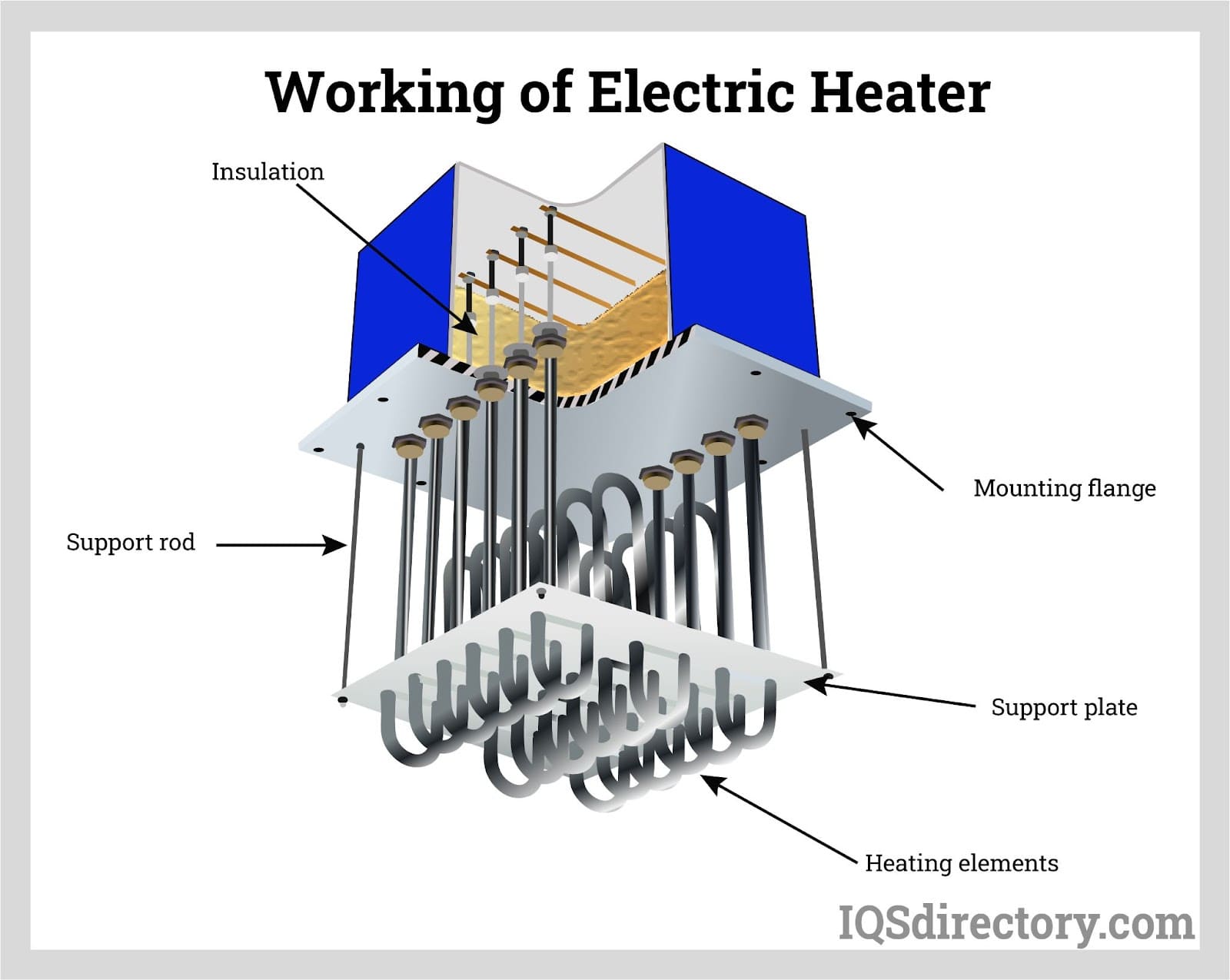
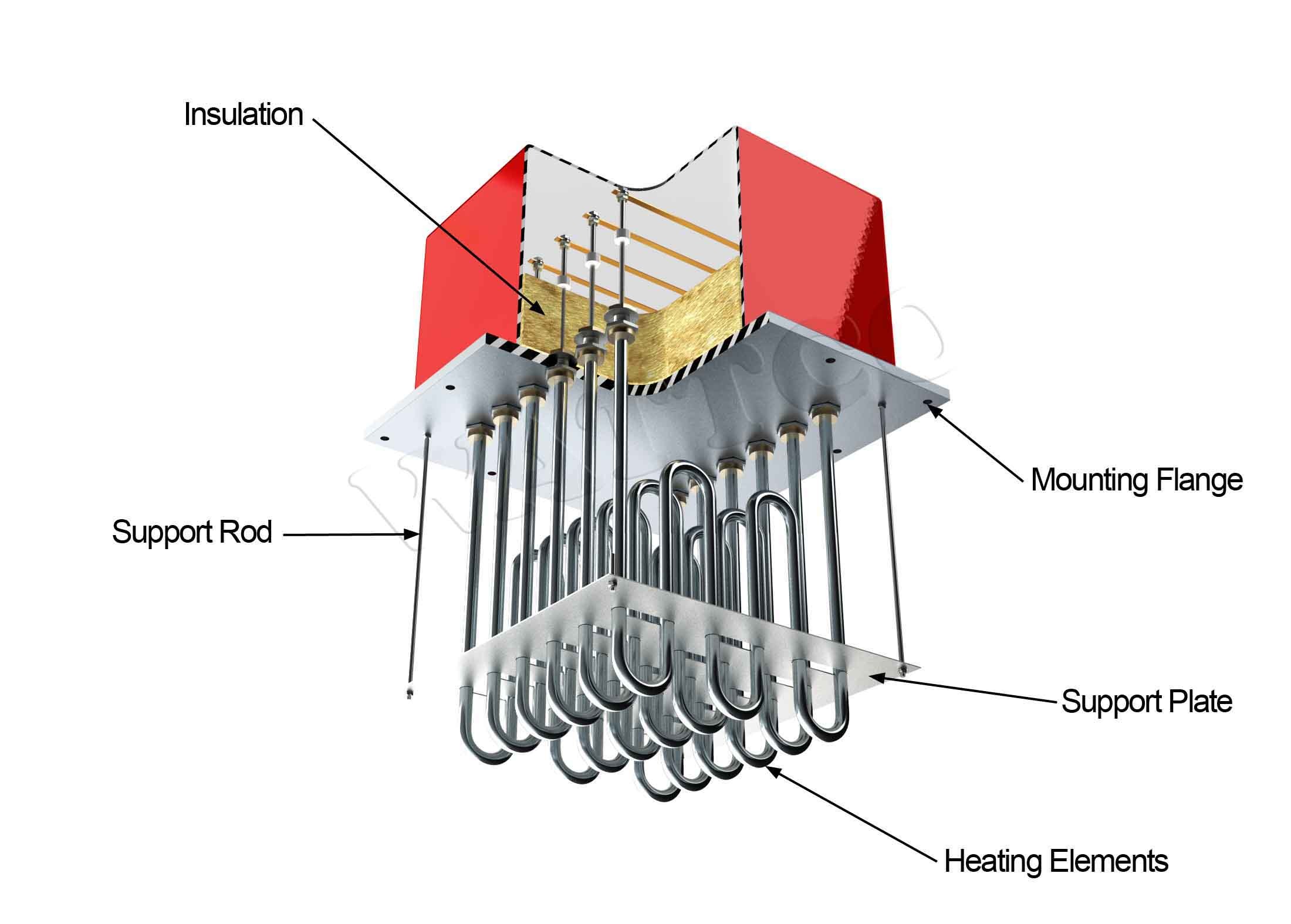
Top 2 Components Of A Heater Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for components of a heater
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right components of a heater can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in rapidly developing markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The need for reliable and efficient heating solutions is critical, whether for industrial applications, residential comfort, or specialized machinery. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of heater components, including band heaters, cartridge heaters, and immersion heaters, each tailored for specific applications and environments.
Navigating the complexities of supplier vetting, understanding cost implications, and assessing quality standards are crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. By offering insights into the latest technologies and materials, this guide empowers buyers to evaluate options effectively, ensuring they select components that meet their operational needs while optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
As you explore the intricacies of heater components, you will gain valuable knowledge about their applications, the importance of compatibility with existing systems, and the nuances of different heating technologies. Armed with this information, B2B buyers can confidently engage with suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency and product offerings. Whether you’re in Nigeria, Vietnam, or elsewhere, this guide is your strategic resource for mastering the global market for heater components.
Understanding components of a heater Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band Heaters | Clamps onto objects; delivers external heat via conduction | Plastics processing, packaging | Pros: Versatile, precise heating. Cons: Limited to surface applications. |
| Cartridge Heaters | Tubular design; provides internal heating through insertion | Manufacturing machinery, molds | Pros: Focused heating, compact design. Cons: Requires precise installation. |
| Immersion Heaters | Directly inserted into liquids; efficient and quick heating | Chemical processing, food industry | Pros: Rapid heating, versatile for various liquids. Cons: Maintenance can be challenging. |
| Ceramic Heaters | Uses PTC ceramic elements; high electrical resistance | HVAC systems, medical devices | Pros: Energy-efficient, stable performance. Cons: Higher upfront costs. |
| Flexible Heaters | Adaptable to surfaces; made from flexible materials | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Pros: Customizable shapes, lightweight. Cons: Durability can vary by material. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Band Heaters?
Band heaters are designed to clamp around cylindrical objects, providing external heat through both radiant and conductive methods. They are particularly useful in applications requiring precise temperature control, such as in plastics processing and packaging. When considering a band heater, B2B buyers should evaluate the material compatibility, watt density, and mounting options to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications.
How Do Cartridge Heaters Function and Where Are They Used?
Cartridge heaters feature a cylindrical design that allows them to be inserted directly into the item being heated. This configuration delivers focused and efficient heat, making them ideal for manufacturing machinery and molds. Buyers should consider factors such as the heater’s watt density, temperature range, and material compatibility to ensure it meets the operational requirements of their processes.
What Makes Immersion Heaters a Popular Choice in Various Industries?
Immersion heaters are inserted directly into liquids, providing a quick and efficient solution for heating. They are widely used in industries like chemical processing and food production due to their ability to heat large volumes rapidly. When purchasing immersion heaters, buyers should assess the heater’s power requirements, compatibility with different liquids, and maintenance needs to ensure long-term reliability.
Why Should B2B Buyers Consider Ceramic Heaters?
Ceramic heaters utilize a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic element, which allows for energy-efficient heating with stable performance. They are commonly found in HVAC systems and medical devices. B2B buyers should weigh the initial costs against the long-term energy savings and reliability, particularly in applications requiring consistent temperature management.

Illustrative image related to components of a heater
What Are the Advantages of Flexible Heaters in Diverse Applications?
Flexible heaters are designed to conform to various shapes, making them suitable for applications in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. They are made from materials such as polyimide film and silicone rubber, providing adaptability in heating solutions. Buyers should focus on the heater’s durability, material properties, and customization options to ensure they meet the specific needs of their applications.
Key Industrial Applications of components of a heater
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of components of a heater | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Immersion heaters for pasteurization processes | Ensures consistent heating, improving safety and quality | Compliance with food safety standards, energy efficiency |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Cartridge heaters for engine component testing | Provides precise temperature control, enhancing testing accuracy | Material compatibility, thermal stability, and power requirements |
| Chemical Processing | Band heaters for heating pipes and tanks | Reduces the risk of product solidification, ensuring process continuity | Operating temperature range, corrosion resistance |
| Medical Equipment | Flexible heaters for medical diagnostic devices | Enables precise temperature management for sensitive applications | Regulatory compliance, reliability, and performance metrics |
| Electronics and Semiconductor | Thick film heaters in circuit board assembly | Enhances manufacturing efficiency and product reliability | Thermal characteristics, substrate compatibility, and cost-effectiveness |
How Are Immersion Heaters Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, immersion heaters are crucial for pasteurization processes. By directly heating liquids in tanks, these heaters ensure uniform temperature distribution, which is vital for food safety and quality. International buyers must consider compliance with local food safety regulations, energy efficiency, and the heater’s material compatibility with various food substances to avoid contamination.
What Role Do Cartridge Heaters Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Cartridge heaters are widely utilized in the automotive industry for testing engine components. They provide precise and consistent heating, which is essential for accurate testing results. Buyers in this sector should focus on the heater’s thermal stability, power requirements, and compatibility with various materials to ensure optimal performance and safety during testing.
How Are Band Heaters Beneficial in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, band heaters are employed to maintain the temperature of pipes and tanks, preventing the solidification of materials. This application is critical for ensuring continuous operations and minimizing downtime. Buyers should prioritize the heater’s operating temperature range and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh chemical environments, to ensure long-term reliability.
Why Are Flexible Heaters Important for Medical Equipment?
Flexible heaters are integral to medical diagnostic devices, where precise temperature control is essential. These heaters can conform to various shapes, enabling effective heating of sensitive components. For international buyers, it is vital to ensure regulatory compliance, reliability, and performance metrics are met, particularly in applications involving human health and safety.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
How Do Thick Film Heaters Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
Thick film heaters are increasingly used in the electronics and semiconductor industry, particularly in circuit board assembly. They provide uniform heating, enhancing the efficiency of manufacturing processes and improving product reliability. Buyers should consider thermal characteristics, substrate compatibility, and cost-effectiveness when sourcing these heaters to optimize their production lines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘components of a heater’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Heating Element for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to identify the appropriate heating element for their specific applications. With various types of heaters available—like cartridge heaters, immersion heaters, and flexible heaters—each offers unique advantages and limitations. For instance, a manufacturing plant may require precise heating for a specialized process but lacks clarity on which heating component aligns best with their operational requirements. This uncertainty can lead to inefficient heating solutions, increased costs, and potential downtime, severely affecting production schedules.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their heating requirements. This includes analyzing the thermal and electrical specifications of the heating application, such as the desired temperature range, the nature of the materials being heated, and the physical constraints of the installation area. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customizable heating solutions can also provide insights into the best options. For example, if the application requires compact heating, a cartridge heater might be ideal due to its ability to deliver focused heat in confined spaces. Furthermore, engaging with manufacturers that offer testing services can help validate the selected heating element’s performance before full-scale implementation.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs Associated with Inefficient Heating Systems
The Problem: Energy efficiency is a top concern for many B2B buyers, especially in regions where energy costs are high. Inefficient heating systems can lead to excessive energy consumption, resulting in inflated operational costs. Buyers may face challenges in optimizing their existing heating components, such as outdated heaters or poorly designed systems, leading to significant financial strain over time. This issue is particularly prevalent in industries that rely heavily on continuous heating, such as food processing or chemical manufacturing.

Illustrative image related to components of a heater
The Solution: To mitigate energy costs, businesses should consider upgrading to more efficient heating components. Investing in modern technologies, such as ceramic heaters or infrared heating systems, can significantly enhance energy efficiency. These systems typically consume less energy while providing effective heating solutions. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule for existing heating components can improve their efficiency and lifespan. Conducting energy audits can also help identify inefficiencies in the heating process, allowing companies to make informed decisions about necessary upgrades or replacements.
Scenario 3: Integration Challenges with Existing Systems
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the difficulty in integrating new heating components with existing systems. As industries evolve, companies often find themselves needing to upgrade or replace heating elements without disrupting their operational flow. However, compatibility issues can arise, leading to project delays and unexpected costs. This challenge is particularly evident in sectors that employ complex machinery where heating components must align perfectly with existing setups.
The Solution: To ensure seamless integration, buyers should prioritize sourcing components from manufacturers that specialize in customized solutions. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive technical support can also facilitate smoother integration processes. Before making a purchase, conducting compatibility assessments and requesting detailed technical documentation from manufacturers can help identify potential issues early on. Additionally, involving engineering teams in the selection process can ensure that the new heating components meet operational standards and fit within the existing system framework. By taking these proactive steps, businesses can minimize downtime and maintain productivity during the transition phase.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for components of a heater
When selecting materials for heater components, it’s crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This analysis will focus on four common materials used in heater components: stainless steel, aluminum, ceramic, and silicone rubber. Each material has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications, particularly in diverse international markets.
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Heater Components?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it a preferred choice for various heater components, such as housings and heating elements. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) and can handle significant pressure, which is essential for applications involving steam or high-pressure liquids.
Pros and Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, offering a long service life even in harsh environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process may involve complex machining, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and various chemicals, making it versatile for different heater applications.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can be harsh, selecting the right grade of stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316) is critical.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for Heater Components?
Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for components like heat sinks and housings. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and is resistant to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, allowing for intricate designs and rapid production. However, it has a lower melting point than stainless steel, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications.

Illustrative image related to components of a heater
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal conductivity makes it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. However, it may not be compatible with highly corrosive media without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards regarding aluminum alloys, particularly in regions with varying environmental conditions. Compliance with JIS standards may also be necessary for buyers in Japan and neighboring countries.
What Advantages Do Ceramics Offer for Heater Components?
Ceramics, particularly advanced ceramics, are used in applications requiring high thermal resistance and electrical insulation, such as insulators and substrates for thick film heaters. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 2,000°F (1,093°C) and are chemically inert, making them ideal for corrosive environments.
Pros and Cons: The high-temperature tolerance and insulation properties are significant advantages. However, ceramics are brittle, which can pose challenges during manufacturing and installation, potentially leading to breakage.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly suited for high-temperature applications where electrical insulation is critical, such as in semiconductor manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the ceramic materials meet relevant international standards for thermal and mechanical properties, particularly in industries such as aerospace and electronics.
How Does Silicone Rubber Contribute to Heater Component Design?
Silicone rubber is flexible and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -60°F to 500°F (-51°C to 260°C). It is often used in flexible heaters and as insulation materials due to its excellent electrical properties and thermal stability.
Pros and Cons: The flexibility and ease of installation are major advantages, allowing for custom shapes and applications. However, silicone rubber may not be suitable for high-temperature applications beyond its thermal limits and can be more expensive than traditional rubber materials.
Impact on Application: Silicone rubber is ideal for applications requiring conformability and flexibility, such as in automotive and medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards for silicone materials, especially in medical applications where biocompatibility is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heater Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for components of a heater | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Heating elements, housings | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Heat sinks, housings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower melting point limits use | Medium |
| Ceramic | Insulators, substrates for thick film heaters | High thermal resistance and insulation | Brittle, potential breakage | High |
| Silicone Rubber | Flexible heaters, insulation materials | Flexibility and ease of installation | Limited high-temperature use | Medium |
This guide should assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding material selection for heater components, taking into account specific applications and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for components of a heater
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heater Components?
The manufacturing of heater components is a complex process that involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Heater Components?
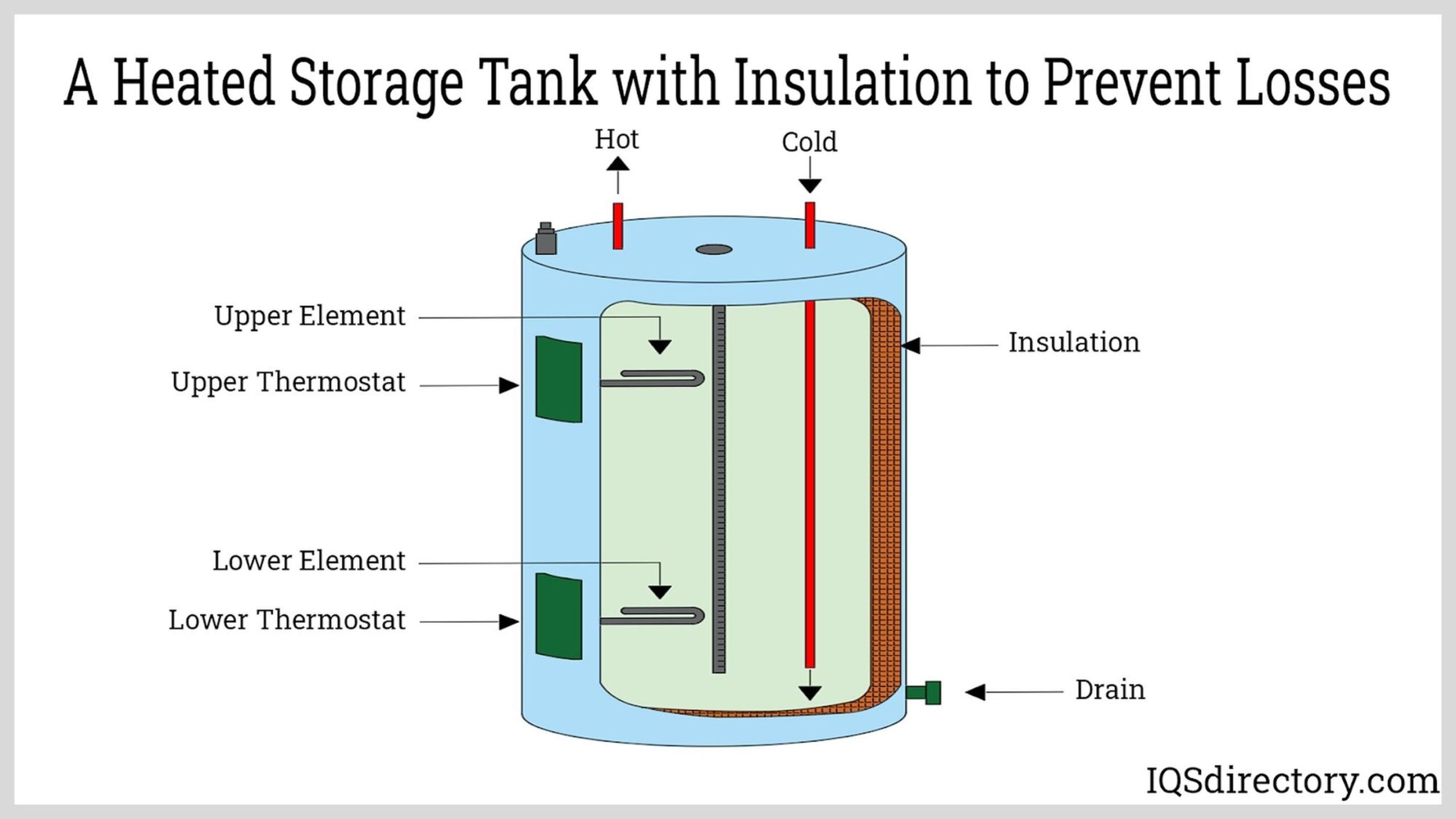
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing process. This stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials suited for the specific type of heater component being produced. For instance, band heaters may require metal alloys with excellent thermal conductivity, while ceramic heaters utilize specialized ceramics with high electrical resistance.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
Once the materials are selected, they undergo various treatments, such as cleaning and drying, to remove impurities that could affect performance. Advanced techniques like material characterization may also be employed to analyze the physical and chemical properties of the materials, ensuring they meet industry standards and specifications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Heater Components?
Forming techniques vary depending on the type of heater component being manufactured. Common methods include:
- Casting: Used for creating complex shapes, particularly in metal components. Liquid metal is poured into a mold to form the desired shape.
- Machining: Involves cutting and shaping materials using tools and machines to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances.
- Printing: For thick film heaters, resistive inks are printed onto substrates using screen printing or inkjet techniques. This allows for high precision and flexibility in design.
Each technique must be optimized based on the component’s requirements, including thermal performance and mechanical strength.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Heater Components?
Assembly is a critical phase that requires meticulous attention to detail. Components are brought together to create the final heater assembly. For example, in cartridge heaters, the resistive elements are inserted into their respective casings, followed by the installation of electrical connections.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
During this phase, manufacturers often employ automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. However, manual assembly is still common for more intricate components, allowing for better quality control.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Heater Components?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of heater components. Techniques such as coating, painting, or anodizing are applied to protect against corrosion and improve thermal efficiency.
Quality assurance measures, such as visual inspections and surface testing, are implemented to ensure that the finishing meets the required standards. Additionally, manufacturers may conduct aging tests to simulate long-term use and assess performance over time.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Heater Components?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that heater components meet international standards and customer expectations. The QC process typically includes several checkpoints and testing methods.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
B2B buyers should be aware of several international standards relevant to the manufacturing of heater components. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures consistent quality across products and services. Other industry-specific standards, such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for oil and gas applications, may also apply.
Compliance with these standards not only ensures product quality but also builds trust with international clients.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials before they enter production. This step is critical for ensuring that only high-quality materials are used.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing to monitor processes and detect deviations from standards. This includes measuring dimensions, inspecting assembly quality, and verifying adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure they meet the required performance and safety standards. This often includes electrical testing, thermal performance assessments, and visual inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Heater Components?
Testing methods for heater components vary based on their application and specifications. Common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that components can handle the required voltage and current without failure.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses the heating efficiency and temperature distribution of the components.
- Durability Testing: Simulates real-world conditions to evaluate the longevity and reliability of the components under different operating environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial to ensuring product reliability. Here are effective ways to conduct due diligence:
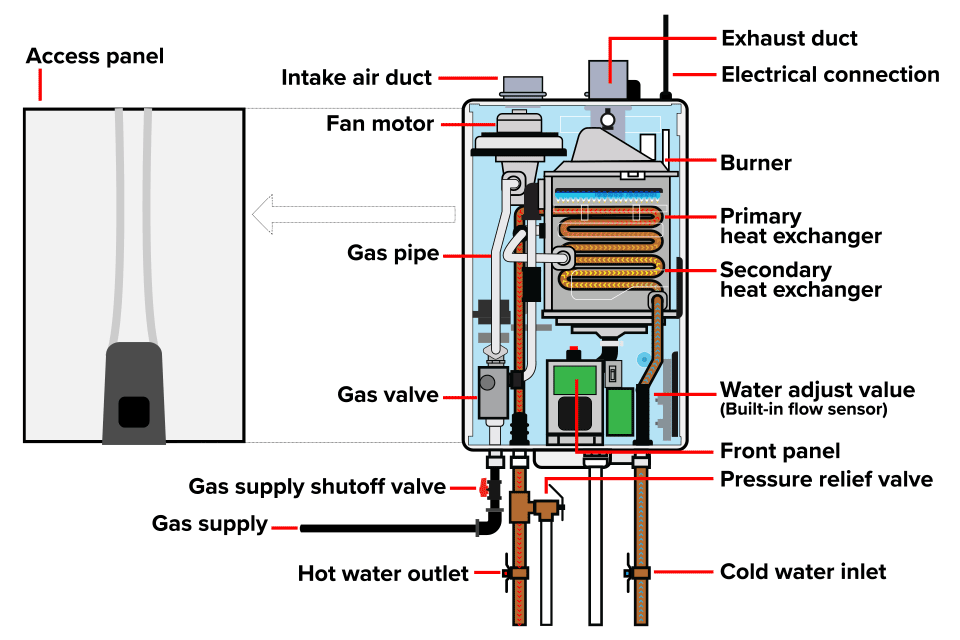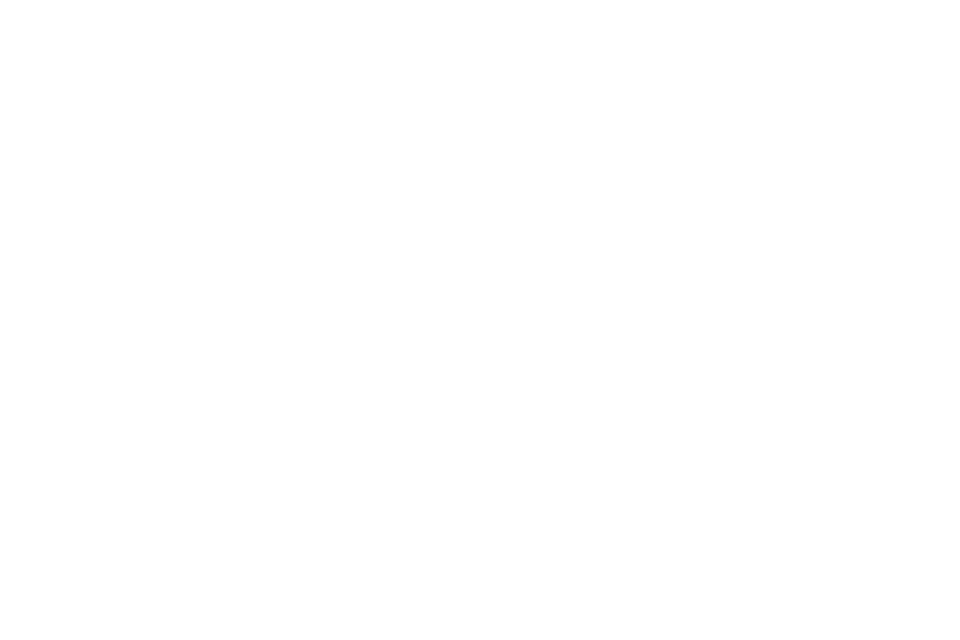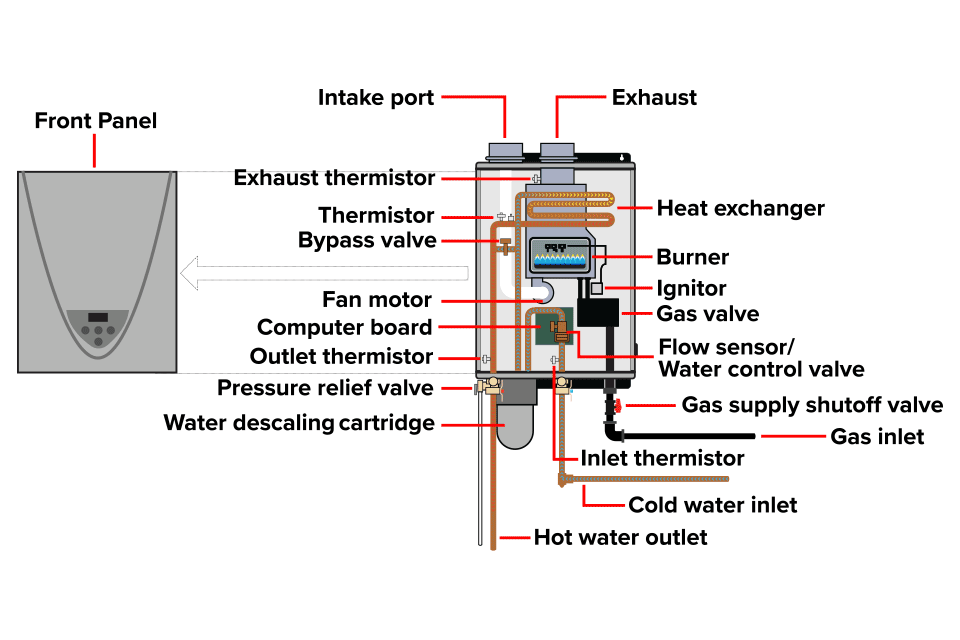
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
What Steps Can Be Taken for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems. Buyers should request audits to ensure compliance with industry standards and evaluate the supplier’s commitment to quality. This can include reviewing documentation, observing manufacturing processes, and assessing QC practices firsthand.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Quality reports and certifications provide valuable insights into a supplier’s performance. Buyers should request copies of quality management system certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and specific product certifications (e.g., CE, API). These documents serve as proof of the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and regulatory requirements.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities conduct thorough evaluations of manufacturing processes and finished products, providing unbiased assessments. B2B buyers can rely on third-party reports to make informed purchasing decisions and mitigate risks associated with product quality.
How Do QC and Certification Nuances Affect International Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is particularly important for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Variations in regulatory requirements and standards can impact product acceptance in different markets.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific certifications required in their target markets and ensure that their suppliers are compliant. This proactive approach will streamline import processes and enhance product acceptance, ultimately contributing to successful international trade relationships.
By prioritizing quality assurance and understanding the manufacturing processes involved, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers for heater components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘components of a heater’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring components of heaters effectively. By following these actionable steps, buyers can ensure they select high-quality components that meet their specific requirements, whether for industrial applications or consumer products. Understanding the nuances of heater components will lead to better decision-making and long-term supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before approaching suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of heater components needed, such as band heaters, cartridge heaters, or flexible heaters. Specify material compatibility, power ratings, and thermal requirements to ensure that the components will function optimally in your intended application.
- Power and Watt Density: Determine the necessary watt density to meet your heating needs.
- Material Selection: Consider the environmental conditions the components will face, such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to chemicals.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on suppliers who specialize in heater components. Focus on their industry reputation, product range, and experience in your specific sector. A reliable supplier will not only provide quality products but also offer valuable insights into the latest technologies and trends.
- Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry.
- Product Diversity: Evaluate whether they offer a wide range of components to meet various needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, verify the certifications and quality standards of your potential suppliers. Certifications such as ISO, CE, or UL can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety, which is crucial for ensuring that the components meet international standards.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the components meet relevant regulations for your target markets, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures during manufacturing.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Always request samples of the components you intend to purchase. Testing these samples under real operational conditions will help you assess their performance and reliability. This step is essential for identifying any potential issues before committing to a larger order.
- Performance Evaluation: Conduct tests to evaluate heating efficiency, durability, and compatibility with your systems.
- Feedback Loop: Use the testing phase to provide feedback to the supplier, ensuring they can address any concerns.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you are satisfied with the samples and the supplier’s capabilities, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Clear communication at this stage will help set expectations and build a strong partnership.
- Volume Discounts: Discuss pricing strategies based on order quantities to secure better rates.
- Delivery Timelines: Clarify lead times for production and shipping to ensure timely delivery.
Step 6: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After the initial procurement, focus on building a long-term relationship with your suppliers. Regular communication and feedback can foster collaboration, leading to improved product offerings and services over time.
- Performance Reviews: Schedule periodic evaluations to discuss product quality and service.
- Innovation Collaboration: Work together on new developments or improvements to enhance your heating solutions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for heater components, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for components of a heater Sourcing
When sourcing components for heaters, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis focuses on the cost components involved, the factors influencing pricing, and practical tips for buyers looking to maximize value while minimizing expenses.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heater Component Sourcing?
The cost structure of heater components can be broken down into several key areas:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. For instance, high-quality ceramics or metals used in band and cartridge heaters tend to be more expensive than lower-grade alternatives. Prices fluctuate based on market demand and availability of raw materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Skilled labor may command higher wages, but can also lead to better product quality and efficiency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help lower these costs, benefiting the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for customized components. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating the feasibility of custom designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO or specific industry standards can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the supplier, shipping methods, and the chosen Incoterms. Efficient logistics management can mitigate some of these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can be influenced by competition and market demand.
How Do Volume and Customization Influence Heater Component Pricing?
Pricing is often contingent upon order volume and product specifications. High-volume orders generally yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, custom components tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs due to the need for specialized materials, tooling, and labor.
Buyers should carefully assess their needs to negotiate better terms. For example, committing to larger orders can lead to significant discounts, while customization requests should be clearly defined to avoid unexpected costs.
What Factors Should Buyers Consider When Sourcing Heater Components?
Several critical factors influence pricing and sourcing decisions:
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with higher quality and relevant certifications may come at a premium but can offer better performance and reliability in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, flexible payment terms, and priority service. Researching supplier reputations and capabilities is essential.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and responsibilities. Different terms can affect pricing and logistics, especially for international transactions.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
To achieve cost-efficiency, buyers should adopt a proactive negotiation approach:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with a component, including maintenance, energy efficiency, and replacement frequency, rather than just the initial purchase price.
-
Leverage Market Research: Use market insights to inform negotiations, particularly regarding material costs and competitor pricing.
-
Build Strong Relationships: Foster partnerships with suppliers to create a collaborative environment that can lead to better pricing and service flexibility.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be cognizant of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can significantly impact costs. Consider negotiating prices in a stable currency to mitigate risks.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Be aware of potential tariffs and taxes that can add to the final cost of components.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and negotiation styles can enhance communication and lead to favorable outcomes.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influences, and negotiation strategies is essential for B2B buyers sourcing heater components. By considering these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing components of a heater With Other Solutions
When evaluating the components of a heater, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives that achieve similar heating goals. These alternatives can provide different benefits and drawbacks, influencing the decision-making process based on specific application needs, costs, and operational environments.
| Comparison Aspect | Components Of A Heater | Alternative 1: Heat Pumps | Alternative 2: Steam Heating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly efficient for localized heating; precise control over temperature. | Can provide both heating and cooling; efficiency can vary based on climate. | Effective for large-scale heating; provides consistent temperature. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; energy-efficient leading to lower operational costs. | Higher upfront costs but lower operating costs over time; often eligible for incentives. | Lower initial costs; ongoing costs can be high due to fuel prices. |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward installation; requires electrical connections. | Installation can be complex; may need ductwork or space for outdoor units. | Installation can be straightforward; requires boiler setup and piping. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional checks needed for electrical components. | Requires regular servicing; potential for refrigerant leaks. | Regular maintenance needed for boilers and safety checks for steam systems. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for localized heating in industrial applications. | Best for residential and commercial spaces needing both heating and cooling. | Suitable for large facilities like factories or hospitals needing consistent heating. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Pumps as an Alternative to Heater Components?
Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide heating in winter and cooling in summer. They work by transferring heat rather than generating it, making them highly energy-efficient. However, their performance can significantly decline in extremely cold temperatures, which may limit their effectiveness in some regions. The initial installation costs are typically higher than traditional heating systems, but the long-term savings on energy bills can offset this investment. Additionally, some regions offer incentives for heat pump installations, enhancing their economic viability.
How Does Steam Heating Compare to Traditional Heater Components?
Steam heating systems utilize steam to transfer heat through pipes, providing consistent and effective heating, especially in larger buildings. The initial installation costs are relatively low, but the ongoing operational costs can be significant, particularly if fossil fuels are used to generate steam. Maintenance requirements are higher than those for electric heaters, as boilers need regular servicing, and safety checks are essential to prevent leaks and ensure efficiency. Steam heating is particularly advantageous in industrial settings where large volumes of heat are necessary, but may not be as adaptable for residential applications.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Select the Most Suitable Heating Solution?
Choosing the right heating solution requires a careful assessment of specific operational needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. While components of a heater provide efficient and localized heating, alternatives like heat pumps and steam heating offer unique benefits that may align better with certain applications. B2B buyers should consider factors such as performance requirements, cost implications, ease of implementation, and maintenance demands when making their decision. By aligning their choice with operational goals and environmental considerations, buyers can ensure they invest in the most effective heating solution for their business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for components of a heater
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heater Components?
Understanding the essential technical properties of heater components is critical for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and longevity in their applications. Here are some key specifications:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in heater components, such as metals, ceramics, or polymers. The choice of material affects heat conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion. For instance, stainless steel is commonly used for its strength and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for harsh environments. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the heater performs optimally in specific applications, ultimately affecting long-term operational costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a component’s dimensions. In heater components, maintaining tight tolerances is crucial for ensuring proper fit and function. For example, a cartridge heater must be precisely sized to fit snugly in its designated hole to ensure efficient heat transfer. Poor tolerances can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy consumption, or even equipment failure, making this a vital specification for B2B buyers to consider. -
Watt Density
Watt density is the amount of power (in watts) applied per unit area of the heating element. It is a crucial factor in determining how quickly and effectively a heater can raise the temperature of a material. High watt density can lead to faster heating but may also increase the risk of overheating. Understanding watt density helps buyers select heaters that meet their specific heating requirements while maintaining safety standards. -
Operating Temperature Range
This property defines the range of temperatures in which a heater can operate safely and effectively. It is critical for ensuring that the heater will perform within the environmental conditions of its application. For example, a heater designed for high-temperature applications must utilize materials that can withstand significant thermal stress. Selecting the appropriate operating temperature range helps avoid premature failure and enhances the heater’s lifespan. -
Power Supply Requirements
Power supply requirements specify the voltage and current needed for the heater to function correctly. Different regions may have varying electrical standards, so understanding these requirements is crucial for international buyers. Ensuring compatibility with local power supply standards helps avoid operational issues and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Heater Component Industry?
Familiarity with trade terminology can streamline communication and negotiations between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the heater industry, OEMs often manufacture heating elements or components that are integrated into larger systems. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking for reliable sources of high-quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory costs and purchasing decisions. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their needs without incurring excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For heater components, an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, specifications, and lead times, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. These terms govern shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations, making them essential for buyers sourcing heater components globally. Understanding Incoterms helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures compliance with international trade regulations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the heater component industry, lead times can vary significantly based on customization and manufacturing processes. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their projects to ensure timely delivery and avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their heater component selections align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the components of a heater Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Heater Components Market?
The heater components market is witnessing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions. Factors such as industrial automation, the rising need for temperature control in manufacturing processes, and the growth of sectors like food and beverage, automotive, and healthcare are propelling market dynamics. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the push for improved infrastructure and energy access is leading to a surge in heating applications, thereby increasing the demand for various heater components such as band heaters, cartridge heaters, and infrared heating systems.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
Emerging technologies in the heating sector are also shaping sourcing trends. For instance, the adoption of IoT-enabled heating solutions allows for real-time monitoring and control, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering operational costs. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer advanced materials like ceramic and polymer-based heaters that provide better thermal management and durability. In addition, the integration of smart technology is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions, as companies seek to optimize energy consumption and improve operational efficiencies.
How Is Sustainability Shaping B2B Sourcing for Heater Components?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the heater components sector. Buyers are now more aware of the environmental impact associated with their supply chains and are prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials, such as recyclable plastics and energy-efficient components, which not only reduce waste but also enhance the overall product lifecycle.
The importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to social and environmental standards, often verified through certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management). These certifications provide assurances that suppliers are committed to minimizing their environmental footprint, thereby aligning with the growing consumer demand for responsible production practices.
Additionally, the trend toward ‘green’ materials is influencing product development. Manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable materials and energy-efficient technologies, such as PTC and NTC heating elements that optimize energy consumption. By sourcing components with these attributes, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also appeal to a growing market segment that values sustainability.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Heater Components Industry?
The evolution of heater components can be traced back to the early 20th century when electrical heating became a viable alternative to traditional heating methods. Initially, basic resistive heating elements dominated the market, but advancements in materials science led to the development of more efficient and versatile heating solutions. The introduction of ceramic heaters and flexible heating technologies revolutionized the sector, allowing for greater application versatility and improved energy efficiency.
Over the decades, the focus has shifted toward enhancing performance through innovative designs and materials. The rise of industrial automation and the demand for precise temperature control have further propelled the need for advanced heater components. Today, B2B buyers benefit from a rich array of options, including customized solutions that cater to specific industry needs, thus enhancing operational efficiency and energy savings.
In summary, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical developments can equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed sourcing decisions in the heater components sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of components of a heater
-
How do I choose the right heating element for my application?
Choosing the appropriate heating element depends on several factors, including the material you need to heat, the required temperature range, and the heating method. For instance, cartridge heaters are ideal for targeted heating applications, while immersion heaters work well for heating liquids. Consider the environment in which the heater will operate, as some elements are better suited for harsh conditions. Additionally, consult with suppliers about their specific products’ capabilities and limitations to ensure compatibility with your application. -
What are the key specifications to look for in heater components?
When sourcing heater components, focus on specifications such as watt density, operating temperature range, and material compatibility. Ensure that the heating element’s construction aligns with your application’s requirements, including dielectric properties if applicable. Pay attention to certifications and compliance with international standards, as these can affect performance and safety. Understanding these specifications will help you select components that optimize efficiency and longevity. -
What customization options are available for heater components?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for heater components, including size, shape, and power specifications. Customization can be crucial for unique applications where standard components may not suffice. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to explore available materials, heating patterns, and integration options. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your customization requests without compromising quality or delivery timelines. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for heater components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary by supplier and can depend on the type of component and manufacturing process. Some suppliers may have an MOQ as low as 50 units, while others may require orders of several hundred. It’s essential to clarify MOQs before engaging in negotiations to understand your budget and inventory needs. If you require smaller quantities, inquire about flexibility or alternative suppliers who specialize in low-volume production. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing heater components internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Common practices include upfront payments, payment upon delivery, or letters of credit for larger orders. As an international buyer, consider negotiating terms that balance risk and cash flow, such as partial upfront payments with the remainder upon successful delivery. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and compliant with international trade regulations to avoid potential disputes. -
How do I vet suppliers of heater components effectively?
Vetting suppliers is critical to ensuring reliability and quality. Start by researching their business history, customer reviews, and industry certifications. Request samples to evaluate product quality and performance. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, lead times, and customer service responsiveness. Consider visiting the facility if possible, or arranging virtual tours, to gain insight into their operational standards and practices. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider for heater components?
Quality assurance measures are vital for ensuring that heater components meet industry standards and perform reliably. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing procedures for temperature accuracy, durability, and safety compliance. Request documentation of certifications and test results, and establish clear criteria for quality acceptance. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the production process can help address any issues proactively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing heater components?
When importing heater components, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping regulations. Understand the import tariffs and duties applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, ensure that your order is packaged appropriately to prevent damage during transit, and maintain open communication with your supplier regarding shipping updates and potential delays.
Top 2 Components Of A Heater Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Industrial Electric Heaters
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Industrial Electric Heaters operate through a resistor within a circuit, generating heat as electrical energy is converted through Joule heating. Key components include heating cores (oil-filled heaters and dry core electric radiators), heating elements (made from materials like nichrome wire), and various types of resistance heating wires (open wire, open ribbon wire, tubular cased wire). Electri…
2. Sigler’s – Electric Heat Sequencer & Parts
Domain: siglers.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Collector Box Drain Plug, Item: 336835-402; Exhaust Regulator, Item: 50DK506358; Electric Heat Sequencer, 3 Switch, 2 Timing, Item: 24A34-5; Loose Parts Bag, Item: 337668-701; Electric Heat Sequencer, 2 Switch, 1 Timing, Item: 24A34-3; Heat Exchanger Gasket, Item: 50DK503911; Electric Heat Sequencer, 2 Switch, 1 Timing, Item: 24A34-4; Flame Retainer, Item: 50DK502662; Universal Air Pressure Switch…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for components of a heater
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of heater components is essential for maximizing efficiency and ensuring quality. By understanding the diverse array of heating solutions—from band heaters and cartridge heaters to flexible and infrared options—buyers can tailor their sourcing strategies to meet specific operational needs. Each component, whether it be the heating elements or power cords, plays a pivotal role in the overall performance of heating systems, impacting both energy efficiency and output quality.
Illustrative image related to components of a heater
Moreover, the selection of materials, such as ceramics or stainless steel for substrates, can influence not only thermal performance but also the longevity and reliability of the heaters. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate strong R&D capabilities and a commitment to innovative solutions, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As we look ahead, embracing sustainable practices and advanced technologies in sourcing will not only enhance competitive advantage but also align with global energy efficiency trends. Engage with trusted suppliers who can provide tailored solutions to your heating needs and foster partnerships that drive mutual growth and innovation. Now is the time to take action and secure the best components for your heating applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
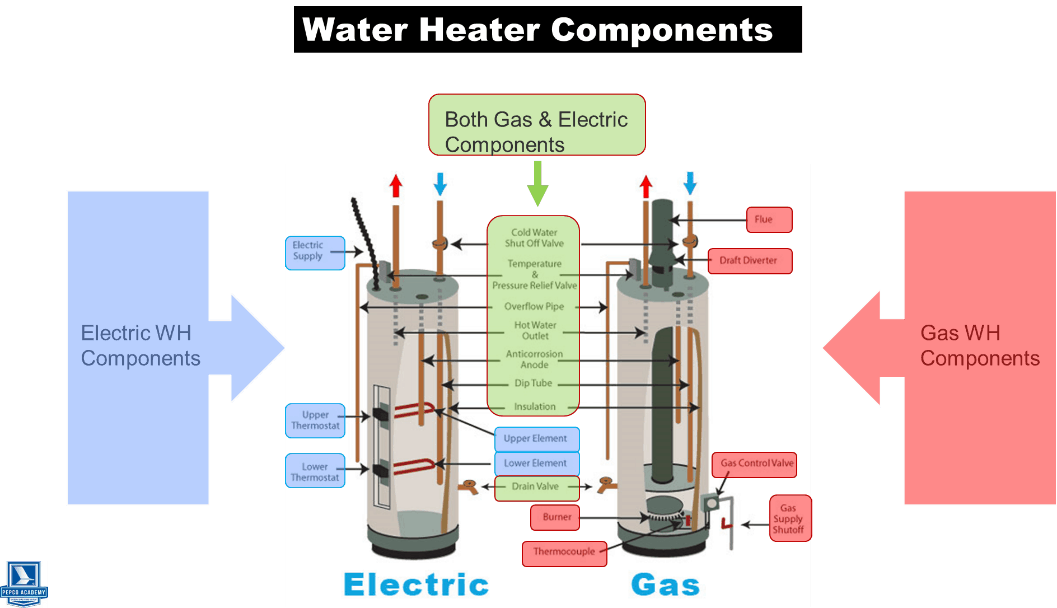
Illustrative image related to components of a heater