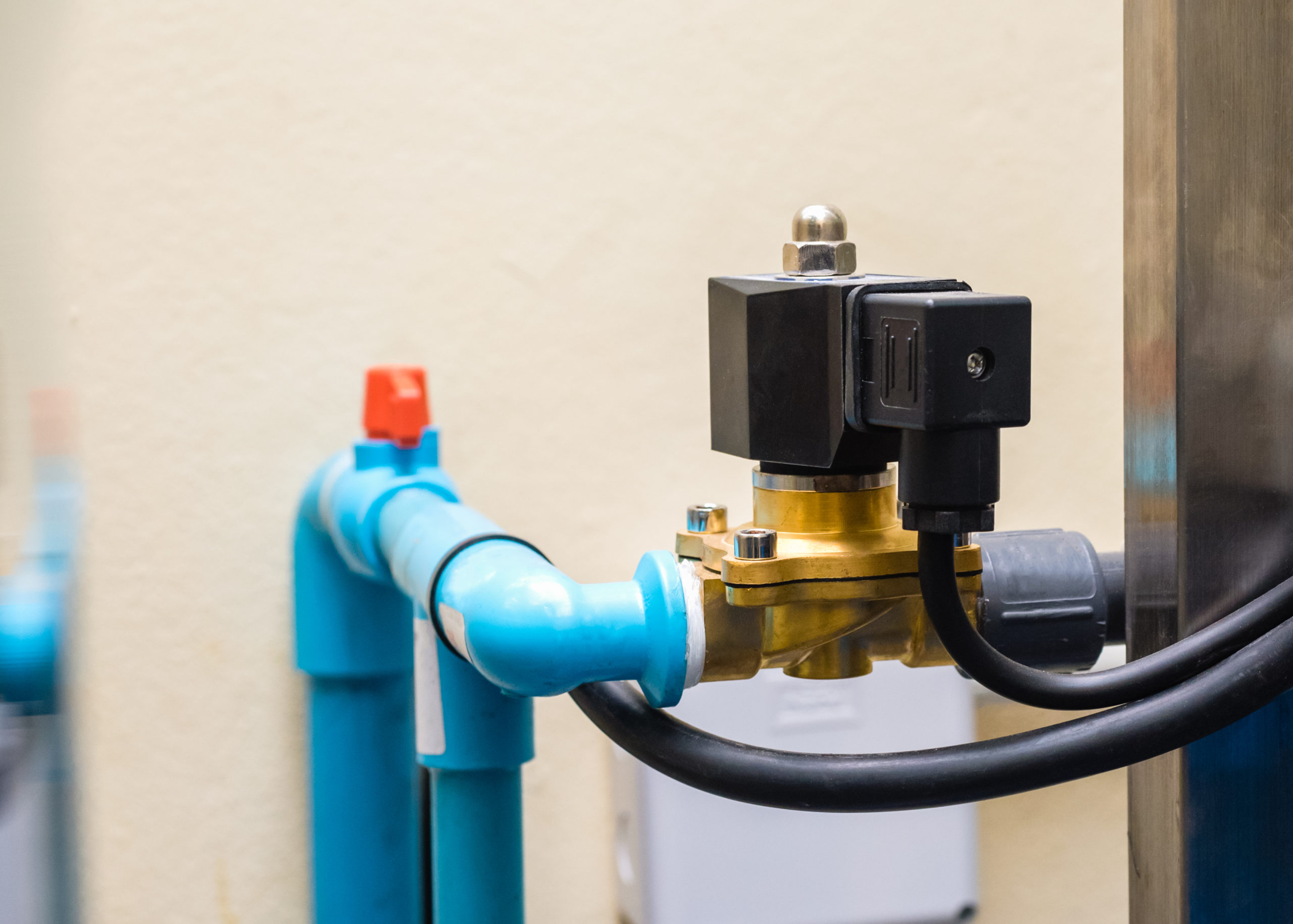
The Definitive Guide to Solenoid Control Valve: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid control valve
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing the right solenoid control valve can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These electromechanical devices are crucial for managing the flow of liquids and gases in various applications—from water management systems to complex manufacturing processes. However, the complexity of options available, coupled with varying regional standards and supplier reliability, can make the procurement process overwhelming.
This guide aims to streamline your decision-making journey by providing a comprehensive overview of solenoid control valves. We will delve into different types of valves, their specific applications, and crucial factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will explore the cost implications and offer insights into optimizing your purchasing strategy to ensure you make informed, cost-effective decisions.
By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the global market for solenoid control valves confidently. Whether you are a procurement officer in Nigeria looking to enhance your water infrastructure or a manufacturing manager in Brazil seeking to improve operational efficiency, this resource will empower you to select the right solutions that meet your operational needs and comply with local regulations. Prepare to unlock the potential of solenoid control valves and elevate your business operations to new heights.
Understanding solenoid control valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting Solenoid Valve | Operates directly with minimal pressure; compact design. | Water control, irrigation systems, HVAC. | Pros: Simple installation, quick response. Cons: Limited flow capacity. |
| Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valve | Utilizes pilot pressure to control larger valve flows. | Industrial automation, water treatment plants. | Pros: Handles larger flows, energy efficient. Cons: More complex installation. |
| 3-Way Solenoid Valve | Diverts flow between two outlets; versatile configuration. | Pneumatic systems, chemical processing. | Pros: Flexible flow control, space-saving. Cons: More susceptible to failure. |
| Proportional Solenoid Valve | Adjusts flow rate based on input signal; precise control. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, automation. | Pros: High precision, adaptable. Cons: Higher cost, requires advanced control systems. |
| Pneumatic Solenoid Valve | Specifically designed for air or gas control; robust construction. | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. | Pros: Durable, reliable for gas applications. Cons: Limited to gas applications only. |
What are the characteristics of Direct-Acting Solenoid Valves?
Direct-acting solenoid valves are designed to operate with minimal pressure, making them suitable for applications that require quick and reliable actuation. Their compact design allows for easy installation in tight spaces, making them ideal for water control and HVAC systems. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the specific flow requirements of their application, as these valves may have limitations in handling large flow capacities.
How do Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valves function in industrial settings?
Pilot-operated solenoid valves leverage pilot pressure to manage larger flows, making them a preferred choice for industrial automation and water treatment facilities. Their ability to control significant flow rates while using less energy makes them efficient for high-demand applications. Buyers should consider the complexity of installation and maintenance, as these valves may require more intricate setups compared to direct-acting models.
What advantages do 3-Way Solenoid Valves offer for fluid control?
3-way solenoid valves are versatile, allowing for the diversion of flow between two outlets, which is particularly beneficial in pneumatic systems and chemical processing. Their space-saving design enhances flexibility in system layouts. However, potential buyers should be aware of their susceptibility to failure due to increased mechanical complexity and ensure adequate maintenance protocols are in place.
Why choose Proportional Solenoid Valves for precision applications?
Proportional solenoid valves provide fine-tuned control over flow rates based on input signals, making them essential in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals where precision is critical. While they offer exceptional adaptability and accuracy, buyers should factor in the higher costs and the necessity for advanced control systems to optimize their performance.
In what scenarios are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves most effective?
Pneumatic solenoid valves are specifically engineered for controlling air or gas flows, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Their robust construction ensures reliability in demanding environments. However, potential buyers should recognize that these valves are limited to gas applications and may not be suitable for fluid control, necessitating careful consideration of application requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid control valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Solenoid Control Valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Automated flow control in treatment plants | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces labor costs | Reliability in harsh environments, compatibility with chemicals |
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems for precise water control | Optimizes water usage, improving crop yields | Voltage options for local power availability, durability against weather conditions |
| Oil & Gas | Pressure regulation in pipeline systems | Ensures safety and prevents leaks, minimizing downtime | High-pressure ratings, material compatibility with various fluids |
| HVAC Systems | Temperature control in cooling systems | Improves energy efficiency and system reliability | Compact design for limited space, responsiveness to control signals |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Fluid dosing in production processes | Ensures accuracy in formulations, complying with regulations | Certification for pharmaceutical use, ease of integration into existing systems |
How Are Solenoid Control Valves Utilized in Water Treatment?
In water treatment facilities, solenoid control valves play a crucial role in automating the flow of water through various treatment stages. These valves ensure precise control over water pressure and flow, which is essential for effective filtration and disinfection processes. By automating these controls, businesses can significantly reduce labor costs and enhance operational efficiency. International buyers should consider sourcing valves that are reliable in harsh chemical environments, ensuring compatibility with the specific treatment chemicals used in their processes.
What Role Do Solenoid Control Valves Play in Agriculture?
In agricultural applications, solenoid control valves are integral to modern irrigation systems. They provide precise control over water distribution, allowing farmers to optimize water usage based on crop requirements. This not only conserves water resources but also enhances crop yields by ensuring that plants receive the right amount of hydration. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, it is essential to consider the voltage options available to match local power supplies, as well as the durability of valves against varying weather conditions.
How Are Solenoid Control Valves Used in Oil & Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas sector, solenoid control valves are vital for regulating pressure in pipeline systems. These valves help maintain safe operational pressures, preventing leaks and potential environmental hazards. By ensuring consistent pressure control, businesses can minimize downtime and enhance safety protocols. When sourcing these valves, international buyers must focus on high-pressure ratings and material compatibility to withstand the diverse fluids encountered in oil and gas applications.
What Benefits Do Solenoid Control Valves Provide in HVAC Systems?
Solenoid control valves are essential in HVAC systems for managing temperature and airflow. They enable precise control of refrigerant flow, which is critical for maintaining energy efficiency and system reliability. By integrating these valves into HVAC systems, businesses can achieve better climate control and reduce energy costs. Buyers should prioritize compact designs that fit into limited spaces and ensure that the valves respond quickly to control signals for optimal performance.
How Are Solenoid Control Valves Essential in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, solenoid control valves are used for accurate fluid dosing during production processes. Their precise control ensures that formulations meet stringent regulatory requirements, which is crucial for product safety and efficacy. Buyers in this sector must source valves that are certified for pharmaceutical use and can be easily integrated into existing production systems, ensuring compliance and operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solenoid control valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Solenoid Control Valve for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion when selecting solenoid control valves due to the multitude of options available. With various types like direct-acting, pilot-operated, and proportional valves, it can be challenging to determine which type is suitable for specific applications. This confusion can lead to purchasing the wrong valve, resulting in operational inefficiencies, increased costs, and potential downtime in critical systems.
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
The Solution: To make informed decisions, buyers should first conduct a thorough analysis of their system requirements. Consider factors such as the type of fluid (liquid or gas), operating pressure, and the necessary flow rate. Buyers should also evaluate whether they need a normally closed or normally open valve based on the operational context. Engaging with manufacturers or suppliers to clarify specifications can help avoid missteps. Additionally, leveraging resources such as technical datasheets and application guides from reputable suppliers can provide valuable insights into which solenoid control valve will best meet specific operational needs.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Valve Maintenance and Reliability
The Problem: Solenoid control valves are integral to many industrial processes, but they can be susceptible to wear and failure over time. B2B buyers often encounter issues related to the reliability and longevity of these valves, especially in harsh environments or when exposed to corrosive substances. Frequent breakdowns can disrupt production schedules and lead to costly repairs, affecting overall operational efficiency.
The Solution: Implementing a robust maintenance schedule is crucial for ensuring the reliability of solenoid control valves. Buyers should prioritize sourcing valves made from high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials tailored to their specific environment. Regular inspections and performance evaluations can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, investing in training for maintenance personnel to understand the operational intricacies of solenoid valves can enhance their ability to troubleshoot effectively. Utilizing predictive maintenance technologies can also provide data-driven insights into valve performance, allowing for proactive maintenance actions that minimize unexpected failures.
Scenario 3: Integration Issues with Existing Control Systems
The Problem: Many businesses face challenges when integrating new solenoid control valves into existing automated control systems, such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. Compatibility issues can arise due to differing communication protocols or voltage requirements, leading to operational delays and frustrations during installation.
The Solution: Before purchasing solenoid control valves, it is essential for buyers to assess their current control systems comprehensively. This involves understanding the communication protocols in use and ensuring that the new valves can interface seamlessly with existing hardware and software. Buyers should consult with system integrators or valve manufacturers to identify valves designed for easy integration. Additionally, considering valves that support multiple voltage options can provide flexibility in adapting to various operational setups. Pre-installation testing in a controlled environment can also mitigate integration risks, allowing for troubleshooting before full deployment in the field.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid control valve
What Are the Key Materials Used in Solenoid Control Valves?
When selecting materials for solenoid control valves, it’s crucial to consider the properties that affect performance, durability, and application compatibility. The following analysis covers four common materials used in solenoid control valves: brass, stainless steel, plastic, and aluminum. Each material has distinct advantages and disadvantages that can influence the decision-making process for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
How Does Brass Perform in Solenoid Control Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for solenoid control valves due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically handles pressures up to 150 psi and temperatures ranging from -20°F to 250°F. Brass is also relatively affordable, making it a cost-effective option for many applications.
Pros: Brass offers good durability and is suitable for a wide range of fluids, including water, oil, and gas. Its thermal conductivity is beneficial in applications requiring heat dissipation.
Cons: While brass is resistant to corrosion, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive environments, such as seawater or certain chemical applications. Additionally, brass can be prone to dezincification, which may affect its longevity.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in HVAC systems, irrigation, and water control systems, making it suitable for many industries, especially in regions like South America and Africa where these applications are prevalent.
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding brass usage, especially in potable water applications.
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel in Solenoid Control Valves?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for demanding applications. It can withstand high pressures (up to 300 psi) and temperatures (up to 400°F), which makes it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and can handle aggressive media, including chemicals and high-temperature fluids. Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, which is cost-effective in the long run.
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost compared to brass and plastic. Additionally, its manufacturing process can be more complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for the oil and gas industry, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with DIN and JIS standards, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations apply.
How Do Plastic Solenoid Control Valves Compare?
Plastic solenoid control valves are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for specific applications. They typically operate effectively at lower pressures (up to 100 psi) and temperatures (up to 180°F).
Pros: The low cost and ease of manufacturing make plastic valves an attractive option for many applications. They are also resistant to many chemicals, which is beneficial in various industrial settings.

Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
Cons: Plastic valves may not be suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications. They can also be more susceptible to wear and tear over time compared to metal options.
Impact on Application: Plastic solenoid valves are often used in irrigation systems, chemical processing, and water treatment, particularly in regions with less aggressive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards is essential, particularly in chemical applications. Buyers should also consider the specific chemical compatibility of the plastic material.

Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solenoid Control Valves?
Aluminum is another lightweight option that offers good corrosion resistance and strength. It typically handles pressures up to 150 psi and temperatures ranging from -40°F to 250°F.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective and provides a good strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments. Its thermal conductivity can also be a disadvantage in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are commonly used in pneumatic applications and automotive systems, especially in regions where weight reduction is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum valves comply with relevant international standards, particularly in automotive and aerospace applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solenoid Control Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid control valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | HVAC systems, irrigation | Good machinability and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion in aggressive media | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Oil & gas, food processing | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Irrigation, chemical processing | Lightweight and low cost | Limited pressure and temperature range | Low |
| Aluminum | Pneumatic applications, automotive | Good strength-to-weight ratio | Not suitable for highly corrosive environments | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in selecting the most appropriate solenoid control valve materials based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid control valve
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solenoid Control Valves?
The manufacturing of solenoid control valves involves several critical stages that ensure high-quality production. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each step is essential in producing a reliable and efficient valve that meets industry standards.
How is Material Prepared for Solenoid Control Valves?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing solenoid control valves. It typically involves selecting high-grade materials such as stainless steel, brass, or engineering plastics, which are chosen based on their corrosion resistance, durability, and compatibility with various fluids.
Once materials are selected, they undergo various processes like cutting, machining, and surface treatment to ensure they meet precise specifications. Techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are commonly employed to achieve the necessary dimensions and tolerances, ensuring that each component fits perfectly in the assembly phase.
What Techniques are Used in the Forming Stage of Solenoid Control Valve Production?
The forming stage is where the prepared materials are shaped into the components of the solenoid control valve. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and injection molding are prevalent in this phase. For instance, metal components may be stamped out of sheets, while plastic parts are produced using injection molding to create complex shapes with high precision.
This stage also includes the creation of the solenoid coil, which involves winding copper wire around a ferromagnetic core. The quality of the coil is crucial as it directly affects the valve’s responsiveness and efficiency. Proper heat treatment may also be applied to enhance the mechanical properties of metal components.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Solenoid Control Valves?
The assembly phase involves bringing together all the components manufactured in the previous stages. This process is typically performed in a clean room environment to avoid contamination. Skilled technicians or automated assembly lines are used to ensure precision in the assembly of critical parts, such as the solenoid, valve body, and diaphragm.
During assembly, each component is meticulously inspected for defects or inconsistencies. This is crucial because any flaws could lead to malfunctions or failures in the field. The use of jigs and fixtures can help maintain alignment and facilitate efficient assembly.
What Quality Assurance Standards Apply to Solenoid Control Valves?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for solenoid control valves. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers implement a robust quality management system. This standard focuses on process efficiency, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement, which are critical for producing high-quality products.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas industry are essential for compliance and market access. These certifications often require rigorous testing and documentation, which assures buyers of the product’s reliability and safety.
What are the Key QC Checkpoints in Solenoid Control Valve Production?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks at various stages of production. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins. This includes checking for material specifications, dimensions, and any signs of damage.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This ensures that any deviations from the required standards are identified and rectified promptly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing. This includes functional tests, pressure tests, and leak tests to ensure the valve operates as intended under specified conditions.
Which Testing Methods are Commonly Used for Solenoid Control Valves?
Various testing methods are utilized to ensure the quality and reliability of solenoid control valves. Common methods include:
-
Functional Testing: Verifying that the valve opens and closes correctly when energized.
-
Pressure Testing: Assessing the valve’s ability to withstand operational pressures without leaking.
-
Leak Testing: Using methods like water immersion or gas testing to identify any potential leaks in the valve assembly.
-
Durability Testing: Subjecting the valve to repeated cycles of operation to ensure longevity under real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial to ensuring that they receive reliable products. Here are some strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. This helps buyers understand how well the supplier adheres to international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation of quality tests and certifications. This includes records of IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, as well as any third-party inspection reports.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspection agencies to evaluate the production processes and finished products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in QC and certification:
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. For example, products exported to the European Union must comply with CE marking requirements, while products intended for the Middle East may need to meet specific Gulf Standards.
-
Understanding Cultural Differences: Buyers should recognize that manufacturing practices and quality expectations may vary across cultures. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce additional risks such as damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures in place to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for solenoid control valves is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, and verification strategies, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solenoid control valve’
In this practical sourcing guide, we provide a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure solenoid control valves. This guide aims to streamline your purchasing process, ensuring that you select the most suitable products for your operational needs while minimizing risks associated with procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical requirements of the solenoid control valves you need. Consider factors such as the type of medium (liquid or gas), pressure ratings, flow rates, and operational environment (temperature, humidity, etc.). This clarity helps in identifying the right product that meets your application demands, reducing the likelihood of costly returns or modifications later.
Step 2: Research Available Types of Solenoid Valves
Understand the different types of solenoid control valves available, including direct-acting, pilot-operated, and proportional solenoid valves. Each type serves distinct purposes and functions, so knowing their differences can guide you toward the best fit for your application. For instance, pilot-operated valves are suitable for high-pressure applications, while direct-acting valves are ideal for low-pressure scenarios.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to understand their capabilities and experience in your industry. Additionally, check for references from existing customers, especially those in similar regions or sectors, to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE marking). This step is crucial for ensuring product quality and safety, especially in industries with stringent regulations. Ask suppliers for documentation that proves their adherence to these standards.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the solenoid control valves you are considering. Testing samples allows you to assess their performance, compatibility with your systems, and durability under real-world conditions. This hands-on evaluation can reveal potential issues that might not be apparent from specifications alone.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a preferred supplier, discuss and negotiate terms of sale, including pricing, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Clear agreements on these aspects help prevent misunderstandings later and ensure that both parties have aligned expectations. Consider discussing payment terms that are favorable for your cash flow needs.
Step 7: Plan for Long-term Supplier Relationships
Finally, consider the potential for long-term partnerships with your chosen supplier. Establishing a solid relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved support over time. Regular communication and feedback can help both parties adapt to changing needs and enhance the overall procurement experience.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solenoid control valves, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes that meet operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid control valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Solenoid Control Valve Manufacturing?
When sourcing solenoid control valves, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of materials varies significantly based on the type of solenoid valve being manufactured. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. The choice of material affects not only the valve’s durability and compatibility with various fluids but also its cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. This can vary by region, with labor in emerging markets like Nigeria or Brazil typically being lower than in Europe. Labor costs also depend on the complexity of the valve’s design and assembly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead costs, which is an important consideration for international buyers.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial investment in molds and dies required for valve production. Custom designs or specialized applications may require higher tooling costs, which can be a significant factor for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance protocols ensure that the valves meet industry standards and specifications. QC costs can add to the overall price but are essential for minimizing failures and ensuring compliance with regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs play a critical role, especially for international transactions. These costs can fluctuate based on the chosen shipping method, distance, and local tariffs.
-
Margin: Finally, the profit margin applied by manufacturers and distributors will influence the final price. Margins can vary widely based on market competition and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Solenoid Control Valve Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of solenoid control valves beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it advantageous for buyers to plan their procurement strategically.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized valves tailored to specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the associated price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications, such as ISO or API standards, typically lead to higher prices. However, investing in certified products can result in long-term savings through enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to their proven track record and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affect the total landed cost of the products. Understanding the implications of terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) versus FOB (Free on Board) can help buyers manage costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Solenoid Control Valves Internationally?
-
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Building a strong relationship can lead to better deals and favorable terms in the long run.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. This approach can provide a clearer picture of the value of your investment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect the overall cost of procurement. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide insights into the regional market dynamics and help mitigate risks.
-
Supplier Diversification: Consider sourcing from multiple suppliers to reduce dependency and enhance bargaining power. This strategy can also help in understanding market pricing trends and variations.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay updated on industry trends and technological advancements that may influence valve pricing. Understanding these trends can help buyers anticipate changes in supply chain dynamics and pricing structures.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
While indicative prices for solenoid control valves may range widely based on the factors discussed, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes tailored to their specific requirements. Prices are subject to change based on market conditions, supplier policies, and other external factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solenoid control valve With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Solenoid Control Valves
In the realm of fluid control systems, solenoid control valves are widely recognized for their efficiency and reliability. However, various alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar objectives, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Solenoid Control Valve | Pneumatic Control Valve | Electric Actuator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Fast response time; reliable switching | High force output; suitable for larger systems | Precise control; variable speed capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operating costs | Higher installation and maintenance costs | Higher upfront costs; potential for energy savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; compatible with SCADA systems | Requires more complex setup and pneumatic infrastructure | Installation can be complex, but straightforward in many systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; generally long service life | Regular maintenance required for air compressors | Low maintenance; longevity depends on usage |
| Best Use Case | Waterworks, irrigation, and HVAC systems | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Robotics, automated systems, and precision tasks |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
1. Pneumatic Control Valve
Pneumatic control valves leverage compressed air to operate, providing high force output that is particularly beneficial for larger systems. They excel in heavy machinery applications where significant pressure and flow control are essential. However, the initial setup can be more complex due to the need for air compressors and pneumatic infrastructure, which may increase overall costs. Moreover, these systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent air leaks.
2. Electric Actuator
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, allowing for precise control over fluid flow. They can be used in applications requiring variable speed and torque, making them suitable for automation and robotics. Although electric actuators typically have a higher upfront cost compared to solenoid valves, they offer significant energy savings in the long run and are relatively low-maintenance. However, their complexity in installation may deter some buyers, particularly those operating in less technologically advanced environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When selecting a fluid control solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and operational complexity. Solenoid control valves are ideal for straightforward applications requiring quick response times and low maintenance. In contrast, pneumatic control valves may be more suited for heavy-duty industrial environments, while electric actuators excel in precision tasks requiring variable control. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific needs of the operation, balancing immediate costs against long-term performance and maintenance considerations. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, buyers can ensure they choose the best solution for their unique applications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid control valve
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Solenoid Control Valves?
Understanding the essential technical properties of solenoid control valves is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating options for specific applications. Here are some critical specifications:
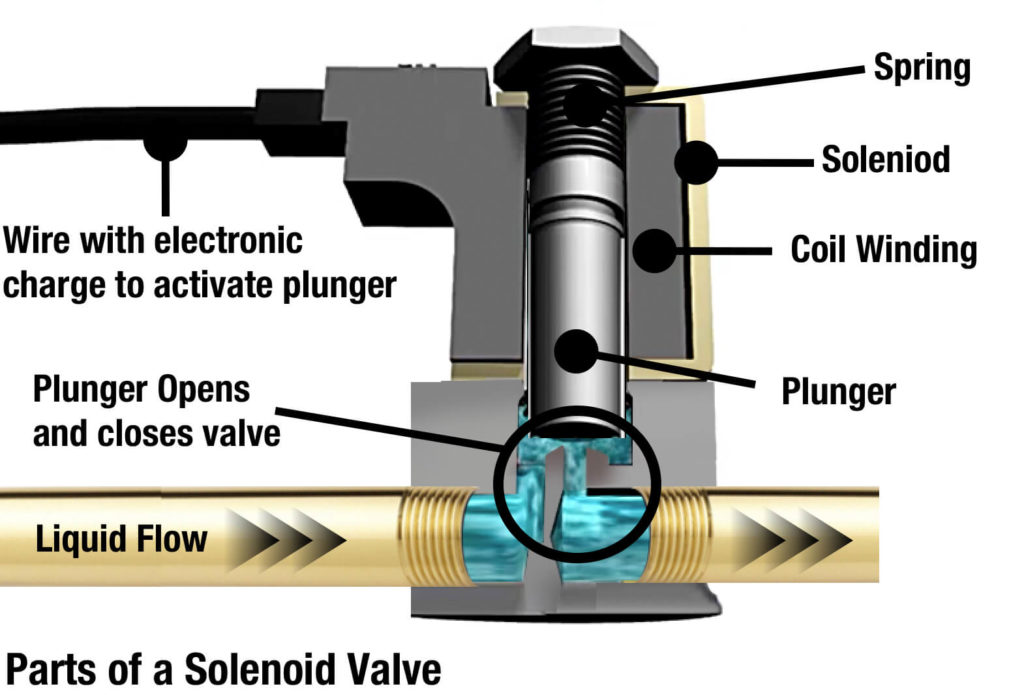
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
-
Material Grade
Solenoid control valves are typically manufactured from materials such as stainless steel, brass, and plastic. The material grade impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with various fluids or gases. For instance, stainless steel is favored for its strength and resistance to rust, making it suitable for harsh environments. Selecting the right material grade ensures long service life and minimizes maintenance costs. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating of a solenoid valve indicates the maximum pressure it can handle without failure. This specification is vital for applications involving high-pressure systems, such as oil and gas or industrial processes. Understanding the pressure rating helps buyers ensure that the valve can operate safely within their system’s parameters, preventing leaks or catastrophic failures. -
Voltage and Power Consumption
Solenoid valves operate using electrical power, which can range from 12V to 240V. The voltage required affects the valve’s compatibility with existing electrical systems. Additionally, lower power consumption is advantageous for energy efficiency, especially in large-scale operations. Buyers should consider their power supply and energy costs when selecting a valve. -
Flow Rate
The flow rate is a measure of how much fluid can pass through the valve per unit of time, typically expressed in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM). This specification is critical for ensuring that the valve meets the operational demands of the system. A valve with an inadequate flow rate can lead to inefficiencies and performance issues. -
Response Time
The response time refers to how quickly the valve can open or close after receiving an electrical signal. Fast response times are essential for applications requiring precise control over fluid dynamics, such as in automation systems. Buyers must assess the response time to ensure that it aligns with their operational requirements. -
Port Configuration
Solenoid valves come in various port configurations, including two-port and three-port designs. A two-port valve either allows or stops the flow, while a three-port valve can direct flow between two outlets. Understanding port configuration is essential for integrating the valve into existing systems and ensuring it meets specific operational needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Solenoid Control Valve Procurement?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of solenoid control valves, sourcing from OEMs ensures that buyers receive high-quality products that meet industry standards and specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budget management and inventory planning, especially for businesses looking to optimize their purchasing strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process that allows buyers to gather competitive pricing and make informed decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers negotiate shipping costs and responsibilities effectively, ensuring smooth international transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is essential for project planning and inventory management, as longer lead times can impact production schedules and operational efficiency. -
Certification Standards
These are industry-specific standards that products must meet to ensure safety, reliability, and performance. Understanding the relevant certification standards (such as ISO or CE) is crucial for buyers to ensure compliance and quality assurance in their procurement processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing solenoid control valves, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solenoid control valve Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Solenoid Control Valve Sector?
The solenoid control valve market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. Increasing automation across industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and water treatment is a primary driver. The demand for precision in fluid control and the integration of solenoid valves into sophisticated systems like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) reflect the ongoing trend towards smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0. Additionally, the rise of renewable energy projects in regions such as Africa and South America is propelling the need for efficient fluid control solutions, positioning solenoid control valves as essential components in these systems.
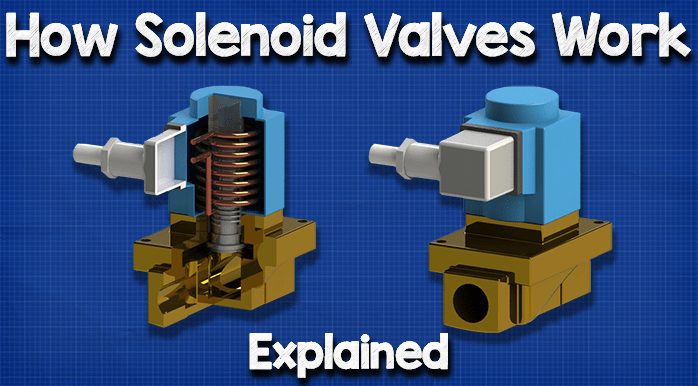
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the sourcing landscape for B2B buyers. The adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) has led to the development of smart solenoid valves that can provide real-time data and analytics, thereby enhancing decision-making processes for operations managers. Furthermore, the trend towards modular designs, which allow for easy integration and maintenance, is becoming increasingly popular. Buyers are encouraged to focus on suppliers that invest in R&D to stay ahead of these technological advancements.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Brazil, Nigeria, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the local market conditions is crucial. Economic factors, regulatory frameworks, and regional supply chain dynamics can significantly influence sourcing decisions. Engaging with local suppliers who understand these nuances can lead to more effective procurement strategies and cost efficiencies.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Solenoid Control Valve Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal aspect of sourcing in the solenoid control valve sector. As environmental concerns continue to rise, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. This includes using materials that minimize environmental impact and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes. For instance, solenoid valves made from recyclable materials or designed for low energy consumption are gaining traction among eco-conscious buyers.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is crucial for maintaining brand reputation and compliance with regulatory standards. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough audits of their supply chains to ensure adherence to environmental and labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can provide assurance of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
In addition, the integration of life cycle assessments (LCA) in the procurement process can help buyers evaluate the environmental impact of solenoid valves throughout their lifecycle. This approach not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also aligns with corporate social responsibility goals, thereby enhancing brand loyalty among customers who value sustainability.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Solenoid Control Valves?
The evolution of solenoid control valves dates back to the early 20th century when the first electromechanical devices were developed. Initially used in simple on-off applications, advancements in technology led to the introduction of more sophisticated designs capable of precise flow control. By the mid-20th century, solenoid valves became integral to automation in various sectors, including manufacturing and automotive.
The introduction of digital control systems in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for enhanced functionality and integration into complex systems. Today, solenoid control valves are characterized by their versatility, reliability, and efficiency, making them essential components across a myriad of applications from irrigation systems to advanced industrial processes.
This historical context underscores the importance of innovation and adaptability in the solenoid control valve market, providing valuable lessons for B2B buyers looking to navigate current trends and future developments effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid control valve
-
How do I select the right solenoid control valve for my application?
Choosing the appropriate solenoid control valve involves considering several factors, including the type of fluid (liquid or gas), pressure and temperature specifications, and the required flow rate. You should also assess whether you need a direct-acting or pilot-operated valve based on your application’s demands. Additionally, ensure that the materials used in the valve construction are compatible with the fluid to prevent corrosion or degradation. Consulting with suppliers who understand your industry can also provide valuable insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What are the common applications for solenoid control valves?
Solenoid control valves are widely used in various industries, including water treatment, HVAC systems, irrigation, and manufacturing processes. Their primary roles include controlling flow, pressure, and fluid levels, making them essential for automated systems. For instance, in agricultural applications, solenoid valves regulate irrigation systems, while in industrial settings, they may control fluid delivery in machinery. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will help you select the right type and configuration of solenoid valve. -
What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing solenoid control valves?
When sourcing solenoid control valves, MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers. It’s essential to discuss your requirements upfront to avoid overcommitting to quantities that exceed your needs. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, while others may have strict limits. Evaluate your inventory management capabilities and the financial implications of larger orders to ensure you make a cost-effective decision that aligns with your operational needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of solenoid control valves from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing solenoid control valves from international suppliers, conduct thorough due diligence. Verify the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples before placing large orders to assess the product’s performance and reliability. Additionally, consider utilizing third-party inspection services to evaluate products at the manufacturing facility, ensuring they meet your specifications and quality standards before shipment. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of solenoid control valves?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, especially in international transactions. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or payment upon shipment. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or require a deposit before production begins. When negotiating payment terms, consider the financial stability of your business and the supplier’s reputation. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods and possibly escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for solenoid control valves sourced internationally?
Effective logistics management is crucial when sourcing solenoid control valves internationally. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight forwarding, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply in your country. Establish a clear communication channel with your supplier to track the shipment and address any potential delays or issues promptly. Utilizing a reliable logistics partner can streamline the process and help ensure timely delivery. -
Can solenoid control valves be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for solenoid control valves to meet specific application requirements. Customizations may include modifications to size, pressure ratings, materials, and electrical specifications. When considering customization, clearly outline your requirements and work closely with the supplier’s engineering team to ensure that the final product aligns with your operational needs. Custom solutions can enhance performance and reliability in specialized applications. -
What factors influence the pricing of solenoid control valves?
The pricing of solenoid control valves is influenced by several factors, including the materials used, valve size, complexity of design, and customization requirements. Additionally, the manufacturing location and supplier’s reputation can affect costs. Volume orders may qualify for discounts, while urgent requests could incur higher prices due to expedited processing. Understanding these factors can help you negotiate better pricing and assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement over time.
Top 6 Solenoid Control Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Watts – Solenoid Control Valves
Domain: watts.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Solenoid control valves are automatic control valves used to control pressure, level, or flow control. They can be configured for either on-off or electric positioning service that interfaces with SCADA systems.
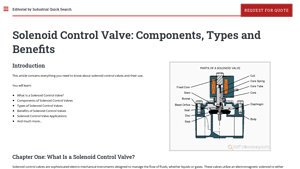
2. IQS Directory – Solenoid Control Valves
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Solenoid control valves are electro-mechanical instruments designed to manage the flow of fluids (liquids or gases) using an electromagnetic solenoid. Key components include: 1. Solenoid Coil – Generates an electromagnetic field for valve operation. 2. Plunger/Armature – Moves within the coil to open/close the flow path. 3. Valve Body – Houses the valve and contains the media flow path, available …
3. Electric Solenoid Valves – 1/2 Stainless Electric Solenoid Valve
Domain: electricsolenoidvalves.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electric Solenoid Valves available in 12V, 24V, and 110 Volt for various applications including gas, water, air, and oil. Free shipping on domestic orders over $99. Key products include: 1/2″ Stainless Electric Solenoid Valve ($81.86), 1/4″ 110V AC Stainless Electric Solenoid Valve ($44.10), 1/2″ 24V AC Electric Brass Solenoid Valve ($59.16), 2″ 12V DC Electric Brass Solenoid Valve ($278.46), 2″ S…
4. Summit Hydraulics – Hydraulic Monoblock Solenoid Control Valve
Domain: summit-hydraulics.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Monoblock Solenoid Control Valve, 4 Spool, 13 GPM, 12V DC; Price range: $824.95 – $1,499.95; Flow Rate: 13 GPM (50 l/min); Max Operating Pressure: P = 3625 PSI, T = 725 PSI, A & B = 4350 PSI; Voltage Options: 12V DC, 24V DC; Spool Options: A Spool (Double Acting Cylinder), D Spool (Motor); Features: Precision ground and hard chrome-plated spools, high-tensile strength cast iron construct…
5. Burkert – Type 2875 Solenoid Control Valve
Domain: burkert.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Type: 2875 – Direct-acting 2 way standard solenoid control valve. Features: Used as a regulating unit in control loops, elastomeric seat seal for tight closure, frictionless plunger for extraordinary adjustment characteristic, suitable for demanding control tasks (high control range, dry gases). Specifications: Orifice sizes 2…9.5 mm, optional explosion-protected coil. Compatible with Type 8605 …
6. Bailey Hydraulics – Chief D03 Solenoid Control Valve
Domain: baileyhydraulics.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Chief D03 Solenoid Control Valve”, “type”: “Solenoid Control Valve”, “features”: {“DIN”: true, “voltage”: “12VDC”, “configuration”: “4 Way 3 Pos”, “design”: “Tandem”, “series”: “Chief D03”}, “pricing”: {“sale_price”: “$70.01”, “msrp”: “$206.04”, “was_price”: “$154.53”, “savings”: “$136.03”}, “specifications”: {“weight”: “5.00 LBS”, “max_pressure”: “4480 PSI”, “flow_rate”: “16 GPM”, “amps…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid control valve
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, strategic sourcing of solenoid control valves emerges as a critical component for enhancing operational efficiency and reliability. These electromechanical devices play a pivotal role in managing fluid dynamics across various applications, making them indispensable for sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and water management. By leveraging robust supply chains and understanding the diverse types of solenoid valves available, international B2B buyers can ensure they select the right products that align with their operational needs and local market conditions.
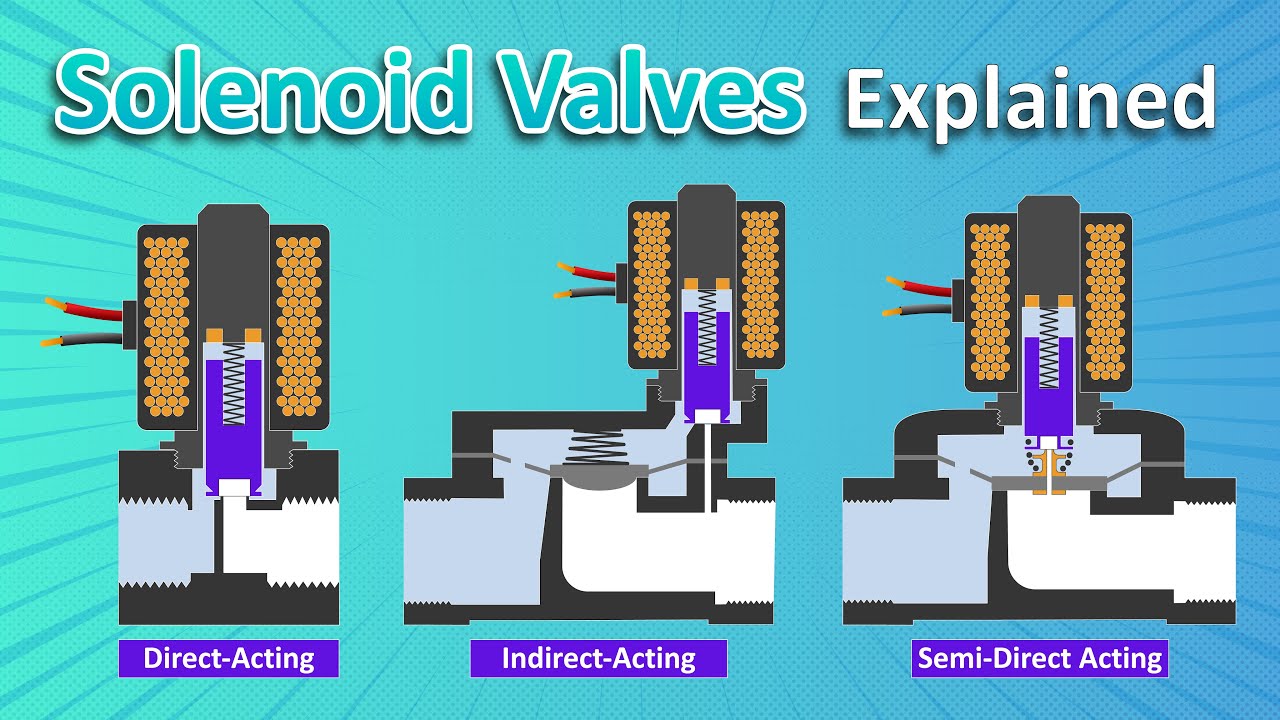
Illustrative image related to solenoid control valve
Investing in high-quality solenoid control valves not only leads to improved performance but also contributes to reduced maintenance costs and prolonged equipment lifespan. Furthermore, by establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers, businesses can gain access to innovative technologies and tailored solutions that enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Looking ahead, the demand for solenoid control valves is set to rise, driven by increasing automation and the need for efficient resource management. We encourage B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage with trusted suppliers, explore the latest advancements in solenoid technology, and invest in solutions that will propel their operations into the future. Your strategic sourcing decisions today will shape the success of your business tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.