The Definitive Guide to Hydraulic Lift System: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic lift system
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing a reliable hydraulic lift system can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With numerous options available, understanding the right fit for your specific operational needs is crucial. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding hydraulic lift systems, offering insights into various types, applications, and critical factors to consider during the purchasing process. From holed to hole-less systems, we delve into the unique advantages and limitations of each, empowering you to make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Our comprehensive resource also covers essential aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who can deliver quality and support. Additionally, we discuss cost considerations, maintenance needs, and regulatory compliance, particularly relevant for buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany. By equipping you with the necessary knowledge and actionable insights, this guide serves as a valuable tool in navigating the global market for hydraulic lift systems, enabling you to secure solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety in your projects.
Understanding hydraulic lift system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holed Hydraulic Lift | Requires deep excavation; piston extends underground. | High-rise buildings, commercial complexes | Pros: Smooth operation, higher travel distances. Cons: Expensive installation, space-intensive. |
| Hole-less Hydraulic Lift | No underground excavation; pistons located at the lift’s corners. | Low to mid-rise buildings, residential units | Pros: Easier installation, minimal site disruption. Cons: Limited travel height (20-30m). |
| Scissor Lift | Platform raises and lowers via an accordion-like mechanism. | Warehouses, construction sites | Pros: Versatile, compact design. Cons: Limited horizontal reach, requires stable ground. |
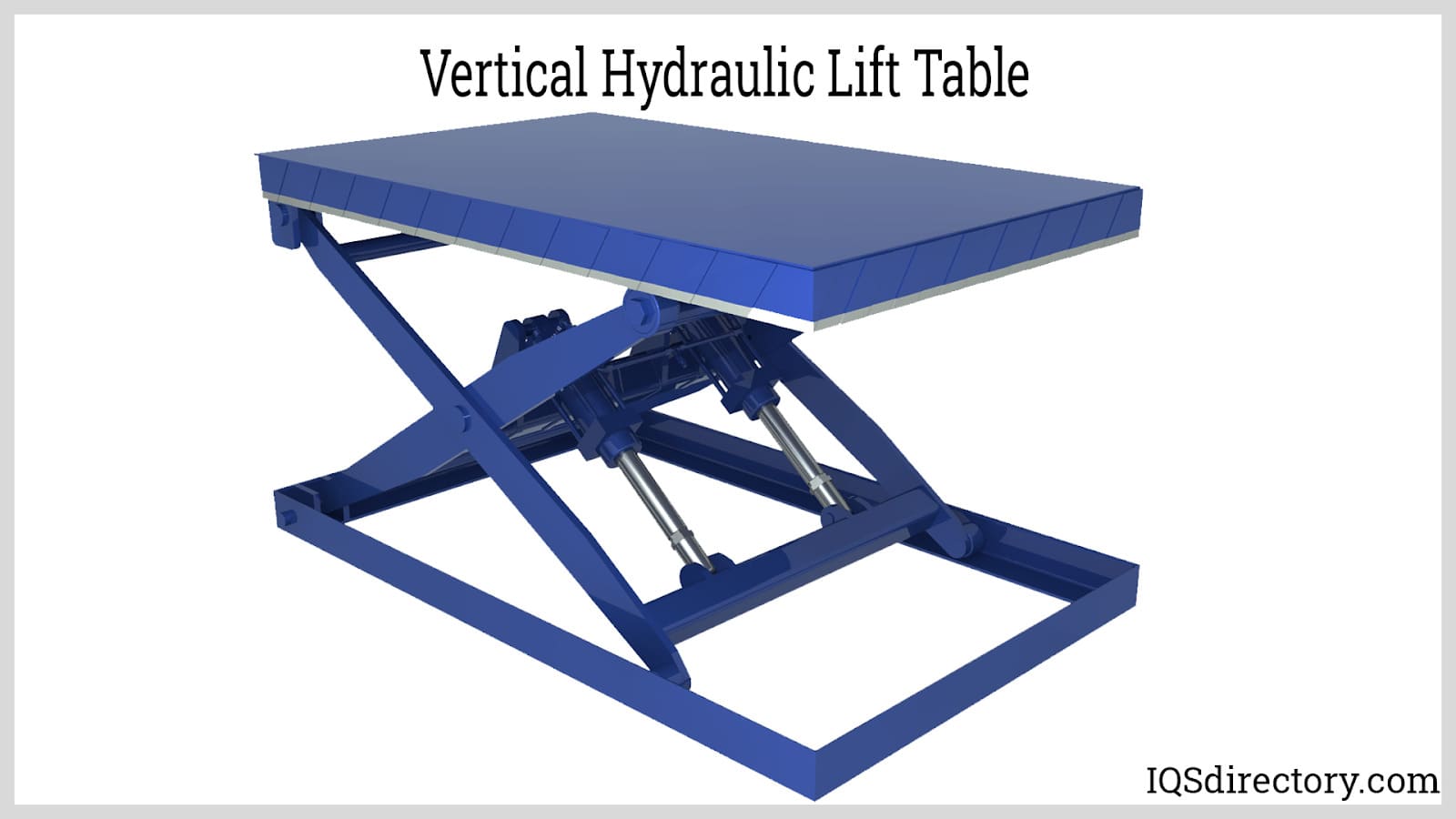
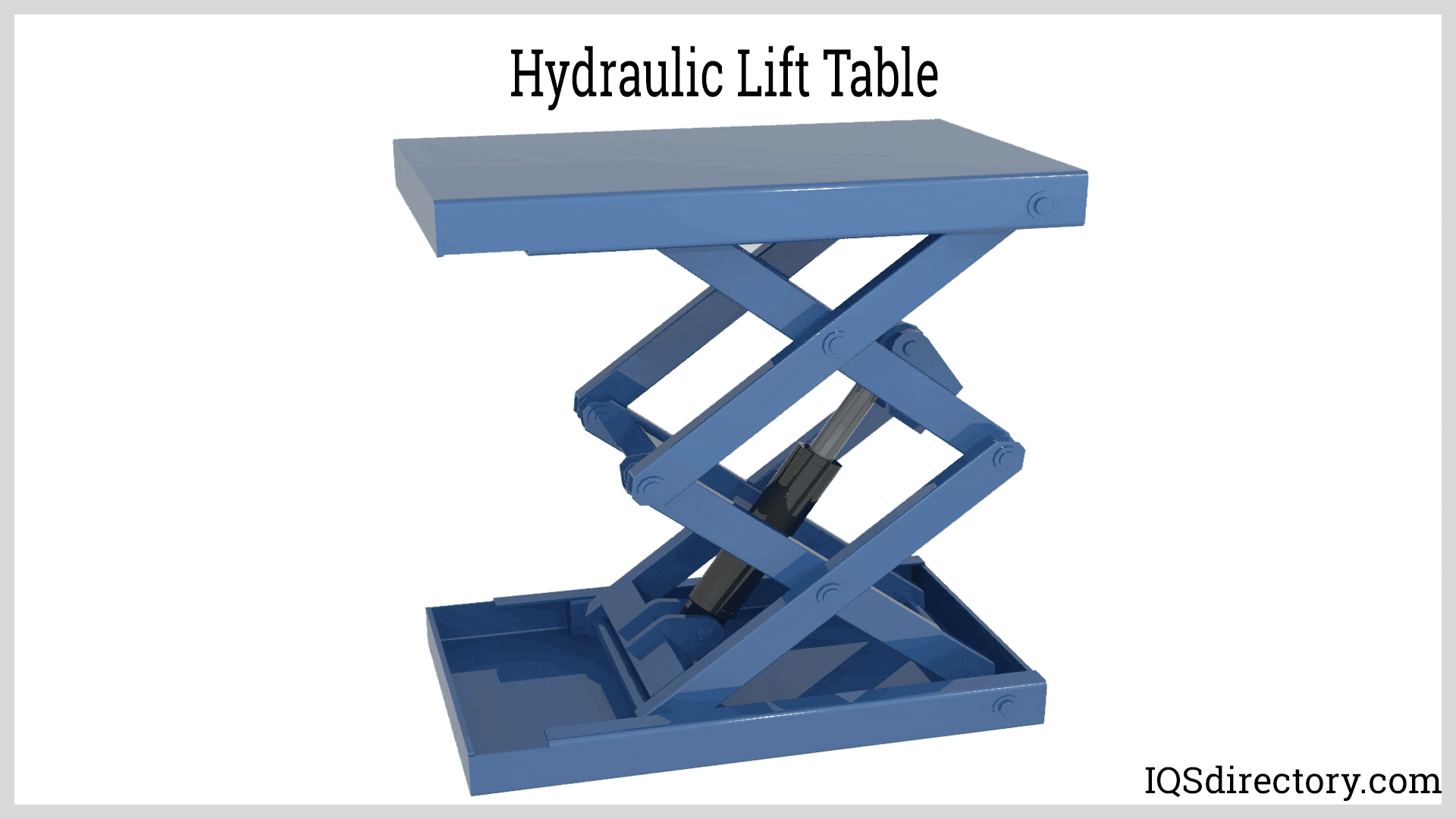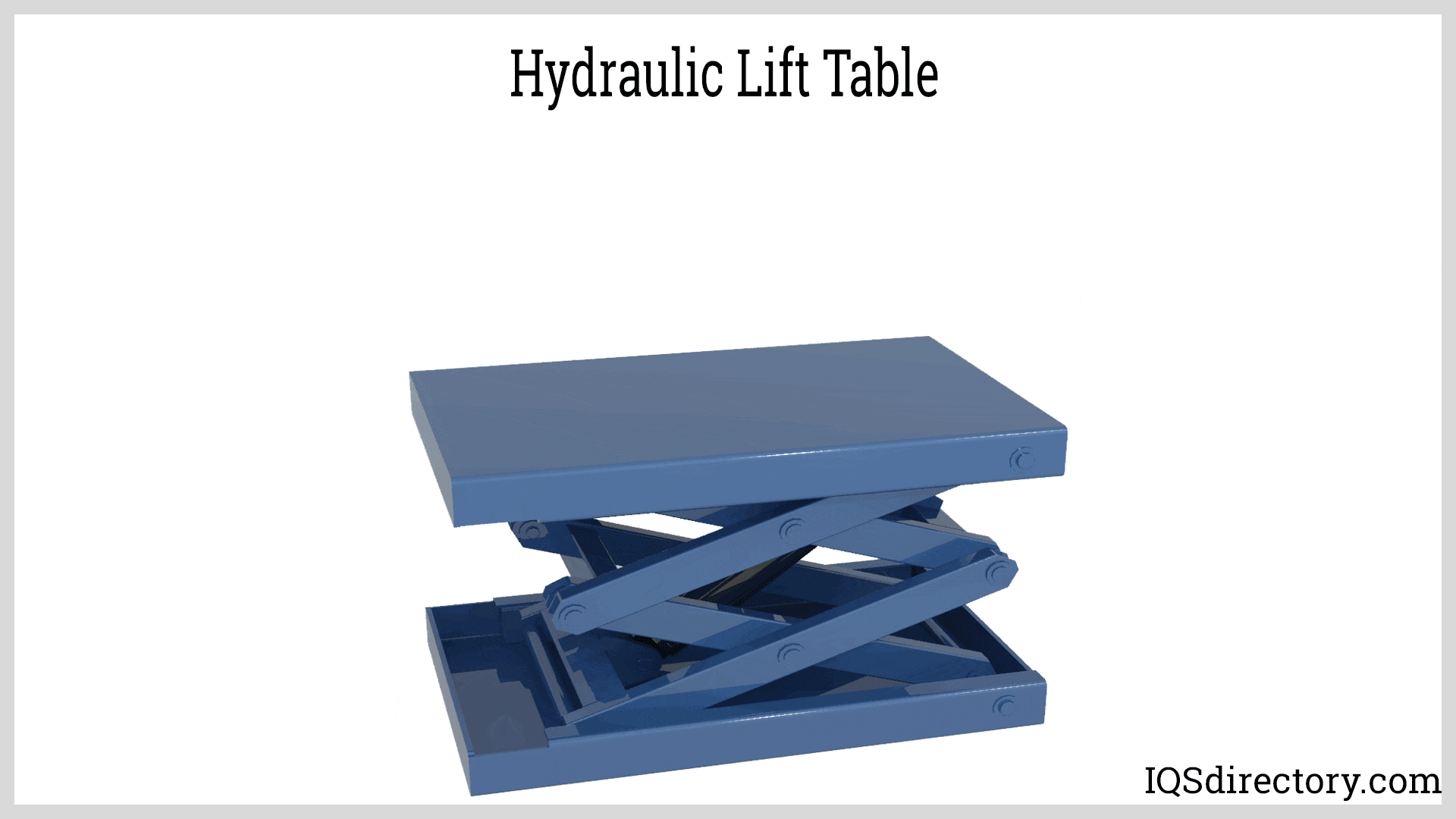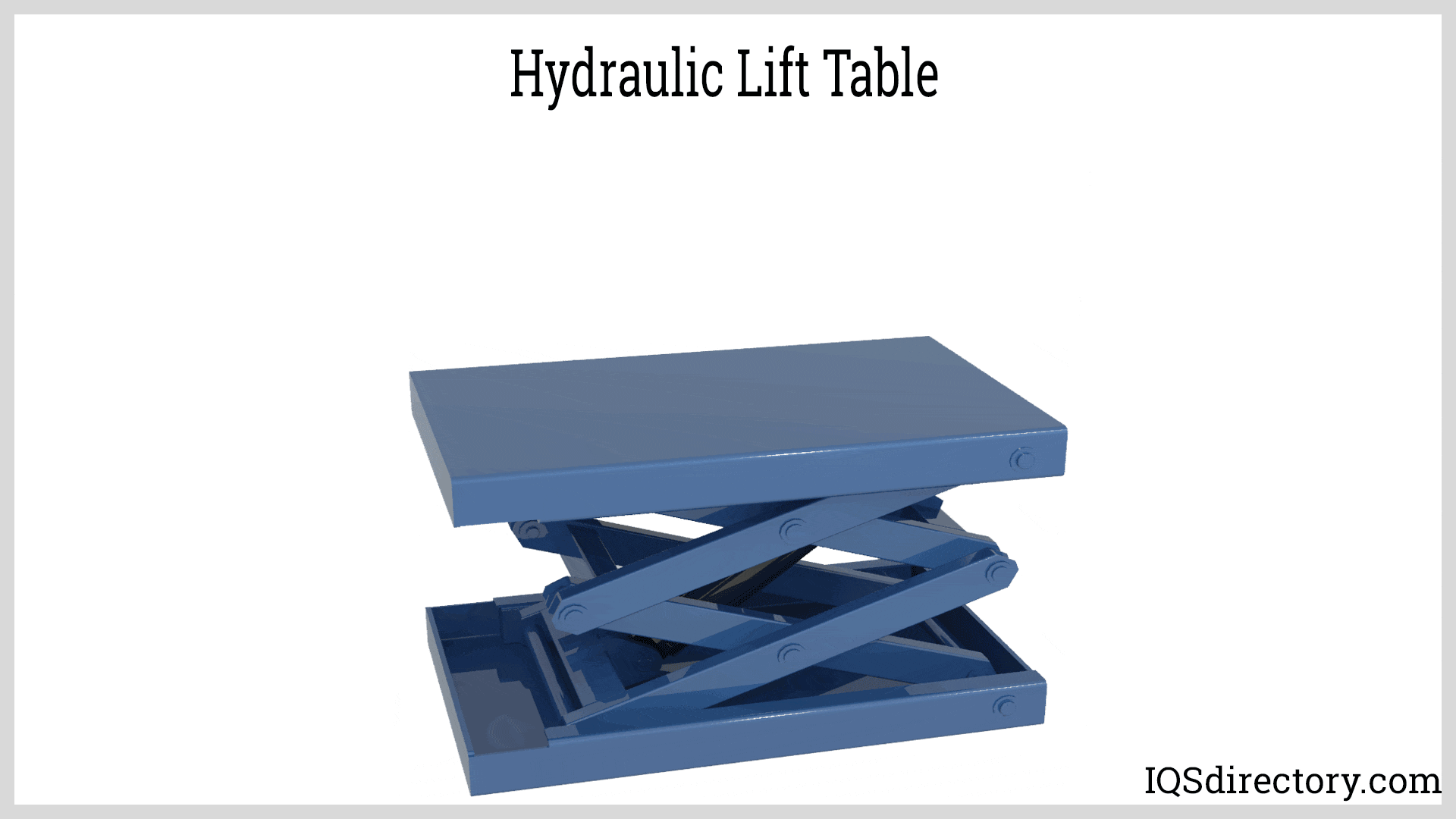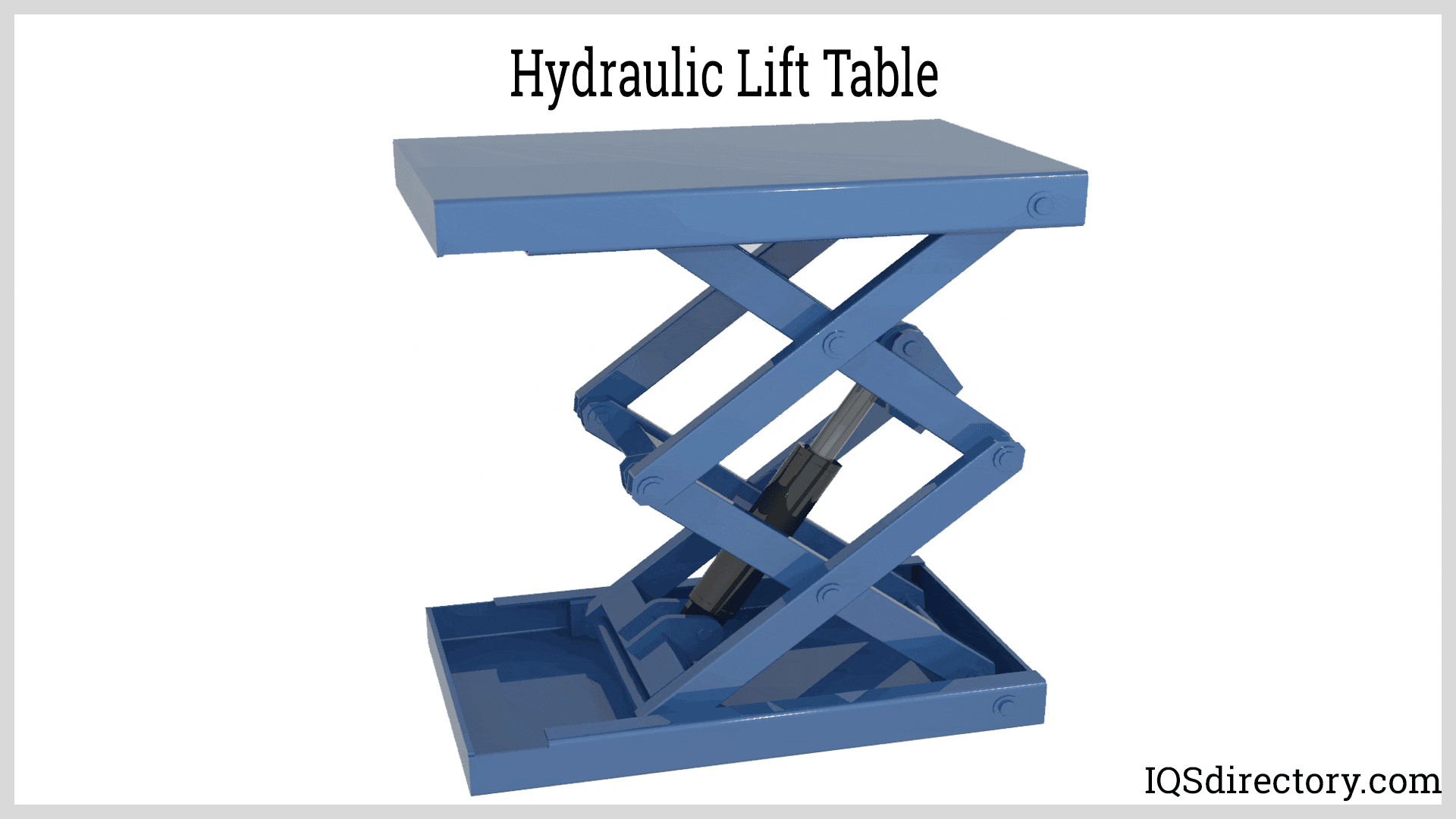
| Lift Tables | Adjustable platform for material handling and assembly tasks. | Manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: Enhances productivity, customizable heights. Cons: Requires regular maintenance for safety. |
| Electric Hoist | Powered by an electric motor, used for lifting heavy materials. | Factories, construction sites | Pros: Efficient for heavy loads, precise control. Cons: Dependent on electrical supply, can be costly. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Holed Hydraulic Lifts?
Holed hydraulic lifts utilize a piston system that extends below ground, making them ideal for high-rise buildings where stability and smooth operation are paramount. These lifts can travel greater distances, typically accommodating buildings with up to 8 floors or more. When considering this option, buyers should evaluate the feasibility of deep excavation and the associated installation costs. While they provide a reliable solution, the need for significant groundwork may limit their use in certain locations.
How Do Hole-less Hydraulic Lifts Differ in Application?
Hole-less hydraulic lifts are designed for buildings where underground excavation is impractical. The pistons are positioned at the corners of the lift car, allowing for a more straightforward installation process. These systems are typically limited to travel heights of 20-30 meters, making them suitable for low to mid-rise applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of easier installation against the limitations in travel height, particularly in urban settings where building codes may restrict lift specifications.
What Makes Scissor Lifts a Unique Option for Businesses?
Scissor lifts provide a flexible lifting solution with a platform that elevates using an accordion-like mechanism. They are commonly used in construction and maintenance work to raise personnel and equipment to required heights. While their compact design allows for easy maneuverability, they require stable ground for safe operation. Businesses should consider the specific operational needs and ensure that the scissor lift can accommodate the required load and height while maintaining safety standards.
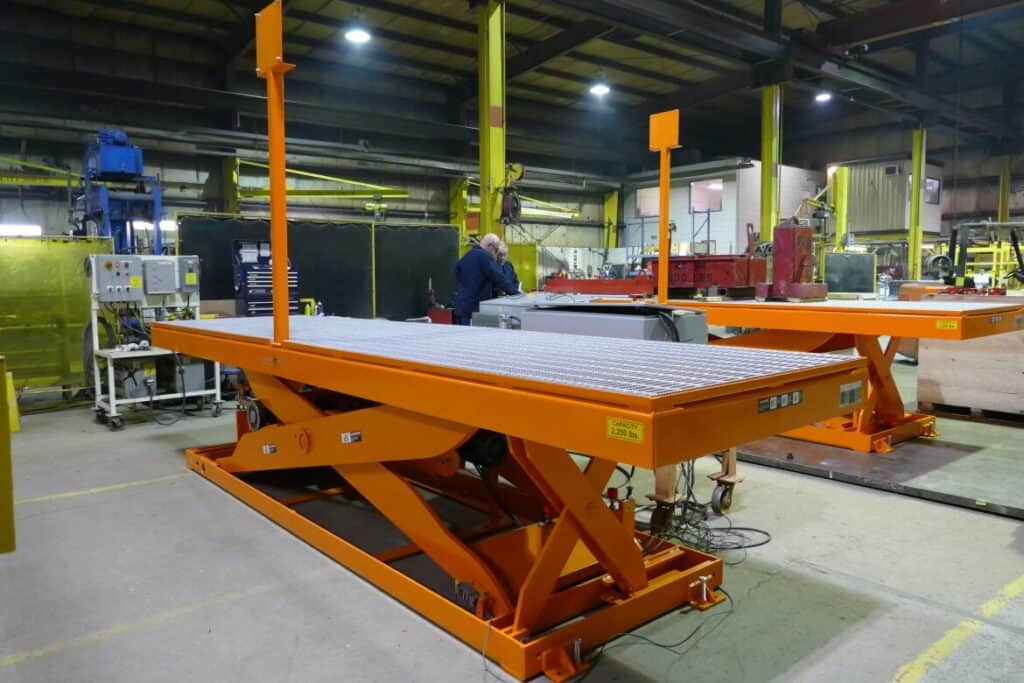
Why Choose Lift Tables for Material Handling?
Lift tables are specialized hydraulic systems designed to raise and lower materials to specific heights, enhancing productivity in manufacturing and assembly environments. They can be customized to meet various operational requirements, making them versatile for different tasks. However, regular maintenance is essential to ensure safety and performance. Buyers should assess the load capacity and height range needed for their applications, as well as the frequency of use to determine the best fit for their operations.
How Do Electric Hoists Serve Industrial Needs?
Electric hoists are powerful lifting devices that utilize an electric motor to handle heavy materials efficiently. They are widely used in factories and construction sites for their ability to lift substantial loads with precision. While their performance is excellent, they are dependent on electrical infrastructure, which may pose challenges in remote locations. Buyers should evaluate the electric hoist’s load capacity, height, and power requirements to ensure it aligns with their operational needs.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic lift system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Hydraulic Lift System | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Scissor Lifts for Elevated Work Platforms | Enhances worker safety and efficiency on job sites | Load capacity, lift height, and safety certifications |
| Manufacturing | Lift Tables for Material Handling | Streamlines production processes and reduces manual labor | Custom dimensions, weight capacity, and durability |
| Transportation and Logistics | Hydraulic Loading Docks | Optimizes loading/unloading processes for heavy goods | Compatibility with existing infrastructure and energy efficiency |
| Automotive Repair | Vehicle Lifts | Facilitates vehicle maintenance and repairs | Weight capacity, lift height, and safety features |
| Warehousing and Distribution | Pallet Jacks and Lift Trucks | Improves warehouse efficiency and product movement | Maneuverability, lifting capacity, and ease of use |
How are Hydraulic Lift Systems Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, hydraulic scissor lifts are invaluable for providing workers with safe access to elevated work areas. These lifts enable teams to perform tasks at significant heights, such as installing fixtures or conducting inspections, while minimizing the risk of falls. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying safety regulations, sourcing lifts that comply with local standards and certifications is crucial. Additionally, understanding the load capacity and height requirements specific to construction projects can lead to more efficient operations.
What Role Do Hydraulic Lift Systems Play in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing facilities utilize hydraulic lift tables to enhance productivity by enabling the easy movement and adjustment of materials at optimal heights. This reduces the physical strain on workers and accelerates assembly line processes. When sourcing lift tables, buyers should consider custom dimensions and weight capacities to meet specific production needs. Additionally, durability is critical, especially in high-usage environments, to ensure longevity and minimize maintenance costs.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
How Do Hydraulic Lift Systems Enhance Operations in Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, hydraulic loading docks are essential for efficiently moving heavy goods in and out of vehicles. These systems streamline the loading and unloading process, reducing turnaround times and improving operational efficiency. Buyers should focus on the compatibility of hydraulic systems with existing infrastructure and energy efficiency to minimize operational costs. Understanding the specific requirements of different cargo types can also lead to better sourcing decisions.
Why are Hydraulic Lift Systems Important in Automotive Repair?
Hydraulic vehicle lifts are a staple in automotive repair shops, allowing technicians to elevate vehicles for maintenance and inspection. This not only improves accessibility but also enhances safety during repairs. When sourcing vehicle lifts, it is vital to consider factors such as weight capacity, lift height, and built-in safety features. International buyers should also be aware of regional regulations regarding equipment safety and maintenance standards to ensure compliance.
How Do Hydraulic Lift Systems Improve Efficiency in Warehousing and Distribution?
In warehousing and distribution, hydraulic pallet jacks and lift trucks are key for moving products efficiently within storage facilities. These systems enhance operational efficiency by allowing quick and safe transport of goods, thereby reducing labor costs and increasing throughput. Buyers should evaluate the maneuverability and lifting capacity of these systems to ensure they meet the demands of their specific warehouse layouts. Furthermore, ease of use is essential to facilitate training and adoption among staff.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hydraulic lift system’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Installation Challenges in Limited Spaces
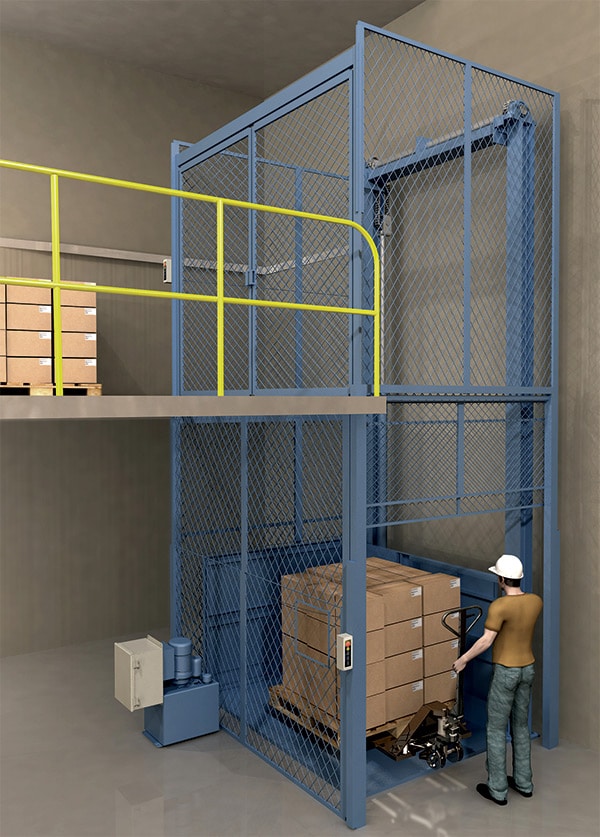
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers, particularly in urban environments, is the limitation of available space for hydraulic lift installation. Companies may find themselves in older buildings where the structural design does not accommodate a traditional hydraulic lift with a machine room. This can lead to frustration when trying to provide essential vertical transportation for goods and personnel without compromising the building’s integrity or violating local regulations.
The Solution: One viable solution is to consider machine-room-less (MRL) hydraulic lift systems. These systems are designed to fit into tighter spaces by integrating the machinery within the shaft itself, which eliminates the need for additional overhead space. When sourcing an MRL lift, it’s essential to work closely with manufacturers to ensure that the specific dimensions of the lift can accommodate your building’s design. Additionally, proper structural assessments should be conducted to verify that existing foundations can support the lift’s weight and operational demands. Engaging with local engineers familiar with hydraulic systems can help navigate building codes and optimize installation.
Scenario 2: Maintenance and Downtime Issues
The Problem: Hydraulic lifts are crucial for many businesses, especially in manufacturing and logistics. However, without regular maintenance, these systems can face unexpected downtimes due to oil leaks, valve failures, or pump issues. Such disruptions not only affect operational efficiency but can also lead to safety hazards, resulting in potential liabilities for businesses.
The Solution: To mitigate these maintenance challenges, B2B buyers should establish a proactive maintenance schedule. This includes regular inspections of hydraulic fluid levels, checking for leaks, and monitoring the condition of the pump and valve systems. Partnering with a reliable service provider that specializes in hydraulic lifts can ensure that these inspections are carried out professionally. Additionally, investing in an advanced monitoring system that alerts operators to potential issues before they escalate can significantly reduce downtime. Training staff on basic maintenance checks can also foster a culture of safety and efficiency, ensuring that the lift operates smoothly and remains compliant with safety standards.
Scenario 3: Energy Efficiency and Cost Concerns
The Problem: As businesses become more environmentally conscious, the energy consumption of hydraulic lift systems has come under scrutiny. Traditional hydraulic lifts can be less energy-efficient compared to newer alternatives, leading to higher operational costs that strain budgets. This is particularly relevant for companies in regions with high energy costs or strict sustainability mandates.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
The Solution: To address energy efficiency concerns, consider investing in hydraulic lifts that feature energy-saving technologies, such as variable speed pumps and regenerative drives. These advancements can significantly reduce energy consumption by adjusting the power used according to the load and operational requirements. When procuring hydraulic lift systems, ask manufacturers about energy performance ratings and potential energy-saving features. Additionally, conducting a lifecycle cost analysis can help in understanding the long-term savings associated with higher upfront investments in energy-efficient systems. Collaborating with energy consultants can also provide insights into optimizing your hydraulic lift operations for better sustainability outcomes, ultimately aligning with your corporate responsibility goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic lift system
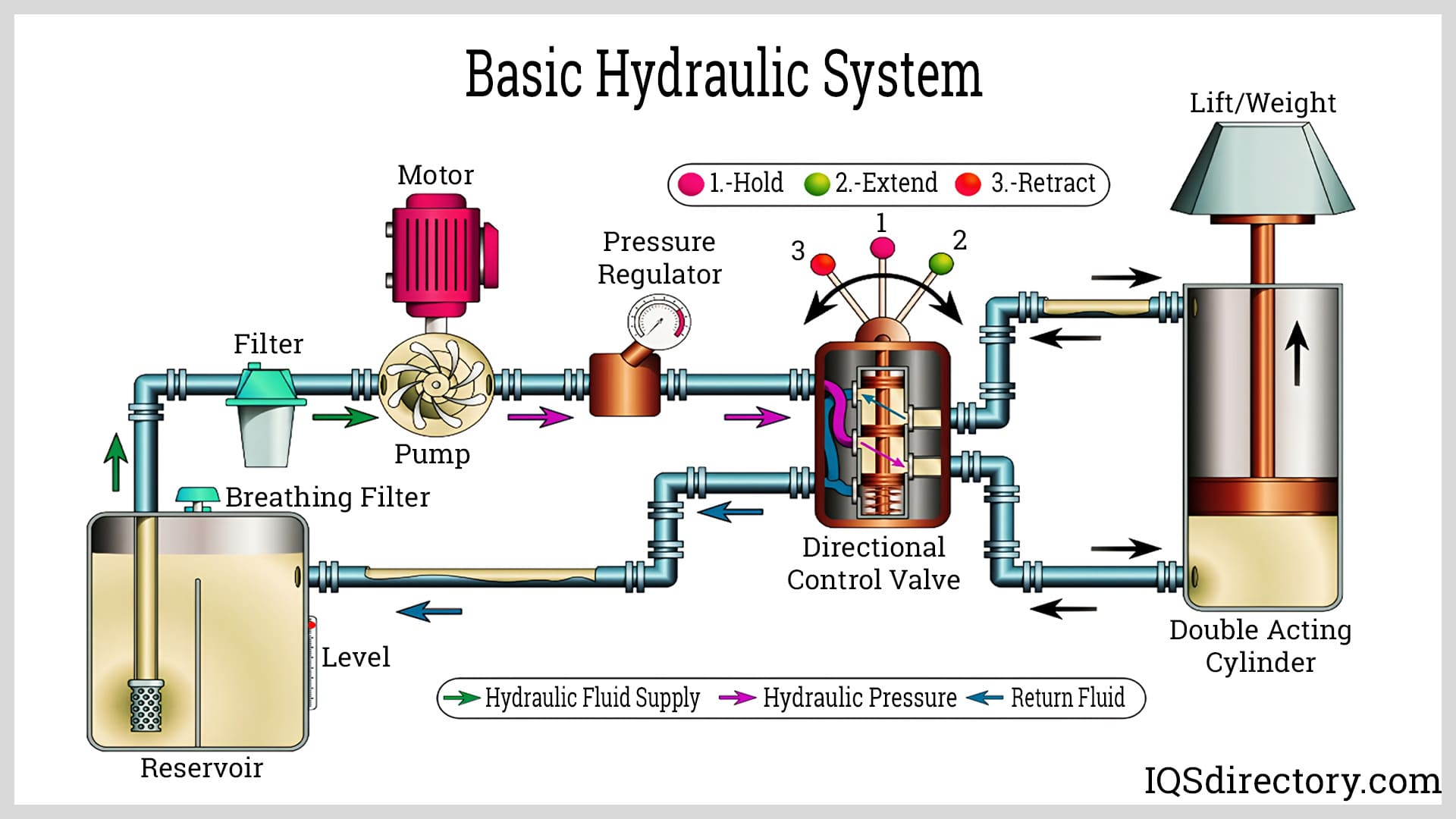
What Are the Key Materials Used in Hydraulic Lift Systems?
When selecting materials for hydraulic lift systems, it is crucial to consider their properties, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic lift systems: steel, aluminum, rubber, and hydraulic fluid.
How Does Steel Perform in Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for structural components in hydraulic lifts. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and can withstand high pressure, often exceeding 3000 psi.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of steel include its excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation under stress. However, it is heavier than other materials, which can complicate installation and maintenance. Additionally, steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used for the frame and support structures of hydraulic lifts, where strength and stability are paramount. Its compatibility with various media, including hydraulic fluids, makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Steel must comply with international standards such as ASTM in the USA, DIN in Germany, and JIS in Japan. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the steel used is sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to these standards to avoid quality issues.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for components that require mobility and ease of installation. Its temperature rating is generally lower than steel, around 150°C, and it can handle moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which simplifies installation and reduces the overall weight of the lift system. However, it has a lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often utilized in the construction of lift car frames and other non-structural components where weight reduction is beneficial. Its corrosion resistance is particularly advantageous in humid or coastal environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for aluminum that meets international standards, such as ASTM and EN in Europe. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures may affect material performance, it is essential to select aluminum alloys that can withstand local conditions.
How Important Is Rubber in Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Key Properties: Rubber is primarily used for seals and gaskets in hydraulic systems. It has excellent elasticity and can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, depending on the type of rubber.
Pros & Cons: Rubber’s flexibility and ability to form a tight seal make it ideal for preventing leaks in hydraulic systems. However, it can degrade over time due to exposure to heat, oil, and UV light, necessitating regular replacement.
Impact on Application: Rubber components are critical for maintaining the integrity of hydraulic fluid systems, as they prevent leaks that could compromise lift performance. Compatibility with various hydraulic fluids is essential to ensure longevity.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that rubber seals and gaskets comply with relevant standards such as ISO and ASTM. In regions with extreme temperatures, selecting the right type of rubber is crucial for maintaining performance.
What Is the Role of Hydraulic Fluid in Lift Systems?
Key Properties: Hydraulic fluids are specially formulated liquids that transmit power in hydraulic systems. They must have a high viscosity index, excellent lubricating properties, and resistance to thermal breakdown.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of hydraulic fluid is its ability to efficiently transfer power while lubricating system components. However, it can be sensitive to temperature changes, which may affect performance if not properly managed.
Impact on Application: The choice of hydraulic fluid directly impacts the efficiency and reliability of the lift system. It is essential to select fluids compatible with the materials used in the system to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ISO 6743 and ASTM D6158 is crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of hydraulic fluids. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding fluid disposal and environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Lift Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic lift system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lift car frames and non-structural parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets | Excellent sealing properties | Degrades over time | Low |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Power transmission | Efficient power transfer and lubrication | Sensitive to temperature changes | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, ensuring informed decisions that align with regional standards and specific application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic lift system
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Manufacturing hydraulic lift systems involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets operational and safety standards. Each stage plays a vital role in the overall quality and performance of the hydraulic lift.
Material Preparation: Which Materials Are Essential for Hydraulic Lift Systems?
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials used in hydraulic lifts include:
- Steel and Aluminum: For the structural components such as the frame, platform, and cylinder, high-strength steel or lightweight aluminum is often used to provide durability and support.
- Hydraulic Fluid: A specialized hydraulic oil is essential for smooth operation. The fluid must have specific properties such as viscosity and thermal stability to ensure optimal performance.
- Seals and Gaskets: These components are crucial for preventing leaks in the hydraulic system. They are often made from rubber or synthetic materials designed to withstand high pressure and temperature fluctuations.
After selecting the materials, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications before moving on to the forming stage.
How Are Hydraulic Lift Components Formed and Assembled?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the necessary components. Key techniques include:
- Cutting and Machining: Steel and aluminum sheets are cut to size and machined to create precise components like the cylinder, pistons, and frame.
- Welding and Fabrication: Components are welded together to form the structural framework of the lift. This step requires skilled labor to ensure strong joints that can withstand significant loads.
- Hydraulic Cylinder Assembly: The cylinder is assembled with precision, as it is the heart of the hydraulic system. This involves inserting the piston and ensuring all seals are correctly fitted to prevent leaks.
Once the components are formed, they proceed to assembly, where the entire hydraulic lift system is put together. This stage often includes:
- Integration of Electrical Components: Motors, pumps, and control systems are integrated into the lift assembly, ensuring that all electrical systems function correctly and safely.
- Final Assembly and Testing of Components: Before the lift is fully assembled, each component is tested for proper fit and functionality.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Hydraulic Lift Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and aesthetics of hydraulic lifts. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo galvanization or powder coating to protect against corrosion, especially for lifts installed in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
- Quality Control Inspections: After finishing, each component is inspected for defects. This includes visual inspections and measurements to ensure compliance with specifications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Quality assurance is paramount in manufacturing hydraulic lift systems. Various international and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining quality throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards globally, applicable across various industries, including lift manufacturing. It emphasizes a systematic approach to managing processes and ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
Additionally, hydraulic lifts must comply with specific safety and performance standards, such as:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, ensuring they meet safety and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for lifts used in industrial settings, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply to hydraulic systems operating in oil and gas sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Hydraulic Lift Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring that each hydraulic lift system meets safety and performance standards. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before being used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, components are regularly tested and inspected. This may involve dimensional checks, functional tests, and visual inspections to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the hydraulic lift is fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes testing the hydraulic system for leaks, checking the operation of safety mechanisms, and verifying compliance with all relevant standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Hydraulic Lift Quality?
Testing methods are crucial in validating the performance and safety of hydraulic lift systems. Common testing methods include:
- Hydraulic Pressure Testing: This involves pressurizing the hydraulic system to ensure it can operate safely under maximum load conditions without leaks.
- Load Testing: The lift is tested with weights that exceed its rated capacity to ensure it operates correctly under stress.
- Functional Testing: All operational features, including emergency systems, are tested to ensure they function as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential to ensure reliable and safe hydraulic lift systems. Consider the following strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from tests and inspections.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control systems and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific quality control nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations and standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local laws and international standards relevant to their markets.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication and expectations regarding quality standards and delivery timelines.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: International shipping may introduce risks that affect quality, such as damage during transport. Buyers should consider suppliers who have robust logistics and handling practices.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for hydraulic lift systems is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, assembly techniques, quality control checkpoints, and relevant standards, buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hydraulic lift system’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring hydraulic lift systems. By following these steps, you will ensure that your sourcing process is efficient, effective, and aligned with your operational requirements. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, these actionable insights will help you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search for a hydraulic lift system, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the lift’s intended use, load capacity, travel height, and speed. Understanding these specifications will help you narrow down your options and communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
- Consider environmental factors: Assess the location and conditions where the lift will be installed, such as temperature extremes or humidity levels, which can impact system performance.
- Identify compliance requirements: Ensure that your specifications adhere to local and international safety standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in hydraulic lift systems. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry.
- Utilize industry directories: Resources such as IQS Directory or local trade associations can provide a list of reputable suppliers.
- Check online reviews and case studies: This will give you insight into the reliability and performance of their products.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
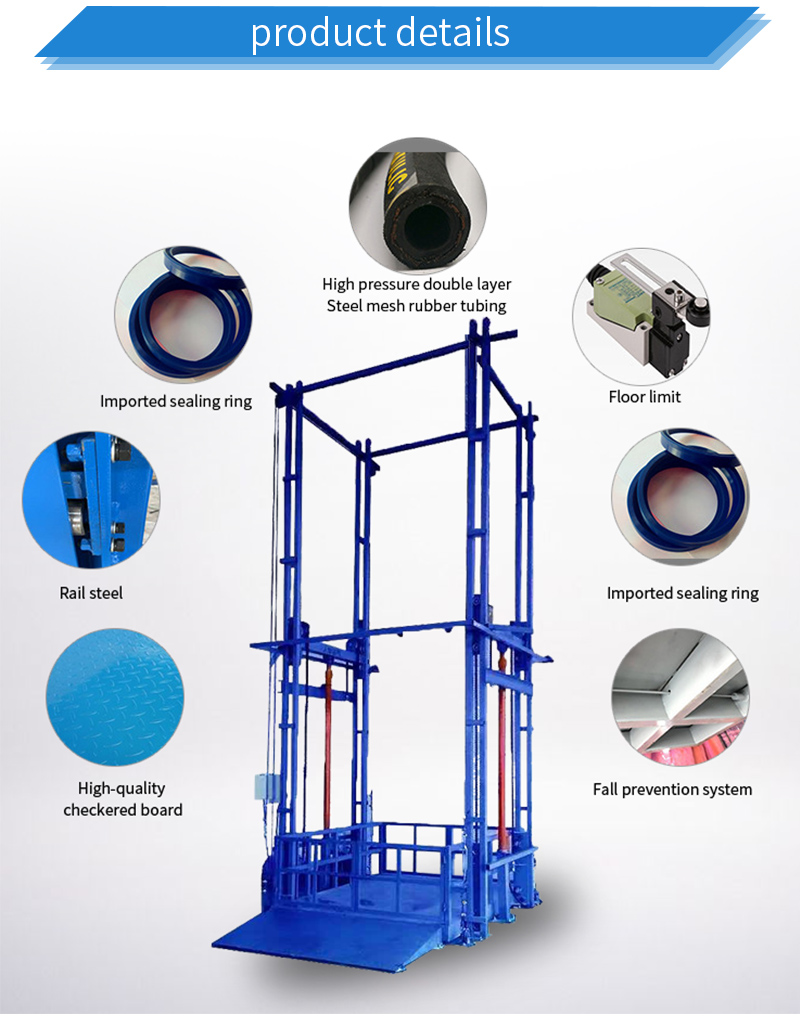
Before making a commitment, verify the certifications and quality standards of your shortlisted suppliers. This is crucial for ensuring compliance with safety regulations and industry standards.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
- Look for ISO certifications: Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate a commitment to quality management.
- Check for local compliance: Ensure that the supplier meets specific regional regulations, which may vary by country.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that include pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information. This will facilitate a comparative analysis.
- Examine total cost of ownership: Look beyond initial pricing to consider installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the lift’s lifespan.
- Assess warranty and support options: A robust warranty and customer support can save you significant costs and downtime in the long run.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits and Inspections
If feasible, arrange site visits to the suppliers’ facilities. This will allow you to assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and overall professionalism.
- Inspect existing installations: Talk to current customers about their experiences with the supplier’s products and services.
- Evaluate production processes: Understanding how the lifts are manufactured can give insights into potential quality issues.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of your purchase. This is a critical step to ensure that you receive the best value for your investment.
- Clarify payment terms: Discuss payment schedules and conditions to avoid misunderstandings later.
- Include service agreements: Ensure that the contract includes service and maintenance provisions for the hydraulic lift system.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
After securing your hydraulic lift, plan for installation and operator training. Proper installation and training are vital for ensuring safe and efficient operation.
- Schedule a site assessment: Have the supplier conduct a pre-installation assessment to identify any site-specific considerations.
- Arrange training sessions: Ensure that your staff receives comprehensive training on the lift’s operation and safety protocols.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to source a hydraulic lift system that meets your specific needs while ensuring compliance, safety, and reliability.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic lift system Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing factors associated with hydraulic lift systems is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will help buyers make informed decisions and optimize their sourcing strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Hydraulic Lift Systems?
The cost of hydraulic lift systems is influenced by several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include high-quality steel for the frame and components, hydraulic fluid, and electronic parts. The choice of materials can significantly impact durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the manufacturing and installation processes. Skilled labor is required for assembly and maintenance, which can vary based on regional labor market conditions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities, which can fluctuate depending on the production scale and location.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized tools and molds can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs are typically amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with safety standards and certifications requires investment in QC processes. This is critical for maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, are vital considerations, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and import duties can affect overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely based on market competition, brand reputation, and the perceived value of the hydraulic lift system.
What Influences Pricing for Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic lift systems:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it essential to evaluate minimum order quantities (MOQ).
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as size, weight capacity, and additional safety mechanisms can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of premium versus standard materials can affect pricing. Higher-quality materials typically result in longer-lasting products but at a higher initial cost.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international safety and quality standards may come with a premium price tag. Buyers should verify certifications relevant to their region to ensure compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and customer support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international purchases. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, risk, and insurance, which can significantly impact total expenses.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
To navigate the complexities of pricing and ensure cost efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. A clear understanding of mutual expectations can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and pricing fluctuations. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them identify the right time to purchase.
-
Consider Regional Variations: Pricing may differ significantly between regions. For instance, buyers in Europe may face different regulatory costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can foster trust and lead to better pricing and service agreements over time.
Conclusion
Hydraulic lift systems are a significant investment for businesses, and understanding their cost structure and pricing influencers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By considering the outlined cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation tips, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve better overall value. Always remember that indicative prices may vary based on specific project requirements and market conditions, making thorough research and strategic planning imperative.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hydraulic lift system With Other Solutions
When evaluating lift systems for commercial or industrial applications, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to hydraulic lifts. Each technology has distinct advantages and disadvantages that cater to different operational needs and environments. This analysis will compare hydraulic lift systems with traction lifts and scissor lifts, both of which are popular alternatives in various sectors.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
| Comparison Aspect | Hydraulic Lift System | Traction Lift System | Scissor Lift System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Smooth operation; max height 6-8 floors | Faster speeds; higher travel | Limited to lower heights; stable |
| Cost | Generally lower installation costs | Higher initial costs | Moderate costs; versatile use |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space for machinery | Requires overhead space | Easily transportable; minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Regular oil checks needed | Requires cable maintenance | Simple maintenance; easy access |
| Best Use Case | Low to mid-rise buildings | High-rise buildings | Construction sites; maintenance tasks |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traction Lifts Compared to Hydraulic Lifts?
Traction lifts utilize a system of cables and pulleys, which allows for faster travel speeds and a higher lifting capacity compared to hydraulic lifts. They are suitable for buildings with more than eight floors and can cover greater distances. However, they require more overhead space for installation, which may not be feasible in all buildings. The initial installation cost is typically higher due to the complexity of the system and the need for additional structural support. Maintenance involves regular inspections of cables and pulleys, which can lead to higher long-term costs.
How Do Scissor Lifts Compare with Hydraulic Lifts in Terms of Functionality?
Scissor lifts are primarily used for temporary access to heights and are popular in construction and facility maintenance. They operate on a different principle, using a scissor mechanism that provides vertical lifting. While they are highly maneuverable and can be easily transported between job sites, their lifting height is limited compared to hydraulic lifts. Scissor lifts are cost-effective for short-term projects but may lack the durability and continuous use capability of hydraulic systems. Maintenance is relatively simple, requiring regular checks of hydraulic systems and battery power.
How Should B2B Buyers Decide Between These Lift Systems?
Choosing the right lift system involves assessing specific project requirements, including building height, load capacity, space availability, and budget constraints. Hydraulic lifts are an excellent choice for low to mid-rise buildings where space is limited and cost-effectiveness is a priority. For high-rise applications requiring speed and efficiency, traction lifts may be more appropriate, despite their higher costs and space requirements. Scissor lifts serve well in temporary applications where flexibility and mobility are paramount. By carefully evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can select the most suitable lift solution for their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic lift system
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Lift Systems?
Understanding the technical specifications of hydraulic lift systems is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making investment decisions. Here are some essential properties that should be considered:
-
Load Capacity
The load capacity indicates the maximum weight a hydraulic lift can safely carry. This specification is vital for ensuring that the lift can handle the intended loads without compromising safety or performance. Buyers should assess their specific operational needs to choose a lift that meets or exceeds these requirements. -
Travel Height
The travel height refers to the vertical distance the lift can cover. Hydraulic lifts typically have limitations, with holed systems capable of reaching higher than hole-less variants. Understanding travel height is essential for applications in multi-story buildings or specific industrial settings, ensuring that the lift aligns with building design and user requirements. -
Speed of Operation
Measured in meters per second (m/s), the speed of operation indicates how quickly a lift can move between floors. Hydraulic lifts generally operate at slower speeds compared to traction lifts, usually not exceeding 1 m/s. This characteristic is important for applications where efficiency and quick access are priorities, influencing the overall workflow of operations. -
Power Requirements
This specification outlines the electrical or hydraulic power needed to operate the lift effectively. Knowing the power requirements helps businesses assess energy consumption and operational costs. It also aids in planning for adequate electrical supply and maintenance needs, particularly in regions with variable power availability. -
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of hydraulic lifts, such as steel or aluminum, impact durability and maintenance needs. Higher-grade materials may offer better corrosion resistance and strength, which is particularly important in harsh environments. Buyers should consider local conditions when evaluating material grades to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Safety Features
Safety features, such as emergency stop buttons, backup power systems, and overload sensors, are critical for ensuring safe operation. Understanding these features is essential for compliance with local regulations and for providing peace of mind to operators and users.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know in the Hydraulic Lift Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation processes. Here are some key terms relevant to hydraulic lift systems:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the hydraulic lift industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are purchasing quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of products a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers looking to manage inventory and budget constraints. Knowing the MOQ can influence procurement strategies, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. For hydraulic lift systems, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and detailed proposals tailored to their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. In the hydraulic lift industry, lead times can vary significantly based on manufacturing and shipping processes. Buyers should factor lead times into project timelines to avoid delays in installation. -
Certification Standards
These are regulatory or industry standards that hydraulic lifts must meet to ensure safety and performance. Familiarity with relevant certification standards (such as ISO or EN standards) can help buyers ensure compliance and quality assurance in their procurement processes.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and ensure that their hydraulic lift systems meet operational needs and regulatory standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hydraulic lift system Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Hydraulic Lift System Sector?
The hydraulic lift system market is experiencing significant growth, driven by urbanization, industrial expansion, and increasing demand for efficient vertical transportation solutions. Global trends indicate a rising need for energy-efficient and space-saving lift systems, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, where rapid urban development is underway. In regions like the Middle East, particularly Saudi Arabia, mega construction projects and smart city initiatives are further accelerating the demand for hydraulic lifts.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Technological advancements are also shaping the market. Innovations such as machine-room-less (MRL) hydraulic lifts are gaining traction due to their compact design, making them suitable for urban settings with limited overhead space. Additionally, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring is becoming increasingly popular, allowing businesses to optimize operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the varying regulatory standards across regions, particularly in Europe, where stringent safety and environmental regulations dictate lift design and installation. Staying informed about these regulations and their implications on sourcing can provide a competitive edge.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Hydraulic Lift System Sector?
Sustainability has become a central focus for businesses across all sectors, and the hydraulic lift system industry is no exception. The environmental impact of hydraulic lifts primarily stems from the hydraulic fluids used, which can be hazardous if not managed properly. Therefore, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who utilize eco-friendly hydraulic fluids and materials that comply with environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Ethical sourcing is crucial in establishing a responsible supply chain. B2B buyers should seek manufacturers that adhere to ethical labor practices and sustainable sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can serve as benchmarks for assessing a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, as global markets shift toward sustainable practices, buyers should consider the lifecycle of hydraulic lift systems, from production through to end-of-life disposal. Opting for products that can be recycled or repurposed helps mitigate environmental impact and aligns with corporate sustainability goals. By prioritizing these factors, companies not only enhance their brand image but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of Hydraulic Lift Systems?
The hydraulic lift system has a rich history that dates back to the early 19th century when it was first developed for industrial applications. Utilizing Pascal’s principle of fluid dynamics, the hydraulic lift provided a safe and efficient means of elevating heavy loads, revolutionizing industries such as construction and manufacturing. Over the decades, advancements in technology led to the development of more compact, reliable, and energy-efficient systems.
In recent years, the hydraulic lift sector has adapted to meet modern demands for sustainability and efficiency, evolving from basic mechanical systems to sophisticated, integrated solutions that leverage digital technology. The focus has shifted toward creating systems that not only meet operational needs but also align with broader environmental and ethical standards, marking a significant transformation in the industry.
Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions, as it highlights the importance of selecting suppliers that are not only technologically advanced but also committed to sustainability and ethical practices.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic lift system
-
1. How do I choose the right hydraulic lift system for my business?
Selecting the right hydraulic lift system depends on several factors, including the building’s height, available space, and intended use. Consider whether you need a holed or hole-less system based on excavation capabilities. Additionally, assess the lift’s load capacity and speed requirements. It’s also wise to evaluate your budget and long-term maintenance costs. Engaging with a supplier who can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific operational needs can facilitate a more informed decision. -
2. What are the key components to look for in a hydraulic lift system?
When evaluating hydraulic lift systems, focus on essential components like the piston and cylinder (ram), oil reservoir, pump, motor, and valve. Ensure that the materials used are of high quality for durability and reliability. Check for features such as machine-room-less designs for space efficiency and energy-efficient pumps. It’s also vital to inquire about the safety mechanisms, including emergency lowering systems and overload protection, to ensure the lift operates safely under all conditions. -
3. What are the common applications of hydraulic lifts in different industries?
Hydraulic lifts are versatile and widely used across various industries. Common applications include low to mid-rise buildings for passenger transport, warehouses for material handling, and construction sites for equipment mobility. They are also utilized in automotive workshops for vehicle lifts and in hospitals for patient transportation. Understanding the specific needs of your industry will help you identify the most suitable hydraulic lift type for your operations. -
4. How can I ensure the supplier is reliable and meets international standards?
To vet suppliers effectively, research their reputation by checking customer reviews and testimonials. Ensure they have relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate compliance with international quality management systems. It’s beneficial to request references from previous clients and inquire about their experience with after-sales support. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes firsthand. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for hydraulic lift systems?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the hydraulic lift system. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for custom or standard units, while others may have set quantities based on production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and negotiate terms that align with your business requirements, especially if you are a smaller operation or starting a new project. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing hydraulic lifts?
Payment terms for hydraulic lift purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms may include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or extended payment plans, especially for larger orders. Always clarify the payment schedule, currency, and any applicable taxes or tariffs before finalizing the agreement to avoid surprises. -
7. How do I handle logistics and shipping for hydraulic lifts internationally?
International shipping for hydraulic lifts requires careful planning. Collaborate with your supplier to understand the shipping methods they offer and ensure compliance with local regulations in your destination country. Consider engaging a freight forwarder who specializes in heavy machinery to facilitate smooth logistics, including customs clearance. Additionally, confirm the estimated delivery timeline and any associated costs to budget effectively and avoid delays in your project timeline. -
8. What maintenance practices are essential for hydraulic lift systems?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and safety of hydraulic lift systems. Key practices include checking for oil leaks, monitoring oil quality, and inspecting the pump and valves for any signs of wear or malfunction. Schedule routine professional inspections to ensure all components function optimally and comply with safety standards. Keeping the machine room cool and free of debris will also help maintain efficient operation. Establishing a maintenance schedule with your supplier can ensure your lift remains in top condition.
Top 6 Hydraulic Lift System Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Hydraulic Lifts
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic lifts are mechanisms designed to elevate objects using force generated through liquid pressure within a cylinder. They operate based on Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied to an incompressible fluid is transmitted evenly throughout the liquid. Key components include hydraulic circuits, hydraulic pumps (gear, vane, or piston), hydraulic motors, hydraulic cylinders (single-act…
2. KW Suspensions – HLS Hydraulic Lift System
Domain: kwsuspensions.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: KW HLS Hydraulic Lift System offers adjustable ride height for improved ground clearance. It is designed for performance vehicles and can be integrated with various KW coilover kits. The system features a hydraulic pump that raises the vehicle’s suspension by up to 45mm at the push of a button, allowing for better maneuverability over obstacles. The HLS system is compatible with both street and tr…
3. Ergoswiss – Hydraulic Lifting Systems
Domain: ergoswiss.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic lifting systems are single-action hydraulic systems consisting of cylinders, linear units, or table legs, driven by a hydraulic pump. They operate synchronously through flexible tubing and can be powered by a hand crank or electric drive unit. These systems are designed for height-adjustable workplaces in various sectors including industry, assembly, machinery, and furniture manufacturin…
4. SUSPA® – Movotec Lift System
Domain: suspa.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic adjustment systems from SUSPA® for the industrial sector include the Movotec lift system, which consists of cylinders and a pump driven by a hand crank or electric motor. The systems are designed for retrofitting existing work tables to make them height-adjustable. Key product offerings include: 1. Bolt-On System with Hand Crank: – Kit for retrofitting – Includes pump with hand crank, fo…
5. Auto Body Toolmart – Vehicle Lifts
Domain: autobodytoolmart.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Vehicle Lifts – Hydraulic Car Lifts – Auto Body Toolmart offers various types of vehicle lifts including Two-Post Lifts, Four-Post Lifts, Scissor Lifts, Alignment Lifts, and Parking Lifts, along with Lift Accessories.
6. Unidex – Hydraulic Lifts
Domain: unidex-inc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic lifts handle heavy and bulky loads across various applications such as construction, aerospace, automotive, industrial, marine, and mining. They operate using hydraulic cylinders, which can be single acting, double acting, or telescoping. Key components include a rod, piston, cylinder body, caps, seals, and a pump. Unidex offers a variety of hydraulic lifts including table lifts, aircraf…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic lift system
In the competitive landscape of hydraulic lift systems, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of hydraulic lift technologies, such as holed and hole-less systems, empowers decision-makers to select the best solutions tailored to their specific needs. The cost-effectiveness, reliability, and safety features of hydraulic lifts make them an attractive option for various applications across diverse industries.
Moreover, the importance of regular maintenance cannot be overstated; ensuring optimal performance can significantly extend the lifespan of hydraulic systems. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including installation and ongoing maintenance services. This strategic partnership not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates potential risks associated with equipment failure.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, the demand for efficient lifting solutions will rise. Now is the time for international buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to identify reputable suppliers and stay ahead of the competition. By investing in high-quality hydraulic lift systems, businesses can enhance their operational capabilities and drive future growth. Reach out to industry experts today to explore tailored solutions that meet your unique lifting requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic lift system
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.