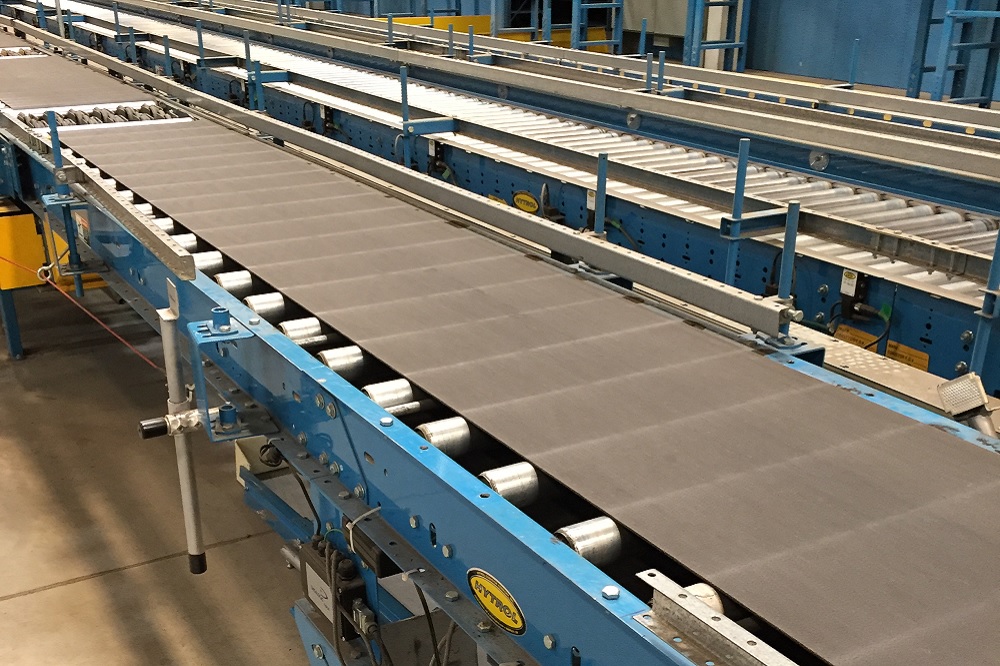
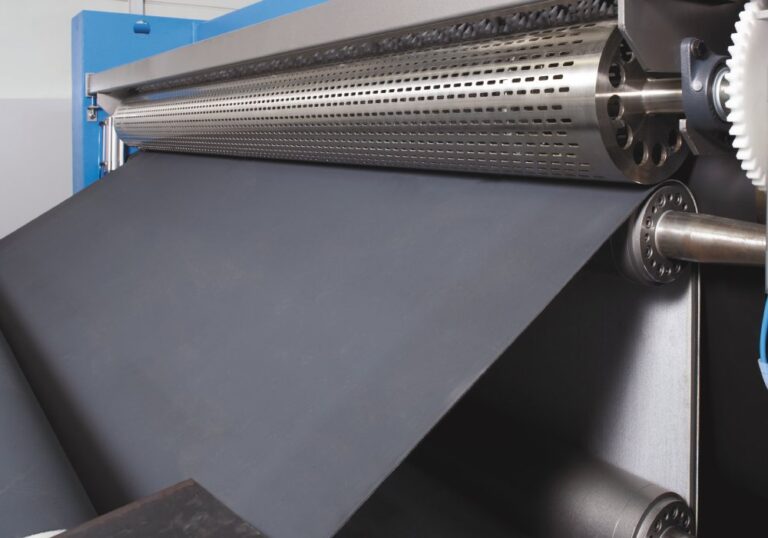
The Definitive Guide to Rolling Belt Conveyor: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rolling belt conveyor
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the right rolling belt conveyor can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the need for efficient material handling systems growing, understanding the nuances of various conveyor types, applications, and supplier options is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, illuminating the various types of rolling belt conveyors available, their specific applications across industries, and effective strategies for vetting suppliers.
From gravity and powered options to specialized systems like skatewheel and ball transfer conveyors, this guide dives deep into the functionalities and benefits each type offers, ensuring you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations, including the potential savings of opting for used equipment, which can provide significant financial advantages without compromising quality.
Arming international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the conveyor market confidently. Whether you’re based in Vietnam, Germany, or elsewhere, our focus is on helping you select the most suitable rolling belt conveyor solutions that enhance productivity and streamline operations, ultimately driving your business success in today’s dynamic landscape.
Understanding rolling belt conveyor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity Roller Conveyor | Utilizes gravity to move products; no power source required. | Warehouses, assembly lines, and shipping areas. | Pros: Low maintenance, cost-effective. Cons: Limited to downhill or flat surfaces. |
| Power Belt Conveyor | Uses a motorized belt to transport products; versatile design. | Manufacturing, packaging, and distribution centers. | Pros: Handles various product shapes, reliable. Cons: Higher energy costs, requires electrical setup. |
| Chain Driven Live Roller (CDLR) | Features rollers driven by a chain; ideal for heavy loads. | Heavy-duty applications like pallet handling. | Pros: Durable, efficient for heavy loads. Cons: More complex installation and maintenance. |
| Skatewheel Conveyor | Uses small wheels to facilitate movement; lightweight design. | Light-duty applications like sorting and packing. | Pros: Flexible, easy to set up. Cons: Limited load capacity, requires flat-bottomed items. |
| Ball Transfer Conveyor | Allows products to move in multiple directions; spherical rollers. | Sorting and assembly operations. | Pros: Versatile movement, space-saving. Cons: Can be less stable for heavier items. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Gravity Roller Conveyors?
Gravity roller conveyors are designed to transport products without the need for power, relying solely on gravity. They are typically composed of a series of rollers mounted on a frame, allowing items to roll down an incline or be pushed manually. These conveyors are ideal for applications in warehouses and assembly lines where products need to be moved efficiently from one point to another. When considering a gravity roller conveyor, buyers should evaluate the incline angle, roller diameter, and spacing, as these factors impact load capacity and product stability.
How Do Power Belt Conveyors Function in Various Industries?
Power belt conveyors utilize a motorized belt to move items along a defined path. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, from manufacturing to packaging, and are particularly effective for transporting products with uneven surfaces. Buyers should consider the type of materials being conveyed, the required speed, and the conveyor’s layout when selecting a power belt conveyor. While they offer versatility and reliability, prospective buyers should also factor in energy costs and the need for electrical installations.
What Makes Chain Driven Live Roller Conveyors Ideal for Heavy Loads?
Chain Driven Live Roller (CDLR) conveyors are engineered to handle heavy loads effectively. They consist of rollers that are driven by a chain mechanism, making them suitable for transporting pallets and other substantial items. CDLR conveyors are commonly used in industries where durability and efficiency are paramount. When purchasing, businesses should assess the load capacity, roller spacing, and overall system design to ensure optimal performance. While they are robust, they may require more intricate installation and maintenance compared to other conveyor types.
In What Scenarios Are Skatewheel Conveyors Most Effective?
Skatewheel conveyors feature small wheels that allow lightweight items to roll easily, making them ideal for sorting and packing applications. Their lightweight design and flexibility allow for quick assembly and reconfiguration, catering to dynamic warehouse environments. Buyers should consider the type of products being transported and the required layout when opting for skatewheel conveyors. While they are easy to set up and cost-effective, they are limited in terms of load capacity and are best suited for items with flat bases.
Why Choose Ball Transfer Conveyors for Versatile Movement?
Ball transfer conveyors utilize spherical rollers that enable products to move in multiple directions, making them particularly useful in sorting and assembly operations. This design allows for efficient handling of items, especially in tight spaces. When considering ball transfer conveyors, businesses should evaluate the weight of the products and the specific layout of their operations. Although they provide excellent versatility, buyers should be aware that they may not offer the same stability for heavier items as other conveyor types.
Key Industrial Applications of rolling belt conveyor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rolling belt conveyor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly Line Transport | Streamlines production, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. | Durability under continuous use, compatibility with existing systems. |
| Food & Beverage | Packaging and Sorting | Ensures hygiene and efficiency in moving products through processing stages. | Compliance with food safety standards, ease of cleaning. |
| E-commerce & Retail | Order Fulfillment and Shipping | Accelerates order processing, improving customer satisfaction and reducing delivery times. | Flexibility for different package sizes, integration with warehouse management systems. |
| Automotive | Parts Handling and Distribution | Optimizes the flow of components, reducing bottlenecks in assembly processes. | Load capacity, adaptability to heavy-duty applications. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Automated Drug Packaging and Distribution | Increases accuracy in packaging, reduces human error, and enhances traceability. | Compliance with regulatory standards, precision in handling sensitive products. |
How is Rolling Belt Conveyor Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, rolling belt conveyors are vital for transporting materials along assembly lines. They facilitate the movement of products between various stages of production, minimizing manual handling and enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should consider the durability of the conveyor system, as it must withstand continuous use and heavy loads. Additionally, compatibility with existing equipment is essential to ensure seamless integration and functionality.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
What Role Does Rolling Belt Conveyor Play in Food & Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage industry, rolling belt conveyors are employed for packaging and sorting products. They help maintain hygiene standards while efficiently moving items through different processing stages, from production to packaging. International buyers should prioritize conveyors that comply with food safety regulations and are easy to clean, thus preventing contamination. Sourcing from manufacturers with certifications can ensure adherence to these standards.
How is Rolling Belt Conveyor Essential for E-commerce & Retail?
E-commerce and retail businesses leverage rolling belt conveyors for order fulfillment and shipping processes. These systems streamline the movement of products, significantly reducing the time taken to process orders and enhancing customer satisfaction. Buyers should look for flexible conveyor solutions that can accommodate various package sizes and integrate smoothly with warehouse management systems to optimize inventory handling and logistics.
In What Ways Does Rolling Belt Conveyor Benefit the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rolling belt conveyors are crucial for parts handling and distribution. They optimize the flow of components, effectively reducing bottlenecks during assembly processes. Buyers in this industry must consider the load capacity of the conveyor systems, as automotive parts can be heavy and bulky. Additionally, adaptability to different layouts and production requirements can enhance overall productivity.
How Does Rolling Belt Conveyor Enhance Pharmaceutical Operations?
Rolling belt conveyors play a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in automated drug packaging and distribution. They increase accuracy in packaging processes, minimize human error, and enhance traceability, which is critical for compliance with regulatory standards. Buyers should focus on sourcing conveyors that meet stringent regulations and specifications for handling sensitive pharmaceutical products, ensuring reliability and precision in operations.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rolling belt conveyor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Maintaining Optimal Conveyor Speed for Different Products
The Problem: One common challenge B2B buyers face is maintaining the appropriate speed of rolling belt conveyors, especially when handling a variety of products. Different materials may require different handling speeds to ensure they are transported safely without damage. For instance, fragile items like glass or electronics need slower speeds to prevent breakage, while heavier, sturdier products can move faster. This variability can lead to increased downtime and inefficiency if the system isn’t properly calibrated.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should consider investing in adjustable-speed conveyor systems. These systems allow for real-time speed adjustments based on the type of product being transported. When selecting a rolling belt conveyor, ensure it comes equipped with a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controller. This technology enables precise speed control, allowing operators to switch between different speeds effortlessly. Additionally, conducting a thorough analysis of the product flow and categorizing items based on their handling requirements can lead to improved operational efficiency. Regular training for staff on how to adjust settings based on product type can further enhance the conveyor’s functionality.
Scenario 2: Frequent Mechanical Failures Leading to Downtime
The Problem: Mechanical failures in rolling belt conveyors can lead to significant operational disruptions. B2B buyers often report issues such as belt slippage, misalignment, or roller failure, which can halt production lines and lead to costly downtime. Such failures not only affect productivity but can also result in additional repair costs and potential loss of revenue due to delayed shipments.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
The Solution: To mitigate mechanical failures, buyers should prioritize regular maintenance and invest in high-quality components. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections, lubrication, and alignment checks can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakdowns. When sourcing rolling belt conveyors, choose models that feature durable materials and robust construction. It’s also advisable to work with suppliers that provide comprehensive warranties and support services. Incorporating smart monitoring technologies, like sensors that detect wear and tear, can alert operators to potential issues before they lead to failures, ensuring smoother operations and less downtime.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Space Utilization in Warehouse Layouts
The Problem: Many businesses struggle with inadequate space utilization due to poorly designed conveyor systems. A common issue arises when rolling belt conveyors are fixed in a way that doesn’t allow for flexibility in the warehouse layout, making it difficult to adapt to changing inventory needs. This can lead to congestion, reduced efficiency, and limited access to products, ultimately affecting overall productivity.
The Solution: To address space utilization challenges, consider implementing modular conveyor systems that can be easily reconfigured. These systems offer flexibility, allowing businesses to adjust their layouts based on changing operational requirements. When selecting a rolling belt conveyor, prioritize those that are designed for easy installation and dismantling. Additionally, consult with a conveyor system expert to analyze your current layout and identify opportunities for improvement. Using software tools that simulate different configurations can help visualize how changes can optimize space and workflow. Investing in flexible conveyors can lead to more efficient use of floor space and improved accessibility to products, enhancing overall warehouse operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rolling belt conveyor
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Rolling belt conveyors are integral to material handling across various industries, and the selection of the right materials is crucial for optimal performance. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of rolling belt conveyors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Steel is a widely used material for rolling belt conveyors due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high-temperature rating and excellent pressure resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization or powder coating, increasing its lifespan in harsh environments.
Pros: Steel offers high load capacity, durability, and ease of fabrication. It is often more cost-effective than other materials for large-scale applications.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to rust if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, steel is heavier, which may complicate installation and increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for transporting heavy items and in environments where durability is paramount, such as manufacturing and logistics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM for the U.S. or DIN for Germany, particularly regarding corrosion resistance and load ratings.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Aluminum is another popular choice for rolling belt conveyors, especially in applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials. It has a lower temperature rating than steel but is still effective in moderate environments.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, making it easier to handle and install. It also has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is generally less strong than steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. The cost of aluminum is typically higher than that of steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is well-suited for applications where weight is a concern, such as in mobile conveyor systems or in environments with moisture.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should be aware of specific standards for aluminum alloys, such as JIS in Japan or EN standards in Europe, to ensure compatibility with their applications.
How Do Plastic Materials Compare in Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Plastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are increasingly being used in rolling belt conveyors, particularly in industries dealing with food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. These materials offer unique properties such as chemical resistance and lightweight characteristics.
Pros: Plastics are resistant to corrosion, lightweight, and can be molded into various shapes, making them versatile for different applications. They are also non-conductive, which is beneficial in electronic applications.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic is its lower load-bearing capacity compared to metals. Additionally, plastics may degrade under high temperatures or UV exposure.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for light to medium-duty applications, especially where hygiene is critical, such as food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with food safety regulations, such as FDA standards in the U.S. or EU regulations in Europe, especially when used in food-related applications.
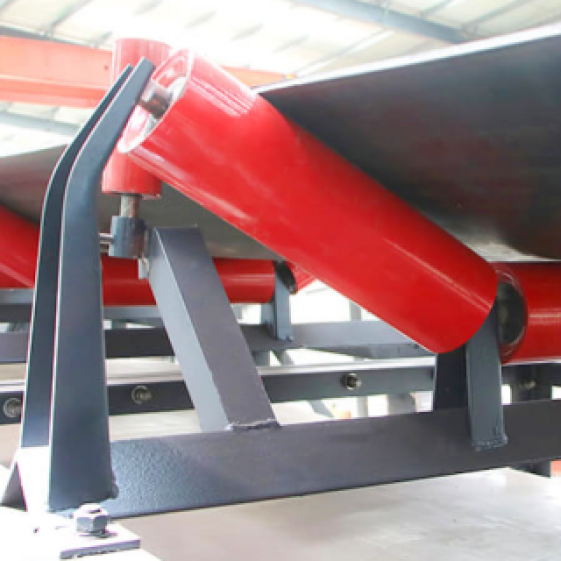

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Stainless steel is a premium material choice for rolling belt conveyors, particularly in environments that require high levels of hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as food and pharmaceutical industries.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and easy to clean, making it ideal for sanitary applications. It also maintains structural integrity under high temperatures.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is significantly higher than that of carbon steel or aluminum, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. It can also be more challenging to fabricate.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is essential in applications where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in food processing and medical equipment manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of specific grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316) and their compliance with international standards, ensuring they meet local regulations for food safety and hygiene.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rolling Belt Conveyors
| Material | Typical Use Case for rolling belt conveyor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | High load capacity and durability | Susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and mobile systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
| Plastic | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Chemical resistance and versatility | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Sanitary applications | High corrosion resistance and hygiene | Higher cost and fabrication complexity | High |
This guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of material selection for rolling belt conveyors, facilitating informed decision-making tailored to their specific industry needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rolling belt conveyor
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Rolling Belt Conveyor?
The manufacturing process of rolling belt conveyors involves several key stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets both functional requirements and quality standards.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first stage of manufacturing begins with material preparation. Common materials for rolling belt conveyors include steel, aluminum, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). The selection of materials largely depends on the intended use of the conveyor, such as load capacity and environmental conditions. For instance, galvanized steel is often chosen for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for humid environments, while aluminum is favored for lightweight applications.
During this stage, raw materials are cut to size according to specifications. Advanced cutting techniques, such as laser cutting or water jet cutting, are commonly employed to achieve precise dimensions and minimize waste. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who need exact specifications for integration into existing systems.
Forming: How Are the Components Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, the next phase is forming. This process involves bending, welding, or stamping the raw materials into the desired shapes. For rolling belt conveyors, forming techniques such as roll forming and extrusion are frequently used.
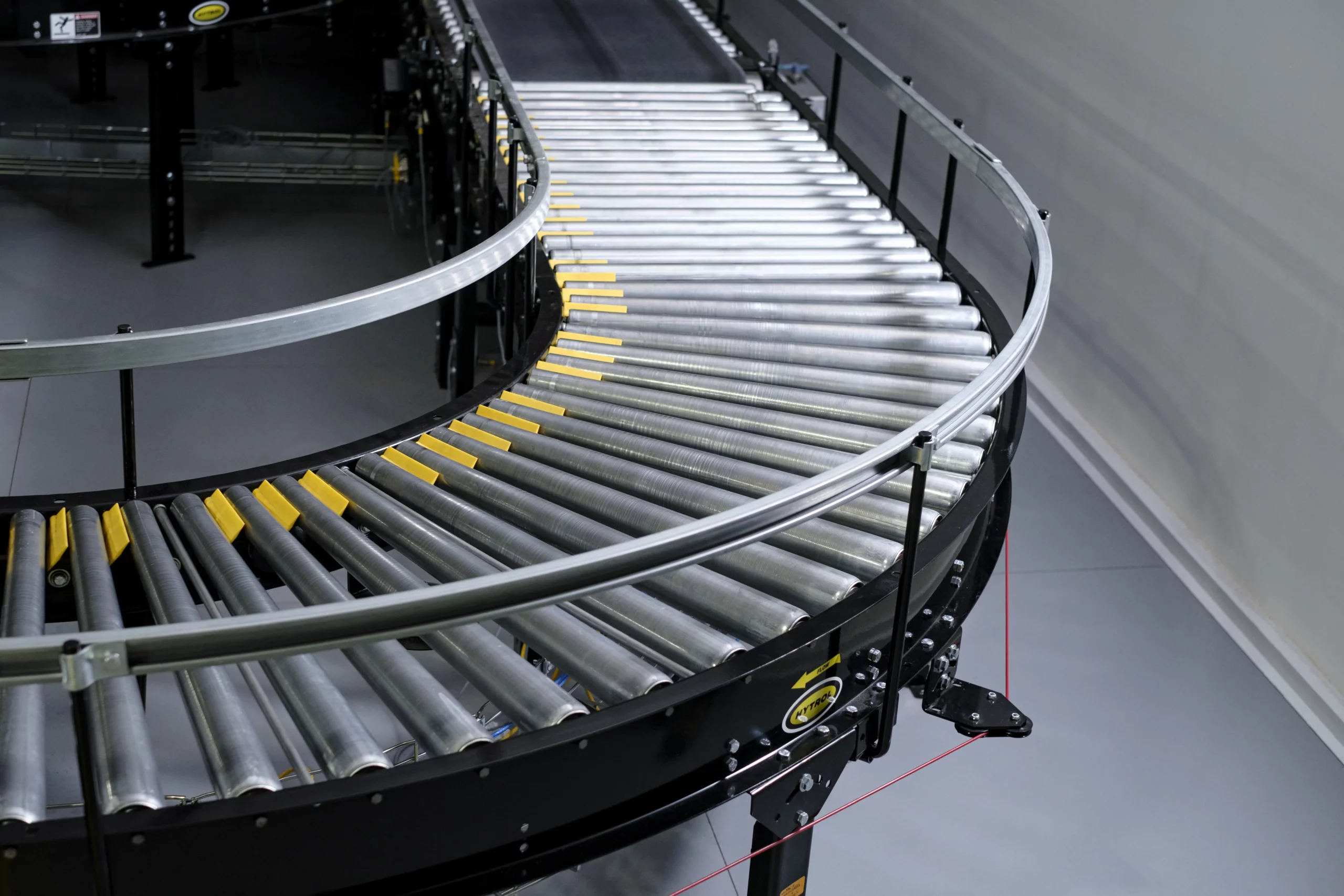

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
Roll forming is ideal for producing long, continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, which is essential for conveyor frames and supports. Welding is often employed to join different components securely, ensuring structural integrity. This stage must be performed with precision, as any flaws can impact the conveyor’s performance and longevity.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
After the components are formed, assembly begins. This stage involves integrating various parts, such as rollers, belts, and drive systems, into a cohesive unit. Each component is assembled according to detailed engineering drawings and specifications.
Quality checks are conducted throughout the assembly process, focusing on alignment, fit, and functionality. For example, rollers must be aligned correctly to ensure smooth operation and minimize wear. Automated assembly systems may be used to enhance efficiency and consistency, particularly in high-volume production scenarios.
Finishing: How Is the Conveyor Prepared for Use?
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which includes surface treatments and coatings. This process not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the conveyor but also provides additional protection against wear and corrosion. Common finishing techniques include powder coating, painting, and anodizing.
Quality assurance during the finishing stage is crucial, as improper coatings can lead to premature failure. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific finishing processes used by suppliers to ensure that the product will withstand the intended operational conditions.
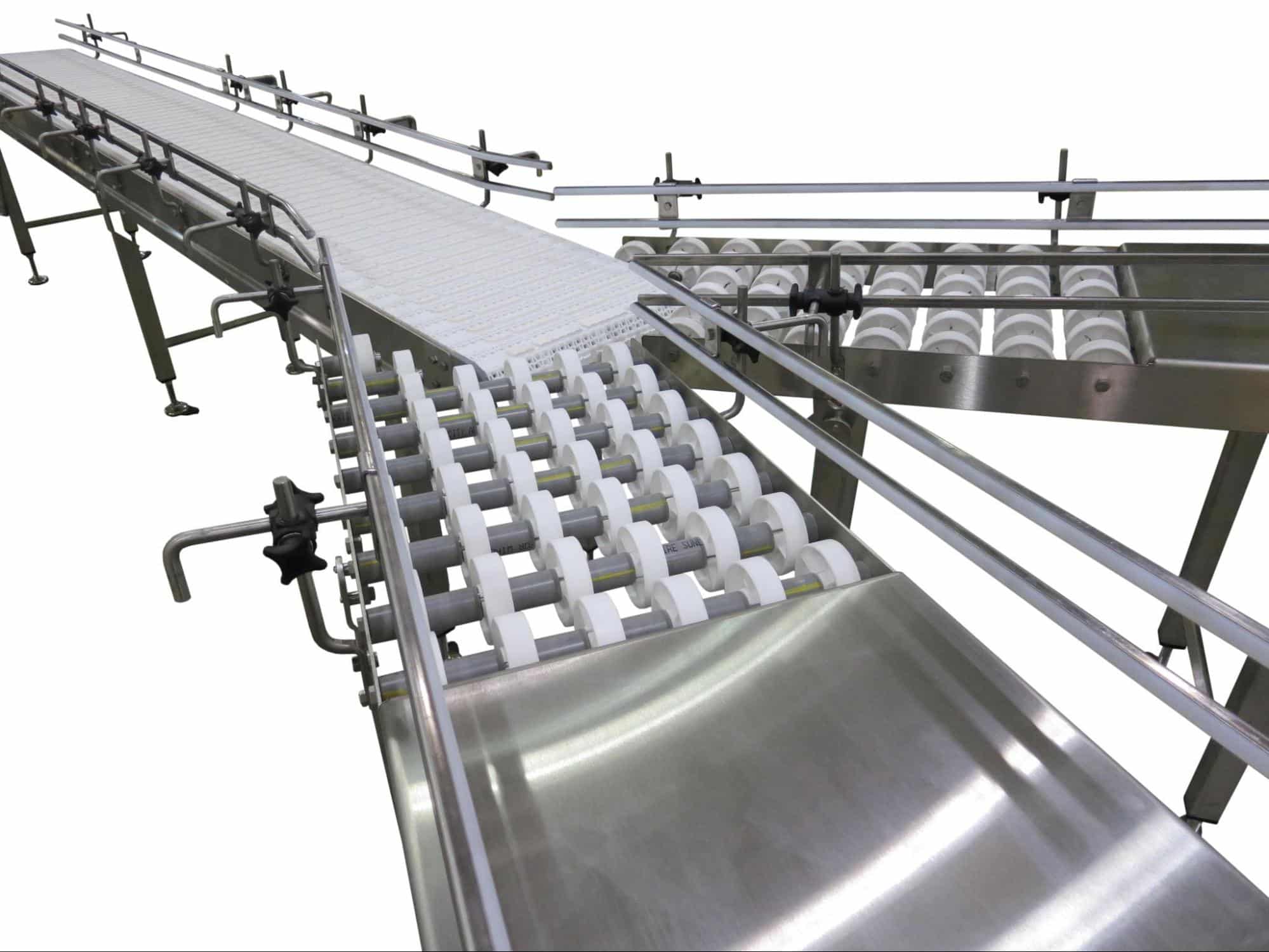

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for rolling belt conveyors. Adhering to international and industry-specific standards ensures that products meet safety and performance criteria.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It outlines criteria for organizations to ensure consistent quality in products and services. For rolling belt conveyors, compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe, signify compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers possess these certifications, as they demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects. The main QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards. This is crucial for preventing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Quality checks during the manufacturing stages, such as measuring dimensions and testing for weld integrity, help catch issues early in the process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing, which may include load testing, operational testing, and visual inspections, to ensure it meets all performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are some strategies:
What Audit and Inspection Options Are Available?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities allows buyers to evaluate the quality management systems in place. This includes assessing compliance with international standards and the overall production environment.
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, test results, and any corrective actions taken for defects. These documents can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations can conduct random inspections and provide certification that the products meet specified standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding QC and Certification?
When sourcing rolling belt conveyors from international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of certain nuances that can affect the purchasing process:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local certifications required in their markets, such as UL certification in North America or EN standards in Europe.
-
Language Barriers: Communication can be a challenge when dealing with international suppliers. Buyers should ensure that documentation is clear and available in a language they understand to avoid misunderstandings regarding quality specifications.
-
Cultural Differences: Different countries may have distinct approaches to quality assurance. Buyers should be prepared to adapt their expectations and methods of communication to align with the practices of their suppliers.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for rolling belt conveyors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they select reliable suppliers capable of meeting their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rolling belt conveyor’
In the fast-paced world of material handling, sourcing a rolling belt conveyor requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure rolling belt conveyors efficiently and effectively, ensuring that the chosen solution meets operational needs and contributes to overall productivity.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by detailing the technical requirements of your conveyor system. Consider factors such as the types of materials to be transported, load capacities, and the conveyor’s speed. It’s essential to ensure that the specifications align with the operational demands of your facility to avoid costly adjustments later.
- Material Type: Identify whether the conveyor will handle boxes, pallets, or bulk materials.
- Weight Capacity: Determine the maximum weight per load to avoid overloading the conveyor.
Step 2: Assess Your Space Requirements
Evaluate the physical space where the conveyor will be installed. This includes measuring the dimensions of the installation area and considering the layout for optimal workflow. A well-planned installation will enhance efficiency and reduce operational bottlenecks.
- Length and Width: Ensure the conveyor fits within your available space, allowing for necessary clearances.
- Height Adjustments: Consider if adjustable height features are needed for ergonomic operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry and a proven track record of successful installations. Request documentation such as company profiles, case studies, and customer references.
- Certifications: Verify if the supplier meets industry standards and holds relevant certifications.
- Client Feedback: Seek testimonials from clients in similar sectors to gauge satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: Review Warranty and Support Options
Investigate the warranty terms and support services provided by the supplier. A robust warranty can protect your investment and ensure that you have access to necessary maintenance and repairs without incurring additional costs.
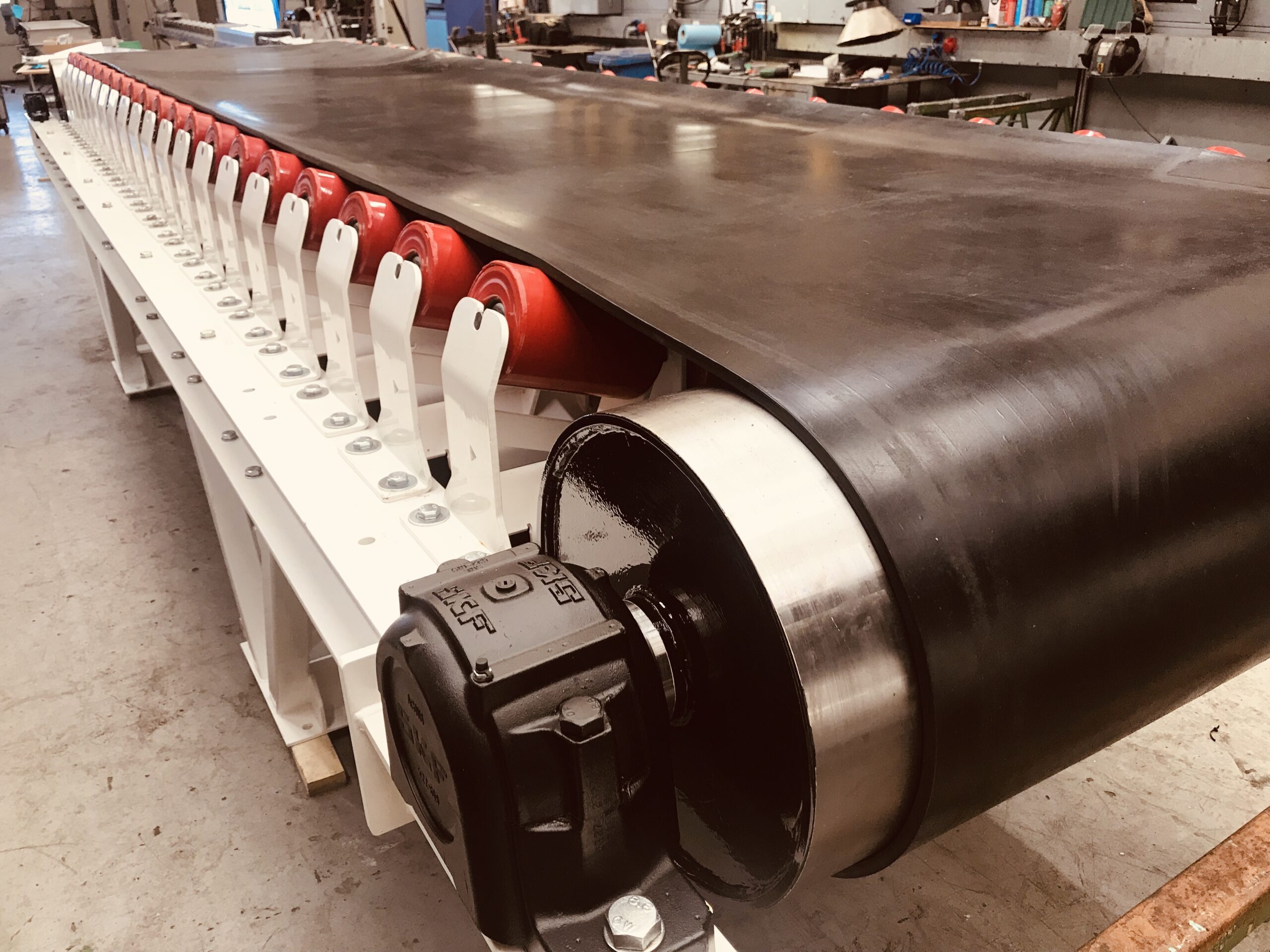

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
- Warranty Duration: Longer warranties often indicate confidence in product durability.
- Support Services: Check if the supplier offers installation assistance and ongoing technical support.
Step 5: Consider Cost vs. Value
While budgeting is crucial, focus on the overall value of the conveyor rather than just the initial cost. Assess the long-term benefits, including operational efficiency, energy consumption, and maintenance costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Evaluate how the conveyor improves productivity and reduces labor costs.
- Energy Consumption: Investigate energy-efficient models to lower operational expenses over time.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
If possible, request a sample conveyor or arrange for a trial period. This allows you to assess the conveyor’s performance in real-world conditions and ensure it meets your specifications before finalizing the purchase.
- Performance Testing: Check for reliability and functionality during the trial period.
- Adaptability: Ensure the conveyor can accommodate any changes in your operational needs.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract Terms
Once a supplier has been selected, carefully review and finalize the contract terms. Ensure all specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and support services are clearly outlined to prevent misunderstandings later.
Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
- Clarity on Deliverables: Specify what is included in the purchase, such as installation and training.
- Payment Terms: Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing rolling belt conveyors, ensuring they select the right system to enhance their operations effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rolling belt conveyor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rolling Belt Conveyor Manufacturing?
When sourcing rolling belt conveyors, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the price. Steel is commonly used due to its durability, while aluminum offers lighter options. The cost of raw materials can fluctuate based on market conditions and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and complexity of the conveyor system. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembly and installation, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these expenses.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be required for custom designs, which can increase upfront costs. Standardized tooling can reduce expenses but may limit customization options.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the conveyors meet safety and performance standards, which can incur additional costs but ultimately leads to higher product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering the conveyors to the buyer’s location can vary based on distance, shipping method, and the Incoterms agreed upon. Understanding these logistics can help buyers plan their budgets effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary significantly between suppliers based on their market positioning and service offerings.
What Influences Pricing for Rolling Belt Conveyors?
Several factors can influence the pricing of rolling belt conveyors:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts. Buyers should negotiate for lower prices when ordering in higher volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs will generally incur higher costs. Standard models are more cost-effective but may not meet all operational requirements.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can increase initial costs but may provide long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance.
-
Supplier Factors: Different suppliers offer varying pricing structures based on their reputation, experience, and service levels. It’s advisable to compare multiple suppliers before making a decision.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact the total cost. Buyers should be aware of who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Rolling Belt Conveyors?
To achieve the best pricing and terms, international B2B buyers should consider the following negotiation strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market prices and competitor offerings to negotiate from an informed position.
-
Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy efficiency, to make an informed decision.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: Being open to alternative materials or designs can lead to significant cost reductions.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, specific nuances can affect pricing:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of how currency exchange rates can affect the overall cost when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understand the local regulations regarding import duties and taxes, as these can add to the total cost.
-
Cultural Differences: Negotiation styles can vary significantly across cultures. Being aware of these differences can facilitate smoother negotiations.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost and pricing landscape for rolling belt conveyors requires a comprehensive understanding of various components and influencing factors. By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that pricing can vary significantly, so it’s advisable to seek multiple quotes and consider the total cost of ownership when making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rolling belt conveyor With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Conveyor Alternatives for Material Handling
In the realm of material handling, selecting the right conveyor system is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency. While rolling belt conveyors are a popular choice due to their versatility and effectiveness, other alternatives offer unique advantages depending on specific application needs. This analysis will compare rolling belt conveyors with two viable alternatives: gravity roller conveyors and powered roller conveyors. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each solution can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their operational requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Rolling Belt Conveyor | Gravity Roller Conveyor | Powered Roller Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; suitable for various product types | Moderate efficiency; best for lighter, stable loads | High efficiency; ideal for heavy loads and accumulation |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Lower initial cost, especially for used models | Moderate to high; cost-effective for automation |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful installation and alignment | Simple installation; often modular | More complex; may require electrical setup |
| Maintenance | Requires regular belt replacements and tension adjustments | Low maintenance; rollers may need occasional lubrication | Moderate maintenance; electrical components need monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for transporting diverse materials, especially those with uneven bases | Best for lightweight packages and manual handling | Suitable for heavy loads and automated systems with accumulation needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Gravity Roller Conveyor
Gravity roller conveyors use the force of gravity to move products along a series of rollers. They are particularly beneficial in environments where manual handling is common, and they can easily be integrated into existing workflows. The primary advantage of gravity roller conveyors is their cost-effectiveness, especially when purchasing used equipment, which can save businesses 30-40% compared to new options. However, their performance is limited to lighter loads, and they require a slight incline to function effectively, which may not suit all applications.
Powered Roller Conveyor
Powered roller conveyors utilize a motorized system to drive the rollers, providing a reliable solution for transporting heavier items and enabling accumulation. This type of conveyor is particularly advantageous in automated environments, as it can facilitate smoother transitions between different stages of production or packaging. While the initial investment can be higher than gravity systems, powered roller conveyors often lead to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs over time. However, the complexity of installation and the need for regular monitoring of electrical components can be seen as drawbacks, especially for businesses with limited technical resources.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Conveyor Solution
When selecting the right conveyor solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors such as load type, operational efficiency, and budget constraints. Rolling belt conveyors offer versatility and high performance, making them suitable for diverse applications. However, if cost or specific handling requirements are primary concerns, gravity roller conveyors may provide a more economical solution for lighter loads. Conversely, powered roller conveyors excel in automated settings where heavy loads and accumulation are necessary. By assessing the specific needs of their operations, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their long-term business goals, ensuring optimal efficiency and productivity in their material handling processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rolling belt conveyor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Rolling Belt Conveyor?
When evaluating rolling belt conveyors, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key properties:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a conveyor is fundamental as it determines durability and load capacity. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and plastic. Steel offers high strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy loads, while aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for environments where weight is a concern. Choosing the right material can significantly affect the operational lifespan and performance of the conveyor.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
2. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum weight a conveyor can handle safely. This specification is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts efficiency and safety. Conveyors with higher load capacities can transport heavier items without risk of failure, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Understanding the load requirements of your operations helps in selecting a conveyor that meets your needs.
3. Belt Width and Length
Belt dimensions, including width and length, affect the flow of materials through the conveyor system. A wider belt can accommodate larger items or more products at once, improving throughput. The length must be appropriate for the layout of the facility. Incorrect sizing can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs, making it essential to assess your specific requirements beforehand.
4. Roller Diameter
The diameter of the rollers impacts the smoothness of operation and the weight distribution across the conveyor. Standard roller diameters range from 1.375 inches to 1.9 inches, with larger diameters generally providing better load distribution and less friction. This is particularly important for ensuring the longevity of both the conveyor and the materials being transported.
5. Drive Type
The type of drive system—such as belt-driven, chain-driven, or gravity-driven—affects how materials are moved along the conveyor. Belt-driven systems are typically more efficient for continuous operation, while gravity-driven systems are cost-effective for shorter distances. Understanding the pros and cons of each drive type helps businesses align their conveyor systems with operational needs and energy efficiency goals.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Conveyor Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of conveyors, it often involves manufacturers that provide specialized parts or complete systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it impacts budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases and ensure they are not overcommitting to stock they may not need.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain price quotes for specific products or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs, specifications, and delivery times, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers regarding the delivery of goods. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks associated with transportation. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, particularly for international buyers, to avoid disputes and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the conveyor industry, this can vary significantly based on the complexity of the system and the supplier’s location. Knowing the lead time helps businesses plan their operations and manage customer expectations effectively.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they select the right rolling belt conveyor for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rolling belt conveyor Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting Rolling Belt Conveyor Sourcing?
The rolling belt conveyor market is experiencing a dynamic shift driven by several global factors. The rise of e-commerce and the need for efficient logistics solutions are major catalysts, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. In these areas, businesses are increasingly investing in automation technologies to streamline operations and reduce labor costs. This trend is further supported by advancements in conveyor technology, such as the integration of IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which enhances operational efficiency.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a growing preference for customizable conveyor systems that can be tailored to specific operational needs. This is particularly relevant in markets like Vietnam and Germany, where manufacturers are adapting their offerings to accommodate diverse applications, from heavy-duty industrial settings to lightweight packaging environments. Additionally, the demand for used conveyor systems is on the rise as companies seek cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. B2B buyers are advised to consider both new and refurbished options, as they can yield significant savings—often between 30% to 50%—while still meeting operational requirements.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Rolling Belt Conveyor Supply Chain?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern supply chain management, and the rolling belt conveyor sector is no exception. As environmental regulations tighten and consumer demand for sustainable practices grows, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship. This includes evaluating suppliers based on their use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and adherence to green certifications such as ISO 14001.
Incorporating sustainable practices not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation. Buyers should seek out conveyor systems constructed from eco-friendly materials, such as recycled metals and biodegradable components. Furthermore, companies that invest in energy-efficient conveyor solutions can significantly reduce operational costs over time, aligning economic benefits with environmental responsibility. As a result, sustainability is not just a trend; it’s becoming a competitive differentiator in the global conveyor market.
What Is the Historical Context of Rolling Belt Conveyors in B2B?
The history of rolling belt conveyors dates back to the late 19th century, when they were first introduced in manufacturing and distribution sectors to enhance material handling efficiency. Initially designed for simple tasks, these systems have evolved significantly, driven by technological advancements and changing industrial needs. The introduction of powered belt conveyors in the mid-20th century revolutionized logistics, enabling the transport of heavier loads over longer distances without manual intervention.

Illustrative image related to rolling belt conveyor
Today, rolling belt conveyors are integral to various industries, including automotive, food processing, and warehousing. The evolution of automation and digital technologies continues to reshape their design and functionality, making them an essential investment for businesses aiming to enhance productivity and operational efficiency in an increasingly competitive landscape. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the value and potential of modern conveyor solutions in their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rolling belt conveyor
-
How do I choose the right rolling belt conveyor for my needs?
Choosing the right rolling belt conveyor involves assessing various factors including the type of materials being transported, the weight and size of the products, and the layout of your facility. For lighter items, a gravity roller conveyor may suffice, while heavier loads may require a powered belt conveyor. Considerations such as the conveyor’s speed, incline requirements, and integration with existing systems are also crucial. Consulting with a supplier who offers a range of options can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific operational needs. -
What is the best rolling belt conveyor for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, a powered belt conveyor with a robust frame and high-capacity rollers is ideal. Look for options that utilize durable materials such as steel or reinforced polymers, which can withstand the stress of transporting heavy loads. Additionally, ensure the conveyor has a reliable motor and adjustable speed settings to accommodate varying operational demands. Suppliers often provide specifications on load capacities and suitable applications, helping you make an informed choice. -
What customization options are available for rolling belt conveyors?
Customization options for rolling belt conveyors can include varying lengths, widths, and heights to fit your specific space requirements. You can also select features such as adjustable speed controls, specialized belt materials (e.g., food-grade belts for food handling), and integration with sensors or automation systems. When discussing customization with suppliers, be clear about your operational needs and any specific challenges you face to ensure the solution is tailored effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rolling belt conveyors?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rolling belt conveyors can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may offer MOQs as low as one unit, particularly for custom or specialized orders, while others may require larger orders for standard models. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs upfront, especially if you’re considering multiple conveyors or specific configurations, to avoid unexpected costs and ensure you meet your operational needs. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by conveyor suppliers?
Payment terms offered by conveyor suppliers can differ widely based on factors such as order size, customer history, and geographical location. Common terms include a percentage upfront with the balance due upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). International buyers should also consider currency fluctuations and potential tariffs that could affect total costs. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing an order to ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers for rolling belt conveyors?
Vetting suppliers for rolling belt conveyors involves assessing their reputation, experience, and product quality. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and testimonials. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, especially for safety and quality. Request samples or visit their facilities if possible. Engaging in discussions about their manufacturing processes and after-sales support can also provide insight into their reliability as a partner. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing rolling belt conveyors?
When importing rolling belt conveyors, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Determine whether the supplier handles shipping or if you need to arrange logistics independently. Understanding import duties, taxes, and any additional fees is crucial to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborating with a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial equipment can streamline the process and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from conveyor manufacturers?
Quality assurance measures from conveyor manufacturers should include rigorous testing of materials and equipment before shipping. Look for suppliers that adhere to industry standards and offer warranties on their products. Inquire about their quality control processes, such as inspections and certifications. Manufacturers that provide detailed documentation of compliance with international standards demonstrate their commitment to producing reliable, high-quality conveyors, which is essential for long-term operational success.
Top 7 Rolling Belt Conveyor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wh1 – Conveyor Roller Tables
Domain: wh1.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: New & Used Conveyor Roller Tables for Sale. Condition: New (74), Used (19). Stocking location: In Stock @ Wh1 in KC (23), Ships from Factory (70). Styles include: Ball Transfer (6), Belt (2), Belt Driven (3), Chain Drive (2), Expanding Conveyors (23), Flat Motor (3), Gravity Roller (16), Gravity Skatewheel (6), Lineshaft Drive (3), Motorized Roller (3), Plastic Belt (3). Height options: 2.38″ (2),…
2. Ashland Conveyor – Pop Out Rollers
Domain: ashlandconveyor.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pop Out Rollers are designed for use in conveyor systems to facilitate smooth product movement. They feature a unique design that allows for easy removal and replacement, ensuring minimal downtime during maintenance. These rollers are available in various sizes and configurations to meet specific operational needs. Constructed from durable materials, they provide reliable performance in demanding …
3. AMC – Custom Conveyor Solutions
Domain: amcautomation.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: AMC’s Belt Conveyor and Roller Conveyor models are custom built for every order. Belt Conveyors can be made in any size with various belt options including: Black PVC, White Food Grade PVC, Ruff Top, Polyurethane, High Temperature, Check-Out Style, Cleated, and more. Roller Conveyors offer a variety of sizing options and configurations such as: Chain Driven Live Roller, Gravity Fed Roller, Belt Dr…
4. Matrix OK – Roach Roller Bed Belt Conveyor
Domain: matrixok.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Roach Roller Bed Belt Conveyor”, “price_range”: “$3,645.60 – $11,309.50”, “color”: “Green”, “sizes”: [“24’OAW x 10’L”, “24’OAW x 20’L”, “24’OAW x 30’L”, “24’OAW x 40’L”, “24’OAW x 50’L”, “30’OAW x 10’L”, “30’OAW x 20’L”, “30’OAW x 30’L”, “30’OAW x 40’L”, “30’OAW x 50’L”, “36’OAW x 10’L”, “36’OAW x 20’L”, “36’OAW x 30’L”, “36’OAW x 40’L”, “36’OAW x 50’L”, “42’OAW x 10’L”, “42’OAW x 20’L”,…
5. Belt Power – Live Roller Belting (LRB)
Domain: beltpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Live Roller Belting (LRB) is used in Live Roller Conveyors, commonly found in distribution centers and manufacturing plants. It drives gravity rollers in a Live Roller System. Belt Power offers various specifications used on OEM equipment like Dematic, Intelligrated, Hytrol, and TGW. Popular drive options include Belt Driven Round Belt (O-Ring), Chain & Sprocket, Driver Pad, and Motorized Pulley. …
6. MathMec – Conveyors for Material Handling
Domain: mathmec.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Belt conveyors and live roller conveyors are essential for material handling. Live roller conveyors consist of steel rollers that directly contact products, requiring maintenance to ensure smooth operation. They are often used for heavier products. Belt conveyors run products over slider beds or rollers, providing control on inclines and declines, and are powered by motors that require careful man…
7. Monk Conveyors – Roller Conveyors
Domain: monk-conveyors.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Roller conveyors by Monk Conveyors are designed to automate product movement, optimize workflow, and enhance safety. They are available in gravity or powered sections, suitable for various configurations. Key features include: robust powder-coated steel beams, quiet operation, modular design, and low maintenance. They come with a 1-year mechanical warranty and are CE marked. The Lineshaft Roller C…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rolling belt conveyor
As the global market for rolling belt conveyors continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Key takeaways from this guide emphasize the importance of understanding the diverse types of conveyors available, including powered, gravity, and specialized systems tailored for specific applications. Investing in the right conveyor solution not only streamlines material handling but also significantly boosts productivity and safety in warehouses and production environments.
Moreover, considering both new and used options can lead to substantial cost savings—up to 40% for used equipment. Buyers should also evaluate the electrical requirements and overall capacity needs to ensure that the selected systems align with their operational demands.
Looking ahead, the trend towards automation and energy-efficient solutions will likely reshape the conveyor landscape. By fostering partnerships with reliable suppliers and leveraging innovative technologies, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can position themselves for future growth. Engage with your suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that will enhance your material handling processes and drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.