The Definitive Guide to Power Cords Types: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power cords types
In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing the right power cord types can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With an array of standards, connector types, and regional variations, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate complex requirements to ensure compatibility and safety for their electrical devices. This guide aims to demystify the world of power cords, providing a comprehensive overview of different types, their applications, and crucial factors to consider when making purchasing decisions.
From the widely recognized IEC 60320 standards to country-specific plug types like NEMA and CEE 7/7, understanding these nuances is essential for effective procurement. We will delve into the specific applications for each type, helping you identify the best solutions for your needs. Additionally, this guide will offer insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and safety standards, empowering you to make informed choices that align with your operational requirements.
By equipping you with the knowledge needed to navigate this intricate market, we aim to enhance your purchasing strategy, minimize risks, and ultimately support your business’s growth in a globalized economy. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the field, this guide is designed to be an invaluable resource as you seek reliable power cord solutions for your organization.
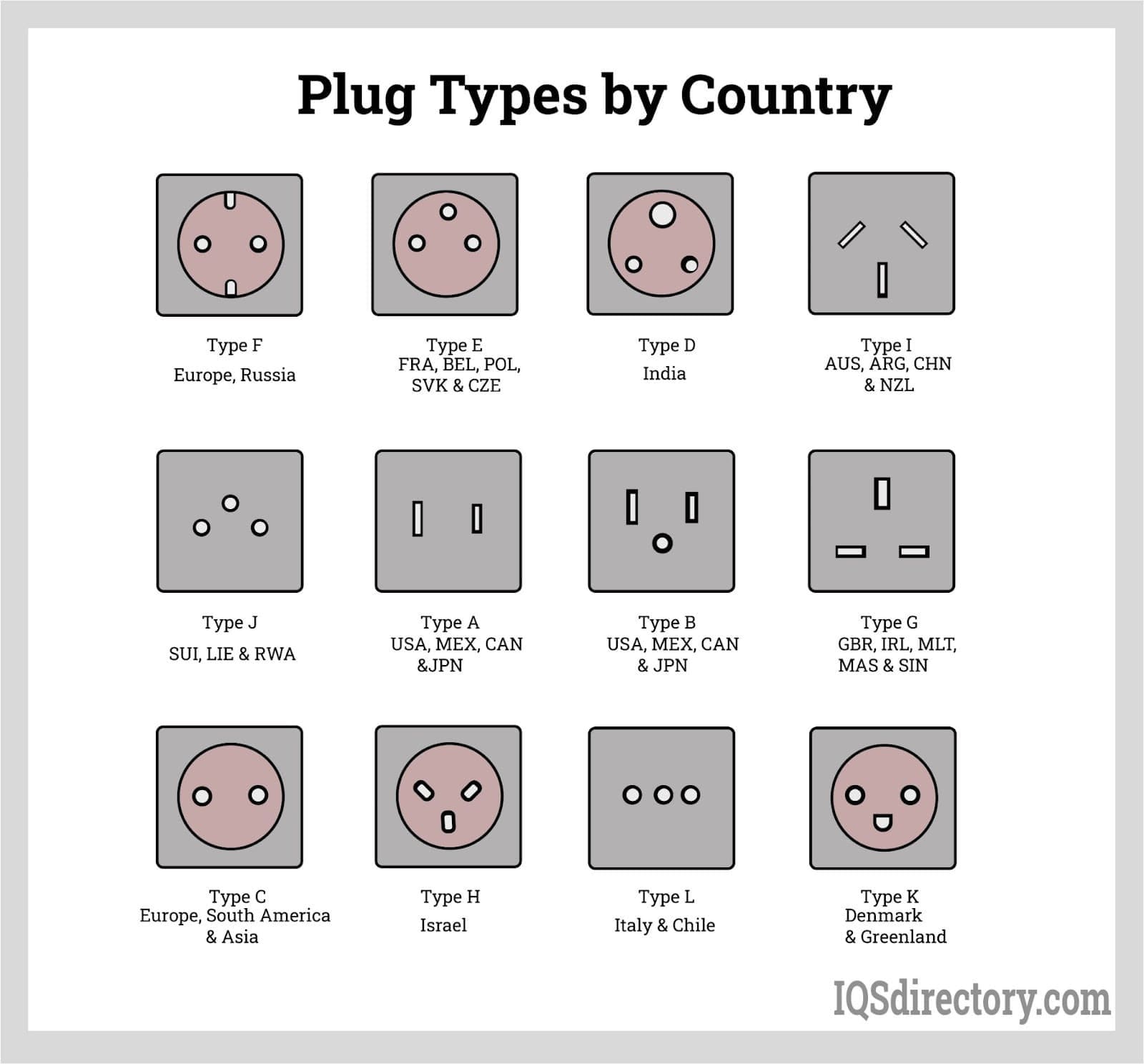
Understanding power cords types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
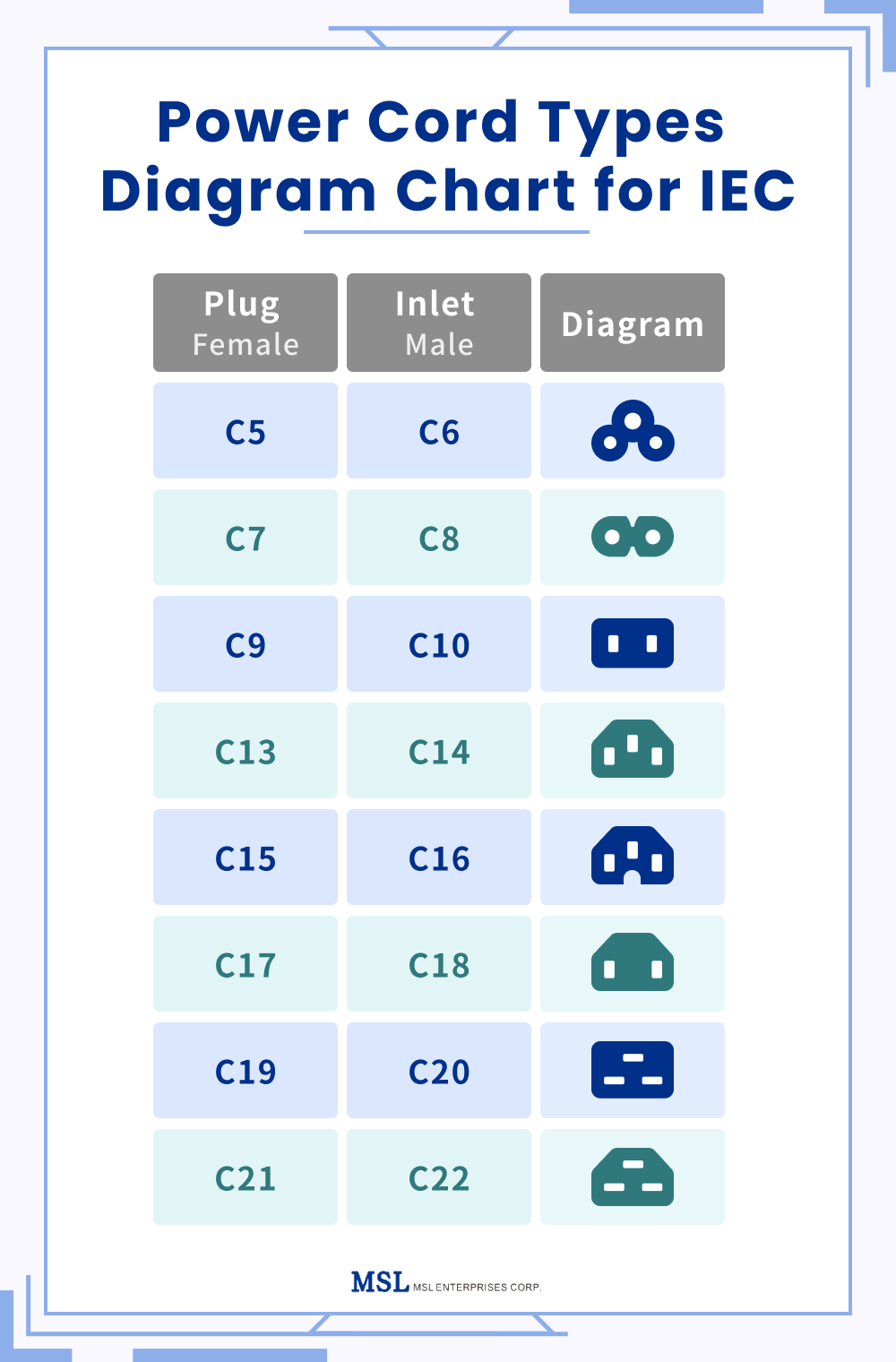
| IEC 60320 C13 | Standardized connector for devices up to 250V, 10A; versatile. | Data centers, IT equipment, consumer electronics. | Pros: Widely compatible; Cons: Limited to specific voltage/current ratings. |
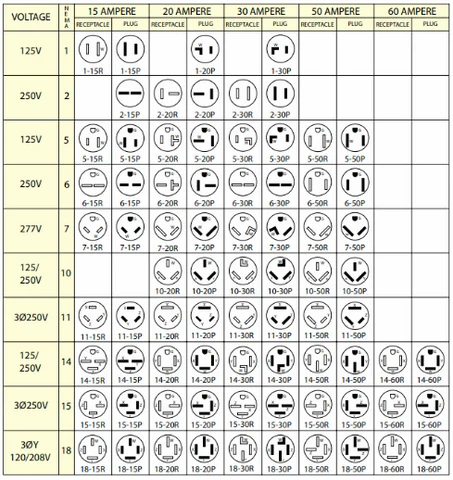
| NEMA 5-15P | Common in North America; three-wire system rated for 15A, 125V. | Office equipment, home appliances, electronics. | Pros: Readily available; Cons: Not suitable for higher voltages. |
| CEE 7/7 | Used widely across Europe; dual compatibility for Type E and F. | Industrial equipment, appliances, consumer electronics. | Pros: Versatile across many countries; Cons: Varying standards can cause confusion. |
| AS/NZS 3112 | Australian standard; designed for safety with unique pin layout. | Electrical appliances, commercial machinery. | Pros: High safety standards; Cons: Limited to Australia and New Zealand. |
| JIS C 8303 | Japanese standard; includes Type A and B plugs with specific configurations. | Consumer electronics, industrial devices. | Pros: Common in Japan; Cons: Not compatible with international standards. |
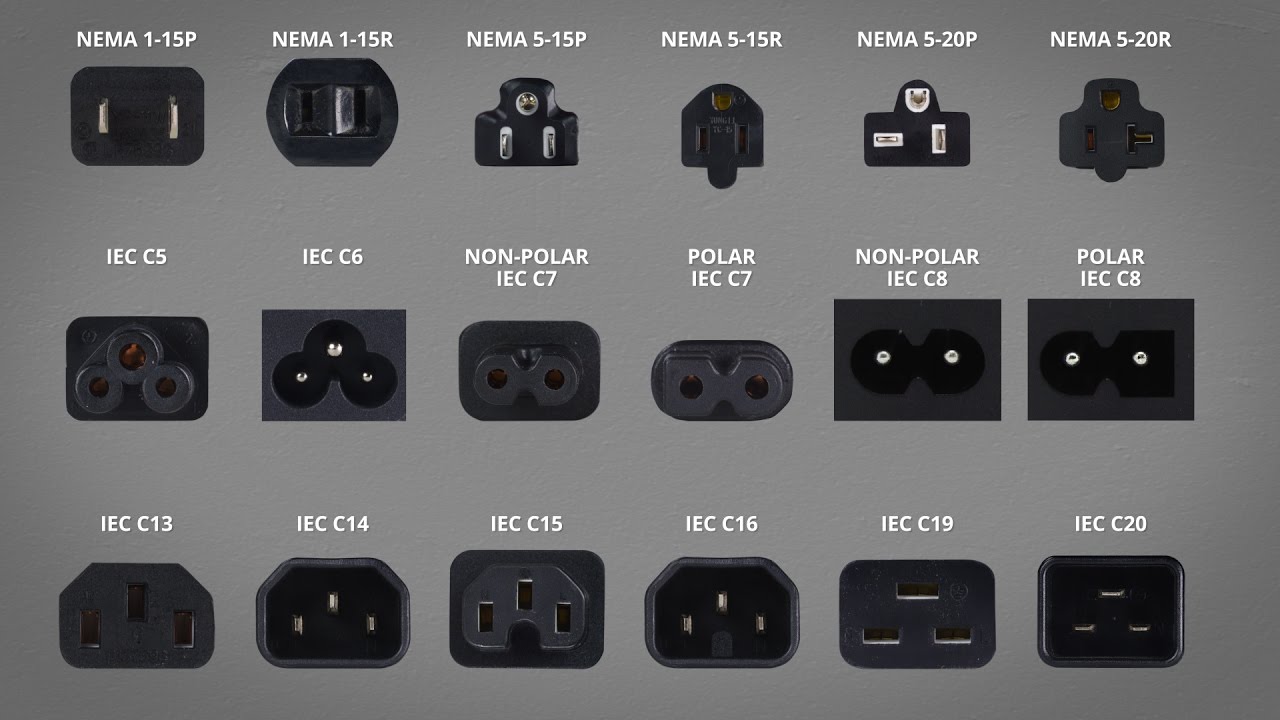
What Are the Characteristics of IEC 60320 C13 Power Cords?
The IEC 60320 C13 power cord is characterized by its standardized connector, which is suitable for appliances requiring up to 250V and 10A. This type is prevalent in data centers and IT environments, where compatibility with various devices is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the cord’s versatility and widespread acceptance, but they must also ensure that their equipment does not exceed the voltage and current ratings specified.
How Does the NEMA 5-15P Power Cord Stand Out?
The NEMA 5-15P is a three-wire power cord commonly used in North America, rated for 15A at 125V. It is often found in office equipment and home appliances, making it a staple for many businesses. Buyers benefit from its easy availability and compatibility with most North American outlets. However, its limitation to lower voltage applications may necessitate alternative options for higher power needs.
What Are the Advantages of CEE 7/7 Power Cords in Europe?
CEE 7/7 power cords serve as a dual connector standard across Europe, supporting both Type E and F plugs. This adaptability makes them ideal for industrial equipment and consumer electronics that need to operate across various European countries. B2B buyers should appreciate the versatility of this standard; however, they must remain aware of the potential for confusion arising from differing national standards.
Why Choose AS/NZS 3112 Power Cords in Australia?
AS/NZS 3112 power cords are specifically designed for Australia and New Zealand, featuring a unique pin layout that enhances safety. They are widely used for electrical appliances and commercial machinery. Buyers in these regions will find these cords to meet high safety standards, although their use is limited to specific geographic areas, which may be a drawback for businesses operating internationally.
What Should Buyers Know About JIS C 8303 Power Cords?
JIS C 8303 power cords encompass Type A and B plugs, primarily used in Japan. Their configurations cater to local electrical standards, making them essential for consumer electronics and industrial devices within the country. While B2B buyers can leverage these cords for domestic operations, they must consider compatibility issues when dealing with international markets, as these plugs do not align with many global standards.
Key Industrial Applications of power cords types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of power cords types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Centers | Power supply for servers and networking equipment | Ensures reliable operation of critical IT infrastructure | Compliance with IEC standards, durability, and compatibility |
| Healthcare | Medical equipment connections, including imaging devices | Vital for patient safety and operational efficiency | Certification for hospital-grade cords, voltage ratings |
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and assembly lines | Enhances productivity and minimizes downtime | Robustness, length options, and local voltage standards |
| Construction | Temporary power supply for tools and equipment | Facilitates on-site operations and enhances safety | Weather-resistant materials, length, and connector types |
| Retail | Powering displays and point-of-sale systems | Supports customer engagement and operational efficiency | Aesthetic design, length flexibility, and compliance with local standards |
How Are Power Cords Used in Data Centers, and What Are the Key Considerations for B2B Buyers?
In data centers, power cords are essential for connecting servers, switches, and routers to the power supply. The reliability of these cords is paramount, as downtime can lead to significant financial losses. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize cords that comply with IEC standards, ensuring compatibility with local power systems. Durability is another critical factor; cords must withstand the rigors of high-density installations while maintaining efficient power delivery.
What Role Do Power Cords Play in Healthcare Settings?
In healthcare, power cords connect critical medical devices such as MRI machines, ventilators, and surgical equipment to power sources. These cords must meet stringent safety standards to prevent electrical hazards that could compromise patient care. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing hospital-grade power cords, which are designed to minimize risks in sensitive environments. Certification for safety and reliability is vital, as is ensuring that the cords can handle the specific voltage and current requirements of medical equipment.
Illustrative image related to power cords types
How Are Power Cords Utilized in Manufacturing Industries?
Manufacturing facilities rely heavily on power cords to connect machinery and tools to electrical sources. The efficiency of production lines is directly impacted by the reliability of these connections. Buyers should look for robust cords that can withstand industrial environments, including exposure to heat, chemicals, and physical stress. Length options are also crucial, as different setups may require varying distances from power sources. Ensuring compliance with local voltage standards is essential for international buyers to avoid operational disruptions.
What Are the Applications of Power Cords in Construction Sites?
On construction sites, power cords are vital for supplying electricity to tools and temporary lighting. These environments can be harsh, requiring cords that are both weather-resistant and durable. B2B buyers should consider the length and gauge of the cords to ensure they meet the demands of various tools and equipment. Additionally, safety features such as grounding and surge protection are essential to prevent accidents and equipment damage. Understanding local regulations regarding electrical equipment is also important for compliance and safety.
How Do Retailers Benefit from Specialized Power Cords?
In the retail sector, power cords are used to connect point-of-sale systems and display units, playing a crucial role in customer engagement. Retailers benefit from aesthetically pleasing cords that blend with store designs while providing reliable power. B2B buyers should consider the flexibility of cord lengths to accommodate various layouts. Compliance with local electrical standards is also necessary to ensure safety and efficiency. Ultimately, the right power cords can enhance the shopping experience and operational efficiency in retail environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power cords types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Diverse Power Cord Standards in Global Operations
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face the daunting challenge of navigating the myriad of power cord standards and plug types used across different countries. For example, a company sourcing equipment for deployment in Europe may inadvertently purchase devices fitted with NEMA connectors, which are standard in North America but incompatible with European sockets. This oversight can lead to delays in project timelines, increased costs due to last-minute procurement, and operational disruptions, as teams scramble to find suitable adapters or replacement cords.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific power cord standards applicable in the target markets. This involves understanding the differences between standards like IEC 60320 for connectors and local plug types such as CEE 7/7 in Europe or NBR 14136 in Brazil. Establishing a standardized procurement checklist that includes the required plug types and cord specifications for each region will facilitate smoother operations. Additionally, partnering with suppliers that offer a diverse range of power cords tailored to various international standards can streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that equipment arrives ready for use without the need for additional adapters or modifications.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility with Legacy Equipment
The Problem: Many businesses operate with a mix of legacy and modern equipment, which can complicate the power supply logistics. For instance, a facility might have older machines that require specific power cord types that are no longer commonly available. This can result in prolonged downtime as teams search for compatible power cords or face the cost of retrofitting equipment to accept newer cord types. The challenge intensifies in regions where certain standards are outdated or less prevalent.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that specialize in both contemporary and legacy power cords. By establishing relationships with manufacturers who can provide custom solutions or longer-run production of specific power cord types, companies can secure the necessary components without compromising on quality or safety. Implementing a proactive inventory management system that tracks the types of power cords in use across all equipment will also help in planning for future needs and ensuring that replacements are readily available before they become critical.
Scenario 3: Addressing Safety and Compliance Concerns
The Problem: Safety and compliance are paramount in any industrial setting, and power cords are no exception. B2B buyers may encounter power cords that do not meet the required safety standards for their region, leading to potential hazards such as electrical shocks, fire risks, or equipment damage. This is particularly concerning in sectors like healthcare or manufacturing, where compliance with international safety standards is mandatory. Failing to adhere to these regulations can result in legal repercussions and harm to a company’s reputation.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
The Solution: To avoid these risks, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing power cords that are compliant with relevant safety standards, such as UL, CE, or IEC certifications. Conducting due diligence on suppliers to verify their compliance with industry regulations is crucial. Implementing a robust quality assurance process that includes regular audits of power cord safety features—such as insulation quality, grounding capabilities, and strain relief—will further enhance safety. Additionally, investing in training for procurement teams about the importance of compliance and safety standards can ensure that all future purchases align with the company’s commitment to safety and quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power cords types
What Are the Key Materials Used in Power Cords and Their Properties?
When selecting power cords for various applications, understanding the materials used is critical for ensuring performance, safety, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in power cords, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Perform in Power Cords?
PVC is one of the most widely used materials in power cord manufacturing due to its excellent insulation properties and flexibility. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -10°C to 70°C, making it suitable for a variety of environments. PVC is also resistant to moisture and many chemicals, which enhances its durability.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for mass production. Its flexibility makes it ideal for applications requiring movement or bending.
Cons: While PVC is durable, it can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures. Additionally, it is not biodegradable, raising environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and oils, but it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and IEC when sourcing PVC power cords. In regions like Europe, the RoHS directive may also influence material selection, requiring the exclusion of hazardous substances.
Illustrative image related to power cords types
What Are the Advantages of Using Rubber in Power Cords?
Rubber, particularly thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), is another popular choice for power cords. It offers excellent flexibility, high-temperature resistance (up to 90°C), and good electrical insulation properties. Rubber is also inherently resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for rugged environments.
Pros: The durability and flexibility of rubber make it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Its resistance to environmental factors like moisture and UV light enhances its longevity.
Cons: Rubber can be more expensive than PVC and may require more complex manufacturing processes. It can also be heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Illustrative image related to power cords types
Impact on Application: Rubber power cords are often used in outdoor or industrial settings where exposure to harsh conditions is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that rubber power cords meet local safety standards, such as IEC 60227 for insulated cables. In markets like Africa and South America, where outdoor applications are prevalent, the robustness of rubber can be a significant advantage.
How Does Silicone Compare as a Material for Power Cords?
Silicone is increasingly being used in power cord applications due to its exceptional temperature resistance (from -60°C to 200°C) and flexibility. It is also highly resistant to ozone, UV light, and extreme weather conditions, making it suitable for outdoor use.
Pros: Silicone’s high-temperature tolerance and durability make it ideal for applications requiring consistent performance under varying conditions.
Cons: The primary drawback of silicone is its cost, which is significantly higher than PVC and rubber. This can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Silicone power cords are particularly well-suited for environments where high temperatures or chemical exposure is a concern, such as in laboratories or manufacturing facilities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that silicone power cords comply with international standards like IEC 60754 for cable materials. In regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe, silicone’s compliance can be a selling point.
What Role Does Polyurethane Play in Power Cord Manufacturing?
Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile material known for its excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility. It can operate effectively in a temperature range of -40°C to 80°C, making it suitable for various applications, including those requiring movement.
Pros: PU offers superior flexibility and durability compared to PVC, making it ideal for dynamic applications where cords are frequently moved or bent.
Cons: Like rubber, polyurethane can be more expensive to produce, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, it may not have the same level of chemical resistance as PVC.
Impact on Application: PU power cords are often used in robotics and automation, where flexibility and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with relevant standards, such as UL and CE marking, especially in markets like the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory compliance is crucial.
Summary of Material Selection for Power Cords
| Material | Typical Use Case for power cords types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | General-purpose applications | Cost-effective and flexible | Can become brittle over time | Low |
| Rubber | Heavy-duty and outdoor applications | Excellent durability and flexibility | More expensive and heavier | Med |
| Silicone | High-temperature and chemical exposure | Exceptional temperature resistance | High cost | High |
| Polyurethane | Robotics and dynamic applications | Superior flexibility and durability | More expensive, less chemical resistance | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in various international markets, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power cords types
What Are the Key Stages in Power Cord Manufacturing Processes?
Power cord manufacturing involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and safety standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Sourced and Processed?
The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection of raw materials, which typically include copper for the conductors and various types of plastic for insulation. Suppliers often source these materials from certified vendors to ensure compliance with international quality standards.
Once the materials are acquired, they undergo preparation, including processes like annealing for copper to enhance its conductivity and flexibility. Insulation materials are also prepared, which may include PVC, rubber, or silicone, depending on the intended application and environmental conditions.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Power Cords?
The forming stage involves several techniques to create the desired shapes and components of power cords. The copper wires are drawn into specific gauges, which are then twisted together to form multi-strand cables. This construction increases flexibility and reduces the risk of breakage.
Illustrative image related to power cords types
For the insulation, extrusion is a common method where heated plastic is forced through a die to create a continuous sheath around the conductors. This process ensures uniform thickness and consistency. Additionally, molding techniques are used to create connectors and plugs that will be attached to the ends of the cords.
Assembly: How Are Power Cords Assembled for Final Production?
In the assembly phase, the insulated conductors are cut to length and connected to the appropriate connectors. This may involve crimping, soldering, or molding processes. Quality assurance begins in this stage, as proper assembly is critical to the performance and safety of the power cords.
Automated machines are often used to streamline the assembly process, but manual inspections are still essential to ensure each connection meets the required standards. This dual approach minimizes human error while maintaining quality.
Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to Ensure Quality?
The finishing stage includes several processes designed to enhance durability and safety. This often involves applying strain reliefs to the joints between the cable and connectors, ensuring that the cable does not become disconnected or damaged under stress.
Power cords may also undergo surface treatments to improve resistance to environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and UV exposure. Finally, labeling and packaging are performed, ensuring that each product is clearly marked with safety certifications and specifications.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Critical for Power Cords?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of power cords, as it ensures that products meet international safety standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be well-versed in these processes to assess supplier reliability.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently produce high-quality products. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) are essential for electrical components, as they indicate compliance with safety regulations in different markets.
B2B buyers should also be aware of specific standards relevant to their regions. For instance, in South America, the INMETRO certification is crucial, while in Africa, SABS certification may be required. Understanding these standards will help buyers avoid non-compliant products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
Illustrative image related to power cords types
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to verify that processes adhere to established standards. This includes checking insulation thickness and connector integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished products undergo rigorous testing, including electrical testing, mechanical stress tests, and safety inspections to ensure they function correctly and safely.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
To ensure that potential suppliers adhere to high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider several verification methods:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Supplier audits are a vital tool for assessing manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes. Buyers should schedule regular audits to evaluate the supplier’s adherence to international standards, production capabilities, and quality control measures. During these audits, it’s beneficial to review documentation related to quality control, including inspection reports and test results.
How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies conduct thorough inspections of the manufacturing process, testing, and compliance with regulatory standards. Buyers should request inspection reports as part of the supplier evaluation process, especially when sourcing from regions with less stringent regulations.
What Are the Challenges in Quality Assurance for International Buyers?
B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges in quality assurance. These challenges can stem from varying standards, language barriers, and different regulatory requirements across countries.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Product Quality?
Different regions may have distinct electrical safety standards that affect the design and manufacturing of power cords. Buyers should ensure that the products they source comply with the relevant standards in their target markets. This may involve additional testing and certification processes, which could delay product availability.
What Role Does Communication Play in Quality Assurance?
Effective communication between buyers and suppliers is crucial for maintaining quality assurance. Buyers should establish clear expectations regarding quality standards, certifications, and testing procedures. Regular updates and feedback can help resolve issues promptly and ensure that products meet the required specifications.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control Important for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse international markets, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for power cords is essential. This knowledge enables buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable, compliant, and high-quality products that meet their specific needs. By prioritizing suppliers that adhere to rigorous quality control measures, buyers can minimize risks and enhance operational efficiency in their respective industries.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power cords types’
To assist international B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring power cords, this guide offers a step-by-step checklist. Understanding the various types of power cords and their specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility and safety in your operations.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly identifying the technical requirements for your power cords. This includes voltage ratings, current ratings, and connector types. Understanding these specifications is crucial as different regions use varying standards, such as IEC 60320 for connectors or NEMA for plugs in North America.
- Key Considerations:
- Voltage and current requirements based on your equipment.
- Compatibility with local electrical standards in your target market.
Step 2: Research International Standards
Familiarize yourself with the international and regional standards applicable to power cords. While IEC 60320 is widely recognized, other standards like NEMA and CEE 7/7 are prevalent in specific regions. Compliance with these standards ensures safety and reliability in your products.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify the standards relevant to your target countries (e.g., Brazil, South Africa).
- Ensure that the power cords you source meet these standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. It’s essential to assess their reliability, quality of products, and adherence to industry standards. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other businesses in your industry.
Illustrative image related to power cords types
- Key Considerations:
- Look for suppliers with certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) that demonstrate quality assurance.
- Seek testimonials or case studies that reflect successful partnerships with similar companies.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Safety
Product quality is paramount when sourcing power cords. Verify that the cords are manufactured using high-quality materials and undergo rigorous safety testing. Poor quality can lead to failures that jeopardize equipment and safety.
- Key Considerations:
- Request samples for testing before bulk purchases.
- Inquire about the safety standards the products meet, such as UL or RoHS compliance.
Step 5: Understand Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in discussions about pricing structures and payment terms with potential suppliers. Understanding the cost per unit, bulk discounts, and payment flexibility can impact your overall budget and cash flow management.
- Key Considerations:
- Compare prices among different suppliers to ensure competitiveness.
- Clarify payment terms, including upfront payments, deposits, and credit options.
Step 6: Consider Shipping and Logistics
Shipping logistics can significantly affect your procurement timeline. Assess the supplier’s ability to deliver to your region efficiently and reliably. Understanding lead times and shipping costs will help you plan effectively.
- Key Considerations:
- Inquire about shipping methods and estimated delivery times.
- Ensure the supplier can provide tracking information and has contingency plans for delays.
Step 7: Establish After-Sales Support
After-sales support is critical for maintaining operational efficiency. Confirm that your supplier offers robust customer service, warranty options, and support for any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Key Considerations:
- Ask about the warranty period and what it covers.
- Ensure there are clear channels for customer support and troubleshooting.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for power cords, ensuring they meet the necessary standards and operational requirements while establishing reliable supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power cords types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power Cord Manufacturing?
When sourcing power cords, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used significantly impact costs. Common materials include copper for conductors, PVC for insulation, and various grades of plastic for connectors. Higher quality materials generally lead to better durability and performance but also increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, making it a crucial factor in overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and machinery can be substantial. Custom designs or specialized connectors may require unique tooling, which can increase the upfront costs for buyers.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure safety and compliance with international standards, such as IEC 60320. Investing in quality control may increase costs but also protects against costly recalls and reputational damage.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers must consider these costs when evaluating total pricing.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will depend on market conditions and competition. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power Cord Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of power cords, making it crucial for B2B buyers to consider these elements during the sourcing process.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding minimum order quantities (MOQ) can lead to significant savings, making it vital for buyers to assess their needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom power cords designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as UL, CE, or RoHS compliance) can elevate prices. However, these factors also enhance safety and reliability, which are paramount in B2B transactions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may command higher prices but often offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the final cost significantly.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Power Cord Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can help optimize costs in power cord sourcing.
-
Negotiation: Strong negotiation skills can lead to better pricing. Buyers should research market rates and be prepared to discuss terms with suppliers.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like longevity, warranty, and potential replacement costs.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that can affect pricing. Building relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms and pricing.
-
Quality vs. Price: While lower prices may be tempting, compromising on quality can lead to increased costs in the long run due to failures or replacements. Prioritize suppliers that offer a balance between cost and quality.
-
Market Insights: Stay informed about regional market trends and emerging technologies that may impact pricing and availability. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for power cords can vary widely based on numerous factors, including specifications, quantities, and supplier negotiations. Therefore, the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power cords types With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions for Power Supply Needs
In today’s interconnected world, various power supply solutions exist to address the energy needs of businesses across different sectors. While power cords types remain a staple for connecting devices to electrical outlets, alternatives such as wireless power transmission and power over Ethernet (PoE) present innovative methods for powering equipment. This analysis will compare these alternatives against traditional power cords to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Power Cords Types | Wireless Power Transmission | Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for high loads and distances | Limited range; less efficient at high power | Good for low to moderate power needs |
| Cost | Generally low, but varies by type | Higher installation and equipment costs | Moderate initial investment, cost-effective over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to install and replace | Complex setup; requires specific infrastructure | Easy to integrate into existing networks |
| Maintenance | Low; replacement as needed | Higher; requires monitoring of alignment and efficiency | Low; mostly network maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Data centers, industrial applications | Portable devices, medical equipment | Office environments, IP cameras |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Wireless Power Transmission?
Wireless power transmission utilizes electromagnetic fields to transfer energy from a power source to an electrical load without physical connectors. Its primary advantage is the elimination of cables, which can reduce clutter and enhance mobility. This technology is ideal for portable devices and applications where cables may pose safety risks, such as in medical environments. However, its limitations include a shorter effective range and lower efficiency for high-power applications, making it unsuitable for large data centers or industrial machinery.
How Does Power over Ethernet (PoE) Compare to Traditional Power Cords?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers electrical power along with data over standard Ethernet cables. This method simplifies installations by combining power and data transmission into a single cable, making it especially beneficial in office environments for devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. PoE offers a moderate initial investment, but its operational efficiency can lead to long-term savings. The main drawback is that it is only effective for low to moderate power requirements, so it is not suitable for high-demand equipment typically powered by traditional power cords.
Conclusion: Which Power Supply Solution Is Right for Your Business?
Selecting the right power supply solution depends on specific operational needs, equipment requirements, and budget constraints. Power cords types remain a reliable choice for high-load environments like data centers and industrial applications. In contrast, wireless power transmission and PoE offer innovative alternatives for businesses seeking flexibility and streamlined installations. B2B buyers should assess their unique situations, considering factors such as power demand, installation complexity, and long-term maintenance costs, to choose the most effective solution for their power supply needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power cords types
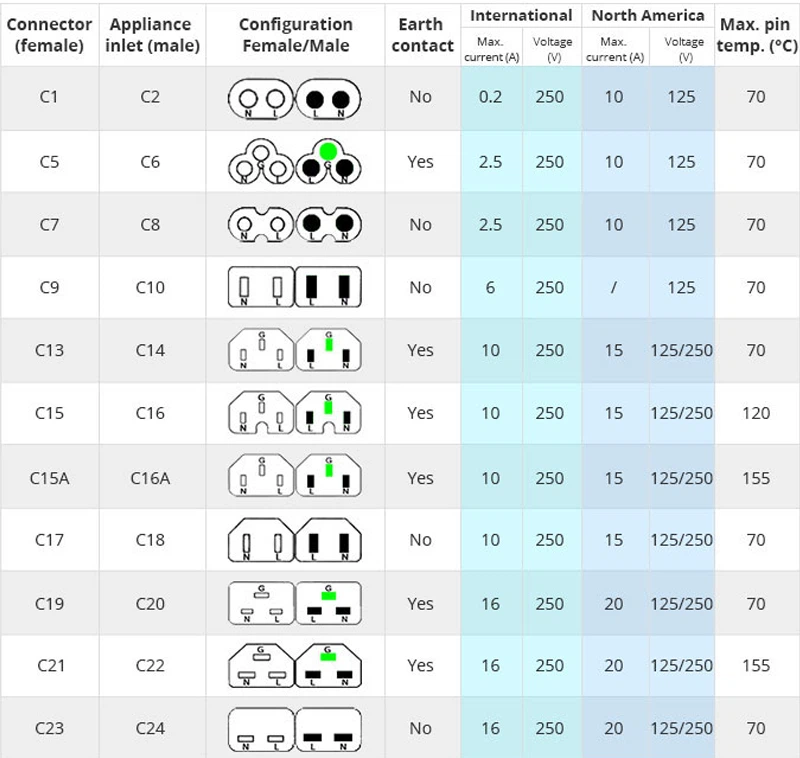
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power Cords?
When considering power cords for various applications, understanding their essential technical properties is crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and compatibility. Here are some critical specifications that buyers should evaluate:
-
Material Grade
The material used in power cords typically includes copper for conductors and PVC or rubber for insulation. Copper is favored for its excellent conductivity, while PVC and rubber provide flexibility and durability. Choosing the right material impacts the cord’s electrical efficiency and lifespan, which is essential for maintaining operational reliability in industrial settings. -
Voltage and Current Rating
Power cords are rated for specific voltage and current limits, often expressed in volts (V) and amperes (A). For instance, a cord rated at 250V and 15A can safely handle devices that operate within those limits. Understanding these ratings is vital for ensuring that the selected power cord can support the electrical load of the connected equipment without risk of overheating or failure. -
Connector Type
Different regions and applications utilize various connector types, such as IEC 60320 (C13, C19) and NEMA standards. The connector type determines compatibility with sockets and devices. Buyers must ensure that the power cord connectors align with their equipment’s requirements to avoid connectivity issues, which could result in operational downtime. -
Cable Length
The length of the power cord can affect installation flexibility and convenience. Shorter cords may limit placement options, while excessively long cords can lead to voltage drops. It is essential to select the appropriate length to meet specific operational needs without compromising performance. -
Temperature Rating
Temperature ratings indicate the maximum ambient temperature at which the power cord can operate safely. For example, cords may be rated for 60°C or 90°C. This specification is crucial in environments with high heat, ensuring that the cord will not degrade or fail, potentially leading to safety hazards. -
Compliance Standards
Compliance with local and international safety standards (e.g., UL, CE, IEC) ensures that the power cords meet essential safety and performance criteria. Buyers should verify these certifications to ensure the cords are suitable for their intended applications and comply with legal requirements in their region.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Navigating the procurement process for power cords requires familiarity with specific trade terms that can impact purchasing decisions. Here are several key terms to know:
Illustrative image related to power cords types
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of power cords, buyers may source cords from OEMs who specialize in specific specifications for branded products, ensuring compatibility and quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory management and upfront costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This is a critical step in the purchasing process, allowing buyers to compare offers from multiple vendors and make informed decisions based on cost, quality, and delivery timelines. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and negotiate better terms, minimizing risks associated with international procurement. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is vital for planning inventory and ensuring that production schedules are not disrupted. Buyers should factor lead times into their procurement strategy to maintain smooth operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing power cords, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability in their respective industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power cords types Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Power Cords Market for International Buyers?
The power cords market is experiencing dynamic shifts influenced by several global drivers, particularly relevant to international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The increasing reliance on technology across various sectors—such as telecommunications, data centers, and consumer electronics—has led to a surge in demand for reliable power solutions. Notably, the rise of e-commerce and remote work has created a growing need for adaptable power cord types that cater to diverse electrical standards worldwide.
A significant trend is the standardization of power cord types, with the IEC 60320 standard gaining traction among manufacturers and users. This standardization simplifies sourcing for international buyers, allowing them to procure power cords that comply with multiple regional standards. Additionally, the market is witnessing the emergence of smart power solutions, including power cords with integrated surge protection and energy monitoring features, which appeal to businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and safety.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
Moreover, regional dynamics play a crucial role in shaping sourcing strategies. For instance, in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure can be inconsistent, power cords that offer durability and flexibility are increasingly sought after. Understanding local compliance regulations and standards, such as NEMA in North America or CEE 7/7 in Europe, is essential for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility and safety in their operations.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Power Cords Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing of power cords, with businesses increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly practices. The production and disposal of power cords can have significant environmental impacts, including plastic waste and energy consumption. As a result, international buyers are seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing carbon footprints in manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are concerned about labor practices within the supply chain. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor standards not only enhances a company’s reputation but also mitigates risks associated with unethical practices. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliance are becoming critical for B2B buyers. These certifications assure that power cords are manufactured with minimal environmental impact and that end-of-life products can be recycled responsibly.
Additionally, the trend toward eco-friendly power cords—made from sustainable materials or designed for energy efficiency—is gaining momentum. Buyers are increasingly looking for products that not only meet their technical requirements but also align with their corporate sustainability goals. This shift not only supports environmental stewardship but also appeals to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Power Cords Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the power cords market reflects significant advancements in technology and manufacturing practices. Initially, power cords were simplistic in design, primarily serving the basic function of electrical connectivity. However, as technology progressed, the demand for specialized power cords grew, leading to the development of various types that cater to specific needs, such as C13, C15, and C19 connectors.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
The standardization efforts, particularly the adoption of IEC 60320, have streamlined the manufacturing process and enhanced compatibility across different devices and regions. This evolution has been crucial for international B2B buyers, enabling them to source power cords that meet specific regional standards while ensuring reliability and safety.
As we move forward, the focus on sustainability and technological integration will continue to shape the power cords landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers seeking to navigate this complex market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power cords types
-
How do I choose the right power cord type for my equipment?
Choosing the right power cord involves understanding both the equipment’s requirements and the electrical standards of your region. Start by identifying the voltage and amperage specifications of your devices. Next, consider the plug type used in your country; for example, North America primarily uses NEMA connectors, while Europe often uses CEE 7/7. Ensure compatibility with the IEC 60320 standards for connectors, such as C13, C15, or C19, which are widely used in data centers. Always consult technical specifications to ensure safety and efficiency. -
What is the best power cord type for data centers?
For data centers, the most commonly recommended power cord types are those that conform to the IEC 60320 standard, specifically C13 and C19 connectors. These are designed to handle high-density power loads and are compatible with a variety of server and networking equipment. Using power cords that meet the NEMA or CEE standards, depending on your location, is essential for reliable performance. Additionally, consider using cords with a higher gauge for better current handling and to reduce heat generation. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing power cords internationally?
When sourcing power cords internationally, key factors include compliance with local electrical standards, quality certifications, and supplier reliability. Verify that the cords meet regional safety regulations, such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the U.S. Additionally, assess the supplier’s track record, including reviews and case studies, to ensure they can meet your quality and delivery expectations. Understanding logistics, such as shipping times and customs requirements, is also crucial for timely procurement. -
How can I ensure the quality of power cords from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of power cords, request certifications from suppliers that demonstrate compliance with international standards like IEC 60320 or NEMA. Consider conducting factory audits or requesting samples for testing. Establish clear quality assurance protocols, including regular inspections and testing procedures for voltage and current ratings. Additionally, maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations and performance metrics can help foster a reliable supply chain. -
What customization options are available for power cords?
Customization options for power cords can include variations in length, connector types, and cable colors. Many manufacturers also offer the ability to modify cord specifications to meet unique electrical requirements, such as higher gauge wire for increased current capacity or specific insulation materials for environmental resilience. Discussing your specific needs with suppliers can yield tailored solutions that enhance compatibility and performance for your equipment. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cords?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cords can vary significantly by supplier and the type of cord required. Generally, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the customization and production capabilities. For bulk orders, negotiating lower MOQs is often possible, especially if you are willing to commit to ongoing purchases. Always clarify MOQs upfront to align your sourcing strategy with supplier expectations. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing power cords?
Payment terms when purchasing power cords can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include full payment in advance, a 30% deposit with the balance upon shipment, or net 30 days after delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring supplier trustworthiness. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods or trade financing options to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How do I manage logistics for international power cord shipments?
Managing logistics for international power cord shipments requires careful planning. Start by selecting reliable freight forwarders who understand customs regulations and shipping procedures in both the exporting and importing countries. Ensure all documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, is accurate to avoid delays. Additionally, consider potential tariffs and taxes, and choose shipping methods that balance cost and delivery speed to meet your operational needs. Regular communication with your logistics partners is key to addressing any issues that may arise during transit.
Top 7 Power Cords Types Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Power Cords
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Power cords, also known as line cords or power cables, connect electronic devices to power sources, facilitating electricity transmission. They typically consist of copper wires insulated and covered by a non-conductive layer. Power cords can be classified into basic power cords (plug at one end, bare wires at the other) and connector power cords (connector at one end, wires at the other). The Nat…
2. Cables To Go – AC Power Cords & Surge Protectors
Domain: cablestogo.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: AC Power Cords, Splitters, Surge Protectors
3. Cables.com – Essential Power Cords and Connectors
Domain: cables.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Power cords and cables are essential for delivering electricity to devices, with various specifications including voltage and current ratings, connectors, and material construction. Key types include AC power cords, C14 to C13 connectors for data centers, C19 to C20 for high-power devices, and 5-15P to C13 for office electronics. Specialty options include colored power cables for easy identificati…
4. MSL – Power Cable Solutions
Domain: msl-tw.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Power Cable Types: IEC, NEMA, CEE. Key components include conductors (copper or aluminum), insulation (XLPE, PVC, EPR), shielding (metallic tapes or braids), and sheath/jacket (PVC, TPU, polyethylene). Main types of power cables and connectors: IEC (global use), NEMA (North America), CEE (European countries). Common IEC connectors: C5/C6 (2.5A, 250V), C7/C8 (2.5A, 250V). NEMA connectors include NE…
5. CableWholesale – NEMA Power Cords
Domain: cablewholesale.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NEMA Power Cord Types: 1. NEMA 1-15P: 2-wire non-grounding, rated for 120V. 2. NEMA 5-15P: 3-wire grounding, rated for 125V, common in U.S. 3. NEMA 5-15R: Receptacle version of 5-15P. 4. NEMA 14-30: 4-wire grounding, used for electric dryers, allows 120/240V. 5. NEMA 14-50: 4-wire grounding, used for electric stoves, found in RV parks. 6. NEMA TT-30: 30 amp grounding device, rated for 125V, used i…
6. StayOnline – Power Cord Types Reference Chart
Domain: stayonline.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Power Cord Types Reference Chart – Various types of power cords including C14, C20, NEMA, international cords, hospital grade, splitter cords, and locking power cords. Specific types include C14 to C13, C14 to C15, C20 to C19, NEMA 5-15 to C13, and many others. Cords available in different colors, angled designs, and locking mechanisms. Includes international standards and compatibility with vario…
7. Reddit – IEC C13 Power Cord
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: IEC C13 power cord, also known as a ‘kettle lead’, commonly used for desktop PCs and various electronics. It supports a voltage range of 100V to 240V and has a maximum rating of 10A/250V.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power cords types
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers on Power Cords Types?
In conclusion, understanding the diverse types of power cords and their respective standards is critical for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The international standard IEC 60320 serves as a foundational reference, but local plug types like NEMA in North America and CEE 7/7 in Europe highlight the importance of regional specifications. Strategic sourcing of power cords should focus on compatibility, safety, and compliance with local regulations to ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
Moreover, businesses should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who can provide a comprehensive range of power cord options, ensuring that they can meet the varying demands of their operations. By doing so, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce downtime associated with equipment incompatibility.

Illustrative image related to power cords types
Looking ahead, the shift towards more sustainable and efficient power solutions presents an opportunity for B2B buyers to innovate in their sourcing strategies. Investing in high-quality, versatile power cords will not only support current needs but also position businesses for future technological advancements. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure the best power cord solutions that align with your operational goals and regional requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.