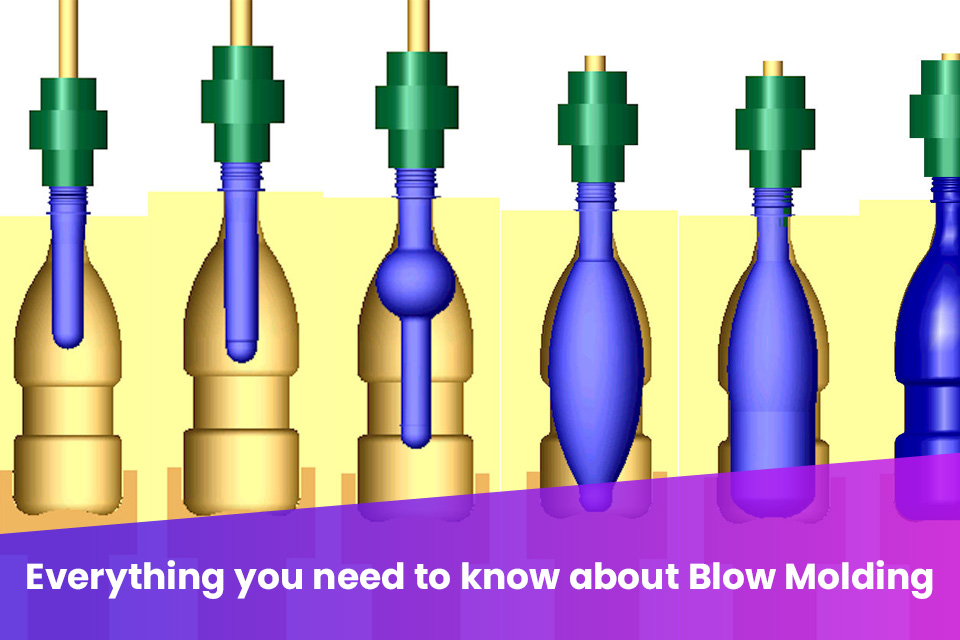
The Definitive Guide to How To Make Blow Molds: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make blow molds
Navigating the complexities of sourcing blow molds can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially in rapidly evolving markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding how to make blow molds not only involves technical know-how but also requires strategic insight into supplier capabilities, material selection, and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide addresses these crucial aspects, empowering businesses to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the various types of blow molding processes, including extrusion and injection molding, and their applications in industries ranging from packaging to automotive manufacturing. You will learn how to effectively vet suppliers to ensure quality and reliability, analyze the total cost of ownership, and identify the best materials for your production needs.
By arming yourself with this knowledge, you can streamline your sourcing process, minimize production costs, and enhance product quality. This guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers looking to navigate the global market for blow molds, ultimately driving business success in competitive landscapes like those found in Nigeria and Brazil. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the industry, this guide will provide the insights necessary to elevate your sourcing strategy.
Understanding how to make blow molds Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | Continuous production; parison formed by extrusion | Bottles, containers, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs; versatile designs. Cons: Limited to simpler shapes. |
| Injection Blow Molding (IBM) | Combines injection molding and blow molding | High-precision bottles, medical devices | Pros: High accuracy; excellent surface finish. Cons: Slower than EBM; higher tooling costs. |
| Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) | Uses preforms; stretch for enhanced strength | Beverage bottles, jars | Pros: Lightweight yet strong; good for high-volume production. Cons: More complex setup. |
| Reheat Stretch Blow Molding (RSBM) | Utilizes preforms reheated before inflation | PET bottles for soft drinks | Pros: Ideal for high clarity; good for complex shapes. Cons: Requires additional heating equipment. |
| Multi-layer Blow Molding | Creates products with multiple material layers | Food packaging, chemical containers | Pros: Improved barrier properties; customization. Cons: More expensive; complex machinery needed. |
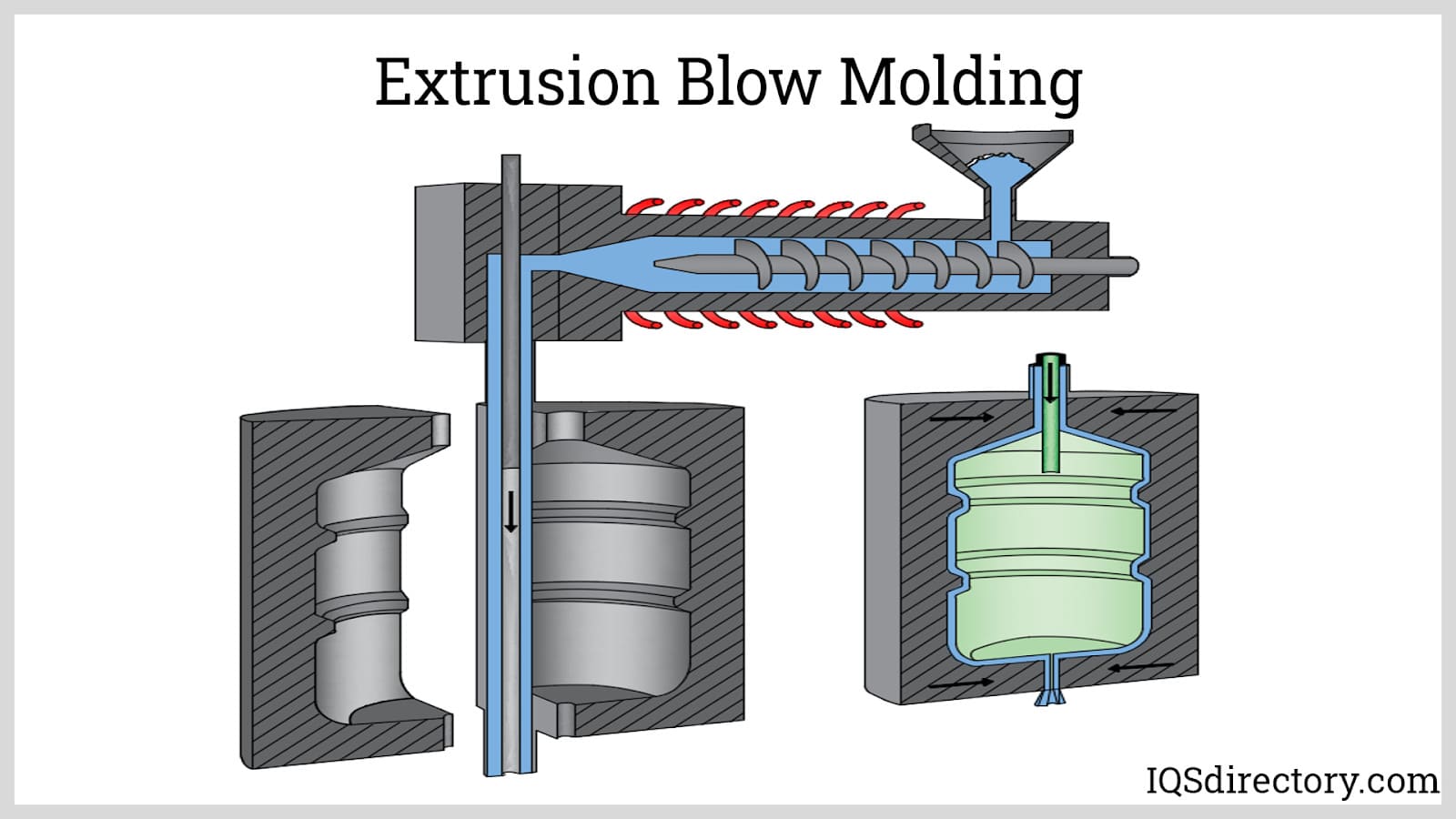
What Are the Key Characteristics of Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)?
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) is characterized by its continuous production process, where plastic is extruded into a parison that is then inflated within a mold. This method is particularly suitable for producing hollow containers and parts in high volumes, making it ideal for industries such as beverage packaging and automotive components. B2B buyers should consider the simplicity of design, cost-effectiveness for large runs, and the versatility of materials used in EBM. However, the limitations in producing complex shapes might require buyers to evaluate their design needs carefully.
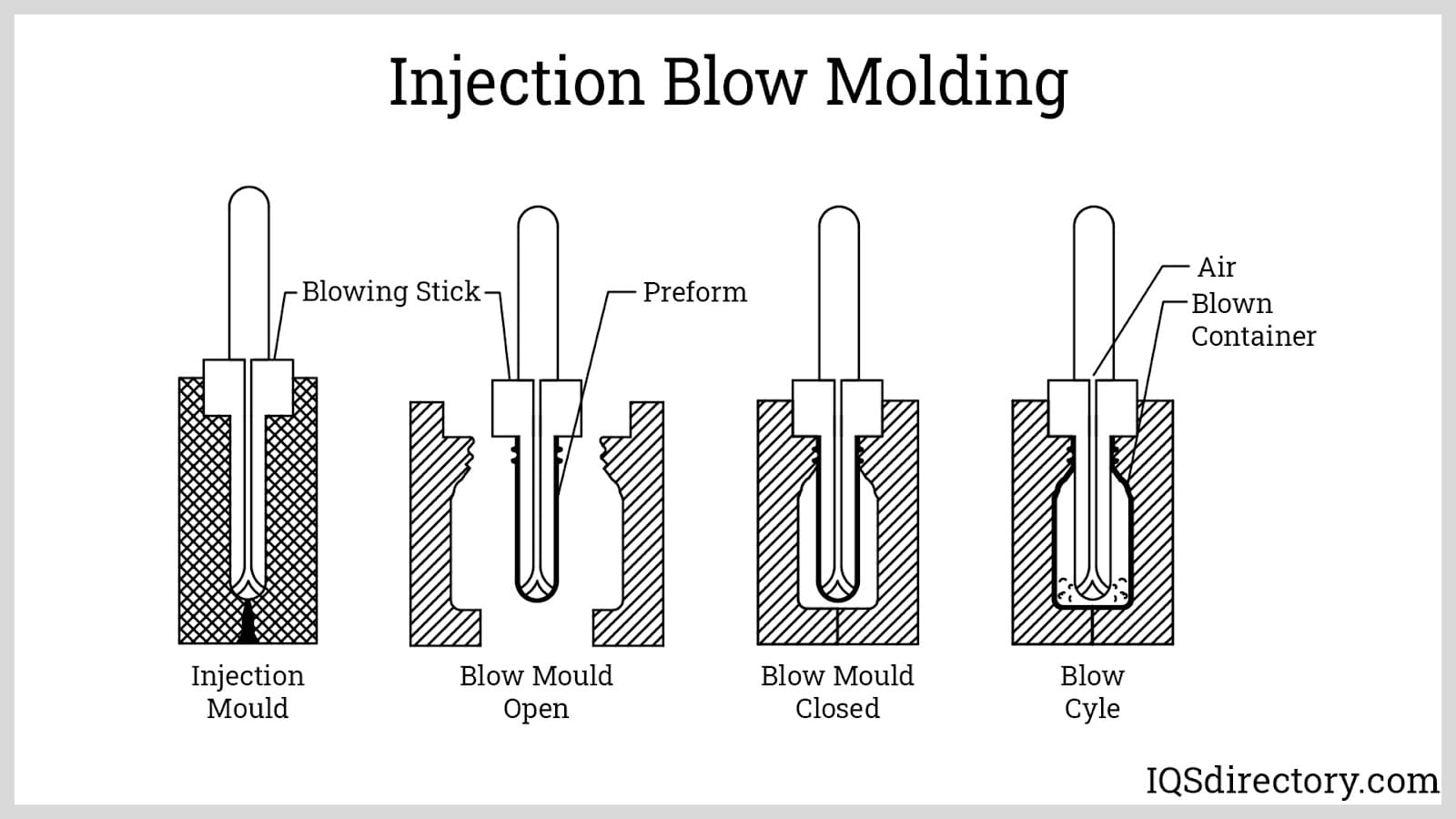
How Does Injection Blow Molding (IBM) Stand Out?
Injection Blow Molding (IBM) integrates the precision of injection molding with the hollow formation of blow molding. This method is well-suited for applications requiring high precision, such as medical devices and high-end bottles. B2B buyers benefit from the superior surface finish and tight tolerances that IBM offers, making it ideal for products that require aesthetic appeal and functionality. However, the process can be slower than EBM and may involve higher tooling costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
What Makes Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) a Preferred Choice?
Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) employs preforms that are stretched during the blow molding process, resulting in enhanced strength and clarity. This method is particularly advantageous for producing lightweight beverage bottles and jars, where strength is crucial. Buyers in the beverage industry should consider ISBM for its ability to create robust products while maintaining lightweight characteristics. The complexity of the setup and the need for specialized equipment may pose challenges, but the benefits often outweigh these drawbacks for high-volume production.
Why Choose Reheat Stretch Blow Molding (RSBM)?
Reheat Stretch Blow Molding (RSBM) involves reheating preforms before inflation, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and high clarity in PET bottles. This method is widely used in the soft drink industry, where visual appeal and product integrity are essential. B2B buyers should focus on the clarity and strength of the final products, which are significant selling points in competitive markets. However, the additional heating requirements and complexity of machinery may lead to higher initial investments.
What Advantages Does Multi-layer Blow Molding Offer?
Multi-layer Blow Molding allows for the creation of products with multiple layers of different materials, enhancing barrier properties and customization options. This method is particularly beneficial in food packaging and chemical containers, where protection against external elements is critical. B2B buyers should evaluate the added value of improved shelf life and product integrity that multi-layer designs provide. However, the increased complexity and cost of machinery may require careful consideration of the return on investment for potential applications.
Key Industrial Applications of how to make blow molds
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to make blow molds | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Production of plastic bottles and containers | Cost-effective mass production with minimal waste | Material quality, compliance with food safety regulations |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of automotive parts like reservoirs | Lightweight, durable components that enhance performance | Precision in mold design, compatibility with automotive standards |
| Construction | Creation of safety barriers and construction barrels | Enhanced safety and visibility on job sites | Material durability, UV resistance, and compliance with safety norms |
| Consumer Goods | Development of toys and sporting goods | Attractive designs and lightweight products for consumers | Safety certifications, material safety, and design flexibility |
| Medical Devices | Production of medical containers and equipment | Sterile, reliable products that meet strict health standards | Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and material sourcing |
How is Blow Molding Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, blow molding is crucial for producing plastic bottles and containers that are lightweight yet durable. These products must meet stringent food safety regulations, making the choice of materials paramount. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, must ensure that the suppliers can provide high-quality, food-grade plastics that comply with local and international standards. Additionally, the efficiency of blow molding helps in minimizing waste, making it a cost-effective solution for mass production.

Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
What Role Does Blow Molding Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive industry leverages blow molding for creating essential components like liquid reservoirs and ductwork. The lightweight nature of blow-molded parts contributes to fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who can deliver precision-engineered molds that adhere to automotive standards. Furthermore, the ability to produce complex shapes without assembly reduces costs and leads to faster production timelines, which is critical in the competitive automotive market.
How is Blow Molding Beneficial for Construction Applications?
Blow molding is widely used in the construction industry for manufacturing safety barriers and barrels that enhance job site safety. These products are designed to be lightweight yet sturdy, providing visibility and protection. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, sourcing from manufacturers who can ensure UV resistance and compliance with safety regulations is essential. This not only improves safety on construction sites but also promotes longevity and durability of the products used.
How Does Blow Molding Impact the Consumer Goods Sector?
In consumer goods, blow molding facilitates the production of various items, including toys and sporting goods. The process allows for creative designs while maintaining a lightweight structure, appealing to consumers. Buyers in this sector should consider suppliers that offer flexibility in design and can meet safety certifications, particularly for children’s products. The ability to produce in large volumes without sacrificing quality is a significant advantage for companies looking to scale their product offerings.
What is the Importance of Blow Molding in Medical Device Production?
Blow molding plays a vital role in the production of medical containers and equipment, where sterility and reliability are paramount. Manufacturers must adhere to rigorous regulatory standards, making the selection of high-quality, compliant materials critical. International buyers should focus on suppliers with proven quality assurance processes and the ability to provide documentation for regulatory compliance. This ensures that the medical products not only meet safety standards but also perform effectively in critical healthcare environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make blow molds’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Product Quality in Blow Molding
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of producing blow-molded products with inconsistent quality. This inconsistency can manifest in variations in wall thickness, surface finish, or structural integrity, leading to increased waste and customer dissatisfaction. Factors such as improper machine calibration, variations in raw material quality, and inadequate operator training contribute to these issues. As a result, businesses may struggle to meet client specifications and regulatory standards, which can hinder their competitive edge in the market.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
The Solution: To address quality consistency, it is crucial to implement a robust quality assurance program throughout the blow molding process. Start by investing in high-quality machinery that features advanced monitoring systems to ensure accurate parison formation and inflation. Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment will help maintain optimal performance. Additionally, establish strict quality control protocols that include routine inspections of raw materials and finished products. Training operators on best practices for handling materials and machine operation can significantly reduce variability. Collaborating with reliable suppliers who provide consistent material quality will also enhance the overall output and reduce defects.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs and Inefficiencies
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter high production costs and inefficiencies during the blow molding process. These can stem from outdated machinery, excessive energy consumption, and waste generated from defective products. For companies in price-sensitive markets, these increased costs can erode profit margins and make it challenging to compete with lower-cost alternatives. Furthermore, inefficient workflows can lead to longer lead times, delaying product delivery and frustrating clients.
The Solution: To minimize production costs and inefficiencies, consider investing in modern blow molding technologies that enhance energy efficiency and reduce material waste. For example, switching to machines that utilize energy-saving technologies can significantly lower operational costs. Additionally, adopting lean manufacturing principles can streamline workflows, reduce cycle times, and minimize waste. Implementing a robust tracking system can help identify bottlenecks in the production process, allowing for timely adjustments. Regular training sessions for staff on efficient operating techniques will ensure that everyone is equipped to maximize the capabilities of the machinery. Lastly, conducting periodic audits of production processes can uncover hidden inefficiencies that can be rectified for improved performance.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Material Selection for Blow Molding
The Problem: Selecting the right material for blow molding can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. Different applications require specific properties, such as strength, flexibility, or resistance to chemicals. Misjudging material requirements can lead to product failures, increased returns, and reputational damage. Furthermore, with a vast array of plastics available, the decision-making process can become overwhelming, especially for companies entering new markets or developing innovative products.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of material selection, it is essential to conduct thorough research and analysis based on the specific requirements of the end product. Start by defining the product’s intended use, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance needs. Engaging with material suppliers can provide valuable insights into the performance characteristics of various plastics, such as PET, HDPE, and PVC. Utilizing simulation software can also aid in predicting how different materials will behave during the blow molding process. Finally, consider prototyping with multiple materials to evaluate their performance before making a bulk purchase. Collaborating with experienced engineers or consultants can further ensure that the right material is chosen, tailored to the product’s specific demands and market expectations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make blow molds
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Blow Molding?
When selecting materials for blow molds, it is essential to consider their properties that directly influence product performance. Below are analyses of four common materials used in blow molding, focusing on their suitability for various applications and the implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polyethylene (PE) Perform in Blow Molding Applications?
Polyethylene, particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is one of the most widely used materials in blow molding. It exhibits excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical stability, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including bottles and containers.
Pros: Polyethylene is cost-effective and offers good durability against environmental stress. It is easy to process, which simplifies manufacturing.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
Cons: However, it has a relatively low temperature resistance, which may limit its use in high-heat applications. Additionally, it is less rigid compared to other materials, which can affect the structural integrity of certain products.
Impact on Application: PE is compatible with a wide range of media, including food and beverages, but may not be suitable for high-temperature liquids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards (like FDA regulations in the U.S. and EFSA in Europe) is crucial. Buyers should ensure that the material meets local regulations and standards, such as ASTM or DIN.
What Role Does Polypropylene (PP) Play in Blow Molding?
Polypropylene is another popular choice for blow molding, known for its higher melting point and excellent chemical resistance. This material is often used for automotive parts, containers, and industrial applications.
Pros: Polypropylene is lightweight, has good impact resistance, and can withstand higher temperatures than polyethylene. Its versatility allows for various applications, including those requiring sterilization.
Cons: On the downside, polypropylene can be more expensive than polyethylene and may require more complex processing techniques, which can increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: PP’s chemical resistance makes it suitable for storing aggressive substances, but it may not be ideal for applications requiring transparency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of material certifications and compliance with international standards, particularly in the automotive sector, where safety regulations are stringent.
Why Is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Considered for Blow Molding?
PVC is often used in blow molding for applications requiring rigidity and durability, such as pipes and construction materials. It offers excellent chemical resistance and is flame-retardant.
Pros: PVC is highly durable and resistant to environmental degradation, making it suitable for outdoor applications. It is also cost-effective for large-scale production.
Cons: However, PVC can be more challenging to process and may require additives to enhance its flexibility. It also has a lower impact resistance compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: PVC’s chemical resistance makes it ideal for construction and plumbing applications, but it may not be suitable for food-grade products without proper modifications.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations is critical, especially in regions like Europe, where restrictions on PVC use are becoming more common.
How Does Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Enhance Blow Molding?
ABS is a thermoplastic known for its strength and impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for producing durable consumer goods and automotive components.
Pros: ABS offers excellent toughness and rigidity, along with good thermal stability. It is also easy to paint and finish, which is beneficial for aesthetic applications.
Cons: The primary drawback of ABS is its higher cost and the need for more complex processing methods compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: ABS is suitable for high-impact applications, but it may not perform well in environments with high chemical exposure.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ABS products comply with relevant safety standards and certifications, particularly in the electronics and automotive industries.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Blow Molds
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to make blow molds | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Bottles, containers | Cost-effective and durable | Low temperature resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive parts, industrial containers | High melting point and chemical resistance | More expensive and complex to process | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Pipes, construction materials | Durable and cost-effective | Difficult to process | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer goods, automotive components | High strength and impact resistance | Higher cost and complex processing | High |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a foundation for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding blow mold production. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will facilitate better alignment with specific application needs and compliance standards across different regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make blow molds
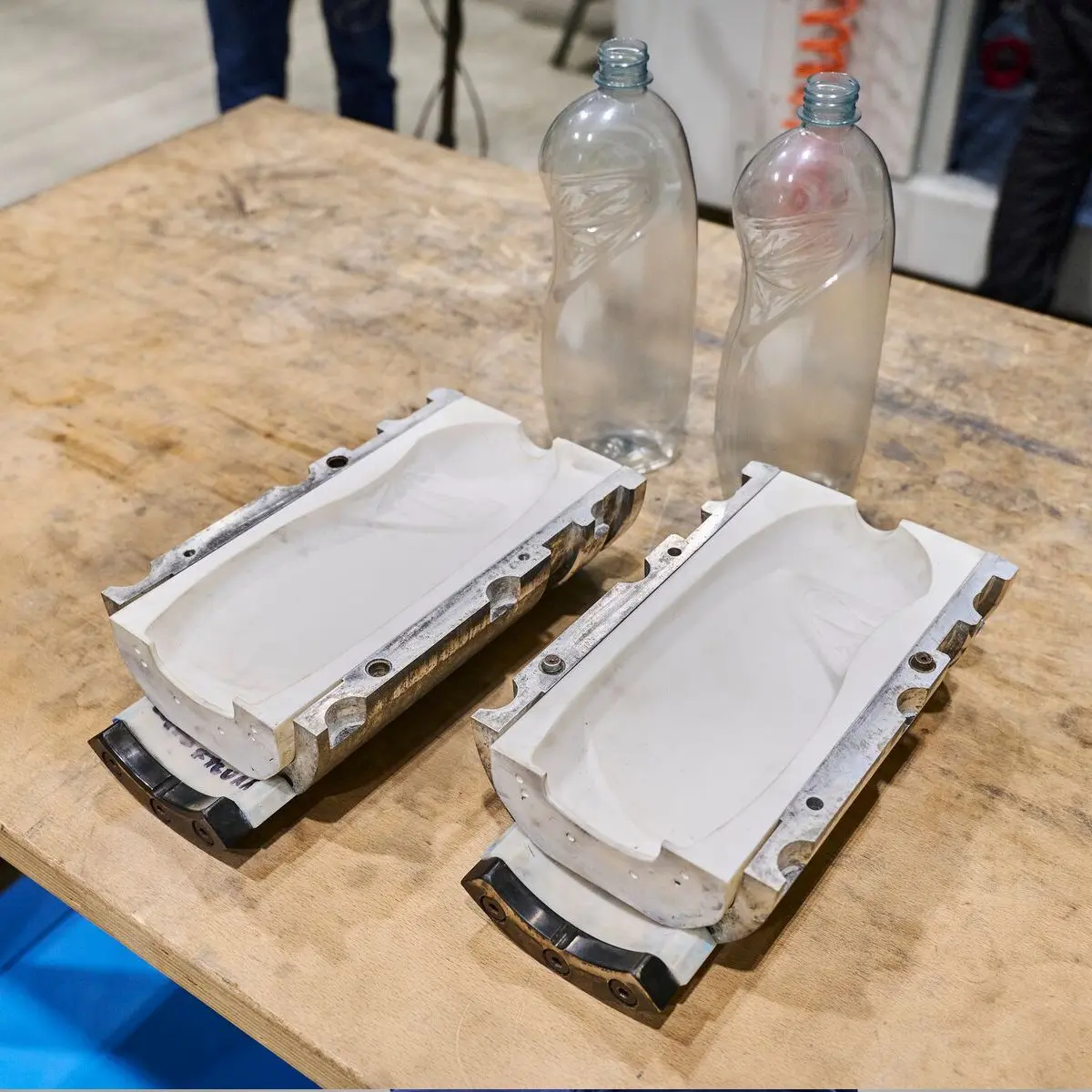
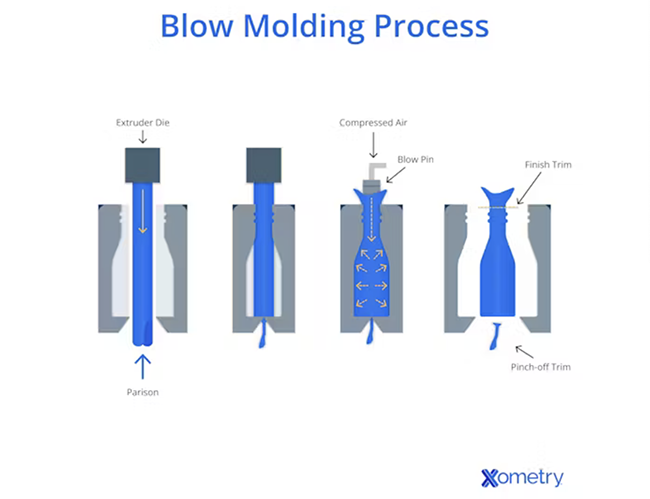
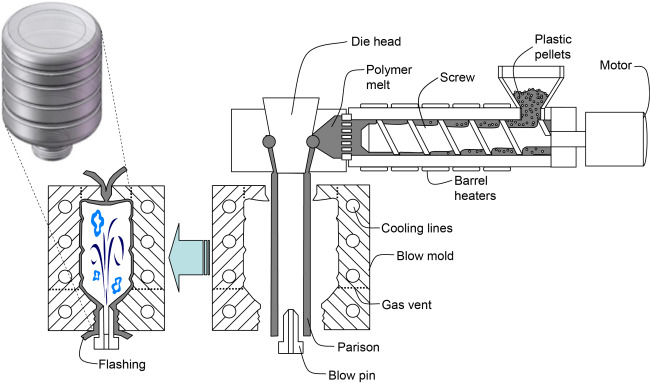
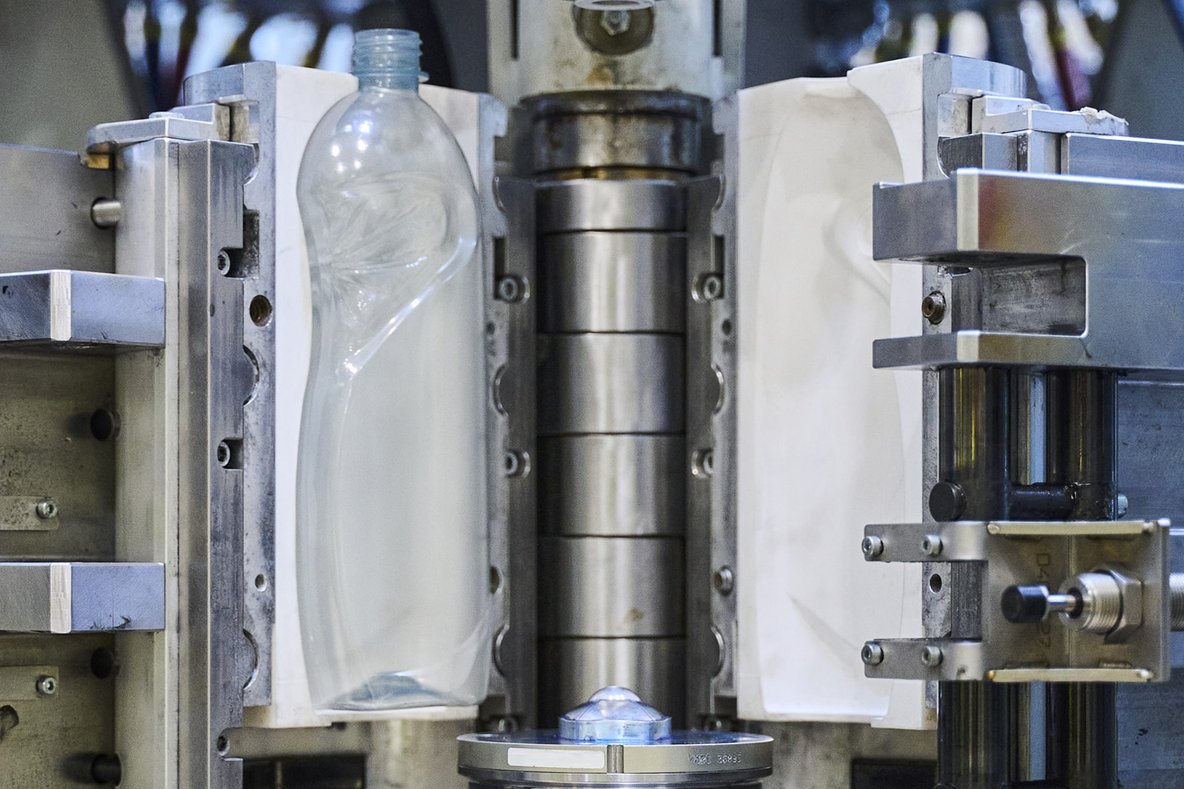
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Blow Molds?
The manufacturing of blow molds is a sophisticated process involving multiple stages, each crucial for producing high-quality molds that meet the demands of various industries. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Blow Mold Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing blow molds is the preparation of raw materials. Typically, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polycarbonate, or polypropylene are used due to their favorable properties for blow molding. The materials are usually in pellet form and are fed into a hopper where they are heated until they reach a molten state.
Once heated, the plastic is extruded into a parison—a tube-like shape that will be formed into the final product. The consistency of the material is monitored closely to ensure uniformity, which is essential for achieving the desired wall thickness and strength of the final product.
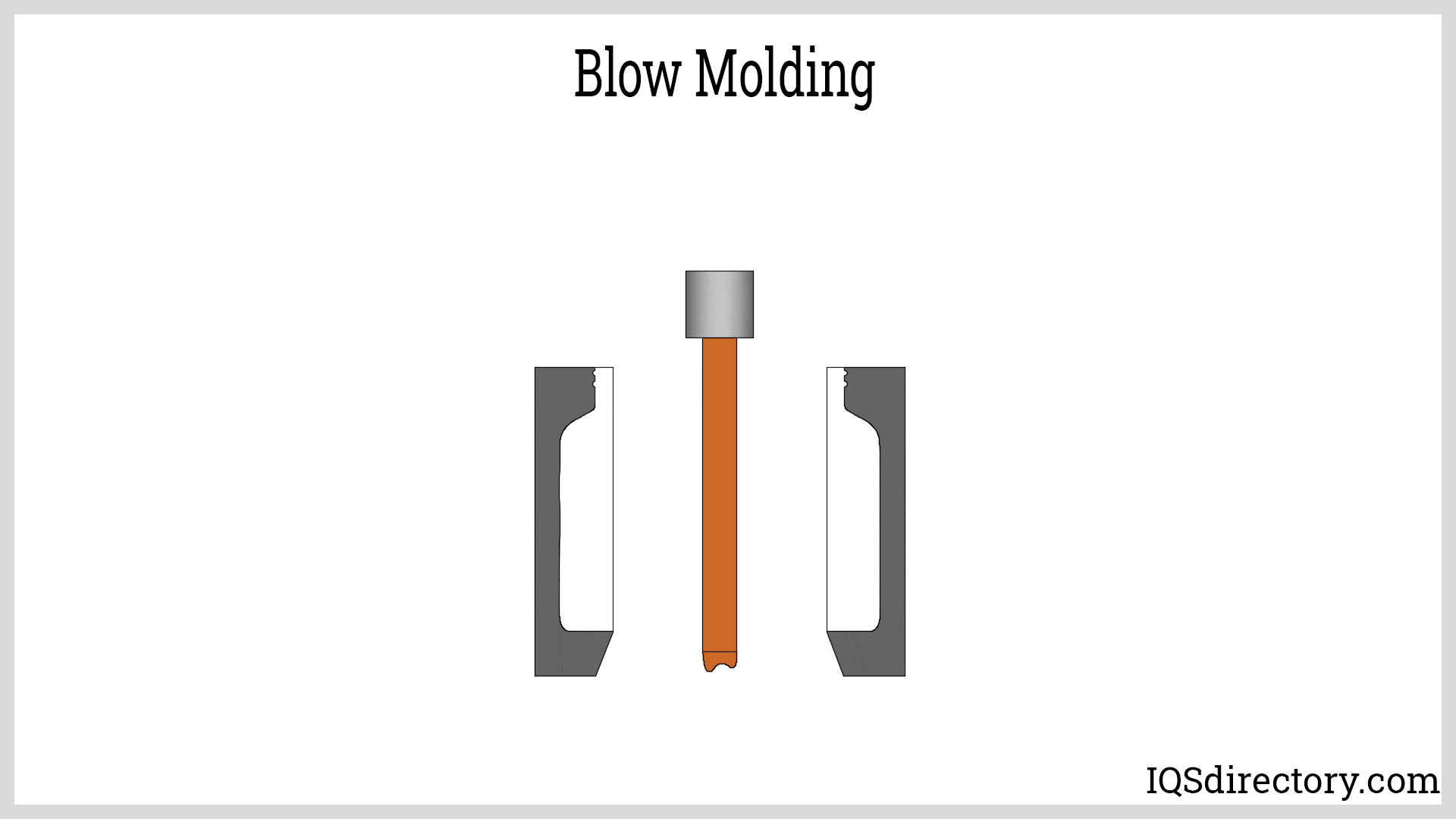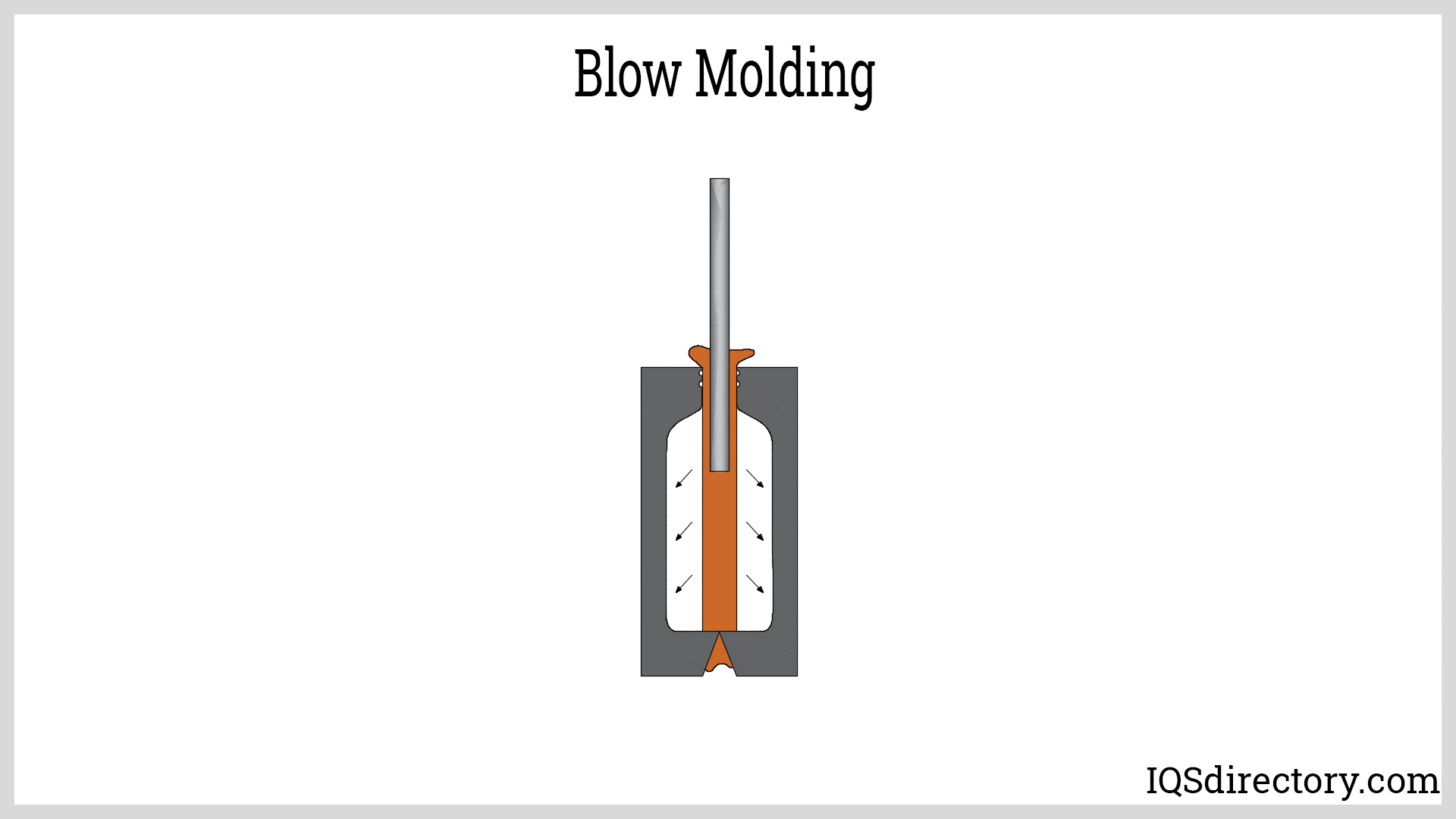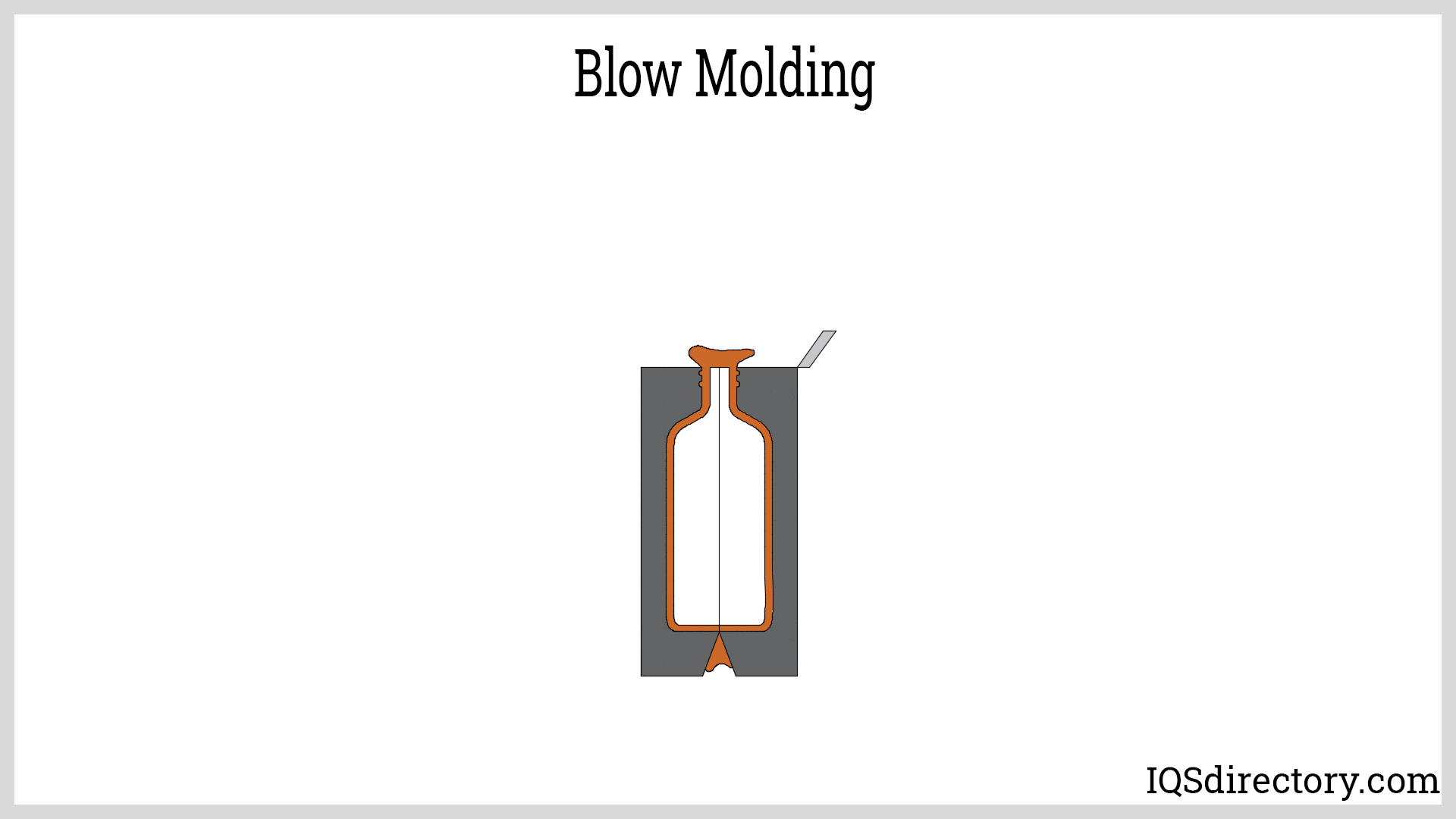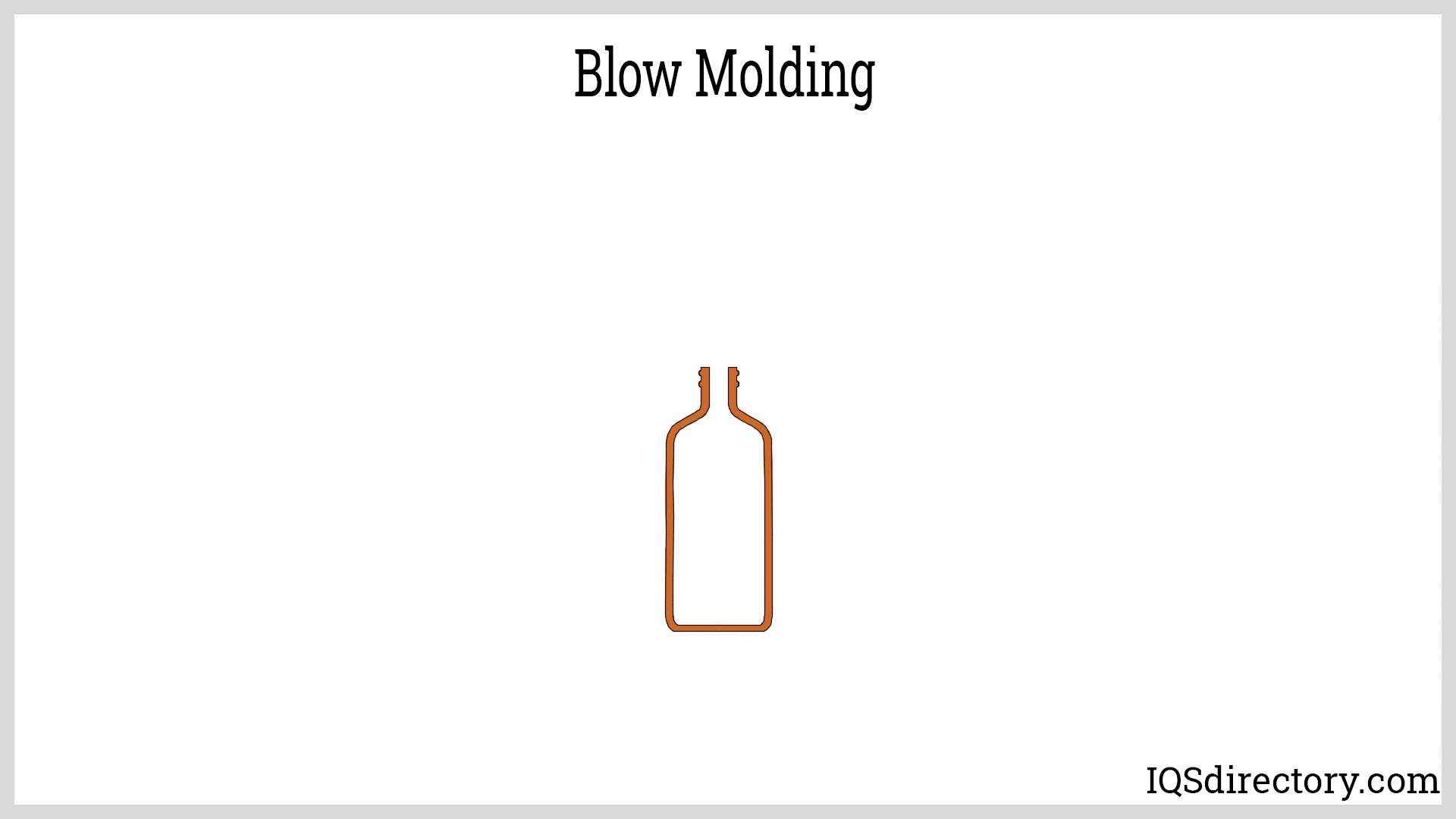
What Are the Key Techniques Used in Blow Mold Forming?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming the blow mold. This can be accomplished through various techniques, including:
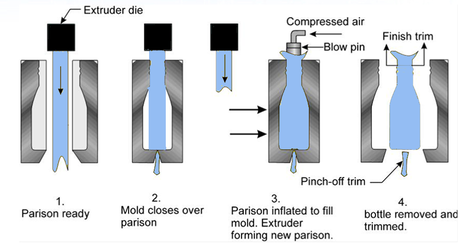
- Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM): In this method, the parison is extruded and then clamped into the mold. Compressed air is used to inflate the parison, filling the mold cavity.
- Injection Blow Molding (IBM): Here, a preform is created via injection molding before being transferred to the blow mold. This technique is particularly useful for producing complex shapes and high-precision products.
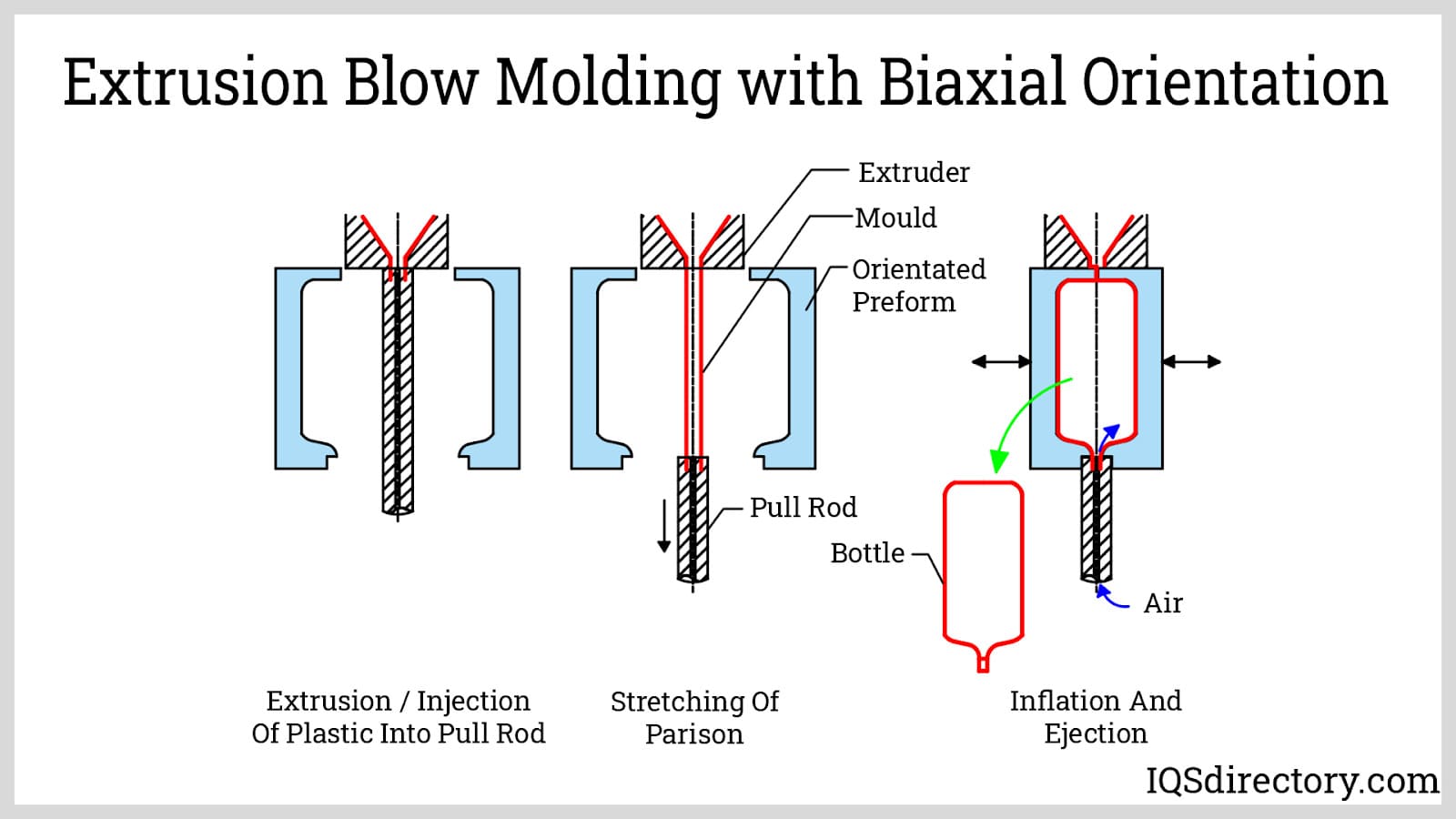
- Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM): This combines injection and blow molding, allowing for a high-quality finish and enhanced mechanical properties, ideal for products like beverage bottles.
Each technique offers distinct advantages in terms of production speed, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility. The choice of method will depend on the specific requirements of the product being manufactured.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed in Blow Mold Manufacturing?
In the assembly stage, various components of the blow molds are put together. This may include the integration of multiple parts, such as handles or fittings, depending on the design specifications. Precision is key during assembly to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly, which is vital for the mold’s performance.
The assembly process may also involve the application of seals or gaskets to prevent leakage, especially in products designed to contain liquids. Quality checks are typically performed at this stage to ensure that the mold components meet the necessary specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Blow Molds?
Finishing processes play a significant role in the overall quality and appearance of blow molds. This stage may involve:
- Trimming: Excess material, known as flash, is removed to ensure a smooth finish.
- Polishing: The surface of the mold may be polished to improve aesthetics and reduce friction during the molding process.
- Coating: Some molds may receive a coating to enhance durability or resistance to chemicals.
These finishing touches not only improve the visual appeal of the molds but also enhance their functionality and lifespan.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical for Blow Mold Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the blow mold manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Key measures include adherence to standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for an effective quality management system.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international B2B buyers, understanding relevant certifications is crucial. Common certifications include:
- ISO 9001: Ensures quality management systems are in place.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: For molds used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific performance criteria.
These certifications not only provide reassurance about product quality but also facilitate smoother international trade.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Blow Mold Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are caught early. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are tested upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing monitoring during production helps identify issues as they arise.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all design specifications and quality standards.
By implementing these checkpoints, manufacturers can minimize defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality assurance processes of suppliers is essential to ensure reliable partnerships. Buyers can take several steps to validate supplier QC:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality management systems and practices.
- Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers assess the consistency and reliability of the manufacturing process.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate manufacturing facilities and processes can provide an unbiased assessment of quality.
These actions not only build trust between buyers and suppliers but also help mitigate risks associated with poor quality.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider in Quality Assurance?
International buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges in quality assurance. Factors to consider include:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding varying standards and practices in different regions is critical for effective communication and expectations management.
- Logistics: Transportation and storage conditions can impact product quality, necessitating careful planning.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that products meet local regulations in their respective countries, which can differ significantly from international standards.
By being aware of these nuances, international buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing blow molds more effectively.
In summary, the manufacturing process of blow molds is a multi-faceted operation requiring careful attention to material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and finishing. Coupled with robust quality assurance measures, these processes ensure that the final products meet the high standards demanded in today’s global marketplace. For B2B buyers, understanding these elements is crucial for making informed decisions and establishing successful supplier relationships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make blow molds’
To successfully navigate the procurement process for blow molds, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a checklist that will help B2B buyers streamline their sourcing efforts, ensuring they obtain high-quality molds that meet their production needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for aligning your production requirements with potential suppliers. Consider factors such as mold dimensions, material compatibility, and production volume. Documenting these specifications will facilitate better communication with suppliers and help them understand your exact needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in blow molding. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation and experience in producing molds for your specific industry. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the capabilities of each supplier to ensure they can meet your specifications. Inquire about their machinery, technology, and production processes. Key aspects to consider include:
– Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can handle your required volume.
– Material Expertise: Confirm they have experience with the types of plastics you intend to use.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a significant investment, request samples or prototypes of the blow molds. This step allows you to evaluate the quality of the molds and their suitability for your products. Pay attention to:
– Precision and Finish: Check for any defects or inconsistencies.
– Functionality: Ensure the molds perform as intended during trials.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It is vital to ensure that your chosen supplier adheres to industry standards and regulations. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific compliance documents relevant to your industry. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and can reduce the risk of future production issues.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in detailed discussions regarding pricing structures and payment terms. Understand what factors influence the cost, including materials, complexity, and production timelines. Aim for transparency to avoid unexpected expenses later on. Consider:
– Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing for larger orders.
– Payment Flexibility: Negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership with your supplier. Set up regular check-ins and updates throughout the production process. This helps to address any issues promptly and ensures that both parties remain aligned on expectations and timelines.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for blow molds, leading to successful partnerships and efficient production processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make blow molds Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Blow Molding Sourcing?
When sourcing blow molds, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary cost components in blow molding include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of plastic materials—such as PVC, PET, or polypropylene—directly impacts cost. Prices can fluctuate based on global oil prices and supply chain dynamics. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally when possible to minimize costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers might find more competitive pricing. However, the skill level of labor in regions with higher costs can lead to better quality and faster production times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, making it essential to choose suppliers with advanced technologies and automation capabilities.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized molds. Initial investments in high-quality tooling can lead to lower per-unit costs over time, making it a critical factor in the overall cost structure.
-
Quality Control: Implementing strict QC measures is essential to ensure product consistency and compliance with international standards. While this may add to initial costs, it can prevent costly defects and returns in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Buyers must account for these costs in their total budget and consider local vs. international suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and profits. Understanding the market rates for similar products can help buyers negotiate more effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Blow Mold Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing for blow molds, which can vary significantly based on volume, specifications, and supplier conditions.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider their long-term needs to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized molds typically incur higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling and production processes. Buyers should carefully evaluate whether the added features justify the higher price.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects initial costs but also influences durability and performance. Buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement costs over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific international quality standards or certifications may come at a premium. However, investing in certified products can reduce risks associated with product recalls and compliance issues.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can significantly influence pricing. Buyers should conduct due diligence to select suppliers with proven track records in quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms is vital for budgeting logistics and overall costs. Familiarity with terms like EXW (Ex Works) or DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Blow Mold Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing blow molds, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate terms, especially regarding pricing for bulk orders and long-term contracts. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your position.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Factor in logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime costs to get a clearer picture of the true investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware that currency fluctuations and tariffs can affect pricing for international transactions. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Brazil should consider these factors when budgeting for sourcing.
-
Build Strong Supplier Relationships: Developing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts or favorable terms to loyal customers.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is crucial for B2B buyers in the blow mold market. By applying these insights, companies can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgets.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make blow molds With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Blow Molding: A Comparative Analysis
In the quest for efficient and cost-effective manufacturing methods, businesses often find themselves evaluating various production techniques for plastic products. Blow molding is a popular choice for creating hollow plastic items, but it’s essential to consider alternative solutions that may better suit specific operational needs or product requirements. Below, we explore several alternatives to blow molding, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Make Blow Molds | Injection Molding | Rotational Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed production of hollow parts with minimal flash | High precision for complex shapes and detailed designs | Suitable for large, hollow items with uniform wall thickness |
| Cost | Generally lower for high volumes | Higher initial costs due to mold fabrication | Moderate costs, often lower than injection molding |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machinery and skilled labor | Complex setup, requires extensive training | Simpler setup but slower production rates |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; requires regular checks on molds | Moderate maintenance; molds can wear and require replacement | Low maintenance; molds are durable but can be heavy |
| Best Use Case | Large volume production of simple shapes | Detailed products like automotive components and consumer goods | Large, hollow products like tanks, playground equipment, and furniture |
Pros and Cons of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a method that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create precise shapes. This method is highly effective for producing intricate designs and components requiring tight tolerances. One of the main advantages of injection molding is its ability to create complex geometries, making it ideal for consumer electronics and automotive parts. However, the initial costs for mold creation can be significantly higher compared to blow molding, making it less viable for low-volume production runs.
Understanding Rotational Molding
Rotational molding, or rotomolding, is another alternative that involves heating plastic in a mold while it rotates, allowing the material to coat the interior surface evenly. This method is particularly beneficial for creating large, hollow items such as tanks and outdoor furniture. The key advantages of rotational molding include lower tooling costs and the ability to produce seamless designs. However, the production speed tends to be slower, which may not meet the demands of high-volume manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Plastic Manufacturing Solution
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing method for plastic products, B2B buyers must weigh the advantages and limitations of each option against their specific requirements. Blow molding excels in producing hollow shapes at lower costs for high-volume production, while injection molding offers precision for detailed designs at a higher initial investment. Rotational molding provides a balance of cost and versatility for larger items, albeit at a slower production rate. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by factors such as production volume, design complexity, and budget constraints to ensure alignment with operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make blow molds
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for Making Blow Molds?
When considering blow molding, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for ensuring product quality and operational efficiency. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The choice of plastic material significantly affects the performance and durability of the blow-molded product. Common materials used include PET, HDPE, and PVC. Each material has distinct properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and temperature tolerance. Selecting the right material grade is vital for meeting the specific requirements of end-use applications, such as food safety or chemical resistance.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In blow molding, maintaining tight tolerances is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assembly processes and function as intended. Poor tolerance control can lead to increased scrap rates and higher production costs, making it essential for manufacturers to define acceptable tolerances early in the design phase.
3. Wall Thickness
Wall thickness influences both the strength and weight of the final product. It is crucial to balance the need for a robust structure with material cost efficiency. Thicker walls may enhance durability but can increase material costs, while thinner walls may reduce weight but compromise strength. Understanding the required wall thickness is essential for optimizing production and maintaining product integrity.
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to produce one blow-molded part, including cooling and ejection. Shorter cycle times increase productivity and reduce manufacturing costs. Manufacturers must analyze their machinery and process to optimize cycle times without sacrificing quality. This is particularly important in competitive markets where speed to market can be a decisive factor.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of blow-molded parts can impact both aesthetics and functionality. A smooth surface can reduce friction and improve the appearance of consumer products, while a textured finish may enhance grip or reduce visibility of scratches. Understanding the desired surface finish is important for meeting customer expectations and achieving market differentiation.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Blow Molding?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In blow molding, OEMs can provide specialized molds or components tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help businesses leverage expertise and reduce production costs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In blow molding, MOQs can affect inventory management and financial planning. It’s important for businesses to negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used to solicit bids from suppliers for specific products or services. When looking for blow molding services, an RFQ allows businesses to compare pricing and capabilities across different suppliers. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can lead to better pricing and quality outcomes.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing logistics and costs associated with shipping blow-molded products. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses mitigate risks and clarify obligations in cross-border trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In blow molding, lead time is influenced by factors such as material availability, production schedules, and logistics. Businesses should assess lead times to ensure they meet market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when engaging with suppliers in the blow molding industry, ultimately leading to more successful partnerships and product outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make blow molds Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Blow Molding Market for International Buyers?
The blow molding market is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors. As industries increasingly shift toward lightweight and cost-effective solutions, blow molding is gaining traction for its ability to create hollow plastic products efficiently. Notably, the automotive and consumer goods sectors are primary drivers, with rising demand for blow-molded components such as fuel tanks and packaging solutions. Furthermore, advancements in automation and digital technologies are reshaping the production landscape. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, allows manufacturers to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take note of emerging trends such as the increasing preference for customized products. The ability to produce tailored solutions quickly and cost-effectively is becoming a competitive advantage. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is pushing manufacturers to adopt more flexible production lines to meet diverse customer demands. This shift is particularly relevant for markets in Nigeria and Brazil, where local manufacturers are increasingly focusing on adapting global best practices to cater to regional needs.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Blow Molding Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of business strategy in the blow molding sector. With growing awareness of environmental issues, B2B buyers are prioritizing sustainable practices within their supply chains. The environmental impact of plastic production is prompting manufacturers to explore alternative materials and processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. For instance, recycled PET (rPET) is emerging as a preferred choice for blow molding applications, particularly in the beverage industry.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining importance, with buyers seeking suppliers who comply with environmental regulations and possess ‘green’ certifications. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Global Recycled Standard provide assurance of responsible practices. Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe are particularly attuned to these trends, as regulatory pressures and consumer expectations push for transparency in sourcing. By aligning with sustainable suppliers, businesses can not only mitigate risk but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Blow Molding Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
The blow molding process has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially rooted in glass-blowing techniques, the commercial viability of blow molding emerged with the advent of synthetic plastics like polyethylene. This transformation allowed for mass production capabilities, particularly in the bottling and automotive industries.
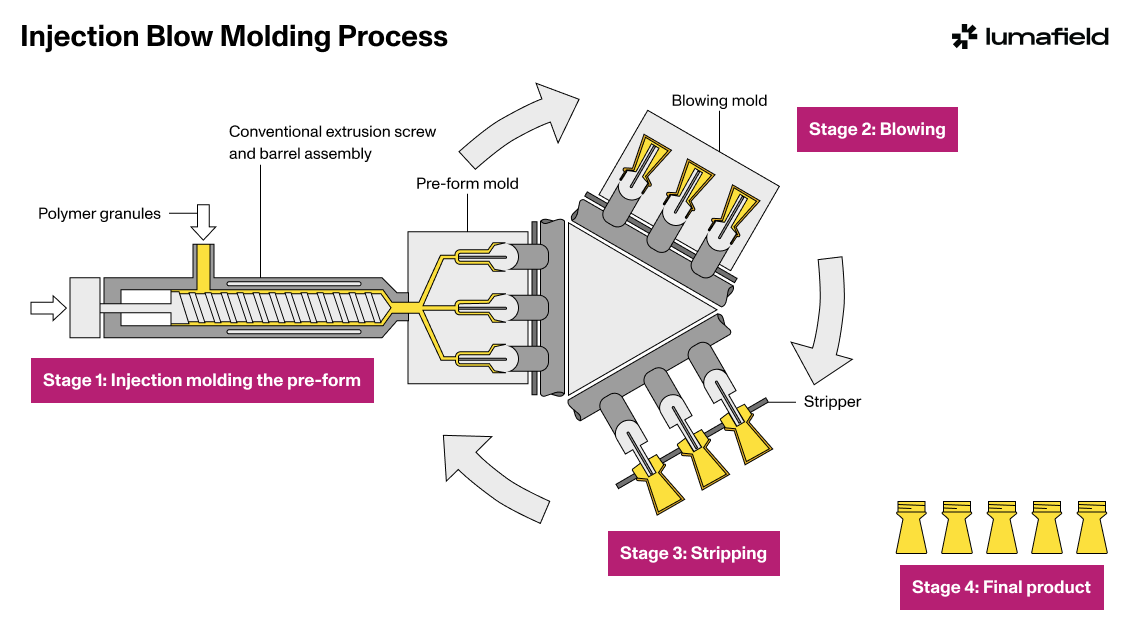
Illustrative image related to how to make blow molds
As technology progressed, various blow molding techniques such as extrusion blow molding (EBM) and injection stretch blow molding (ISBM) were developed, enhancing production efficiency and product versatility. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing innovation in materials and processes. Today, the legacy of blow molding continues to influence modern manufacturing, enabling businesses to meet the demands of a dynamic market landscape effectively.
In summary, navigating the blow molding market requires an awareness of current trends in sustainability, technological advancements, and the historical evolution of manufacturing processes. By leveraging these insights, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make blow molds
-
How do I solve production delays in blow molding?
To address production delays in blow molding, first, assess your machinery and workflow. Ensure that your equipment is well-maintained and capable of handling the required output. Streamlining operations through automation can significantly reduce downtime. Additionally, consider sourcing raw materials in advance to avoid bottlenecks. Establishing strong communication with suppliers can also help you anticipate and resolve issues before they affect production schedules. -
What is the best material for blow molding containers?
The optimal material for blow molding containers largely depends on the intended application. For food and beverage packaging, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is preferred due to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability. For more industrial applications, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers durability and resistance to impact. Always evaluate the specific requirements of your end product, including temperature tolerance and chemical exposure, before selecting a material. -
How can I vet suppliers for blow molding services?
Vetting suppliers for blow molding services is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by checking their certifications and industry experience. Request references and case studies from previous clients to gauge their performance. Conduct factory visits if possible to inspect their operations and quality control processes. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer transparency in pricing and communication to foster a long-term partnership. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for blow molded products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for blow molded products can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Typically, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. When negotiating, consider your production needs and discuss the possibility of lower MOQs for initial orders. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new clients or smaller companies to build a working relationship. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing blow molds internationally?
When sourcing blow molds internationally, payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) followed by the balance upon completion or before shipping. Some suppliers might offer letters of credit for larger orders to mitigate risk. Always clarify payment options, including currency preferences and potential transaction fees, before finalizing any agreements. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in blow molding production?
To ensure quality assurance in blow molding production, establish a comprehensive quality control plan that includes regular inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process. Work with suppliers who follow international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Implement testing protocols for raw materials and final products to ensure they meet your specifications. Frequent communication with your supplier can help address any quality issues promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international blow molding orders?
When planning logistics for international blow molding orders, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with the import/export processes in your region. Be aware of any potential tariffs and taxes that could affect your overall costs. Additionally, plan for storage and distribution upon arrival to ensure a smooth transition from supplier to your business. -
How can I customize my blow-molded products?
Customization of blow-molded products can be achieved through various methods, including altering mold designs and selecting different materials or colors. Discuss your specific needs with your supplier, as many are equipped to accommodate custom designs based on your specifications. Consider factors like functionality, aesthetics, and target market preferences when designing your products. Prototyping can also be useful to test and refine your design before full-scale production.
Top 1 How To Make Blow Molds Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Western Case – Blow Molding Solutions
Domain: westerncase.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Western Case specializes in blow molding, creating high-quality plastic products through an extrusion blow molding technique. They offer services including design assistance with CAD drawings, crafting durable molds from machined aluminum, and ensuring quality assurance with documented product characteristics and checklists. Their molds can be single or multiple cavity, aimed at providing low prod…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make blow molds
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Blow Mold Production?
In the dynamic landscape of blow molding, strategic sourcing is paramount for achieving competitive advantages. By selecting reliable suppliers and optimizing material procurement, businesses can not only reduce costs but also enhance product quality and innovation. The diverse applications of blow molding—from automotive components to consumer goods—demand a keen understanding of materials like PET and HDPE, which are essential for producing high-quality molds.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and technological advancement. This approach not only ensures compliance with global standards but also fosters long-term relationships that can adapt to market changes.
As the demand for blow-molded products continues to rise, leveraging strategic sourcing will be critical for maintaining a competitive edge. We encourage you to explore partnerships that align with your operational goals and invest in innovative solutions that propel your business forward. Embrace the future of blow molding and position your organization for sustained success in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.