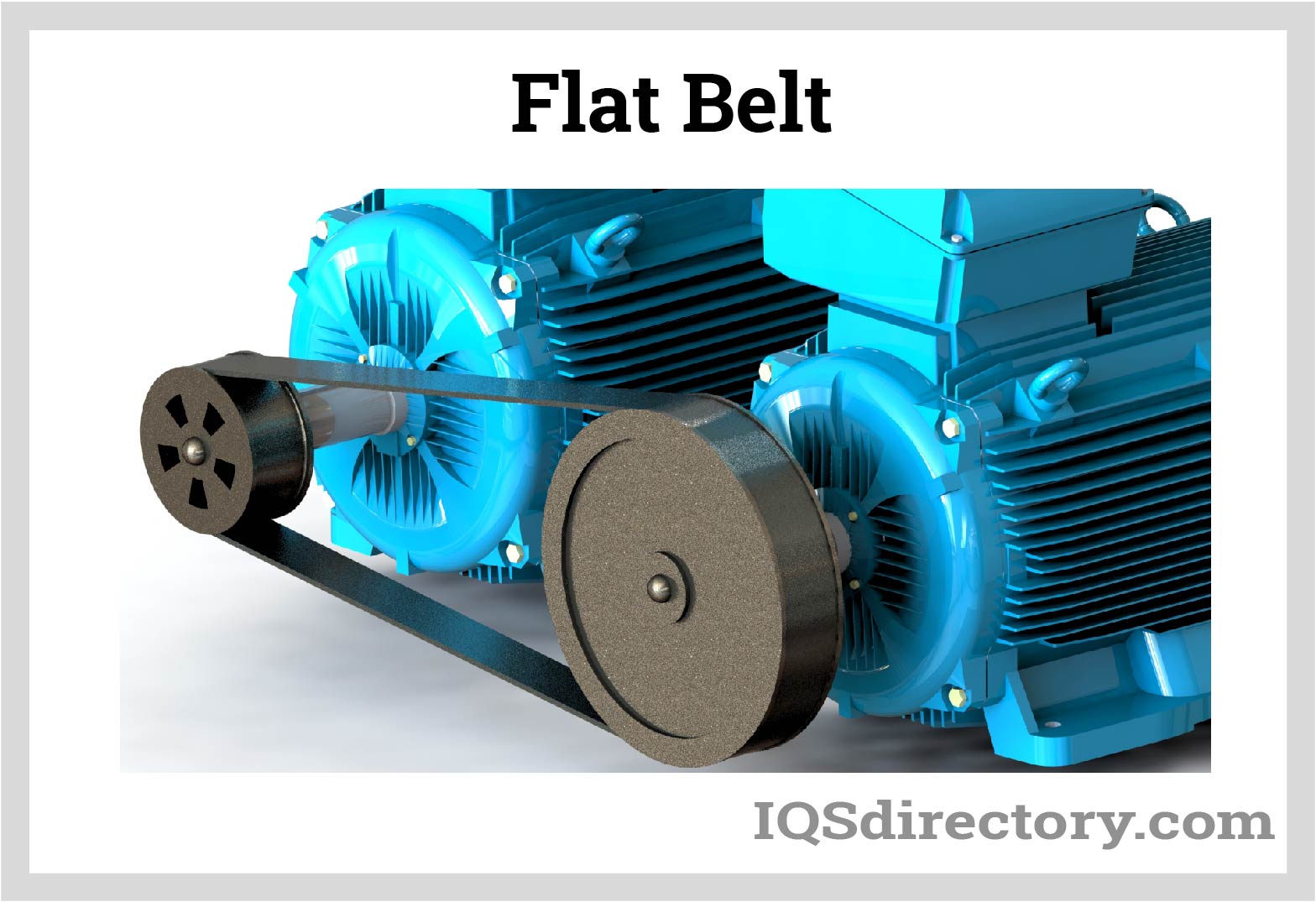
Top 2 Flat Bel Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for flat bel
Navigating the complexities of sourcing flat belts can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various types of flat belts available, their specific applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of flat belts, including their design features, material options, and performance characteristics, ensuring that buyers can effectively match their operational needs with the right products.
In addition to detailing the various types of flat belts, this resource will cover essential aspects such as cost considerations, sourcing strategies, and tips for evaluating suppliers. By addressing these key areas, the guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the global market with confidence, mitigating risks associated with procurement. Whether you are in Brazil looking for durable options for industrial machinery or in Germany seeking reliable components for automotive applications, this comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to streamline your sourcing process. With the right insights at your fingertips, you can enhance operational efficiency and drive greater value within your supply chain.
Understanding flat bel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose Flat Belts | Flat surface, versatile design, made from rubber or synthetic materials | Conveyor systems, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: May wear out faster in high-load applications. |
| Sliding Flat Belts | Minimized friction, optimized for smooth movement | Material handling, packaging machinery | Pros: Extends equipment lifespan, reduces maintenance. Cons: Performance can degrade in extreme conditions. |
| Oil-Resistant Flat Belts | Resistant to oils and chemicals, robust construction | Food processing, automotive applications | Pros: Durable in harsh environments, protects sensitive systems. Cons: Higher initial cost compared to standard belts. |
| Electronic Parts Flat Belts | Designed for high efficiency and minimal vibration | Robotics, precision machinery | Pros: Ensures reliable performance, ideal for sensitive equipment. Cons: Specificity may limit broader applications. |
| Grip Flat Belts | Made from thermoplastic polyurethane, high friction surface | High-torque applications, heavy machinery | Pros: Excellent grip, suitable for demanding tasks. Cons: Can be more expensive and less flexible. |
What are General Purpose Flat Belts and Their Applications?
General purpose flat belts are designed for a wide range of mechanical systems, characterized by their flat surface and construction from rubber or synthetic materials. These belts are ideal for applications such as conveyor systems and various industrial machinery. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the operating conditions, as these belts may wear out more quickly in high-load environments, potentially leading to increased replacement costs.
How Do Sliding Flat Belts Enhance Performance?
Sliding flat belts are engineered to minimize friction, facilitating smooth movement in material handling and packaging operations. Their design optimizes performance and extends equipment life, making them suitable for industries that prioritize efficiency. Buyers should consider the operational environment, as extreme conditions may affect the belt’s performance, leading to maintenance challenges.
Why Choose Oil-Resistant Flat Belts?
Oil-resistant flat belts are specifically constructed to withstand exposure to oils and chemicals, making them essential for food processing and automotive sectors. Their robust design enhances durability and protects sensitive machinery from wear. While they offer significant advantages in harsh environments, buyers should be prepared for a higher initial investment compared to standard options.
What Advantages Do Electronic Parts Flat Belts Offer?
Electronic parts flat belts are crafted for high efficiency and minimal vibration, making them ideal for robotics and precision machinery applications. Their reliable performance is crucial for sensitive equipment, ensuring smooth operation. However, buyers should be aware that their specific design may limit broader applications, necessitating careful consideration of compatibility with existing systems.
When to Consider Grip Flat Belts for High-Torque Applications?
Grip flat belts feature a high-friction surface made from thermoplastic polyurethane, making them suitable for high-torque applications in heavy machinery. Their exceptional grip is beneficial in demanding tasks where slippage can lead to inefficiencies. However, potential buyers should weigh the higher costs and reduced flexibility against the specific performance needs of their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of flat bel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of flat bel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhances efficiency in material handling | Durability, resistance to wear, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Automotive | Engine Power Transmission | Reliable performance under high load conditions | Material quality, temperature resistance, and compliance with industry standards. |
| Food Processing | Packaging and Sorting Equipment | Maintains hygiene and prevents contamination | Food-grade materials, resistance to chemicals, and ease of cleaning. |
| Textile Industry | Fabric Transport and Processing | Increases throughput and reduces downtime | Flexibility, strength, and adaptability to various machinery configurations. |
| Mining and Heavy Machinery | Equipment Drive Systems | Ensures reliable operation in harsh conditions | Resistance to oil, moisture, and heavy loads; sourcing from trusted suppliers. |
How are flat belts used in manufacturing conveyor systems?
In manufacturing, flat belts are integral to conveyor systems that transport materials across production lines. These belts facilitate the movement of products, enhancing overall efficiency and productivity. By reducing slippage and ensuring smooth operation, flat belts minimize downtime and maintenance costs. International buyers, particularly from regions with diverse manufacturing needs, should focus on sourcing durable materials that can withstand varying loads and environmental conditions, ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
What role do flat belts play in automotive power transmission?
Flat belts are crucial in automotive engines for power transmission between pulleys. Their ability to handle high loads and maintain performance under stress makes them ideal for this application. By providing reliable power transfer, they help optimize engine efficiency and fuel consumption. Buyers in the automotive sector must prioritize sourcing belts that meet stringent quality standards and can operate effectively in high-temperature environments, particularly those in regions like Europe and South America where automotive regulations are strict.
How do flat belts ensure safety in food processing applications?
In the food processing industry, flat belts are used in packaging and sorting equipment, where hygiene is paramount. These belts are designed to prevent contamination while ensuring efficient transport of food products. Sourcing food-grade materials that are easy to clean and resistant to chemicals is essential for compliance with health regulations. Buyers in this sector, especially from regions with stringent food safety standards, should ensure that their suppliers provide belts that meet both safety and operational efficiency requirements.
Why are flat belts essential for textile processing?
In the textile industry, flat belts are utilized for transporting and processing fabrics. They enhance throughput by facilitating continuous movement, which reduces production downtime. The flexibility and strength of flat belts allow them to adapt to various machinery configurations, making them highly effective. International buyers should consider sourcing belts that are specifically designed for textile applications, ensuring they can withstand the unique stresses associated with fabric handling and processing.
What advantages do flat belts offer in mining and heavy machinery?
Flat belts are employed in mining and heavy machinery for equipment drive systems, where reliability is critical. They provide consistent power transmission in harsh environments, helping to maintain operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize sourcing belts that are resistant to oil, moisture, and heavy loads to ensure longevity and performance. Establishing relationships with trusted suppliers who understand the demanding conditions of mining operations is crucial for maintaining equipment uptime and safety.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘flat bel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty with Flat Belt Slippage in High-Speed Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with flat belts slipping during high-speed operations, especially in conveyor systems or machinery that require consistent power transmission. This slippage can lead to inefficient operation, increased downtime, and heightened wear on both the belt and the associated components. For companies relying on precise manufacturing processes or time-sensitive logistics, such disruptions can significantly impact productivity and profitability.
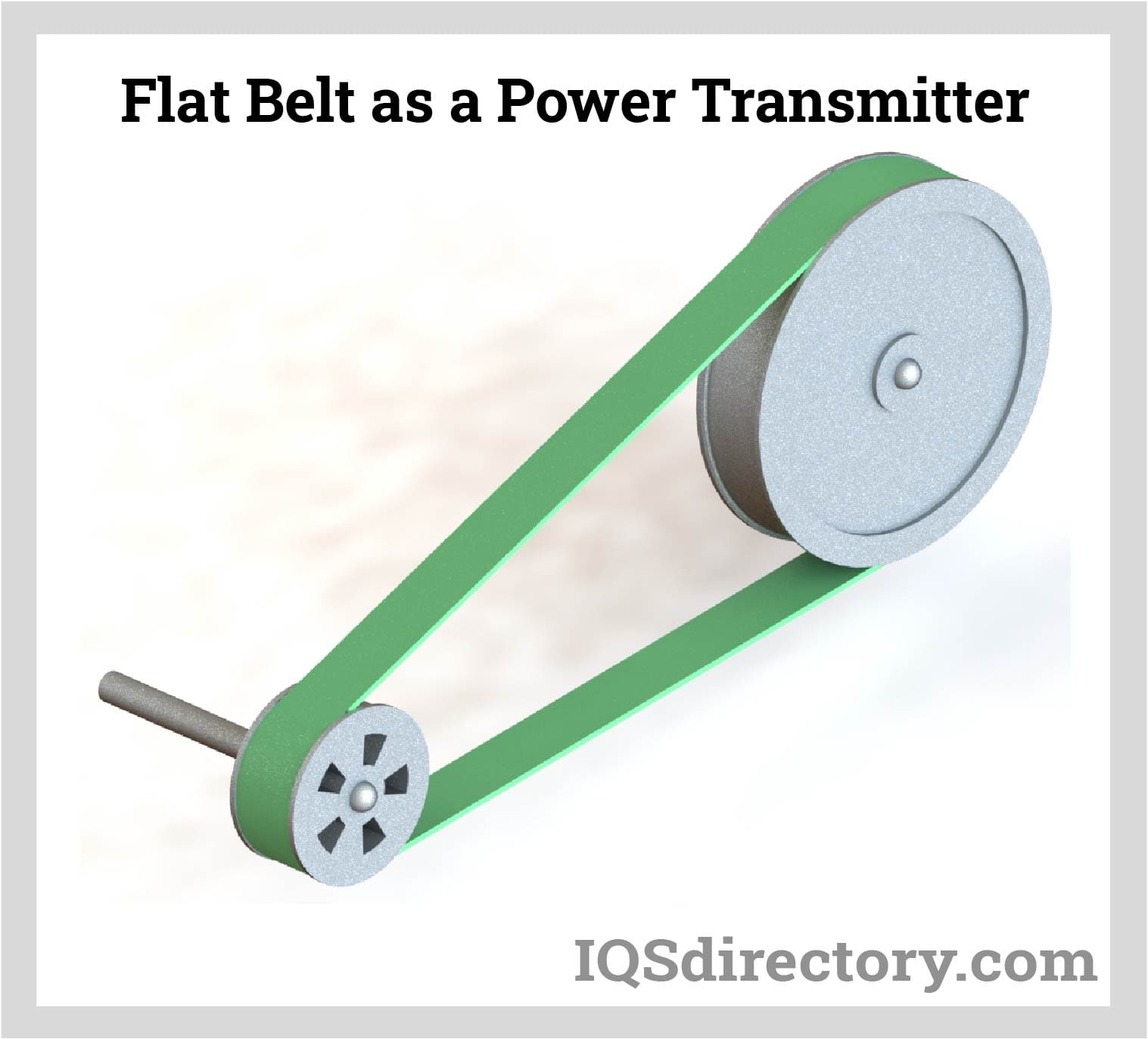
Illustrative image related to flat bel
The Solution: To combat slippage, it’s essential to select flat belts specifically designed for high-speed applications. Buyers should consider belts made from advanced materials such as thermoplastic polyurethane or rubber with enhanced friction properties. Additionally, proper alignment and tensioning of the belt are critical. Investing in tensioning devices or automatic tensioners can help maintain optimal belt tension, reducing the risk of slippage. Regular maintenance checks to ensure proper alignment and wear monitoring will further enhance performance. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customizable solutions can help buyers tailor their flat belt systems to their specific operational needs, maximizing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Scenario 2: Limited Durability of Flat Belts in Harsh Environments
The Problem: Buyers operating in industries exposed to harsh conditions—such as manufacturing environments with high temperatures, oils, or chemicals—often encounter rapid degradation of flat belts. These conditions can lead to frequent replacements, increased operational costs, and unplanned production halts. The challenge lies in finding a belt that not only meets the operational demands but also withstands environmental stresses without compromising performance.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should source flat belts specifically engineered for high resistance to environmental factors. For example, oil-resistant or chemical-resistant flat belts can significantly extend service life in harsh conditions. It’s also beneficial to consult with manufacturers about the specific materials used in the belt construction, such as reinforced rubber or synthetic composites, which can provide superior durability. Buyers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule to inspect and replace belts before they fail, ensuring continuous operation. Utilizing monitoring technology to track belt performance can also help in predicting wear and scheduling timely replacements, thus reducing overall costs and improving operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Selecting the Right Flat Belt for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate flat belt for varied applications within their operations. With a multitude of options available—ranging from general-purpose belts to those designed for specific functions like grip or static conductivity—buyers can feel overwhelmed. This lack of clarity can lead to misapplication, resulting in inefficiencies and increased costs due to improper belt choices.
The Solution: To simplify the selection process, buyers should start by conducting a thorough assessment of their specific operational requirements, including load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive catalogs, including detailed specifications and application guidelines, can aid in making informed decisions. Additionally, utilizing online configurators or CAD tools provided by manufacturers allows buyers to visualize how different belt options will fit within their existing systems. Regular training sessions and knowledge-sharing with suppliers can also empower buyers and their teams to make more strategic selections. This proactive approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a more streamlined procurement process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for flat bel
What Are the Key Materials Used in Flat Belts for B2B Applications?
Flat belts are integral to various mechanical systems, and their material selection plays a critical role in performance and durability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in flat belts, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
How Does Rubber Perform as a Material for Flat Belts?
Rubber is one of the most widely used materials for flat belts due to its excellent elasticity and flexibility. Key properties include a high coefficient of friction, which minimizes slippage, and a temperature rating that typically ranges from -30°C to 80°C. Rubber belts also exhibit good abrasion resistance.
Pros: Rubber belts are durable and can withstand significant wear, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are relatively low in cost, which is advantageous for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: However, rubber can degrade in extreme temperatures and is susceptible to oil and chemical exposure, which may limit its use in certain environments. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can increase with specialized formulations.
Impact on Application: Rubber belts are ideal for general-purpose applications, including conveyor systems in manufacturing and agriculture. However, they may not be suitable for environments involving high temperatures or exposure to oils.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the local climate when selecting rubber belts, as extreme heat can accelerate degradation. Compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial to ensure quality.
What Benefits Do Synthetic Materials Offer for Flat Belts?
Synthetic materials, such as polyurethane and polyester, are increasingly popular due to their superior mechanical properties. These materials can withstand higher temperatures (up to 120°C) and offer excellent chemical resistance.
Pros: Synthetic belts are highly durable, resistant to abrasion, and can handle a variety of media, making them suitable for diverse applications. They also tend to have a longer lifespan compared to rubber belts.
Cons: The primary downside is the higher cost associated with synthetic materials, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
Impact on Application: Synthetic belts are particularly effective in environments where exposure to chemicals or extreme temperatures is common, such as in food processing or automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may prefer synthetic belts due to stringent environmental regulations and standards. Understanding compliance with local manufacturing standards is essential to avoid legal issues.
How Do Oil-Resistant Materials Enhance Flat Belt Performance?
Oil-resistant materials are specifically designed to withstand exposure to oils and chemicals, making them suitable for applications in automotive and industrial machinery. These belts typically feature a unique rubber blend that provides enhanced durability.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
Pros: The primary advantage is their ability to maintain performance in harsh environments, ensuring longevity and reliability. They also help reduce maintenance costs due to their durability.
Cons: The downside is that oil-resistant belts can be more expensive than standard rubber belts. Additionally, they may have limited flexibility compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: These belts are ideal for applications in oil and gas industries or any setting where exposure to lubricants is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Africa, where oil-related industries are prevalent, should prioritize oil-resistant materials to ensure operational efficiency. Compliance with industry standards is vital for safety and performance.
What Role Do Fabric-Reinforced Materials Play in Flat Belts?
Fabric-reinforced materials, often made from polyester or nylon, are used to enhance the tensile strength of flat belts. These materials provide additional support and stability, making them ideal for heavy-load applications.
Pros: The key advantage is their ability to handle high loads and resist deformation. They are also relatively lightweight, which can improve energy efficiency in systems.
Cons: However, fabric-reinforced belts can be more expensive and may require more complex manufacturing processes. They also tend to have lower resistance to chemicals compared to rubber or synthetic options.
Impact on Application: These belts are commonly used in conveyor systems and heavy machinery, where high load-bearing capacity is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Germany and other European countries may favor fabric-reinforced belts due to their compliance with stringent load and safety standards.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
Summary Table of Material Selection for Flat Belts
| Material | Typical Use Case for flat bel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | General-purpose applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to oil and temperature | Low |
| Synthetic | Chemical and temperature-sensitive applications | High durability and chemical resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Oil-Resistant | Oil and gas industry applications | Maintains performance in harsh environments | More expensive and less flexible | Medium |
| Fabric-Reinforced | Heavy-load conveyor systems | High load capacity and lightweight | More expensive and lower chemical resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their flat belt applications. Understanding the properties and considerations of each material will help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for flat bel
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Flat Belts?
The manufacturing of flat belts involves several crucial stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications for performance and durability. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to assess supplier capabilities effectively.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Flat Belt Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Flat belts are commonly made from high-quality rubber or synthetic compounds, which are selected based on the specific application requirements, such as resistance to oils, chemicals, or extreme temperatures.
The materials undergo rigorous testing to verify their properties, including tensile strength, elasticity, and wear resistance. This ensures that the selected materials will perform reliably in demanding environments. Suppliers often source materials from reputable manufacturers to maintain quality standards.
Forming: How Are Flat Belts Shaped and Structured?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This process typically involves cutting the raw materials into specific sizes and shapes, followed by the application of various techniques to create the flat belt structure.
Common techniques include extrusion, where materials are forced through a die to create a continuous flat belt shape, and molding, which allows for the creation of belts with specific profiles. The forming process is critical, as it influences the belt’s performance characteristics, including flexibility and resistance to slippage.
Assembly: What Assembling Techniques Are Used for Flat Belts?
After forming, the assembly stage involves the integration of various components, such as tension members and surface covers. The surface cover can be made from different materials to enhance specific properties, like grip or chemical resistance.
In some cases, the belts are reinforced with fibers or other materials to improve strength and durability. The assembly must be executed with precision to ensure that all components work harmoniously, which directly affects the belt’s operational efficiency.
Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to Flat Belts?
The final stage is finishing, which involves processes like trimming, surface treatment, and quality inspection. Trimming ensures that the belts are cut to the exact lengths required, while surface treatments may include applying coatings to enhance performance attributes such as abrasion resistance.
This stage is vital, as it prepares the belts for their intended applications, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for functionality and quality.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Flat Belt Production?
Quality assurance is a critical component of flat belt manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the various quality control measures in place.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers of flat belts often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. This certification indicates that the manufacturer has implemented effective processes for maintaining quality throughout production.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards may also be relevant. For specialized applications, certifications from organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) may be necessary.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Flat Belt Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that any defects are identified and addressed promptly. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor production processes and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance and adherence to specifications.
Common testing methods include tensile tests, abrasion resistance tests, and elongation tests, which assess the belts’ ability to perform under various conditions.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should implement thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers for flat belts. Here are some actionable steps to verify a supplier’s quality control practices:
What Audit Processes Can Be Employed?
Conducting audits is an effective way to assess a supplier’s quality management system. Buyers can request to observe the manufacturing process, review documentation related to quality control, and evaluate compliance with international standards.
Regular audits can also help establish a long-term relationship with suppliers, ensuring that quality standards are consistently met.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers is crucial. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and reveal any past issues or resolutions.
Buyers should specifically look for evidence of compliance with ISO 9001 and other relevant certifications. Additionally, reviewing third-party inspection reports can provide an objective assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that can impact quality assurance processes. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East may focus on compliance with local standards.
Understanding these regional differences is essential for ensuring that the products meet not only the buyer’s expectations but also any regulatory requirements in their markets.
What Role Do Cultural Factors Play in Quality Control?
Cultural factors can also influence quality control practices. Buyers should be mindful of how cultural attitudes toward quality and manufacturing processes may differ across regions. Establishing clear communication and expectations can help bridge any gaps and foster a collaborative relationship with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
Conclusion
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for flat belts are intricate and require careful consideration from B2B buyers. By understanding the key stages of production, the importance of quality control, and the nuances of international standards, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Prioritizing quality assurance not only ensures product reliability but also enhances the overall efficiency of operations in various industrial applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘flat bel’
Introduction
Sourcing flat belts for industrial applications requires a strategic approach to ensure quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions and secure the best products for your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the right flat belt for your application. Consider factors such as belt width, length, material composition, and intended load capacity. These specifications will guide your search and help you communicate your requirements effectively to suppliers.
Step 2: Research Material Options
Different applications demand various materials for flat belts, such as rubber, polyurethane, or synthetic compounds. Each material offers distinct advantages, including resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations. Evaluate the environmental conditions your belts will face to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies to assess their reliability and industry experience. Consider their manufacturing capabilities and whether they can meet your specific requirements.
- Supplier Certifications: Check for ISO certifications or other industry standards that reflect their commitment to quality.
- Production Capacity: Ensure that the supplier can handle your order volume and timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Obtaining samples of the flat belts you are considering is a critical step in the sourcing process. Testing samples allows you to evaluate their performance under your specific operating conditions. Pay attention to factors such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to wear.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, compare pricing structures and payment terms. Look for volume discounts, shipping costs, and lead times. A transparent pricing strategy is vital for budgeting and ensuring that you receive the best value without compromising quality.
- Negotiation Opportunities: Be prepared to negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
Strong after-sales support is essential for maintaining operational efficiency. Inquire about warranty terms and support services offered by the supplier. A reliable supplier should provide assistance with installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order with Clear Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all agreements are documented clearly. This includes specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. Clear contracts help mitigate risks and establish accountability, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for flat belts, ensuring they select the right products that meet their operational needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for flat bel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Flat Belt Sourcing?
When sourcing flat belts, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: Flat belts are commonly made from rubber or synthetic compounds, with prices varying based on the quality and specifications required. For instance, oil-resistant or high-performance belts may incur higher material costs due to the specialized compounds used.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate significantly depending on the manufacturing region. Regions with higher labor costs may result in increased pricing for flat belts. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who may face varying labor rates across different countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with factory operations, including utilities and facility maintenance. Manufacturers with advanced technologies may have higher overheads, but they might also offer better-quality products.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom designs can be substantial. For buyers requiring specific dimensions or features, these costs should be factored into the overall pricing analysis.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that flat belts meet specified performance standards necessitates rigorous quality checks, which can add to the overall cost. Certifications for quality and compliance may also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and customs duties, play a crucial role in the total cost of ownership. These expenses can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and the chosen Incoterms.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin, which can vary based on competition, demand, and market conditions.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Flat Belt Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of flat belts, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger order volumes often result in discounted pricing. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to take advantage of bulk pricing without incurring excess inventory costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed belts will generally command higher prices due to the additional tooling and engineering required. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential cost benefits of standard products.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials that meet specific certifications can increase costs but also enhance durability and performance. Buyers should evaluate whether the investment in higher-quality belts aligns with their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but they often provide better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is crucial, as they dictate who bears the risk and costs during shipping. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the overall landed cost.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help International Buyers?
International buyers can employ various strategies to ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing flat belts.

Illustrative image related to flat bel
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and transparency about needs and expectations can foster loyalty and favorable negotiations.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all associated costs, including maintenance and operational efficiency, rather than just upfront pricing. This approach can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should remain aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that may impact pricing. Understanding local market dynamics can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Transparent Pricing: Ask suppliers for detailed breakdowns of pricing components. This transparency can help identify areas for potential cost savings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers for flat belts is essential for B2B buyers. By leveraging negotiation strategies and considering the total cost of ownership, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so it’s prudent to keep abreast of current trends and supplier capabilities.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing flat bel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Flat Belts in Power Transmission Solutions
When considering power transmission solutions, flat belts are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate alternative options that may better suit specific operational needs. This analysis compares flat belts with two viable alternatives: V-belts and roller chains, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Flat Bel | V-Belt | Roller Chain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency with minimal slippage | Good efficiency, but prone to slippage under heavy loads | Excellent power transmission, suitable for high torque |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, cost-effective for large applications | Generally lower cost than flat belts | Higher initial costs, but durable over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires proper tensioning | Easy to install but requires proper alignment | More complex installation; requires precise setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic inspection recommended | Moderate maintenance; periodic replacement necessary | High maintenance; lubrication and tension adjustments required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for conveyor systems and general machinery | Best for variable speed drives and light to medium loads | Suitable for heavy machinery and high torque applications |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using V-Belts as an Alternative?
V-belts are a widely used alternative to flat belts, particularly in applications where space constraints exist. They are known for their ability to handle variable loads and their compatibility with a range of drive configurations. The primary advantage of V-belts is their lower cost, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. However, they can experience slippage when under heavy loads, which may reduce their efficiency in demanding environments. Regular maintenance, including tension adjustments and replacements, is also necessary to ensure optimal performance.
How Do Roller Chains Compare to Flat Belts?
Roller chains are another alternative that excels in high-torque applications. They provide robust power transmission and are less prone to slippage, making them ideal for heavy machinery. The durability of roller chains means they can handle harsh conditions, providing a long service life. However, the initial investment is typically higher, and they require more maintenance, including regular lubrication and tension checks. Their installation can be complex, demanding precise alignment to avoid premature wear. This complexity may deter businesses looking for straightforward solutions.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Power Transmission Solution?
When selecting the appropriate power transmission solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including load conditions, installation space, and maintenance capabilities. Flat belts offer versatility and ease of use for general applications, while V-belts provide a cost-effective option for moderate loads. In contrast, roller chains may be the best choice for high-torque scenarios, despite their higher maintenance needs. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for flat bel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Flat Belts?
When selecting flat belts for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Flat belts are typically constructed from materials such as rubber, polyurethane, or polyester. The material grade affects the belt’s flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors like oil and temperature. For instance, oil-resistant belts are essential in environments where exposure to lubricants is common, ensuring the belt maintains its integrity and performance over time.
2. Belt Width and Length
The dimensions of the flat belt, including its width and length, are critical for compatibility with specific pulleys and machinery. Choosing the correct size helps prevent slippage and ensures efficient power transmission. In B2B contexts, providing precise dimensions during ordering can minimize delays and reduce the risk of costly mistakes.
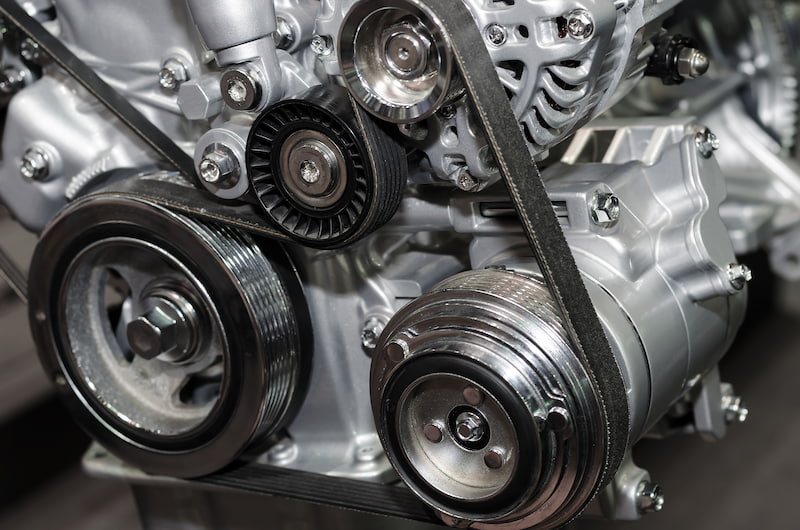
Illustrative image related to flat bel
3. Tensile Strength
This property measures the maximum load the belt can bear before failure. High tensile strength is vital for applications involving heavy loads and high-speed operations. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers select belts that will withstand operational stresses, thus reducing maintenance costs and extending equipment life.
4. Operating Temperature Range
Flat belts often operate under various temperature conditions. The ability to function effectively within a specified temperature range is vital for maintaining performance. For instance, belts that can withstand extreme temperatures are necessary in industries like automotive and aerospace, where operational environments can vary significantly.
5. Static Conductivity
In specific applications, especially in environments with flammable materials, static conductivity is an important property. This feature helps prevent the buildup of static electricity that could lead to sparks or explosions. Buyers should consider this property to enhance safety and compliance with industry regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Flat Belts?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of flat belts, buyers often seek OEM suppliers to ensure compatibility and quality. Identifying an OEM can lead to better pricing and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. In industries where flat belts are used, knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases more effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the flat belt industry, submitting an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers and negotiate better deals. This process is vital for strategic sourcing and cost control.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for navigating shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities. For flat belt buyers, familiarity with Incoterms can mitigate risks associated with international logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In the flat belt industry, shorter lead times can improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Buyers should inquire about lead times when sourcing to ensure timely delivery.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs associated with flat belts.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the flat bel Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the Flat Belt Sector?
The flat belt sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Key global drivers include the push for automation in manufacturing processes and the increasing need for energy-efficient machinery. Industries such as automotive, food processing, and logistics are particularly focused on enhancing operational efficiency, which has led to a surge in demand for high-performance flat belts. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has necessitated efficient material handling solutions, further propelling the growth of flat belt applications in conveyor systems.
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping sourcing practices in this sector. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enabling real-time monitoring of belt performance and predictive maintenance. This shift allows buyers to source more reliable products that enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Moreover, digital platforms are streamlining the procurement process, making it easier for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Brazil and Germany) to access a wider range of flat belt options. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer customizable solutions, enabling them to meet specific operational requirements.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Flat Belt Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the flat belt sector, with increasing awareness of environmental impacts prompting companies to adopt greener practices. The production of flat belts traditionally involves materials that may not be environmentally friendly, leading to a growing demand for sustainable alternatives. Manufacturers are now exploring biodegradable and recyclable materials, such as thermoplastic polyurethane, which can reduce the carbon footprint of products.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing practices, including fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and products made from recycled materials are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to conscientious buyers. This trend not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty among environmentally aware consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Flat Belts and Their Relevance Today?
The flat belt has a rich history dating back to the early industrial era, initially used in water-powered mills and later in steam engines. Their design has evolved significantly, transitioning from simple leather and fabric constructions to advanced synthetic materials that offer superior durability and efficiency. Today, flat belts are integral components in various applications, from conveyor systems to high-speed machinery, reflecting their adaptability to modern technological advancements.
As industries continue to prioritize automation and efficiency, flat belts remain a crucial element in achieving these goals. Their evolution from basic mechanical components to sophisticated, high-performance systems underscores their ongoing relevance in contemporary manufacturing and logistics sectors. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution provides valuable insights into selecting the right products that align with both current market demands and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of flat bel
1. How do I solve slippage issues with flat belts in my machinery?
Slippage in flat belts can often be remedied by ensuring proper tensioning of the belt. Check the alignment of pulleys, as misalignment can cause uneven wear and slippage. Additionally, consider using belts with higher friction materials or surface textures designed to enhance grip. Regular maintenance and inspection of the belts for wear and tear are also essential to prevent slippage and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
2. What is the best flat belt material for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, flat belts made from materials like silicone or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) are ideal. These materials can withstand elevated temperatures without degrading, ensuring efficient power transmission. When selecting a belt, ensure it is rated for the specific temperature range of your application to avoid premature failure and maintain operational efficiency.
3. How do I choose the right flat belt for my conveyor system?
Selecting the right flat belt for your conveyor system involves assessing the load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions. Look for belts specifically designed for conveyor applications, considering factors such as oil resistance, chemical exposure, and temperature tolerance. Additionally, evaluate the surface texture for grip and slippage reduction, ensuring compatibility with your pulleys and overall system design.
4. What customization options are available for flat belts?
Many suppliers offer customization options for flat belts, including specific lengths, widths, and materials tailored to your application needs. You can also request specialized surface textures, colors, or additional features like oil resistance or static conductivity. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications to ensure the final product meets your operational requirements effectively.
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for flat belts from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for flat belts can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the type of belt and the materials used. Generally, MOQs can range from a few meters for standard belts to larger quantities for custom orders. It is advisable to communicate your needs directly with suppliers to understand their specific MOQ policies and negotiate terms that suit your procurement strategy.
6. How can I vet suppliers for flat belts in international markets?
To vet suppliers for flat belts in international markets, start by researching their reputation and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards, such as ISO or other relevant quality certifications. Additionally, request samples to assess product quality and reliability. Establishing communication channels and understanding their logistics capabilities will also help ensure they can meet your supply chain needs.
7. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing flat belts internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of flat belts can vary widely based on the supplier and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payments, or letters of credit. It is essential to discuss and agree upon terms that provide security for both parties, considering factors like order size and supplier reputation. Always ensure that payment methods comply with international trade regulations.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing flat belts?
When importing flat belts, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping to ensure timely delivery. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply, and ensure that all documentation is complete to avoid delays at customs. Planning for potential delays in the supply chain is also advisable, especially in regions with less predictable logistics infrastructure.
Top 2 Flat Bel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Weinig USA – 30-Day Returns
Domain: tooling.weinigusa.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Weinig USA – 30-Day Returns, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Optibelt – ALPHA LINEAR/V Polyurethane Belts
Domain: optibelt.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Optibelt ALPHA LINEAR/V Polyurethane flat belts; endlessly weldable; cleats can be applied; sections available: F2, F2.5, F3, FL3, F4.5; roll lengths: 50 m or 100 m (over 100 m on request); minimum welding length: 700mm – 900mm (width dependent).
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for flat bel
In the competitive landscape of industrial operations, strategic sourcing of flat belts is not just a procurement decision but a crucial factor in optimizing performance and enhancing productivity. By prioritizing high-quality materials and suppliers, businesses can ensure that their flat belts provide reliable power transmission, minimize slippage, and withstand harsh operational environments. This focus on quality translates to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extended equipment lifespan, ultimately driving profitability.
International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider the diverse applications and innovative solutions offered by manufacturers worldwide. Engaging with reputable suppliers can yield significant advantages, from customized solutions to rapid delivery times that meet market demands.
Looking ahead, the flat belt market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in materials and technology. As industries evolve, so too should your sourcing strategies. We encourage B2B buyers to leverage this momentum by exploring new partnerships and investing in cutting-edge solutions that align with their operational needs. Embrace the future of power transmission with confidence, and elevate your business’s performance through strategic sourcing today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.