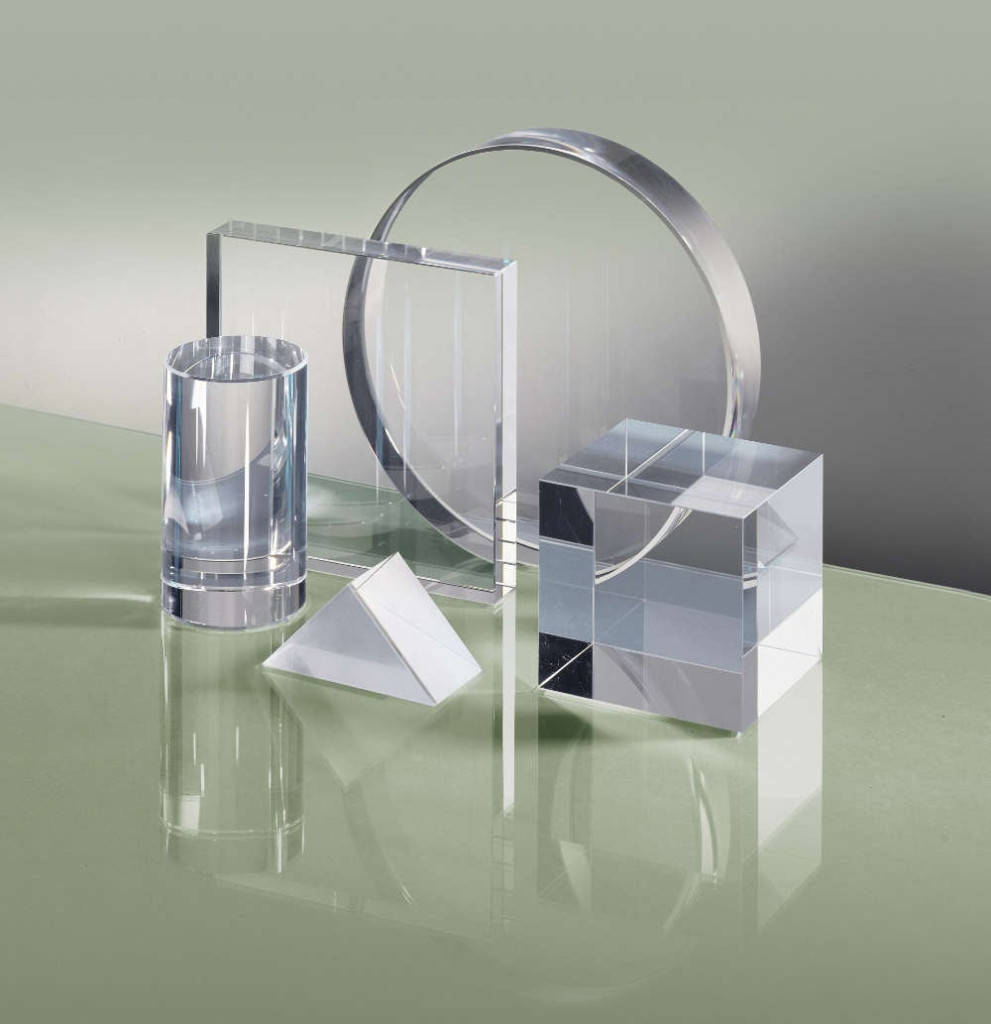
The Definitive Guide to Quarts Glass: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for quarts glass
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing quartz glass can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The unique properties of quartz glass—such as its thermal resistance, optical clarity, and chemical durability—make it essential across various industries, from semiconductors to solar energy. However, buyers often face challenges in identifying reliable suppliers, understanding product specifications, and evaluating cost-effectiveness. This guide addresses these challenges by offering a comprehensive overview of the quartz glass market, including different types of products, their applications, and strategic insights into supplier vetting.
In this guide, you will find detailed information on the diverse range of quartz glass products available, including fused quartz plates, tubing, and custom fabrication options. We will also explore the industries that rely on these materials and the specific performance characteristics that make quartz glass a preferred choice. Additionally, our guide will provide actionable advice on how to assess potential suppliers, ensuring that your purchasing decisions are informed and aligned with your business goals. By equipping you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market for quartz glass, this resource aims to empower you to make strategic purchasing decisions that drive efficiency and innovation in your operations.
Understanding quarts glass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | High purity, excellent thermal and chemical resistance | Semiconductor manufacturing, optics | Pros: High durability, low contamination risk. Cons: Higher cost compared to other types. |
| Quartz Glass Tubing | Tubular shape, customizable dimensions | Laboratory glassware, chemical processing | Pros: Versatile, can be tailored for specific applications. Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid breakage. |
| Opaque Quartz | Non-transparent, good thermal insulation properties | Industrial applications, heat exchangers | Pros: Effective for thermal insulation. Cons: Limited optical applications. |
| UV Grade Quartz | Exceptional UV transmission and optical clarity | UV applications, photonics | Pros: Ideal for UV-sensitive processes. Cons: May not be suitable for high-temperature uses. |
| Machined Quartz | Precision-engineered, can be customized for fit | Custom laboratory equipment, precision tools | Pros: Tailored solutions for specific needs. Cons: Longer lead times for custom orders. |
What are the characteristics of Fused Quartz and its B2B relevance?
Fused quartz is recognized for its high purity and exceptional thermal and chemical resistance. It is commonly used in semiconductor manufacturing and optical applications where low contamination levels are crucial. Buyers should consider its durability and performance in extreme conditions, which often justify the higher price point. For industries that prioritize quality and reliability, investing in fused quartz can lead to better long-term outcomes.
How does Quartz Glass Tubing serve various industries?
Quartz glass tubing is available in customizable dimensions, making it highly versatile for various applications, including laboratory glassware and chemical processing. Its adaptability allows businesses to create specialized equipment that meets specific operational needs. However, buyers must handle quartz tubing carefully to prevent breakage during installation and use, which can lead to increased costs.
In what scenarios is Opaque Quartz most beneficial?
Opaque quartz is characterized by its non-transparent nature and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it suitable for industrial applications such as heat exchangers. Its ability to insulate against heat can enhance energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. While it offers clear advantages for thermal applications, buyers should note its limitations in optical uses, which may restrict its versatility in certain projects.
What advantages does UV Grade Quartz provide for businesses?
UV grade quartz is specifically designed to offer exceptional UV transmission and optical clarity, making it ideal for UV-sensitive applications in photonics and other industries. Its performance in UV environments ensures that processes relying on ultraviolet light can operate effectively. However, businesses should consider the temperature limitations of UV grade quartz, as it may not withstand high-temperature applications as effectively as other types.
How can Machined Quartz fulfill specific B2B needs?
Machined quartz is precision-engineered to meet the specific requirements of various applications, particularly in custom laboratory equipment and precision tools. This customization allows businesses to optimize their operations and enhance productivity. While tailored solutions can be highly beneficial, buyers should be aware of potentially longer lead times for custom orders, which may affect project timelines.
Key Industrial Applications of quarts glass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Quartz Glass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Fused Quartz Tubing for Process Equipment | High purity and thermal stability ensure reliable performance in sensitive processes. | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and verify purity levels. |
| Laboratory Equipment | Quartz Microscope Slides and Cover Slips | Exceptional optical clarity enhances research accuracy and results. | Look for UV-grade options and consider custom sizes for specific applications. |
| Solar Energy | Quartz Glass for Solar Cell Production | High thermal resistance and UV transparency improve efficiency in solar applications. | Assess supplier’s ability to provide customized dimensions and quality certification. |
| Chemical Processing | Quartz Boiling Flasks and Reaction Vessels | Chemical resistance and thermal stability facilitate safe and effective reactions. | Verify the chemical compatibility of quartz glass with intended substances. |
| Optical Systems | UV-Grade Quartz Plates for Optical Applications | Superior UV transmission and durability enhance performance in optical devices. | Check for optical specifications and ensure conformity with international standards. |
How is Quartz Glass Used in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
In semiconductor manufacturing, fused quartz tubing is critical for various process equipment, including reaction chambers and transport systems. Its high purity minimizes contamination risks, while its thermal stability allows it to withstand extreme temperatures during production. International buyers, particularly those in regions like Europe and the Middle East, should ensure that suppliers can meet stringent purity standards and provide compatibility with existing manufacturing systems to maintain operational efficiency.
What Role Does Quartz Glass Play in Laboratory Equipment?
Quartz microscope slides and cover slips are essential in laboratories for their superior optical clarity, which is crucial for precise research and diagnostics. These slides can withstand high temperatures and are resistant to chemical damage, making them ideal for various applications. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider sourcing UV-grade quartz options and be open to custom sizes to fit specialized equipment, ensuring optimal performance in their research environments.
How Does Quartz Glass Enhance Solar Energy Applications?
In the solar energy sector, quartz glass is utilized in the production of solar cells, thanks to its excellent thermal resistance and UV transparency. These properties help improve the efficiency and durability of solar panels, making them a preferred choice for renewable energy solutions. Buyers should assess potential suppliers for their ability to deliver customized quartz glass solutions that meet specific project requirements, including size and quality certifications to ensure compliance with international standards.
Why is Quartz Glass Important in Chemical Processing?
Quartz boiling flasks and reaction vessels are widely used in chemical processing due to their high chemical resistance and thermal stability. These properties facilitate safe and effective reactions, minimizing the risk of breakage or contamination. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, it’s vital to verify the chemical compatibility of quartz glass with the substances being processed to ensure safety and efficiency in operations.
What Advantages Does UV-Grade Quartz Glass Offer in Optical Systems?
In optical systems, UV-grade quartz plates are favored for their superior UV transmission and durability, enhancing the performance of various optical devices, including lenses and filters. The exceptional clarity and resistance to thermal shock make them ideal for high-precision applications. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can provide detailed optical specifications and ensure compliance with international optical standards, particularly in highly regulated markets like Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘quarts glass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Purity Requirements for Sensitive Applications
The Problem: In industries such as pharmaceuticals and semiconductors, the demand for high-purity materials is paramount. B2B buyers often struggle to find quartz glass that meets stringent purity standards. Contaminants in quartz glass can lead to product failures, compromised data, and significant financial losses. Buyers may also face challenges in verifying the quality and sourcing of quartz glass, particularly when dealing with international suppliers or navigating regional regulations.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
The Solution: To ensure the quartz glass meets high purity requirements, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers that provide comprehensive certification and documentation. Look for suppliers who can demonstrate their quartz glass products are made from high-grade raw materials and are subjected to rigorous quality control processes. Request material safety data sheets (MSDS) and certificates of analysis (CoA) to verify the absence of contaminants. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer custom fabrication services, as this allows for tailored solutions that align with specific industry standards and application requirements.
Scenario 2: Thermal Stability Issues in High-Temperature Applications
The Problem: Industries that operate under extreme temperatures, such as aerospace or materials processing, often face challenges with thermal stability in their glass components. Quartz glass, while known for its high thermal resistance, can still suffer from thermal shock if not properly specified. B2B buyers may find themselves encountering cracked or shattered components, leading to costly downtime and safety concerns in their operations.
The Solution: When sourcing quartz glass for high-temperature applications, it is crucial to assess its thermal expansion coefficient and maximum operating temperature. Buyers should consult with suppliers about the specific thermal properties of the quartz glass they intend to use. Opt for UV-grade or fused silica quartz, which is designed to withstand extreme conditions and thermal cycling. Moreover, implementing proper installation techniques, such as gradual heating and cooling, can mitigate the risk of thermal shock. Engaging in detailed discussions with suppliers about the intended application can also lead to recommendations for the best types of quartz glass suited for specific operational parameters.
Scenario 3: Compatibility with Other Materials
The Problem: In laboratory and industrial settings, quartz glass is often used in conjunction with various other materials, such as metals and plastics. Compatibility issues can arise, especially when dealing with thermal expansion differences or chemical interactions. B2B buyers may encounter significant challenges when attempting to create effective seals or connections between quartz glass and other materials, leading to leaks or equipment failures.
The Solution: To address compatibility issues, buyers should choose quartz glass products that are specifically designed for integration with other materials. For example, quartz-to-Pyrex graded seals can provide a reliable connection between quartz and borosilicate glass, accommodating differing thermal expansion rates and minimizing stress. It is also beneficial to consult with manufacturers about the best practices for sealing and connecting quartz glass with other materials to avoid leaks. Conducting thorough compatibility testing in controlled environments can help identify potential issues before full-scale implementation, ensuring a seamless integration of quartz glass within existing systems. Additionally, consider custom solutions from suppliers that specialize in multi-material assemblies to streamline the design and manufacturing process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for quarts glass
What Are the Key Properties of Different Quartz Glass Materials?
When selecting quartz glass for industrial applications, understanding the properties of various materials is crucial. Here, we explore four common types of quartz glass, their advantages and disadvantages, and their implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Fused Quartz
Key Properties:
Fused quartz is known for its exceptional thermal stability, high purity, and excellent optical clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C and exhibits low thermal expansion, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of fused quartz is one of its standout features, as it resists thermal shock and chemical corrosion. However, it can be more expensive than other glass types, and its manufacturing process is complex, requiring specialized equipment. This material is ideal for applications in laboratories, semiconductor production, and optical systems.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
Impact on Application:
Fused quartz is compatible with various media, including aggressive chemicals and high-energy UV light. Its purity makes it suitable for sensitive applications, such as analytical chemistry and photonics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and Europe should be aware of compliance standards such as ASTM and DIN. Additionally, sourcing from reputable suppliers ensures adherence to quality specifications.
2. Borosilicate Glass
Key Properties:
Borosilicate glass offers a good balance of thermal resistance and chemical durability, with a thermal expansion coefficient lower than that of standard glass.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
Pros & Cons:
While borosilicate glass is less expensive than fused quartz, it is not as thermally stable and can be prone to breakage under extreme conditions. It is widely used in laboratory glassware and kitchen items due to its affordability and versatility.
Impact on Application:
This material is suitable for applications involving moderate temperatures and corrosive substances, making it ideal for laboratory environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of borosilicate glass in their region and any local standards that may apply, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe.
3. UV Grade Quartz
Key Properties:
UV grade quartz is specifically designed to transmit ultraviolet light effectively, with minimal absorption. It is typically made from high-purity silica.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of UV grade quartz is its optical clarity in the UV spectrum, making it essential for applications in UV photochemistry and sterilization. However, it can be more costly than standard quartz glass and may require specialized handling to avoid scratches.
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly suitable for UV light applications, such as photolithography and UV curing processes, where clarity and transmission are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure that UV grade quartz meets specific optical standards and certifications, especially for applications in the medical or semiconductor industries.
4. Quartz Glass with Graded Seals
Key Properties:
Quartz glass with graded seals combines the properties of quartz and borosilicate glass, allowing for effective thermal expansion compatibility.
Pros & Cons:
These seals provide a reliable hermetic connection, making them ideal for applications requiring airtight seals. However, the complexity of manufacturing graded seals can lead to higher costs and longer lead times.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly useful in scientific and industrial applications that require secure connections between different glass types, such as in laboratory setups.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the graded seals comply with international sealing standards to ensure compatibility and reliability in their applications.
Summary Table of Quartz Glass Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for quartz glass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | Semiconductor production, optical systems | Exceptional thermal stability | High manufacturing complexity | High |
| Borosilicate Glass | Laboratory glassware, kitchen items | Affordable and versatile | Less thermal stability | Medium |
| UV Grade Quartz | UV photochemistry, sterilization | High optical clarity in UV spectrum | Higher cost, requires careful handling | High |
| Quartz Glass with Graded Seals | Laboratory setups requiring airtight seals | Reliable hermetic connections | Higher costs, longer lead times | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of quartz glass materials, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on specific application needs and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for quarts glass
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Quartz Glass?
The manufacturing process of quartz glass involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent industry standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
-
Material Preparation
The process begins with sourcing high-purity silica sand, which is the primary raw material for quartz glass. This silica is processed to remove impurities and ensure a uniform grain size. The preparation phase may also involve the addition of other materials to enhance specific properties, such as thermal resistance or optical clarity. -
Forming Techniques Used in Quartz Glass Production
The forming stage encompasses various techniques, including melting, molding, and extrusion. The most common method is melting silica at high temperatures, typically around 1700°C. The molten silica is then poured into molds to create desired shapes, such as plates, rods, or tubes. For applications requiring high precision, techniques like flame fusion or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) may be employed, producing high-quality quartz glass with excellent optical properties. -
Assembly and Integration
After forming, the components may require assembly, especially for products like laboratory glassware where multiple parts need to be joined. Techniques such as fusing and sealing are employed to ensure airtight connections. For example, quartz-to-Pyrex graded seals are often used to join quartz components to borosilicate glass, accommodating differences in thermal expansion and minimizing stress during temperature changes. -
Finishing Processes for Enhanced Quality
The final stage involves finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, and coating. Grinding is used to achieve precise dimensions and flatness, while polishing enhances optical clarity. Additional coatings may be applied to improve chemical resistance or reduce reflectivity, depending on the intended application.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the quartz glass manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
-
International Standards Relevant to Quartz Glass Production
Many manufacturers adopt ISO 9001 as a foundational quality management system, which emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Other relevant certifications include CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for applications in the oil and gas sector. These standards assure buyers that the products have been manufactured under stringent quality controls. -
Quality Control Checkpoints During Production
The quality control process typically involves several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, samples are taken at various stages to check for defects or deviations from specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the final products undergo rigorous testing to verify their compliance with quality standards. -
Common Testing Methods for Quartz Glass
Various testing methods are employed to ensure product quality, including:
– Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to measure the physical dimensions of the glass.
– Optical Testing: Assessing the optical clarity and light transmission properties using spectrophotometers.
– Thermal Resistance Testing: Evaluating the glass’s ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks.
– Chemical Durability Tests: Determining how well the glass resists corrosive substances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process. Here are some strategies to verify supplier quality control practices:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. Buyers should look for evidence of adherence to international standards, such as ISO 9001 certification. -
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality control reports, including results from testing and inspections conducted at various stages of production. These reports should outline any issues detected and corrective actions taken. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be particularly useful for high-stakes projects where compliance with specific standards is crucial.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various nuances in quality control when sourcing quartz glass.
-
Understanding Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements. For instance, products sold in the European Union must comply with CE marking standards, while North American buyers may require compliance with ASTM standards. Understanding these requirements is essential for ensuring product acceptance in the target market. -
Language and Communication Barriers
Language differences can pose challenges in understanding quality documentation and specifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide documentation in a language they are comfortable with and that all technical terms are clearly defined. -
Cultural Considerations in Quality Assurance
Cultural attitudes toward quality and compliance can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should establish clear communication and expectations with suppliers regarding quality standards and practices to avoid misunderstandings. -
Logistics and Transportation Concerns
When sourcing quartz glass internationally, the potential for damage during transportation must be considered. Quality assurance processes should include packaging and handling protocols to minimize the risk of breakage or defects during shipping.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for quartz glass, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with suppliers that meet their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘quarts glass’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in the procurement of quartz glass, a material critical for various industrial applications. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that you select the right suppliers and products that meet your specific requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it is essential to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements for quartz glass. Consider factors such as purity levels, thermal resistance, and optical clarity, which will significantly impact the material’s suitability for your application.
- Purity Levels: Depending on the intended use, you may require high-purity fused quartz to avoid contamination.
- Thermal Resistance: Specify the temperature range the glass must withstand, especially for high-heat applications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in quartz glass manufacturing. Look for companies with a proven track record and expertise in your specific industry.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
- Industry Reputation: Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge the supplier’s reliability.
- Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a diverse range of quartz glass products, such as plates, rods, and custom fabrication options.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, which can indicate adherence to industry standards and quality assurance. Certifications like ISO 9001 or specific industry-related qualifications can be critical in ensuring product quality.
- Quality Assurance: Certification ensures that the supplier has established processes for maintaining product quality.
- Compliance: Check if they meet international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions.
Step 4: Request Samples
Before placing a large order, request samples of the quartz glass products you are interested in. This step allows you to evaluate the material’s quality, clarity, and suitability for your application firsthand.
- Quality Assessment: Inspect the samples for defects, clarity, and compliance with your specifications.
- Testing: If applicable, conduct tests to ensure the samples meet your thermal and chemical resistance requirements.
Step 5: Understand Pricing and Terms
Discuss pricing structures, payment terms, and delivery timelines with potential suppliers. Understanding these elements can help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about price breaks for bulk orders, as this could significantly lower your costs.
- Lead Times: Clarify delivery schedules to ensure they align with your project timelines.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of your purchase. This includes discussing warranties, return policies, and any potential penalties for delays.
- Warranties: Ensure that warranties are in place for the quality of the glass, especially for critical applications.
- Flexibility: Look for suppliers who offer flexible terms in case project requirements change.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
After successfully sourcing quartz glass, consider building a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. A reliable partnership can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaboration on future projects.
- Feedback Loop: Provide feedback to the supplier to help them improve their offerings and service.
- Future Needs: Discuss potential future needs to ensure your supplier can scale with your operations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing quartz glass effectively, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for quarts glass Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of quartz glass sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement strategy. This analysis breaks down the various cost components, identifies price influencers, and offers actionable tips for negotiation and cost-efficiency.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
The cost structure of quartz glass involves several critical components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the raw material itself—high-purity silica. The quality and source of silica can significantly impact pricing. Suppliers may offer different grades, which can affect both performance and cost.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the manufacturing process, particularly in the fabrication of custom quartz glass products. Labor costs can vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the production processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory management. High-temperature furnaces used in the quartz glass production process contribute significantly to overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific product requirements can add a substantial upfront cost. This factor is particularly relevant for buyers needing unique shapes or dimensions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining stringent QC standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability. The costs associated with QC processes can vary based on the certifications required (ISO, ASTM, etc.) and the testing methods employed.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can be significant, especially for international shipments. Factors such as freight, insurance, and potential tariffs must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin, which can vary based on market conditions and the competitive landscape.
What Influences Quartz Glass Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of quartz glass products:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced unit costs. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs for tooling and labor. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or specific certifications can justify a premium price. Buyers should ensure that the material meets their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with strong track records may command higher prices but offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (like FOB, CIF, etc.) can affect overall costs. Buyers should be clear about responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Quartz Glass Prices?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet or exceed MOQs to negotiate better pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with sourcing quartz glass, including maintenance, durability, and potential downtime from subpar products.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understand market trends and competitor pricing to strengthen your negotiation position. Awareness of market conditions can lead to better deals.
-
Communicate Clearly with Suppliers: Clearly outline specifications and expectations to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to increased costs.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Don’t rely on a single supplier. Comparing offers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Recognize that international buyers might face additional costs related to currency fluctuations and geopolitical factors affecting trade.
Disclaimer on Pricing Information
Prices for quartz glass products can fluctuate based on various factors such as market demand, raw material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. The indicative prices provided in catalogs or online listings should be considered as a starting point for negotiations and not as final costs. Always confirm pricing with suppliers directly to ensure accuracy.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
By understanding these cost structures and pricing influences, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions and effectively manage their sourcing strategies for quartz glass.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing quarts glass With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Quartz Glass in Industrial Applications
When evaluating materials for high-performance applications, businesses often consider various alternatives to quartz glass. Quartz glass is renowned for its thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity, making it a preferred choice in industries such as semiconductors, laboratory equipment, and UV applications. However, it is essential to explore other viable options that may offer different advantages or cater to specific requirements.
Comparison of Quartz Glass with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Quartz Glass | Borosilicate Glass | Sapphire Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent thermal stability, high UV transmission | Good thermal resistance, moderate UV transmission | Superior hardness, high thermal resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and fabrication | Lower cost, widely available | Very high cost due to rarity and fabrication complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and fabrication | Easy to work with, standard processes | Requires specialized machining and handling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; chemical resistant | Low maintenance; can be prone to thermal shock | Low maintenance; scratch-resistant but can chip |
| Best Use Case | Semiconductor manufacturing, optical applications | General laboratory use, cookware | High-end optical applications, jewelry |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is a popular alternative that offers good thermal resistance and is readily available at a lower cost compared to quartz glass. It is commonly used in laboratory glassware and household items, such as cookware. However, while it performs adequately in many applications, it does not match the high UV transmission and chemical resistance of quartz glass. Additionally, borosilicate can be more prone to thermal shock, which could limit its effectiveness in extreme temperature environments.
Sapphire Glass
Sapphire glass is an advanced alternative known for its exceptional hardness and high thermal resistance. It is often utilized in high-end applications such as optical components, watches, and protective covers for electronic devices. The primary downside of sapphire glass is its cost, which is significantly higher than both quartz and borosilicate glass due to its rarity and complex manufacturing process. Furthermore, while it provides excellent durability, the machining process requires specialized techniques, making it less accessible for some manufacturers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate material for your specific application, consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. Quartz glass remains an excellent choice for applications demanding high purity and thermal stability, particularly in semiconductor and optical industries. However, for general laboratory use or where budget is a primary concern, borosilicate glass may serve adequately. In scenarios where durability and resistance to scratching are paramount, sapphire glass could be the ideal solution despite its higher cost.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific needs of your operations, balancing performance characteristics with economic feasibility to ensure optimal outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for quarts glass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Quartz Glass That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When sourcing quartz glass, understanding its technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that define the quality and applicability of quartz glass products:

Illustrative image related to quarts glass
-
Material Grade
Quartz glass is categorized into different grades, such as Fused Quartz and Fused Silica. Fused Quartz is composed of high-purity silica and is preferred for applications requiring high chemical durability and thermal stability. Understanding the material grade helps buyers select the right product for their specific applications, especially in industries like semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory research. -
Thermal Resistance
One of the standout features of quartz glass is its ability to withstand extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1200°C. This property is vital for applications in high-heat environments, such as in furnaces or as optical components in laser systems. Buyers must assess thermal resistance to ensure the material can handle the operational conditions of their processes. -
Optical Clarity
Quartz glass offers exceptional optical clarity and UV transmission, making it suitable for optical instruments and applications requiring precision light transmission. This characteristic is particularly important for buyers in the scientific and medical sectors, where accuracy can affect outcomes and results. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in dimensions. In quartz glass, standard tolerances might include length, width, and thickness variations, typically within ±0.010 inches. Precise tolerances are critical for applications where components must fit together seamlessly, such as in laboratory setups or manufacturing processes. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can meet their specific tolerance requirements. -
Scratch and Dig Ratings
These ratings indicate the surface quality of quartz glass, with lower numbers signifying better quality. For instance, a scratch/dig rating of 80/50 means the surface has relatively few imperfections. High-quality surfaces are essential in optical applications where clarity and precision are paramount, influencing product selection for buyers.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Purchasing Quartz Glass?
Navigating the procurement of quartz glass involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are some commonly used terms that can aid buyers in their purchasing processes:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of quartz glass, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for custom components that meet their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is critical for B2B buyers as it affects inventory costs and production planning. Buyers should confirm MOQs before finalizing their orders to ensure they align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and other relevant information from suppliers. Crafting a detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, enabling buyers to compare offers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers gauge shipping costs, risk, and insurance responsibilities, essential for effective supply chain management. -
Custom Fabrication
This term refers to the process of producing specialized quartz glass products tailored to specific requirements. Buyers often require custom fabrication to meet unique project specifications, making it essential to inquire about this capability when engaging with suppliers. -
Hermetic Sealing
This refers to a type of sealing that prevents the escape of gases or liquids, crucial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive instruments. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide hermetic sealing solutions, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing quartz glass, ensuring they procure products that meet their specific needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the quarts glass Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Quartz Glass Market Today?
The quartz glass market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors, including semiconductors, optics, and laboratory equipment. The global push for high-purity materials has amplified interest in fused quartz, particularly due to its unique properties like thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity. As industries become more specialized, the need for customized solutions is rising. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional demands and technological advancements is essential for effective sourcing.
Emerging trends in sourcing include a shift towards digital platforms for procurement, enabling international buyers to access a wider array of suppliers and products. The integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning in supply chain management is optimizing inventory control and reducing lead times. Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a key consideration, with many companies seeking suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that offer transparency in their sourcing processes and can demonstrate compliance with international standards.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Quartz Glass Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the quartz glass sector, especially as consumers and businesses alike demand environmentally responsible practices. The production of quartz glass involves significant energy consumption and resource extraction, which can impact the environment. As a result, many companies are adopting sustainable practices such as utilizing recycled materials and reducing waste during manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are crucial for B2B buyers who want to align with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. Suppliers that obtain green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, demonstrate a commitment to minimizing their ecological footprint. Additionally, sourcing from companies that prioritize fair labor practices ensures that the entire supply chain is ethical. Buyers can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty by choosing suppliers that are recognized for their commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of Quartz Glass Development Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of quartz glass can be traced back to the early 20th century when fused quartz was first developed for its superior thermal and optical properties. Initially used in laboratories and scientific research, the material gained traction in various industrial applications as its benefits became more widely recognized. Over the decades, advancements in manufacturing techniques have enabled the production of high-purity fused quartz, which is now essential for industries such as semiconductor fabrication and optical systems.
Today, quartz glass is a critical material in various high-tech applications, and its historical significance informs B2B buyers about its reliability and importance in modern manufacturing processes. Understanding the evolution of quartz glass can aid buyers in making informed decisions about sourcing and collaborating with suppliers who have a proven track record in quality and innovation.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers in the quartz glass sector, staying attuned to market dynamics, sustainability practices, and the historical context of the material is essential. The current trends indicate a robust demand for high-purity quartz glass driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and offer customized solutions, businesses can position themselves competitively in the global market while adhering to ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of quarts glass
-
1. How do I ensure the quality of quartz glass products before purchase?
To ensure the quality of quartz glass products, request certifications and specifications from suppliers, such as ASTM or ISO standards. Conduct thorough supplier vetting by reviewing their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and customer testimonials. Consider ordering samples for initial evaluation. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance protocols, including testing for purity, thermal resistance, and optical clarity. Establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier can also help address any concerns regarding product quality. -
2. What is the best type of quartz glass for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, fused quartz glass is the best option due to its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. It can withstand temperatures up to 1200°C without deforming, making it suitable for applications like laboratory equipment, semiconductor manufacturing, and UV systems. When sourcing fused quartz, ensure that you specify the required dimensions and tolerances to meet your specific application needs, as custom fabrication may be necessary. -
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for quartz glass products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for quartz glass products can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as 10 pieces, while others may require orders of 100 or more, depending on the product type and customization. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQs and explore the possibility of smaller trial orders, especially if you are testing a new product line. Understanding the MOQ will help you manage inventory and cost effectively. -
4. How can I customize quartz glass products to meet my specific requirements?
Most suppliers offer customization options for quartz glass products, including size, shape, and specific features like holes or notches. To initiate customization, provide detailed specifications and drawings to your supplier. Discuss your needs for tolerance levels and any specific applications the quartz glass will serve. Custom orders may involve longer lead times and additional costs, so it’s advisable to confirm these details upfront to avoid surprises during production. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing quartz glass internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of quartz glass can vary by supplier but typically include options like advance payment, net 30, or letter of credit. It’s essential to discuss and agree upon payment terms before finalizing orders. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. Ensure you understand the implications of each payment method, including any fees or currency exchange rates that may affect the total cost. -
6. How do I handle logistics and shipping for quartz glass products?
Handling logistics for quartz glass products involves selecting a reliable shipping partner experienced in handling fragile materials. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effective solutions. Ensure that proper packaging is used to minimize the risk of damage during transit. Additionally, confirm the estimated delivery times and any customs requirements for your region to avoid delays upon arrival. -
7. What industries commonly use quartz glass, and how can I identify potential buyers?
Quartz glass is widely used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, laboratory research, and optical systems due to its high purity and thermal stability. To identify potential buyers, conduct market research to understand industry needs and trends. Attend industry trade shows, join relevant associations, and leverage online B2B platforms to connect with potential customers. Tailoring your marketing efforts to highlight the benefits of quartz glass in specific applications can help attract interest. -
8. How can I verify the reputation of a quartz glass supplier?
Verifying a quartz glass supplier’s reputation involves researching their business history, customer reviews, and industry standing. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn to check for endorsements and feedback from other businesses. Request references from previous clients and follow up to inquire about their experiences. Additionally, consider checking for any industry certifications or awards that the supplier has received, as these can be indicators of reliability and quality in their products and services.
Top 5 Quarts Glass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Technical Glass – Fused Silica & UV Grade Quartz Plates
Domain: technicalglass.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Durable Fused Silica Plates & UV Grade Quartz Plates for Precision Applications. Clear fused silica plates and UV grade quartz plates are suitable for various industries due to their exceptional UV transmission and optical clarity. They can withstand high temperatures up to 1200°C, making them ideal for heat-resistant applications like microscope slides. Custom sizes are available upon request. Op…
2. IQS Directory – Quartz Glass Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Quartz glass, also known as fused quartz or fused silica, is produced from high-purity silica sand (SiO2) and is characterized by its purity and adaptability across various applications. Key properties include a low coefficient of thermal expansion, superior gas permeability, and a wide range of optical transmission. The production process involves several stages: washing and drying to remove cont…
3. Azom – Fused Silica and Quartz Solutions
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fused silica and quartz are both primarily composed of silica (SiO2). Quartz is a naturally occurring crystalline mineral with impurities, while fused silica is a processed, nominally pure amorphous solid formed by melting silica. Fused silica has high-performance applications due to its distinct electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties, including a low coefficient of thermal expansion, high…
4. Continental Trade – High-Purity Quartz Glass
Domain: continentaltrade.com.pl
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Quartz glass is a high-purity silica glass (SiO2 ≥ 99.9%) resistant to water and strong acids (except hydrofluoric acid) with low resistance to alkali. It has a high melting point, low thermal expansion, and thermal shock resistance. It transmits ultraviolet and infrared light, with transmittance depending on additives. Types include natural quartz (suitable for high temperatures > 1000°C) and syn…
5. PGO Online – Fused Silica & Quartz Solutions
Domain: pgo-online.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Fused Silica and Fused Quartz are two distinct types of quartz glass with different properties and applications. Fused Silica is made from high-purity synthetic silica powder, offering superior optical quality, high light transmission (over 80% at 185 nm), and is suitable for demanding optical applications. It is ideal for high imaging accuracy, flatness, surface quality, and high purity requireme…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for quarts glass
In the evolving landscape of quartz glass procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. Companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize partnerships with suppliers who not only offer high-quality fused quartz products but also demonstrate a commitment to innovation and customization. The unique properties of quartz glass—such as exceptional thermal resistance, optical clarity, and chemical durability—make it indispensable in industries ranging from semiconductors to laboratory applications.
By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, buyers can ensure they are securing the best prices and maintaining supply chain resilience. Engaging with suppliers who understand regional market dynamics can also enhance operational efficiency and foster long-term collaboration.
As we look ahead, the demand for quartz glass is expected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications in various sectors. International buyers are encouraged to explore new opportunities, invest in supplier relationships, and stay informed about market trends to capitalize on the potential of quartz glass. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategy and secure a competitive edge in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to quarts glass