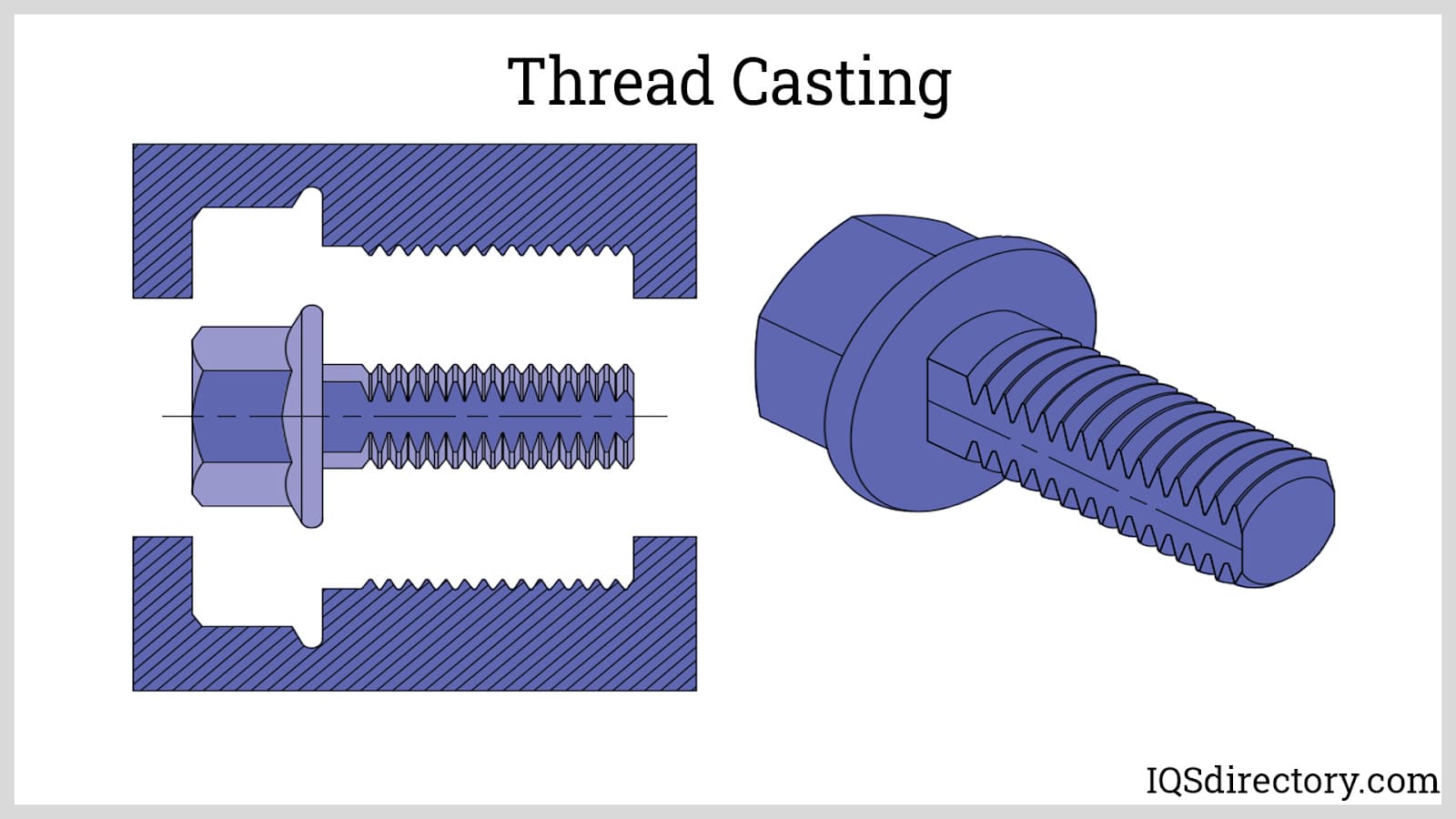
Thread Casting: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thread casting
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing reliable thread casting solutions can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly demand precision-engineered components for various applications—from automotive to construction—understanding the intricacies of thread casting becomes paramount. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into various types of thread casting methods, their applications, and critical factors for supplier vetting.
By equipping buyers with knowledge on cost considerations, production capabilities, and quality standards, this guide empowers stakeholders to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are seeking to source complex threaded components or mass-produce simpler designs, understanding the nuances of thread casting will enhance your ability to navigate the global market effectively.
In an era where operational efficiency and product reliability are non-negotiable, this resource aims to demystify the thread casting landscape, ensuring that your procurement strategies align with industry demands and standards. From identifying reputable suppliers to evaluating cost-effectiveness, the insights provided here will enhance your strategic sourcing efforts and ultimately contribute to your organization’s success.
Understanding thread casting Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Casting Threads | Formed directly in molds; suitable for mass production | Automotive, construction, machinery | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes; Cons: Limited design flexibility. |
| Precision Casting Threads | High precision molds; often used for intricate designs | Aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Excellent accuracy; Cons: Higher production costs. |
| Sand Casting Threads | Utilizes sand molds; adaptable for various thread types | Oil & gas, heavy machinery | Pros: Versatile and economical; Cons: Surface finish may require post-processing. |
| Investment Casting Threads | Uses wax patterns; allows for complex geometries | Electronics, high-performance parts | Pros: Superior surface finish; Cons: Longer lead times. |
| Die Casting Threads | Metal is forced into molds; ideal for high-volume production | Consumer goods, automotive components | Pros: Fast production rates; Cons: High initial tooling costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Casting Threads?
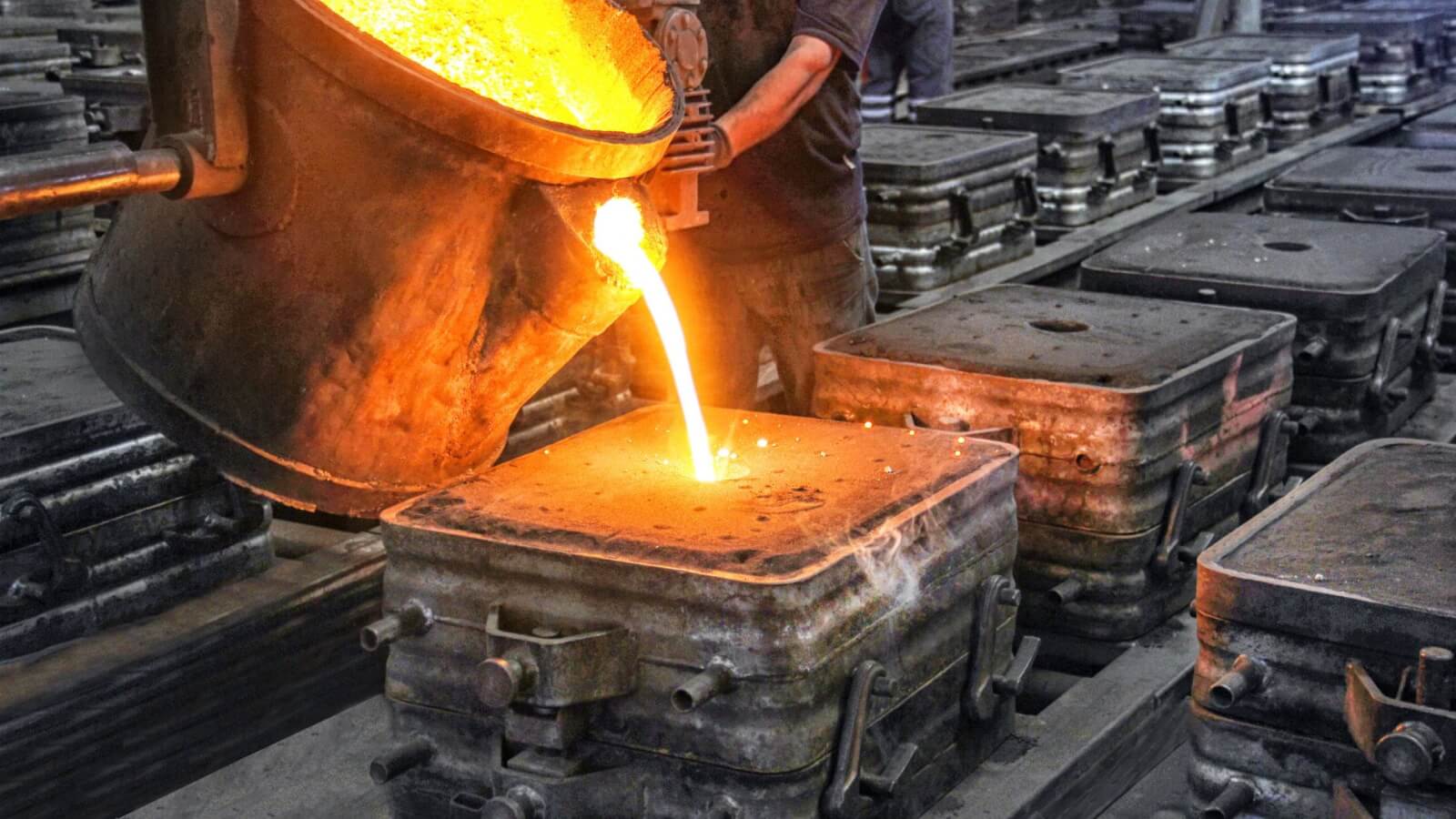
Standard casting threads are produced by pouring molten metal into molds that contain the desired thread shape. This method is particularly advantageous for mass production, allowing companies to produce large quantities efficiently. Commonly used in industries such as automotive and construction, standard casting threads provide a cost-effective solution. However, buyers should consider that the design flexibility is limited compared to other methods, which may restrict customization options.
How Do Precision Casting Threads Differ from Other Methods?
Precision casting threads are made using high-precision molds that allow for intricate designs and tight tolerances. This method is essential in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where accuracy is paramount. While the benefits include exceptional surface quality and dimensional accuracy, buyers should be aware that the production costs are typically higher, making it less suitable for low-budget projects.
Illustrative image related to thread casting
What Are the Advantages of Sand Casting Threads?
Sand casting threads involve creating molds from sand, which can be easily shaped and reused. This process is adaptable and can accommodate various thread types, making it popular in sectors like oil and gas and heavy machinery. The primary advantage of sand casting threads is their versatility and cost-effectiveness, especially for low to medium production runs. However, buyers should keep in mind that the surface finish may require additional processing to meet specific quality standards.
Why Choose Investment Casting Threads for Complex Designs?
Investment casting threads utilize a wax pattern that is melted away to create intricate mold cavities. This method is particularly suited for producing complex geometries found in electronics and high-performance parts. While investment casting offers superior surface finishes and the ability to create detailed designs, buyers should note that it often involves longer lead times, which may impact project timelines.
When to Consider Die Casting Threads for High-Volume Needs?
Die casting threads are created by forcing molten metal into molds, making this method ideal for high-volume production. It is widely used in consumer goods and automotive components due to its fast production rates. The key advantages include the ability to produce large quantities quickly and consistently. However, buyers must be prepared for high initial tooling costs, which may be a barrier for smaller projects or companies with limited budgets.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Key Industrial Applications of thread casting
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thread casting | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing engine components | High precision and durability for threaded connections | Quality assurance, compliance with industry standards |
| Oil & Gas | Production of pipe fittings and valves | Enhanced reliability in high-pressure environments | Material specifications, resistance to corrosion |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural components | Cost-effective mass production of complex shapes | Lead times, customization options |
| Aerospace | Creation of lightweight fasteners | Improved performance and weight savings | Certification requirements, stringent quality checks |
| Electronics | Housing for electronic components | Integration of threads for secure assembly | Compatibility with existing components, precision demands |
How is Thread Casting Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thread casting is crucial for producing engine components such as cylinder heads and manifolds. This process allows for the integration of complex threaded structures directly into cast parts, reducing the need for additional machining. The primary advantage is the enhanced strength and durability of these components, which are essential for high-performance vehicles. Buyers in this industry must ensure that suppliers adhere to strict quality standards and provide components that meet specific regulatory requirements.
What Role Does Thread Casting Play in the Oil & Gas Sector?
Thread casting is extensively used in the oil and gas industry for manufacturing pipe fittings and valves. These components must withstand extreme pressures and corrosive environments, making the integrity of threaded connections vital. By utilizing thread casting, manufacturers can create robust fittings that reduce the risk of leaks and failures. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that meet industry specifications for strength and corrosion resistance, as well as suppliers who can ensure consistent quality across large orders.
How is Thread Casting Beneficial in Construction Applications?
In construction, thread casting is employed to fabricate structural components like beams and support brackets. This method enables the production of complex shapes with integrated threads, facilitating easier assembly and reducing labor costs. The ability to mass-produce these parts efficiently offers significant cost savings for construction projects. Buyers should consider lead times and customization options when sourcing these components, as project timelines can be tight and specific requirements may vary.
Why is Thread Casting Important for Aerospace Fasteners?
The aerospace industry relies on thread casting for creating lightweight fasteners that are essential for aircraft assembly. These fasteners must meet rigorous performance standards while minimizing weight to enhance fuel efficiency. By using thread casting, manufacturers can produce fasteners with integrated threads that maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. Buyers must pay close attention to certification requirements and quality checks, as the aerospace sector demands the highest safety standards.
How is Thread Casting Utilized in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, thread casting is used to create housings for various electronic components, ensuring secure assembly and protection from environmental factors. The integration of threaded features directly into the cast housing simplifies the manufacturing process and enhances product reliability. Buyers should focus on compatibility with existing components and the precision of the threads, as these factors are critical for the overall performance of electronic devices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thread casting’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Thread Accuracy and Integrity
The Problem: One of the most significant issues faced by B2B buyers in thread casting is the challenge of maintaining thread accuracy and integrity. In industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is paramount, any deviation in thread dimensions can lead to catastrophic failures. Buyers often encounter situations where the threads do not meet the specified tolerances, leading to improper fittings or even product recalls. This not only affects operational efficiency but also incurs substantial costs in terms of rework, scrappage, and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing suppliers with robust quality assurance processes. It’s crucial to request detailed documentation of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures used in thread casting. Buyers should consider implementing thorough inspection protocols, including the use of calibrated measuring equipment to verify thread dimensions against specifications. Additionally, establishing long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers can facilitate better communication and continuous improvement in product quality, ensuring that the casting meets exact tolerances consistently.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Material Selection for Thread Casting
The Problem: Another pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity of selecting the right material for thread casting. Different applications require specific materials that can withstand various environmental factors such as temperature, pressure, and corrosion. Buyers often struggle with balancing the mechanical properties of materials like strength and durability against cost-effectiveness. Inadequate material selection can lead to premature failures or the need for additional coatings, further complicating the production process.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should engage in thorough research and consultation with material specialists before finalizing their choices. It’s advisable to create a comprehensive material specification sheet that outlines the application requirements, including load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and any industry-specific standards. Collaborating with suppliers who offer a range of materials—such as high-strength alloys or corrosion-resistant metals—can provide more options. Additionally, conducting pilot tests with various materials can help identify the best fit for specific applications, minimizing risks associated with material failure.
Scenario 3: Inefficiencies in Production Lead Times
The Problem: Production lead times can be a significant concern for B2B buyers involved in thread casting, particularly when there is a high demand for threaded components. Delays in the casting process can stem from various factors, such as inefficient mold designs, lengthy setup times, or supply chain disruptions. These delays can lead to missed deadlines and lost contracts, creating a ripple effect that impacts the entire supply chain.
The Solution: To streamline production lead times, buyers should focus on optimizing their supply chain and production processes. This can be achieved by implementing advanced manufacturing techniques, such as lean manufacturing principles, which aim to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Additionally, investing in flexible mold designs can allow for quicker changes between different thread configurations, minimizing downtime. Buyers should also consider diversifying their supplier base to prevent bottlenecks caused by reliance on a single source. Regular communication with suppliers about demand forecasts can further enhance production planning and responsiveness to changing needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thread casting
When selecting materials for thread casting, it is essential to consider various factors, including performance characteristics, manufacturing complexities, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in thread casting, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Ductile Iron for Thread Casting?
Ductile iron is a popular choice for thread casting due to its excellent mechanical properties. It boasts high tensile strength and good ductility, allowing it to withstand significant stress and deformation without fracturing. Additionally, ductile iron exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when treated with protective coatings, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of ductile iron include its durability and ability to be cast into complex shapes, which is crucial for intricate thread designs. However, its higher cost compared to traditional gray cast iron can be a drawback for budget-conscious buyers. Moreover, the manufacturing process can be more complex due to the need for specific alloying elements.
Impact on Application:
Ductile iron is particularly effective in applications requiring high strength and impact resistance, such as automotive components and industrial machinery. Its compatibility with various media, including oil and gas, enhances its applicability in diverse sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A536 or DIN 1693. In markets like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is higher, the balance between performance and expense is critical.
How Does Aluminum Alloy Perform in Thread Casting?
Aluminum alloys are increasingly favored for their lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. They are ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Aluminum also offers good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum alloys is their low density, which contributes to energy efficiency in transportation applications. However, they may not provide the same tensile strength as ductile iron, which can limit their use in high-stress environments. Additionally, casting aluminum can be more expensive due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum alloys are suitable for applications requiring high corrosion resistance, such as marine environments. Their compatibility with various media, including water and chemicals, makes them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B108 and the need for specific alloy certifications. In regions such as Saudi Arabia and Germany, adherence to environmental regulations regarding aluminum recycling and waste management is also crucial.
What are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Thread Casting?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance, making it an excellent choice for thread casting in harsh environments. It maintains its strength and integrity at elevated temperatures, which is essential for applications in the oil and gas sector.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and ability to withstand extreme conditions, which reduces maintenance costs over time. However, the higher material cost and complexity in machining can be significant drawbacks, especially for large-scale production.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly effective in applications involving corrosive substances, such as chemical processing and marine environments. Its compatibility with various media, including acids and salts, enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 and EN 10088 is essential for international buyers. In markets like Europe, where quality and safety standards are stringent, ensuring traceability and certification of materials is critical.
How Does Bronze Compare in Thread Casting Applications?
Bronze is a traditional material known for its excellent wear resistance and low friction properties. It is particularly well-suited for applications requiring high durability, such as marine fittings and bearings.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of bronze is its resistance to corrosion and fatigue, which makes it ideal for long-lasting applications. However, the cost of bronze can be higher than other materials, and its casting process may require more careful handling due to its brittleness.
Impact on Application:
Bronze is highly compatible with seawater and other corrosive environments, making it a preferred choice in marine applications. Its properties allow for smooth operation in moving parts, reducing wear and tear.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B150 and JIS H 3250. In regions like South America and Africa, understanding local sourcing and availability of bronze can impact procurement strategies.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Thread Casting
| Material | Typical Use Case for thread casting | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ductile Iron | Automotive components, industrial machinery | High tensile strength and ductility | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Aluminum Alloy | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength compared to iron | High |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, chemical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher material cost and machining complexity | High |
| Bronze | Marine fittings, bearings | Excellent wear resistance and low friction | Higher cost and potential brittleness | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for thread casting, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thread casting
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thread Casting?
Thread casting is a specialized manufacturing process that enables the direct formation of threads on components, such as bolts, nuts, and other fasteners. The process is structured into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
How is Material Prepared for Thread Casting?
The first step in thread casting involves selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials for thread casting include various grades of steel, aluminum alloys, and other metals that offer good casting properties.
-
Material Selection: It is vital to choose materials that can withstand the mechanical stresses and environmental conditions the final product will face. For instance, steel is often preferred for its strength, while aluminum may be chosen for its lightweight properties.
-
Melting and Alloying: Once materials are selected, they are melted in a furnace. Alloying agents may be added at this stage to enhance properties like corrosion resistance and tensile strength.
-
Mold Preparation: Molds are designed to create the specific thread profile required. They can be made from sand, metal, or ceramic, depending on the complexity of the thread design and the production volume.
What Techniques Are Used in the Thread Forming Process?
After the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. The casting process itself can be categorized into several techniques:
-
Sand Casting: This is the most common method used for thread casting. A sand mold is created based on the desired thread design. The molten metal is poured into the mold, and once cooled, the mold is removed to reveal the threaded component.
-
Investment Casting: This technique allows for higher precision and complex geometries. A wax pattern is coated with a ceramic shell, and after the shell hardens, the wax is melted away, leaving a cavity for the molten metal.
-
Die Casting: For high-volume production, die casting is often employed. This method involves forcing molten metal into a mold under high pressure, resulting in excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
-
3D Printing: Increasingly, additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, are being used to create molds or even direct thread structures, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization.
How Does the Assembly Process Fit into Thread Casting?
In many cases, the casting process is followed by assembly, especially when multiple components are involved. The assembly stage may include:
-
Thread Inspection: After casting, the threads are inspected for dimensional accuracy and surface finish. This can include visual inspections and the use of gauges.
-
Machining: Sometimes, additional machining processes are required to refine the threads or add other features to the component, such as holes or additional threads.
-
Joining Components: If the final product consists of multiple parts, they are assembled using appropriate methods, such as welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Thread Casting?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and aesthetics of the threaded components. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, galvanizing, or coating can provide additional corrosion resistance and improve surface hardness.
-
Polishing and Deburring: These processes are crucial for improving the surface finish and removing any sharp edges or burrs that may affect the component’s performance or safety.
-
Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure the product meets all specifications before delivery.
What Are the Quality Control Standards Relevant to Thread Casting?
Quality assurance is critical in thread casting to ensure that the final products meet international standards and customer requirements. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This international standard specifies requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products marketed in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensures that products meet the rigorous demands of these sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Thread Casting?
The quality control process in thread casting encompasses several checkpoints to ensure the integrity and reliability of the products:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. Verification of certificates of compliance and material properties is essential.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are performed to monitor the process. This includes measuring dimensions and inspecting the quality of the cast threads at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that the finished product meets all specified requirements. This may involve non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or X-ray inspection to detect any internal defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers adhere to quality control standards. Here are effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting equipment, and assessing staff qualifications.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s performance and adherence to standards over time. This should include metrics related to defect rates, production efficiency, and compliance with industry regulations.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly useful for verifying compliance with international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider for Quality Control?
International buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can help buyers navigate supplier relationships effectively.
-
Regulatory Variations: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local laws and international standards relevant to their products.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Quality control extends beyond the manufacturing floor. Buyers should consider logistics and transportation factors that could affect product quality during shipping.
By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing process and the critical importance of quality assurance in thread casting, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain effectiveness and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thread casting’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for thread casting. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that you select the right supplier and materials for your needs, ultimately leading to successful production and cost efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your thread casting needs. This includes the type of material, dimensions, thread types, and any specific tolerances required. Having precise specifications is crucial for communicating your needs effectively to suppliers and ensuring that the final products meet your operational standards.
- Material Selection: Consider the properties of materials such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weight.
- Thread Standards: Specify whether you need standard or custom threads based on your application.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in thread casting. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and geographical region. A well-curated list of suppliers will streamline your evaluation process.
- Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers that have experience with similar applications or industries.
- Geographical Considerations: Assess the logistical implications of sourcing from different regions, including shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the technical capabilities of each shortlisted supplier to determine if they can meet your specifications. This includes their production capacity, technology used, and quality assurance processes.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
- Production Technology: Look for suppliers that utilize advanced casting technologies, such as CNC machining or 3D printing, which can enhance precision.
- Quality Control: Inquire about their quality assurance protocols and certifications, such as ISO standards, to ensure consistent product quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality of the thread casting. This step is essential to verify that the supplier can deliver products that meet your specifications.
- Performance Testing: Assess the samples for functionality and durability under simulated operational conditions.
- Design Verification: Ensure that the prototypes align with your design requirements and specifications.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in discussions regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. This negotiation phase is critical for establishing a mutually beneficial partnership.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for bulk orders to optimize your budget.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment schedules and any potential penalties for late payments or delivery delays.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before finalizing your order, ensure that your chosen supplier complies with industry standards and regulations. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and ensures product reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Confirm that the supplier adheres to international and local regulations relevant to your industry.
- Certifications: Look for certifications that demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific certifications.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Lastly, set up a clear communication plan with your supplier to facilitate ongoing collaboration. This plan should outline points of contact, reporting frequency, and escalation procedures for any issues that arise.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss production progress and address any potential concerns.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a feedback loop to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with your requirements.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for thread casting, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thread casting Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Thread Casting Sourcing?
When sourcing thread casting components, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials for thread casting include various alloys, such as aluminum, brass, and steel. Prices fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and regional sourcing capabilities.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it is essential to balance this with quality control measures to ensure the finished product meets required standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. A thorough understanding of a supplier’s overhead costs can provide insight into their pricing strategies.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom molds used in the casting process. The complexity of the design affects tooling costs, and these should be factored into the total project budget.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality standards incurs additional costs but is essential to minimize defects and returns. Implementing robust QC measures can enhance the product’s reliability, particularly in international markets where compliance with local regulations is critical.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can add a significant layer to the total cost, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, chosen Incoterms, and shipping method will influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Influences Pricing in Thread Casting Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of thread casting components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to bulk pricing discounts. Establishing clear volume commitments can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific quality certifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should assess whether the added features justify the price increase.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: The level of material quality, along with necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM), will affect pricing. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide the required documentation to avoid future compliance issues.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographic location of the supplier can impact costs. Suppliers in regions with established manufacturing capabilities may offer better pricing structures due to economies of scale.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) used in contracts is crucial. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, all of which can significantly influence the final price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Thread Casting Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing thread casting components, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, focusing on total cost rather than just the unit price. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can lead to favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider factors such as maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime associated with lower-quality products. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to significant savings in the long run.
-
Leverage Regional Advantages: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics and supplier capabilities can yield cost benefits. Establishing relationships with regional suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Monitoring global commodity prices and market trends can provide insights into when to purchase materials or services at more favorable rates.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
While indicative pricing can provide a baseline for negotiations, it is essential to approach each sourcing decision with a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play. Given the variability in costs and the complexity of thread casting, B2B buyers should prioritize building strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring they are aligned with both cost efficiency and quality requirements.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thread casting With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Thread Casting for B2B Applications
In the realm of manufacturing, selecting the right method for producing threaded components is critical. While thread casting offers unique advantages, it is essential to evaluate alternative solutions to ensure that businesses make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. This analysis compares thread casting with thread rolling and 3D printing, two prominent alternatives that serve similar purposes in producing threaded parts.
| Comparison Aspect | Thread Casting | Thread Rolling | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex threads | Excellent for large batches | Versatile but may lack precision |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Low cost per unit in mass production | Higher cost for low volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized molds | Relatively simple setup | Requires advanced technology |
| Maintenance | Moderate; mold wear over time | Low; regular inspection needed | High; technology and software upkeep required |
| Best Use Case | Complex shapes, mass production | High-volume production of standard threads | Prototyping and low-volume custom parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Thread Rolling?
Thread rolling is a highly efficient method that uses rolling dies to form threads on a workpiece. This method excels in high-volume production settings where uniformity and speed are paramount. The cost per unit is significantly lower in mass production scenarios, making it an attractive option for manufacturers focused on reducing expenses. However, thread rolling is best suited for standard thread shapes and may not accommodate complex geometries as effectively as thread casting. Additionally, the initial setup can be straightforward, but the process may require specific equipment and trained personnel.
How Does 3D Printing Compare to Thread Casting?
3D printing represents a transformative technology that allows for rapid prototyping and the production of intricate designs without the need for extensive tooling. This method is particularly advantageous for low-volume production runs or custom parts, where traditional methods may be impractical. However, while 3D printing offers great design flexibility, it may not provide the same level of precision or surface finish as thread casting or rolling. Furthermore, the material costs can be higher, making it less economical for high-volume applications. Maintenance of 3D printers can also be demanding, as it requires ongoing software updates and technical expertise.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Thread Production Method?
When evaluating thread production methods, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the complexity of the thread design, production volume, cost constraints, and available technology. Thread casting is ideal for complex shapes and mass production, while thread rolling is better suited for high-volume, standard threading. On the other hand, 3D printing offers unmatched versatility for custom projects but may come with higher costs and maintenance needs. Understanding these aspects will enable businesses to select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thread casting
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thread Casting?
Understanding the essential technical properties of thread casting is crucial for B2B buyers involved in manufacturing and procurement. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
Material Grade
The material grade directly influences the durability and application of the cast threads. Common materials used in thread casting include various alloys, such as aluminum, steel, and bronze. Each material offers different mechanical properties, like tensile strength and corrosion resistance. For buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures that the final product meets specific performance requirements and industry standards.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in thread casting. It is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, especially in high-precision applications. A tight tolerance can enhance the performance of threaded connections, while a loose tolerance may lead to failures in mechanical assemblies. Buyers must specify tolerance levels to maintain product reliability and quality.
Surface Finish
The surface finish of cast threads can affect both aesthetics and functionality. A smooth surface finish reduces friction during assembly and operation, while a rough finish might be suitable for applications requiring better adhesion. For B2B buyers, understanding surface finish specifications helps in selecting the right threads for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and performance.
Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum load a threaded connection can withstand before failure. This property is vital for applications in construction, automotive, and machinery sectors. Buyers should evaluate load capacity to ensure that the threaded components can handle operational stresses without risking structural integrity.
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability refers to the ability of the cast threads to maintain their shape and dimensions under varying environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity. This property is particularly important for applications in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. B2B buyers should consider this specification to avoid issues related to thermal expansion or contraction.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
What Are Common Trade Terms in Thread Casting?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the thread casting sector. Below are some common trade terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In thread casting, OEMs often provide customized threaded components for specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure tailored solutions that meet their unique requirements.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers when negotiating orders, as it can impact inventory levels and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategies effectively.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In thread casting, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers, negotiate terms, and make informed purchasing decisions. This practice is essential for securing competitive pricing and favorable terms.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help B2B buyers navigate global transactions effectively, ensuring that they are aware of their obligations and risks during the shipping process.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. In thread casting, understanding lead times is vital for inventory management and production scheduling. Buyers should factor in lead times to ensure that they receive their components when needed, preventing delays in their projects.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, enhancing their procurement processes and ensuring the successful integration of threaded components into their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thread casting Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Thread Casting Market?
The global thread casting market is influenced by several dynamic factors, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for precision-engineered components in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction. As manufacturers seek to optimize production processes, they are increasingly turning to advanced technologies such as 3D printing and automated casting techniques, which allow for the rapid production of complex thread designs with enhanced quality.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Emerging trends in sourcing are also shaping the market landscape. Digital transformation is fostering a shift towards online marketplaces and platforms that connect buyers and suppliers more efficiently. In addition, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is enabling manufacturers to streamline operations, improve inventory management, and enhance supply chain transparency. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany are particularly focused on sourcing from suppliers who demonstrate technological proficiency and innovation.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and trade policies are influencing sourcing decisions, as international buyers navigate tariffs and regulatory challenges. As a result, many are looking to diversify their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with reliance on a single market. Understanding these market dynamics and trends is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions in the thread casting sector.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Thread Casting?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly becoming pivotal considerations for B2B buyers in the thread casting sector. The environmental impact of traditional casting methods, which often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable materials, is prompting companies to seek out greener alternatives. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who utilize sustainable practices, such as recycling scrap materials and adopting energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical supply chains are also under scrutiny. Businesses are expected to uphold social responsibility standards, ensuring fair labor practices and transparency throughout their sourcing processes. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who have obtained certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or those that utilize eco-friendly materials in their casting processes. Such certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In regions such as Europe, where regulatory frameworks around sustainability are becoming stricter, the push for ethical sourcing is more pronounced. Buyers who align with suppliers that share their sustainability values can gain a competitive edge, attracting environmentally conscious clients and meeting increasingly stringent market demands.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
How Has the Thread Casting Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of thread casting has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demands. Initially, traditional methods dominated the sector, with manual processes and basic machinery used to create threaded components. However, the introduction of automated casting techniques and computer-aided design (CAD) systems has transformed the landscape, allowing for greater precision and efficiency.
In recent years, the rise of additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, has further revolutionized thread casting. This technology enables the production of complex thread geometries that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods. As industries continue to innovate and seek more efficient production methods, the thread casting sector is poised for continued growth and transformation, adapting to the needs of modern manufacturing.
Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements and sourcing from suppliers who are at the forefront of these developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thread casting
-
How do I choose the right supplier for thread casting?
Selecting a reliable supplier for thread casting involves several key steps. First, assess their experience and expertise in the industry, particularly in your specific sector. Request samples of their previous work to evaluate quality. Check their certifications and adherence to international standards, which can indicate reliability. Additionally, consider their production capacity, lead times, and customer reviews. Establishing clear communication and understanding their terms of service will also help ensure a successful partnership. -
What are the advantages of using thread casting over other methods?
Thread casting offers several advantages, particularly for large-scale production. It allows for complex thread designs to be integrated directly into the casting, reducing the need for secondary machining processes, which can save time and costs. The method is efficient for mass production, providing consistent quality across batches. Additionally, casting can accommodate various materials, making it versatile for different applications, such as automotive, construction, and industrial components. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect for thread casting?
Minimum order quantities for thread casting can vary widely based on the supplier, material requirements, and complexity of the thread design. Typically, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially if they see potential for long-term collaboration. Always confirm the MOQ in advance to ensure it aligns with your project budget and timeline. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my thread casting orders?
To ensure quality assurance in your thread casting orders, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes. This may include inspection reports, testing protocols, and compliance with international standards such as ISO. Consider implementing a third-party inspection service to verify product quality before shipment. Establishing a clear communication channel for addressing potential quality issues during production can also help mitigate risks. -
What payment terms are typically offered for thread casting suppliers?
Payment terms for thread casting can vary depending on the supplier and the nature of the order. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (usually 30% to 50% of the total order) with the balance due upon completion or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established customers. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms in your contract, including acceptable payment methods, to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing thread casting internationally?
When sourcing thread casting internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and delivery timelines. Evaluate whether the supplier can handle logistics or if you need to engage a freight forwarder. Be aware of customs regulations and duties that may apply to your shipments, particularly for countries in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Insurance for your cargo can mitigate risks associated with damage or loss during transport. Clear communication with your supplier about logistics expectations is essential for smooth operations. -
How customizable are thread casting products?
Thread casting products can be highly customizable based on your specific requirements. Most suppliers can accommodate modifications in thread dimensions, designs, and materials. Discuss your project needs in detail with the supplier to explore customization options, including surface treatments and finishing processes. Providing detailed specifications and prototypes can help ensure that the final products meet your expectations. Customization may affect lead times and costs, so factor this into your planning. -
What are the common challenges faced in thread casting, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges in thread casting include defects such as porosity, dimensional inaccuracies, and surface finish issues. To address these, choose a reputable supplier with proven quality control measures. Ensure that the mold design is optimized for the casting process, which can help reduce defects. Conducting pre-production trials and regular quality checks during manufacturing can also mitigate issues. Establishing a feedback loop with the supplier will facilitate continuous improvement and enhance the overall quality of the final products.
Top 3 Thread Casting Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – 3D Printing and Casting Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Introduction: 3D printed screws/threads, custom gear shift knob, Form 2 3D printer, castable wax 40 resin, casting in copper, thread size 16×1.5, modeling software (Maya, ZBrush, 3DSMax), advice on casting threads, using a void for casting, cutting threads with a tap, drilling into final copper part, modeling a hole for drill guidance.
2. iForge Iron – Threading Solutions
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the process of adding threads to cast parts for specific applications, particularly for attaching to plastic resin components. Key considerations include the size of the threads (e.g., under 3/4″ can be hand threaded), the type of threads (internal or external), and the material being cast (brass, steel, aluminum, resin). Participants suggest using taps and dies for …
3. Toth Mold – Injection Molded Thread Solutions
Domain: tothmold.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Casting threads on injection molded parts can involve male or female threads. Male threads are simpler to produce and are cast using an open and shut injection mold. If male threads are vertical, cam action or hydraulic slides are needed due to undercuts. Female threads always present undercuts and require unscrewing to remove from the mold, typically using hydraulic or electrical motors. Hydrauli…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thread casting
As the demand for high-quality threaded components continues to grow across various industries, strategic sourcing of thread casting presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse methods of thread formation, including cutting, forming, and direct casting, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize production efficiency and product quality.

Illustrative image related to thread casting
Investing in strategic sourcing allows companies to not only streamline their supply chains but also enhance their competitive edge in the global market. With the ability to produce complex thread structures directly during the casting process, buyers can benefit from reduced lead times and lower production costs, making it an attractive option for manufacturers in sectors ranging from automotive to construction.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to embrace innovative sourcing strategies that leverage the advantages of thread casting. By forging strong partnerships with reliable suppliers and staying updated on technological advancements, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected marketplace. Take the next step—explore your sourcing options today and unlock the potential of thread casting for your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.