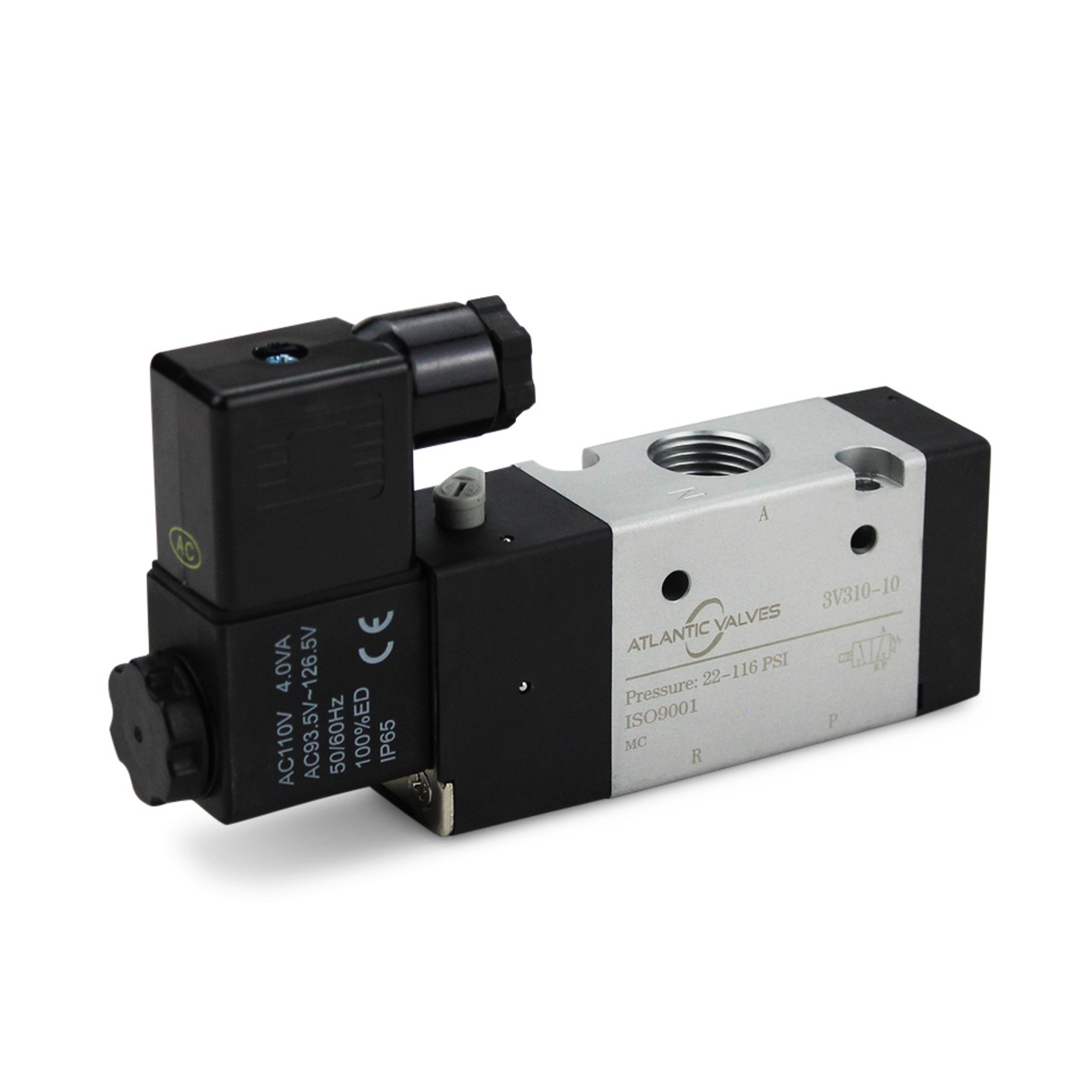
The Definitive Guide to Pneumatic Solenoids: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic solenoids
In today’s global market, sourcing pneumatic solenoids can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in dynamic regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexity of navigating diverse suppliers, varying product specifications, and fluctuating costs adds layers of difficulty to procurement processes. However, understanding the nuances of pneumatic solenoids—ranging from their operational principles to their wide array of applications—can empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and productivity.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of pneumatic solenoids, including the different types available, their applications across various industries, and practical strategies for supplier vetting. By offering insights into cost factors, regulatory considerations, and performance metrics, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to select the right solenoid for their specific needs.
Whether you are in manufacturing, automotive, or any sector reliant on pneumatic systems, this resource will serve as your go-to reference for optimizing your sourcing strategy. With actionable insights tailored to the unique challenges faced by buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, you will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of the global market for pneumatic solenoids, ensuring you make choices that align with your operational goals.
Understanding pneumatic solenoids Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Way Solenoid Valves | Controls flow in two directions; simple design. | General automation, HVAC systems | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to install. Cons: Limited control options. |
| Three-Way Solenoid Valves | Offers three ports for versatile flow control. | Pneumatic actuators, mixing applications | Pros: Greater flexibility; allows for complex operations. Cons: More expensive than two-way valves. |
| Five-Way Solenoid Valves | Can control multiple actuators; often used in double-acting cylinders. | Robotics, industrial machinery, pneumatic tools | Pros: Efficient for complex systems; reduces the need for multiple valves. Cons: Higher initial cost; requires careful installation. |
| Latching Solenoid Valves | Maintains position without continuous power; uses magnetic latching. | Emergency systems, safety applications | Pros: Energy-efficient; reduces power consumption. Cons: More complex; may require specialized knowledge for installation. |
| Miniature Solenoid Valves | Compact design; suitable for tight spaces. | Medical devices, portable equipment | Pros: Space-saving; lightweight. Cons: Limited flow capacity; may not be suitable for high-pressure applications. |
What Are Two-Way Solenoid Valves and Their Applications?
Two-way solenoid valves are fundamental components in pneumatic systems, allowing air to flow in two directions. Their simplicity makes them ideal for general automation tasks and HVAC systems. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the valve’s compatibility with their existing systems and its cost-effectiveness, as these valves often represent a lower upfront investment. However, their limited control options may not suit more complex applications where precise flow management is required.
How Do Three-Way Solenoid Valves Enhance Flexibility?
Three-way solenoid valves are designed with three ports, enabling versatile flow control that can switch between different pathways. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in pneumatic actuators and mixing applications. Buyers should assess the operational requirements of their systems, as these valves can provide enhanced functionality compared to two-way valves. While they are typically more expensive, their ability to manage complex operations justifies the investment for many industrial applications.
Why Choose Five-Way Solenoid Valves for Complex Systems?
Five-way solenoid valves are essential for controlling multiple actuators and are commonly used in robotics and industrial machinery. Their design allows for efficient management of double-acting cylinders, reducing the need for multiple valves. B2B buyers should consider the initial cost against the efficiency gains in complex systems. Although these valves require careful installation and may have a higher upfront cost, their operational efficiency can lead to long-term savings.
What Are the Advantages of Latching Solenoid Valves?
Latching solenoid valves maintain their position without requiring continuous power, utilizing magnetic latching mechanisms. They are particularly useful in emergency systems and safety applications where power conservation is crucial. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the complexity of installation, as latching valves may require specialized knowledge. Despite their more complex nature, the energy efficiency they offer can significantly reduce operational costs.
How Do Miniature Solenoid Valves Fit in Compact Applications?
Miniature solenoid valves are designed for applications where space is a premium, making them ideal for medical devices and portable equipment. Their compact nature allows for integration into tight spaces, but buyers should be mindful of their limited flow capacity and suitability for high-pressure applications. When considering these valves, it’s essential to balance the need for space savings against the potential limitations in performance.
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic solenoids
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic solenoids | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automation of assembly lines | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and reliability in high-volume operations. |
| Automotive | Control of air braking systems | Enhances safety and response times | Look for high durability and compliance with safety standards. |
| Food and Beverage | Control of packaging and filling machines | Improves accuracy and reduces waste | Consider hygiene standards and resistance to corrosion. |
| HVAC Systems | Regulation of air flow in climate control systems | Optimizes energy consumption and comfort levels | Evaluate energy efficiency and adaptability to different climates. |
| Chemical Processing | Control of gas flow in reactors and mixers | Ensures precision in chemical reactions and safety | Prioritize materials that withstand corrosive environments and high pressures. |
How Are Pneumatic Solenoids Used in Manufacturing Automation?
In the manufacturing sector, pneumatic solenoids are integral to automating assembly lines. They facilitate the precise control of machinery, ensuring that components are assembled with accuracy and speed. This automation not only boosts productivity but also reduces labor costs, which is critical for businesses looking to enhance their competitive edge. For buyers in regions like Nigeria or Brazil, sourcing pneumatic solenoids that are compatible with existing systems and can withstand the rigors of high-volume production is essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
What Role Do Pneumatic Solenoids Play in Automotive Air Braking Systems?
In the automotive industry, pneumatic solenoids are vital for controlling air braking systems. They enable quick and reliable actuation, which is crucial for vehicle safety and performance. The ability to respond rapidly to braking commands can significantly reduce stopping distances, enhancing overall safety. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia or South Africa should prioritize sourcing solenoids that meet rigorous safety standards and demonstrate high durability to withstand harsh driving conditions.
How Do Pneumatic Solenoids Enhance Food and Beverage Packaging?
In the food and beverage industry, pneumatic solenoids are used in packaging and filling machines to control the flow of products. This precision ensures that containers are filled accurately, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency. For businesses in Latin America or Europe, it is important to consider solenoids that comply with hygiene standards and are resistant to corrosion, given the frequent cleaning and high sanitation requirements in food processing environments.
Why Are Pneumatic Solenoids Critical in HVAC Systems?
Pneumatic solenoids are essential in HVAC systems for regulating air flow and maintaining climate control. By enabling precise adjustments to air distribution, these solenoids help optimize energy consumption and enhance comfort levels in buildings. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East where climate control is crucial, evaluating the energy efficiency and adaptability of pneumatic solenoids to varying environmental conditions can lead to significant cost savings and improved system performance.
What Benefits Do Pneumatic Solenoids Provide in Chemical Processing?
In the chemical processing industry, pneumatic solenoids control gas flow in reactors and mixers, ensuring precise chemical reactions and maintaining safety protocols. Their ability to manage high pressures and corrosive substances makes them indispensable in this sector. Buyers should prioritize sourcing solenoids made from materials that can withstand harsh chemical environments, especially in regions with stringent safety regulations, to ensure reliable and safe operations in their facilities.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pneumatic solenoids’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Pneumatic Solenoid for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate pneumatic solenoid valves for their specific operational needs. This issue arises from the vast array of options available in the market, which can lead to confusion over specifications such as voltage, size, and functionality. For instance, a manufacturing facility may require solenoids that can operate under high-pressure conditions, but without a clear understanding of their system’s requirements, buyers risk selecting a valve that is either underperforming or incompatible. This can result in operational downtime, increased costs, and frustration.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to conduct a thorough needs assessment before purchasing pneumatic solenoids. Begin by gathering detailed specifications of your existing systems, including the required flow rates, pressure ratings, and voltage compatibility. Engage with technical experts from manufacturers to gain insights into which solenoid models best suit your applications. Additionally, consider investing in solenoid valves with adjustable features that can accommodate future changes in your operational requirements. Utilizing simulation tools or software can also help visualize how different solenoid options will interact within your system, ensuring a more informed decision.
Scenario 2: Frequent Failures and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the frequent failure of pneumatic solenoids, leading to unexpected maintenance costs and operational interruptions. Buyers often face the dilemma of whether to choose lower-cost options that may not be durable or to invest in higher-quality products that fit within budget constraints. Frequent solenoid failures can stem from various issues, including improper installation, inadequate maintenance, or environmental factors such as dust and moisture.
The Solution: To enhance the longevity and reliability of pneumatic solenoids, prioritize quality over cost when making purchases. Opt for solenoids that are designed for specific environmental conditions and include features such as IP-rated enclosures to prevent moisture ingress. Implement a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections and cleaning to ensure that solenoids are functioning optimally. Additionally, training maintenance staff on proper installation techniques and troubleshooting can significantly reduce the likelihood of failures. Collaborating with suppliers who offer robust warranties and customer support can also provide peace of mind and assistance when issues arise.
Scenario 3: Complicated Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when integrating new pneumatic solenoids into existing systems. This integration can be complicated by factors such as differing electrical requirements, incompatible fittings, or the need for additional control equipment. For example, a company may purchase a new solenoid valve that does not align with their existing control systems, leading to delays in implementation and increased project costs.
The Solution: To streamline the integration process, take a proactive approach by involving system engineers in the selection phase of pneumatic solenoids. Conduct a compatibility analysis to ensure that the new solenoids can seamlessly integrate with existing electrical and mechanical systems. Consider using modular solenoids that allow for easy installation and adjustments without extensive reconfiguration. Additionally, reach out to suppliers who offer comprehensive technical support and documentation, which can aid in the installation and setup process. Investing in programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that can accommodate multiple solenoid types may also provide greater flexibility and control over pneumatic systems, reducing future integration headaches.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic solenoids
When selecting materials for pneumatic solenoids, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, compatibility with media, and regulatory standards. Here are analyses of four common materials used in pneumatic solenoids, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Brass in Pneumatic Solenoids?
Brass is a popular choice for pneumatic solenoids due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 150°C and can handle moderate pressure levels. Brass is also known for its good electrical conductivity, which is beneficial in solenoid applications where electrical performance is crucial.
Pros and Cons of Brass:
– Pros: Durable, corrosion-resistant, cost-effective, and easy to machine.
– Cons: Limited high-temperature performance and can be susceptible to dezincification in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
Brass is suitable for air and non-corrosive gas applications. However, it may not be ideal for aggressive media, which could lead to premature failure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Brass components should comply with standards such as ASTM B16 for fittings and ASTM B283 for alloy specifications. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the brass used meets local corrosion resistance requirements.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Pneumatic Solenoids?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and high-pressure applications, typically rated for pressures exceeding 200 psi.
Pros and Cons of Stainless Steel:
– Pros: High durability, excellent corrosion resistance, and suitability for high-pressure applications.
– Cons: Higher cost and more complex manufacturing processes due to its hardness.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive gases and liquids, making it versatile for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 for stainless steel bars and shapes is crucial. Buyers from Europe and South America should consider the specific grades of stainless steel that align with their environmental conditions.
What Are the Benefits of Aluminum in Pneumatic Solenoids?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, making it an attractive option for pneumatic solenoids that require reduced weight without sacrificing performance. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 120°C.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
– Pros: Lightweight, cost-effective, and excellent machinability.
– Cons: Lower strength compared to brass and stainless steel, and can be susceptible to wear in abrasive environments.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is best suited for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in mobile machinery or equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum components should comply with standards like ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum and should be checked for local regulations regarding lightweight materials.
Why Choose Plastic for Pneumatic Solenoids?
Plastics, such as polyamide or polycarbonate, are increasingly used in pneumatic solenoids due to their lightweight nature and excellent chemical resistance. They can typically handle temperatures up to 80°C and moderate pressures.
Pros and Cons of Plastic:
– Pros: Very lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to a wide range of chemicals.
– Cons: Limited temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, and potential for wear over time.
Impact on Application:
Plastic solenoids are ideal for applications involving corrosive gases or where weight is a major concern. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Ensure that plastic components comply with relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties and that they are suitable for the specific media in use.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pneumatic Solenoids
| Material | Typical Use Case for pneumatic solenoids | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Air and non-corrosive gas applications | Durable and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments and high-pressure applications | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications in mobile machinery | Lightweight and excellent machinability | Lower strength than metals | Med |
| Plastic | Corrosive media applications | Very lightweight and chemical resistant | Limited temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for pneumatic solenoids, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic solenoids
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Pneumatic Solenoids?
The manufacturing process for pneumatic solenoids involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
1. Material Preparation: Sourcing Quality Components
The first step in manufacturing pneumatic solenoids is sourcing high-quality materials. Manufacturers typically use materials such as brass, stainless steel, and high-grade plastics to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion. Suppliers must be vetted to confirm compliance with international standards, as the material quality directly affects the solenoid’s performance and lifespan.
2. Forming: Precision Engineering Techniques
Once the materials are ready, the forming process begins. This involves various machining techniques, including CNC machining, stamping, and injection molding. CNC machining allows for precision in creating intricate parts, such as the solenoid body and the plunger. The accuracy of these components is crucial, as even minor deviations can lead to performance issues.
3. Assembly: Integrating Components with Care
The assembly stage involves bringing together the various components, including the solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body. This process may be manual or automated, depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities. Skilled technicians often conduct manual assembly to ensure each part is fitted correctly, while automated systems can enhance efficiency for higher volume production.
4. Finishing: Ensuring Quality and Aesthetics
Finishing processes such as anodizing, painting, or applying protective coatings are employed to enhance the durability and aesthetics of the solenoid. This step not only adds to the product’s visual appeal but also helps in protecting against environmental factors.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Pneumatic Solenoid Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing of pneumatic solenoids, ensuring that products are reliable and meet regulatory standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Pneumatic Solenoids?
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas industry may apply, depending on the solenoid’s intended application.
Which QC Checkpoints Are Essential During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for conformity to specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks ensure that components are being produced within acceptable tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to verify that the finished solenoids function correctly and meet all specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Pneumatic Solenoids?
Testing is a vital part of the QC process. Common methods include:
- Leak Testing: Ensures that there are no leaks in the solenoid, which could compromise performance.
- Pressure Testing: Validates that the solenoid can withstand specified pressure levels.
- Functional Testing: Checks that the solenoid operates correctly under different conditions, simulating real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial.
What Audit Procedures Should Be Followed?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control measures. Buyers should request to see documentation of the supplier’s quality management system, including ISO certifications and internal audit reports.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality control processes. These inspections can occur at various stages, from raw material sourcing to final product testing, ensuring compliance with international standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital for international B2B buyers. Different regions may have specific requirements that affect product acceptance and market entry. For instance:
- CE Certification: In Europe, products must have CE marking to demonstrate compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- Local Regulations: Buyers must be aware of any local regulations in their respective countries, which may require additional certifications or testing.
Conclusion: The Importance of Quality Manufacturing in Pneumatic Solenoids
For B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for pneumatic solenoids is essential in making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards and employing rigorous QC checkpoints, buyers can ensure that they are investing in reliable, high-quality products that will perform effectively in their applications. Investing time in supplier verification can lead to stronger partnerships and better long-term outcomes in the competitive landscape of pneumatic systems.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pneumatic solenoids’
The procurement of pneumatic solenoids requires careful consideration and a systematic approach to ensure that the products meet your operational needs and quality standards. This guide outlines key steps to facilitate a successful sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is critical when sourcing pneumatic solenoids. Identify the operational parameters such as voltage, pressure ratings, and flow rates that your application demands. This clarity will guide you in selecting the right type and size of solenoid valve, ensuring compatibility with your existing systems.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
- Voltage and Current: Determine whether you need AC or DC solenoids, and specify the voltage levels (e.g., 12V, 24V) relevant to your operation.
- Pressure Ratings: Assess the maximum pressure your system will encounter to avoid selecting a solenoid that cannot withstand operational demands.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest developments in pneumatic solenoid technology. Understanding emerging trends can help you identify new products that may enhance your operations.
- Innovative Features: Look for solenoids with advanced features, such as energy efficiency or enhanced durability, which can provide long-term cost savings.
- Industry Applications: Investigate how other companies in your industry are utilizing pneumatic solenoids to improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure that suppliers meet international quality standards (like ISO certifications) and understand local regulations that may impact product performance.
- Customer Support: Assess the level of customer service provided, including technical support and warranty terms, which can be vital for troubleshooting and ongoing maintenance.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples to test their performance in your specific application. This step is vital to ensure the solenoids meet your operational requirements.
- Performance Testing: Conduct tests to evaluate the solenoid’s response time, durability, and reliability under real-world conditions.
- Compatibility Checks: Verify that the solenoid integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, including electrical connections and pneumatic configurations.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and tested the products, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, and payment conditions.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
- Volume Discounts: If you anticipate large orders, negotiate bulk pricing to maximize savings.
- Lead Times: Clarify lead times to ensure that the supplier can meet your project timelines without delays.
Step 6: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a strong relationship with your supplier can yield benefits beyond the initial transaction. A reliable supplier can provide insights into product updates and support future procurement needs.
- Feedback Loop: Share feedback on product performance and service quality to foster continuous improvement in the supplier’s offerings.
- Partnership Opportunities: Explore opportunities for collaborative projects or joint ventures, which can enhance both parties’ operational capabilities.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively source pneumatic solenoids that align with their technical requirements and operational goals, ensuring a successful and efficient procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic solenoids Sourcing
To effectively navigate the procurement of pneumatic solenoids, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved in their sourcing, as well as the pricing influencers that can impact your final expenditure. This analysis aims to provide international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with actionable insights for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Pneumatic Solenoid Manufacturing?
-
Materials: The raw materials for pneumatic solenoids typically include metals such as aluminum and brass, along with plastic components for housings and seals. The choice of materials significantly impacts cost; for instance, using high-grade materials can enhance durability but increase the price.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled technicians involved in assembly, testing, and quality assurance. Regions with lower labor costs may present more favorable pricing, but this must be balanced against potential quality issues.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative costs. Manufacturers often allocate these overheads across their product lines, affecting the overall pricing structure of pneumatic solenoids.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized solenoid designs can be a substantial upfront cost. Buyers should inquire about tooling fees, especially for unique specifications that deviate from standard models.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that pneumatic solenoids meet industry standards. While this adds to the cost, it is a crucial investment for ensuring reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on distance, mode of transport, and volume. Understanding the logistics involved can help in anticipating additional costs, particularly for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup to cover their costs and profit margins. This can vary widely depending on the supplier’s market positioning and competition.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Pneumatic Solenoid Costs?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts, significantly reducing per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs to optimize cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific features (like certifications for hazardous environments) can increase costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and compliance with industry certifications (ISO, CE) can drive up costs. While these are important for operational reliability, they should align with the buyer’s application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (like FOB, CIF) is essential. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, which can influence the overall cost structure.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Leverage Negotiation: Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their requirements and market prices. Gathering multiple quotes can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than simply looking at purchase prices, consider the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs. This holistic view can justify higher upfront costs for more reliable solenoids.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties can affect international purchases. Buyers from regions like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia should factor these into their budget when sourcing from global suppliers.
-
Request for Prototypes or Samples: Before committing to larger orders, requesting samples can help assess quality and suitability, potentially avoiding costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers of pneumatic solenoids is crucial for international B2B buyers. By strategically analyzing each component and engaging in informed negotiations, buyers can enhance their procurement process, ensuring they achieve both quality and value. While the indicative prices provided in this guide serve as a benchmark, actual costs may vary based on specific supplier agreements and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pneumatic solenoids With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Pneumatic Solenoids
In the realm of industrial automation and control systems, pneumatic solenoids are widely utilized for regulating airflow and facilitating machine operations. However, various alternative technologies can achieve similar outcomes, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations while balancing performance, cost, and reliability.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Pneumatic Solenoids | Electric Actuators | Hydraulic Actuators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and rapid response | High torque and continuous motion | Exceptional power and force |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront costs | High cost due to complex systems |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration into systems | Requires electrical infrastructure | Complex installation and setup |
| Maintenance | Relatively low maintenance | Moderate maintenance requirements | High maintenance due to fluid issues |
| Best Use Case | Light to medium-duty applications | Heavy machinery and robotics | Heavy-duty applications, such as construction |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making them a powerful alternative to pneumatic solenoids. They offer high torque and continuous motion capabilities, making them suitable for applications requiring precise control. However, their initial costs can be significantly higher than pneumatic systems. Additionally, they necessitate an electrical infrastructure, which can complicate installation. While electric actuators require moderate maintenance, their longevity and efficiency can offset the higher upfront costs, especially in heavy machinery or robotic applications.
Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators use pressurized fluid to produce motion and are renowned for their exceptional power and force generation capabilities. They excel in heavy-duty applications, such as construction and manufacturing, where high force is necessary. However, the complexity of hydraulic systems often results in higher initial costs and maintenance demands. Issues related to fluid leaks can also arise, requiring diligent upkeep. Despite these challenges, hydraulic actuators are ideal for scenarios where immense power and reliability are paramount, making them a compelling option for large-scale operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between pneumatic solenoids and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific application requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Pneumatic solenoids provide an excellent balance of performance and cost-effectiveness for light to medium-duty applications. In contrast, electric actuators are better suited for tasks demanding precision and continuous motion, albeit at a higher cost. Hydraulic actuators should be reserved for applications where substantial force is needed. By assessing these factors carefully, businesses can select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their operational goals and resource availability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic solenoids
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Pneumatic Solenoids?
Understanding the technical specifications of pneumatic solenoids is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations. Here are key properties that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
The material used in pneumatic solenoids, such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic, affects durability, corrosion resistance, and performance under various environmental conditions. For industries like automotive or food processing, selecting the right material is vital to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards.
2. Operating Pressure
Operating pressure defines the maximum pressure the solenoid can handle effectively. This specification is critical for applications in heavy machinery or chemical processing where high-pressure systems are common. Understanding the operating pressure ensures that the solenoid will function reliably within the required parameters, preventing failures and downtime.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
3. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the electrical input required for the solenoid to operate. Common ratings include 12V DC, 24V DC, and 110V AC. Selecting the correct voltage is essential for compatibility with existing systems and helps to prevent electrical failures that can lead to costly repairs.
4. Flow Rate
The flow rate, typically measured in liters per minute (LPM) or cubic feet per minute (CFM), determines how much air can pass through the solenoid in a given time. This metric is critical for applications requiring precise control over air supply, such as in automated manufacturing processes. An inadequate flow rate can lead to inefficiencies and affect the overall performance of pneumatic systems.
5. Response Time
Response time measures how quickly a solenoid can open or close. This specification is particularly important in applications where rapid actuation is needed, such as in robotics or high-speed assembly lines. A shorter response time can enhance productivity and improve the reliability of automated systems.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in the Pneumatic Solenoid Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source high-quality pneumatic solenoids that meet specific standards and specifications.
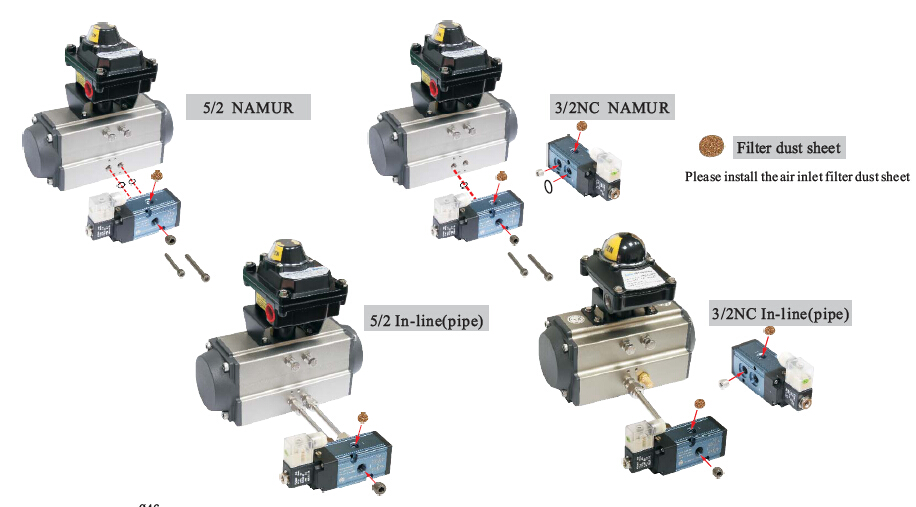
Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases more effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, utilizing RFQs can facilitate competitive pricing and ensure that they receive the best value for their pneumatic solenoid purchases.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery terms, which can significantly impact total costs.
5. Actuation Type
Actuation type refers to how a solenoid is activated, which can be either electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. Knowing the actuation type is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and for determining the appropriate control methods for specific applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting pneumatic solenoids, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pneumatic solenoids Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Pneumatic Solenoids Market?
The global pneumatic solenoids market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and HVAC systems. As businesses seek to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs, pneumatic solenoids are becoming integral to automated processes. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 are influencing sourcing trends, enabling real-time data collection and process optimization. This technological shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where industrial automation is on the rise.
Additionally, manufacturers are focusing on enhancing product performance and reliability. There is a growing trend towards customizable pneumatic solenoids that meet specific application requirements, allowing businesses to tailor solutions to their unique operational needs. For buyers in the Middle East, where industries are rapidly evolving, the availability of such customizable options can lead to significant competitive advantages. Moreover, the demand for energy-efficient products is shaping the market dynamics, prompting manufacturers to invest in research and development for more sustainable solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Pneumatic Solenoids?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the pneumatic solenoids sector, as companies increasingly recognize their environmental responsibilities. The production of pneumatic solenoids can have a notable environmental impact, particularly regarding energy consumption and material waste. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing carbon footprints.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing standards, ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly and that labor practices are fair. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. For international buyers, especially in regions with stringent regulations, partnering with certified suppliers not only enhances brand reputation but also mitigates risks associated with non-compliance.
What Is the Evolution of Pneumatic Solenoids in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of pneumatic solenoids dates back to the early 20th century when their initial designs were primarily mechanical. As industries expanded and the need for automation grew, the integration of electrical components transformed pneumatic solenoids into sophisticated electromechanical devices. This evolution allowed for precise control of airflow, essential for modern applications ranging from industrial machinery to medical equipment.
In recent years, advancements in materials science and digital technology have further enhanced the functionality and reliability of pneumatic solenoids. The introduction of smart solenoid valves equipped with IoT capabilities marks a significant leap forward, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This evolution not only underscores the importance of pneumatic solenoids in contemporary industrial processes but also highlights the need for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements to make informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic solenoids
-
How do I select the right pneumatic solenoid for my application?
Choosing the right pneumatic solenoid involves understanding your specific application requirements, including the type of media (air or gas), pressure specifications, and flow rates. Assess whether you need a normally closed or normally open valve, and consider the size and port configuration that best fits your system. It’s also essential to evaluate the voltage requirements (DC or AC) and compatibility with your existing machinery. Consulting with suppliers for technical specifications and performance data can further aid in making an informed decision. -
What is the best pneumatic solenoid valve for industrial automation?
The best pneumatic solenoid valve for industrial automation typically features a reliable, high-response design capable of handling varying pressure and flow rates. Look for valves with quick actuation times and durable materials that can withstand harsh environments. Brands that offer customizable options may also be advantageous for tailored applications. Specific models with features like built-in safety mechanisms and low power consumption can enhance operational efficiency and reliability in automation systems. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic solenoids?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic solenoids can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 10 to 100 units. Factors influencing MOQs include the manufacturer’s production capacity, the complexity of the solenoid design, and the customization options required. For international buyers, discussing MOQs directly with suppliers can sometimes lead to flexibility, especially for first-time orders or long-term partnerships. Always clarify these details during the negotiation phase to avoid surprises. -
How can I ensure the quality of pneumatic solenoids from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing pneumatic solenoids internationally, vet suppliers thoroughly. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 to confirm their adherence to quality management standards. Ask for product samples to assess material and performance firsthand. Additionally, consider suppliers with a solid reputation and positive customer reviews in your industry. Implementing a quality assurance process, including third-party inspections, can further safeguard against subpar products. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing pneumatic solenoids internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of pneumatic solenoids can vary widely. Common terms include advance payment, partial payment upon order, and balance payment before shipping. Some suppliers may offer net terms, allowing payment within a specified period post-delivery. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, to mitigate financial risks. Establishing a clear understanding of payment conditions upfront can foster a smoother transaction. -
What shipping options are available for pneumatic solenoids, and how do they affect delivery times?
Shipping options for pneumatic solenoids typically include air freight, sea freight, and courier services. Air freight is faster but often more expensive, making it suitable for urgent orders. Sea freight is more economical for larger shipments but may take longer, affecting overall delivery times. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify shipping methods and estimated delivery times to align with your project timelines. Additionally, consider logistics partners with experience in international shipping to ensure smooth customs clearance. -
Can pneumatic solenoids be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for pneumatic solenoids to meet specific application needs. Customizations may include changes in size, port configuration, voltage specifications, and material selection based on environmental conditions. When seeking customized solutions, communicate your requirements clearly and inquire about lead times and cost implications. Collaborating closely with suppliers can yield tailored products that enhance the efficiency and performance of your systems. -
What are common applications of pneumatic solenoids in different industries?
Pneumatic solenoids are widely used across various industries, including automotive for air braking systems, manufacturing for automated assembly lines, and HVAC systems for airflow control. They play a crucial role in controlling the direction and flow of compressed air or gases, facilitating efficient operation of machinery and equipment. Understanding these applications can help B2B buyers identify the right solenoid valves that align with their operational needs and industry standards.
Top 6 Pneumatic Solenoids Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. US Solid – Pneumatic Valves
Domain: ussolid.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, US Solid – Pneumatic Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Pneumatic Plus – Solenoid Valves
Domain: pneumaticplus.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valves: G1/8 – 1/8″ NPT (18mm Body) – MSRP: $46.50; M5/10-32 UNF (15mm Body) – MSRP: $46.13; G1/8 – 1/8″ NPT (23mm Body) – MSRP: $46.88; G1/4 – 1/4″ NPT (26mm Body) – MSRP: $46.88; G3/8 – 3/8″ NPT (32mm Body) – MSRP: $67.13.
4. AutomationDirect – Directional Control Solenoid Valves
Domain: automationdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, AutomationDirect – Directional Control Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. AI Motion – Air Solenoid Valves
Domain: ai.motion.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Choosing the right air solenoid valve for pneumatic systems involves understanding the differences between single and double solenoid valves. Single solenoid valves operate with a single coil, allowing the valve to shift and return to its original position automatically when power is removed. Double solenoid valves require energizing a second coil to return to the original position, providing more…
6. VEX Robotics – SMC SY3140-6LZ Single Solenoid Valve
Domain: vexrobotics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”SMC SY3140-6LZ Single Solenoid Valve (use with Base Mount)”,”sku”:”217-3233″,”price”:”$32.99″,”weight”:”0.11 lb”},{“name”:”SMC SY3240-6LZ Double Solenoid Valve (use with Base Mount)”,”sku”:”217-2948″,”price”:”$45.99″,”weight”:”0.151 lb”},{“name”:”SMC SS5Y3-41-03-N7T 3 Station Base Mount”,”sku”:”217-2951″,”price”:”$26.99″,”weight”:”0.309 lb”},{“name”:”SMC SS5Y3-41-04-N7T 4 Sta…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic solenoids
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Pneumatic Solenoids?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of pneumatic solenoids is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring the reliability of your pneumatic systems. By understanding the diverse range of solenoid valve configurations and their specific applications across industries, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Prioritizing suppliers who offer high-quality products and robust customer support is crucial for long-term success.
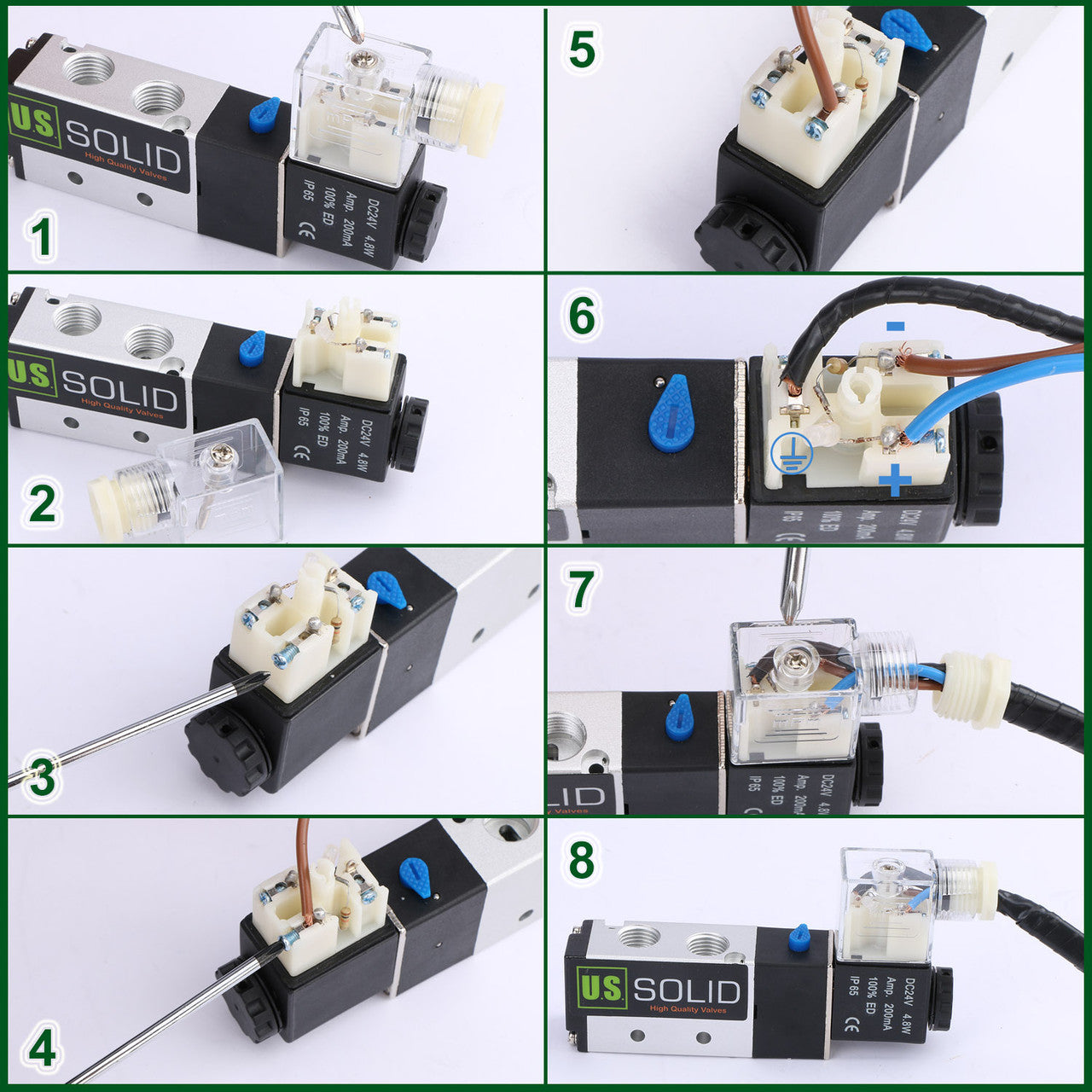
Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoids
How Can International Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing for Competitive Advantage?
For international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of pneumatic solenoids presents an opportunity to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce costs. Engaging with manufacturers who provide customizable solutions can facilitate tailored applications that meet unique market demands. Additionally, fostering relationships with local distributors can streamline logistics and reduce lead times.
What Is the Future Outlook for Pneumatic Solenoid Sourcing?
Looking ahead, the demand for pneumatic solenoids is expected to grow, driven by advancements in automation and industrial processes. Companies should stay abreast of emerging technologies and market trends to leverage these developments effectively. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing and integrating innovative solutions, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and partner with reputable suppliers to secure a competitive edge in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.