The Definitive Guide to Steam Boiler How It Works: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steam boiler how it works
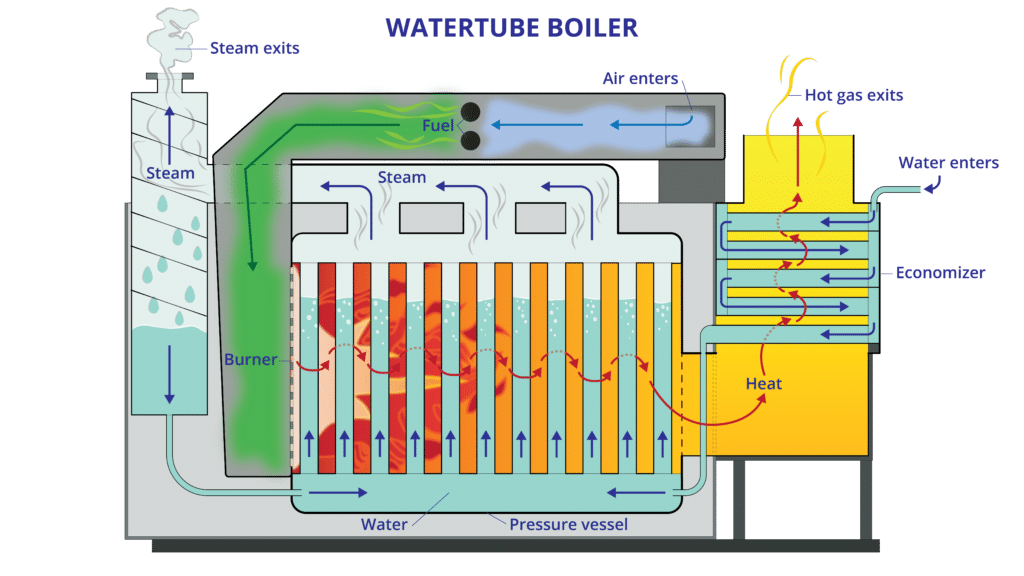
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing an efficient steam boiler that meets both operational demands and regulatory standards can be a formidable challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding how steam boilers work is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific industry needs. This guide delves deep into the mechanics of steam boilers, exploring various types such as firetube and watertube boilers, and their respective applications across industries ranging from food processing to manufacturing.
We will also provide insights into essential factors such as boiler efficiency, fuel types, and the importance of regular maintenance. Additionally, the guide addresses key aspects of supplier vetting, including reliability and compliance with international standards, which are critical for ensuring safe and continuous operations. By navigating through the complexities of steam boiler functionality, B2B buyers can confidently evaluate their options, optimize operational costs, and enhance overall productivity.
This comprehensive resource empowers international buyers with actionable insights, enabling them to make strategic decisions that not only meet immediate needs but also align with long-term business goals. Whether you’re operating in the bustling markets of Vietnam or the industrial hubs of Germany, understanding the intricacies of steam boilers is essential for your success in the global market.
Understanding steam boiler how it works Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firetube Boiler | Flame passes through tubes; simpler design | Manufacturing, food processing, HVAC | Pros: Lower upfront cost; easy maintenance. Cons: Lower efficiency; limited steam pressure. |
| Watertube Boiler | Water flows through tubes; higher pressure capability | Chemical plants, power generation, hospitals | Pros: Higher efficiency; safer at high pressures. Cons: Higher initial investment; complex maintenance. |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electricity to heat water; no combustion required | Residential heating, small-scale industrial use | Pros: Low emissions; compact design. Cons: Higher operational costs; limited capacity. |
| Biomass Boiler | Burns organic materials; renewable energy source | Agriculture, waste management, district heating | Pros: Sustainable; reduces carbon footprint. Cons: Requires fuel supply logistics; potential for higher maintenance. |
| Condensing Boiler | Recovers heat from flue gases; high efficiency | Large industrial processes, commercial buildings | Pros: Very high efficiency; lower fuel costs. Cons: More complex system; higher upfront costs. |
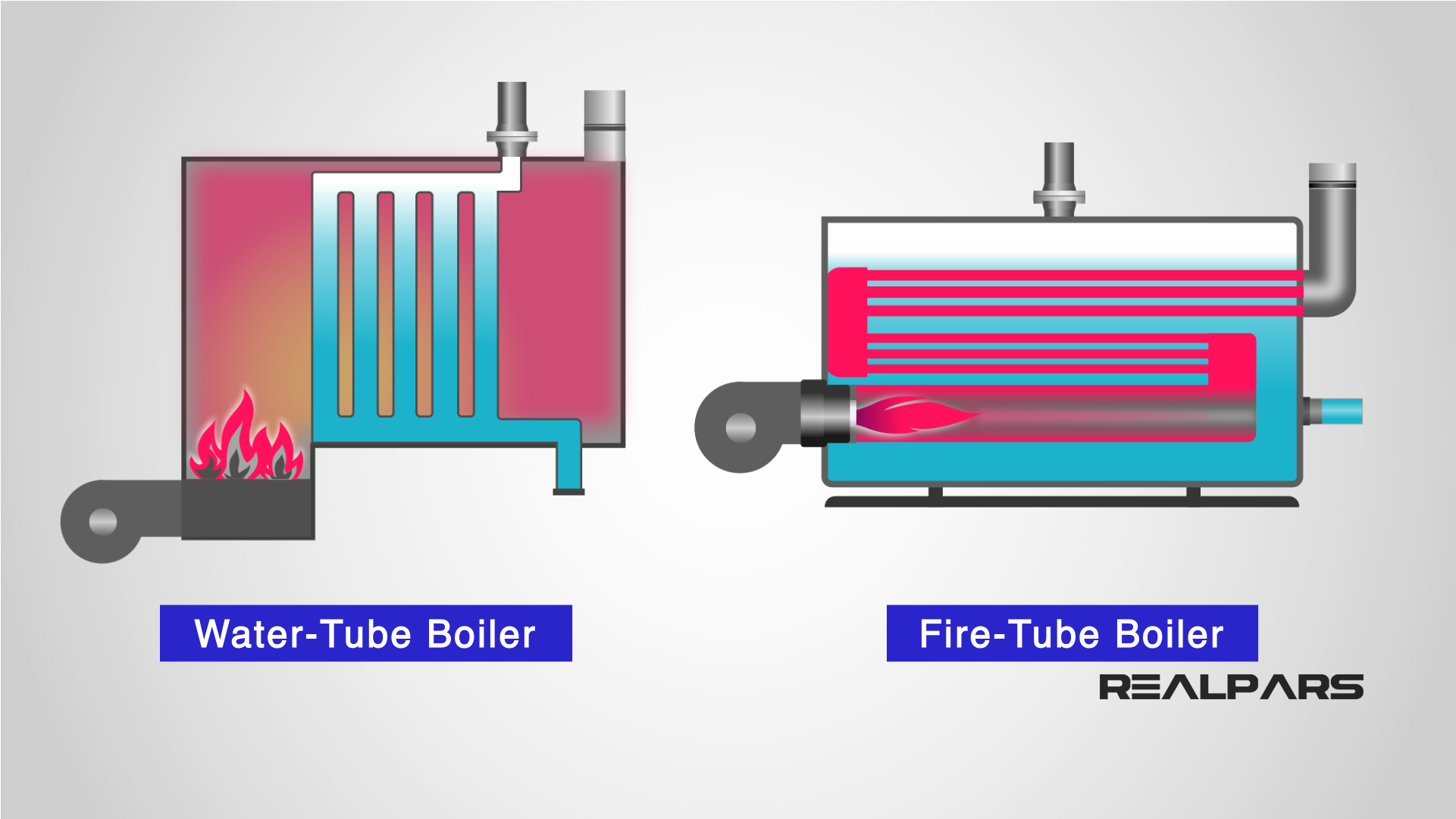
What Are the Characteristics of Firetube Boilers?
Firetube boilers are characterized by their simple design, where hot gases from combustion pass through tubes that are submerged in water. This design makes them easier to maintain and typically results in lower initial costs, making them suitable for smaller manufacturing facilities and food processing plants. However, they operate at lower efficiencies and steam pressures compared to other types, making them less ideal for high-demand applications.
How Do Watertube Boilers Stand Out?
Watertube boilers feature a design where water circulates through tubes heated externally by combustion gases. This allows them to generate higher steam pressures and efficiencies, which is essential for applications in chemical plants and hospitals where reliability is critical. Although they have a higher initial investment and require more complex maintenance, their efficiency and safety in high-pressure environments often justify the costs for larger operations.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers operate without combustion, using electricity to heat water directly. They are particularly well-suited for residential heating and small-scale industrial applications where space is limited and emissions need to be minimized. While they boast a compact design and low emissions, buyers should consider the higher operational costs associated with electricity and the limited capacity for larger industrial applications.
Why Choose Biomass Boilers?
Biomass boilers utilize organic materials, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, as fuel. This renewable energy source appeals to businesses focused on sustainability and reducing their carbon footprint. They are commonly used in agriculture and waste management sectors. However, buyers must account for the logistics of fuel supply and the potential for increased maintenance due to the nature of the fuel.
What Makes Condensing Boilers Efficient?
Condensing boilers are designed to recover heat from flue gases, significantly enhancing their efficiency. They are ideal for large industrial processes and commercial buildings where energy savings can lead to substantial cost reductions over time. Despite their high efficiency and lower fuel costs, the complexity of their systems and higher upfront costs can deter some buyers, necessitating careful consideration of long-term benefits versus initial investments.
Key Industrial Applications of steam boiler how it works
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steam boiler how it works | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Steam generation for cooking, sterilization, and pasteurization | Ensures food safety and compliance with health regulations | Efficiency ratings, safety certifications, and maintenance support |
| Pharmaceutical | Steam for sterilization of equipment and production processes | Guarantees product safety and quality control | Compliance with industry standards and reliable supply chain |
| Textile Manufacturing | Steam for dyeing, finishing, and drying processes | Enhances product quality and operational efficiency | Energy efficiency, boiler capacity, and water treatment systems |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Steam for heating and chemical reactions | Improves reaction efficiency and product quality | Pressure ratings, fuel type compatibility, and safety features |
| Energy Sector | Steam for power generation in thermal power plants | Maximizes energy output and operational reliability | Fuel-to-steam efficiency, regulatory compliance, and scalability |
How is Steam Boiler Technology Applied in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, steam boilers are crucial for various applications, including cooking, sterilization, and pasteurization. These processes ensure food safety and compliance with stringent health regulations. For B2B buyers, sourcing efficient steam boilers is essential to minimize energy costs and ensure consistent steam quality. Key considerations include efficiency ratings, safety certifications, and the availability of maintenance support, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where local service options may vary.
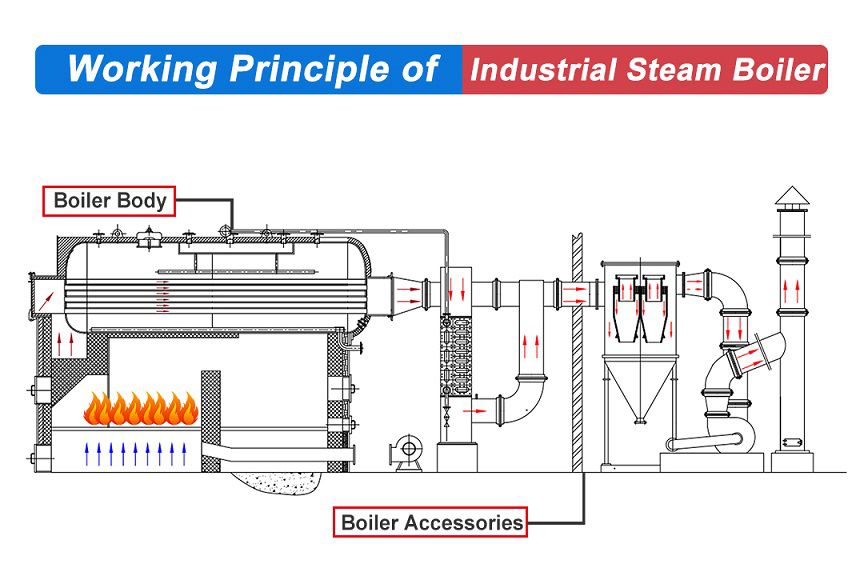
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
What Role Do Steam Boilers Play in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers rely heavily on steam boilers for sterilizing equipment and ensuring the safety of production processes. The high temperatures achieved by steam eliminate harmful pathogens, thereby guaranteeing product quality. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that their steam boilers comply with strict industry standards, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Sourcing considerations should focus on reliable suppliers who can provide equipment with proven safety records and robust support networks, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
How are Steam Boilers Utilized in Textile Manufacturing?
In the textile industry, steam boilers are employed for dyeing, finishing, and drying processes. The use of steam enhances product quality by ensuring even dye application and efficient moisture removal. For international B2B buyers, especially in developing regions, it is essential to consider energy-efficient models that reduce operational costs. Additionally, the capacity of the boiler and the integration of effective water treatment systems are critical factors in sourcing decisions.
What is the Importance of Steam Boilers in Chemical Manufacturing?
Steam boilers are integral to the chemical manufacturing process, providing heat for various chemical reactions and facilitating heating processes. Efficient steam generation can significantly improve reaction rates and product quality, leading to higher profitability. Buyers should prioritize sourcing boilers that meet specific pressure ratings and fuel type compatibility to match their operational needs. Safety features are also paramount, given the hazardous nature of many chemicals involved, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
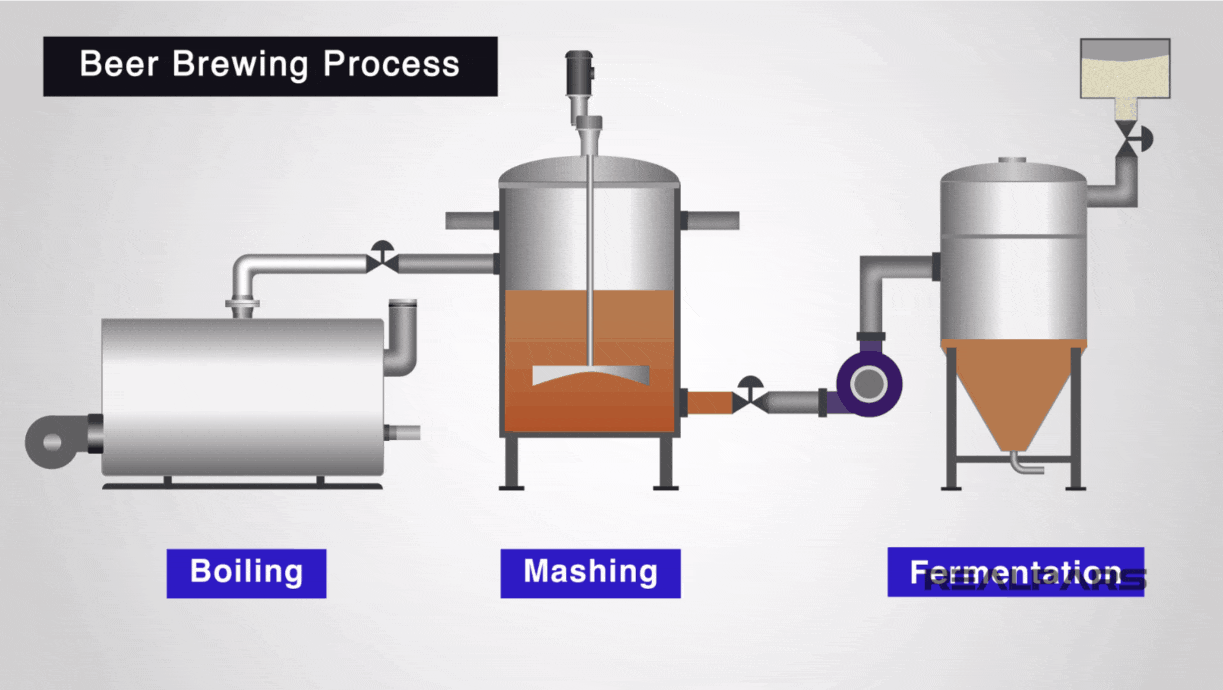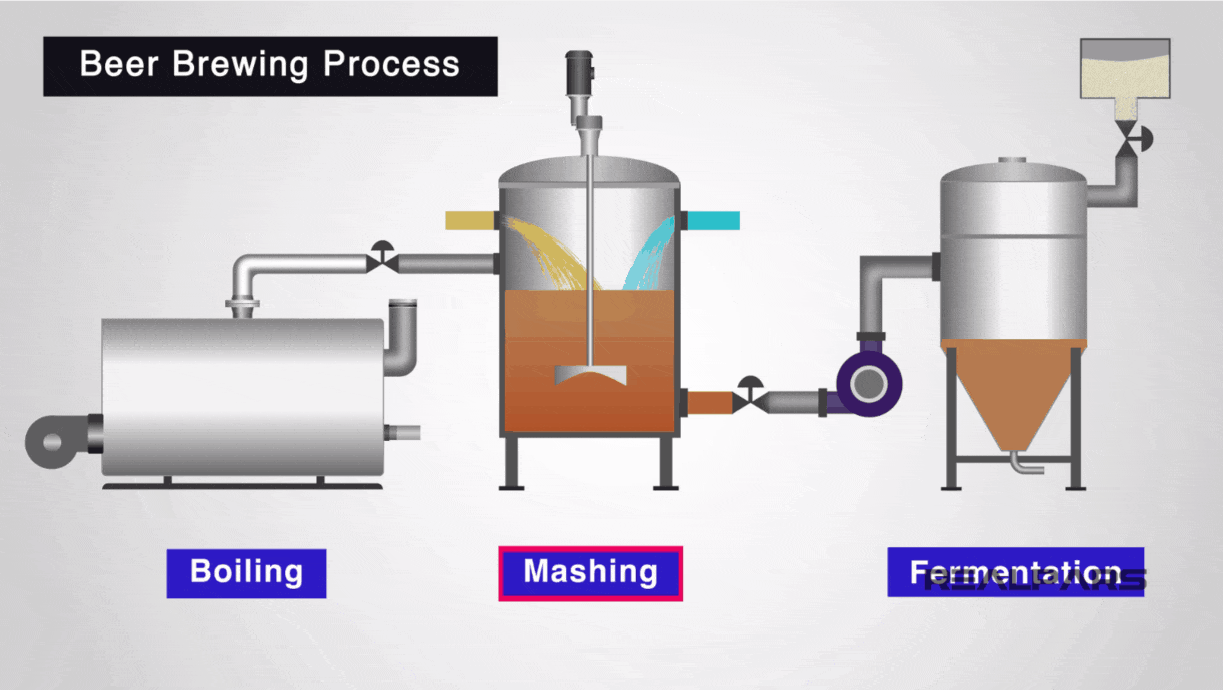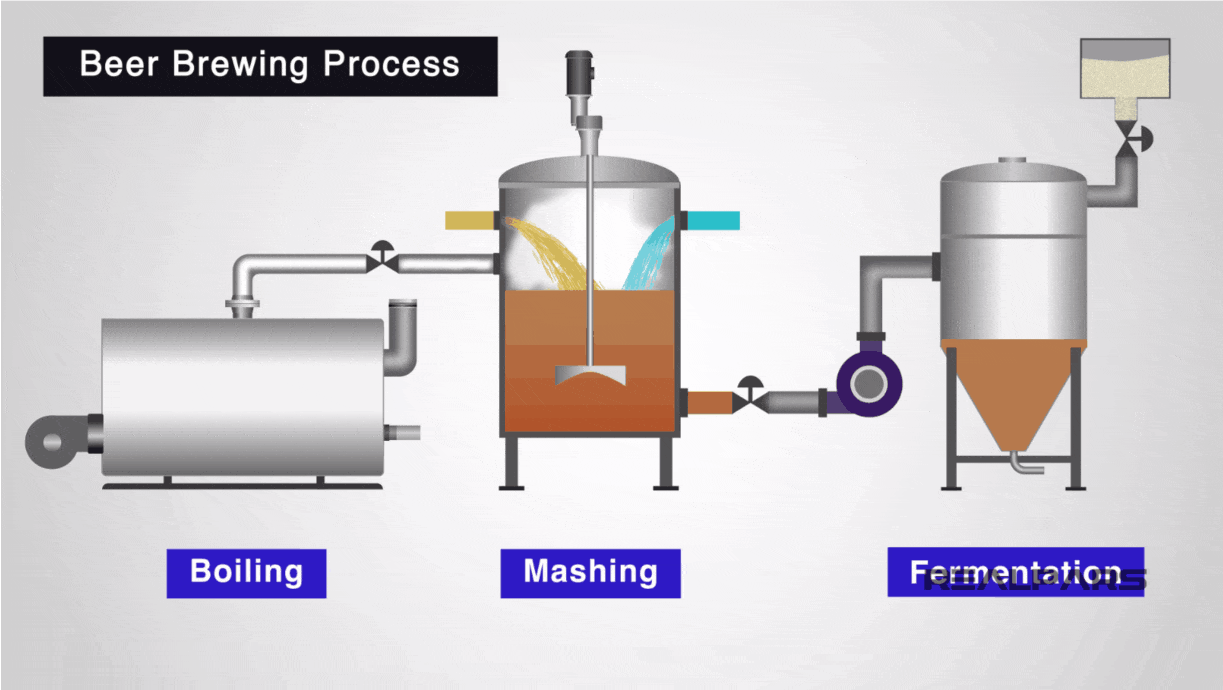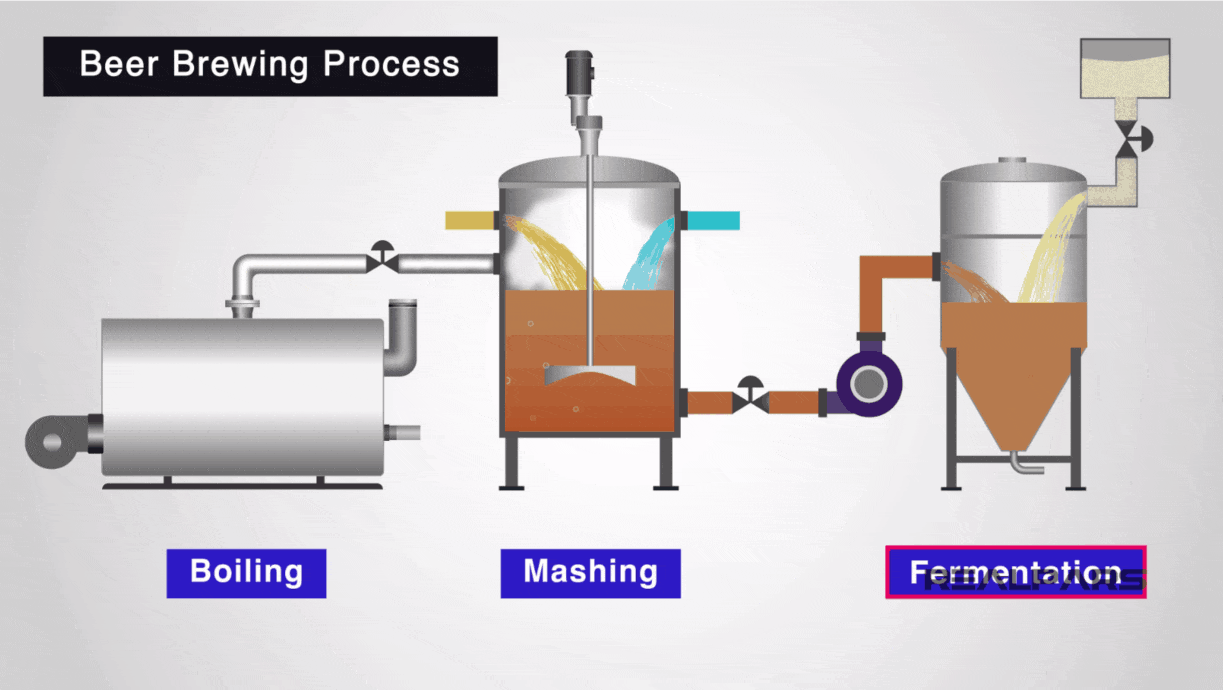
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
How Do Steam Boilers Contribute to the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, steam boilers are essential for power generation in thermal power plants. They maximize energy output by converting heat into steam, which drives turbines for electricity generation. For B2B buyers, sourcing boilers with high fuel-to-steam efficiency is crucial for maximizing operational reliability and minimizing costs. Additionally, understanding regulatory compliance and scalability options is vital for businesses looking to expand their operations in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, and Europe.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steam boiler how it works’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Boiler Efficiency for Cost Control
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing or food processing often grapple with the high operational costs associated with steam boilers. Many do not fully understand how efficiency ratings, like fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency, impact their bottom line. Without a solid grasp of these concepts, businesses may select boilers that are not suited to their operational needs, leading to wasted fuel, increased emissions, and higher maintenance costs. This lack of understanding can significantly affect profitability, particularly in competitive markets.
The Solution: To optimize costs, buyers should prioritize a comprehensive understanding of boiler efficiency ratings before making a purchase. Begin by conducting a thorough analysis of your facility’s steam demand patterns. Utilize this data to assess both fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency ratings of potential boilers. When consulting with manufacturers or suppliers, request detailed operational data and case studies that illustrate how similar businesses have benefited from specific boiler models. Additionally, consider boilers with high turndown ratios; these units can adjust steam output to match varying operational demands, thus improving overall efficiency and reducing unnecessary fuel consumption. Investing in training for operational staff on monitoring efficiency metrics will also foster a culture of cost-consciousness and optimize boiler performance over time.
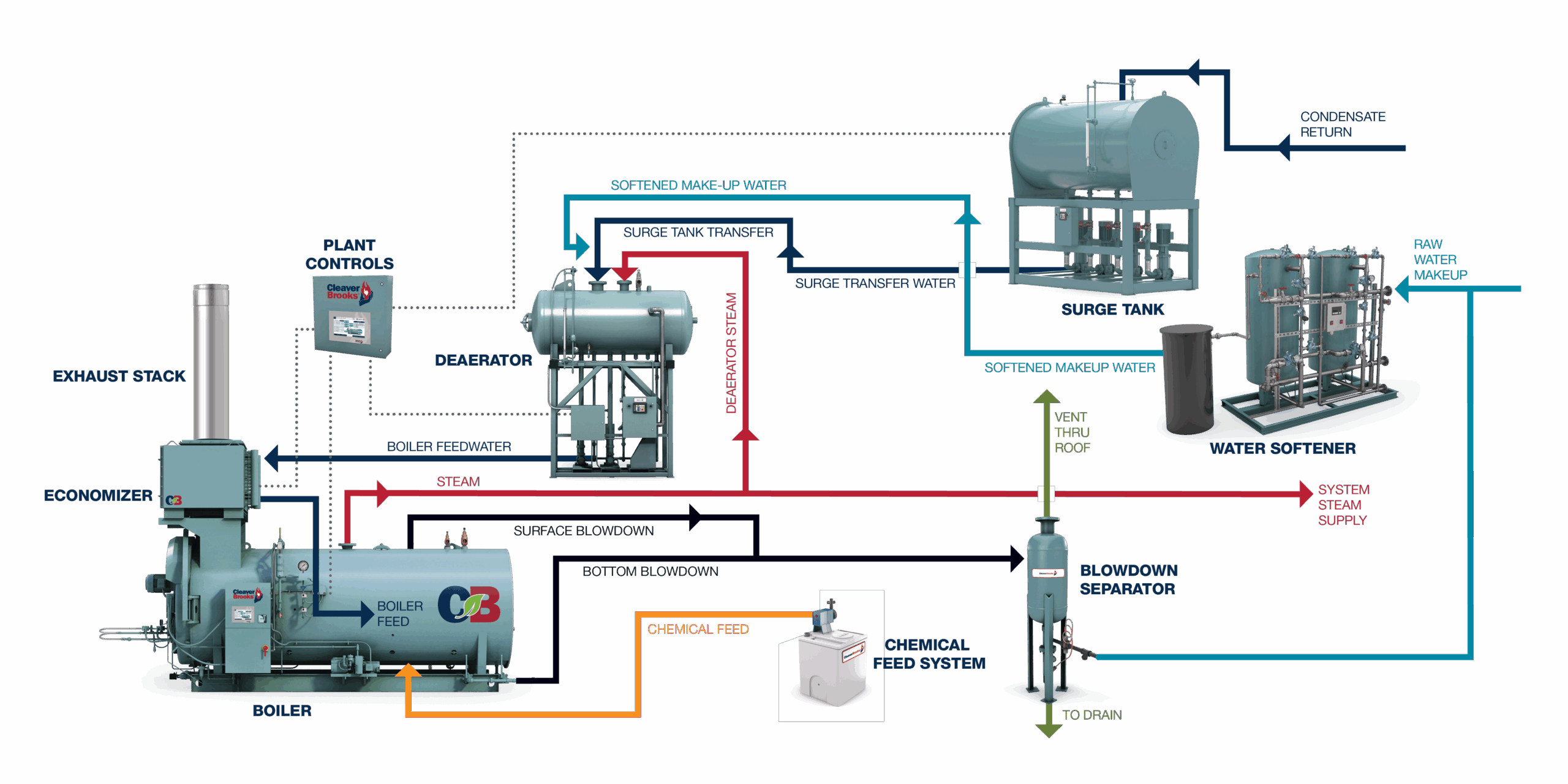
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
Scenario 2: Navigating Boiler Safety Regulations and Compliance
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face the complex landscape of safety regulations and compliance standards for steam boilers. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, stringent regulations govern the operation of boilers, including emissions standards and safety protocols. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, operational shutdowns, and damage to a company’s reputation. This concern is exacerbated in industries where safety is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals and food production, where boiler malfunctions can lead to product contamination or workplace accidents.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the regulatory landscape, buyers should engage with local regulatory bodies early in the procurement process to understand the specific requirements applicable to their operations. Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential compliance gaps, and work with manufacturers who offer boilers designed to meet or exceed these regulations. When selecting a boiler, prioritize features such as advanced emissions control systems and robust safety mechanisms. It’s also advisable to implement a comprehensive training program for employees on safety protocols and emergency procedures associated with boiler operation. Regular audits and maintenance checks conducted by certified professionals can further ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Scenario 3: Efficient Water Treatment for Boiler Longevity
The Problem: Many B2B buyers underestimate the importance of water quality in boiler operations, which can lead to premature equipment failure and increased maintenance costs. Poor water quality can result in scale build-up, corrosion, and operational inefficiencies. This is particularly relevant in regions with hard water or where water treatment practices are not adequately managed. Such issues not only affect the boiler’s performance but can also lead to costly downtime and repairs.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should invest in a comprehensive water treatment program tailored to their specific boiler system. Start by conducting a thorough analysis of the feedwater quality, identifying contaminants such as dissolved solids, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Based on this analysis, consider integrating advanced water treatment solutions such as reverse osmosis systems and chemical dosing systems that can effectively remove impurities before water enters the boiler. Additionally, establish a regular monitoring routine to check water quality and treatment efficacy. Training staff on the significance of water treatment and its direct impact on boiler performance will foster accountability and ensure that best practices are consistently followed. By prioritizing water treatment, businesses can significantly extend the life of their boilers, reduce maintenance costs, and improve operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steam boiler how it works
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Steam Boilers?
When selecting materials for steam boilers, it’s crucial to understand their properties, advantages, limitations, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in steam boiler construction: carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and alloy steels.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Steam Boiler Applications?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and excellent weldability, making it a popular choice for boiler construction. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, typically rated up to 600°F (315°C) and 300 psi, depending on the specific grade.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantages of carbon steel include its durability and low cost, making it an economical choice for many applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance, which can lead to premature failure in harsh environments. Additionally, it may require protective coatings or treatments to enhance its lifespan.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for water and steam applications but may not perform well in environments with high levels of chlorides or other corrosive agents.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A106 or A53 is essential when sourcing carbon steel. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that local suppliers can meet these specifications.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Steam Boiler Construction?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance due to the presence of chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer. It can handle temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and pressures exceeding 1,500 psi, depending on the grade.
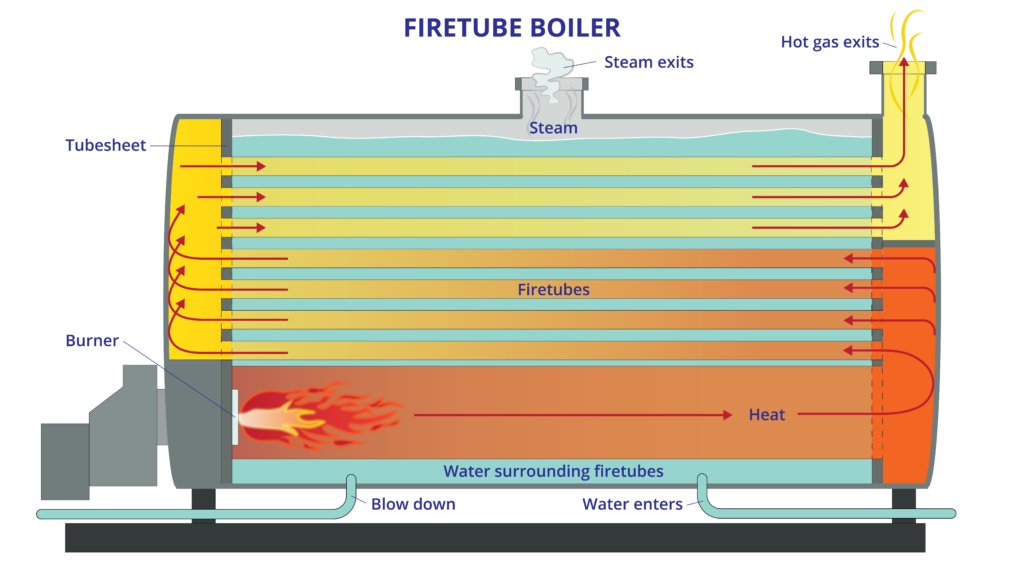
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to oxidation and scaling, making it ideal for high-purity applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to fabricate due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly beneficial in applications involving high-purity steam, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, where contamination must be minimized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A312 and DIN 17440. In Europe, the preference for stainless steel may be driven by stringent environmental regulations.
How Does Cast Iron Compare for Steam Boiler Use?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures. It is typically rated for pressures up to 250 psi and is often used in lower-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of cast iron include its durability and ability to retain heat, which can lead to energy savings. However, it is brittle and can crack under thermal shock or high-stress conditions, limiting its application range.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is suitable for residential and commercial steam boilers but may not be ideal for high-pressure industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A48 is crucial. Buyers in regions with varying climates, such as the Middle East, should consider the thermal shock resistance of cast iron.
What Are the Benefits of Using Alloy Steels in Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Alloy steels are engineered to provide enhanced properties, including improved strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and corrosion. They can operate at high temperatures (up to 1,200°F) and pressures (over 2,000 psi).
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steels is their versatility and performance in demanding environments. However, they are typically more expensive and may require specialized fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application: Alloy steels are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as power generation and chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A335 or JIS G3461, especially in regions like Europe, where regulations may be stricter.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Boilers
| Material | Typical Use Case for steam boiler how it works | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General industrial applications | Low cost and high strength | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-purity steam applications | Superior corrosion resistance | High cost and fabrication complexity | High |
| Cast Iron | Residential and low-pressure commercial boilers | Excellent thermal conductivity | Brittle, prone to cracking | Medium |
| Alloy Steels | High-pressure and high-temperature applications | Enhanced strength and toughness | Higher cost and specialized fabrication | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for steam boilers, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steam boiler how it works
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Steam Boilers?
The manufacturing process of steam boilers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the high standards required for safety and efficiency. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically steel or alloys specifically designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures. The materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry specifications and standards. This includes chemical composition analysis and mechanical property testing to assess tensile strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion.
Once the materials are selected, they are cut to size using advanced technologies such as laser cutting or plasma cutting. This precision ensures that the components will fit together seamlessly during assembly. Additionally, the prepared materials may undergo pre-treatment processes, such as shot blasting, to remove any surface contaminants that could affect the quality of the welds or coatings applied later.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the necessary components for the boiler. This is often achieved through processes such as bending, rolling, and forging. For example, the pressure vessels are typically formed by rolling steel plates into cylindrical shapes and welding the edges together.
Advanced techniques, including hydroforming and stamping, may also be employed to create complex shapes that optimize the boiler’s efficiency and performance. The use of computer numerical control (CNC) machines in this stage allows for high precision and repeatability, crucial for maintaining quality across multiple units.
How is the Assembly Process Conducted?
Assembly is a critical phase where the individual components come together to form the complete steam boiler system. This process typically involves several key steps:
-
Welding: High-quality welding techniques, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or MIG (Metal Inert Gas), are utilized to join components securely. The welding process is closely monitored to ensure that it meets the required standards for strength and integrity.
-
Installation of Internal Components: Internal components such as burners, economizers, and heat exchangers are installed. Each component is checked for compatibility and functionality to ensure optimal performance.
-
Pressure Testing: Once assembled, the boiler is subjected to pressure testing to verify that it can withstand operational pressures without leaks. This is a critical safety measure that helps identify potential weaknesses in the structure.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings and conducting final inspections to ensure the boiler is ready for operation. Common finishing processes include:
-
Surface Treatment: Coatings such as epoxy or polyurethane are applied to protect against corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for boilers that will operate in harsh environments.
-
Final Assembly Checks: All connections, fittings, and controls are thoroughly inspected and tested to ensure they function correctly. This includes calibration of control panels and safety devices.
-
Documentation: Comprehensive documentation is prepared, detailing the specifications, test results, and certifications of the boiler. This documentation is crucial for compliance with international standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an essential aspect of steam boiler manufacturing, ensuring that products meet safety and efficiency standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 are commonly adopted, focusing on quality management systems to enhance customer satisfaction.
How Do Industry-Specific Standards Apply to Steam Boilers?
In addition to general quality management standards, steam boilers must comply with industry-specific certifications such as:
-
CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For boilers used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that products are designed and manufactured to withstand the specific conditions of this sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and verify compliance with standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages helps identify any deviations from quality standards early in the process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection and testing phase before the boiler is shipped. This includes pressure tests, performance tests, and safety checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers seeking to ensure the quality of their steam boiler suppliers can implement several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices and adherence to industry standards. This allows buyers to assess the effectiveness of the supplier’s QA processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the testing and inspection processes conducted during manufacturing. This documentation can reveal the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing processes and final products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality. Such inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is vital. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations, which can affect product acceptance. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Ensure that the supplier meets the specific regulatory requirements of the buyer’s region. This may include obtaining local certifications or compliance with regional codes.
-
Documentation of Compliance: Suppliers should provide documentation proving compliance with international standards, which can facilitate smoother importation processes.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can enhance communication and collaboration with suppliers, ensuring a more effective quality assurance process.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing steam boilers, ensuring they select reliable and efficient products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steam boiler how it works’
To assist international B2B buyers in understanding and procuring steam boilers effectively, this practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist. The aim is to streamline the selection process and ensure that buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential to ensure the steam boiler meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as steam pressure, capacity, fuel type, and efficiency ratings. Understanding these specifications will help narrow down options that align with your industrial processes.
Step 2: Research Different Boiler Types
Familiarize yourself with the two main types of steam boilers: firetube and watertube. Firetube boilers are generally more compact and simpler, suitable for smaller applications, while watertube boilers are designed for higher pressures and larger capacities, making them ideal for extensive industrial use. Knowing the differences will aid in selecting the right type for your facility.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients, especially those in similar industries. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in delivering reliable and efficient steam boilers to ensure you partner with a reputable source.
Step 4: Check for Certifications and Compliance
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with local and international standards. Certifications such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) are indicators of quality and reliability. This step is crucial to ensure safety and performance in your operations.
Step 5: Assess Boiler Efficiency Ratings
Investigate the fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency ratings of the boilers you are considering. Higher efficiency ratings mean lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact. Look for boilers with advanced features like economizers, which enhance efficiency by recovering waste heat.
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
Step 6: Inquire About Maintenance and Support Services
Understanding the maintenance requirements and support services offered by the supplier is vital for long-term operations. Ask about the availability of spare parts, maintenance contracts, and technical support. A reliable supplier should provide comprehensive service options to minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of your boiler.
Step 7: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Finally, request detailed quotes from shortlisted suppliers and compare costs against the specifications and services provided. Ensure that you account for both initial purchase costs and long-term operational expenses, including maintenance and fuel. This comprehensive comparison will help you make a financially sound decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of steam boiler procurement with confidence, ensuring they select the right solution for their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steam boiler how it works Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Steam Boilers?
When sourcing steam boilers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-strength steel, used in pressure vessels, and specialized alloys for high-efficiency boilers can drive up costs. Additionally, the use of advanced materials for components such as heat exchangers and burners can further increase expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the boiler design. Skilled labor is required for assembly, welding, and quality assurance, which can be more expensive in developed markets compared to emerging economies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with the production of steam boilers, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Understanding the overhead costs can provide insights into the overall pricing strategy of a supplier.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery can be significant, especially for custom boiler designs. This cost is often amortized over the production volume, affecting unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that a boiler meets safety and efficiency standards is critical. QC processes, including testing and certification, add to the cost but are essential for compliance, especially in international markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the destination and the Incoterms agreed upon. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can affect the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences Pricing for Steam Boilers in B2B Markets?
Several factors can influence the pricing of steam boilers, particularly in international B2B transactions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide discounts for larger order quantities, making it cost-effective for buyers to consider bulk purchases. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help in negotiating better prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized boilers tailored to specific applications typically incur higher costs. Buyers should assess their requirements carefully to balance customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of fuel type and boiler design (firetube vs. watertube) can affect the cost. For instance, watertube boilers, while more efficient, generally have higher upfront costs than firetube models.
-
Quality and Certifications: Boilers that meet specific international quality standards may command higher prices. Buyers should factor in the costs associated with certifications when evaluating suppliers.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and service levels of suppliers can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may offer premium products with better after-sales support, justifying a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs, insurance, and risk. Understanding these terms can help buyers accurately calculate total costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers Negotiating Steam Boiler Prices?
-
Leverage Negotiation Skills: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing. Buyers should come prepared with market research and an understanding of competitor pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and longevity.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional price differences and currency fluctuations. Engaging local representatives can provide valuable insights into market conditions.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market landscape. This practice helps in making informed decisions and identifying potential cost-saving opportunities.
-
Be Mindful of Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s crucial to recognize that prices may vary significantly based on the factors discussed. Buyers should seek detailed quotes and clarifications on pricing structures to avoid unexpected costs.
Understanding these aspects of cost and pricing analysis will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing steam boilers, ultimately leading to better procurement outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steam boiler how it works With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Steam Boilers
In the quest for efficient heat generation and steam production, businesses often consider various technologies. While steam boilers have long been a staple in industrial processes, alternative solutions can provide different benefits depending on the specific application and requirements. This section explores several viable alternatives to steam boilers, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Steam Boiler How It Works | Electric Boiler | Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-pressure steam generation; suitable for various applications | Lower steam pressure; suitable for smaller applications | Efficient heating and cooling; lower temperature steam |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing fuel costs | Lower initial cost; higher electricity costs | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant infrastructure; complex setup | Easier to install; minimal infrastructure changes | Requires space for outdoor unit; installation can be complex |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; checks on pressure and efficiency | Low maintenance; mainly electrical checks | Moderate maintenance; refrigerant checks needed |
| Best Use Case | Large industrial operations needing high steam output | Small commercial or residential settings | Climate-controlled environments needing heating and cooling |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Boiler
Electric boilers utilize electrical energy to heat water and generate steam. They are more suitable for smaller applications, such as residential or light commercial settings, where high steam pressure is not a critical requirement. The main advantage of electric boilers is their ease of installation and low maintenance needs, as they do not require extensive fuel storage or handling. However, their operational costs can be higher due to electricity prices, making them less ideal for larger industrial operations where steam demand is significant.
Heat Pump
Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide both heating and cooling. They work by transferring heat from one location to another, making them energy-efficient options for temperature control. While heat pumps can generate low-temperature steam, they are primarily designed for space heating and cooling rather than high-pressure steam applications. Their moderate initial investment and lower operational costs make them attractive for businesses looking to enhance energy efficiency. However, their installation can be complex and may require significant space for outdoor units, which could be a limitation in some settings.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the right heat generation solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the scale of steam production, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance capabilities. Steam boilers remain the preferred choice for large industrial processes requiring high-pressure steam. In contrast, electric boilers and heat pumps can serve effectively in smaller or more energy-conscious environments. A thorough analysis of each alternative’s advantages and limitations will guide businesses in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial strategies. By understanding the nuances of each option, buyers can optimize their investments in heat generation technology.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steam boiler how it works
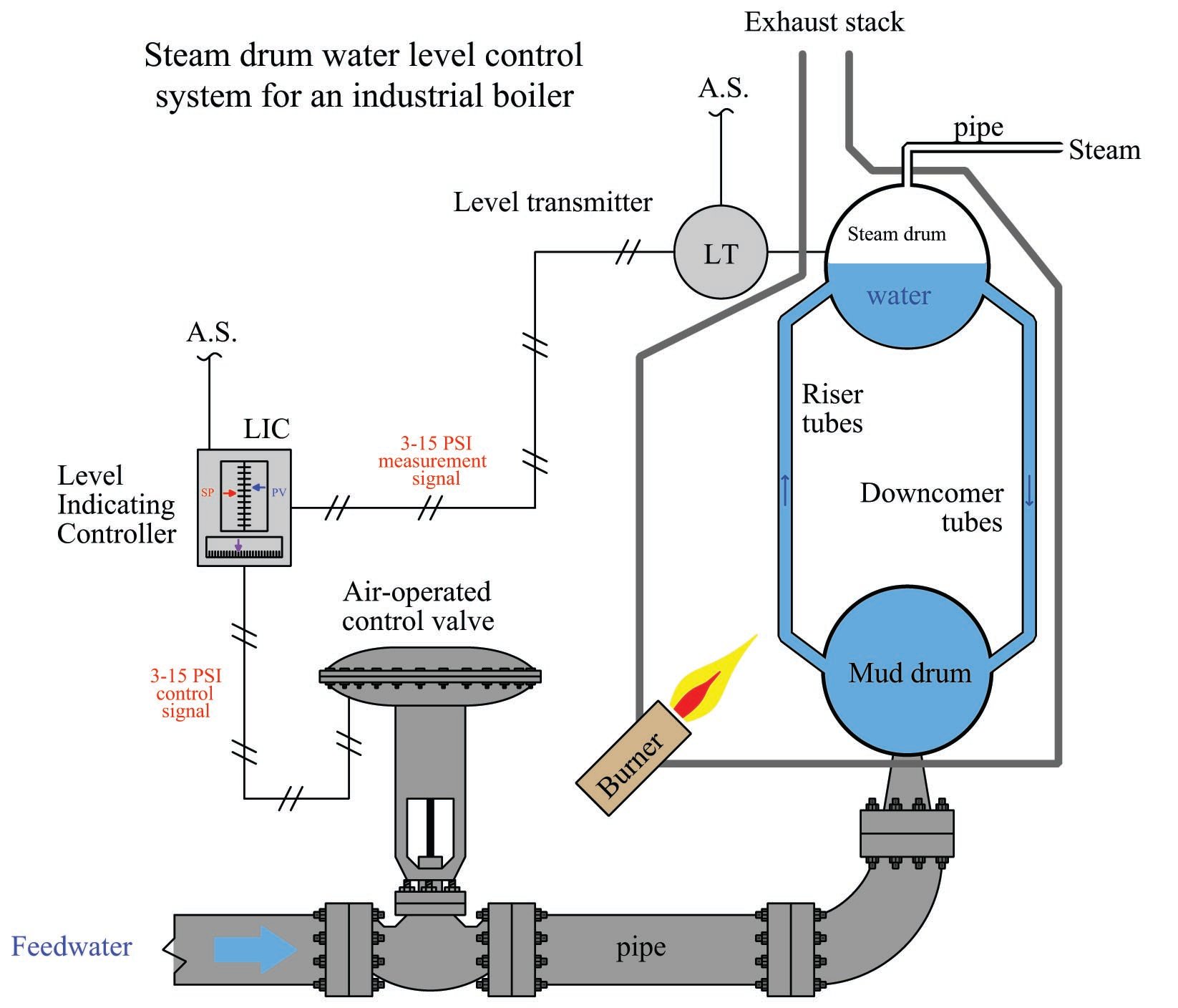
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steam Boilers?
When evaluating steam boilers, several critical specifications can significantly influence the purchasing decision. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and safety in their operations.
1. Material Grade
Steam boilers are typically constructed from high-strength materials such as carbon steel or stainless steel. The material grade affects the boiler’s durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature. For international buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial to meet local regulations and ensure the longevity of the equipment.
2. Maximum Operating Pressure
This specification indicates the highest pressure at which the boiler can safely operate. It’s vital for determining the boiler’s suitability for specific applications. A higher maximum operating pressure often translates to greater steam output and efficiency, making it a critical consideration for industries that require large volumes of steam, such as manufacturing and food processing.
3. Heat Transfer Efficiency
This property measures how effectively the boiler converts fuel into usable steam. High heat transfer efficiency reduces fuel consumption, which can lead to significant cost savings over time. For B2B buyers, understanding this metric is essential for evaluating the long-term operational costs of a steam boiler.
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
4. Turndown Ratio
The turndown ratio reflects the boiler’s ability to modulate its output to match varying steam demands. A higher turndown ratio allows for better efficiency and energy conservation, particularly in facilities with fluctuating steam needs. This feature is particularly beneficial for industries that experience seasonal or demand-based variations.
5. Boiler Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of a boiler are typically measured in horsepower or BTUs (British Thermal Units). This specification determines how much steam can be generated in a given time frame. B2B buyers must assess their specific operational needs to select a boiler that can provide adequate steam without being oversized, which can lead to inefficiencies.
6. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in steam boiler operations. Essential safety features include pressure relief valves, low-water cutoffs, and automatic shut-off systems. Understanding these components is crucial for ensuring compliance with safety regulations and minimizing the risk of operational hazards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Steam Boiler Industry?
Navigating the steam boiler market requires familiarity with specific trade terms that can affect procurement processes and negotiations.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the steam boiler industry, buyers may source boilers from OEMs that provide specific configurations or customizations. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are getting quality equipment tailored to their needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For steam boilers, MOQs can affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies that may not require large quantities. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers negotiate better terms and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications and quantities needed. In the steam boiler market, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and features from various manufacturers, ensuring they make informed decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms is critical for B2B buyers as they clarify costs, risks, and logistics associated with transporting steam boilers from manufacturers to their facilities.
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
5. ASME Certification
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) certification indicates that a boiler meets specific safety and performance standards. This certification is often required for compliance in many industries. Buyers should prioritize ASME-certified boilers to ensure they meet legal and safety requirements.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period specifies the time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the boiler against defects. A longer warranty can provide peace of mind to buyers, indicating the manufacturer’s confidence in their product. Understanding warranty terms is essential for assessing the long-term value of the investment.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements in the steam boiler market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steam boiler how it works Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Steam Boiler Sector?
The steam boiler sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and market demands. Globally, the push for energy efficiency and reduced emissions is prompting businesses to adopt more efficient boiler technologies, such as high-efficiency watertube boilers that offer superior performance over traditional firetube models. Additionally, the rise of digitalization in manufacturing processes is leading to the integration of IoT technologies, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America are increasingly investing in industrial infrastructure, creating a surge in demand for steam boilers in sectors like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and textiles. In Europe and the Middle East, stringent environmental regulations are compelling companies to upgrade their boiler systems to comply with emission standards, particularly regarding nitrogen oxides (NOx). Furthermore, the advent of alternative fuels, such as biomass and waste-to-energy systems, is reshaping sourcing strategies, encouraging buyers to consider sustainable options in their procurement processes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Steam Boiler Market?
Sustainability is now a core consideration for international B2B buyers in the steam boiler market. The environmental impact of traditional fuel sources necessitates a shift toward greener alternatives, as organizations strive to reduce their carbon footprints. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders. The use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient boiler technologies significantly minimizes emissions and operational costs.
Moreover, ethical sourcing has gained traction, with companies increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains. Buyers are looking for manufacturers that prioritize transparency and sustainability, often seeking certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 50001 for energy management. These certifications can provide assurance that suppliers are committed to reducing their environmental impact, which is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles. Additionally, investing in suppliers that utilize recycled materials or sustainable practices can lead to long-term cost savings and improved brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context of Steam Boiler Technology?
The evolution of steam boiler technology dates back to the early 18th century, where the first steam engines revolutionized industries by providing a reliable source of power. Initially, steam boilers were rudimentary and often unsafe, but advancements in metallurgy and engineering led to the development of safer, more efficient designs. The transition from firetube to watertube boilers marked a significant turning point, as watertube designs offered enhanced safety and efficiency, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
In the 20th century, the introduction of automatic controls and improved combustion technologies further transformed the industry, allowing for better energy management and reduced emissions. Today, steam boilers are integral to various sectors, including manufacturing, energy production, and food processing, showcasing their enduring relevance and adaptability in an ever-evolving market landscape.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of the steam boiler market requires an understanding of its dynamics, a commitment to sustainability, and a keen awareness of historical advancements that shape current practices. International B2B buyers must leverage these insights to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and environmental responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steam boiler how it works
-
How do I solve inefficiencies in my steam boiler operation?
To address inefficiencies in steam boiler operations, start by conducting a comprehensive efficiency audit. This includes assessing fuel-to-steam efficiency and in-service efficiency. Implement regular maintenance schedules to clean heat exchangers and check for leaks. Consider upgrading to a boiler with a higher turndown ratio, which allows for better matching of steam production to demand. Additionally, investing in advanced control systems can optimize performance and reduce energy consumption, ultimately lowering operational costs. -
What is the best type of steam boiler for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, watertube boilers are often the preferred choice due to their higher efficiency and ability to generate steam at greater pressures compared to firetube boilers. They are particularly suitable for facilities with large steam demands, such as chemical plants or food processing facilities. Consider factors such as the specific steam requirements, available fuel types, and space constraints when selecting the best boiler type for your needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of steam boilers from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of steam boilers from international suppliers, conduct thorough due diligence. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ASME certification for pressure vessels. Request references from previous clients and review case studies to gauge the supplier’s reliability. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility to assess production standards and quality control measures. Establishing a clear communication channel throughout the procurement process can also help maintain quality assurance. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steam boilers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steam boilers can vary significantly by supplier and boiler type. Typically, larger manufacturers may have an MOQ ranging from 1 to 5 units, especially for custom models. For standard models, MOQs may be lower. Always clarify MOQ details before entering negotiations, and consider your operational needs to ensure that your order aligns with your production capacity and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing steam boilers internationally?
Payment terms for international steam boiler purchases can vary widely. Common terms include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation and the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans based on creditworthiness. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Ensure that all payment terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How do I handle logistics for importing steam boilers?
When importing steam boilers, partner with experienced logistics providers familiar with international shipping regulations and customs clearance. Assess shipping options such as container shipping for bulk orders or breakbulk shipping for larger boilers. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is prepared to facilitate smooth customs processing. Additionally, consider insurance for your shipment to protect against potential damages during transit. -
What customization options are available for steam boilers?
Most steam boiler manufacturers offer a range of customization options to meet specific operational needs. Customizations may include adjustments to capacity, pressure ratings, fuel types, and control systems. Additionally, options for enhanced safety features, such as advanced monitoring systems or automatic shut-off valves, can be specified. Engage with suppliers early in the design process to discuss your requirements and ensure that the final product meets your exact specifications. -
How can I ensure compliance with safety standards for steam boilers?
To ensure compliance with safety standards for steam boilers, familiarize yourself with local and international regulations, such as those set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the European Union’s Pressure Equipment Directive (PED). Work with suppliers who adhere to these standards and can provide documentation to confirm compliance. Regular safety inspections and maintenance checks should be conducted to ensure ongoing adherence to safety protocols, thus minimizing operational risks.
Top 4 Steam Boiler How It Works Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CN Control Valve – Steam Boiler Solutions
Domain: cncontrolvalve.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are heating systems that generate steam by boiling water. They convert thermal energy from various fuels (gas, coal, biomass, fuel oil) into steam for industrial and domestic purposes. Key types include:
1. **Electric Boilers**: Use electric components for heating, environmentally friendly, durable, and require less maintenance.
2. **Hot Water Boilers**: Composed of stainless steel,…
2. Burner Combustion – Steam Boilers
Domain: burnercombustion.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are essential for various industrial applications, providing reliable and efficient heat generation. Key components include burners, combustion chambers, heat exchangers, feedwater systems, and control systems. Types of steam boilers include fire-tube, water-tube, and electric boilers. Fire-tube boilers are compact and designed for quick heat transfer. Steam boilers are crucial in in…
3. EPCB – Industrial Steam Boilers
Domain: epcbboiler.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: EPCB Boiler offers various types of industrial steam boilers including: 1. Coal Fired Boiler: Features large heating surface, advanced steam-water separation technology, high efficiency economizer, and achieves thermal efficiency up to 84.61%. 2. Oil/Gas Fired Boiler: 3-pass wet back structure, automatic control system, high-efficiency economizer, widely used in textile, food, and chemical industr…
4. IQS Directory – Steam Boilers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are apparatuses designed to produce steam by heating water, functioning as heat exchangers. They come in various sizes and types, including hot water boilers, electric boilers, gas boilers, low pressure boilers, high pressure boilers, and oil boilers. Hot water boilers transfer thermal energy to water for heating and are made from materials like stainless steel and cast iron. Electri…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steam boiler how it works
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Steam Boiler Procurement?
In conclusion, understanding the mechanics of steam boilers is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Effective strategic sourcing not only streamlines the procurement process but also ensures that businesses select the right boiler systems tailored to their specific operational needs. Key considerations include the type of boiler—firetube versus watertube—fuel efficiency, and maintenance requirements, all of which can significantly impact long-term operational costs.
Investing in high-efficiency boilers with robust monitoring systems can lead to substantial energy savings and reduced environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals. As industries evolve, the demand for innovative, reliable steam solutions will only increase, making it imperative for buyers to stay informed about the latest technologies and trends.
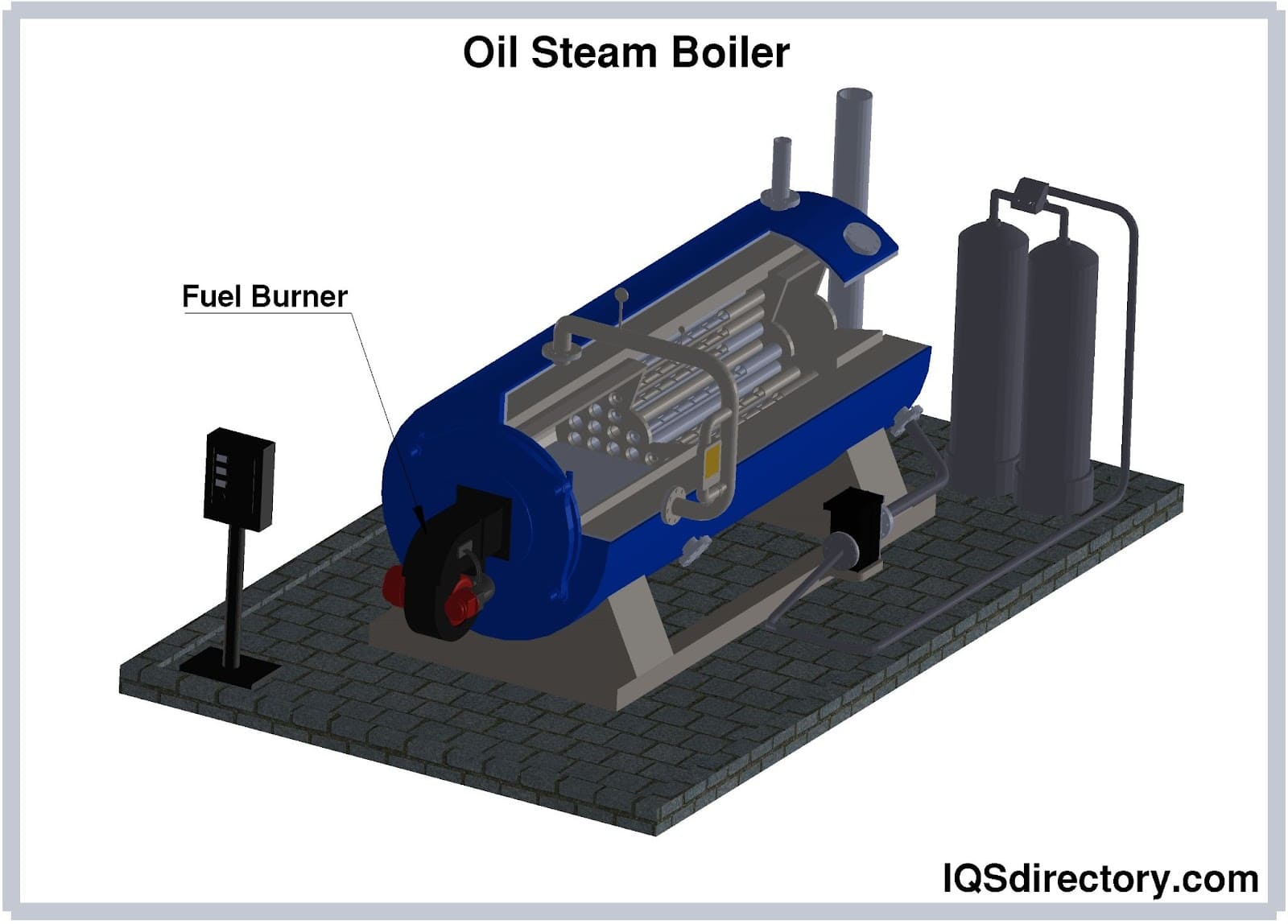
Illustrative image related to steam boiler how it works
Moving forward, we encourage you to engage with reputable suppliers who can provide not only products but also insights into optimizing your boiler systems. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you position your organization for enhanced performance and competitiveness in the global marketplace. Take the next step and explore tailored solutions that meet your unique steam requirements today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.