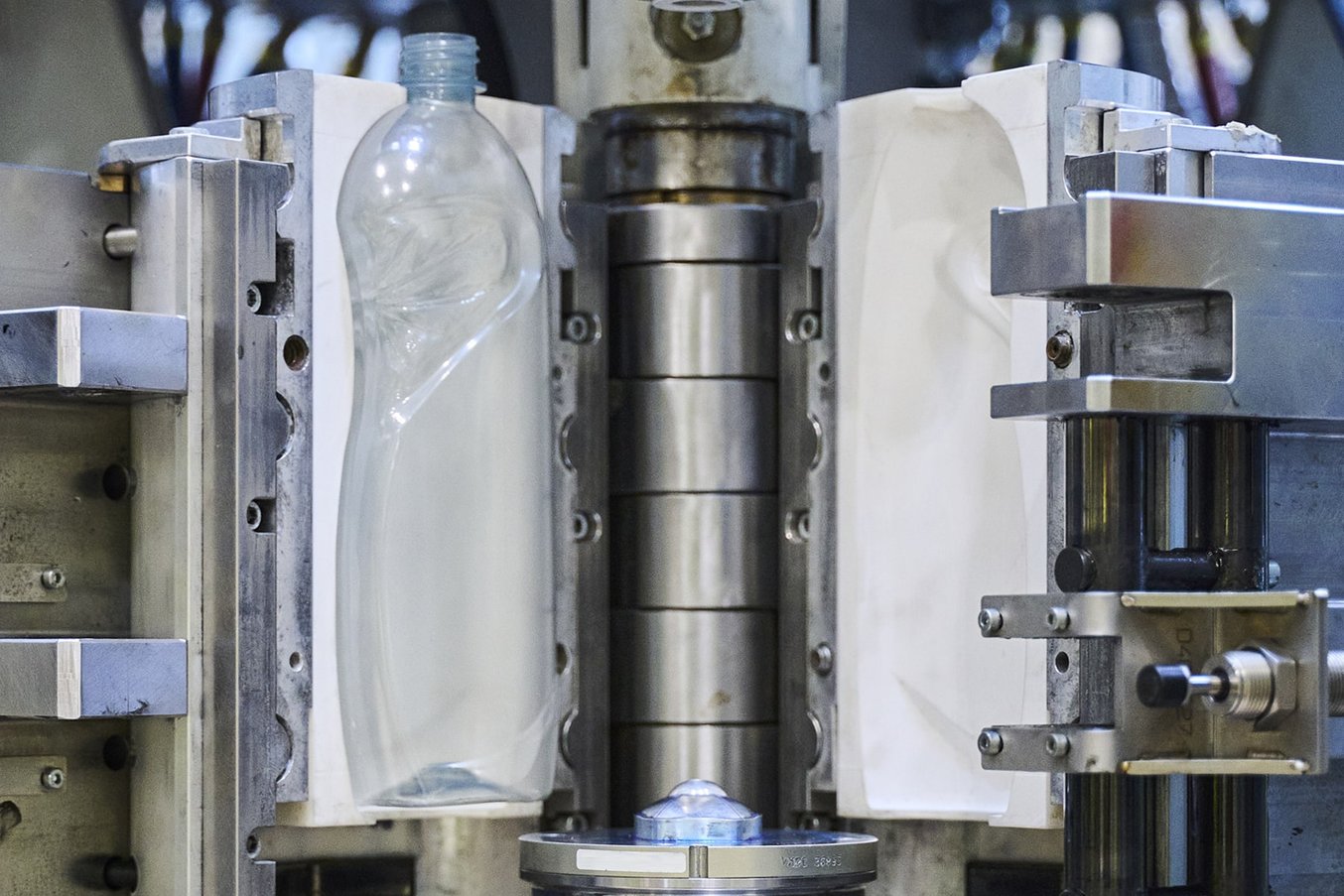
Top 2 Blow Molding Mold Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for blow molding mold
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, sourcing high-quality blow molding molds poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on blow molding to produce hollow plastic parts at scale, understanding the nuances of this process becomes crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of blow molding molds—extrusion, injection, and injection stretch blow molding—while exploring their applications across diverse sectors such as packaging, automotive, and agriculture.
In addition to outlining the technical aspects of blow molding, this resource addresses critical considerations for international buyers, including supplier vetting, cost implications, and logistical challenges. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical strategies, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of sourcing blow molding molds effectively. With a clear focus on enhancing procurement strategies, our aim is to facilitate successful partnerships that drive innovation and efficiency in your manufacturing processes. Whether you are in Brazil, Nigeria, or any other region, understanding the global market for blow molding molds will enable you to make strategic decisions that align with your business goals.
Understanding blow molding mold Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | Simple process, low cost, limited structural complexity | Bottles, tanks, containers | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs. Cons: Limited design flexibility. |
| Injection Blow Molding (IBM) | Combines injection and blow molding, higher precision | High-quality bottles, jars, and complex shapes | Pros: Better detail and strength. Cons: Higher tooling costs. |
| Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) | Uses stretching for enhanced strength and clarity | Beverage containers, cosmetic bottles | Pros: Superior clarity and strength. Cons: More complex process. |
| Reusable Blow Molds | Designed for multiple uses, often made from aluminum or steel | High-volume production runs | Pros: Cost-effective over time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| 3D Printed Blow Molds | Rapid prototyping, customizable, and lower upfront costs | Small batches, product testing | Pros: Quick turnaround and design flexibility. Cons: Limited durability for high-volume runs. |
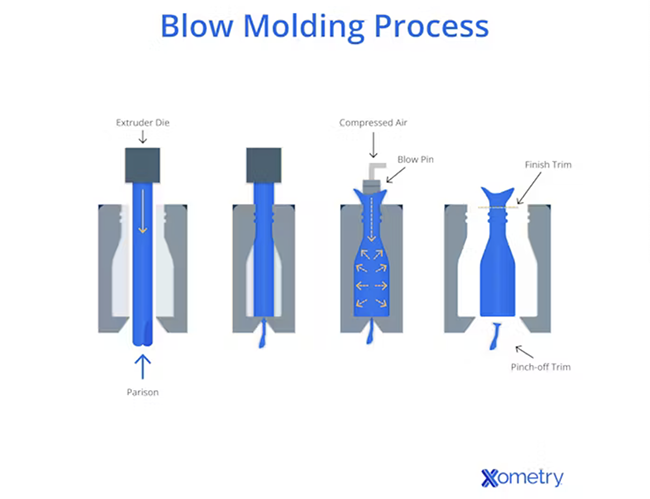
What Are the Key Characteristics of Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)?
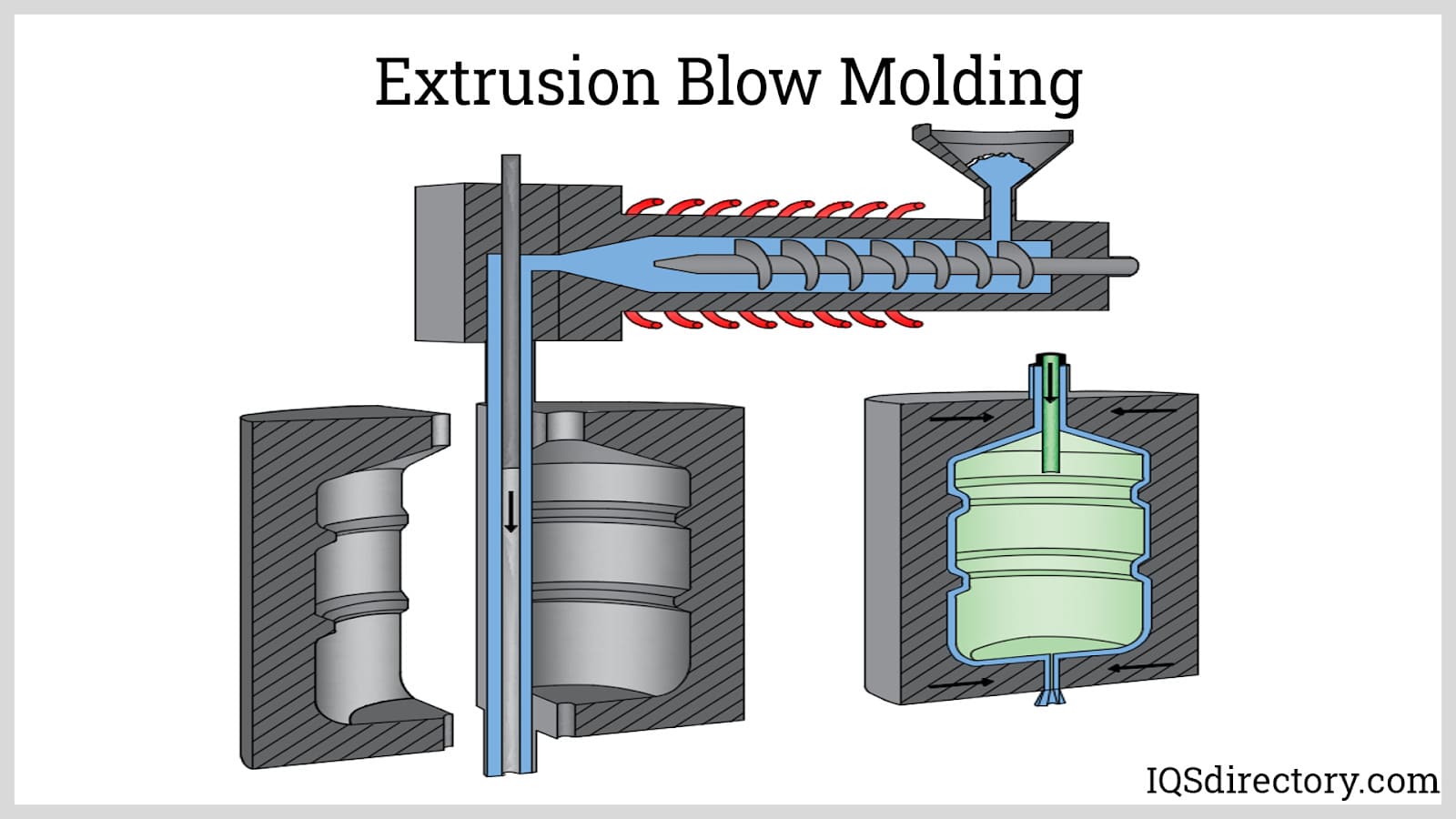
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) is the most straightforward blow molding technique, where molten plastic is extruded to form a hollow parison that is then inflated into a mold. This method is particularly suited for producing larger, simpler shapes like bottles and tanks at a lower cost. B2B buyers should consider EBM for high-volume production of less complex items, as it offers a lower tooling cost compared to other methods. However, the limited design complexity may necessitate alternative methods for specialized applications.
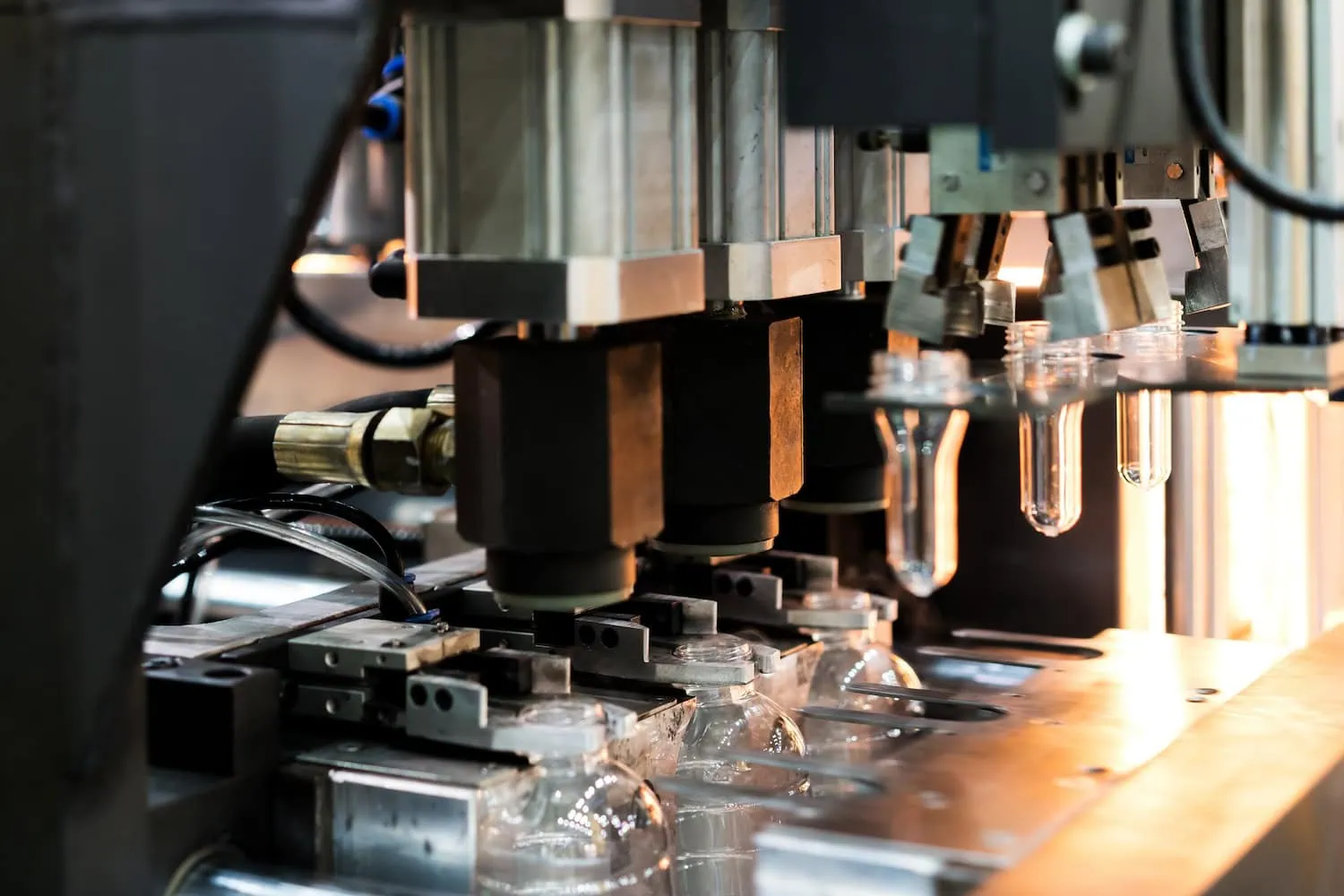
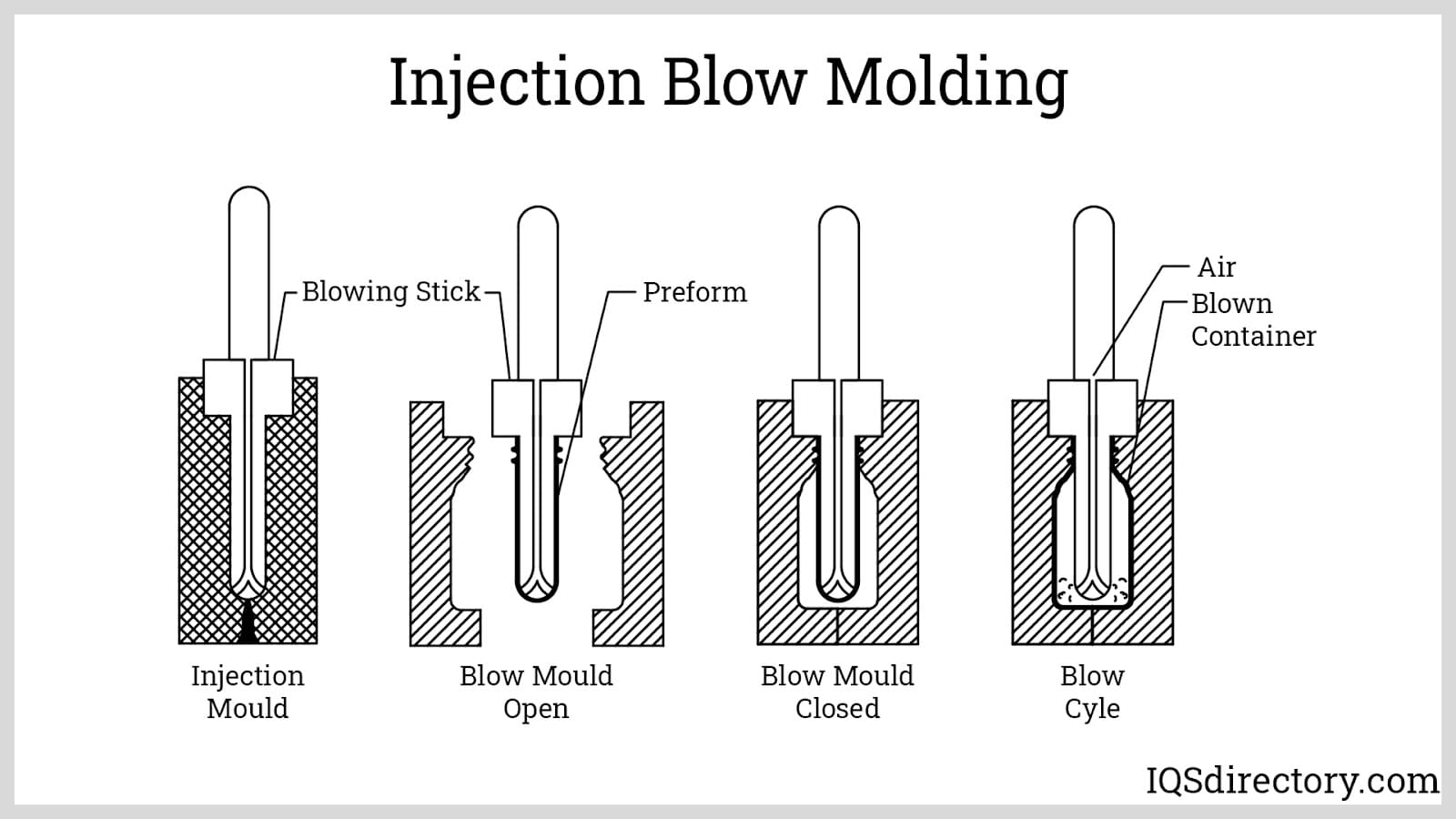
How Does Injection Blow Molding (IBM) Enhance Product Quality?
Injection Blow Molding (IBM) merges the benefits of injection and blow molding, allowing for the production of high-precision, detailed items. This process creates a preform through injection molding before transferring it to a blow mold. IBM is ideal for applications requiring intricate designs or tighter tolerances, such as cosmetic jars or medical containers. While IBM provides superior quality, buyers must be aware of the higher initial tooling costs, which could impact budget considerations for smaller production runs.
Why Choose Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) for High-Performance Products?
Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) is a specialized technique that combines stretching with blow molding to produce strong, transparent products. It is commonly used for beverage containers that require both clarity and durability. This method allows for a greater degree of design complexity and improved mechanical properties. B2B buyers looking for high-performance packaging solutions should consider ISBM, but must also account for the complexities and costs associated with this process.
What Are the Advantages of Using Reusable Blow Molds?
Reusable blow molds are designed for multiple production cycles, typically constructed from durable materials like aluminum or steel. They are suitable for high-volume production runs, providing a cost-effective solution over time. B2B buyers should evaluate the long-term savings against the higher initial investment. This approach is particularly beneficial for companies anticipating consistent demand for specific products, as the mold’s durability can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
How Can 3D Printed Blow Molds Benefit Rapid Prototyping?
3D Printed Blow Molds are revolutionizing the prototyping phase of product development, offering rapid production and customization capabilities. This method is particularly useful for small batch runs or testing new designs without the substantial investment required for traditional molds. B2B buyers interested in innovative product development should consider 3D printed molds for their flexibility and quick turnaround. However, they should also note that these molds may not withstand the rigors of high-volume production, limiting their application in large-scale operations.
Key Industrial Applications of blow molding mold
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of blow molding mold | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Production of plastic bottles | Cost-effective mass production of lightweight, durable containers | Material compatibility, mold design complexity, and production volume requirements |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of fuel tanks | Enhanced strength and reduced weight of components, leading to better fuel efficiency | Compliance with safety standards, durability under extreme conditions, and cost efficiency |
| Agriculture | Creation of irrigation and storage tanks | Efficient water management and storage solutions, promoting sustainable farming practices | Resistance to environmental factors, customization options for size and shape, and logistical considerations for transportation |
| Consumer Goods | Production of household cleaning bottles | Attractive, functional designs that enhance user experience and brand visibility | Design flexibility, material safety for food-grade applications, and scalability for varying production needs |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of medical fluid containers | Ensures safety and reliability in healthcare applications, critical for patient care | Compliance with regulatory standards, material biocompatibility, and precision in mold design |
How is Blow Molding Mold Used in Packaging?
In the packaging industry, blow molding molds are pivotal for producing plastic bottles used in beverages, cosmetics, and cleaning products. The process allows manufacturers to create lightweight yet durable containers that meet consumer demand for sustainability and convenience. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing molds that can accommodate local material specifications and production capacities is crucial. Ensuring compatibility with various polymers and understanding local regulations can significantly impact the success of packaging solutions.
What Role Does Blow Molding Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Blow molding molds are extensively utilized in the automotive sector for creating components such as fuel tanks and air ducts. The process allows for the production of complex shapes that are both lightweight and robust, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency. For businesses in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing high-quality molds that meet stringent safety standards is essential. Considerations such as material durability and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures are critical for ensuring long-term performance of automotive parts.
How Does Blow Molding Benefit Agricultural Applications?
In agriculture, blow molding molds are crucial for the production of large storage tanks and irrigation systems. These molds facilitate the creation of robust, UV-resistant containers that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, essential for effective water management. For buyers in regions like Africa, where agriculture plays a significant role in the economy, sourcing molds that allow for custom sizes and shapes can enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, logistical aspects such as transportation and storage of these large components must be factored into sourcing decisions.
What Advantages Does Blow Molding Offer for Consumer Goods?
The consumer goods sector leverages blow molding molds to manufacture aesthetically pleasing and functional bottles for cleaning products and personal care items. This method allows brands to enhance their product appeal while maintaining cost efficiency. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, it’s important to consider design flexibility and material safety, particularly for products that may come into contact with food or skin. Understanding local market trends can also inform the design process, ensuring products resonate with consumers.
How is Blow Molding Used in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical field, blow molding molds are utilized to create specialized containers for fluids and other medical applications. The reliability and safety of these products are paramount, as they are integral to patient care. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with health regulations and material biocompatibility is critical when sourcing blow molding molds. Precision in mold design is also vital to ensure that the final products meet stringent quality standards, thus enhancing patient safety and care outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘blow molding mold’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with High Production Costs
The Problem: Many manufacturers in regions like Africa and South America face the challenge of high initial costs associated with blow molding molds. When scaling production, the financial burden can be significant, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This can lead to hesitation in adopting blow molding technology, as the cost of mold creation, maintenance, and modification may seem prohibitive compared to other manufacturing processes.
The Solution: To alleviate high production costs, B2B buyers should consider investing in 3D-printed molds for low-volume runs or prototyping. This method drastically reduces tooling costs and lead times compared to traditional steel molds. Buyers can partner with local 3D printing service providers to create rapid prototypes, allowing for quicker iterations and adjustments based on market feedback. By transitioning to 3D printing, manufacturers can test designs and make necessary changes without incurring the high costs associated with conventional mold-making processes. Furthermore, leveraging local suppliers for materials can reduce shipping costs and lead times, making the overall production more economical.

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality and Defects in Final Products
The Problem: Quality control is a critical concern for buyers in the blow molding industry. Issues such as inconsistent wall thickness, surface defects, and dimensional inaccuracies can lead to significant waste and increased costs, particularly when producing high-stakes products like automotive parts or consumer packaging. This inconsistency often stems from inadequate mold design or poor maintenance practices, which can compromise the integrity of the final products.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-precision molds designed with advanced CAD software that can account for material properties and flow dynamics. It’s essential to collaborate with mold manufacturers that have a proven track record and can provide detailed mold flow analysis to predict how the material will behave during the blow molding process. Regular maintenance and inspections of existing molds should also be scheduled to prevent wear and tear that can lead to defects. Implementing a quality management system (QMS) can help track production metrics and identify deviations early, allowing for timely interventions before products reach the market.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Designs
The Problem: In diverse markets across Europe, the Middle East, and beyond, buyers often face challenges when it comes to customizing blow-molded products to meet specific consumer demands or regulatory standards. The rigidity of traditional molds can limit design flexibility, making it difficult to adapt to changing market trends or customer preferences.
The Solution: To overcome design limitations, manufacturers should explore the use of modular mold systems that allow for easy adjustments and reconfigurations. By sourcing molds that incorporate interchangeable components, companies can adapt their production lines without the need for entirely new molds. Additionally, investing in advanced simulation software can facilitate better design processes, allowing for virtual testing of new shapes and features before physical production begins. Manufacturers should also engage with end-users early in the design process to gather insights on preferences, which can inform modifications that enhance product appeal and compliance with local regulations. This proactive approach not only ensures relevance in the market but also fosters innovation, allowing businesses to stay ahead of competitors.

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
Strategic Material Selection Guide for blow molding mold
What Are the Key Materials for Blow Molding Molds?
When selecting materials for blow molding molds, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact the manufacturing process, costs, and the quality of the final product. Here are four common materials used in blow molding molds, analyzed from a B2B perspective.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for Blow Molding Molds?
Aluminum is a popular choice for blow molding molds due to its excellent thermal conductivity and relatively low weight. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. Aluminum molds are often easier to machine than steel molds, which can reduce manufacturing complexity.
Pros: Aluminum molds offer faster cooling rates, leading to shorter cycle times. They are also less expensive than steel molds, making them a cost-effective option for lower production runs.
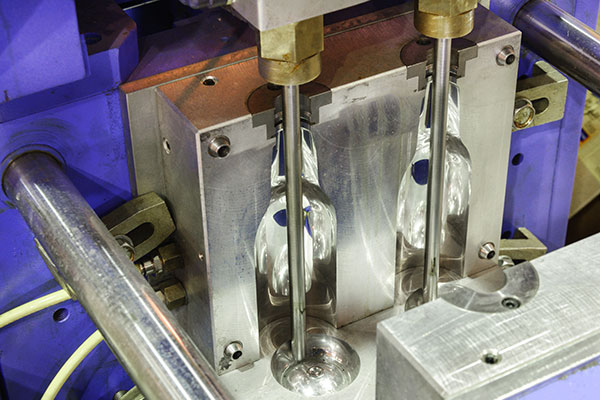

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
Cons: However, aluminum has lower durability compared to steel and may not be suitable for high-volume production where wear and tear are significant concerns. It also has limited resistance to certain chemicals, which could impact its longevity in specific applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum molds are ideal for producing less complex shapes and are commonly used in packaging applications. However, they may not be the best choice for products requiring high strength or chemical resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, especially if the end products are intended for food or medical applications.
What Are the Benefits of Steel in Blow Molding Mold Manufacturing?
Steel, particularly tool steel, is another widely used material for blow molding molds. It offers high strength, durability, and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for high-volume production runs.
Pros: Steel molds can handle higher temperatures and pressures, making them versatile for various applications. Their longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, which can be a significant cost saver in the long run.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher initial cost and complexity in manufacturing. Steel molds are heavier and require more energy to heat and cool, potentially increasing cycle times.
Impact on Application: Steel molds are often used for complex shapes requiring high precision, such as automotive components or specialized packaging. They are also better suited for applications involving aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of steel used and ensure they meet international standards. In regions like Europe, compliance with EU regulations is crucial, especially for safety-critical applications.
How Does Composite Material Compare for Blow Molding Molds?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, are increasingly being used in blow molding molds. They offer a unique combination of lightweight properties and good thermal stability.
Pros: Composites can be molded into complex shapes easily and are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They can also be more cost-effective for low-volume production runs.
Cons: However, composites may not have the same strength and durability as metals, limiting their use in high-pressure applications. They can also be more expensive than aluminum, depending on the formulation.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in industries where corrosion resistance is critical, such as chemical processing or marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet relevant safety and performance standards, particularly in regions where environmental regulations are stringent.
What Role Does 3D-Printed Materials Play in Blow Molding Mold Production?
3D-printed molds are an emerging option in blow molding, utilizing materials like nylon or specialized polymers. These molds can be produced quickly and at a lower cost, making them ideal for prototyping or small production runs.
Pros: The primary advantage is the speed of production and the ability to create complex geometries that traditional methods may not easily achieve. They also allow for rapid iteration during the design phase.
Cons: However, 3D-printed molds may not withstand the same pressures and temperatures as traditional molds, limiting their application in high-volume production.
Impact on Application: 3D-printed molds are excellent for testing new designs or producing small batches of customized products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the material properties and ensure they meet local manufacturing standards, especially in regions with strict quality regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Blow Molding Molds
| Material | Typical Use Case for blow molding mold | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Packaging containers | Faster cooling, lower cost | Less durable, limited chemical resistance | Medium |
| Steel | Automotive components | High strength, long-lasting | Higher cost, heavier, longer cycle times | High |
| Composite | Chemical processing equipment | Corrosion-resistant, complex shapes | Lower strength than metals | Medium |
| 3D-Printed | Prototyping, small production runs | Quick production, design flexibility | Limited durability under pressure | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for blow molding molds, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for blow molding mold
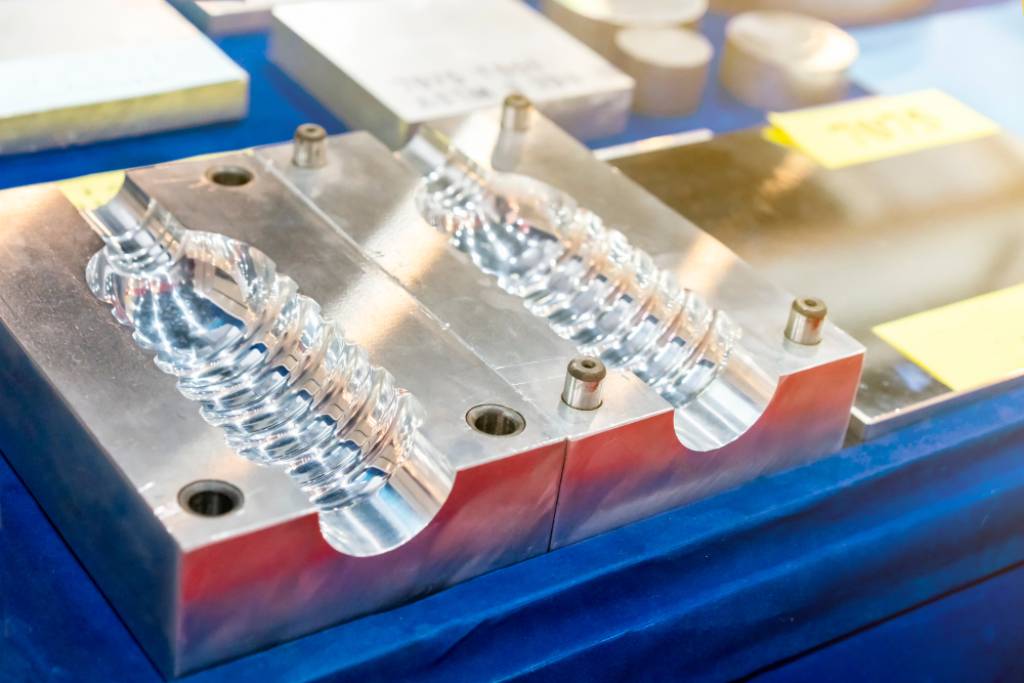
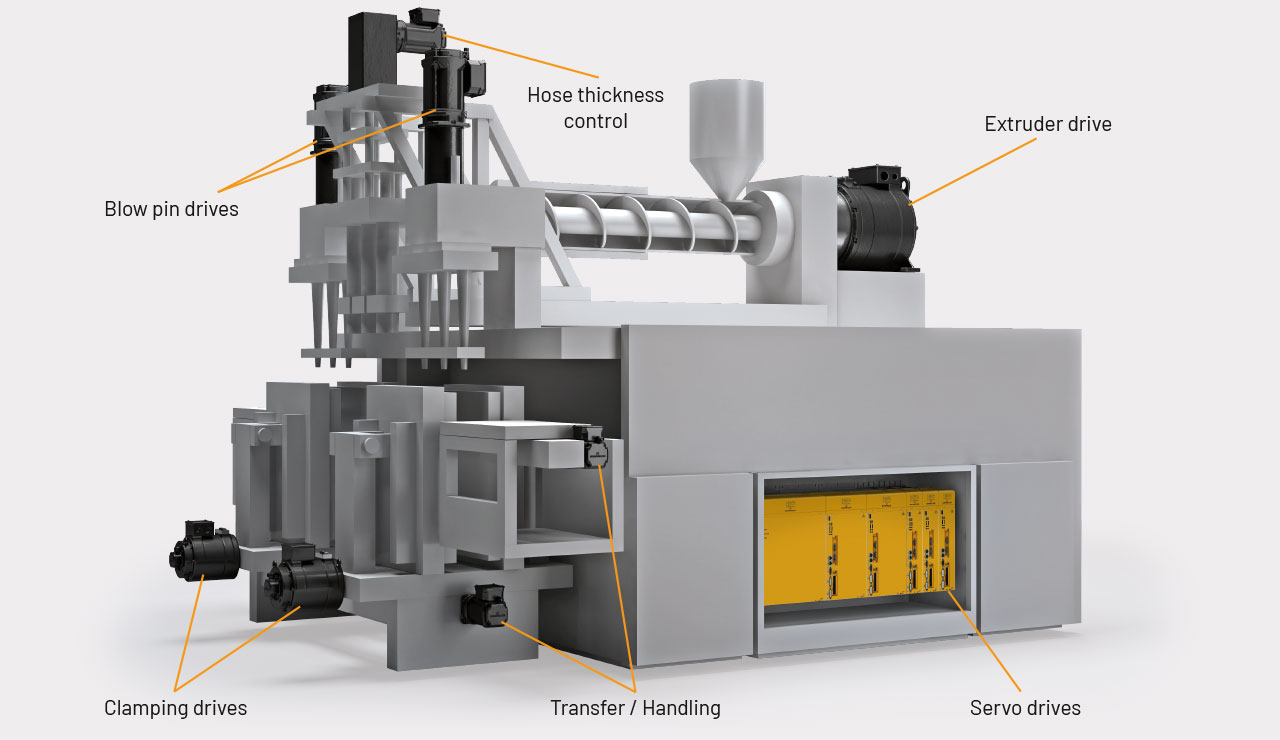
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Blow Molding Molds?
The manufacturing process for blow molding molds is critical in ensuring high-quality end products. The process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages employs specific techniques to achieve precision and efficiency.
How Is Material Prepared for Blow Molding Molds?
Material preparation begins with selecting the appropriate steel or aluminum, which must possess high durability and heat resistance. Common materials include tool steel, such as P20 or H13, which provide excellent wear resistance.
Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
Once the material is selected, it undergoes machining processes such as milling and grinding to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. This stage may also include heat treatment processes to enhance material properties, ensuring that the mold can withstand the pressures and temperatures involved in blow molding.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Blow Molding Mold Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves creating the mold cavities that will define the shape of the final blow-molded products. Techniques such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are commonly employed for precision shaping of the mold. This method allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that are essential for producing detailed products.
In addition to CNC machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM) may be used for creating fine details and intricate features. This technique is particularly useful for achieving high precision in areas that are difficult to machine using traditional methods.
How Is the Assembly of Blow Molding Molds Conducted?
Once the individual components of the mold are manufactured, they need to be assembled carefully. This stage involves fitting together various parts, such as cores, cavities, and cooling channels. Proper alignment and secure fastening are crucial to avoid defects in the final products.
During assembly, mold makers often utilize advanced technologies like 3D scanning to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly. This technology helps identify any misalignments before the mold is put into operation, reducing the risk of quality issues during production.
Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
What Finishing Processes Are Necessary for Blow Molding Molds?
Finishing processes enhance the mold’s surface quality and functionality. Techniques such as polishing, coating, and surface treatment are employed to achieve the desired finish. Polishing is essential for reducing surface roughness, which can affect the quality of the blow-molded product.
Coatings may be applied to improve wear resistance and reduce friction, thereby prolonging the mold’s lifespan. Surface treatments, such as nitriding, enhance hardness and corrosion resistance, making the mold more durable in the long run.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Blow Molding Molds?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of blow molding molds is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers. Compliance with recognized international standards like ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers adhere to systematic quality management principles.

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
How Do Industry-Specific Standards Influence Quality Assurance?
In addition to ISO standards, various industry-specific certifications may be applicable. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold within the European Economic Area, while the American Petroleum Institute (API) certification is crucial for components used in oil and gas applications.
These certifications not only guarantee compliance with safety and quality regulations but also provide a competitive advantage in global markets. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold relevant certifications to ensure product reliability and safety.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in the Blow Molding Mold Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are vital at various stages of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
How Does Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Function?
During IQC, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. This includes checking for material properties, dimensions, and any defects. A robust IQC process prevents defective materials from entering production, which can save time and costs.
What Role Does In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) Play?
IPQC involves monitoring the manufacturing process in real-time. This may include regular inspections of machined components, ensuring that they conform to design specifications. Employing statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help identify variations that may affect quality, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
Why Is Final Quality Control (FQC) Essential?
FQC is the last line of defense before the mold is shipped to the customer. This stage typically involves comprehensive testing of the mold, including dimensional checks, functionality tests, and surface quality evaluations. Ensuring that molds meet all specifications at this stage is crucial for customer satisfaction and compliance with industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Buyers can conduct audits, request quality reports, and seek third-party inspection services to ensure compliance with industry standards.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
During supplier audits, buyers should focus on the supplier’s adherence to quality management systems, documentation of processes, and evidence of continuous improvement initiatives. This insight provides confidence that the supplier is committed to maintaining high-quality standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services offers an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. This additional layer of scrutiny can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that buyers receive products that meet their quality expectations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, including differences in regulations and standards across regions. Understanding local requirements and ensuring that suppliers comply with both international and regional standards is crucial.

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
How Can Buyers Stay Informed About Quality Standards?
Staying informed about evolving quality standards and regulations is essential for B2B buyers. Regularly reviewing industry publications, attending conferences, and participating in relevant training can help buyers remain knowledgeable about quality assurance practices in blow molding mold manufacturing.
By understanding these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for blow molding molds, ultimately ensuring the delivery of high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘blow molding mold’
Introduction
Sourcing blow molding molds is a critical process for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality plastic products efficiently. This checklist serves as a practical guide to ensure that B2B buyers navigate the complexities of mold procurement effectively, especially in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. Specify the type of blow molding process you will use—whether it’s extrusion, injection, or injection stretch blow molding—and detail the materials needed, such as polyethylene or PET. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the molds meet your product standards.
Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in blow molding molds. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your industry, and prioritize those that have experience with your specific mold requirements. Consider factors such as production capabilities, past projects, and customer reviews to gauge their reliability and expertise.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verification of supplier certifications is crucial for ensuring quality and compliance with industry standards. Request documentation that confirms adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. This not only assures you of their manufacturing capabilities but also enhances trust, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, it’s wise to request samples or prototypes of the molds. This step allows you to assess the quality, precision, and design compatibility with your production needs. Ensure that the prototypes are tested under your specific production conditions to evaluate performance and durability.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capacity
Understanding the supplier’s lead times and production capacity is vital for aligning with your project timelines. Inquire about their current workload and estimated delivery times for your order. A reliable supplier should provide transparent timelines and have the capacity to scale production as your needs grow.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and warranty conditions. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality and complexity of the molds. Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that safeguard your interests, such as payment milestones linked to production stages or warranty provisions for defects.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is essential throughout the sourcing process. Set up a communication plan that outlines how you will interact with the supplier during the project. Specify points of contact, preferred communication channels, and frequency of updates to ensure that both parties are aligned and any issues are addressed promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for blow molding molds, ensuring that they secure high-quality products that meet their production needs efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for blow molding mold Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Blow Molding Mold Sourcing?
When sourcing blow molding molds, several cost components must be carefully evaluated to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the overall expenditure. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The type of materials selected for the mold significantly impacts costs. Common materials include aluminum and steel, with aluminum generally being less expensive but offering shorter lifespans compared to steel. Higher-quality materials with enhanced durability can lead to increased costs but may also provide long-term savings.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with skilled personnel involved in the design, manufacturing, and assembly of molds. This can vary by region, with labor costs in emerging markets like Nigeria or Brazil typically lower than in Europe. However, the skill level required for complex molds can necessitate higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to the production process, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Understanding these overhead costs is crucial as they contribute significantly to the final price of the molds.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often one of the most significant expenses in the mold-making process. This includes the design and fabrication of the mold itself. Custom molds designed for specific applications will typically incur higher tooling costs than standard molds.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that molds meet specified quality standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are essential, especially for industries requiring high precision, such as automotive or medical applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs must also be factored into the total cost. This includes the cost of shipping molds from the supplier to the buyer’s location, which can vary depending on distance, shipping method, and customs duties.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary widely depending on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the complexity of the molds being produced.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Blow Molding Mold Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the blow molding mold market:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, smaller orders may incur higher costs as fixed expenses are spread over fewer units.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom molds tailored to specific requirements typically cost more due to the additional design and engineering work involved. Standard molds are less expensive but may not meet all functional needs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material directly affects cost. For instance, using high-performance polymers can lead to higher initial costs but may reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Molds that meet certain international quality standards or certifications may have higher upfront costs but can offer better performance and reliability, reducing the likelihood of defects.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery (Incoterms) can affect overall pricing. Buyers should understand whether costs include shipping, insurance, and other charges to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation can lead to significant savings:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs such as maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. This holistic view can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to achieve higher volumes. Discussing potential future orders can also incentivize suppliers to offer lower prices.
-
Explore Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help in negotiating better terms.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to improved terms, better service, and potentially lower prices in the long run.
-
Be Aware of Local Market Dynamics: Understanding regional market conditions and supplier capabilities can help buyers make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
Sourcing blow molding molds involves a complex interplay of various cost components and pricing influencers. By comprehensively analyzing these factors and employing effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions and achieve favorable outcomes. It’s essential to approach this process with a clear understanding of both immediate and long-term costs, particularly when engaging with suppliers across different international markets.
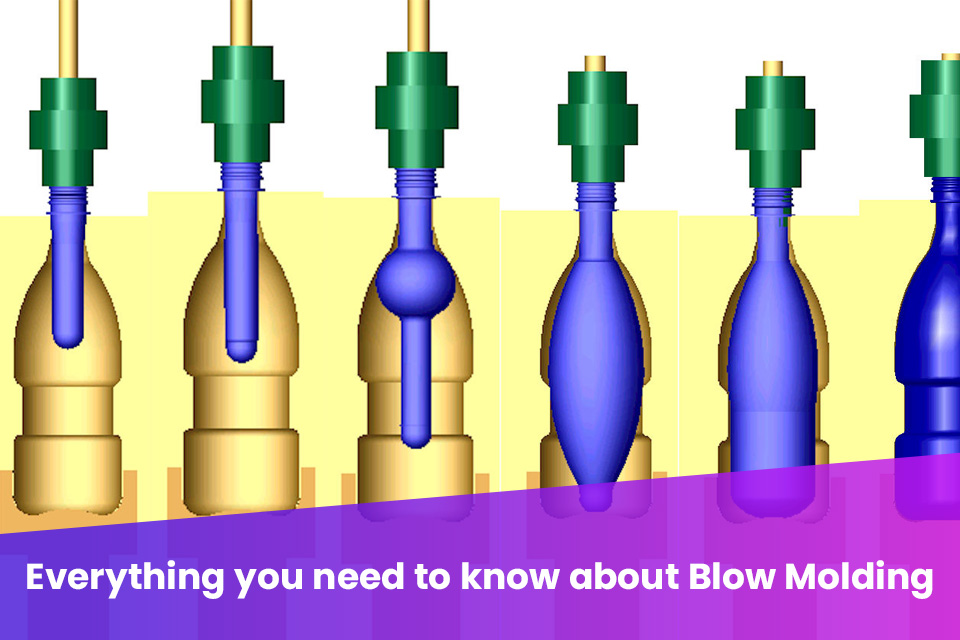
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing blow molding mold With Other Solutions
In the world of manufacturing, particularly for producing hollow plastic parts, blow molding is a widely utilized process. However, there are several alternatives that may better suit specific needs depending on factors like production volume, complexity, and cost. Below, we compare blow molding molds against two viable alternatives: injection molding and rotational molding.
| Comparison Aspect | Blow Molding Mold | Injection Molding | Rotational Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Best for hollow, thin-walled parts; lower per-part cost at scale. | Excellent for complex shapes and high precision; high-quality surface finish. | Good for large, hollow parts; ideal for low-pressure applications. |
| Cost | Lower tooling costs; economical for large volumes. | Higher initial costs; cost-effective for high production runs. | Lower tooling costs; economical for large parts but slower production speed. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery; setup can be complex. | More straightforward for complex designs; requires different molds for each part. | Simple to set up but requires more time for part cooling and curing. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; molds need regular checks for wear. | Generally low maintenance; molds can last long with proper care. | Moderate maintenance; requires regular cleaning to prevent material buildup. |
| Best Use Case | Bottles, containers, and simple shapes in high volumes. | Detailed parts like automotive components and medical devices. | Large tanks, playground equipment, and toys where thickness uniformity is not critical. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a highly effective alternative, especially when producing complex shapes with high precision. This method allows for the creation of parts with intricate geometries and can achieve tight tolerances and superior surface finishes. The initial setup costs for injection molds are generally higher than those for blow molds, making it less economical for low-volume production. However, once the molds are created, injection molding can yield high production rates, making it cost-effective for mass manufacturing.
How Does Rotational Molding Compare to Blow Molding?
Rotational molding is another alternative that stands out for producing large, hollow parts. This method involves rotating a mold while it is heated, allowing the plastic to coat the interior evenly. While rotational molding is excellent for creating large items, it is typically slower than blow molding and may not achieve the same level of detail. Its tooling costs are lower, making it an attractive option for manufacturers needing large parts without the complexity of blow molding.
Conclusion: Which Manufacturing Process Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When deciding between blow molding and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific production needs. For high volumes of hollow, thin-walled products like bottles, blow molding is often the most economical choice. Conversely, if the project requires intricate designs and high precision, injection molding may be the better route. For large, less complex items, rotational molding could provide a good balance between cost and production speed. Ultimately, aligning the chosen method with the product requirements, budget constraints, and expected production volumes will lead to the best outcomes for any manufacturing project.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for blow molding mold
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Blow Molding Molds?
Understanding the technical properties of blow molding molds is essential for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating suppliers or making purchasing decisions. Here are critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material used to construct blow molding molds significantly impacts their durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum and steel, each with distinct advantages. Aluminum molds are lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for low-volume production, while steel molds offer greater strength and longevity, making them ideal for high-volume runs. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the mold can withstand production demands and produce high-quality parts.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in mold design. In blow molding, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring that the final product meets required specifications, particularly for applications requiring precise fits, such as automotive components. Poor tolerances can lead to defects, increased waste, and higher production costs, making it vital to discuss tolerance levels with suppliers before finalizing orders.
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of a blow molding mold affects the appearance and functionality of the final product. A smoother surface finish can enhance the clarity and aesthetic quality of molded parts, particularly in packaging applications. Additionally, specific surface treatments can improve the mold’s resistance to wear and corrosion, extending its lifespan. Buyers should specify their requirements for surface finish to ensure alignment with product goals.
4. Cooling Efficiency
Effective cooling systems integrated into blow molding molds are essential for reducing cycle times and improving production efficiency. Cooling channels must be strategically placed to ensure uniform temperature distribution during the molding process. Buyers should inquire about the cooling capabilities of a mold, as inefficient cooling can lead to defects and longer production times, ultimately impacting overall operational efficiency.
5. Cycle Time
Cycle time refers to the total time taken to complete one production cycle, including heating, molding, cooling, and de-molding. Shorter cycle times can lead to increased production rates and lower costs per unit, making it a critical factor for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes. Understanding the expected cycle time for a specific mold can help buyers assess supplier capabilities and align them with their production requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Blow Molding Molds?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and transactions. Here are some essential trade terms relevant to blow molding molds:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of blow molding, buyers may work with OEMs to develop custom molds tailored to their specific product requirements. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential partners in the supply chain.
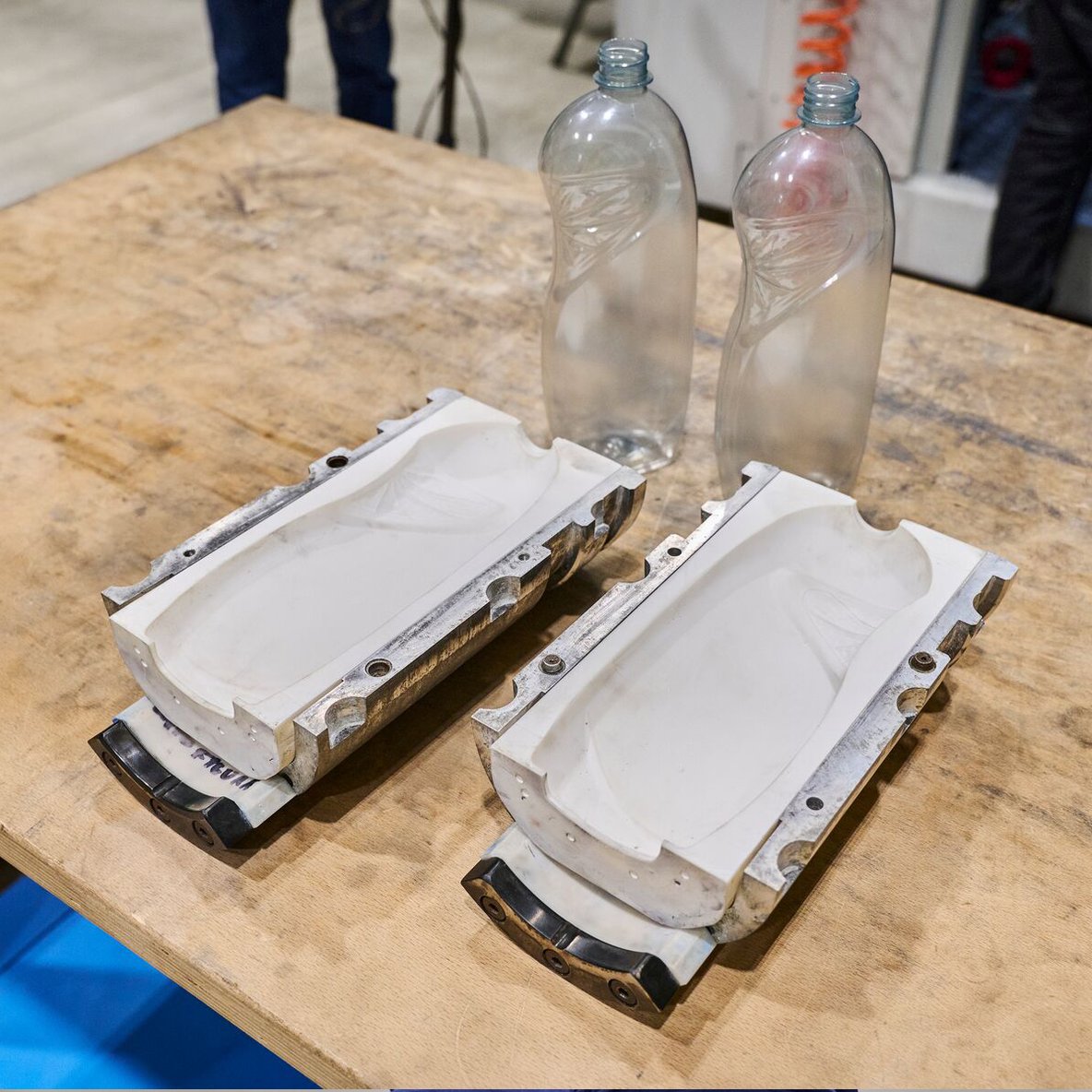

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For blow molding molds, MOQs can vary based on the complexity and material of the mold. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to assess whether a supplier meets their production needs, especially in low-volume scenarios.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process is vital in the B2B landscape, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple vendors for blow molding molds. A well-prepared RFQ helps ensure clarity in specifications, leading to more accurate and competitive quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery points. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing blow molding molds from international suppliers, as they can significantly affect total landed costs and logistics planning.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its delivery. In the context of blow molding molds, lead times can vary based on mold complexity and supplier capabilities. Buyers should clearly communicate their timelines to suppliers to ensure that production schedules align with market demands.

Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their production efficiency and product quality in the competitive landscape of blow molding.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the blow molding mold Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing Blow Molding Mold Sourcing?
The blow molding mold sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable plastic products across various industries—particularly packaging, automotive, and consumer goods—continues to fuel this market. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their production processes, they are turning to advanced blow molding technologies that allow for greater efficiency and lower costs.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing are revolutionizing the blow molding mold landscape, enabling manufacturers to produce molds more quickly and at a lower cost. This trend is particularly beneficial for businesses needing rapid prototyping or low-volume production, as it reduces lead times and allows for design flexibility. Furthermore, the shift towards automation in manufacturing processes is making it easier for companies to maintain consistency and quality in their production lines, which is a critical factor for B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to blow molding mold
In addition to these technological advancements, sustainability is becoming a central focus. Companies are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer eco-friendly materials and sustainable practices, creating a competitive edge for those who can meet these demands. For B2B buyers, understanding these trends and integrating them into their sourcing strategies will be crucial for remaining competitive in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Blow Molding Mold Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a niche consideration; it has become a fundamental aspect of the blow molding mold sector. The environmental impact of plastic production is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek more sustainable practices in their supply chains. Ethical sourcing—ensuring that materials are obtained in a way that is environmentally sound and socially responsible—has become a key priority for international B2B buyers.
The availability of ‘green’ certifications and eco-friendly materials is increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who provide certifications that demonstrate compliance with environmental standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or materials that are recyclable or biodegradable. Additionally, using recycled plastics in blow molding can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of production processes, aligning with global sustainability goals.
For B2B buyers in markets like Africa and South America, where environmental regulations may be evolving, aligning with suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. It also provides a pathway to tap into new markets that value sustainability, ultimately leading to competitive advantage.
What Is the Historical Context of Blow Molding That Shapes Today’s Market?
The blow molding process, with roots tracing back to ancient glass-blowing techniques, has evolved significantly since its patent in 1938. Initially, it was a niche manufacturing method, but the advent of modern plastics transformed it into a mainstream production technique. The introduction of various blow molding processes—such as extrusion blow molding (EBM), injection blow molding (IBM), and injection stretch blow molding (ISBM)—expanded the capabilities and applications of blow molding.
Over the decades, advancements in material science and machinery have led to increased production efficiency and quality. The integration of 3D printing technology for mold design is a recent innovation that highlights how historical processes can adapt to modern demands. This evolution is essential for B2B buyers to understand as they navigate sourcing decisions, ensuring they select suppliers that leverage both traditional expertise and cutting-edge technology to meet current market needs.
In conclusion, staying informed about market dynamics, sustainability practices, and historical context will empower international B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions in the blow molding mold sector, enhancing their competitiveness in a rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of blow molding mold
-
How do I choose the right blow molding mold for my project?
Selecting the right blow molding mold depends on several factors, including the type of product, material specifications, and production volume. Start by defining the shape and size of the hollow parts you need. Consider the complexity of the design, as intricate molds may require injection or stretch blow molding processes. Also, evaluate the material compatibility—common choices include PET, PE, and PP. Lastly, consult with suppliers about their capabilities and experience with similar projects to ensure they can meet your requirements. -
What are the typical lead times for blow molding molds?
Lead times for blow molding molds can vary significantly based on complexity, size, and the supplier’s capabilities. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks for standard molds. However, custom designs or high-precision molds may take longer, sometimes extending beyond 12 weeks. To expedite the process, maintain clear communication with your supplier about your deadlines and consider using rapid prototyping methods, like 3D printing, to validate designs before full-scale production. -
What factors should I consider when vetting a blow molding mold supplier?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience in blow molding and the specific industries they serve. Review their portfolio for past projects similar to yours, and ask for client references to assess reliability. Additionally, consider their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and certifications, such as ISO standards. It’s crucial to understand their supply chain logistics, responsiveness, and customer service, especially for international transactions. -
What customization options are available for blow molding molds?
Customization options for blow molding molds can include variations in mold design, material selection, and surface finishes. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to meet specific product requirements, such as specialized textures or logos. Depending on your needs, you can also explore different molding techniques, such as injection stretch or extrusion blow molding, which can enhance product features. Engage with your supplier early in the design process to discuss these customization options effectively. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for blow molding molds?
Minimum order quantities for blow molding molds vary by supplier and the complexity of the molds. Some suppliers may have an MOQ of just one mold for custom designs, while others may require orders in the range of 50 to 100 units to make production economically viable. Always clarify the MOQ during initial discussions to understand the supplier’s production strategy and to align it with your budget and forecasted demand. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing blow molding molds?
Payment terms for blow molding molds can differ widely among suppliers, often depending on the value of the order and the supplier’s policies. Common arrangements include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon completion or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s trust and commitment to the project. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for blow molding molds?
To ensure quality assurance, it’s vital to establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier before production begins. Request samples or prototypes for evaluation, and consider implementing a quality control plan that includes regular inspections throughout the manufacturing process. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can also indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality. Additionally, consider engaging third-party inspection services for critical projects, especially for international shipments. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing blow molding molds internationally?
When sourcing blow molding molds internationally, pay attention to shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international trade to manage the complexities of cross-border shipping. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Lastly, factor in lead times for shipping and customs processing, as these can significantly impact your overall project timeline.
Top 2 Blow Molding Mold Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Parkway Jars – Blow Molded Plastic Containers
Domain: parkwayjars.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Blow molding is a manufacturing process for hollow plastic parts, primarily using PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) for jars and containers. The main types of blow molding are extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and injection stretch blow molding. Blow molded products include plastic bottles, shampoo bottles, watering cans, coolers, toys, containers, and trays. Parkway offers a selectio…
2. Xometry – Blow Molding Solutions
Domain: xometry.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Blow Molding: A plastic hollow-part forming process ideal for large-scale production, capable of producing 70 parts an hour. Best for simple designs and thin walls, commonly used for bottles and containers. Advantages include shorter cycles, longer mold life, lightweight parts, cost-effectiveness for over 3,000 units per year, and better wall-thickness control. Disadvantages include less design fl…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for blow molding mold
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Blow Molding Mold Procurement?
In the evolving landscape of blow molding, strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chain and manufacturing processes. By understanding the intricacies of blow molding methods—such as extrusion, injection, and stretch blow molding—buyers can align their sourcing strategies with the specific needs of their production lines. This alignment not only helps in reducing costs but also ensures that the quality of molded products meets industry standards.
Investing in high-quality molds and reliable suppliers can significantly enhance production efficiency and product consistency. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, leveraging strategic sourcing will empower businesses to respond swiftly to market demands while maintaining competitive pricing.
Looking forward, the integration of advanced technologies, such as 3D printing for mold production, offers exciting opportunities for innovation and cost reduction. B2B buyers are encouraged to actively seek partnerships with suppliers who embrace these technologies, ensuring they remain at the forefront of the blow molding industry. Embrace strategic sourcing today to secure a sustainable competitive advantage in tomorrow’s market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.