Top 2 Bracket Fasteners Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bracket fasteners
In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing reliable bracket fasteners presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from construction to manufacturing, the need for high-quality fastening solutions is paramount. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the bracket fastener market, covering a wide array of types—including corner braces, angle brackets, and mounting solutions—while addressing critical aspects such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and compliance with regional standards.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this intricate market, the importance of informed decision-making cannot be overstated. Fluctuating material costs, varying quality standards, and the necessity for timely delivery are just a few of the factors that can impact procurement strategies. This comprehensive resource is designed to empower B2B buyers by providing actionable insights and best practices, helping them to identify trustworthy suppliers and secure the best possible deals.
By focusing on the specific needs of diverse markets, including countries like Vietnam and Brazil, this guide will enable buyers to effectively streamline their sourcing processes and make educated choices that align with their operational requirements. Ultimately, understanding the global market for bracket fasteners can lead to enhanced efficiency and cost savings, fostering long-term business success.
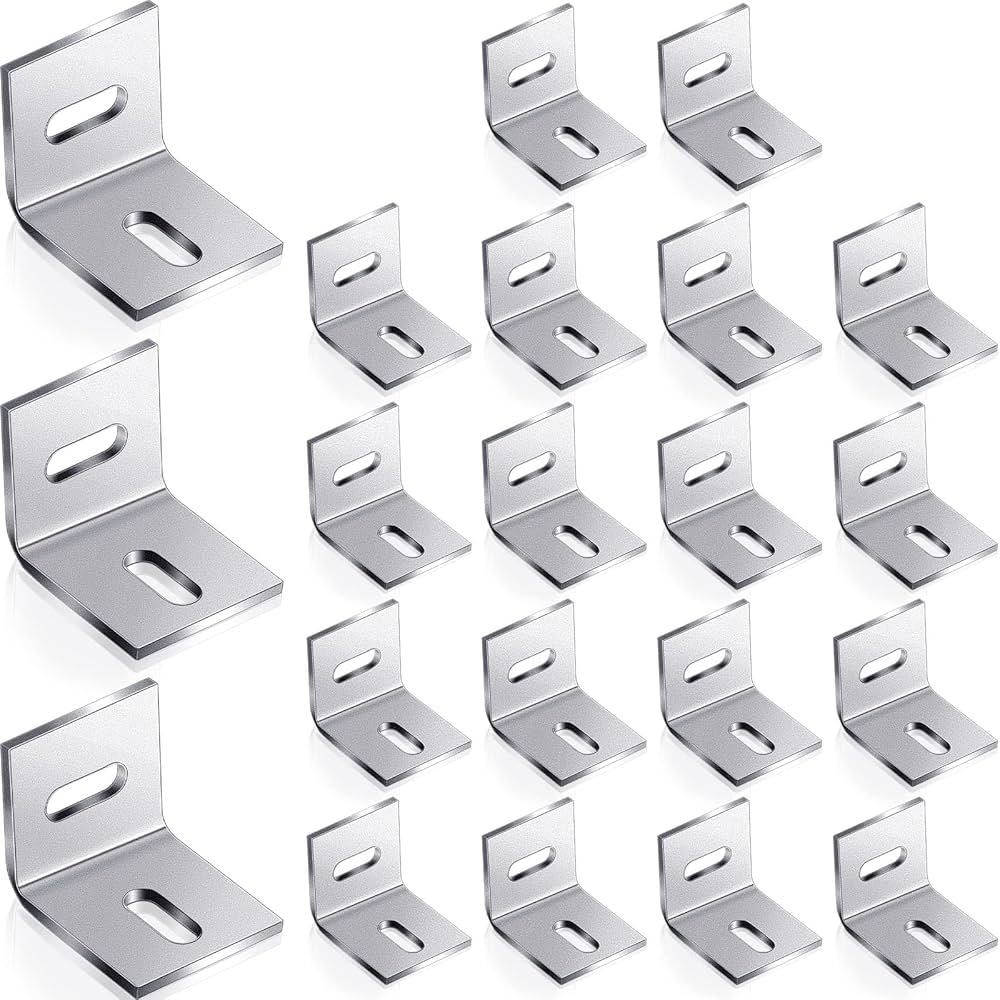
Understanding bracket fasteners Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corner Braces | Right-angle design, typically made of steel or aluminum | Furniture assembly, structural support | Pros: Easy installation, provides strong corner reinforcement. Cons: Limited load capacity compared to other types. |
| Mounting Brackets | Flat design with multiple holes for screws | Equipment mounting, shelving systems | Pros: Versatile and adjustable, suitable for various applications. Cons: Can be less aesthetically pleasing. |
| Angle Brackets | L-shaped configuration, often made from heavy-duty materials | Construction, framing | Pros: High strength and durability, excellent for load-bearing. Cons: May require specialized tools for installation. |
| Weld Brackets | Designed for welding to surfaces, often with a threaded hole | Heavy machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Provides a permanent and robust connection. Cons: Requires welding skills and equipment. |
| Mending Braces | Long, flat design for reinforcing joints | Repairing furniture, structural repairs | Pros: Simple design, effective for reinforcing weak points. Cons: May not provide sufficient support for heavy loads. |
What Are the Characteristics of Corner Braces in Bracket Fasteners?
Corner braces are primarily utilized for reinforcing right-angle joints in furniture and structural applications. These fasteners are typically constructed from steel or aluminum, offering a balance between strength and weight. Their design facilitates easy installation, making them ideal for both DIY projects and professional construction tasks. When purchasing corner braces, B2B buyers should consider factors such as load capacity, material durability, and corrosion resistance, particularly for outdoor applications.
How Do Mounting Brackets Differ in Functionality?
Mounting brackets are characterized by their flat design with multiple pre-drilled holes, allowing for flexible installation options. They are widely used in various applications, from mounting equipment to creating shelving systems. Their versatility makes them a popular choice among B2B buyers looking for adaptable solutions. When considering mounting brackets, it is essential to evaluate their weight capacity, material type, and compatibility with existing structures to ensure optimal performance.
Why Are Angle Brackets Essential for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Angle brackets feature an L-shaped configuration that provides exceptional strength and stability, making them ideal for construction and framing applications. These brackets are often made from heavy-duty materials, ensuring they can bear significant loads. B2B buyers should prioritize the thickness and material of angle brackets when making purchasing decisions, as these factors directly impact their load-bearing capabilities and longevity in demanding environments.
What Advantages Do Weld Brackets Offer in Industrial Settings?
Weld brackets are specifically designed for permanent attachment to surfaces through welding, often featuring a threaded hole for secure fastening. This type of bracket is commonly used in heavy machinery and automotive applications, where a robust connection is critical. B2B buyers interested in weld brackets should consider the welding requirements, as well as the material quality, to ensure they meet the necessary standards for strength and durability in industrial settings.
How Do Mending Braces Provide Support in Structural Repairs?
Mending braces are long and flat, designed primarily for reinforcing joints and repairing structural weaknesses. Their simplicity allows for quick installation and effective support, making them suitable for furniture repair and light structural applications. When selecting mending braces, B2B buyers should assess the material strength and the intended load requirements to ensure they provide adequate reinforcement without compromising structural integrity.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Key Industrial Applications of bracket fasteners
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bracket fasteners | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Building | Structural support for frameworks and bracing | Enhances structural integrity and safety of buildings | Material specifications (e.g., galvanized steel), load ratings, compliance with local regulations |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Mounting components like engines and frames | Ensures secure assembly and performance of vehicles | Precision engineering, corrosion resistance, availability of custom sizes |
| HVAC Systems | Installation of ductwork and equipment supports | Facilitates efficient climate control and airflow | Compatibility with various HVAC components, thermal resistance, and durability |
| Furniture & Fixtures | Assembly of modular furniture and displays | Provides stability and flexibility in design | Aesthetic finishes, load-bearing capacity, and ease of assembly |
| Electrical & Electronics | Mounting electronic components and panels | Ensures safe and reliable operation of electrical devices | Compliance with safety standards, material conductivity, and insulation properties |
How Are Bracket Fasteners Used in Construction and Building Applications?
In the construction industry, bracket fasteners are pivotal for providing structural support in frameworks and bracing systems. They help secure beams, rafters, and other components, enhancing the overall integrity and safety of buildings. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to consider load ratings and local building codes to ensure compliance and safety. Sourcing durable materials such as galvanized steel can also mitigate corrosion risks in diverse climates.
What Role Do Bracket Fasteners Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Bracket fasteners are essential in automotive manufacturing for securely mounting components like engines, frames, and suspension systems. These fasteners ensure that parts remain stable under dynamic conditions, contributing to vehicle safety and performance. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize precision engineering and corrosion-resistant materials to withstand varying environmental conditions and ensure longevity. Custom sizing may also be necessary for specific vehicle models.
How Are Bracket Fasteners Utilized in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, bracket fasteners are used to install and support ductwork and other equipment. They play a vital role in maintaining proper airflow and ensuring efficient climate control. For B2B buyers, especially in regions with extreme weather, sourcing brackets that can withstand thermal stress and corrosion is essential. Compatibility with various HVAC components and ease of installation are also critical considerations for successful implementation.
In What Ways Are Bracket Fasteners Applied in Furniture and Fixtures?
Bracket fasteners are commonly used in the assembly of modular furniture and fixtures, providing stability and flexibility in design. They enable manufacturers to create customizable solutions that meet diverse customer needs. For international buyers, aesthetic finishes and load-bearing capacities are important factors to consider, as they directly impact the product’s marketability. Ensuring ease of assembly can also enhance consumer satisfaction and reduce production times.
Why Are Bracket Fasteners Important in Electrical and Electronics Industries?
In the electrical and electronics sectors, bracket fasteners are crucial for mounting components and panels securely. They ensure the safe and reliable operation of devices, which is vital for maintaining compliance with safety standards. Buyers should consider sourcing materials that offer good conductivity and insulation properties to prevent electrical failures. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding electrical installations can guide sourcing decisions for international markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bracket fasteners’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Compatibility with Structural Requirements
The Problem: One common challenge faced by B2B buyers in the construction and manufacturing sectors is ensuring that bracket fasteners are compatible with the specific structural requirements of their projects. Buyers often grapple with the dilemma of selecting the right type of bracket fastener that meets load specifications, material compatibility, and environmental conditions. For instance, using a standard steel bracket in a high-humidity environment can lead to corrosion, resulting in structural failures and costly repairs.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough assessments of their project specifications and environments before sourcing bracket fasteners. This includes understanding the load-bearing capacities required for their applications, as well as the environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, temperature variations) that may affect the fasteners. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that provide detailed technical data sheets and certifications for their products. Additionally, consider using corrosion-resistant materials, such as galvanized or stainless steel brackets, especially for outdoor applications or in humid climates. Engaging with suppliers who offer expert consultations can also help ensure that the chosen fasteners align with structural engineering standards.
Scenario 2: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the unpredictability of supply chains, which can lead to delays in obtaining the necessary bracket fasteners. Factors such as geopolitical issues, natural disasters, or global pandemics can disrupt manufacturing and logistics, causing projects to stall and increasing costs. Buyers often find themselves scrambling to find alternative suppliers or substitute products, which may not meet the required specifications.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, B2B buyers should develop a diversified sourcing strategy that includes multiple suppliers across different regions. This not only increases the chances of maintaining supply continuity but also provides leverage in negotiating better pricing and terms. Buyers should also consider establishing long-term relationships with key suppliers who demonstrate reliability and responsiveness to market changes. Additionally, investing in inventory management systems that predict demand based on project timelines can help maintain adequate stock levels of critical components, including bracket fasteners. Finally, staying informed about market trends and potential disruptions through industry news and trade networks can equip buyers with foresight and flexibility to adapt quickly.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Scenario 3: Overcoming Installation Complexity
The Problem: Installation complexity can be a significant hurdle when it comes to using bracket fasteners effectively. Many buyers encounter difficulties in ensuring proper installation, leading to structural weaknesses or failures. This is particularly true in large-scale projects where numerous brackets are used, and any misalignment or improper fastening can compromise the integrity of the entire structure. Miscommunication between teams responsible for installation can further exacerbate these issues.
The Solution: To enhance installation success, buyers should invest in comprehensive training and clear communication protocols among their teams. Creating detailed installation guidelines and utilizing checklists can help standardize processes and minimize errors. Furthermore, leveraging technology such as 3D modeling or simulation software can provide visual aids that illustrate proper installation techniques, making it easier for teams to understand complex requirements. Additionally, buyers should consider sourcing bracket fasteners that come with installation kits or include necessary accessories, such as screws and anchors, to simplify the process. Engaging with suppliers who offer technical support or on-site assistance can also facilitate smoother installations and ensure that all components are utilized correctly.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bracket fasteners
When selecting materials for bracket fasteners, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance in various applications. This analysis will focus on four common materials: stainless steel, galvanized steel, plastic, and brass. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the functionality and durability of bracket fasteners in diverse environments.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Bracket Fasteners?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for demanding applications. It typically withstands temperatures ranging from -200°C to 800°C, depending on the grade. The material’s ability to resist rust and staining is crucial for outdoor applications or environments with high humidity.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and longevity, which can reduce replacement costs over time. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process is complex, which may lead to higher initial costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bracket fasteners are ideal for applications involving moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures. They are widely used in construction, automotive, and marine industries.
How Does Galvanized Steel Compare for Bracket Fasteners?
Galvanized steel is carbon steel that has been coated with zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. This coating protects the steel from rust, especially in outdoor or humid environments. The temperature resistance of galvanized steel is similar to that of stainless steel, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros and Cons: Galvanized steel is generally more affordable than stainless steel, making it a cost-effective choice for many projects. However, the zinc coating can wear off over time, especially in abrasive environments, leading to potential corrosion issues.
Impact on Application: Galvanized steel fasteners are commonly used in construction and agricultural applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to relevant standards, such as ASTM A153 for hot-dip galvanizing.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Bracket Fasteners?
Plastic fasteners, often made from materials like nylon or polypropylene, offer lightweight and corrosion-resistant options. They are generally rated for lower temperature applications, typically up to 100°C, depending on the specific type of plastic used.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of plastic fasteners is their resistance to corrosion and chemical exposure, making them suitable for specific environments. They are also lightweight and easy to install. However, plastic fasteners may not provide the same level of strength and durability as metal options, which can limit their use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic bracket fasteners are ideal for electronic and automotive applications where weight reduction is critical, and exposure to moisture is limited. International buyers should consider the specific grades of plastic and their compliance with industry standards.
Why Choose Brass for Bracket Fasteners?
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is often used in applications where appearance matters, such as decorative fittings.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of brass is its resistance to corrosion and its attractive finish, making it suitable for visible applications. However, brass can be more expensive than other materials and may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Brass fasteners are commonly used in plumbing and electrical applications where corrosion resistance is critical. Buyers should ensure that the brass used meets relevant standards, such as ASTM B16 for brass fittings.
Summary of Material Selection for Bracket Fasteners
| Material | Typical Use Case for bracket fasteners | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Marine, automotive, construction | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Construction, agricultural applications | Cost-effective and durable | Zinc coating can wear off | Medium |
| Plastic | Electronics, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than metal options | Low |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical fittings | Attractive finish and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and lower tensile strength | Medium |
Selecting the right material for bracket fasteners is crucial for ensuring performance and longevity in various applications. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bracket fasteners
The manufacturing of bracket fasteners involves a series of methodical processes designed to ensure precision, durability, and compliance with international standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This section will explore the key stages of manufacturing bracket fasteners, the quality assurance practices in place, and how buyers can verify the quality of their suppliers.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Bracket Fasteners?
How Is Material Prepared for Bracket Fasteners?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications. Common materials used for bracket fasteners include low carbon steel, stainless steel, and galvanized steel. The selection of material often depends on the intended application—whether for indoor use or harsh outdoor environments.
During this stage, raw materials are sourced and inspected for quality. Common practices include checking for impurities and ensuring that the material adheres to specific standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Once verified, the materials are cut to size and shaped into preliminary forms, such as sheets or rods, that will be further processed.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing?
Forming is the next critical stage, where the prepared materials are transformed into the desired shapes for bracket fasteners. Techniques employed in this stage include:
- Stamping: High-speed stamping machines are used to create precise shapes and holes in the material. This method is cost-effective for large production runs.
- Bending: The material is bent into angles, typically using hydraulic or mechanical press brakes. This is vital for creating the right angles needed for corner braces or mounting brackets.
- Welding: For certain types of brackets, welding techniques such as spot welding or projection welding may be employed to fuse parts together, ensuring structural integrity.
These forming techniques are pivotal in achieving the exact specifications required for various applications, from light-duty to heavy-duty fastening solutions.
How Does Assembly Work in Bracket Fastener Production?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage involves the integration of different parts, such as adding additional supports or fasteners to the main bracket body. Depending on the design, assembly may include:
- Mechanical Fastening: Using screws, bolts, or rivets to hold components together.
- Adhesive Bonding: In some cases, high-strength adhesives may be applied to enhance the bond between materials.
Quality control measures are critical during assembly to ensure that each product meets the design specifications and can withstand the required load and stress.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Bracket Fasteners?
The finishing stage is essential for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional properties of bracket fasteners. Common finishing processes include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings such as galvanization, powder coating, or painting to prevent corrosion and improve durability.
- Polishing: For stainless steel or decorative brackets, polishing may be applied to enhance surface finish and appearance.
- Heat Treatment: Some fasteners undergo heat treatment processes to improve strength and hardness, which is especially important for high-load applications.
Finishing not only affects the visual appeal of the product but also its performance and longevity in various environments.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are in Place for Bracket Fasteners?
Which International Standards Apply to Bracket Fasteners?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of bracket fasteners is governed by various international standards. The most relevant include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For fasteners used in oil and gas applications, adherence to API standards ensures that products can withstand extreme conditions.
Understanding these standards is vital for B2B buyers, as they indicate that the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process with specific checkpoints, including:

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to confirm they meet design specifications and performance standards.
Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, corrosion resistance tests, and dimensional checks. These procedures are essential for ensuring that each batch of fasteners meets the required performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Verify Quality?
To ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices, B2B buyers should consider the following steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of supplier facilities to evaluate their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation related to their quality control processes, including inspection reports, testing results, and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent assessments of the supplier’s production and quality management systems.
These measures not only provide assurance of product quality but also help establish a trustworthy relationship between buyers and suppliers.
Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
What Are the Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Factors to consider include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations and international standards specific to the region of operation.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural nuances that may affect communication and expectations regarding quality and delivery.
- Logistical Challenges: Consider the impact of logistics on product quality, including shipping conditions and handling processes that could affect fasteners during transit.
By taking these factors into account, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with sourcing bracket fasteners from international suppliers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for bracket fasteners are intricate and essential for delivering reliable products. By understanding these processes and maintaining a proactive approach to supplier verification, B2B buyers can ensure they receive high-quality fasteners that meet their specific needs and standards. This knowledge not only enhances purchasing decisions but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bracket fasteners’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of bracket fasteners can be a complex process, particularly for B2B buyers across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This checklist serves as a practical guide to streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your project requirements and organizational goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for sourcing bracket fasteners that meet your project’s needs. Consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, material properties (e.g., galvanized steel for corrosion resistance), and dimensions. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid costly errors.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Applications
Understanding current market trends and applications for bracket fasteners can provide insights into what products are in demand. Look into emerging technologies or materials being utilized in the industry, such as eco-friendly options or innovative designs. This knowledge can give you a competitive edge and inform your purchasing strategy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other businesses in your sector. Pay attention to their experience with international shipping and compliance with local regulations, especially if you’re sourcing from different continents.
- Check for Certifications: Verify if the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) to ensure quality management.
- Assess Production Capabilities: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume requirements and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Quality
Always request samples of the bracket fasteners you intend to purchase. Testing these samples will allow you to assess their quality, durability, and suitability for your specific applications. This step is particularly important if you are considering bulk orders, as it helps mitigate the risk of defects.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engaging in price negotiations is vital to secure the best deal without compromising quality. Consider factors such as bulk order discounts, payment terms, and shipping costs. Be prepared to discuss your budget constraints and seek flexibility in terms that can benefit both parties.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
- Long-Term Partnerships: If you foresee ongoing needs, discuss potential long-term agreements for better pricing and stability in supply.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure all agreements are documented in a formal contract. This contract should outline pricing, delivery schedules, quality expectations, and return policies. Clear documentation protects both parties and minimizes misunderstandings.
Step 7: Implement Quality Control Measures
Establish quality control measures to monitor the performance of the bracket fasteners upon delivery. This includes inspecting shipments for compliance with specifications and conducting regular checks during usage. Maintaining quality control is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your projects.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of bracket fasteners with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and market conditions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bracket fasteners Sourcing
Analyzing the cost and pricing structure of bracket fasteners is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. Understanding the cost components and price influencers can lead to better negotiation outcomes and improved overall value.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
What Are the Key Cost Components for Bracket Fasteners?
Materials: The primary material used in bracket fasteners, such as steel (galvanized, stainless, or low-carbon), significantly affects pricing. For instance, high-welding quality steel may incur higher costs but offer enhanced durability, which can be vital for structural applications.
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as certain countries in Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing, but it’s crucial to balance this with quality and reliability.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the production facility, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, which may positively influence pricing.
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can add to initial costs. For large orders, suppliers may absorb these costs, but smaller orders could see these expenses passed on to buyers.
Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Quality Control (QC): Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures that products meet required specifications and standards. Suppliers that prioritize QC may charge a premium, but this can save costs in the long run by reducing returns and ensuring compliance with international standards.
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, the mode of transport, and any tariffs or customs fees that may apply. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding local logistics can lead to significant savings.
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation. It’s essential for buyers to understand the typical markup in their specific market segment.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
What Factors Influence Pricing for Bracket Fasteners?
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on order volume. Higher quantities typically result in lower per-unit costs, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher prices due to additional tooling and manufacturing processes. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential cost increase.
Material Quality and Certifications: Products meeting specific industry certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in certified products versus cheaper, uncertified options.
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers may charge more due to their reputation and reliability. Newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market entry, but buyers should assess the risk of potential quality issues.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial. For example, “CIF” (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) might include shipping costs in the quoted price, while “FOB” (Free on Board) might not. This can significantly impact the total cost for buyers.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Bracket Fasteners?
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should aim to consolidate orders to meet MOQ thresholds, thereby securing volume discounts.
Request Detailed Quotations: Obtain itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency allows for better negotiation on specific components, such as materials or logistics.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with the fasteners, including installation, maintenance, and potential failures.
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying price norms due to local supply and demand dynamics. Buyers in Africa or South America should familiarize themselves with local market conditions to negotiate effectively.
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and potential discounts on future orders.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for bracket fasteners can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. The figures provided in various sources are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accurate and current pricing. Always consider local market conditions and supplier capabilities when making sourcing decisions.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bracket fasteners With Other Solutions
When evaluating fastening solutions for various structural applications, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional bracket fasteners. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different methods can help organizations make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and cost structures. Below, we compare bracket fasteners with two viable alternatives: welding and adhesive bonding.
| Comparison Aspect | Bracket Fasteners | Welding | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength; suitable for heavy loads. | Provides excellent structural integrity; ideal for permanent solutions. | Good for lightweight applications; strength varies with adhesive type. |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate; varies by material and design. | Higher initial costs due to equipment and labor. | Cost-effective for small projects; depends on adhesive quality. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires minimal tools. | Requires skilled labor and specialized equipment. | Easy application; requires curing time. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easily replaceable. | Difficult to repair; requires re-welding. | Can degrade over time; may need reapplication. |
| Best Use Case | Furniture assembly, shelving, and general construction. | Heavy machinery, structural beams, and automotive applications. | Lightweight fixtures, electronics, and non-structural applications. |
How Do Bracket Fasteners Compare to Welding?
Welding is a method that involves fusing materials, typically metals, to create a strong bond. Its primary advantage is the high structural integrity it provides, making it ideal for applications that must withstand significant stress, such as in construction and heavy machinery. However, welding requires specialized skills and equipment, leading to higher costs and longer implementation times. Additionally, welded joints can be challenging to repair; if a weld fails, the entire joint may need to be redone, which can incur additional labor and material costs.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Adhesive Bonding?
Adhesive bonding involves using a chemical substance to create a bond between surfaces. This method offers ease of application and is often cost-effective for smaller projects. Adhesives can bond dissimilar materials, which is a significant advantage in industries like electronics. However, the strength of adhesive bonds can vary widely depending on the adhesive used and environmental conditions. Adhesives may also require curing time, which can delay project timelines. Over time, some adhesives can degrade, necessitating maintenance or replacement.
Making the Right Choice: Which Fastening Solution Should You Use?
Choosing the right fastening solution depends on several factors, including the specific application, load requirements, budget constraints, and available resources. For B2B buyers, it is essential to assess the performance needs and long-term maintenance implications of each solution. Bracket fasteners are often the best choice for versatility and ease of use, particularly in furniture and light construction. Welding is preferable for high-stress applications requiring permanent fixtures, while adhesive bonding may be suitable for lighter applications where ease of use and cost are primary concerns. Ultimately, understanding the unique requirements of your project will guide you in selecting the most effective fastening solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bracket fasteners
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bracket Fasteners?
When selecting bracket fasteners for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring performance and durability. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Bracket fasteners are typically made from materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or galvanized steel. The material grade indicates the strength and corrosion resistance of the fastener. For example, stainless steel is preferred for outdoor applications due to its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. -
Load Capacity
– This specification defines the maximum weight a bracket can support without failure. Load capacity is vital for structural integrity in applications such as shelving, machinery support, or construction frameworks. Assessing load capacity helps in selecting the right bracket to prevent premature failure and ensure safety. -
Thickness and Gauge
– The thickness of the bracket, often measured in gauge, affects its strength and durability. Thicker brackets (lower gauge numbers) can withstand greater loads and are more suitable for heavy-duty applications. Understanding gauge specifications allows buyers to choose brackets that meet their specific load-bearing requirements. -
Coating and Finish
– Coatings like zinc plating or powder coating enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetic appeal. For applications exposed to moisture or chemicals, selecting a bracket with an appropriate finish is essential to prolong its lifespan and maintain performance. -
Dimensions
– The dimensions of a bracket, including length, width, and hole size, are critical for compatibility with other components in a system. Proper dimensions ensure easy installation and secure fitting, reducing the risk of assembly errors that could lead to structural failures. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a bracket’s dimensions. Tight tolerances are crucial in precision engineering applications where components must fit together seamlessly. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers ensure that their fasteners will perform reliably in their intended applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Bracket Fasteners?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation with suppliers. Here are some common terms relevant to bracket fasteners:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is essential for ensuring that the bracket fasteners meet the quality and performance standards required by the original product design. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for budget planning and inventory management, as it can impact purchasing decisions, especially for smaller businesses. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and delivery options from multiple vendors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for navigating shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines in cross-border purchases. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Awareness of lead times is vital for project planning, as it affects timelines for construction or manufacturing projects that rely on timely delivery of bracket fasteners. -
Fastener Grade
– Fastener grade indicates the strength and performance characteristics of a fastener. Different grades (e.g., Grade 2, Grade 5, Grade 8) are used to specify load capacities and mechanical properties. Choosing the correct fastener grade is essential for ensuring that the fasteners perform adequately in their intended applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bracket fasteners, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific needs and applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bracket fasteners Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Bracket Fasteners Market?
The bracket fasteners market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for construction and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, is a primary driver. Urbanization and population growth in these regions necessitate robust structural solutions, leading to heightened demand for reliable fasteners. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as automation and precision engineering, are enabling suppliers to offer more innovative and customized products.
Moreover, the trend toward modular construction and prefabrication is reshaping sourcing strategies. As projects become more time-sensitive, the need for quick, efficient sourcing of bracket fasteners is paramount. International buyers are increasingly relying on digital platforms and e-commerce solutions to streamline their procurement processes, ensuring timely access to materials while reducing overhead costs. This shift is particularly prevalent in markets like Vietnam and Brazil, where traditional sourcing methods are being supplemented by digital solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Bracket Fasteners?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the bracket fasteners sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of recycled materials and environmentally-friendly production methods.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into sourcing strategies can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) regulations are becoming increasingly relevant. Buyers are encouraged to seek partnerships with suppliers who can provide transparency regarding their supply chains and sustainability efforts, ensuring that the materials used in bracket fasteners are sourced ethically and responsibly.
What Is the Historical Context of Bracket Fasteners in B2B Markets?
The evolution of bracket fasteners has been shaped significantly by advancements in engineering and manufacturing. Initially, fasteners were simple mechanical devices used primarily in construction. Over time, the introduction of materials like stainless steel and galvanized finishes has improved durability and resistance to environmental factors, expanding their applications beyond traditional settings.
As construction techniques evolved, so did the complexity of bracket designs, leading to specialized products tailored for specific applications. The integration of technology, such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design), has facilitated the development of innovative fastening solutions that cater to diverse market needs. This historical progression underscores the importance of continual innovation in the bracket fasteners sector, aligning with current trends in modular construction and sustainability.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of the bracket fasteners market requires a keen understanding of global drivers, emerging trends, and sustainability considerations. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging technology and prioritizing ethical sourcing practices will be vital in ensuring competitive advantage and long-term success in this dynamic sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bracket fasteners
-
How do I choose the right bracket fastener for my application?
Selecting the appropriate bracket fastener depends on various factors such as load requirements, material compatibility, and environmental conditions. For heavy-duty applications, consider using brackets made from galvanized steel for corrosion resistance. Additionally, ensure that the size and design of the bracket suit the specific structural needs of your project, whether it’s for mounting, support, or reinforcement. Consulting with a technical representative from your supplier can provide valuable insights based on your unique specifications. -
What are the most common materials used for bracket fasteners?
Bracket fasteners are typically made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic. Steel is favored for its strength and durability, while stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance for outdoor or humid environments. Aluminum is lightweight and suitable for applications where weight is a concern, whereas plastic brackets can be ideal for non-load-bearing applications. When sourcing, ensure the material aligns with the intended use and environmental factors of your project. -
What customization options are available for bracket fasteners?
Many suppliers offer customization options for bracket fasteners, including size, finish, and design modifications. Customizations can be tailored to meet specific load capacities or aesthetic preferences. It’s advisable to communicate your requirements clearly to the supplier, including any relevant specifications or drawings. This ensures the final product aligns with your project needs, and you may also discuss volume discounts for larger orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for bracket fasteners?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for bracket fasteners can vary significantly by supplier and product type. While some suppliers may have an MOQ as low as 100 units, others may require a minimum order of 1,000 units or more, particularly for custom products. It is essential to verify the MOQ with your supplier upfront to ensure it aligns with your project budget and timelines. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing bracket fasteners internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, work with reputable suppliers that have established quality control processes. Request certifications, such as ISO 9001, and ask for product samples before committing to a larger order. Additionally, consider third-party inspections during production and prior to shipping to verify that the products meet your specifications. Establishing clear communication regarding quality standards with your supplier is crucial for successful sourcing. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing bracket fasteners?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the scale of your order. Common terms include upfront payment, a 30% deposit with the balance due upon shipment, or net 30-60 days after delivery. It is advisable to discuss and negotiate payment terms before finalizing the order to ensure they are manageable for your cash flow. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to protect your transaction. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing bracket fasteners?
When importing bracket fasteners, consider shipping options, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Choose a logistics provider experienced in handling your specific product category and region. Factor in potential delays due to customs clearance and ensure that all documentation is prepared accurately. Understanding the import regulations of your country, including tariffs and taxes, will help avoid unexpected costs and delays. -
How can I vet a supplier for bracket fasteners?
Vetting a supplier involves assessing their reputation, production capabilities, and customer service. Start by reviewing their certifications, client testimonials, and case studies. Request references from previous clients and verify their experience in your industry. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible or utilizing online resources to research their reliability. Engaging in open communication can also provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs.
Top 2 Bracket Fasteners Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Buckeye Fasteners – Right Angle Projection Weld Bracket
Domain: buckeyefasteners.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: [{‘item_no’: ‘BT 1402’, ‘description’: ‘8-32 RIGHT ANGLE PROJECTION WELD BRACKET’, ‘material’: ‘Plain C1010 High-Welding Quality, Low Carbon Steel’, ‘thread_size’: ‘#8-32’}, {‘item_no’: ‘BT 1403’, ‘description’: ‘8-32 RIGHT ANGLE PROJECTION WELD BRACKET’, ‘material’: ‘Plain C1010 High-Welding Quality, Low Carbon Steel’, ‘thread_size’: ‘#8-32’}, {‘item_no’: ‘BT 1503’, ‘description’: ’10-24 RIGHT AN…
2. Allfasteners – Angle Brackets & Connectors
Domain: allfasteners.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Allfasteners offers a wide range of Angle Brackets & Connectors suitable for strut channel, threaded rod, and other overhead applications. Key products include: 1. Strut Angle Brackets – Starting at $2.90 2. Strut Flat Plate Connectors – Starting at $5.35 3. 4B15LS 1/4 Rod to 1-1/2 Lathers Channel Side Mount (100/Box) – $115.00 4. Side Beam Connector – Starting at $1.80 5. Three Hole Ceiling Flang…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bracket fasteners
Strategic sourcing of bracket fasteners presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse range of products available—from angle brackets to corner braces—allows companies to select materials that best meet their structural and operational needs. By prioritizing suppliers that offer high-quality materials, such as galvanized or stainless steel options, businesses can enhance durability and performance, reducing long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements.
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated; it not only optimizes procurement processes but also fosters stronger supplier relationships. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that provide comprehensive support and flexible solutions tailored to their specific projects. As the global market continues to evolve, leveraging local suppliers while considering international options can provide a competitive edge.
Looking forward, B2B buyers are encouraged to assess their sourcing strategies and engage with innovative suppliers who can offer cutting-edge products and services. By embracing a proactive approach to sourcing bracket fasteners, businesses can ensure they are well-equipped to meet future demands and capitalize on growth opportunities in their respective markets.

Illustrative image related to bracket fasteners
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.