The Definitive Guide to Laboratory Bench Work: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laboratory bench work
In the ever-evolving landscape of laboratory bench work, sourcing the right equipment can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. From navigating varying standards and regulations across regions to ensuring the durability and suitability of workbenches for specific applications, the stakes are high. This guide aims to demystify the complexities associated with laboratory bench work, offering a comprehensive overview of the different types of workbenches available, their applications across various industries, and practical insights on supplier vetting processes.
By delving into aspects such as material options, ergonomic designs, and customization capabilities, this resource empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany—to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the cost implications, lead times, and installation services associated with different suppliers further enhances the buyer’s ability to select the most suitable workbench for their laboratory needs.
With a focus on quality, functionality, and compliance, this guide not only addresses the immediate concerns of sourcing laboratory workbenches but also positions buyers to optimize their laboratory environments for efficiency and productivity. Whether you are outfitting a new lab or upgrading existing furniture, the insights provided here will equip you with the knowledge necessary to invest wisely in your laboratory’s future.
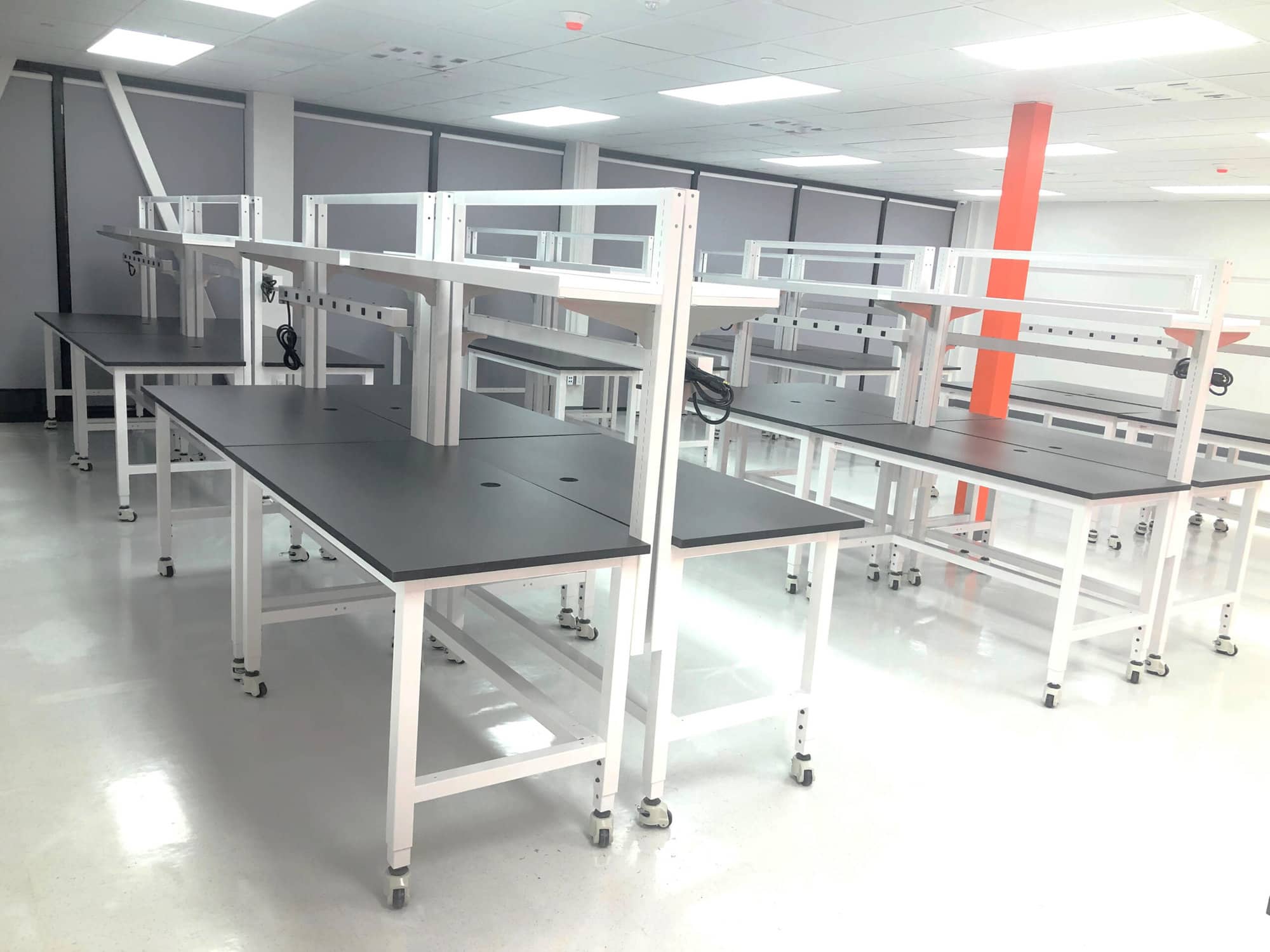
Understanding laboratory bench work Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin Top Lab Workbench | Durable resin surface, chemical resistance | Research labs, educational institutions | Pros: Durable and easy to clean; Cons: Limited aesthetic options. |
| Stainless Steel Workbench | Corrosion-resistant, hygienic, robust structure | Pharmaceutical, food & beverage industries | Pros: Excellent durability and cleanliness; Cons: Higher cost. |
| ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Workbench | Static control features, specialized materials | Electronics manufacturing, semiconductor labs | Pros: Protects sensitive components; Cons: May require grounding. |
| Cleanroom Laminate Workbench | Smooth, non-porous surface, designed for sterile environments | Biotech, pharmaceuticals, and cleanroom applications | Pros: Easy to sanitize; Cons: Limited resistance to heavy impact. |
| Hydraulic Lift Lab Workbench | Adjustable height, ergonomic design | Labs requiring frequent height adjustments for various tasks | Pros: Customizable for user comfort; Cons: Potential mechanical failure. |
What are the Characteristics of Resin Top Lab Workbenches?
Resin top lab workbenches are known for their robust and durable surfaces, which are resistant to chemicals and stains. They are typically constructed with a solid wood core covered by a resin material, making them suitable for a variety of laboratory settings, including research and educational institutions. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific chemical resistance required for their applications, as well as the bench’s weight capacity and configuration options.
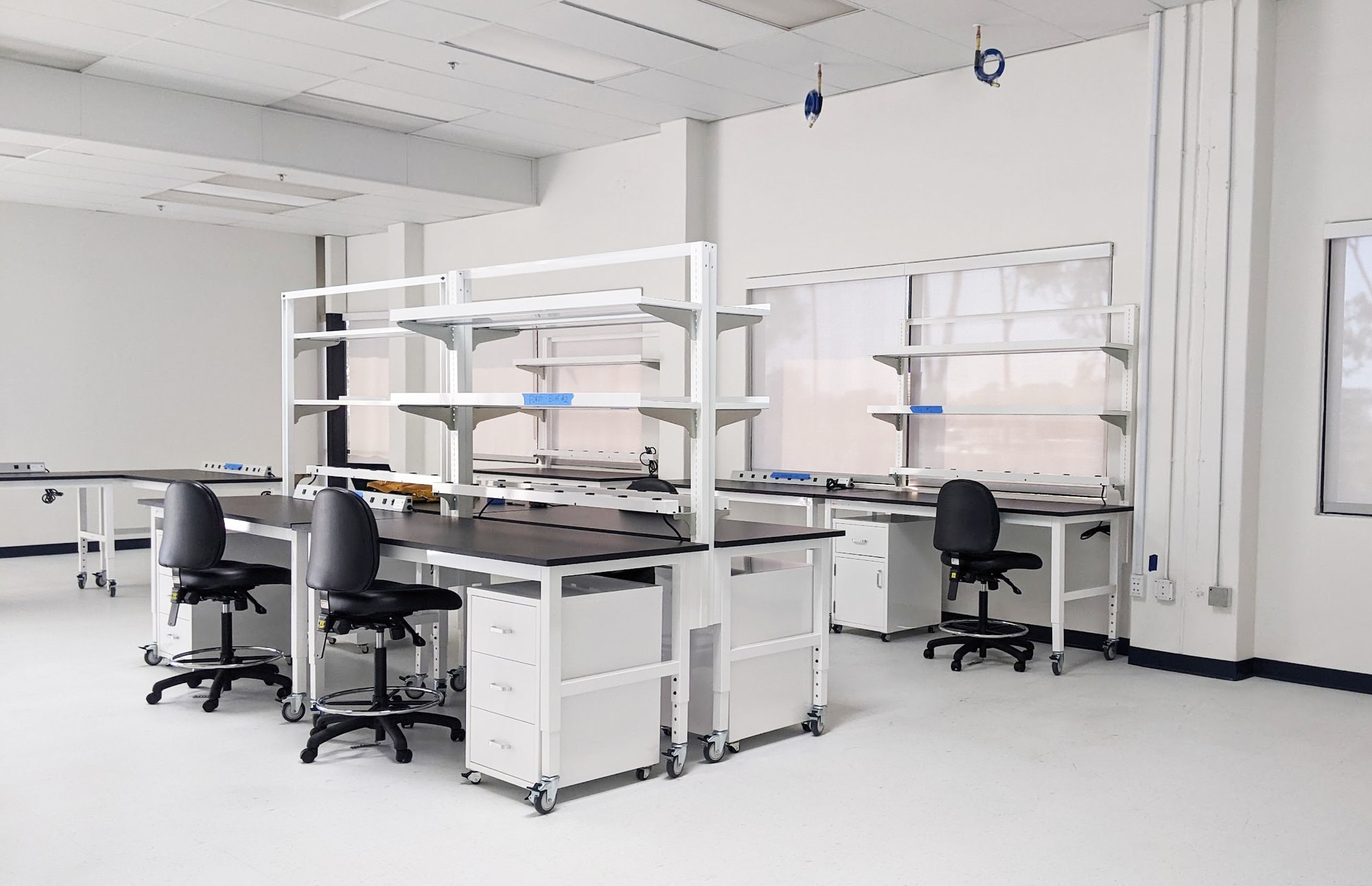

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
How Do Stainless Steel Workbenches Benefit B2B Buyers?
Stainless steel workbenches are favored in industries that prioritize hygiene and durability, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Their non-porous surfaces prevent contamination and are easy to clean, making them ideal for environments that require strict sanitary conditions. B2B buyers should evaluate the thickness of the steel, resistance to corrosion, and the specific applications to ensure that the workbench meets their operational needs.
Why Choose ESD Workbenches for Electronics Manufacturing?
ESD workbenches are specifically designed to prevent electrostatic discharge, which can damage sensitive electronic components. These workbenches often feature static-dissipative surfaces and grounding options. They are essential in electronics manufacturing and semiconductor labs where precision is critical. Buyers should assess the grounding requirements and ensure compatibility with their existing equipment to maximize the effectiveness of these workstations.
What Makes Cleanroom Laminate Workbenches Ideal for Sterile Environments?
Cleanroom laminate workbenches offer smooth, non-porous surfaces that are easy to clean and disinfect, making them suitable for biotech and pharmaceutical applications. These workbenches are designed to minimize contamination and are often used in controlled environments. When selecting a cleanroom laminate workbench, buyers should consider the cleanroom standards required, as well as the durability and maintenance needs of the materials used.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
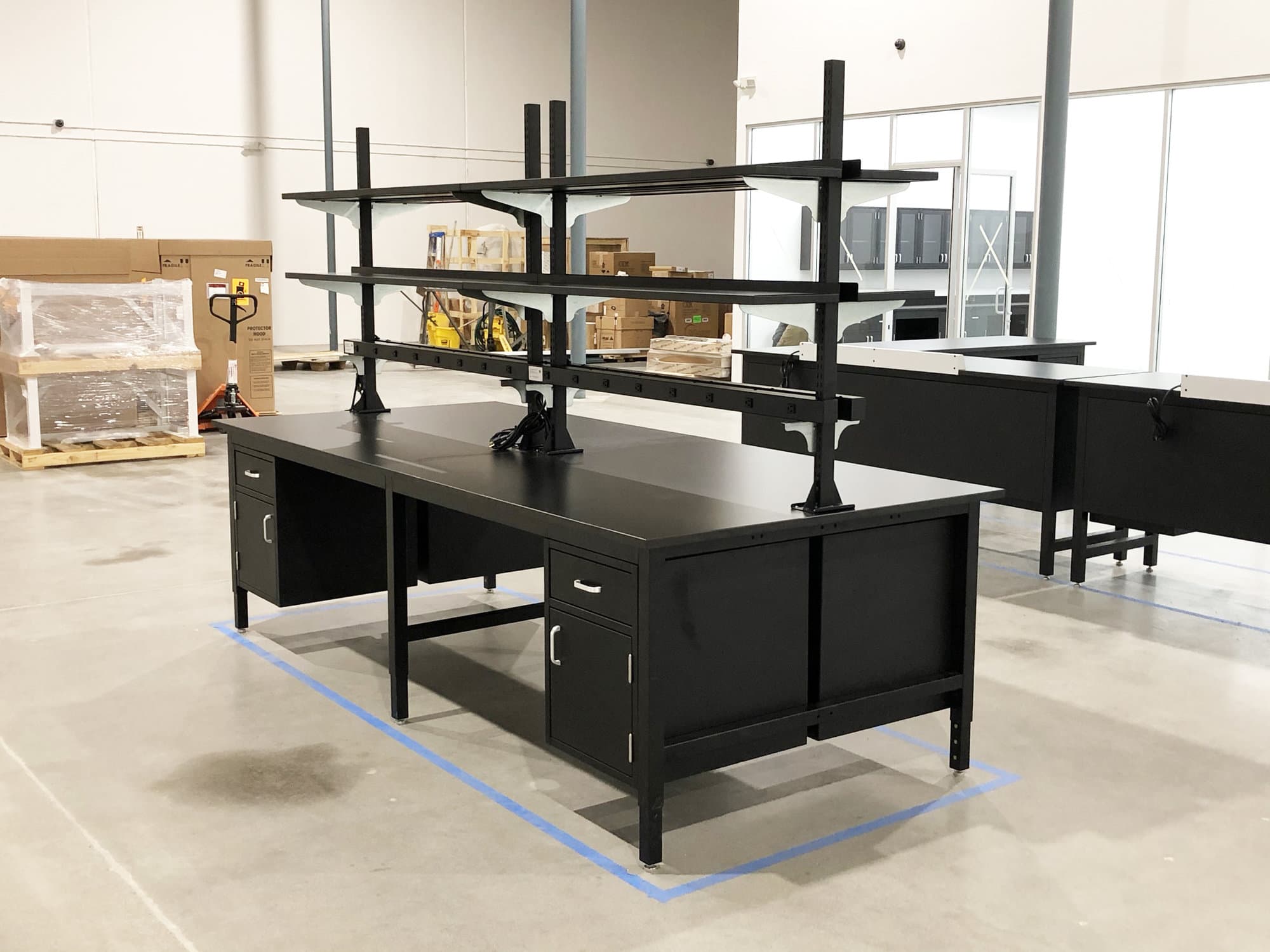
How Do Hydraulic Lift Lab Workbenches Enhance Ergonomics?
Hydraulic lift lab workbenches provide adjustable height features, catering to various tasks and user preferences. This ergonomic design is particularly beneficial in labs where multiple users may need different working heights. Buyers should consider the weight capacity, ease of adjustment, and durability of the hydraulic mechanisms when evaluating these workbenches for their laboratory environments.
Key Industrial Applications of laboratory bench work
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Laboratory Bench Work | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug formulation and testing | Ensures compliance with regulatory standards and improves efficiency in R&D. | Need for chemical-resistant surfaces and customizable configurations. |
| Food & Beverage | Quality control testing and product development | Enhances product safety and quality, ensuring regulatory compliance. | Requirements for easy-to-clean surfaces and modular designs. |
| Biotechnology | Cell culture and genetic analysis | Supports innovative research and accelerates product development cycles. | Need for specialized work surfaces and ergonomic designs. |
| Environmental Testing | Sample preparation and analysis | Facilitates accurate data collection and compliance with environmental regulations. | Consideration for durability and chemical resistance. |
| Education and Research Institutes | Student laboratories and research projects | Provides a practical learning environment and fosters innovation. | Flexibility in design and adaptability for various laboratory activities. |
How is Laboratory Bench Work Applied in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
In the pharmaceutical sector, laboratory bench work is essential for drug formulation and testing. These workbenches provide a controlled environment where researchers can conduct experiments and develop new medications. The need for chemical-resistant surfaces is paramount, as exposure to various substances can compromise safety and results. Additionally, international buyers must consider compliance with stringent regulatory standards, which necessitate durable and customizable workbench solutions to support ongoing research and development efforts.
What Role Does Laboratory Bench Work Play in Food & Beverage Quality Control?
Laboratory bench work in the food and beverage industry is crucial for quality control testing and product development. Workbenches are equipped to handle various tests that ensure food safety and compliance with health regulations. Buyers in this sector require surfaces that are easy to clean and maintain, with modular designs that can accommodate different testing equipment. This flexibility not only enhances efficiency but also allows businesses to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes and consumer demands.
How is Laboratory Bench Work Used in Biotechnology Research?
In biotechnology, laboratory bench work facilitates cell culture and genetic analysis, playing a vital role in innovative research. The workbenches must support specialized applications, such as incubators or laminar flow hoods, which require precise temperature and contamination controls. Buyers should focus on ergonomic designs that enhance productivity and reduce strain during long research hours. Additionally, the ability to customize workstations can significantly improve workflow and efficiency, making it a key consideration for international buyers.
What is the Importance of Laboratory Bench Work in Environmental Testing?
Laboratory bench work is integral to environmental testing, where it aids in sample preparation and analysis. These workbenches support the accurate collection of data necessary for compliance with environmental regulations. Durability and chemical resistance are critical features, as samples may include hazardous materials that require careful handling. Buyers must prioritize sourcing benches that can withstand rigorous testing environments while providing the flexibility to adapt to various analytical methods.
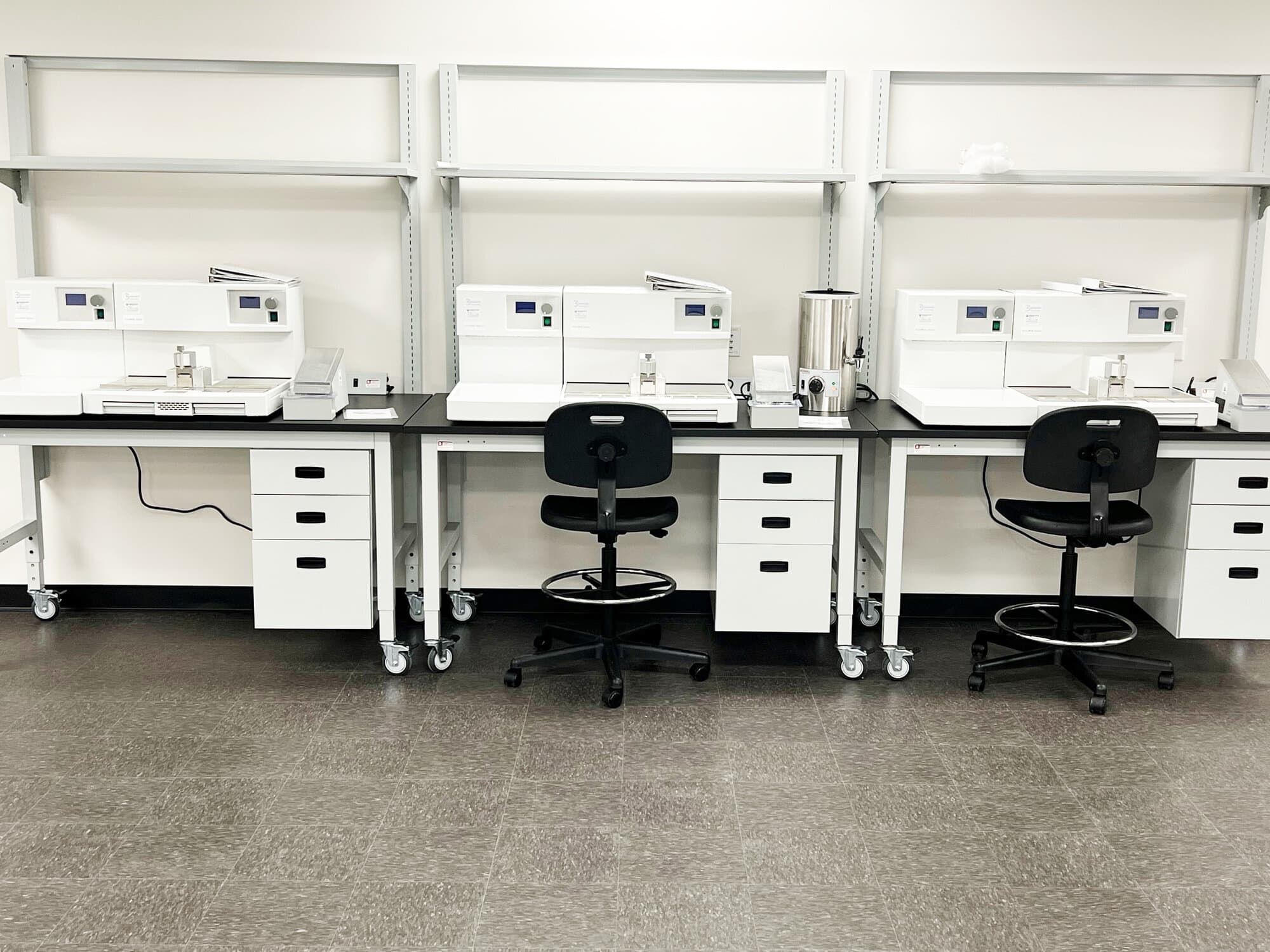

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
How Does Laboratory Bench Work Enhance Learning in Educational Institutions?
In educational institutions, laboratory bench work provides students with hands-on experience in scientific research and experimentation. These workstations must be flexible and adaptable to accommodate various laboratory activities, from chemistry experiments to biological studies. Buyers should consider the need for adjustable heights and modular components to create an inclusive learning environment that caters to diverse student needs. Investing in quality laboratory furniture enhances the educational experience, fostering innovation and practical skills in the next generation of scientists.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laboratory bench work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Bench Space for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often find that standard laboratory workbenches do not accommodate the diverse needs of their laboratory environments. For instance, a laboratory may require spaces for both chemical analysis and biological research, necessitating different configurations and work surfaces. This can lead to overcrowding, inefficient workflows, and frustration among technicians who struggle to juggle multiple tasks in limited space.
The Solution: To effectively address this pain point, buyers should consider investing in modular laboratory workbenches that can be tailored to specific applications. Custom solutions that include adjustable heights, interchangeable surfaces, and additional shelving can significantly enhance workspace versatility. When sourcing these benches, it’s crucial to engage with suppliers who offer consultation services, allowing buyers to evaluate their unique requirements and design a workspace that optimizes efficiency and functionality. Furthermore, incorporating designs that allow for corner or U-shaped configurations can maximize available space, ensuring that technicians have adequate room to perform their tasks without interruptions.
Scenario 2: Safety and Compliance Concerns in Laboratory Work
The Problem: Ensuring safety and regulatory compliance is a top priority for laboratory managers, particularly in regions with stringent health and safety regulations. Buyers often face challenges in sourcing laboratory benches that meet specific safety standards, such as chemical resistance or anti-static properties. Failure to provide adequate safety measures can lead to accidents, regulatory penalties, and loss of productivity.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize workbenches specifically designed for safety and compliance. This includes selecting materials that are chemically resistant, such as epoxy resin or phenolic resin surfaces, which can withstand spills and chemical exposure. Additionally, benches with built-in features like fume extraction systems or static control options are essential for maintaining a safe working environment. When sourcing these products, it’s advisable to collaborate with suppliers who have a proven track record in safety compliance. Conducting thorough due diligence to ensure that the workbenches meet local and international safety standards can help mitigate risks and create a safer laboratory setting.
Scenario 3: Lack of Ergonomics Leading to Technician Fatigue
The Problem: Laboratory work often requires long hours of standing or repetitive tasks, which can lead to technician fatigue and decreased productivity. Buyers may find that conventional lab benches do not accommodate ergonomic needs, resulting in discomfort and potential long-term health issues for their staff.
The Solution: To combat ergonomic challenges, buyers should consider workbenches that feature adjustable heights and designs that promote proper posture. Height-adjustable lab benches allow technicians to switch between sitting and standing positions, reducing strain on their backs and legs. It’s also beneficial to integrate ergonomic accessories, such as anti-fatigue mats and proper tool placements, to enhance comfort during use. When sourcing these benches, engaging with manufacturers who specialize in ergonomic design can provide insights into the best solutions tailored to the specific tasks being performed. Investing in ergonomically designed workbenches not only boosts employee satisfaction but also enhances overall productivity and reduces absenteeism due to work-related injuries.
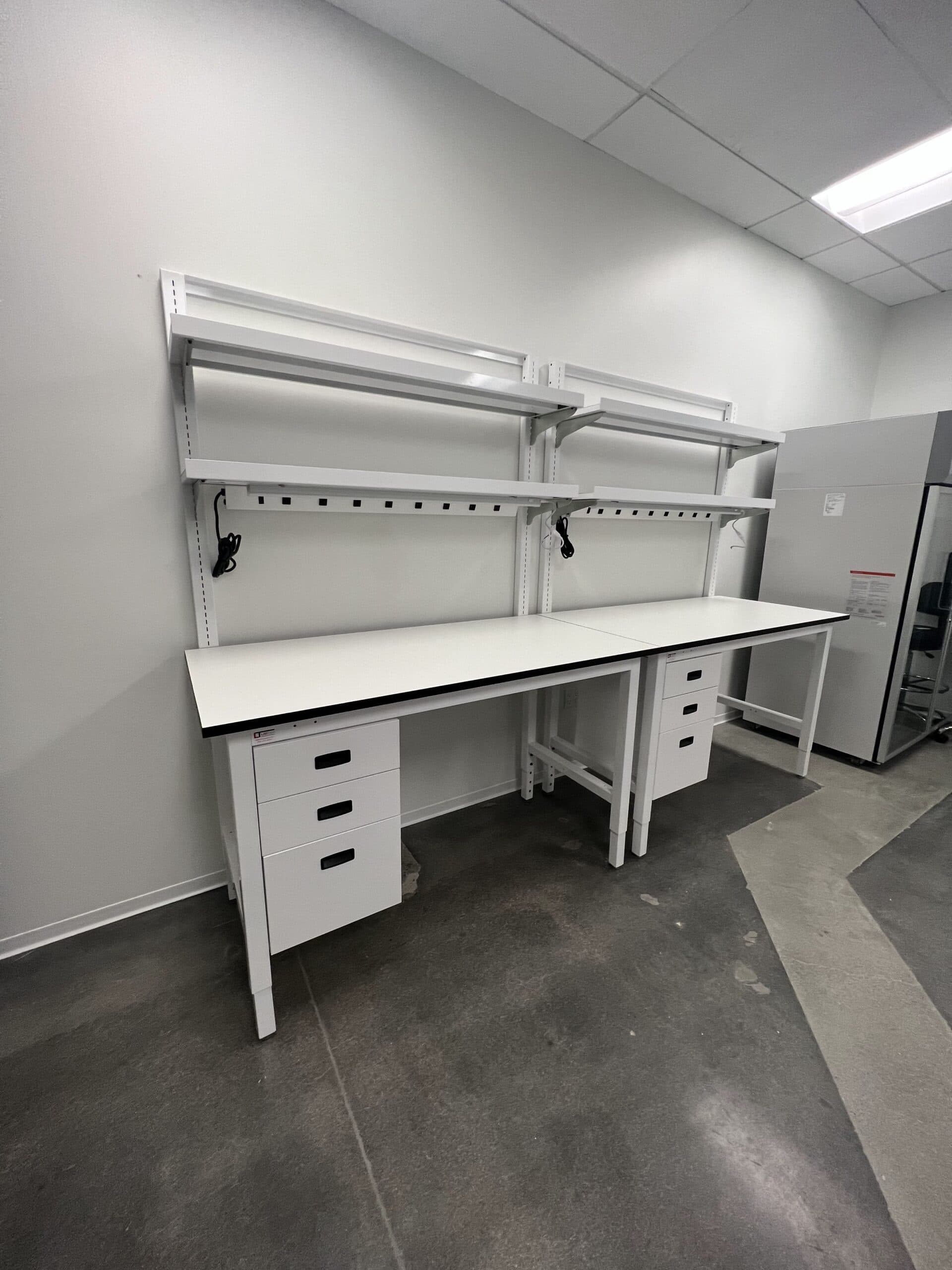

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laboratory bench work
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Laboratory Bench Work?
When selecting materials for laboratory benches, it is crucial to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in laboratory bench work: epoxy resin, stainless steel, phenolic resin, and butcher block.
How Does Epoxy Resin Perform in Laboratory Settings?
Epoxy resin is a popular choice for laboratory workbenches due to its excellent chemical resistance and durability. It can withstand a wide temperature range, typically from -40°F to 140°F (-40°C to 60°C), making it suitable for various laboratory environments. The non-porous surface prevents the absorption of spills, enhancing hygiene and ease of cleaning.
Pros: Epoxy resin offers high durability, is resistant to many chemicals, and is relatively low-maintenance. Its smooth surface is also conducive to easy cleaning.
Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
Cons: The initial cost can be higher than other materials, and while it is durable, it can be prone to scratching and may require careful handling to avoid damage.
Impact on Application: Epoxy resin is ideal for laboratories dealing with corrosive chemicals, making it a preferred option in chemical and pharmaceutical labs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the epoxy resin used complies with local safety and environmental regulations. Standards such as ASTM and DIN may apply, depending on the specific application.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel for Laboratory Benches?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it a staple in laboratory settings. It can endure high temperatures and is easy to sterilize, which is critical in environments requiring strict hygiene standards.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion make stainless steel long-lasting. It is also recyclable, which appeals to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel can be significant, and it may require additional treatments to prevent scratching and denting.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suited for laboratories in the food and beverage industry, as well as healthcare settings, where cleanliness is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should be aware of compliance with EU regulations regarding materials in contact with food. In regions like South America, local standards may also dictate the type of stainless steel used.
How Does Phenolic Resin Compare for Laboratory Workbenches?
Phenolic resin is another widely used material, known for its robust chemical resistance and thermal stability. It can withstand temperatures up to 350°F (177°C), making it suitable for high-heat applications.
Pros: Phenolic resin is highly resistant to chemicals, heat, and impact, making it an excellent choice for demanding laboratory environments. It also has a non-porous surface that resists staining.
Cons: The material can be more expensive than laminate options and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Phenolic resin is particularly effective in laboratories that handle aggressive solvents and chemicals, such as those in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that phenolic resin products meet local safety standards and certifications, particularly in regions with stringent chemical handling regulations.
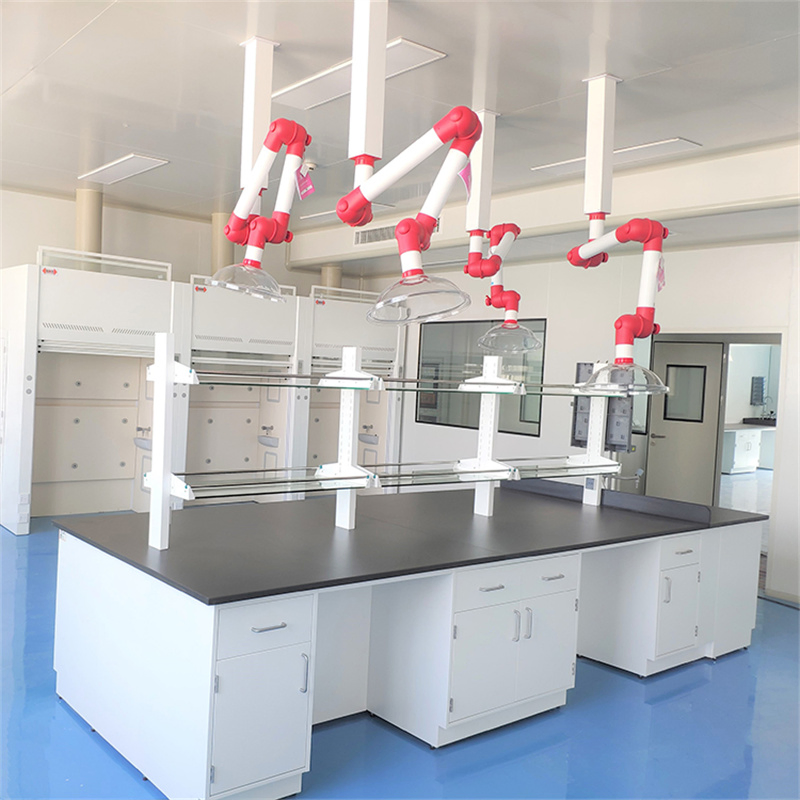

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
What Role Does Butcher Block Play in Laboratory Bench Design?
Butcher block, typically made from hardwoods, offers a unique aesthetic and is often used in educational and research laboratories. It provides a warm, natural surface that is easy to work on.
Pros: Butcher block is cost-effective and provides a sturdy work surface. It is also easy to repair and refinish, extending its lifespan.
Cons: It is less resistant to chemicals and moisture compared to synthetic materials, which can limit its use in certain laboratory applications. Regular maintenance is required to prevent warping and damage.
Impact on Application: Butcher block is best suited for laboratories that do not handle harsh chemicals, such as educational settings or workshops.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local climate conditions, as high humidity can affect the integrity of wood products. Compliance with local environmental regulations regarding wood sourcing may also be necessary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Laboratory Bench Work
| Material | Typical Use Case for laboratory bench work | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resin | Chemical and pharmaceutical labs | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food and healthcare labs | Durability and easy sterilization | High cost, prone to scratching | High |
| Phenolic Resin | Chemical and petrochemical labs | High heat and chemical resistance | More expensive, specialized mfg | High |
| Butcher Block | Educational and workshop labs | Cost-effective, easy to repair | Less chemical resistance, needs maintenance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their laboratory bench work setups, ensuring they choose the right materials for their specific applications and compliance needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laboratory bench work
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Laboratory Benches?
The manufacturing process for laboratory benches involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
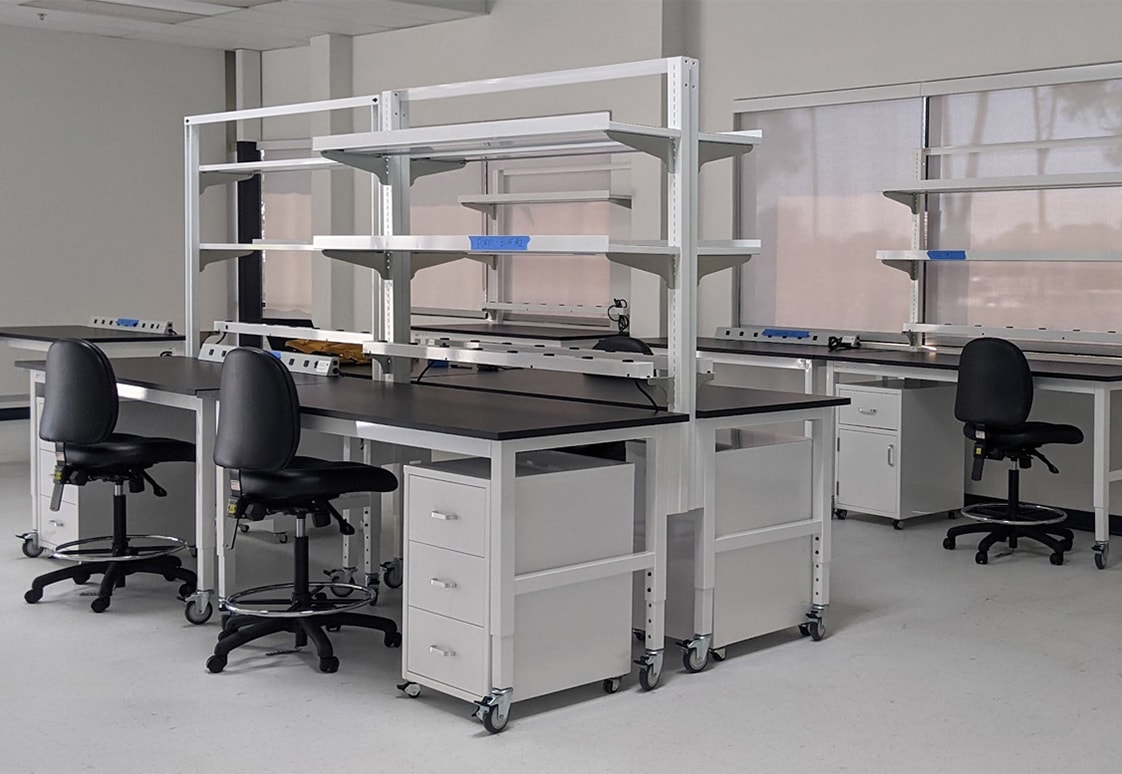

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage in manufacturing laboratory benches is material preparation. This involves selecting the right materials based on the intended use of the benches. Common materials include:
- Epoxy Resin: Known for its chemical resistance, epoxy resin is ideal for labs dealing with corrosive substances.
- Stainless Steel: Durable and easy to clean, stainless steel is often used in environments requiring high hygiene standards, such as medical and food laboratories.
- Butcher Block: This material offers a sturdy surface suitable for mechanical and physical testing.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): This material is lightweight and resistant to impact and chemicals, making it suitable for various laboratory applications.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards, such as ISO certifications.
Forming: How Are Laboratory Benches Shaped?
The forming stage involves cutting and shaping the selected materials into the required dimensions. Techniques used in this stage may include:
- CNC Machining: Automated machines precisely cut materials according to specifications, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
- Laser Cutting: This method provides clean edges and is particularly useful for intricate designs.
- Bending and Molding: For materials like steel or resin, bending and molding techniques are employed to achieve specific shapes that enhance functionality.
Proper forming techniques are crucial as they directly influence the bench’s strength and usability.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
Once the individual components are shaped, they move to the assembly stage. This process typically includes:
- Joining Techniques: Various methods such as welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding are used to assemble the parts. The choice of technique depends on the materials and the intended use of the bench.
- Customization: During assembly, buyers can specify configurations, including drawer placements, shelving, and power outlets, tailored to their specific laboratory needs.
Quality assurance checks at this stage ensure that all components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing: What Are the Final Touches on Laboratory Benches?
The final stage is finishing, which enhances both the aesthetic and functional qualities of the benches. Finishing processes may include:
- Surface Treatments: Applying protective coatings or finishes to improve durability and resistance to chemicals.
- Polishing: For stainless steel surfaces, polishing is done to ensure a clean, professional appearance.
- Quality Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to detect any defects or imperfections that could affect performance.
This stage plays a vital role in the bench’s longevity and usability.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Laboratory Benches?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of laboratory benches, as it ensures compliance with international standards and customer expectations. Here’s an overview of relevant QA measures.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential benchmarks for quality management systems. ISO 9001 focuses on ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Other relevant standards include:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant in laboratories dealing with oil and gas industries, ensuring products meet specific performance criteria.
B2B buyers should seek suppliers who are certified to these standards, as they reflect a commitment to quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks ensure that each stage meets the established quality criteria. This can include dimensional checks and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished products undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet all specifications and standards.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify issues early in the manufacturing process, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including inspection records and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital.
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Cultural perceptions of quality and regulatory requirements can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should be aware of:
- Local Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations regarding laboratory equipment, affecting compliance requirements.
- Cultural Expectations: Understanding local expectations for quality can guide negotiations and supplier relationships.
What Should Buyers Look For in Supplier Certifications?
When evaluating suppliers, buyers should look for:
- ISO Certifications: Ensure that the supplier adheres to recognized international standards.
- Regional Certifications: Certifications relevant to specific markets, such as GCC certifications for Middle Eastern countries or CE markings for European markets, can also be crucial.
Conclusion: How Can Buyers Ensure Quality in Laboratory Bench Work?
Investing time in understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for laboratory benches will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and stringent quality control processes, buyers can ensure that they acquire laboratory furniture that meets their operational needs and complies with international standards. This diligence not only enhances lab functionality but also supports long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers across various regions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laboratory bench work’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure laboratory bench work. Whether you are outfitting a new lab or upgrading existing furniture, following these steps will help ensure that you make informed decisions that meet your specific laboratory requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clarifying the specific needs of your laboratory. Consider the types of experiments or tasks to be conducted, as different applications may require various workbench features, such as chemical resistance or ESD protection.
- Material Selection: Evaluate options like stainless steel for durability or epoxy resin for chemical resistance.
- Size and Layout: Determine the dimensions needed to accommodate your space and workflow, including configurations like L-shaped or U-shaped benches.
Step 2: Identify Compliance and Safety Standards
Ensure that the workbench meets local and international safety standards, particularly if you operate in regions with strict regulations. This is critical for maintaining workplace safety and compliance with health regulations.
- Certification Verification: Look for certifications such as ISO or ANSI that indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
- Ergonomics: Consider workbenches designed with ergonomics in mind to reduce worker fatigue and improve productivity.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. This step is crucial for ensuring that you partner with reliable vendors who can meet your quality and service expectations.
- Supplier Background: Review company profiles, focusing on their experience in your industry and customer testimonials.
- Case Studies: Request case studies that illustrate how the supplier has successfully met the needs of similar clients.
Step 4: Request Customization Options
Many suppliers offer customizable workbenches to better suit your laboratory’s unique requirements. Engaging in this dialogue can lead to solutions that enhance functionality and efficiency.
- Modular Designs: Ask about modular options that allow for flexibility in your lab layout.
- Accessory Availability: Inquire about additional features, such as integrated power sources, storage solutions, or fume extraction systems.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Installation Services
Understanding the timeline for delivery and installation is essential to project planning. Delays can affect your lab’s operational readiness, so be proactive in this regard.
- Production Time: Confirm the estimated lead time for production and delivery of your workbenches.
- Installation Support: Ensure the supplier offers professional installation services to guarantee that the benches are set up correctly and efficiently.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Warranty Options
Finally, evaluate the pricing structures and warranty offerings from different suppliers. This will help you make cost-effective decisions while ensuring that you receive quality products.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
- Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond initial purchase prices; consider long-term durability and maintenance costs.
- Warranty Coverage: A robust warranty can provide peace of mind and protection against manufacturing defects.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing laboratory bench work, ensuring that their investments align with their operational needs and compliance standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laboratory bench work Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Laboratory Bench Work Sourcing?
When sourcing laboratory benches, understanding the cost structure is crucial for informed decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. Options range from high-pressure laminates to stainless steel and epoxy resin. High-quality materials, while more expensive, can enhance durability and performance, making them a better long-term investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the workforce required for manufacturing and installation. Skilled labor, especially in custom configurations, may come at a premium, but it ensures higher quality and compliance with safety standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs and improve overall pricing flexibility.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom designs can be substantial but is often amortized over large production runs. Buyers should consider how tooling costs will be factored into the unit price.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that lab benches meet industry standards requires investment in quality control processes. This can add to upfront costs but is essential for compliance and long-term reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance, weight, and shipping methods. International buyers should factor in potential tariffs and customs duties when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding the average margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of Laboratory Benches?
Several factors can influence the pricing of laboratory benches, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically result in reduced per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also affect the price significantly.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requests may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected price surges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ANSI) often lead to higher prices. However, they can offer better durability and compliance, which may justify the investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for cost forecasting. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the final cost based on who bears shipping and insurance responsibilities.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Laboratory Bench Sourcing?
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of laboratory bench sourcing requires strategic approaches:

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating on price, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to better deals.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacement, and operational efficiency. Investing in higher-quality benches can lead to lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, local market conditions, and regional economic factors that may affect pricing. Staying informed can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes break down costs transparently. This allows for better comparison across suppliers and helps identify hidden costs.
-
Explore Local Options: While sourcing internationally might offer cost benefits, local suppliers may provide faster delivery times and reduced shipping costs, making them a viable alternative.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they secure the best value for their laboratory bench work sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laboratory bench work With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions in Laboratory Settings
In the dynamic environment of laboratory work, selecting the right workspace solution is critical for optimizing productivity and ensuring safety. While traditional laboratory bench work has long been the standard, advancements in technology and workspace design have introduced several viable alternatives. This section will compare laboratory bench work with other innovative solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Laboratory Bench Work | Modular Workstations | Mobile Lab Tables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High stability and durability | Versatile and adaptable | Flexible use in various locations |
| Cost | Moderate, typically $388 – $1,108 | Varies widely based on customization | Generally lower cost, around $200 – $800 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful planning and assembly | Quick setup; can be reconfigured easily | Easy to set up and relocate |
| Maintenance | Requires regular upkeep for durability | Low maintenance due to modular design | Minimal upkeep, easy to clean |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for fixed laboratory environments | Suitable for multi-purpose labs | Excellent for temporary or mobile labs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Modular Workstations
Modular workstations offer a flexible solution for laboratories needing to adapt to changing requirements. These workstations can be customized to fit various tasks, allowing for a combination of workspace types, such as L-shapes or U-shapes. Their quick setup and reconfiguration capabilities make them ideal for dynamic lab environments, such as those in biotech or research settings. However, the cost can vary significantly based on customization, which may present budget challenges for some organizations.
2. Mobile Lab Tables
Mobile lab tables are designed for versatility and ease of movement, making them suitable for laboratories that require frequent changes in layout or use in different locations. Typically more affordable than fixed laboratory benches, these tables can be equipped with wheels for easy transport, accommodating various tasks from experiments to collaborative work. While they provide flexibility, their stability may not match that of traditional lab benches, which could be a concern for tasks requiring precision.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Laboratory Solution
When selecting the most appropriate workspace solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the nature of their laboratory work. Laboratory bench work remains an excellent choice for settings that prioritize stability and durability. In contrast, modular workstations and mobile lab tables offer flexibility and adaptability for laboratories with evolving requirements. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each option, organizations can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and meet their unique laboratory challenges.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laboratory bench work
Understanding the essential technical properties and terminology in laboratory bench work is crucial for decision-makers involved in procurement and setup. This knowledge ensures that the right equipment is selected to meet specific laboratory needs, enhancing efficiency and safety.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Laboratory Workbenches?
-
Material Grade
Laboratory workbenches are constructed from various materials such as stainless steel, epoxy resin, and high-pressure laminate. The material grade determines the bench’s durability, resistance to chemicals, and suitability for specific tasks. For instance, stainless steel workbenches are ideal for sterile environments and chemical resistance, making them a preferred choice in pharmaceutical labs. Understanding material grades allows buyers to select benches that align with their operational requirements and regulatory standards. -
Load Capacity
The load capacity of a workbench indicates how much weight it can safely support. This specification is critical for laboratories that require the use of heavy equipment or materials. For example, a workbench with a load capacity of 20,000 pounds is suitable for industrial applications, while a lighter model may suffice for educational settings. Knowing the load capacity helps ensure that the selected bench can withstand the demands of daily operations without compromising safety. -
Height Adjustability
Height adjustability is an important feature that allows users to modify the workbench’s height for ergonomic purposes. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in environments where multiple users of varying heights operate the same equipment. Investing in height-adjustable benches can lead to improved employee comfort, reduced strain, and enhanced productivity, making it a significant consideration in procurement decisions. -
Chemical Resistance
The ability of a workbench to resist damage from chemicals is a vital property in laboratories that handle hazardous substances. Materials like phenolic resin or epoxy-coated surfaces provide superior chemical resistance, ensuring longevity and safety. Buyers should assess the types of chemicals used in their labs to select a workbench that minimizes the risk of degradation and maintains a safe working environment. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a workbench affects its cleanliness and maintenance. Smooth, non-porous surfaces are easier to clean and less likely to harbor bacteria, making them ideal for laboratories focused on hygiene, such as those in the food and beverage industry. Understanding surface finishes helps buyers choose workbenches that align with their cleanliness standards and operational protocols.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laboratory workbenches, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the source of their equipment and the quality assurance processes involved. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to procure workbenches in bulk. Understanding MOQ helps in budget planning and inventory management, ensuring that purchasing decisions align with operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. When sourcing laboratory benches, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare options, negotiate terms, and select the best suppliers based on price and service. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms used in international trade. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand the logistics and cost implications of their purchases, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
Turnaround Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In laboratory settings, fast turnaround times can be critical for maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers should inquire about suppliers’ turnaround times to ensure they can meet their project timelines. -
Customization Options
Customization options refer to the ability to tailor workbench specifications to meet specific laboratory needs. Understanding available customization can significantly impact the effectiveness of the workspace, ensuring that the bench fits seamlessly into the lab’s operational flow.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance laboratory functionality and safety.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laboratory bench work Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Laboratory Bench Work?
The laboratory bench work sector is currently influenced by several global drivers, including technological advancements, the demand for enhanced productivity, and the need for safer working environments. With a growing emphasis on research and development across various industries, particularly in healthcare, biotechnology, and education, the demand for specialized laboratory workbenches is increasing. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany) are particularly interested in customizable solutions that cater to specific laboratory needs.
Emerging trends in this sector include a shift towards modular and flexible workbench designs that can adapt to various laboratory tasks. This flexibility is crucial for organizations looking to optimize their workspace efficiency and productivity. The integration of technology, such as height-adjustable benches and smart lab workstations equipped with power outlets and data connectivity, is also gaining traction. Furthermore, a growing focus on ergonomic designs is driving the demand for workstations that enhance employee comfort and reduce strain, leading to improved productivity and lower absenteeism.
As international regulations continue to evolve, compliance with safety standards is paramount. Buyers are increasingly seeking manufacturers who can provide lab benches that meet stringent quality and safety requirements, ensuring a reliable and safe working environment.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Laboratory Bench Work?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical components of the laboratory bench work sector. Environmental impact is a significant concern, and B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials, such as recycled metals and sustainably sourced wood, in the manufacturing of lab furniture.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for manufacturers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and who uphold fair labor standards. Certifications for “green” materials, such as those from recognized environmental organizations, are becoming essential for companies aiming to enhance their sustainability profile. This trend is particularly pronounced among buyers in Europe, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly favoring sustainable practices.
Moreover, adopting sustainable lab furniture not only reduces the environmental footprint but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Durable materials and efficient manufacturing processes can result in less waste and lower energy consumption. As a result, B2B buyers are urged to consider the lifecycle of laboratory equipment and the long-term benefits of investing in sustainable solutions.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
What is the Brief Evolution of Laboratory Bench Work for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of laboratory bench work can be traced back to the early 20th century when scientific research began to gain prominence. Initially, lab benches were basic, utilitarian structures designed to support experimentation. As scientific disciplines advanced, the need for specialized workstations emerged, leading to the development of various types of lab benches tailored for specific functions.
The late 20th century saw significant technological advancements, including the introduction of modular designs and customizable features. This shift allowed laboratories to maximize space and adapt to various workflows, aligning with the increasing complexity of scientific research. Today, the focus has shifted towards ergonomic, sustainable, and high-tech solutions that meet the diverse needs of modern laboratories.
As the sector continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest trends and innovations to make strategic sourcing decisions that enhance their laboratory operations. Investing in high-quality, versatile laboratory workbenches is not just a matter of compliance or functionality; it is an integral part of fostering a culture of innovation and sustainability in the laboratory environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laboratory bench work
-
How do I ensure the laboratory workbench meets my specific requirements?
To ensure that your laboratory workbench meets specific needs, start by assessing the tasks and workflows of your laboratory. Identify the required materials, dimensions, and features such as height adjustability or specialized surfaces (e.g., chemical-resistant or ESD). Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options is crucial; provide them with detailed specifications and ask for samples or prototypes. Consider also the ergonomics and safety features to enhance user experience and productivity. -
What is the best type of laboratory workbench for chemical handling?
For chemical handling, the best type of laboratory workbench is typically one made from chemical-resistant materials, such as phenolic resin or epoxy resin. These surfaces can withstand spills and corrosive substances, ensuring safety and longevity. Additionally, look for workbenches with integrated fume hoods or local extraction systems to mitigate exposure to hazardous fumes. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers about specific chemical compatibility to ensure optimal performance. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for laboratory workbenches?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in the industry, customer reviews, and certifications. Evaluate their product range for customization capabilities and quality assurance processes. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their after-sales support, warranty, and installation services. Additionally, assess their ability to meet your timeline and budget requirements, as well as their knowledge of international shipping logistics, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Europe or the Middle East. -
What is the typical lead time for custom laboratory workbench orders?
The lead time for custom laboratory workbench orders can vary significantly based on the supplier and complexity of the design. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks from order placement to delivery. Factors influencing lead time include the availability of materials, production capacity, and shipping logistics. To minimize delays, communicate your timeline requirements clearly with the supplier and consider suppliers who offer expedited services. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for laboratory workbenches?
Minimum order quantities for laboratory workbenches can vary by supplier and the specific product. Some manufacturers may have no MOQ for standard items, while custom designs might require a higher quantity to justify production costs. When sourcing internationally, inquire about MOQs early in the negotiation process to ensure they align with your budget and project needs. Suppliers may offer flexibility for larger orders or ongoing contracts. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering from international suppliers?
Payment terms for international orders can range from upfront payment to net 30 or net 60 terms, depending on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms before finalizing the order to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, ensure that the terms comply with international trade regulations and currency exchange considerations. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for laboratory workbenches?
To ensure quality assurance, work with suppliers who adhere to recognized industry standards and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). Request detailed specifications and test reports for materials used in the workbenches. Implement a quality control plan that includes inspections at various stages of production and before shipment. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate open communication regarding quality expectations and any necessary adjustments. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing laboratory workbenches?
When importing laboratory workbenches, consider shipping methods, customs clearance, and potential duties or tariffs. Collaborate with your supplier to ensure they provide accurate shipping documentation and support with import regulations in your country. Assess the best shipping options based on your timeline and budget, whether by air or sea. Additionally, factor in local transportation arrangements to ensure seamless delivery to your facility.
Top 4 Laboratory Bench Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bench Depot – Lab Workbenches
Domain: benchdepot.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Lab Workbenches:
1. Kennedy Series – Best Seller
– Tested to 6,600 lbs
– 1.2″ Solid Wood Core
– Apron: 2″ x 1″ Tube
– Average Price: $552
2. Roosevelt Series – Economy Design
– Tested to 1,200 lbs
– 1.2″ Solid Wood Core
– Legs: .09″ Steel
– Average Price: $388
3. Hydraulic Lift Designs
– Available designs: Kennedy and Roosevelt
– Average Price: $930
4…
2. Lab Tech Supply Co – Custom Lab Benches & Workstations
Domain: labtechsupplyco.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: High-Quality Lab Bench and Lab Workstation for Industrial Use; Made in the USA; Fast Shipping Options; Custom lab benches and workstations; Modular and custom options; Work surface choices: high pressure laminate, epoxy resin, butcher block, phenolic resin, stainless steel, high density polyethylene; Designed for various laboratory applications; Height adjustability; Various drawer configurations;…
3. Fisher Scientific – Laboratory Benches and Tables
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Laboratory benches and tables designed for safe laboratory tasks and handling of reagents and samples. Features may include corrosion-resistant and vibration-resistant finishes, as well as mobile units. Available colors: Almond, Amber Stain, Auburn Stain, Black, Gray, Gray Maple, Green, Harvest Stain, Honey Stain, Light Gray, Maple, Mocha Stain, Natural Maple, Natural Stain, Oak, Oak Black, Silver…
4. LOC Scientific – Laboratory Benches & Workstations
Domain: locscientific.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Laboratory Benches & Workstations from LOC Scientific are designed for durability, adaptability, and performance. They are engineered to meet the needs of specialized industries with precision, flexibility, and long-term durability. The product range includes:
– ERGO-LINE Workbench
– Millennium II Workbench
– HD Modular Workbench
– BASICS Modular Workbench
– DIMENSION NEXT Expandable Workbenc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laboratory bench work
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Laboratory Bench Work?
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for laboratory bench work is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Buyers should prioritize customizable solutions that cater to specific laboratory needs, such as material durability, ergonomic design, and space optimization. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer a range of options—from basic workbenches to advanced modular setups—can significantly enhance laboratory functionality.

Illustrative image related to laboratory bench work
How Can International Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing Opportunities?
The global market for laboratory furniture presents unique opportunities for international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By tapping into local suppliers and manufacturers, businesses can reduce lead times and shipping costs while supporting regional economies. Engaging in a consultative purchasing process will ensure that the chosen solutions align with both current and future laboratory requirements.
What’s Next for Your Laboratory?
As you look to enhance your laboratory environment, consider reaching out to specialized suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet your specific operational demands. Invest in quality and innovation to create a workspace that promotes productivity and safety. Start your strategic sourcing journey today to position your laboratory for success in a competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.