lightweight applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments and high-pressure use | High strength and corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Plastic | Low-power and insulated applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 4 terminal solenoid
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 4 Terminal Solenoids?
The manufacturing process for 4 terminal solenoids involves several critical stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing journey begins with the selection of high-quality materials, typically including copper for the windings and durable alloys for the casing. Suppliers must ensure that raw materials comply with international standards to avoid issues during production. This phase often includes processes such as cutting and shaping the raw materials into appropriate sizes and forms for the next stages.
Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials undergo various forming techniques, such as stamping and machining. Stamping is frequently used to create the solenoid’s casing, while machining processes are applied to produce components like the plunger and coil. Techniques like precision machining ensure that each component fits perfectly, which is vital for the solenoid’s functionality.
Assembly
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This phase typically involves the careful integration of the solenoid’s coil, plunger, and housing. Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, as they enhance precision and speed. However, manual assembly still plays a role, particularly in quality-critical areas where human oversight is necessary.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that enhance the solenoid’s durability and performance. This includes surface treatments such as plating to prevent corrosion, as well as testing for electrical integrity and performance. Finishing processes are essential for ensuring that the solenoid can withstand the operational demands of various applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in 4 Terminal Solenoid Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for 4 terminal solenoids, aimed at maintaining high standards and reducing defects. The QA process typically encompasses several international standards and industry-specific certifications.
Relevant International Standards
A common standard applied in manufacturing is ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, certifications such as CE mark (indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are crucial for solenoids used in specific industries like oil and gas.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To ensure quality throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established:

Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of incoming materials. Any substandard materials are rejected before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, IPQC involves regular inspections of components and processes to ensure they adhere to specified standards. This could involve checking dimensional tolerances and electrical properties at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed solenoids undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. This includes electrical testing, load testing, and functional testing to confirm the solenoid operates correctly under expected conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure 4 Terminal Solenoid Quality?
Quality assurance in 4 terminal solenoid manufacturing heavily relies on various testing methods. These methods are essential for verifying that the solenoids meet design specifications and performance criteria.
Electrical Testing
One of the primary testing methods involves checking the solenoid’s electrical properties, including resistance and current draw. This ensures that the solenoid functions correctly when energized, which is critical for applications in automotive and industrial sectors.
Load Testing
Load testing evaluates how well the solenoid performs under operational conditions. This testing simulates real-world conditions to measure response time and mechanical movement, ensuring the solenoid can handle the expected load without failure.
Environmental Testing
This testing assesses the solenoid’s performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, humidity, and vibration. Environmental testing is crucial for solenoids used in harsh environments, ensuring they maintain functionality over time.

Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers of 4 terminal solenoids. This can be achieved through several methods:
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards firsthand. Audits should focus on the manufacturing environment, equipment, and quality assurance protocols.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports from suppliers, which should include data on testing results, defect rates, and compliance with international standards. These reports provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These inspectors can verify compliance with industry standards and provide certification that the products meet specified quality criteria.
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific quality control considerations to keep in mind:
Understanding Certification Nuances
Different regions may have varying certification requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards to ensure that the products they import comply with these requirements.
Establishing Clear Communication
Effective communication with suppliers is vital. Buyers should establish clear expectations regarding quality standards, testing methods, and certification requirements upfront to avoid misunderstandings later in the process.
Building Long-Term Relationships
Developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can enhance quality assurance. Regular interactions can lead to improved transparency, better product understanding, and the ability to address quality concerns proactively.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in the production of 4 terminal solenoids, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘4 terminal solenoid’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure 4 terminal solenoids. Given the critical role these components play in various applications, from automotive to industrial machinery, understanding the procurement process is essential. This checklist will help streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring you select a reliable product that meets your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by establishing the technical requirements for your 4 terminal solenoid. Consider voltage ratings (e.g., 12V, 24V) and amperage ratings, as these will affect compatibility with your existing systems. Additionally, specify the type of terminals needed (e.g., blade or threaded) to ensure proper connectivity.
- Voltage: Identify the required voltage level for your application.
- Amperage: Determine the continuous and in-rush current your solenoid must handle.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers with a solid reputation in the market. Look for companies that specialize in electrical components and have experience supplying 4 terminal solenoids.
- Check online reviews and ratings to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Consider suppliers with a history of reliable delivery and customer support.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers. Look for industry-standard certifications such as ISO 9001 or UL approval, which indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
- Confirm that the supplier’s products meet international regulations, especially if you are sourcing from different regions.
- Request documentation to validate their compliance.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the 4 terminal solenoids from shortlisted suppliers. Testing samples will provide insights into the quality and performance of the products.
- Conduct functional tests to ensure the solenoids operate as expected under your specific conditions.
- Assess the build quality and durability of the samples.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and terms. Ensure that all costs, including shipping and taxes, are accounted for in your comparison to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Look for bulk purchase discounts or payment terms that align with your budget.
- Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including potential warranties or service agreements.
Step 6: Confirm Lead Times and Availability
Understanding the lead times for delivery is essential for your planning. Confirm the availability of the solenoids and the expected shipping times from the supplier.
- Inquire about stock levels to avoid delays in production.
- Discuss potential expedited shipping options if you need products urgently.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have completed your evaluations and selected a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and return policies, are clearly outlined.

Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
- Review the contract carefully to ensure it protects your interests.
- Maintain open communication with the supplier throughout the order process to address any issues promptly.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for 4 terminal solenoids, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 4 terminal solenoid Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for 4 terminal solenoid sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the various cost components and factors influencing prices can lead to better negotiation outcomes and overall cost efficiency.
What Are the Key Cost Components in 4 Terminal Solenoid Manufacturing?
The cost structure for 4 terminal solenoids typically includes several key components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing solenoids include metals like copper for coils and durable plastics for housing. Material costs can fluctuate based on global market conditions, impacting overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia or South America, may offer more competitive pricing, but it is essential to consider the skill level of the workforce as it affects product quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, which ultimately influences the pricing of solenoids.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for custom or specialized solenoids. Buyers should be aware that tooling costs may be spread across production runs, affecting unit prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is vital to ensure product reliability. However, enhanced QC processes can add to the overall cost, so it’s essential to balance quality with budget constraints.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping mode (air vs. sea), and customs duties can add substantial costs to the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the standard margins in the industry can help buyers gauge whether a quote is reasonable.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Pricing?
Several factors can influence the price of 4 terminal solenoids:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Many suppliers have Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), which can impact pricing strategies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique voltage ratings or specific materials, can increase costs. Standardized products tend to be more competitively priced.
-
Quality and Certifications: Solenoids with higher quality standards or necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, UL) may command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate whether the certifications justify the additional cost based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their proven quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in transactions is crucial. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can influence the total landed cost of the solenoids.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:

Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always negotiate prices, especially when dealing with large orders. Suppliers may have room to adjust pricing based on order size or payment terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime due to quality issues.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations, as these can significantly impact the final cost.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Frequent communication and transparency about needs can foster trust and improve negotiations.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in various sources are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, location, and specific supplier practices. Always request updated quotes and confirm pricing before finalizing any purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 4 terminal solenoid With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the 4 Terminal Solenoid
In the realm of electrical components, the 4 terminal solenoid is a widely recognized choice for various applications, particularly in automotive and industrial settings. However, as B2B buyers evaluate their options, it’s crucial to consider viable alternatives that may better suit specific operational requirements or budget constraints. This analysis will compare the 4 terminal solenoid with two alternative solutions: a 3 terminal solenoid and a relay switch.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 4 Terminal Solenoid | 3 Terminal Solenoid | Relay Switch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable operation, high efficiency | Good for simpler applications | Versatile control for various loads |
| Cost | Moderate pricing, typically $30-$50 | Generally lower cost, around $20-$30 | Variable costs, generally affordable |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific wiring knowledge | Easier to install, fewer connections | Straightforward installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable construction | Similar durability, but fewer parts | May require more frequent checks |
| Best Use Case | High-demand applications (e.g., starters) | Lightweight applications (e.g., motorcycles) | General-purpose switching (lighting, motors) |
Pros and Cons of Alternatives
3 Terminal Solenoid
The 3 terminal solenoid is a simplified version that is often more cost-effective than its 4 terminal counterpart. It is ideal for applications where a less complex electrical circuit is sufficient. The lower number of terminals means easier installation and reduced wiring, making it an attractive option for smaller vehicles or equipment. However, its performance may not match the 4 terminal solenoid in high-demand scenarios, such as in heavy machinery or vehicles requiring higher current flow.
Relay Switch
Relay switches offer a versatile solution for controlling electrical currents and can operate multiple loads with a single switch. Their adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to industrial settings. While they can be more affordable and easier to implement than solenoids, relays may require more frequent maintenance to ensure reliability, especially under high-load conditions. Additionally, they may not be as effective for direct starter applications, where a solenoid’s specific functionality is necessary.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between a 4 terminal solenoid and its alternatives, consider the specific demands of your application. If your operation requires a robust and reliable solution for high current applications, the 4 terminal solenoid is likely the best choice. However, for lighter applications or budget-conscious projects, exploring 3 terminal solenoids or relay switches could yield significant savings and adequate performance.
Ultimately, understanding the operational requirements and potential trade-offs of each option will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business needs. Prioritizing factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and ease of installation will guide you toward the most suitable electrical component for your application.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 4 terminal solenoid
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a 4 Terminal Solenoid?
Understanding the technical specifications of a 4 terminal solenoid is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing for diverse applications across various industries. Below are some key properties that buyers should consider:
1. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating, typically expressed in volts (e.g., 12V, 24V), indicates the electrical potential required for the solenoid to operate effectively. Selecting the correct voltage is vital to ensure compatibility with the existing electrical systems and to prevent equipment failure. In regions with variable power supply, understanding voltage ratings can help mitigate risks related to power surges or drops.
2. Amperage (Current Rating)
Amperage, measured in amps, defines the maximum current the solenoid can handle. Common ratings may range from 20A to over 300A, depending on the application. A solenoid with a higher amperage rating can manage more substantial electrical loads, making it suitable for demanding applications. B2B buyers should assess their operational requirements to ensure they select a solenoid that can handle the expected current without overheating.
3. Terminal Configuration
The terminal configuration refers to the arrangement and type of terminals on the solenoid. A 4 terminal solenoid typically includes two power terminals and two control terminals. Understanding this configuration is essential for correct installation and functionality. Buyers should ensure that the solenoid’s terminal configuration matches their wiring setup to avoid installation errors.
4. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the environmental conditions under which the solenoid can function optimally. It is crucial for applications exposed to extreme temperatures. Selecting a solenoid with an appropriate temperature tolerance can enhance longevity and reliability, especially in harsh climates typical in regions like Africa and South America.
5. Material Composition
The materials used in a solenoid’s construction, such as copper for windings and durable metals for the housing, influence its performance and durability. High-quality materials can enhance resistance to corrosion and wear, making the solenoid more reliable over time. Buyers should consider the material properties to ensure they meet industry standards and are suitable for their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 4 Terminal Solenoids?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several key terms relevant to 4 terminal solenoids:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another brand’s name. In the context of solenoids, sourcing from OEMs can ensure high-quality components that meet specific industry standards. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers in emerging markets may need to negotiate MOQ terms to align with their purchasing capabilities.

Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms used in international contracts to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and rights in international transactions, particularly when importing components like solenoids.
5. Warranty
A warranty is a manufacturer’s promise regarding the condition of a product, often covering repairs or replacements for a specified period. Understanding warranty terms can protect buyers against defects and ensure long-term reliability of the solenoids they purchase.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing 4 terminal solenoids, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 4 terminal solenoid Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the 4 Terminal Solenoid Sector?
The global market for 4 terminal solenoids is experiencing a surge, driven by the increasing demand for reliable electrical components across various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and renewable energy sectors. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the expansion of infrastructure projects and the rise of electric vehicles are significant contributors to this growth. Buyers in these markets are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality solenoids that meet stringent performance standards while being cost-effective.
Illustrative image related to 4 terminal solenoid
Emerging trends highlight the integration of smart technology in solenoid applications, where automation and IoT connectivity are becoming essential. These advancements allow for enhanced operational efficiency and predictive maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime. Additionally, the push for localized manufacturing and shorter supply chains is reshaping sourcing strategies, as buyers seek to mitigate risks associated with international logistics and tariffs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, as they navigate a landscape that increasingly prioritizes innovation and reliability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Sourcing of 4 Terminal Solenoids?
Sustainability is no longer a mere buzzword; it is a fundamental aspect of modern supply chains, especially in the sourcing of electrical components like 4 terminal solenoids. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, companies are compelled to assess the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. This includes evaluating the lifecycle of solenoids, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
Ethical sourcing practices, including the use of certified green materials and sustainable manufacturing processes, are gaining traction. Buyers should look for suppliers who have obtained certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adhere to sustainable practices. By prioritizing these factors, companies not only enhance their brand reputation but also appeal to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers and businesses. Furthermore, establishing an ethical supply chain can lead to long-term partnerships with suppliers who share similar values, fostering resilience and reliability in the sourcing process.
What Is the Brief Evolution of 4 Terminal Solenoids?
The evolution of 4 terminal solenoids can be traced back to the early 20th century when electrical components began to gain prominence in automotive and industrial applications. Initially, solenoids were used primarily in simple on-off switches. However, as technology advanced, the design and functionality of solenoids became more sophisticated, allowing for better performance, efficiency, and durability.
With the advent of modern materials and manufacturing techniques, today’s 4 terminal solenoids are engineered to handle higher currents and voltages while ensuring reliability and longevity. The introduction of automation and smart technologies has further transformed these components, enabling features like remote operation and diagnostic capabilities. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the technological advancements that have paved the way for the high-performance solenoids available in the market today. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the value of investing in advanced solenoid solutions that meet contemporary demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 4 terminal solenoid
-
How do I troubleshoot a malfunctioning 4 terminal solenoid?
Troubleshooting a malfunctioning 4 terminal solenoid involves several steps. First, ensure that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion. Use a multimeter to check for continuity across the terminals; a lack of continuity may indicate a defective solenoid. Additionally, verify that the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage as specified by the manufacturer. If these checks do not resolve the issue, consider replacing the solenoid or consulting a professional technician for further diagnostics. -
What is the best 4 terminal solenoid for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, look for a 4 terminal solenoid that offers high amperage ratings and robust construction. Products like the Automann Starter Solenoid with an 85A rating are ideal for such uses, as they are designed to withstand demanding conditions. Ensure the solenoid is rated for the specific voltage requirements of your system, and check for features such as weatherproofing and durability to enhance performance in challenging environments. -
What should I consider when sourcing 4 terminal solenoids from international suppliers?
When sourcing 4 terminal solenoids internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Verify their certifications and ask for product samples to assess quality. It’s also crucial to understand the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, lead times, and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Engage in direct communication to clarify terms and establish a trusting relationship, ensuring that the supplier can meet your specific requirements. -
How can I customize a 4 terminal solenoid for my specific needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for 4 terminal solenoids, including modifications in voltage ratings, amperage, and terminal configurations. To initiate customization, reach out to potential suppliers with your specific requirements, including the intended application and environmental conditions. Discuss design features and any special requirements, such as housing materials or mounting options. Ensure you receive prototypes or samples before finalizing the order to confirm that the modifications meet your expectations. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing 4 terminal solenoids internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of 4 terminal solenoids can vary widely. Common terms include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. Consider using secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to protect your investment. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and ensure they are clear and agreed upon before placing an order. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing 4 terminal solenoids?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing 4 terminal solenoids, request detailed specifications and test reports from the supplier. Establish clear QA protocols, including inspection processes for incoming goods. Consider partnering with suppliers who have ISO certifications or other recognized quality standards. Additionally, conducting random quality checks on received products can help maintain quality and reliability in your supply chain. -
What shipping options are available for 4 terminal solenoids, and how do they affect costs?
Shipping options for 4 terminal solenoids typically include air freight, sea freight, and express courier services. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders but takes longer. Evaluate the urgency of your needs and budget constraints when choosing a shipping method. Additionally, factor in customs duties and taxes, which can significantly impact overall costs. Always discuss shipping arrangements with your supplier to find the best balance between cost and delivery time. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering 4 terminal solenoids from international suppliers?
Lead times for ordering 4 terminal solenoids can vary based on factors such as supplier location, order size, and manufacturing capabilities. Generally, expect lead times to range from a few days for stock items to several weeks for custom orders. It’s advisable to discuss lead times upfront and factor them into your project timelines. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer expedited production options if time-sensitive delivery is a priority.
Top 3 4 Terminal Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
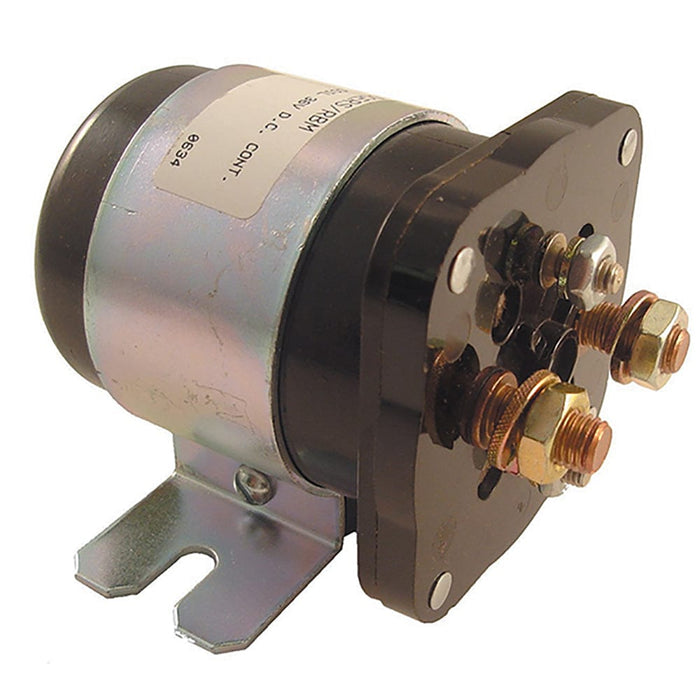
1. PJ Power Inc – 120-904 White Rodgers 24 Volt Solenoid
Domain: pjpowerinc.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “120-904 White Rodgers 24 Volt 4 Terminal Solenoid”, “price”: “$50.00 excl. tax”, “shipping_time”: “3-5 day(s)”, “description”: “This essential component is designed to efficiently regulate the flow of electricity in your system, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. With its durable construction and reliable functionality, the 120-904 solenoid is built to last and wi…
2. Automann – Part Number 5773042-12
Domain: customtruck.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Part Number”:”5773042-12″,”Item Length (in)”:”2.81″,”Item Width (in)”:”2.75″,”Item Height (in)”:”3.37″,”Item Weight (lb)”:”1.8″,”Brand”:”Automann”,”Eligible for Free Shipping”:”Yes”}
3. Grote – Starter Solenoid Switch
Domain: grote.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Part Number”: “82-0307”, “Product Type”: “Starter Solenoid Switch”, “Amperage”: {“Continuous Duty”: “100A”, “In Rush”: “150A”}, “Standards”: “UL”, “Pack Quantity”: “1”, “Conductor”: “5, 16″ – 24”, “Diameter”: “4” , “Feature”: “4 Terminal ground”, “Position”: “Normally Open, Off-On”, “Shape”: “Round”, “Type”: “S.P.S.T.”, “Warranty”: “1 Year”, “Operating Cycles”: “100,000”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 4 terminal solenoid
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement of 4 Terminal Solenoids?
In summary, strategic sourcing for 4 terminal solenoids is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By prioritizing quality suppliers, understanding technical specifications, and leveraging market insights, businesses can ensure they procure reliable components that meet their unique needs. The importance of establishing long-term relationships with suppliers cannot be overstated, as these partnerships can lead to improved negotiation terms, better product availability, and enhanced support services.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing solenoids across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider factors like supplier reliability, product durability, and compliance with local standards. Aligning these elements with your operational goals will not only streamline your procurement process but also strengthen your supply chain resilience.
Looking ahead, now is the time to take action. Evaluate your current sourcing strategies and explore opportunities to collaborate with trusted manufacturers and distributors. By doing so, you can position your business for sustained success in an increasingly competitive market. Embrace the future of procurement and unlock the potential of high-quality 4 terminal solenoids for your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.