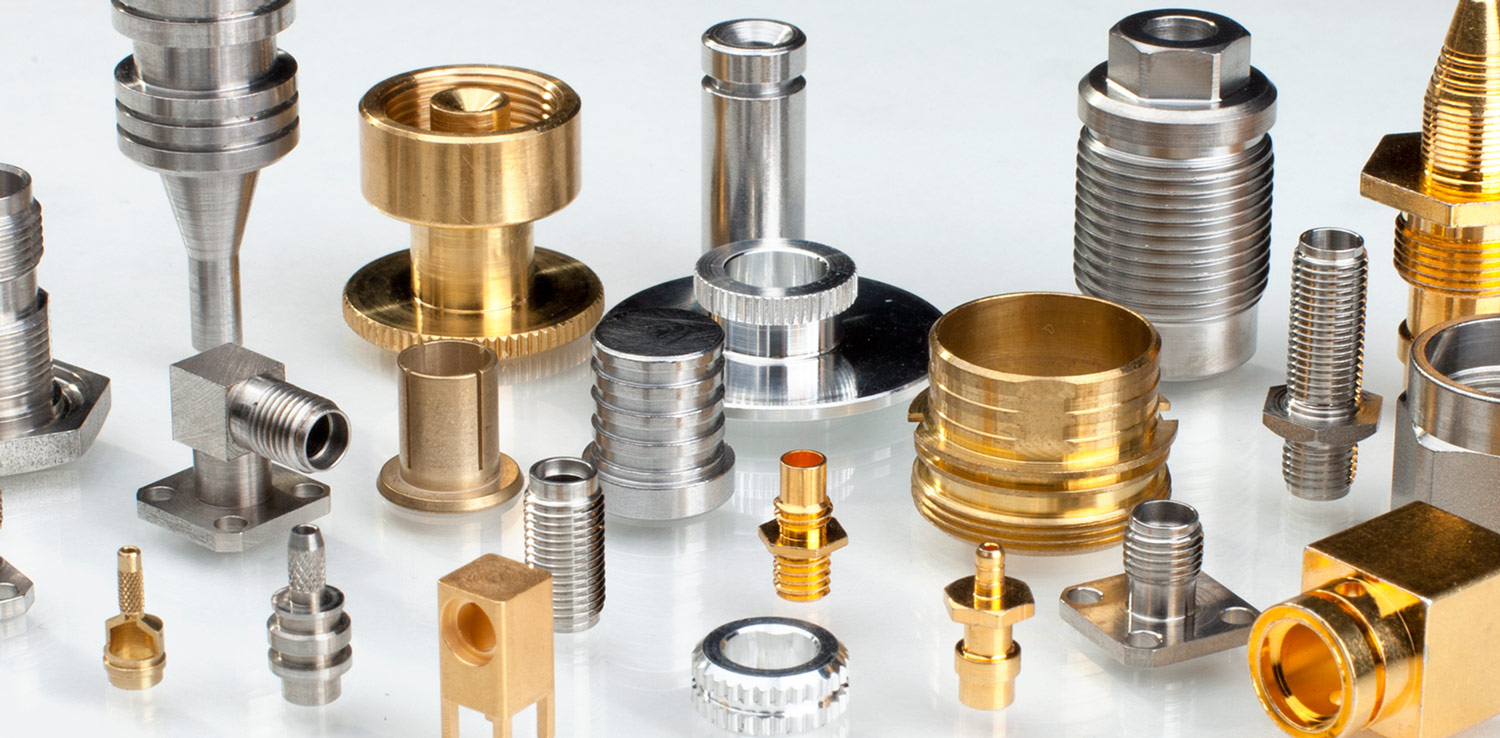
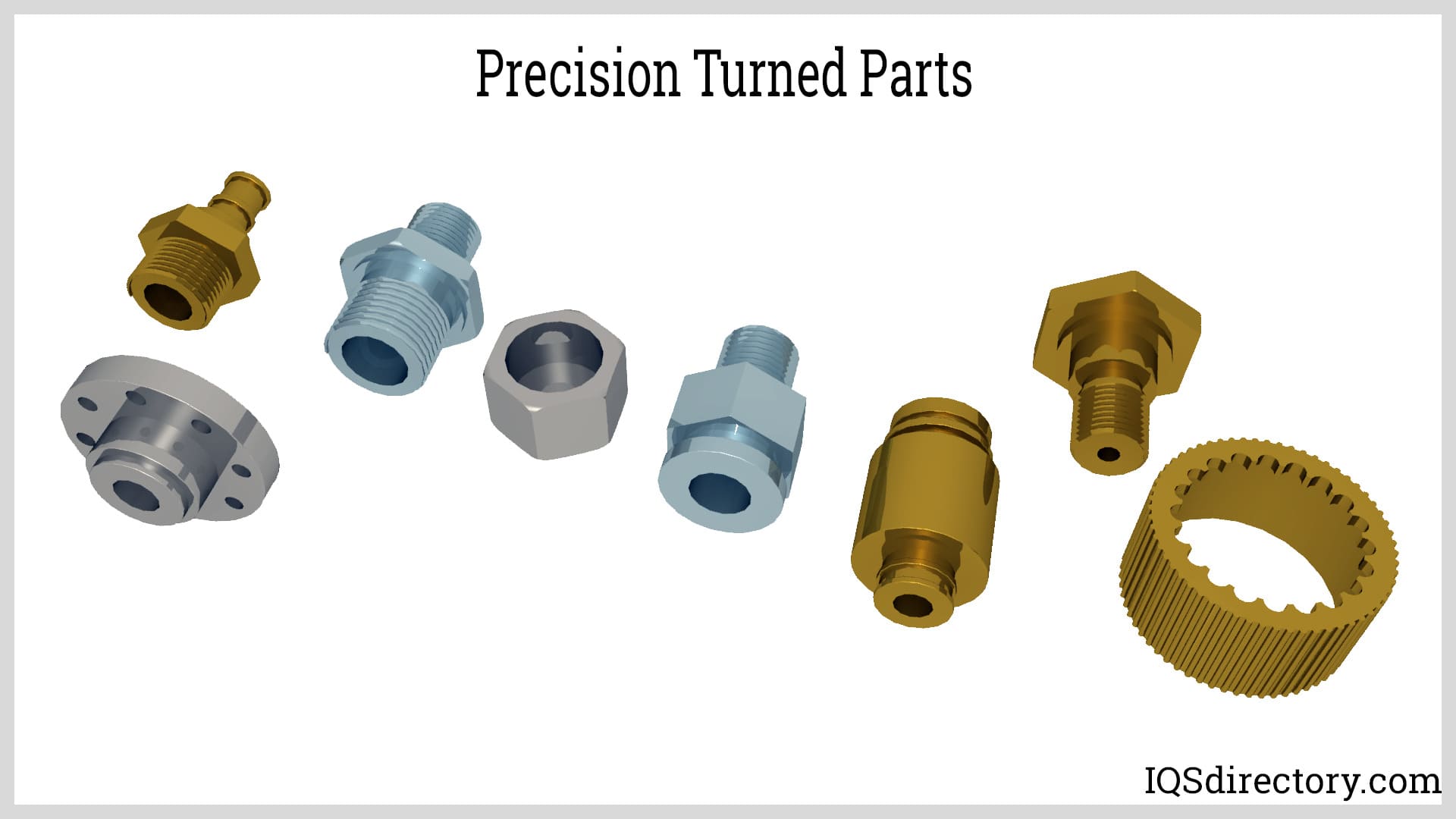
The Definitive Guide to Precision Turning Parts: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for precision turning parts
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing high-quality precision turning parts presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in the fast-paced automotive sector or the stringent aerospace industry, the demand for components that meet exacting standards of quality and performance is paramount. This guide serves as your roadmap, providing a comprehensive overview of precision turning parts, including their various types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Navigating the complexities of supplier selection can be daunting, especially when balancing cost, quality, and delivery timelines. We delve into the nuances of material certifications, manufacturing processes, and the significance of quality management systems, ensuring that you are well-equipped to make informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, we highlight the importance of understanding regional market dynamics, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam.
By leveraging the insights contained within this guide, you will not only enhance your procurement strategies but also foster stronger partnerships with suppliers who can meet your specific needs. With an emphasis on reliability, quality assurance, and cost-effectiveness, this resource aims to empower your organization in achieving operational excellence through superior precision turning components.
Understanding precision turning parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Turned Parts | High precision, complex geometries, automated processes | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Higher upfront costs |
| Swiss Turned Parts | Small diameter, intricate shapes, simultaneous operations | Electronics, Medical Devices | Pros: Excellent for small parts; Cons: Limited to small sizes |
| Brass Turned Components | Good corrosion resistance, excellent machinability | Plumbing, Electrical Connectors | Pros: Durable; Cons: Costlier than some alternatives |
| Stainless Steel Parts | High strength, corrosion-resistant, versatile applications | Aerospace, Defense, Medical | Pros: Long-lasting; Cons: More expensive than carbon steel |
| Custom Precision Parts | Tailored specifications, varied materials and finishes | Various industries, including Automotive | Pros: Meets specific needs; Cons: Longer lead times |
What Are CNC Turned Parts and Their Key Characteristics?
CNC turned parts are manufactured using computer numerical control technology, allowing for high precision and the ability to create complex geometries. These parts are suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive, where tight tolerances are critical. Buyers should consider the initial investment in CNC machinery versus the long-term benefits of increased production efficiency and reduced error rates.
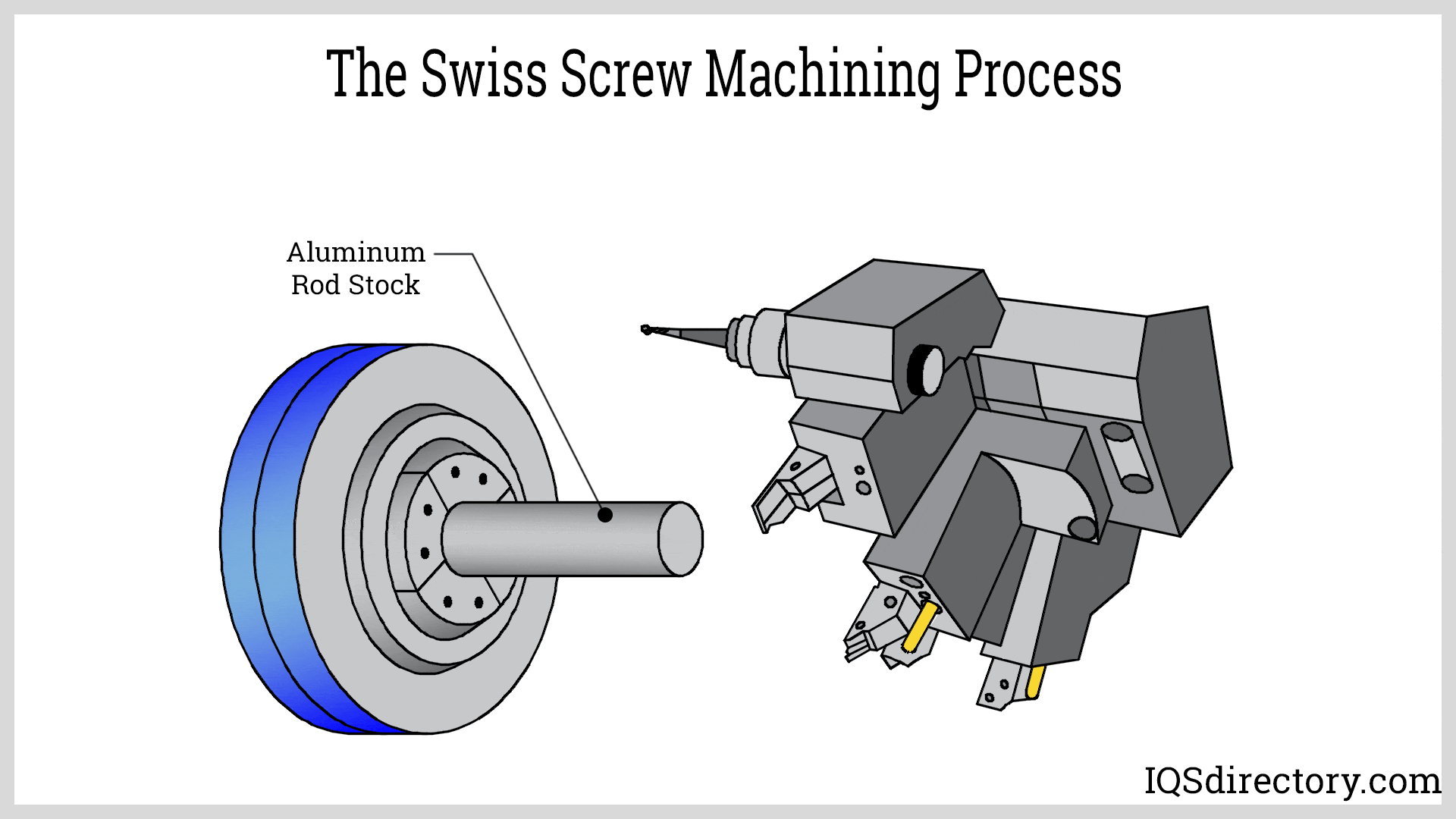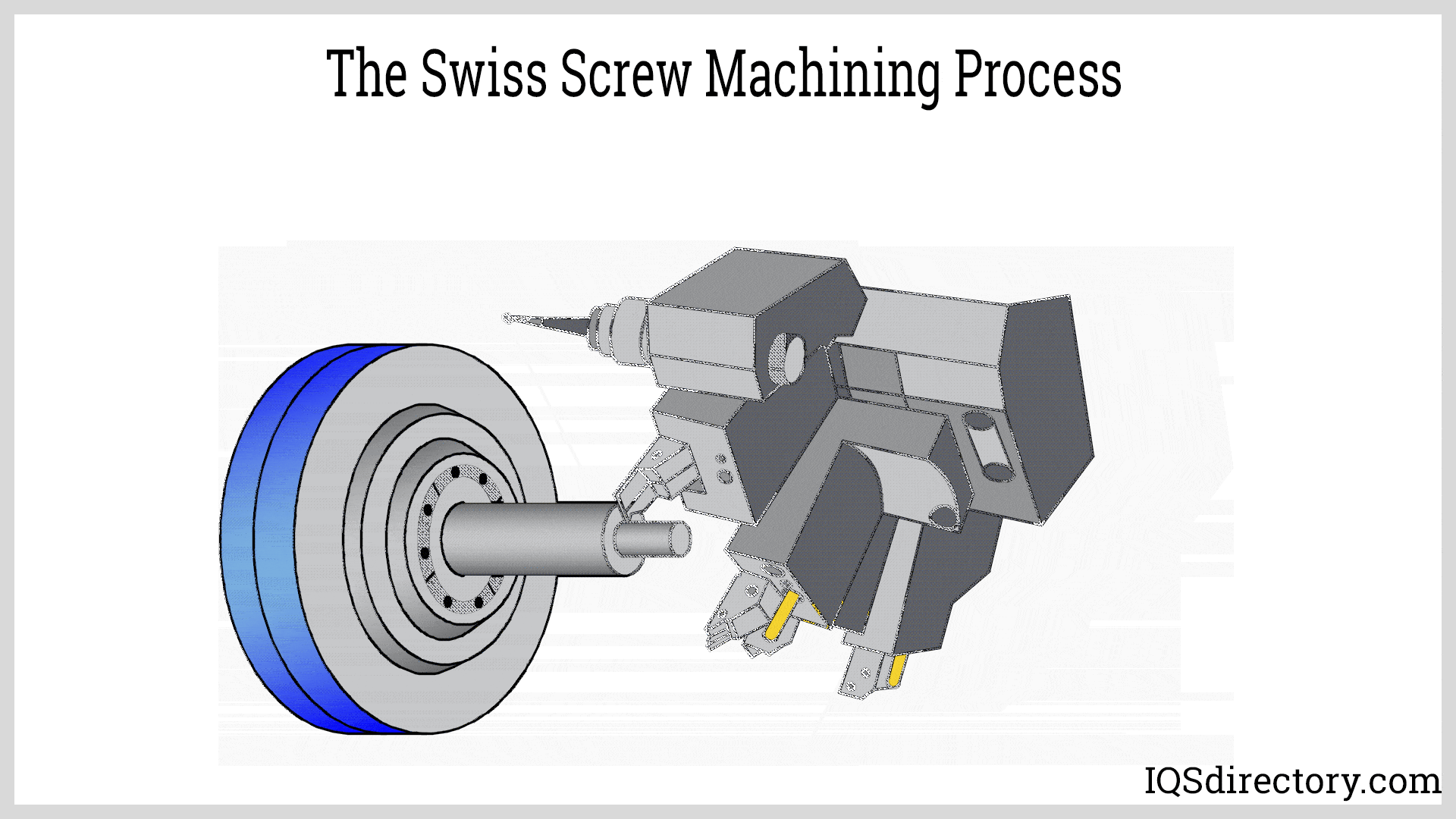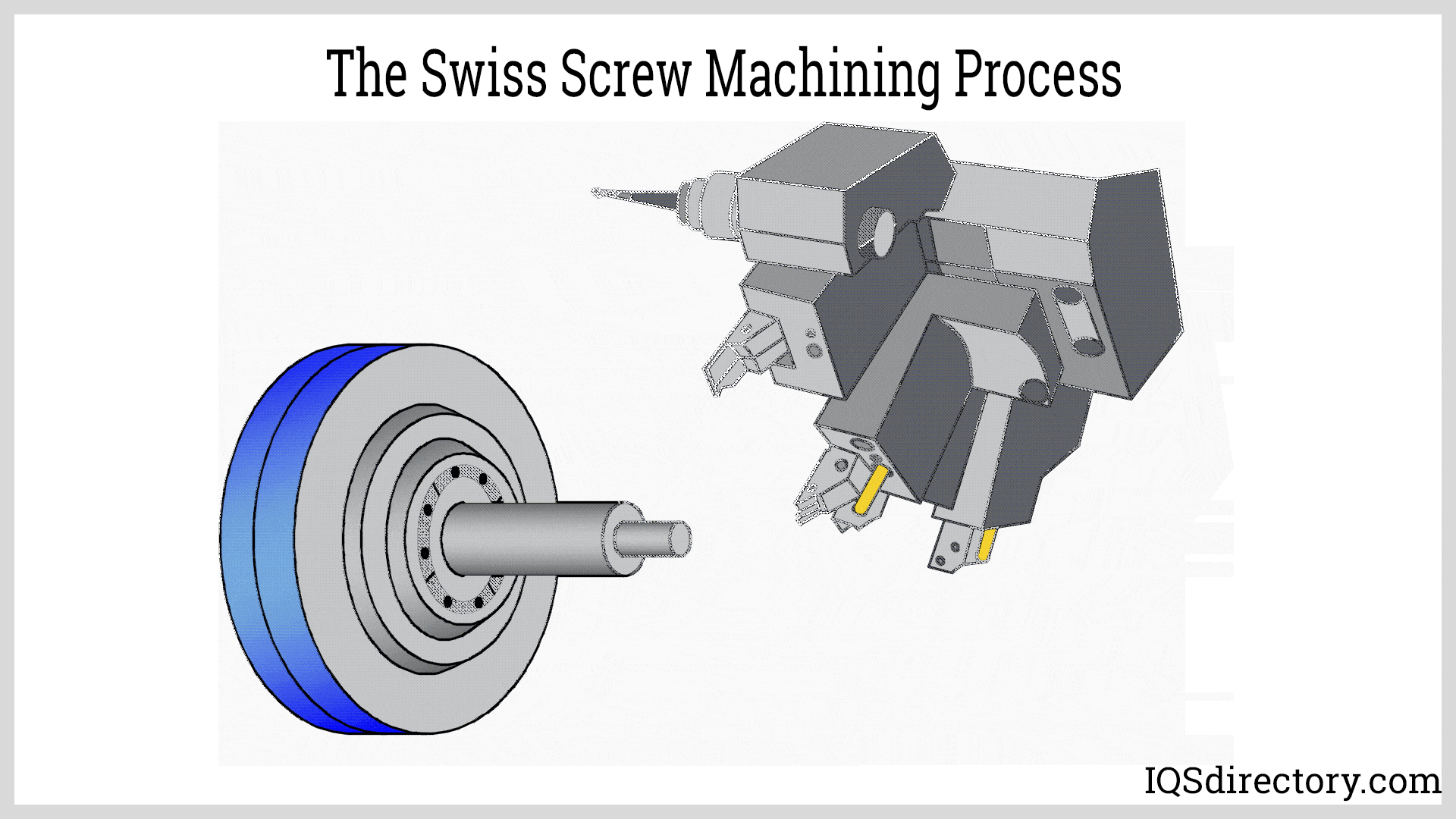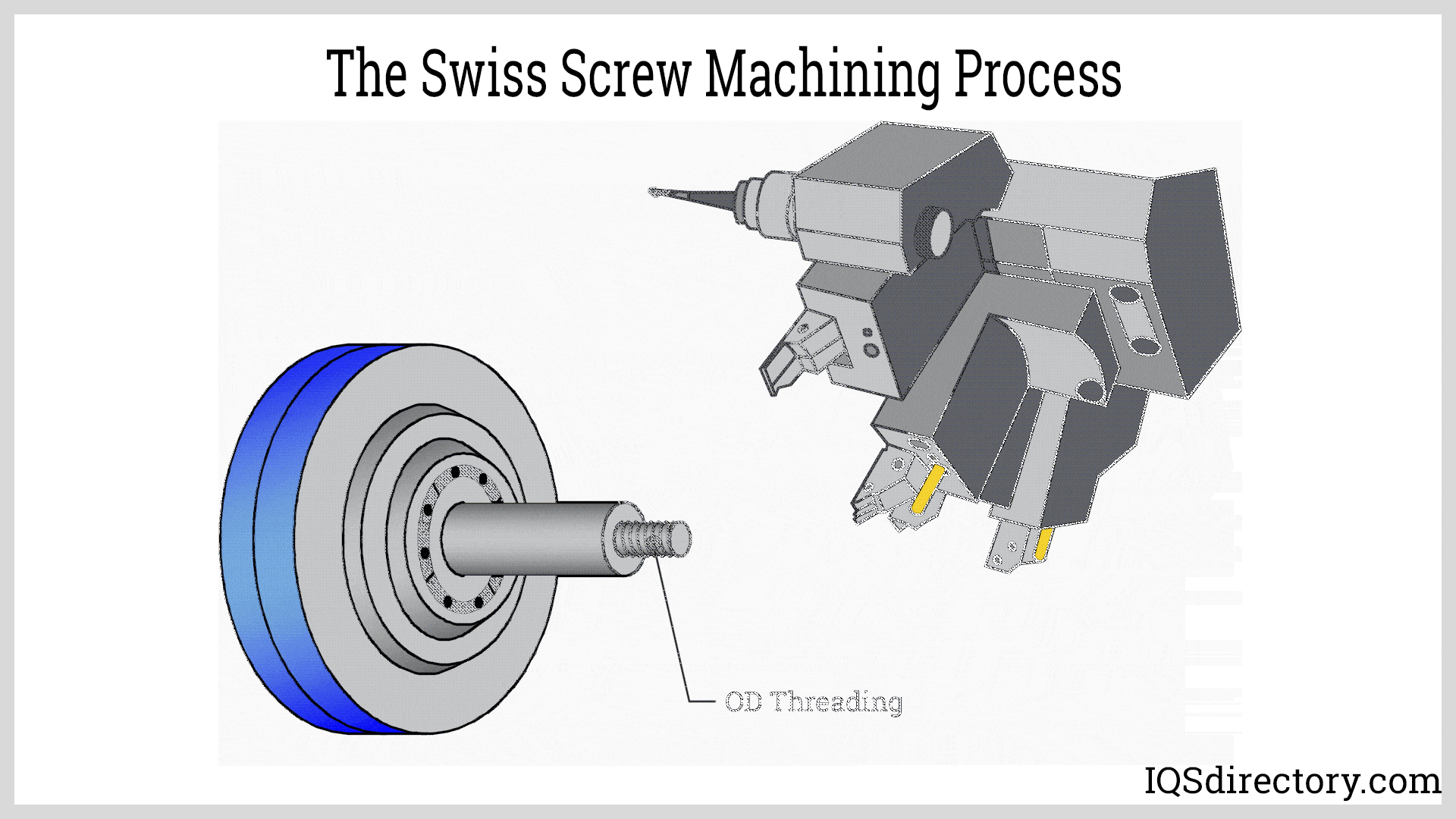
How Do Swiss Turned Parts Stand Out?
Swiss turned parts are characterized by their ability to produce small-diameter components with intricate shapes through simultaneous operations. This method is ideal for applications in electronics and medical devices where precision and detail are crucial. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high accuracy against the limitation of size, as Swiss machining is primarily effective for smaller components.
What Are the Advantages of Brass Turned Components?
Brass turned components are known for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for plumbing and electrical applications. While they offer durability and aesthetic appeal, buyers should consider the cost implications, as brass can be more expensive than alternative materials. The longevity and reliability of brass components can justify the investment in many applications.
Why Choose Stainless Steel Parts for Precision Needs?
Stainless steel parts are recognized for their high strength and resistance to corrosion, making them versatile for use in aerospace, defense, and medical sectors. Although they tend to be pricier than carbon steel options, their durability often results in lower total lifecycle costs. Buyers should evaluate the specific material properties needed for their applications to ensure optimal performance.
What Are Custom Precision Parts and Their Benefits?
Custom precision parts are designed to meet specific client requirements, utilizing various materials and finishes. This flexibility allows businesses to address unique challenges across multiple industries, including automotive and medical. While custom solutions can provide significant advantages, buyers must consider longer lead times and potential cost increases associated with bespoke manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of precision turning parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Precision Turning Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of aircraft components | Enhances safety and reliability through tight tolerances | Certification (e.g., AS9100), material traceability |
| Medical | Production of surgical instruments | Ensures precision in critical applications | Compliance with medical standards, biocompatibility |
| Automotive | Creation of engine and transmission parts | Improves performance and longevity of vehicles | Material quality, lead times, and cost-effectiveness |
| Telecommunications | Production of connectors and fittings | Supports high-speed data transfer and reliability | Customization options, precision requirements |
| Defense & Law Enforcement | Fabrication of firearm components | Guarantees performance under extreme conditions | Strict adherence to quality standards and specifications |
How Are Precision Turning Parts Applied in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, precision turning parts are essential for manufacturing components such as engine mounts, landing gear fittings, and structural elements. These parts require tight tolerances and high strength-to-weight ratios to ensure safety and reliability in flight. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that are AS9100 certified and can provide material traceability to meet stringent regulatory standards. Additionally, the ability to handle complex geometries and provide rapid prototyping can significantly enhance the supply chain efficiency.
What Role Do Precision Turning Parts Play in Medical Applications?
In the medical field, precision turning parts are crucial for producing surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. These components must meet strict biocompatibility and sterilization requirements to ensure patient safety. Buyers need to source from manufacturers that adhere to ISO 13485 standards and can demonstrate a robust quality control process. Effective communication regarding design specifications and lead times is essential to ensure timely delivery and compliance with medical regulations.
How Are Precision Turning Parts Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
Precision turning parts are integral to the automotive sector, particularly in the production of engine components, transmission systems, and braking systems. High-quality turned parts improve vehicle performance and longevity, which is critical in a competitive market. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer a variety of materials and can provide just-in-time (JIT) delivery to maintain production schedules. Additionally, the ability to customize parts to meet specific design requirements can significantly enhance a manufacturer’s competitive edge.
Why Are Precision Turning Parts Important in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, precision turning parts are used to manufacture connectors, fittings, and housings that facilitate reliable data transmission. These components must meet specific dimensional and performance standards to support high-speed networks. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers that can provide tailored solutions and demonstrate a commitment to quality through certifications like ISO 9001. The ability to deliver parts quickly and efficiently can also be a deciding factor for companies looking to maintain competitive service levels.
How Do Precision Turning Parts Impact Defense and Law Enforcement?
Precision turning parts play a critical role in the defense and law enforcement sectors, particularly in the fabrication of firearms, ammunition components, and tactical equipment. These parts must withstand extreme conditions and maintain operational integrity, making quality assurance paramount. Buyers should seek suppliers with proven experience in military specifications and those who can ensure compliance with stringent quality standards. Additionally, understanding the complexities of sourcing materials that meet both performance and regulatory requirements is essential for successful procurement.
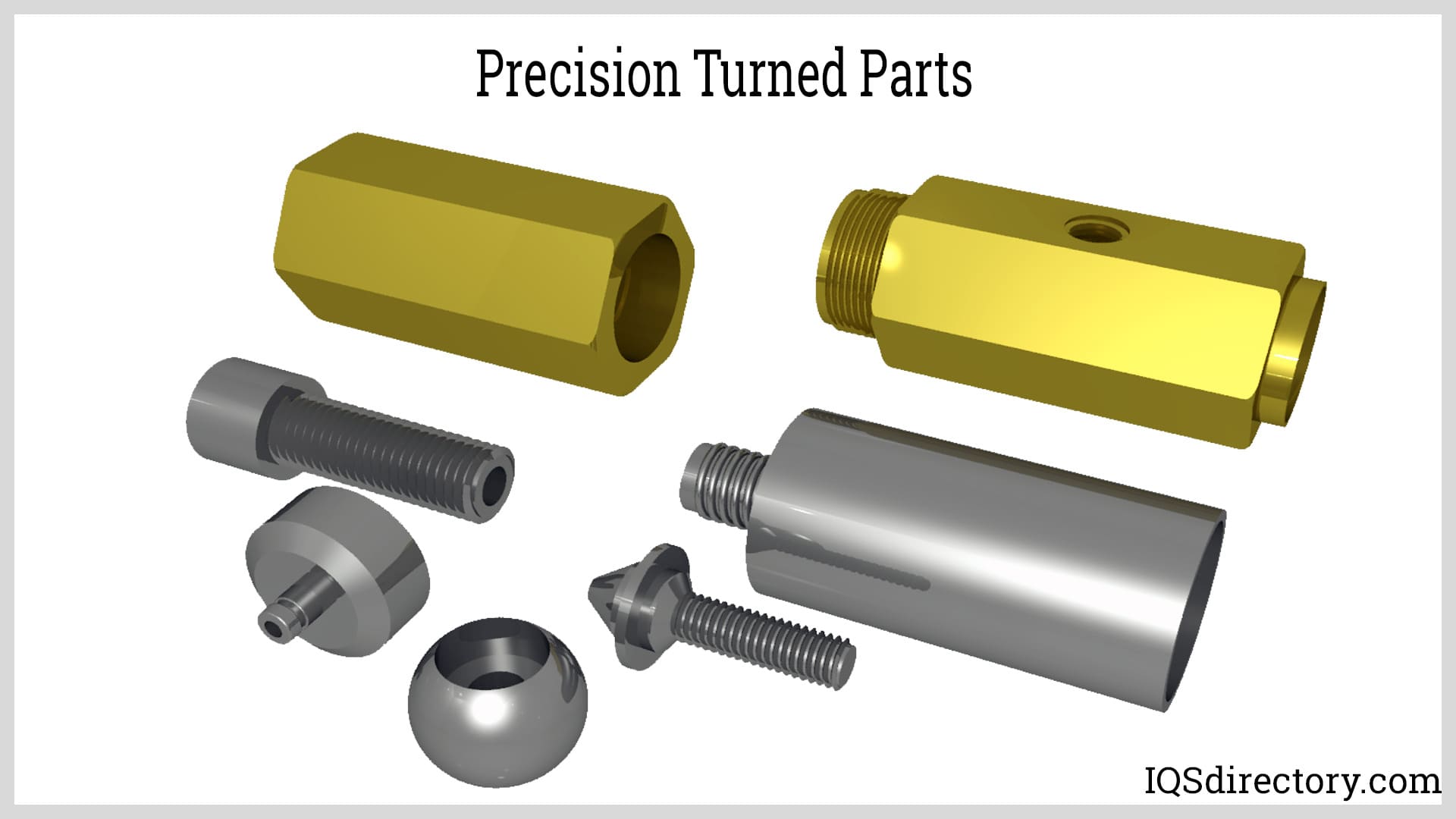
Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘precision turning parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Assurance in Precision Turning Parts
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges B2B buyers face when sourcing precision turning parts is ensuring consistent quality across different batches. Buyers often encounter issues with parts that do not meet specified tolerances, resulting in delays, increased costs, and potential disruptions in their production lines. This inconsistency can stem from variations in manufacturing processes, material quality, or inadequate quality control measures at the supplier’s facility. Such problems can lead to wasted time and resources, eroding trust in the supplier.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing suppliers with robust quality management systems in place, such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 certification. Before placing an order, it is beneficial to request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control processes, including inspection protocols and testing capabilities. Establishing clear specifications and tolerances upfront and including these in the purchase agreement can further safeguard against quality issues. Additionally, consider implementing a first-article inspection process for initial batches, which allows for early detection of any deviations from required specifications. This proactive approach not only ensures that quality standards are met but also fosters a collaborative relationship with the supplier.
Scenario 2: Delivery Delays and Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Timely delivery of precision turning parts is crucial for maintaining production schedules, yet many buyers face chronic delays due to unforeseen supply chain disruptions. Factors such as material shortages, transportation issues, or supplier capacity constraints can lead to extended lead times, forcing companies to halt production or seek costly alternatives. This scenario is especially pressing for companies operating in industries with strict deadlines, such as automotive or aerospace.
The Solution: To combat delivery delays, buyers should establish strong partnerships with multiple suppliers to diversify their sourcing options. This strategy can mitigate risks associated with relying on a single supplier. Additionally, buyers should communicate their production timelines and order forecasts clearly to their suppliers, allowing them to allocate resources effectively. Implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory systems can also streamline operations, reducing the need for large stockpiles and enabling quicker response times to changing demands. Regularly reviewing supplier performance metrics related to on-time delivery can inform future purchasing decisions and encourage suppliers to prioritize timely shipments.

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Scenario 3: Customization and Complexity in Precision Parts
The Problem: As industries evolve, the demand for custom precision turned parts is on the rise. However, many B2B buyers struggle with articulating their specific needs for complex geometries or unique material requirements. This lack of clarity can lead to miscommunication with suppliers, resulting in products that do not meet the intended application or performance standards. Buyers may also encounter limitations in a supplier’s capabilities, leading to frustration and delays in product development.
The Solution: To effectively address customization needs, buyers should invest time in providing comprehensive technical specifications and clear drawings of the desired parts. Engaging in early discussions with suppliers about design feasibility and material options can help identify potential challenges. Utilizing advanced technologies such as 3D modeling can facilitate better communication of complex designs. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who offer engineering support can streamline the design process, ensuring that the final product aligns with both functional and aesthetic requirements. Establishing a feedback loop during the prototyping phase allows for adjustments before mass production, reducing the risk of costly revisions down the line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for precision turning parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Precision Turning Parts?
When selecting materials for precision turning parts, it is essential to understand the properties and performance characteristics of each material. Here, we analyze four commonly used materials: stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and carbon steel, focusing on their suitability for various applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Precision Turning Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, making it suitable for demanding environments. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and good pressure resistance, which is crucial for applications in industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long lifespan for components, while its aesthetic finish can be beneficial for visible parts.
Cons: However, the higher cost and manufacturing complexity can be a drawback, particularly for high-volume production runs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and chemicals, making it versatile across various sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 or EN 10088, which govern the quality of stainless steel.
What Advantages Does Brass Offer for Precision Turned Parts?
Brass is a favored choice for precision turning due to its excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance. It typically performs well in applications involving lower temperatures and pressures, with a maximum service temperature around 400°F (204°C).
Pros: Its ease of machining allows for complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it ideal for intricate components like connectors and fittings.
Cons: On the downside, brass can be more expensive than some alternatives, and its lower strength compared to stainless steel may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is particularly suitable for applications in plumbing and electrical components due to its compatibility with water and electrical conductivity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 or JIS H3250, especially when sourcing from regions like Africa and South America.
Why Choose Aluminum for Precision Turning Parts?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for precision turned parts in industries like automotive and aerospace. It can withstand temperatures of up to 600°F (316°C) and is available in various alloys to suit specific applications.
Pros: The low density of aluminum contributes to reduced overall weight, which is advantageous for applications where weight savings are critical.
Cons: However, aluminum is softer than steel, which may lead to wear in high-friction applications, and it can be more challenging to achieve tight tolerances compared to harder materials.
Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B211 or EN 573 is crucial for ensuring material quality, particularly for buyers in Europe and the Middle East.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Precision Turning?
Carbon steel is known for its high strength and hardness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F (316°C) and can handle significant pressure.
Pros: Its durability and cost-effectiveness make carbon steel a popular choice for a wide range of applications, including automotive components.
Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Cons: However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, which can limit its use in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is best suited for applications where strength is prioritized over corrosion resistance, such as in structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or JIS G3101, particularly when sourcing from regions like South America and Africa.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Precision Turning Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for precision turning parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical components | Good machinability | Lower strength than stainless steel | Medium |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Softer, may wear in high-friction | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
This guide serves as a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions regarding material selection for precision turning parts based on specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for precision turning parts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Precision Turning Parts?
Precision turning parts are crucial in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical, where exact specifications are paramount. The manufacturing process typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques to ensure the highest quality and precision.
How Is Material Prepared for Precision Turning?
The first step in manufacturing precision turned parts is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw materials based on the application requirements, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Common materials used include stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and various alloys.
Once the material is chosen, it is cut into manageable sizes, often in the form of bars or rods. This material is then subjected to processes like heat treatment or annealing to enhance its properties, ensuring it meets the necessary strength and durability standards for the intended application.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Precision Turning?
Forming is the core stage of the manufacturing process, where the actual shaping of the part occurs. Precision turning utilizes several techniques, with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning being the most prevalent. CNC machines offer high precision by controlling the movement of cutting tools against the rotating workpiece, allowing for the production of complex geometries and tight tolerances.
Swiss turning is another advanced technique particularly effective for small and intricate parts. This method allows for simultaneous operations, increasing efficiency and reducing cycle times. Additional processes like multi-spindle machining can enhance production rates, making it feasible to produce large quantities while maintaining quality.
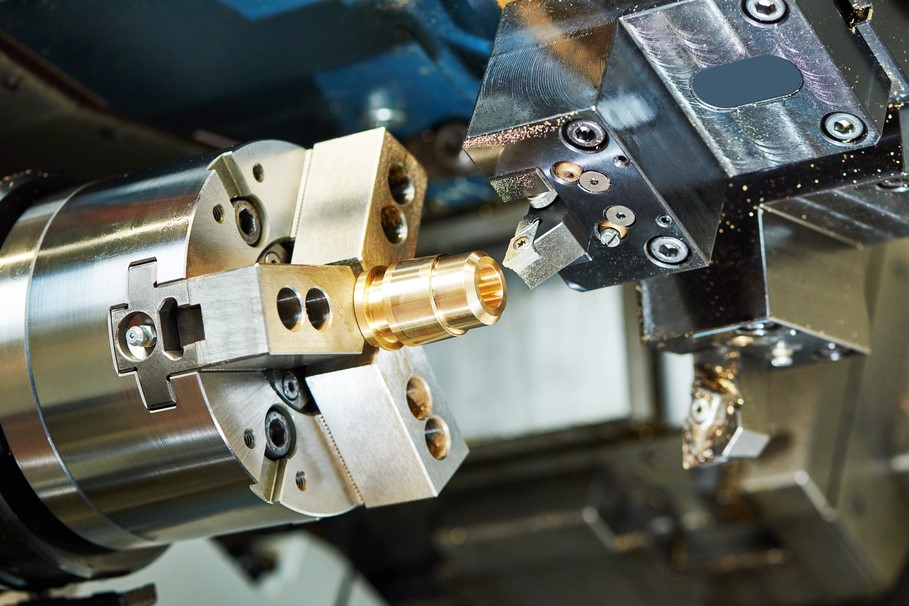

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
How Is Assembly Conducted for Precision Turned Parts?
While many precision turned parts can be utilized as standalone components, some may require assembly with other parts to form a complete assembly. This stage often involves the integration of additional components such as fasteners, seals, or electronic elements.
In this phase, adherence to tight tolerances is essential, as the performance of the final assembly depends on the precision of each individual component. Automated assembly techniques, including robotic systems, are increasingly being employed to enhance accuracy and reduce human error.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Precision Turned Parts?
Finishing is the final stage in the production of precision turned parts, crucial for achieving the desired surface quality and functionality. Common finishing processes include polishing, anodizing, plating, and passivation. These treatments not only improve the aesthetic appeal but also enhance corrosion resistance and wear properties.
Surface finishes often need to meet specific standards, such as achieving a roughness average (Ra) of 32 micro-inches or finer, depending on the application. The choice of finishing technique should align with the part’s intended use, as some industries have stringent requirements for surface integrity.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical for Precision Turning Parts?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for precision turned parts. B2B buyers need assurance that the components meet international standards and specific industry requirements.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
The most recognized international quality management standard is ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for establishing an effective quality management system. Many manufacturers also adhere to industry-specific certifications such as AS9100 for aerospace or API for oil and gas, ensuring compliance with sector-specific quality standards.
Buyers from different regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should look for these certifications when selecting suppliers, as they signify a commitment to quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) in precision turning typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process, where operators perform regular checks on dimensions and tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished parts to verify they meet the required specifications before shipment.
These checkpoints help identify any deviations from quality standards early in the process, reducing waste and ensuring customer satisfaction.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality assurance reports, including results from their QC checkpoints and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased review of the supplier’s quality control processes and the products being manufactured.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing precision turned parts internationally, B2B buyers must navigate various challenges related to quality control. Cultural differences, varying regulations, and logistical complexities can impact quality assurance efforts.
Buyers should establish clear communication channels with suppliers to ensure expectations regarding quality are understood. Additionally, being familiar with local regulations and quality standards in the supplier’s country can aid in assessing compliance and quality assurance effectiveness.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in precision turning parts is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. By paying attention to each stage of production, from material preparation to finishing, and ensuring compliance with quality standards, buyers can secure reliable components that meet their specific needs. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and conducting thorough quality assessments will further enhance the reliability and performance of the precision turned parts sourced for various applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘precision turning parts’
In the world of manufacturing, sourcing precision turning parts requires meticulous planning and execution. This guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a structured approach to ensure they procure high-quality components that meet their specific requirements, particularly when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the precision turning parts you need. This includes dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finishes. Well-defined specifications are crucial as they guide suppliers in understanding your needs and help prevent costly errors during production.
- Considerations: Identify the type of materials (e.g., stainless steel, brass, aluminum) and any industry standards (like ISO certifications) that must be met.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Invest time in researching and identifying potential suppliers. Look for companies with a solid track record in manufacturing precision turned parts, especially those serving your industry.
- Key Actions: Review supplier websites for case studies, certifications, and customer testimonials. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn to connect with industry professionals and gather insights.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before entering into a partnership, verify that the suppliers hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001:2015 or AS9100:2016. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality management and manufacturing excellence.
- Importance: Certified suppliers are often more reliable and adhere to strict quality control processes, which is vital for precision components.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples or prototypes of the precision turning parts. This step allows you to assess the quality of workmanship, materials, and adherence to your specifications.
- What to Look For: Examine the surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall craftsmanship of the samples. This hands-on evaluation can save time and resources later in the production process.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Delivery Options
Openly communicate with potential suppliers about lead times, delivery schedules, and logistics. Understanding their production capabilities and supply chain logistics will help you plan your own project timelines effectively.
- Considerations: Inquire about their ability to meet Just-In-Time (JIT) deliveries and stocking solutions, which can enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 6: Assess Cost and Payment Terms
Analyze the pricing structure and payment terms offered by each supplier. While cost is a significant factor, it should not be the sole criterion; consider the overall value, including quality, service, and support.
- Important Note: Look for transparency in pricing and be wary of suppliers who provide quotes that are significantly lower than the market average, as this could indicate compromised quality.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Ensure that you have clear lines of communication with your chosen supplier, including designated points of contact for technical support and customer service.
- Best Practices: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss ongoing projects, address any issues, and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for precision turning parts, ensuring they partner with suppliers that meet their quality and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for precision turning parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Precision Turning Parts?
When sourcing precision turning parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials like aluminum and stainless steel are generally less expensive compared to specialized alloys or exotic materials that may be required for specific applications. The cost of raw materials can fluctuate based on global supply chains, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is necessary for precision machining, and wages can differ dramatically between countries. For example, labor costs in Europe might be higher than in certain parts of Africa or South America, influencing overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers often factor these costs into their pricing models, which can vary based on operational efficiency and production scale.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom components. The initial investment in specialized tools for CNC or Swiss turning processes can be substantial, but these costs can be amortized over larger production volumes, making bulk orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that precision parts meet strict tolerances requires rigorous QC processes. This may involve both in-process inspections and final testing, which add to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 also involve compliance costs that suppliers may pass on to buyers.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the destination and Incoterms agreed upon. For international buyers, understanding freight charges, customs duties, and delivery timelines is vital for calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers add a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. Margins can vary based on supplier reputation, market competition, and the complexity of the parts being produced.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Precision Turning Parts?
Several factors can affect the pricing of precision turning parts, making it crucial for buyers to understand the nuances involved.

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically benefit from lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ policies can help buyers negotiate better pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts with specific dimensions or features often incur higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling and processes. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Selection: As mentioned earlier, the choice of materials plays a critical role in pricing. Buyers should consider the application requirements and long-term performance to select materials that offer the best balance of cost and quality.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring stringent quality standards or certifications typically come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of such certifications based on their industry requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and manufacturing capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may command higher prices but offer greater assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact overall costs significantly. Buyers should understand the implications of these terms on shipping responsibilities and costs.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing precision turning parts, buyers should adopt a strategic approach.
-
Negotiation: Open communication with suppliers is key. Buyers should be clear about their budget constraints and seek bulk order discounts or alternative material suggestions that may reduce costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider TCO rather than just upfront costs. Factors such as durability, maintenance, and performance can significantly influence long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade agreements can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various suppliers can help buyers benchmark prices and identify competitive offers.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved communication, ultimately enhancing the procurement process.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for precision turning parts can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they are getting a fair price.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing precision turning parts With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Precision Turning Parts
In the realm of precision manufacturing, precision turning parts are often a go-to solution due to their exceptional accuracy and reliability. However, there are alternative methods and technologies that can fulfill similar requirements for different applications. This analysis will compare precision turning parts with two viable alternatives: CNC milling and additive manufacturing (3D printing). Each method has its unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to consider their specific needs when choosing a solution.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Precision Turning Parts | CNC Milling | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with tight tolerances | Versatile with complex geometries | Good for prototypes; variable precision |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on volume | Generally lower for large volumes | Can be high per unit, but low for prototypes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and setup | Relatively straightforward setup | Requires specialized software and training |
| Maintenance | Low; machines are robust | Moderate; tools need regular replacement | Low; minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of small, precise components | Complex parts with intricate designs | Rapid prototyping and low-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. This method excels in producing complex geometries and is highly versatile, making it suitable for various industries, including automotive and aerospace.
Pros: CNC milling can produce intricate designs with excellent surface finishes, often at a lower cost for larger production runs. It allows for quick adjustments in design without extensive retooling.
Cons: While CNC milling is effective for complex parts, it may not achieve the same level of precision as precision turning for small components. The initial setup time can also be significant, requiring skilled operators to program and calibrate the machines.

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, builds parts layer by layer from digital models. This technology is particularly effective for rapid prototyping and custom parts production.
Pros: 3D printing allows for quick iterations in design and is ideal for low-volume production. It can produce highly complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Cons: The cost per unit can be higher compared to precision turning, especially for large quantities. Additionally, the material properties and surface finish may not always meet the stringent requirements of certain applications, particularly in industries like aerospace or medical.

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing method depends on various factors, including the specific application, volume requirements, and budget constraints. Precision turning parts are ideal for high-volume production of small, highly precise components. In contrast, CNC milling offers flexibility for complex designs, while additive manufacturing excels in rapid prototyping and custom solutions. By carefully assessing these alternatives against their unique needs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and quality standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for precision turning parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Precision Turning Parts?
Precision turning parts are characterized by several critical specifications that ensure high performance and reliability in various applications. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers seeking quality components that meet their operational needs.
What Is Material Grade and Why Is It Important?
Material grade refers to the specific classification of materials used in manufacturing precision turned parts. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and carbon steel. Each material offers distinct properties, such as corrosion resistance, strength, and weight, which directly impact the part’s performance and durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is crucial for ensuring that components can withstand the specific environmental conditions and mechanical stresses they will encounter in their applications.
How Do Tolerances Affect Precision Turned Parts?
Tolerance defines the acceptable limit of variation in a part’s dimensions. Precision turned parts often require tight tolerances, sometimes as low as ±0.001 inches, to ensure compatibility and functionality in assemblies. High tolerance levels are essential for industries like aerospace and medical, where even minor deviations can lead to system failures. For buyers, understanding tolerances helps in selecting manufacturers that can meet stringent requirements, thereby reducing the risk of costly rework or failures.
What Role Does Surface Finish Play in Performance?
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a part’s surface, typically measured in micro-inches. A fine surface finish is critical for reducing friction, enhancing aesthetic appeal, and improving the part’s resistance to wear and corrosion. Industries such as automotive and electronics often mandate specific surface finishes to ensure optimal performance. Buyers should assess surface finish requirements to ensure that the parts delivered will function efficiently and meet regulatory standards.
Why Is Quantity Important in Precision Turning Parts?
The quantity of parts ordered, often referred to as Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ), is a significant factor in B2B transactions. Manufacturers may have specific MOQs based on production capabilities and cost efficiencies. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and production schedules effectively. Additionally, ordering in larger quantities can often lead to cost savings per unit, making it an essential consideration for budget-conscious businesses.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Precision Turning Parts?
Navigating the landscape of precision turning parts requires familiarity with specific industry jargon that facilitates clear communication between buyers and suppliers.
What Does OEM Stand For in Precision Manufacturing?
OEM, or Original Equipment Manufacturer, refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of final products. When sourcing precision turning parts, buyers often prefer OEMs for their reputation in quality and reliability. This term is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring that the components meet the necessary specifications for integration into larger systems.
How Important Is an RFQ in the Procurement Process?
An RFQ, or Request for Quotation, is a formal document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. For buyers, issuing an RFQ is vital for comparing offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best price and service for their precision turning parts.
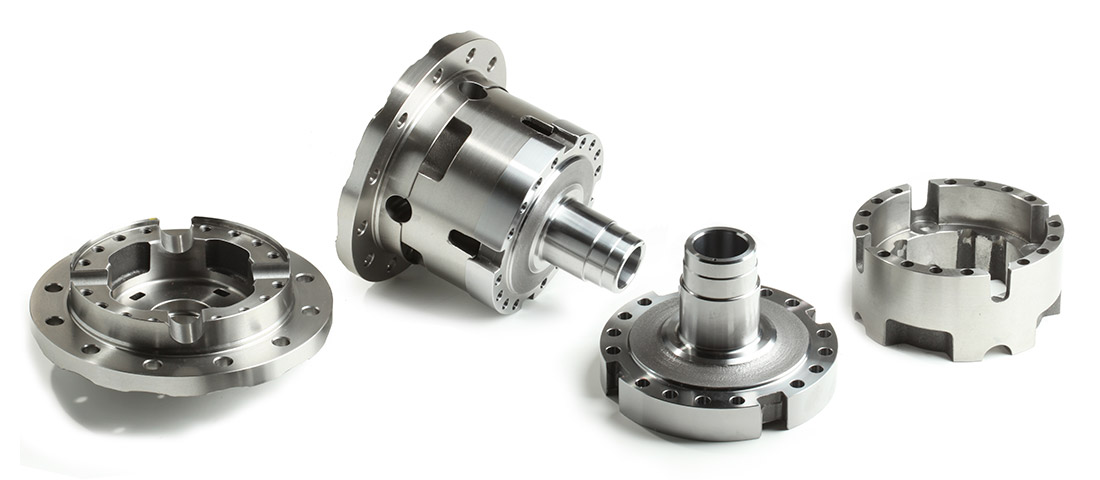

Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
What Are Incoterms and Why Should Buyers Understand Them?
Incoterms, short for International Commercial Terms, are standardized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, insurance, and delivery points. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential to avoid misunderstandings that could affect delivery timelines and cost management.
How Does Just-In-Time (JIT) Delivery Benefit Businesses?
Just-In-Time (JIT) delivery is a strategy that aligns inventory levels with production schedules, minimizing waste and reducing holding costs. For buyers of precision turned parts, JIT can enhance operational efficiency by ensuring that components arrive precisely when needed. This approach is particularly beneficial for businesses operating on tight timelines or those looking to optimize cash flow.
In conclusion, grasping the essential technical properties and trade terminology associated with precision turning parts empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their projects.
Illustrative image related to precision turning parts
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the precision turning parts Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Precision Turning Parts Market?
The precision turning parts market is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for high-quality components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and telecommunications is a key driver. As these sectors evolve, they require precision-engineered parts that meet stringent quality standards and tolerances. Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing technologies, particularly CNC and Swiss turning, have enhanced production efficiency and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to cater to diverse customer needs.
In addition, the rise of Industry 4.0 has facilitated the integration of smart manufacturing practices, such as real-time data analytics and automation, into the production processes. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly adopting these technologies, which enable them to improve operational efficiency and reduce lead times.
Emerging trends also include a growing preference for just-in-time (JIT) delivery systems and lean manufacturing principles. These approaches minimize inventory costs and ensure that businesses can respond swiftly to market changes. Moreover, a shift towards customized solutions is becoming evident, as buyers look for suppliers that can offer tailored products that meet specific application requirements.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affect Precision Turning Parts Procurement?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming crucial considerations for B2B buyers in the precision turning parts sector. With growing awareness of environmental issues, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials, minimizing waste, and reducing carbon footprints in manufacturing processes.
Buyers should seek suppliers who hold green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicate a commitment to environmental management. Furthermore, the use of recycled materials and sustainable sourcing practices can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, particularly in regions where sourcing materials can be fraught with ethical concerns. Buyers are encouraged to vet suppliers for their labor practices and sourcing transparency to ensure compliance with international standards. This not only mitigates risks associated with unethical practices but also fosters long-term partnerships built on trust and integrity.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Precision Turning Parts?
The evolution of precision turning parts can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, when advancements in machining technology began to shape manufacturing processes. Initially, turning was done manually on lathes, but the introduction of mechanized lathes in the late 19th century revolutionized production capabilities.
As industries expanded, the demand for precision components grew, leading to the development of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the mid-20th century. This innovation allowed for higher precision, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex geometries with minimal human intervention.
Today, precision turning parts are integral to various high-tech applications, from aerospace to medical devices. The sector continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for quality and efficiency, establishing a dynamic landscape for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of precision turning parts
-
How do I select the right supplier for precision turning parts?
When choosing a supplier for precision turning parts, consider their certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015 or AS9100:2016, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Evaluate their experience in your specific industry, request samples of previous work, and check for customer testimonials. Additionally, assess their capabilities, including machine technology, material options, and production volume flexibility. Establish open communication to ensure they understand your requirements and can provide technical support throughout the partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for precision turned parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for precision turned parts can vary significantly based on the supplier, material, and complexity of the parts. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 100 pieces to several thousand. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexible MOQs for custom orders, especially if they see potential for long-term collaboration. Always confirm the MOQ in writing to avoid misunderstandings. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing precision turning parts internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of precision turning parts typically include options like upfront payment, partial payments, or net payment terms. Common practices involve a deposit (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipping. Ensure you clarify the payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers or credit terms, and consider using an escrow service for large transactions to protect both parties. Discuss these terms upfront to avoid delays in production. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for precision turned parts?
To ensure quality assurance in your precision turned parts, require suppliers to implement rigorous QA processes, including in-process inspections and final product testing. Ask for detailed documentation of their QA protocols, including certifications and material certifications. Request first-article inspections (FAIs) for initial batches to verify that parts meet specifications. Establishing a clear communication channel for addressing quality issues and implementing corrective actions is also crucial for maintaining product standards. -
What are the common materials used for precision turning parts?
Precision turning parts can be manufactured from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and plastics. The choice of material depends on the application, required strength, corrosion resistance, and budget. Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers, as they can recommend materials that offer the best balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. Be aware that some materials may require specialized machining techniques, which can impact lead times and costs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping of precision parts?
When sourcing precision turning parts internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effective shipping based on your urgency and budget. Ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices, certificates of origin, and compliance with international trade regulations. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can streamline the shipping process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do I handle customization requests for precision turning parts?
To handle customization requests, start by clearly defining your specifications, including dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. Engage with suppliers early in the design process to discuss feasibility and any potential challenges. Good suppliers will offer engineering support to optimize designs for manufacturability. Be prepared for potential additional costs and longer lead times associated with custom orders, and ensure that all modifications are documented in the final agreement to prevent misunderstandings. -
What advantages do precision turned parts offer over general turned parts?
Precision turned parts are manufactured to tighter tolerances and with superior surface finishes compared to general turned parts. This results in lower failure rates, enhanced performance, and increased reliability in applications. Industries such as aerospace and medical require high precision to ensure safety and functionality, making these parts crucial. Investing in precision turned components can lead to lower overall costs due to reduced waste and improved product longevity, offering a better return on investment.
Top 9 Precision Turning Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Groov-Pin – Precision Turned Components
Domain: groov-pin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Precision Turned Components manufactured by Groov-Pin Corp. include high-end, close-tolerance precision machined components for various industries such as Aerospace, Energy, Medical, Defense & Law Enforcement, Farming & Irrigation, Telecommunications, and Automotive. Key specifications include:
– Surface finishes of 32 micro-inches on stainless steel.
– Parts range from 0.030″ to 2.50″ in diameter…
2. Precision Turning Specialties – Swiss Turning & Precision Parts
Domain: precisionturning.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Precision Turning Specialties offers Swiss Turning and precision parts with consistent high quality in every shipment. They manufacture turned parts ranging from .093″ to 2″ in diameter and work with various materials. Their capabilities include CNC Swiss machining with features like live milling, cross drilling, cross tapping, rigid tapping, and subspindles for secondary operations. They provide …
3. Freeway Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: freewaycorp.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components and CNC turned parts manufacturing in the USA. Expertise in producing high-quality precision turned parts with state-of-the-art equipment. Over 30 multiple spindle automatic screw machines and CNC single-spindle turning centers. Capable of machining up to 2 5/8” round and 2 5/16” hex materials, and handling up to 2 7/8” bar stock and chucking up to 7” blanks. Secondary …
4. Tuofa – Precision CNC Machining
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Precision turned parts are manufactured through the turning process, characterized by tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. They are produced using CNC (Computer Numerical Controlled) machines, which automate the machining process for high accuracy and efficiency. Key characteristics include the ability to achieve tight tolerances, ease of machining complex geometries, and suitability f…
5. C-A Design – Precision Turned Components
Domain: c-a-design.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components are essential for the defense industry, providing high accuracy and quality for mission-critical applications. They are produced using advanced twin-spindle, twin-turret, multi-axis, automated CNC lathes, ensuring precision and quality. Key features include:
– High Accuracy/Repeatability: Components produced to exact specifications consistently.
– Tight Tolerances: Achi…
6. Precipart – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: precipart.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Swiss Turning offers precision turned parts ranging from 0.3mm (0.0118″) to 32mm (1.25″) with tolerances less than 10μm (0.0004″). The production utilizes Swiss-type CNC and automatic machines, including single & multi spindle, coil and bar-fed machines, and rotary transfer machines. Materials used include stainless steels, titanium, precious metals, carbon steels, brass and copper alloys, and spe…
7. Precision Turning Corporation – Custom Tight Tolerance Components
Domain: precisionturning.net
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Precision Turning Corporation specializes in manufacturing small, custom tight tolerance components with a tolerance of +-.0001 inches, up to 1-1/4 inches in diameter. They utilize state-of-the-art facilities, including CNC Swiss screw machines and a full range of secondary equipment. The company has been in operation since 1996 and is ISO 9001:2015 certified, ensuring high levels of quality and s…
8. Avant Engineering – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: avantiengineering.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: High-volume precision turned parts are components manufactured using advanced CNC and automatic screw machines to produce large quantities with tight tolerances. They are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics. Materials used include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, carbon and alloy steels, and plastics. Benefits of high-volume production inclu…
9. ANEBON – Precision Turning Components
Domain: anebon.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: ANEBON is an ISO9001-certified CNC turning manufacturer based in China, specializing in high-quality Precision Turning Components for global OEM clients. Key product details include:
– **FOB Price**: US $0.1 – 1 Piece
– **Min. Order Quantity**: 1 Piece
– **Supply Ability**: 1,000,000 Pieces per Month
– **Surface Treatments**: Powder coating, electroplating, oxide, anodization
– **Materials**: Alum…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for precision turning parts
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of precision turning parts is pivotal for businesses seeking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. As outlined in this guide, prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100:2016, ensures adherence to rigorous industry standards. Buyers should also consider the advantages of lean manufacturing practices that not only reduce costs but also improve delivery times and responsiveness.
As global markets expand, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-quality precision components continues to rise. Engaging with reliable suppliers who offer customization and technical support can lead to innovative solutions tailored to specific industry needs, from aerospace to medical applications.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic partnerships with manufacturers that emphasize both quality and service. By doing so, you can secure a competitive edge in your market while ensuring your supply chain remains robust and responsive to evolving demands. Connect with trusted suppliers today to explore how precision turned parts can elevate your production capabilities and drive success in your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.