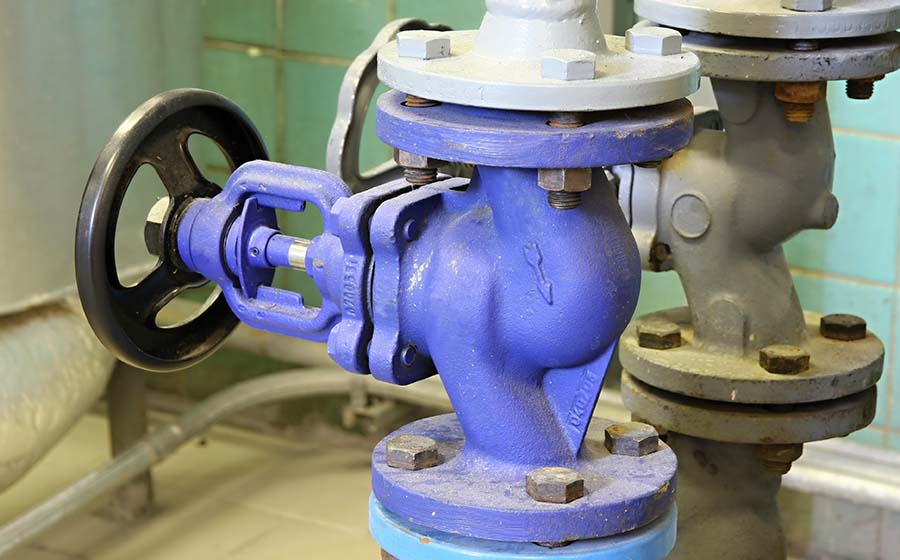
The Definitive Guide to Non Return Valves: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for non return valves
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial operations, sourcing non-return valves that meet specific requirements can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. These critical components play a vital role in ensuring unidirectional fluid flow, preventing backflow, and protecting systems from potential damage. With a myriad of types and applications ranging from water and wastewater management to chemical processing and oil and gas, understanding the nuances of non-return valves is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of non-return valves, their applications across different industries, and best practices for supplier vetting. We address key considerations such as installation requirements, maintenance protocols, and the impact of environmental factors on valve performance. Additionally, we explore cost factors to help you balance quality and budget constraints effectively.
By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Brazil and Vietnam—with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market confidently. Whether you are looking to enhance operational efficiency or mitigate risks associated with fluid systems, this resource will serve as a valuable tool in your procurement strategy, ensuring that you select the right non-return valves for your specific needs.
Understanding non return valves Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swing Check Valve | Hinged disc that swings open and closed with flow direction | Water and wastewater systems, HVAC | Pros: Simple design, low maintenance. Cons: Can be prone to wear over time. |
| Lift Check Valve | Disc or piston lifts to allow flow; reseats to prevent backflow | High-pressure applications, oil and gas | Pros: Effective in high-pressure systems. Cons: More complex design may require more maintenance. |
| Ball Check Valve | Spherical ball moves with flow to open and seals against a seat | Low-pressure systems, irrigation | Pros: Compact size, reliable sealing. Cons: Limited to lower pressure applications. |
| Diaphragm Check Valve | Flexible diaphragm opens with flow and seals to prevent backflow | Chemical processing, food and beverage | Pros: Excellent for corrosive fluids. Cons: More sensitive to pressure fluctuations. |
| Wafer Check Valve | Lightweight and compact, fits between flanges | HVAC systems, industrial processes | Pros: Space-saving design. Cons: May require specific installation methods. |
What Are the Characteristics of Swing Check Valves?
Swing check valves are characterized by their hinged disc, which opens and closes based on the flow direction of the fluid. This type is commonly used in water and wastewater systems as well as HVAC applications. Buyers should consider the valve’s material, as it must withstand the specific fluid characteristics and operating conditions. Additionally, while they are relatively low-maintenance, it’s essential to monitor for wear and tear over time, especially in high-traffic systems.
How Do Lift Check Valves Operate in High-Pressure Applications?
Lift check valves utilize a disc or piston that lifts to allow flow and reseats to block backflow, making them suitable for high-pressure environments such as oil and gas applications. When purchasing, buyers should assess the valve’s cracking pressure and ensure it aligns with their system requirements. Although effective, the complexity of these valves may lead to increased maintenance needs, so understanding the long-term operational costs is crucial.
What Are the Advantages of Ball Check Valves?
Ball check valves feature a spherical ball that moves to allow fluid flow and seals against a seat to prevent backflow, making them ideal for low-pressure systems like irrigation. Their compact design allows for easy installation in tight spaces. Buyers should consider the specific pressure limits and fluid types, as ball check valves are not designed for high-pressure applications. Their reliability and simple mechanics make them a popular choice, though they may not be suitable for all scenarios.
Why Choose Diaphragm Check Valves for Chemical Processing?
Diaphragm check valves are distinguished by their flexible diaphragm, which opens with forward flow and seals closed to prevent reverse flow. This makes them particularly effective in chemical processing and food and beverage applications, where contamination prevention is critical. Buyers should evaluate the diaphragm material to ensure compatibility with the fluid being handled. While they offer excellent sealing capabilities, sensitivity to pressure fluctuations can be a concern, necessitating careful selection based on operational conditions.
What Makes Wafer Check Valves Ideal for Space-Constrained Environments?
Wafer check valves are designed to be lightweight and compact, fitting easily between flanges, which is advantageous in HVAC systems and various industrial processes. Their space-saving design allows for flexibility in installation. Buyers should ensure that the valve’s specifications meet the system’s requirements and consider the installation methods, as proper positioning is crucial for optimal performance. While they offer significant space advantages, buyers should be aware of potential limitations in certain applications.
Key Industrial Applications of non return valves
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Non-Return Valves | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Wastewater | Backflow prevention in municipal water systems | Ensures clean water supply and protects infrastructure | Compliance with local regulations and standards |
| Oil and Gas | Unidirectional flow control in pipeline systems | Prevents leaks and equipment damage | Material compatibility with hydrocarbons and pressures |
| Chemical Processing | Preventing contamination in fluid transfer systems | Maintains product integrity and safety | Resistance to corrosive substances and high temperatures |
| HVAC Systems | Preventing reverse flow in heating and cooling applications | Enhances system efficiency and safety | Space constraints and installation requirements |
| Steam and Boiler Systems | Backflow prevention in multi-boiler operations | Protects equipment and ensures operational safety | High-temperature and pressure ratings for valves |
How Are Non-Return Valves Used in Water and Wastewater Applications?
In municipal water systems, non-return valves are critical for preventing backflow, ensuring that clean water remains uncontaminated. These valves protect treatment facilities and distribution networks from reverse flow caused by pressure changes. For international B2B buyers, sourcing non-return valves requires compliance with local regulations, such as those governing drinking water quality and environmental protection. Suppliers should provide documentation proving adherence to these standards.
What Role Do Non-Return Valves Play in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, non-return valves are essential for controlling the unidirectional flow of hydrocarbons in pipelines. They prevent backflow, which can lead to leaks and severe operational hazards. Buyers in this industry must consider the material compatibility of non-return valves with various hydrocarbons and ensure that they can withstand high pressures and temperatures typical of oil and gas applications.
Why Are Non-Return Valves Important in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, non-return valves prevent cross-contamination between different fluids during transfer. By ensuring that chemicals flow in one direction, these valves protect product integrity and enhance safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing valves made from materials resistant to corrosive substances and capable of handling high-temperature environments, as these factors are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
How Do Non-Return Valves Enhance HVAC Systems?
In HVAC applications, non-return valves prevent reverse flow, which can disrupt heating and cooling processes. This functionality not only improves system efficiency but also contributes to safety by preventing potential water hammer effects. Buyers should consider the specific installation requirements, such as space constraints and the need for compatible fittings, to ensure optimal performance in their HVAC systems.
What Is the Function of Non-Return Valves in Steam and Boiler Systems?
In steam and boiler systems, non-return valves are vital for preventing backflow into idle boilers, which could cause damage or operational hazards. They assist in isolating boilers during maintenance and help mitigate pressure surges. Buyers must ensure that the non-return valves selected can withstand high temperatures and pressures, as well as comply with industry standards for safety and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘non return valves’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Backflow Contamination Risk in Water Treatment Systems
The Problem: In many industrial water treatment facilities, backflow can lead to severe contamination risks, especially when untreated or potentially harmful fluids flow back into clean water supplies. A B2B buyer responsible for maintaining these systems may face significant pressure to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations. Failure to prevent backflow not only jeopardizes public safety but can also lead to costly fines and damage to the company’s reputation. The concern is amplified in regions with stricter regulatory environments or where water quality directly impacts the community’s health.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of backflow contamination, it is crucial to select high-quality non-return valves specifically designed for water treatment applications. Buyers should look for valves that meet industry standards and are constructed from materials resistant to corrosion and biofouling, such as stainless steel or specialized plastics. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules, including inspections and cleaning of the valves, can significantly extend their lifespan and effectiveness. When sourcing these valves, it’s advisable to consult with manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and performance data, ensuring that the chosen non-return valve can handle the specific pressures and flow rates of the system. Training staff on proper installation techniques, such as ensuring the valves are placed at the correct distance from pumps to avoid turbulence, will further enhance system reliability.
Scenario 2: Frequent Valve Failures Due to Debris Accumulation
The Problem: For many industrial operations, particularly in sectors like mining or food processing, non-return valves can frequently fail due to debris buildup. A buyer may find that their valves are not functioning as intended, leading to costly downtime and increased maintenance efforts. The frustration mounts as each failure requires not only replacement costs but also additional labor to diagnose and resolve the issues, affecting overall productivity.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should consider investing in non-return valves with built-in filtration features or those designed to minimize debris accumulation. Regular maintenance protocols should include routine checks for debris and the installation of strainers or filters upstream of the non-return valves to catch contaminants before they enter the valve. Furthermore, implementing a more robust inventory management system to keep track of valve performance and maintenance history can help identify patterns of failure, allowing for proactive replacements before failures occur. Collaborating with valve manufacturers to ensure that the selected valves are appropriate for the specific operational environment will also be beneficial. This proactive approach not only reduces the likelihood of failures but also enhances the overall reliability of the system.
Scenario 3: Inefficient System Performance Due to Inadequate Valve Selection
The Problem: Buyers often encounter challenges when non-return valves do not match the specific requirements of their applications, leading to inefficiencies. For instance, an improperly sized or unsuitable valve can cause pressure drops, flow restrictions, or even system failures. This scenario is common in industries like oil and gas, where precise flow control is critical for both safety and operational efficiency. The repercussions of such mismatches can lead to increased operational costs and jeopardize the safety of the entire system.
The Solution: To avoid inefficiencies caused by inadequate valve selection, buyers must conduct a thorough assessment of their system’s requirements before sourcing non-return valves. This assessment should include evaluating the fluid type, pressure conditions, temperature ranges, and flow rates. Engaging with valve suppliers who can provide expert guidance and perform fluid dynamic analysis can help ensure that the selected valves are not only appropriate in size but also optimized for the specific application. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in adjustable or modular non-return valves that can be fine-tuned post-installation to adapt to changing operational conditions. Keeping an open line of communication with suppliers for future upgrades or changes in requirements will also ensure that the system remains efficient and compliant.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for non return valves
What Are the Key Materials Used for Non-Return Valves?
When selecting non-return valves, the choice of material is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of non-return valves, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Benefit Non-Return Valves?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Typically, grades like 304 and 316 are used, with 316 offering superior resistance to chlorides.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including those involving aggressive media. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact project budgets. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as stainless steel can be welded and machined, but it may require specialized tools.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including water, oil, and chemicals. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for applications in the oil and gas industry, as well as in food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, understanding the local availability of different grades can influence procurement decisions.
Why Choose PVC for Non-Return Valves?
Key Properties: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has good chemical resistance. It operates effectively at lower temperatures and pressures compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for low-pressure applications. However, it has limitations in high-temperature environments and can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in water treatment facilities and irrigation systems due to its resistance to a wide range of chemicals. However, it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications or where high temperatures are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D1784 is essential for PVC products. Buyers in regions like South America should consider local regulations regarding plastic materials in water systems.
What Advantages Do Brass Non-Return Valves Offer?
Key Properties: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and is suitable for moderate temperature and pressure applications. It is typically alloyed with zinc, which enhances its mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: Brass is durable and has a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it easy to handle and install. However, it is more expensive than PVC and can be prone to dezincification in certain environments, which can compromise its integrity.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in plumbing and HVAC applications where moderate pressures are common. Its compatibility with water and gas makes it a versatile choice, but care must be taken in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B283 for brass components. In regions like Africa, understanding local sourcing and availability of brass can influence costs.
When Should You Use Cast Iron for Non-Return Valves?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its high strength and durability, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. It has good wear resistance and can handle a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: While cast iron is robust and can withstand significant stress, it is heavier and more challenging to install than lighter materials. It is also more susceptible to corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
Impact on Application: Cast iron is commonly used in wastewater systems and heavy industrial applications due to its strength. However, its weight can complicate installation and maintenance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A126 is crucial for cast iron valves. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the implications of shipping and handling due to the weight of cast iron products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Non-Return Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for Non-Return Valves | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| PVC | Water treatment, irrigation systems | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
| Brass | Plumbing, HVAC applications | Good mechanical properties | Prone to dezincification in corrosive environments | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Wastewater systems, heavy industry | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
In conclusion, the selection of material for non-return valves greatly influences performance, durability, and cost. Understanding the properties and applications of each material can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for non return valves
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Non-Return Valves?
The manufacturing of non-return valves (NRVs) is a complex process that involves several key stages to ensure product reliability and efficiency. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Non-Return Valve Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. The choice of material is critical, as it must withstand the specific pressures and temperatures of the application. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and various plastics, each chosen for their corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
Once the materials are selected, they undergo processes such as cutting and machining to achieve the desired dimensions. Quality assurance begins at this stage, with incoming quality control (IQC) checks ensuring that materials meet predefined specifications. Any deviations can lead to performance issues in the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Non-Return Valve Production?
The forming stage involves various techniques, including casting, forging, and machining, to shape the valve components.
-
Casting: This method is often used for producing complex shapes and is suitable for materials like iron and certain alloys. It involves pouring molten metal into a mold, allowing it to solidify.
-
Forging: This technique enhances the mechanical properties of the material by deforming it under heat and pressure, resulting in stronger components.
-
Machining: After forming, components are often machined to ensure precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly employed for high accuracy.
At this stage, in-process quality control (IPQC) checks are vital to ensure that components meet specifications and tolerances.
How Are Non-Return Valves Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process typically involves:
- Fitting: Components such as the valve body, disc, and spring are assembled. The design must allow for smooth operation and effective sealing against backflow.
- Welding/Joining: In some designs, components may be welded or joined using adhesives, depending on the materials and application requirements.
- Final Adjustments: After assembly, adjustments may be made to ensure the valve operates correctly under intended conditions.
Quality checks during assembly are crucial. These can include visual inspections for defects and functional tests to ensure that the valve operates as intended.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Non-Return Valves?
Finishing processes improve the valve’s durability and performance. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like plating, painting, or coating are used to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Polishing: This improves the surface finish, reducing friction and ensuring a tight seal.
- Testing: Final quality checks include pressure testing and leak testing to ensure that the valve will perform reliably in its intended application.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Non-Return Valves?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of non-return valves, especially for international B2B buyers. Several international and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining quality.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have consistent processes in place to deliver high-quality products. Other relevant standards for non-return valves include:
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute provides guidelines for valves used in the oil and gas industry, emphasizing safety and reliability.
These standards not only help ensure product quality but also facilitate easier entry into international markets.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. They typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials and components before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring processes during manufacturing to catch issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive tests on the finished product before it is shipped.
These checkpoints help maintain consistent quality and reduce the likelihood of defects reaching customers.
Illustrative image related to non return valves
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring that products meet expectations. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This is particularly important for suppliers in regions with varying quality standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from testing and inspections.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of product quality and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of certain nuances when dealing with suppliers in different regions:
- Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding valve manufacturing, which can affect quality.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and business practices can enhance communication and lead to better partnerships.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Assessing the reliability of a supplier’s supply chain is essential, as delays or issues in sourcing materials can impact quality.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions and ensure that they select suppliers capable of meeting their quality standards for non-return valves.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘non return valves’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of non-return valves (NRVs) can be complex due to the variety of types, applications, and supplier options available. This guide provides a structured checklist to help international B2B buyers make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality non-return valves that meet their specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific technical requirements for the non-return valves you need. Consider factors such as fluid type (liquid or gas), pressure and temperature ranges, and the application environment (e.g., water treatment, chemical processing). Clear specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the valves will perform as required.
Step 2: Research Valve Types and Features
Familiarize yourself with the various types of non-return valves available, such as swing check, ball check, and diaphragm check valves. Each type has distinct features that may suit different applications. For instance, swing check valves are ideal for water systems, while diaphragm check valves are better for corrosive fluids. Understanding these differences will guide your selection process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, certifications, and case studies that demonstrate their expertise in manufacturing non-return valves. It’s beneficial to seek references from other companies in your industry or region to gauge supplier reliability and performance.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold the necessary industry certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Certifications can also include compliance with regional standards, especially if you are sourcing from different continents. This step is crucial to guarantee that the products meet safety and quality regulations.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the non-return valves for testing. Conduct performance assessments under conditions similar to your operational environment to ensure they function correctly. This step helps to identify any potential issues before making a larger commitment.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Options
Inquire about warranty terms and post-purchase support from the supplier. A robust warranty indicates the supplier’s confidence in their product quality. Additionally, consider the availability of technical support or maintenance services, which can be vital for troubleshooting and ensuring optimal valve performance over time.
Step 7: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
After evaluating all the above factors, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be prepared to discuss bulk order discounts, shipping options, and lead times. Effective negotiation can significantly impact your overall procurement costs and project timelines.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently source non-return valves that not only meet their technical requirements but also align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for non return valves Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Non-Return Valve Sourcing?
When sourcing non-return valves, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly influences the cost. Common materials include stainless steel, bronze, and PVC. Higher-grade materials increase durability but also raise prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and manufacturing complexity. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor associated with the production process. Efficient manufacturing practices can reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized non-return valves, adding to initial costs. However, standard tooling can help in keeping expenses lower for bulk orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality checks are essential to ensure reliability and compliance with industry standards. Investing in quality control can prevent costly failures and returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can impact overall expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin on top of their costs. Understanding the margin expectations can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Non-Return Valve Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of non-return valves, making it vital for buyers to consider these when sourcing:

Illustrative image related to non return valves
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often come with volume discounts. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized valves tailored to specific applications will typically cost more than off-the-shelf products. Be clear about your requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used directly affect pricing. Investing in higher-quality materials may lead to increased upfront costs but can reduce the total cost of ownership over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Valves that meet international standards or have certifications (like ISO) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international purchases. They dictate shipping responsibilities and costs, impacting the total price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Non-Return Valves?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to improve their sourcing efficiency and reduce costs:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you are placing a large order. Leverage your purchasing power to secure better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may fluctuate based on market demand, raw material costs, and geopolitical factors. Regularly review market conditions to time your purchases effectively.
-
International Considerations: When sourcing from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider local regulations, import duties, and logistics challenges that may affect pricing.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and preferential treatment in future negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for non-return valves can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing non return valves With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Non-Return Valves in Fluid Control Systems
When assessing fluid control mechanisms, it’s essential to explore various alternatives to non-return valves (NRVs). While NRVs effectively prevent backflow and ensure unidirectional flow, other technologies or methods may also fulfill similar functions. This section compares non-return valves against two viable alternatives: Diaphragm Pumps and Flow Control Valves. Each alternative has unique benefits and limitations, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand their specific requirements before making a decision.
| Comparison Aspect | Non Return Valves | Diaphragm Pumps | Flow Control Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly effective in preventing backflow and maintaining fluid direction. | Excellent for precise flow control and handling various fluid types. | Provides adjustable flow rates but may not prevent backflow effectively. |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate cost depending on type and material. | Higher initial investment due to complexity and technology. | Moderate cost; varies with control complexity and material. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires proper alignment and orientation. | More complex; requires careful setup and calibration. | Generally straightforward, but may need additional components for full functionality. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic inspections; prone to debris blockage. | Requires regular maintenance; diaphragm replacement may be needed. | Low maintenance; typically requires infrequent checks unless under high stress. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for preventing backflow in pipelines and water systems. | Best for applications requiring precise flow control and handling of slurries. | Suitable for applications needing variable flow rates but may require additional backflow prevention measures. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Diaphragm Pumps?
Diaphragm pumps are positive displacement pumps that utilize a diaphragm to create a pumping action. They excel in applications that require precise flow control and can handle a wide variety of fluids, including corrosive and viscous materials. The main advantage of diaphragm pumps is their ability to manage flow rates accurately while ensuring minimal leakage. However, they typically come with a higher upfront cost and more complex installation and maintenance requirements, which may not be ideal for all operations.
How Do Flow Control Valves Compare?
Flow control valves are designed to regulate the flow rate of a fluid within a system. They can adjust the flow based on system demands and are often used in combination with other devices for optimal performance. While they offer the flexibility of flow adjustment, their effectiveness in preventing backflow is limited unless integrated with additional mechanisms. Flow control valves tend to have moderate costs and are relatively easy to install. However, they may require additional equipment to ensure backflow prevention, which can complicate the system design.
Making the Right Choice: How Should B2B Buyers Decide?
When choosing between non-return valves, diaphragm pumps, and flow control valves, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs. Factors such as the type of fluid being handled, system pressure requirements, and budget constraints will significantly influence the best choice. For applications where backflow prevention is critical, non-return valves remain a strong candidate. However, for situations requiring precise flow management or handling of complex fluid types, diaphragm pumps or flow control valves may provide superior performance. Ultimately, a thorough evaluation of the application and operational environment will guide buyers to the most effective solution for their fluid control needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for non return valves
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Non-Return Valves?
When evaluating non-return valves (NRVs), several critical specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, and chemical processing.
1. Material Grade
Non-return valves are typically constructed from various materials such as stainless steel, brass, PVC, and cast iron. The choice of material affects the valve’s durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for high-temperature or high-pressure environments. For example, stainless steel is preferred in chemical processing due to its resistance to corrosion, while PVC is often chosen for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness in water applications.
2. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating, often expressed in psi (pounds per square inch) or bar, indicates the maximum pressure the valve can withstand without failure. Understanding the pressure requirements of your system is vital; using a valve with an inadequate pressure rating can lead to catastrophic failures. Buyers should ensure that the NRV’s pressure rating aligns with the operational conditions of their application.
3. Cracking Pressure
Cracking pressure refers to the minimum upstream pressure required to open the valve. This specification is critical in applications where backflow prevention is essential, as it directly impacts the valve’s responsiveness to changes in flow direction. A well-chosen cracking pressure ensures that the valve operates efficiently without unnecessary strain on the system.
4. Flow Rate
The flow rate is a measure of the volume of fluid that can pass through the valve over a specific period, typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s). Selecting a valve with an appropriate flow rate is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and preventing bottlenecks. It is advisable to consult flow rate charts provided by manufacturers to make informed decisions.
5. End Connections
End connections are the fittings that allow the valve to be attached to piping systems. Common types include threaded, flanged, and welded connections. The choice of end connection affects installation ease and compatibility with existing systems. Buyers must consider their current infrastructure when selecting the appropriate end connection type.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Non-Return Valves?
Navigating the procurement process for non-return valves often involves understanding specific trade terminology. Familiarity with these terms can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communication with suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of non-return valves, purchasing from an OEM can guarantee that the products meet original specifications and quality standards. This term is crucial for buyers looking to maintain consistency in their operations.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about MOQs to ensure that they can meet the supplier’s requirements without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing information from suppliers for specific products. This document typically includes product specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and ensure they are getting the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, as they dictate aspects such as shipping, insurance, and risk allocation during transportation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when scheduling installations or maintenance to avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding non-return valves, ensuring they select the right products for their operational needs while fostering effective supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the non return valves Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Non-Return Valves Market?
The non-return valves market is significantly shaped by global industrial growth, increasing infrastructure investments, and the rising demand for efficient fluid control systems across various sectors such as oil and gas, water and wastewater, and chemical processing. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing rapid urbanization and industrialization, which enhances the demand for reliable fluid management solutions. Technological advancements, particularly in automation and smart manufacturing, are also driving innovations in non-return valve designs, improving their performance and reliability.
Additionally, the market is influenced by the ongoing shift towards sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for non-return valves that not only meet their operational needs but also align with environmental regulations and standards. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, into valve manufacturing and management is becoming a critical trend, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thus reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Non-Return Valves Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the non-return valves sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in valve production are under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and using eco-friendly materials. This shift not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers and partners.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and have transparent supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable and ethical practices. Furthermore, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in the production of non-return valves, such as recycled metals or biodegradable coatings, can significantly enhance the product’s marketability and compliance with environmental standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Non-Return Valves in the B2B Landscape?
The concept of non-return valves has evolved significantly since their inception. Initially developed to prevent backflow in basic plumbing systems, these valves have transformed into sophisticated devices integral to various industrial applications. The industrial revolution marked a pivotal point, where the demand for efficient fluid control systems surged, leading to advancements in valve design and materials.
Over the decades, innovations such as the introduction of spring-loaded mechanisms and advanced materials have enhanced the reliability and efficiency of non-return valves. Today, they play a critical role in ensuring operational safety and efficiency across multiple sectors, including HVAC, water treatment, and chemical processing. This historical evolution underscores the importance of adapting to market needs and technological advancements, which continues to be vital for B2B buyers navigating the current landscape.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability factors, and historical context of non-return valves is essential for B2B buyers. By staying informed about emerging trends and prioritizing ethical sourcing, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and align with global sustainability goals, ultimately leading to better procurement decisions and long-term success in the non-return valves sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of non return valves
-
How do I solve backflow issues in my system?
To address backflow problems, the installation of non-return valves (NRVs) is essential. These valves allow fluid to flow in one direction while preventing reverse flow, thereby protecting your systems from potential damage and contamination. Ensure you select the right type of NRV based on your application—options include swing check valves, ball check valves, and diaphragm check valves. Regular maintenance, including inspection for wear and debris removal, is crucial to ensure the valve operates effectively over time. -
What is the best type of non-return valve for wastewater management?
For wastewater management, swing check valves are often considered the best choice. They feature a hinged disc that opens with forward flow and closes to prevent backflow, making them ideal for fluctuating flow conditions typical in wastewater systems. Lift check valves are also suitable for high-pressure applications, while diaphragm check valves can be used for corrosive fluids. It’s important to assess the specific requirements of your system, including pressure and flow rates, to select the most effective valve type. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing non-return valves internationally?
When sourcing non-return valves, consider factors such as the supplier’s reputation, product certifications, and compliance with international standards. It’s crucial to verify the quality and reliability of the valves, especially for critical applications. Additionally, assess the supplier’s ability to meet your customization needs and minimum order quantities (MOQ). Understanding lead times, payment terms, and shipping logistics is also essential to ensure a smooth procurement process. -
How can I ensure the quality of non-return valves before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test reports from suppliers. Look for products that comply with international standards like ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to your application. Additionally, consider conducting audits or site visits to the manufacturing facility if possible. Engaging in sample testing before placing bulk orders can also provide insights into the valve’s performance and durability. -
What are the common payment terms for international purchases of non-return valves?
Payment terms can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Discussing and agreeing on payment terms upfront is vital to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure you also consider factors such as currency fluctuations, transaction fees, and the reputation of the payment method used. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering non-return valves from international suppliers?
Lead times can vary based on the supplier’s location, production capabilities, and your specific order details. Generally, you can expect lead times ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Factors such as customization, availability of materials, and shipping logistics will also affect delivery times. It’s advisable to communicate your timeline requirements clearly with the supplier to ensure they can meet your deadlines. -
How do I handle customs and logistics when importing non-return valves?
When importing non-return valves, familiarize yourself with the customs regulations of your country. Ensure that all documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is accurate and complete to avoid delays. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider who understands international shipping can help navigate customs efficiently. Additionally, consider potential tariffs and duties that may apply to your import to budget accordingly. -
Can non-return valves be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for non-return valves to meet specific application requirements. Customizations may include size, material, pressure ratings, and design features tailored to unique operational conditions. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers during the sourcing process to ensure they can accommodate your specifications. It’s also beneficial to review previous projects the supplier has completed to assess their capability in providing customized solutions.
Top 2 Non Return Valves Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Adamant Valves – Check Valves
Domain: adamantvalves.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Check valves are two-port valves designed to prevent reverse flow in fluid systems, primarily used in pressure applications. They operate based on pressure differentials and have a minimum operating pressure known as cracking pressure. Common applications include chemical processing, food processing, water treatment, and HVAC systems. Non-return valves are also two-port valves that allow fluid to …
2. McMaster – Non-Return Valves
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Non-Return Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for non return valves
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Non-Return Valves?
In summary, the strategic sourcing of non-return valves is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and system integrity across diverse industries. These valves not only prevent backflow but also protect critical equipment from damage caused by pressure surges and contamination. Understanding the specific applications and types of non-return valves—such as swing, lift, and ball check valves—enables international buyers to select the most suitable options for their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to non return valves
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Your Business?
Investing in high-quality non-return valves and ensuring proper maintenance can significantly extend their lifespan, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, understanding the environmental and operational challenges unique to regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can inform better purchasing decisions, enhancing supply chain resilience.
How Can You Prepare for Future Trends in Valve Technology?
As industries evolve, the demand for innovative and efficient valve solutions will continue to grow. By establishing strong supplier relationships and staying informed about technological advancements, businesses can better navigate the complexities of global sourcing. We encourage international B2B buyers to engage with trusted suppliers and leverage their expertise to enhance operational reliability and drive success in their respective markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.