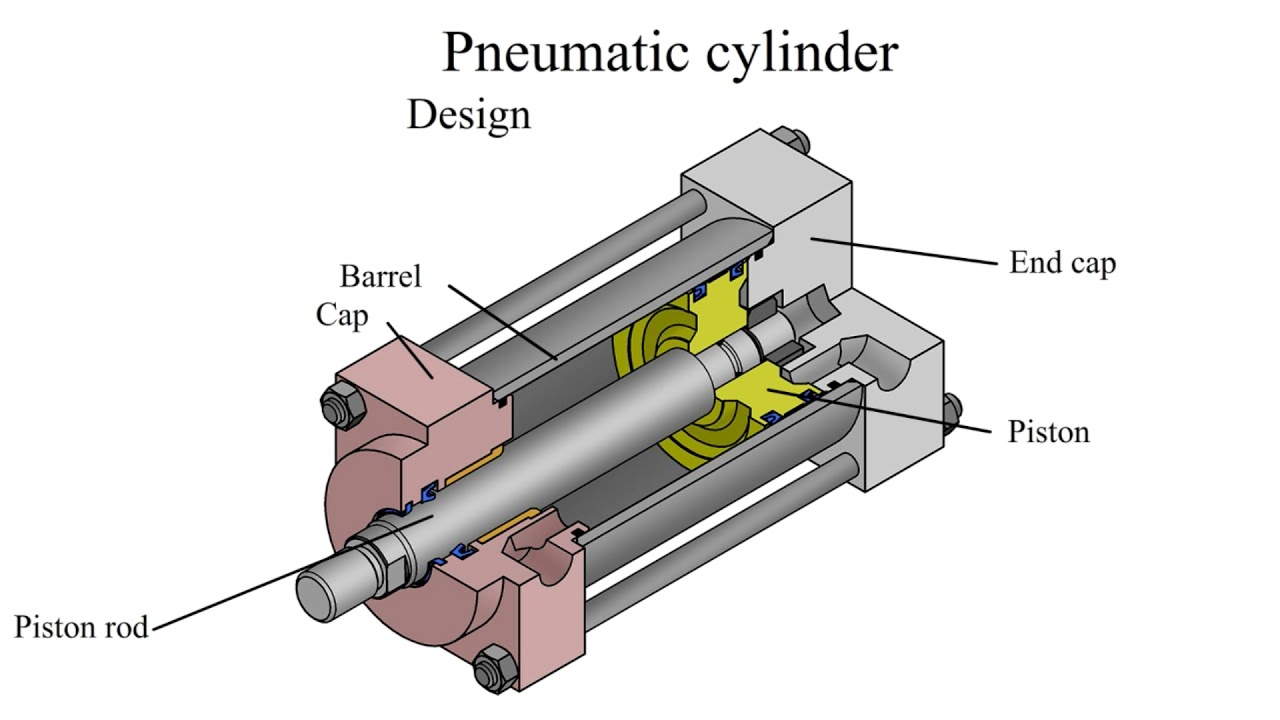
The Definitive Guide to Parts Of A Pneumatic Cylinder: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of a pneumatic cylinder
Navigating the intricate landscape of sourcing parts for pneumatic cylinders can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various components, such as solenoid valves, rods, and seals, is essential for maintaining operational efficiency in manufacturing and automation processes. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of pneumatic cylinder parts, including their types, applications, and the critical role they play in various industrial sectors.
By delving into the nuances of supplier vetting, pricing considerations, and maintenance tips, this resource empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific operational needs. Whether you are in Vietnam, Brazil, or elsewhere, our insights will help you navigate supplier selection, ensuring that you choose reliable sources that can provide quality parts while also meeting your logistical requirements. Furthermore, the guide addresses common pitfalls and best practices in maintaining pneumatic systems, equipping you with actionable strategies to enhance performance and prolong equipment lifespan.
In an era where efficiency and reliability are paramount, having access to a well-rounded understanding of pneumatic cylinder parts is not just an advantage; it is a necessity for sustaining competitive edge in the global market.
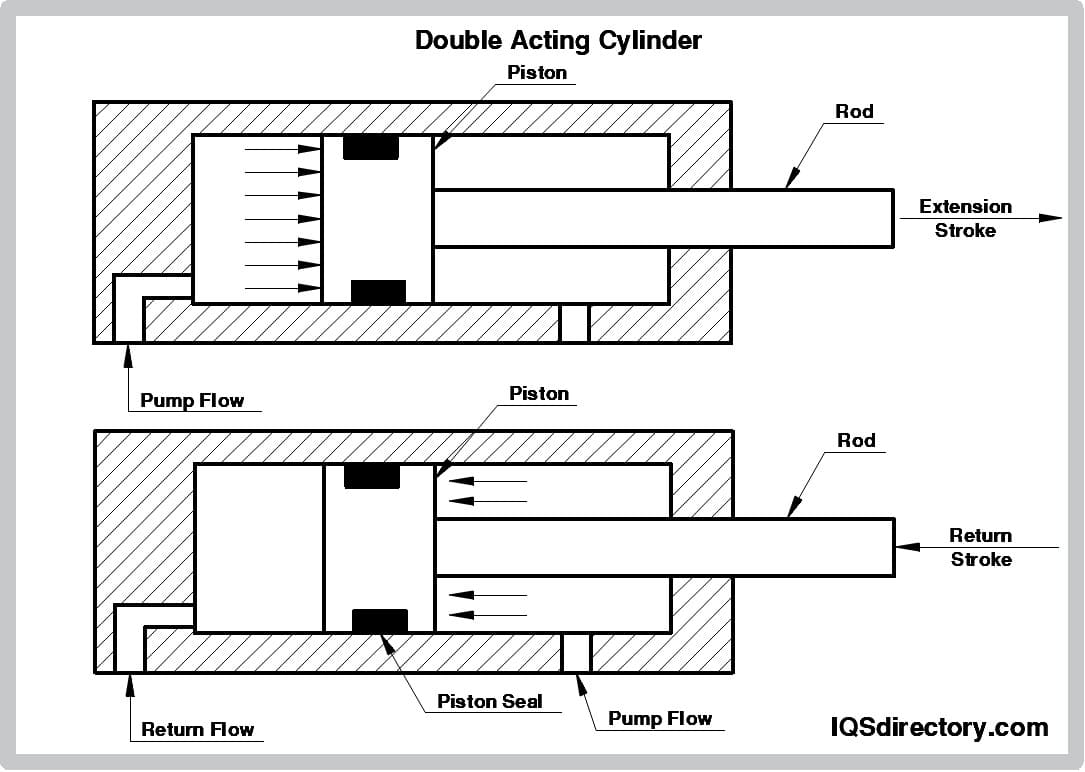
Understanding parts of a pneumatic cylinder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Rod | Transmits force from the piston to the load. | Material handling, assembly lines | Pros: High strength, customizable lengths. Cons: Prone to bending if misaligned. |
| Seals | Prevents air leakage and ensures efficient operation. | Pneumatic systems in manufacturing | Pros: Essential for efficiency, various materials available. Cons: Wear over time, requiring regular replacement. |
| Cushions | Dampens the impact at the end of the stroke. | Robotics, packaging machinery | Pros: Reduces noise and wear, enhances lifespan. Cons: May add complexity to design. |
| End Caps | Secures the cylinder and houses the piston. | Automated machinery, conveyor systems | Pros: Provides structural integrity, easy to replace. Cons: May require specialized tools for installation. |
| Solenoid Valves | Controls airflow and pressure in the system. | Automation, process control | Pros: Quick response time, precise control. Cons: Electrical components may fail and require maintenance. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Piston Rods in Pneumatic Cylinders?
Piston rods are crucial components that connect the piston within a pneumatic cylinder to the external load. Typically made from high-strength materials, they can be customized in length and diameter to meet specific application needs. Buyers should consider the rod’s resistance to bending and buckling, as misalignment can lead to premature wear. Selecting a properly hardened and coated piston rod can significantly enhance durability and operational efficiency.
How Do Seals Impact the Efficiency of Pneumatic Systems?
Seals are vital for preventing air leaks within pneumatic cylinders, ensuring that the system operates at maximum efficiency. Different materials, such as polyurethane or rubber, can be chosen based on the application’s temperature and pressure requirements. Regular inspection and replacement of seals are necessary to maintain performance, as worn seals can lead to decreased power and increased energy costs. Buyers should prioritize seals that are compatible with their specific operating conditions to minimize downtime.
What Role Do Cushions Play in Enhancing System Performance?
Cushions are designed to absorb the energy of the piston as it reaches the end of its stroke, thereby reducing noise and mechanical wear. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications involving high-speed operations, such as robotics and packaging machinery. While cushions can prolong the lifespan of pneumatic cylinders, they may also complicate the design and require more intricate installation. Buyers should evaluate the need for cushions based on the operational speed and load characteristics of their machinery.
Why Are End Caps Important for Structural Integrity?
End caps serve the dual purpose of securing the cylinder and housing the piston, contributing to the overall structural integrity of pneumatic systems. They can be made from various materials, including aluminum and steel, depending on the application’s demands. End caps are generally easy to replace; however, installation may require specialized tools. Buyers should ensure that the end caps are compatible with their specific cylinder design to avoid issues during maintenance or replacement.
How Do Solenoid Valves Facilitate Control in Pneumatic Systems?
Solenoid valves are essential for controlling the airflow and pressure within pneumatic systems, allowing for precise actuation of various components. Their quick response time makes them ideal for automation and process control applications. While they offer significant advantages, solenoid valves are also susceptible to electrical failures, necessitating regular maintenance. Buyers should consider the valve’s specifications, including voltage and flow rate, to ensure compatibility with their pneumatic systems.
Key Industrial Applications of parts of a pneumatic cylinder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of a pneumatic cylinder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated Assembly Lines | Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs | Quality assurance, compatibility with existing machinery |
| Packaging | Material Handling and Carton Erecting | Enhanced speed in packaging processes | Durability, maintenance requirements, and service availability |
| Automotive | Component Placement and Robotic Arm Operation | Precision in assembly and reduced production downtime | Customization options, reliability, and after-sales support |
| Food and Beverage | Filling and Capping Machines | Improved hygiene and operational efficiency | Compliance with food safety standards, ease of cleaning |
| Construction | Heavy Equipment Actuation | Increased lifting capabilities and reduced manual labor | Load specifications, environmental resistance, and warranty |
How Are Pneumatic Cylinder Parts Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, pneumatic cylinder parts are crucial for automated assembly lines, where they facilitate the movement and placement of components. These systems enhance operational efficiency by reducing manual labor and minimizing human error. International buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality components to ensure compatibility with existing machinery and to maintain production quality. Additionally, understanding the local regulations and standards in manufacturing is essential for compliance and operational success.
What Role Do Pneumatic Cylinders Play in Packaging?
In packaging, pneumatic cylinders are used for material handling and carton erecting. They streamline processes by providing rapid and precise movements, which significantly enhance the speed and efficiency of packaging operations. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable and reliable pneumatic parts is critical, as these components must withstand high-frequency cycles. Buyers should also consider the maintenance requirements and availability of local service support to ensure uninterrupted operations.
How Are Pneumatic Cylinders Beneficial in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry employs pneumatic cylinder parts for tasks such as component placement and robotic arm operations. These applications require high precision and reliability to minimize production downtime and ensure quality assembly. B2B buyers in the automotive sector should focus on customization options that meet specific operational needs, as well as the reliability of suppliers to provide ongoing support and parts replacement.
How Do Pneumatic Cylinder Parts Improve Operations in Food and Beverage?
In the food and beverage sector, pneumatic cylinder parts are essential for operations like filling and capping machines. These components ensure that processes are not only efficient but also adhere to strict hygiene standards. When sourcing parts, international buyers must verify compliance with food safety regulations and consider the ease of cleaning and maintenance. This focus on hygiene and efficiency can significantly enhance operational productivity.
What Are the Advantages of Pneumatic Cylinders in Construction?
In construction, pneumatic cylinders are utilized for heavy equipment actuation, allowing for increased lifting capabilities and reduced manual labor. This automation leads to improved safety and efficiency on job sites. Buyers from regions with challenging environments should consider sourcing robust and environmentally resistant components that can withstand harsh conditions. Warranty and after-sales support are also critical factors to ensure long-term operational reliability.
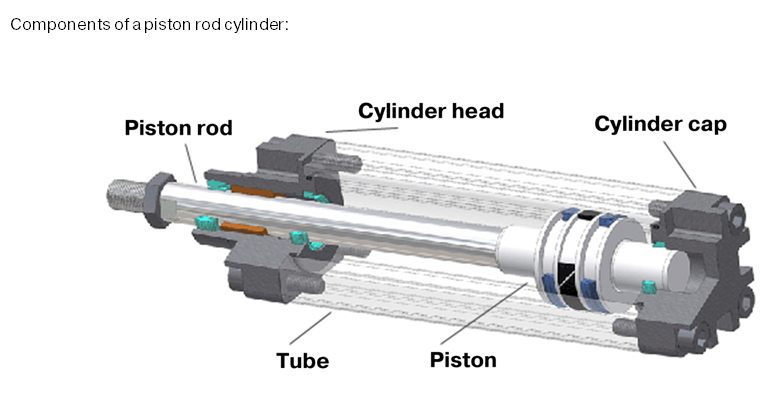
Illustrative image related to parts of a pneumatic cylinder
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of a pneumatic cylinder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Frequent Air Leaks Compromise System Efficiency
The Problem: One of the most common issues faced by B2B buyers of pneumatic cylinder parts is air leaks, which can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of pneumatic systems. These leaks not only lead to wasted energy but also result in increased operational costs and potential downtime. Buyers may struggle to identify the source of the leaks, which could stem from worn-out seals or improper installation. This challenge is particularly acute in high-demand environments, where any loss of pressure can disrupt production schedules and lead to financial losses.
The Solution: To effectively combat air leaks, B2B buyers should prioritize regular maintenance and inspection of pneumatic components. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule can help identify worn seals before they become problematic. When sourcing replacement parts, opt for high-quality seals designed for specific applications to ensure a tight fit and durability. Additionally, consider investing in advanced leak detection technologies, such as ultrasonic leak detectors, which can pinpoint even minor leaks in complex systems. By addressing leaks promptly and using reliable parts, companies can enhance system efficiency and reduce costs associated with lost air pressure.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Cylinder Performance Affects Production
The Problem: Many companies experience inconsistent performance from their pneumatic cylinders, leading to erratic motion and unpredictable cycle times. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, such as improper cylinder sizing, inadequate lubrication, or fluctuating air pressure. For B2B buyers, these performance issues can hinder production lines, resulting in delays and decreased output quality. The frustration of troubleshooting these problems can lead to increased operational costs and a loss of competitive advantage.
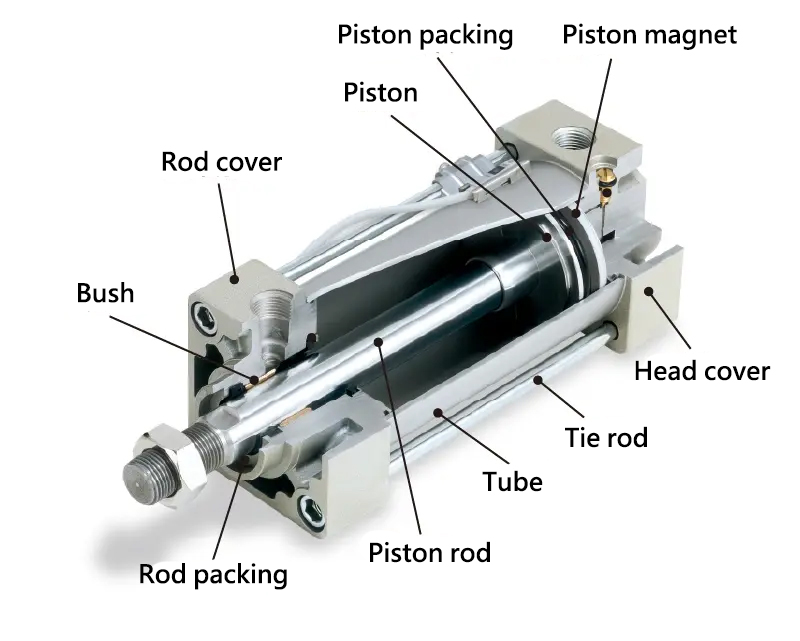
Illustrative image related to parts of a pneumatic cylinder
The Solution: To ensure consistent cylinder performance, buyers should start by accurately sizing their pneumatic cylinders based on the specific application requirements. This involves calculating the required force, speed, and stroke length to match the operational needs. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the air service unit (FRL unit) is crucial, as it regulates air pressure and ensures proper lubrication. Additionally, integrating sensors to monitor cylinder performance in real-time can provide valuable data, allowing for timely adjustments and maintenance. By taking these steps, companies can achieve smoother operations and improve overall productivity.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Replacement Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of sourcing reliable replacement parts for pneumatic cylinders, especially in regions with limited access to quality suppliers. The risk of purchasing subpar components can lead to premature failures, increased maintenance costs, and ultimately, equipment downtime. In markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where supply chain disruptions can be common, finding dependable sources for pneumatic cylinder parts becomes a critical concern.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of sourcing reliable replacement parts, B2B buyers should cultivate relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in pneumatic components. Conduct thorough research and seek suppliers with strong industry reputations and positive customer reviews. Additionally, consider establishing partnerships with local distributors who can provide timely access to parts while minimizing shipping delays. Implementing a vendor assessment program can help ensure that the quality of parts meets the necessary standards. Furthermore, buyers should keep a well-managed inventory of critical spare parts to mitigate the risk of unexpected breakdowns. By developing strategic sourcing practices, companies can enhance their operational resilience and reduce the impact of supply chain challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of a pneumatic cylinder
When selecting materials for parts of a pneumatic cylinder, it is essential to consider various factors such as performance characteristics, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in pneumatic cylinder components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Aluminum is widely used in pneumatic cylinder construction due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels. The material’s strength-to-weight ratio makes it suitable for applications where reducing weight is crucial.
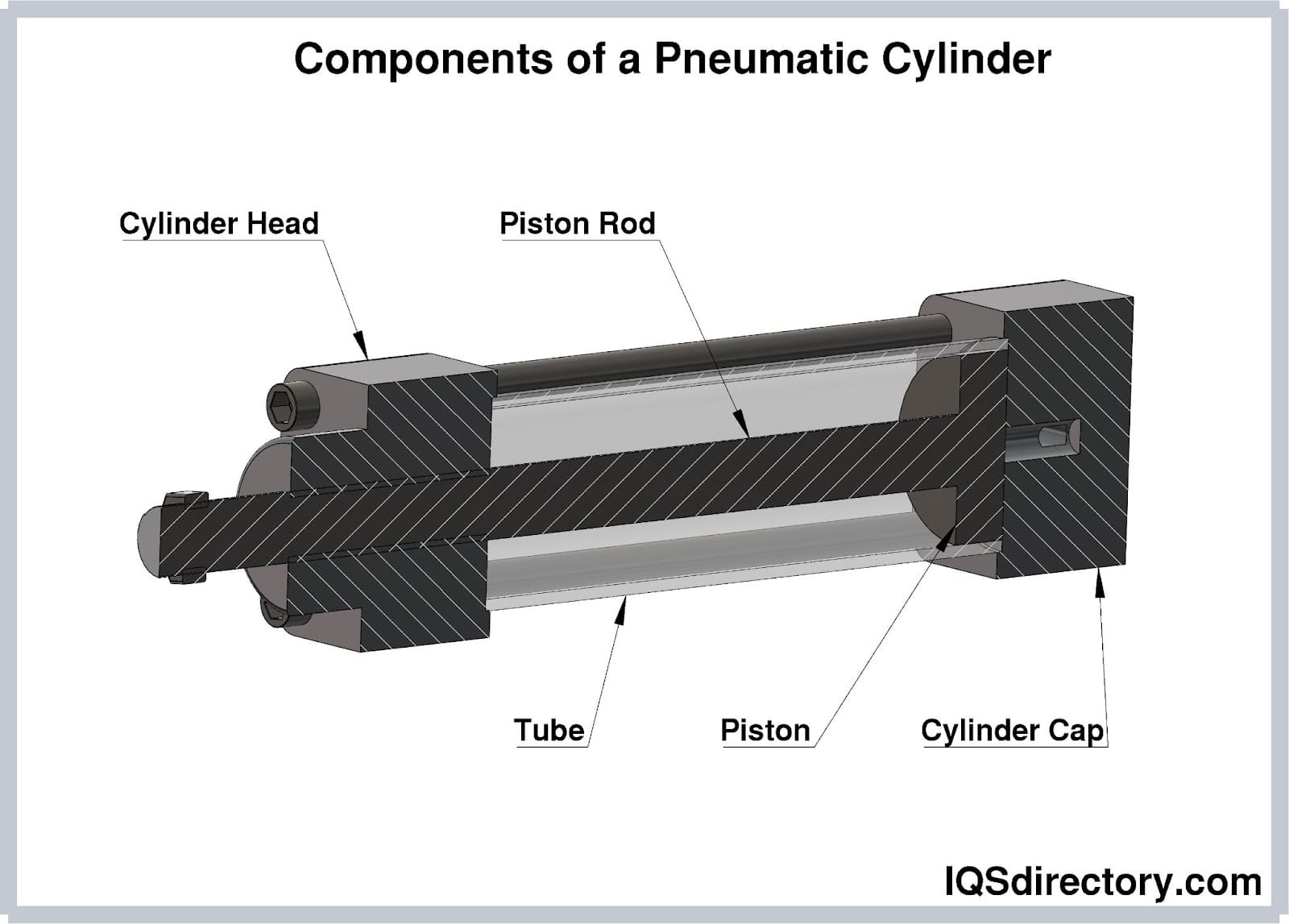
Illustrative image related to parts of a pneumatic cylinder
Pros & Cons: Aluminum offers durability and ease of machining, which can lower manufacturing complexity. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications. Additionally, while it resists corrosion well, it may require anodizing for enhanced protection in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and non-corrosive gases. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals, which could lead to degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or ISO. The availability of aluminum may vary, impacting lead times and costs.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Steel is another common choice for pneumatic cylinder parts, particularly for components that require high strength and durability. It has a higher temperature rating, typically up to 300°C, and can handle higher pressures compared to aluminum.
Pros & Cons: Steel is generally more cost-effective and offers superior strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it is heavier, which can be a disadvantage in weight-sensitive applications. Moreover, steel is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including air and hydraulic fluids. However, its susceptibility to rust in humid environments can limit its use without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for corrosion-resistant coatings, especially in humid regions like the Middle East. Compliance with standards such as DIN or JIS is also crucial for ensuring product quality.
What are the Benefits of Using Composite Materials in Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Composite materials, often a combination of polymers and fibers, are increasingly used in pneumatic cylinder applications due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can be tailored for specific applications, reducing manufacturing complexity. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for applications requiring resistance to chemicals and moisture. However, their performance can be affected by extreme temperatures and pressures.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should verify that composite materials meet local standards and regulations. The availability of specific composites may vary by region, impacting sourcing decisions.
How Do Elastomers Contribute to Pneumatic Cylinder Functionality?
Elastomers, such as rubber and silicone, are critical for seals and gaskets in pneumatic cylinders. They can typically handle temperatures between -40°C and 120°C and provide excellent flexibility and sealing capabilities.
Pros & Cons: Elastomers are cost-effective and provide excellent sealing performance, reducing the risk of air leaks. However, they can degrade over time, especially when exposed to oils or extreme temperatures, necessitating regular replacements.
Impact on Application: Elastomers are compatible with air and many hydraulic fluids but may not withstand aggressive chemicals. Their performance is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of pneumatic systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that elastomers comply with relevant standards and are suitable for the specific media used in their applications. Availability and sourcing can vary significantly across regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pneumatic Cylinder Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of a pneumatic cylinder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Cylinder bodies and end caps | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, limited high-pressure use | Medium |
| Steel | Rods and heavy-duty components | High strength and cost-effective | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Composite | Lightweight components in specialized applications | Tailored properties and lightweight | Higher cost, limited high-pressure use | High |
| Elastomer | Seals and gaskets | Excellent sealing performance | Degrades over time | Low |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of a pneumatic cylinder
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
The manufacturing process for pneumatic cylinder parts is intricate and involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage involves selecting high-quality materials suitable for the demanding operational conditions of pneumatic cylinders. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and brass, known for their strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. The material is then cut to size, and any necessary treatments—like heat treatment for strength enhancement—are applied. Ensuring the right material selection is crucial, as it directly impacts the longevity and performance of the cylinder parts.
How Are Pneumatic Cylinder Parts Formed?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes processes such as machining, extrusion, and forging. Machining is often employed for precision parts, where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are utilized to achieve exact dimensions. For components that require a uniform cross-section, extrusion might be the method of choice, particularly for aluminum components. Forging is used for parts that need to withstand high stress, enhancing their strength and fatigue resistance.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Following the forming stage, assembly is conducted. This involves fitting together various components such as the cylinder body, piston, seals, and end caps. Proper alignment and assembly techniques are vital to prevent issues such as air leaks or mechanical failure. Specialized tools may be employed to ensure that all parts fit together securely, and the assembly process must be performed in a clean environment to avoid contamination.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The finishing stage is essential for enhancing the durability and appearance of pneumatic cylinder parts. Techniques such as anodizing, plating, or powder coating are often applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Anodizing, for example, is particularly common for aluminum components, providing a hard, wear-resistant surface. Additionally, surface treatments may include polishing to reduce friction and enhance performance.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Essential for Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of pneumatic cylinder parts, ensuring that every component meets international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For pneumatic cylinder manufacturers, adhering to international standards is critical for ensuring product quality and safety. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, standards such as CE marking in Europe and API specifications in specific industries provide guidelines for safety and performance.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) assesses raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors the manufacturing process, checking for deviations and ensuring that parts are being manufactured correctly. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) is conducted before shipment, where finished products undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet all specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Testing methods for pneumatic cylinder parts can include pressure tests, leak tests, and dimensional inspections. Pressure testing ensures that the components can withstand the operational pressures they will encounter. Leak testing, often conducted using helium or air, checks for any air leaks that could compromise performance. Dimensional inspections utilize tools such as calipers and gauges to verify that all parts conform to specified dimensions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that a supplier adheres to rigorous quality control standards, B2B buyers should engage in thorough supplier verification processes.
What Audit Processes Should Be Considered?
Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should assess the supplier’s adherence to international standards, review their quality management system, and evaluate their inspection and testing protocols. Audits can be performed in person or through third-party services, depending on the buyer’s resources and the complexity of the supplier’s operations.
How Can Buyers Obtain Quality Reports and Certifications?
Buyers should request documentation that outlines the quality assurance processes of their suppliers. This includes quality control reports, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and compliance with industry-specific standards. Reviewing these documents can help buyers understand the supplier’s commitment to quality and their operational capabilities.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Transactions?
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of international quality control is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect the manufacturing and quality assurance processes. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements and consider engaging local representatives or consultants who understand the regional landscape.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for pneumatic cylinder parts involve meticulous attention to detail across multiple stages. By understanding these processes and implementing robust verification practices, B2B buyers can ensure they source high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of a pneumatic cylinder’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, sourcing the right parts for pneumatic cylinders is crucial for operational efficiency and reliability. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process, ensuring that they select high-quality components that meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the first step in the sourcing process. This includes understanding the operational parameters such as size, force, stroke length, and the type of pneumatic cylinder (e.g., single-acting or double-acting) required for your application. Precise specifications help eliminate confusion and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
- Key Considerations:
- Operating pressure range.
- Environmental factors like temperature and humidity.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding reputable suppliers is essential for acquiring high-quality pneumatic cylinder parts. Conduct research to compile a list of potential vendors, focusing on their industry experience, customer reviews, and product range. A well-established supplier can provide insights and support that can enhance your procurement process.
- What to Look For:
- Years in business and expertise in pneumatic systems.
- Customer testimonials and case studies.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier choice, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 ensure that the supplier adheres to quality management practices, which is critical for maintaining consistency and reliability in the parts supplied.
- Certification Types:
- ISO 9001 for quality management.
- CE marking for compliance with European safety standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once potential suppliers are identified, request samples of the pneumatic cylinder parts you are considering. This step is crucial for assessing the quality and compatibility of components with your existing systems. It allows you to physically inspect materials and craftsmanship.
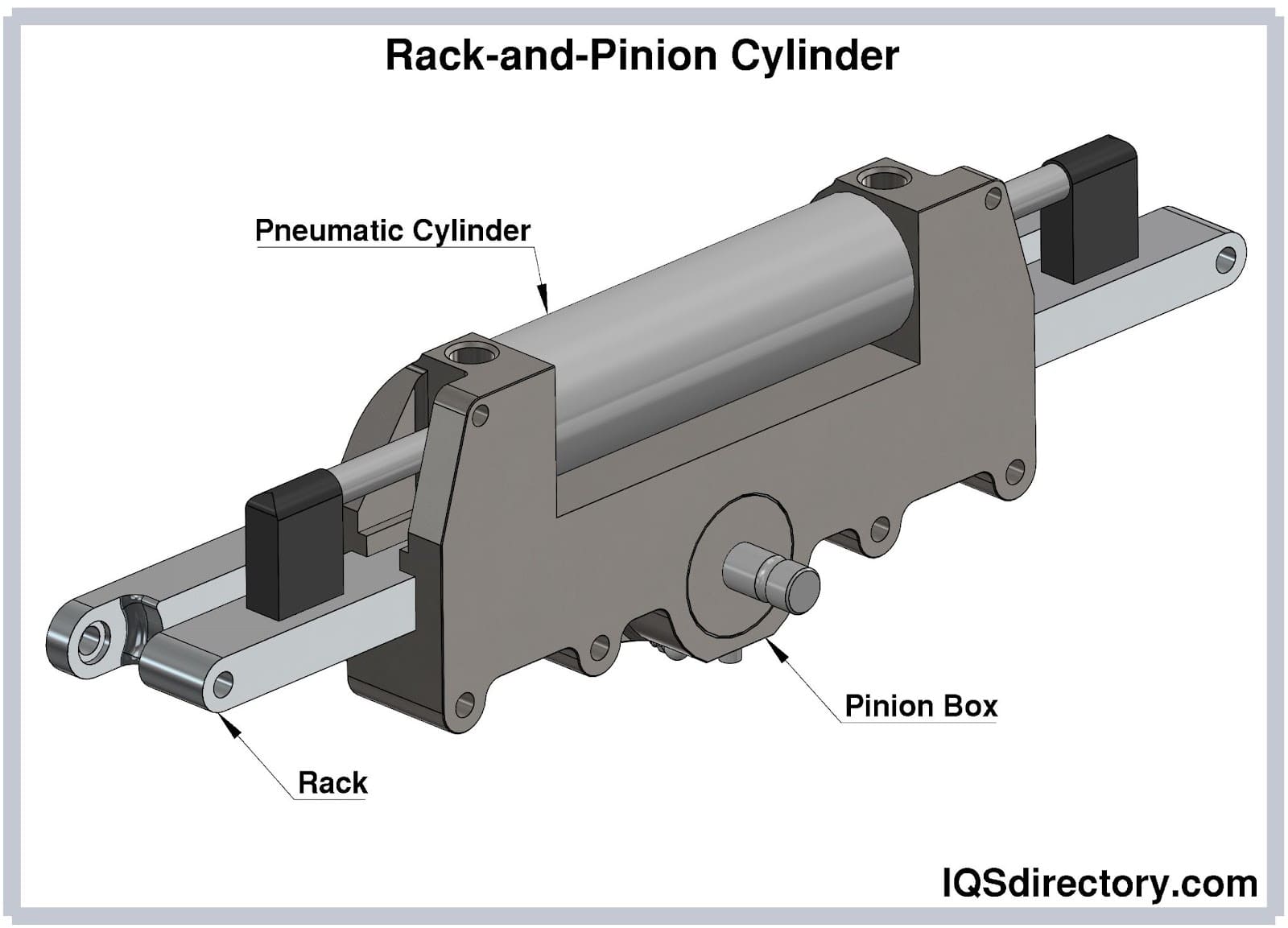
Illustrative image related to parts of a pneumatic cylinder
- Sample Evaluation:
- Check for dimensional accuracy and material quality.
- Test samples under operational conditions if feasible.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing is a critical factor in the procurement process. Compare quotes from multiple suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership, including shipping, taxes, and potential tariffs. Additionally, review payment terms to ensure they align with your budgeting and cash flow requirements.
- Considerations:
- Bulk pricing discounts.
- Flexible payment options to manage cash flow.
Step 6: Understand Warranty and Support Services
A robust warranty and reliable support services are vital for protecting your investment in pneumatic cylinder parts. Inquire about warranty terms and the supplier’s policy on returns and replacements. Strong after-sales support can significantly reduce downtime in case of component failures.
- Support Services:
- Availability of technical assistance.
- Response times for emergency support.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a long-term partnership with your supplier can lead to better pricing, improved service, and access to new technologies. Engage in regular communication to discuss future needs and innovations in pneumatic technology, ensuring that you remain competitive in your industry.
- Long-Term Benefits:
- Consistency in quality and supply.
- Opportunities for collaboration on custom solutions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process, ensuring they secure the right parts for pneumatic cylinders to enhance their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of a pneumatic cylinder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
When sourcing pneumatic cylinder parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used in manufacturing pneumatic cylinder parts significantly influences pricing. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and various polymers. Higher quality materials often lead to higher costs but may offer increased durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region. In developing markets, labor may be less expensive, but skilled labor for precision manufacturing is essential to ensure quality. Buyers should consider the balance between labor cost and the skill level required for high-quality production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can vary based on geographical location and the scale of the manufacturing facility.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can add significant upfront costs to the production of pneumatic cylinder parts. Buyers should evaluate whether the tooling cost is justified based on expected order volumes and part specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures ensures that parts meet required specifications, which can reduce long-term costs related to failures or defects. However, stringent QC processes can also increase initial costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, import duties, and insurance are crucial components in the total cost structure. Logistics can become particularly complex for international transactions, requiring careful consideration of Incoterms to clarify responsibilities.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their profit margins when quoting prices. Understanding the market rates and competitive pricing can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of pneumatic cylinder parts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders typically qualify for volume discounts, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders where possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts will usually incur higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling and production processes. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Parts that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may come at a premium but can ensure compliance with international standards, which is particularly important for buyers from regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and geographic location can all impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is vital for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) define responsibilities for shipping and can affect total landed costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Pneumatic Cylinder Parts Pricing?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing pneumatic cylinder parts, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always approach suppliers with the intent to negotiate. Establishing a good relationship can lead to better pricing and terms, especially for repeat orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial price. Consider factors such as maintenance, potential downtime, and the longevity of parts when making purchasing decisions.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to factors like tariffs, shipping costs, and local demand. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Conduct Market Research: Benchmark pricing with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive rates. This can also give leverage in negotiations.
-
Plan for Contingencies: Always have a backup supplier or alternative sourcing strategy to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependency.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies can empower B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed decisions when sourcing pneumatic cylinder parts. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, so it’s advisable to request indicative prices while keeping the broader economic landscape in mind.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of a pneumatic cylinder With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Pneumatic Cylinder Parts
In the industrial landscape, pneumatic cylinders are widely used for their efficiency in converting compressed air into linear motion. However, there are alternative solutions available that may better suit certain applications. This analysis explores how pneumatic cylinder parts compare against electric actuators and hydraulic cylinders, offering insights that can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Of A Pneumatic Cylinder | Electric Actuators | Hydraulic Cylinders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed operation; effective in repetitive tasks | Excellent precision; suitable for complex motions | Strong force output; ideal for heavy loads |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost; maintenance can add up | Higher upfront investment; lower maintenance costs | Higher cost due to hydraulic fluid and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple setup; requires air supply | Moderate complexity; requires electrical setup | More complex; requires hydraulic lines and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Regular checks for leaks and seal integrity | Minimal maintenance; mostly electrical components | Regular fluid changes and inspections needed |
| Best Use Case | Assembly lines, packaging, and material handling | Robotics, automation, and applications needing fine control | Heavy machinery, construction, and industrial lifting |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, offering high precision and control. They are ideal for applications requiring accurate positioning, such as robotics and automated assembly lines. While they typically come with a higher initial cost than pneumatic systems, they often incur lower maintenance expenses over time due to fewer moving parts and no need for compressed air systems. However, the complexity of installation can be a drawback, especially in environments where existing pneumatic systems are in place.
Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders utilize pressurized fluid to generate high force, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as construction and industrial machinery. They provide significant lifting power and can operate under extreme conditions. However, they come with a higher cost due to the need for hydraulic fluid and more intricate maintenance procedures, which can deter some users. Additionally, hydraulic systems can be more complex to install and maintain compared to pneumatic systems.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between pneumatic cylinder parts and alternative solutions like electric actuators or hydraulic cylinders, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Pneumatic systems are excellent for applications demanding speed and reliability, while electric actuators excel in precision tasks. Hydraulic cylinders are best reserved for scenarios requiring substantial lifting power. Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make choices that enhance productivity and operational efficiency in their respective industries.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of a pneumatic cylinder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of pneumatic cylinder parts is crucial for B2B buyers who need reliable and efficient solutions in their operations. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in pneumatic cylinder parts significantly affects their durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials. Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for various applications. Stainless steel offers enhanced strength and resistance to harsh environments, which is vital for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. Tight tolerances ensure that parts fit together correctly, minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency. In pneumatic cylinders, maintaining proper tolerances is essential for sealing and preventing air leaks, which can lead to system inefficiencies and increased operational costs. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure a pneumatic cylinder can safely handle. It is critical for selecting components that match the operational requirements of a system. Understanding pressure ratings helps prevent failures and ensures safety, especially in high-pressure applications. -
Stroke Length
Stroke length defines the distance the piston travels within the cylinder. This property is vital for determining how much force the cylinder can exert and the range of motion required for specific tasks. Buyers must consider stroke length when designing systems to ensure that pneumatic cylinders meet their operational needs. -
Operating Temperature
The operating temperature range of a pneumatic cylinder is crucial for maintaining functionality in various environments. Different materials and seals can withstand different temperature ranges, affecting performance and longevity. Understanding this property helps prevent premature wear and failure in extreme conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Pneumatic Cylinder Industry?
Navigating the pneumatic cylinder market requires familiarity with certain industry jargon. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of pneumatic cylinders, buyers often seek OEM parts to ensure compatibility and reliability in their systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers as it can affect inventory levels and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while ensuring they can meet demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, helping buyers compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, ensuring clarity in logistics and cost responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for a supplier to deliver goods after an order is placed. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers, as it affects production schedules and inventory management. Knowing the lead times helps in planning and ensures that operations remain uninterrupted. -
Cylindrical Assembly
This term refers to the complete assembly of components that make up a pneumatic cylinder, including the body, piston, seals, and rods. Understanding cylindrical assemblies is essential for buyers looking to ensure compatibility and function in their pneumatic systems.
These technical properties and trade terms provide valuable insights for B2B buyers in the pneumatic cylinder market, enabling them to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of a pneumatic cylinder Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Impacting Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
The pneumatic cylinder parts market is witnessing a dynamic shift driven by several global factors. Increased automation across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and packaging is one of the primary drivers. As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including regions like Vietnam and Brazil) seek to enhance operational efficiency, the demand for reliable pneumatic systems is rising. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as the integration of IoT and smart sensors, are transforming traditional pneumatic systems into more efficient and predictive solutions, enabling real-time monitoring and maintenance.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends include a growing preference for suppliers who can offer comprehensive solutions rather than just individual components. International buyers are increasingly looking for vendors that provide value-added services such as maintenance support, rapid response times for repairs, and customized solutions tailored to specific industrial needs. Additionally, the trend towards digital platforms for sourcing components is gaining traction, enabling buyers to compare products and suppliers more effectively, streamlining procurement processes.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Pneumatic Cylinder Parts?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the pneumatic cylinder parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used is under scrutiny, with many companies striving to minimize their carbon footprint. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing waste during production.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, with an emphasis on transparency within supply chains. Companies are looking for partners who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can provide assurance to buyers that suppliers are committed to sustainability. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, businesses not only improve their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of Pneumatic Cylinder Parts in B2B Procurement?
The evolution of pneumatic cylinder parts dates back to the industrial revolution when the need for efficient mechanical motion became apparent. Initially, pneumatic systems were limited in scope and primarily used in large industrial applications. Over time, advancements in materials and engineering led to the development of more compact, reliable, and versatile pneumatic components.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the introduction of automation and control technologies significantly expanded the use of pneumatic systems across various industries. This shift has transformed pneumatic cylinder parts into essential components for modern manufacturing and automation processes. Today, the focus on efficiency, reliability, and sustainability continues to shape the market, driving innovations that meet the evolving needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of a pneumatic cylinder
-
How do I solve issues with pneumatic cylinder parts that frequently fail?
To address frequent failures in pneumatic cylinder parts, start with a thorough inspection and routine maintenance. Check for air leaks, worn seals, and the condition of the piston rod. Implement regular lubrication and ensure that air filters are clean and functioning. Additionally, consider upgrading to high-quality components designed to withstand your specific operational conditions. If problems persist, consult with your supplier for potential redesigns or enhancements tailored to your application. -
What is the best material for pneumatic cylinder rods?
The best material for pneumatic cylinder rods typically includes case-hardened steel or stainless steel, which provides excellent strength and durability. These materials resist corrosion and wear, ensuring a longer lifespan under high-stress conditions. Additionally, rods should be plated with hard chrome to enhance their resistance to scratches and surface degradation. Selecting the appropriate material based on your operational environment will significantly impact the performance and reliability of your pneumatic system. -
How can I ensure the quality of pneumatic cylinder parts from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing pneumatic cylinder parts internationally, vet suppliers thoroughly. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to evaluate the manufacturing quality and perform thorough inspections upon receipt. Establish clear quality assurance agreements that outline specifications and tolerances, and consider conducting audits or inspections on-site or through third-party services to ensure compliance with your standards. -
What are the typical payment terms for international purchases of pneumatic cylinder parts?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely based on supplier policies and buyer negotiations. Common terms include letters of credit, advance payments, or net 30/60/90 days, depending on the buyer’s creditworthiness and the supplier’s risk assessment. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that balance cash flow needs while providing security for both parties. Ensure that all terms are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings during the transaction. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for pneumatic cylinder parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for pneumatic cylinder parts can differ among suppliers, often ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on the part’s complexity and production costs. For specialized or custom components, MOQs may be higher due to setup and production expenses. When engaging with suppliers, discuss your specific needs and explore options for reducing MOQ if you are testing new parts or entering a new market. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for pneumatic cylinder parts?
Handling logistics for pneumatic cylinder parts involves selecting reliable shipping partners familiar with international regulations and customs procedures. Choose a shipping method that balances cost and delivery speed, such as air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost-effective bulk shipments. Ensure that all documentation, including commercial invoices and packing lists, is complete to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Establish clear communication with your supplier to track shipments and address any potential issues proactively. -
Can pneumatic cylinder parts be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for pneumatic cylinder parts to meet specific application requirements. Customization may include alterations in size, material, or design features based on the operational environment or performance needs. When seeking customized solutions, clearly communicate your specifications and intended use to the supplier. Collaborating on design prototypes may also help ensure that the final product meets your expectations. -
What are common maintenance practices for pneumatic cylinder parts?
Common maintenance practices for pneumatic cylinder parts include regular inspections for wear and tear, checking and replacing seals, and ensuring proper lubrication of moving components. Implement a preventive maintenance schedule that includes cleaning air filters and monitoring system pressure to prevent leaks. Additionally, train staff on proper operational procedures to minimize side loading and other stresses that could lead to premature failure of pneumatic components.
Top 7 Parts Of A Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical systems that produce force using compressed air. Key components include: 1. Bore: Main body housing internal components, precision-machined for air-tightness. 2. Piston: Divides the cylinder chamber, moves with air pressure, and generates force. 3. Piston Rod: Transmits force to external loads, measures stroke length for linear motion. 4. Piston Cushioning: Reduc…
2. Bawalaksana – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: bawalaksana.co
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders, also known as pneumatic actuators, are mechanical devices that convert compressed air into linear motion. They are widely used in industrial automation systems for various applications such as moving production items, cutting raw materials, operating conveyors, and packaging tasks. Key types of pneumatic cylinders include: 1. Linear Pneumatic Cylinder – Generates straight-line…
3. Compact Automation – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: compactautomation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical devices that use compressed air to generate linear force and motion. They are known for their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, making them widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automation, packaging, and automotive. Key types include single-acting and double-acting cylinders, with various designs like round body, square body, compact, r…
4. Yates Industries – Pneumatic Cylinder Parts
Domain: yatesind.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Yates Industries offers a wide variety of pneumatic cylinder parts, including accessories such as brackets, couplers, and pins. They provide cylinder repairs and rebuilds with 24/7 emergency service. Regular maintenance is recommended for maximum reliability, including checking for air leaks, inspecting air filters, lubricating components, and checking seals for damage. Pneumatic cylinders rely on…
5. Trimantec – Cylinder Joints & Pneumatic Solutions
Domain: trimantec.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: This company, Trimantec – Cylinder Joints & Pneumatic Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. CKD – Air Cylinders
Domain: ckd.co.jp
Introduction: Air cylinders are devices that utilize compressed air as a power source, converting compressed air energy into linear or reciprocating motions. Key components include:
– Cylinder tube: Forms the cylinder chamber and guides the piston.
– Cover: Houses supply and exhaust ports, split into head and rod covers.
– Tie Rod: Connects the cylinder tube to the cover.
– Piston: Moves within the cylinder…
7. Omchele – Pneumatic Cylinders & Components
Domain: omchele.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic Cylinders: Standard Cylinders, Mini Cylinders, Guided Cylinders, Compact Cylinders, Rodless Cylinders; Pneumatic Grippers; FRL Units; Air Regulators; Air Filter Regulators; Filter Regulator Lubricators; Compressed Air Filters; Air Lubricators; Pneumatic Valves; Pneumatic Solenoid Valves; Flow Control Valve; Fitting & Tubing & Accessories; Air Hoses; Quick Connectors; Stainless Steel Fitt…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of a pneumatic cylinder
In summary, effective strategic sourcing of pneumatic cylinder parts can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reliability for businesses across various industries. By prioritizing quality components such as seals, rods, and valves, international buyers can minimize downtime and maintenance costs, ultimately leading to improved productivity. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn parts are crucial in extending the lifespan of pneumatic systems, thereby securing a competitive edge in the market.
As the global demand for automation and efficient production processes continues to rise, the importance of sourcing high-quality pneumatic components cannot be overstated. Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage robust supplier relationships and consider local sourcing options to reduce lead times and improve service levels.
Looking ahead, investing in state-of-the-art pneumatic technology and maintenance practices will be essential for businesses aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. We encourage B2B buyers to explore new partnerships and innovations in pneumatic cylinder parts to stay ahead of industry trends and meet the evolving needs of their operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to parts of a pneumatic cylinder
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.