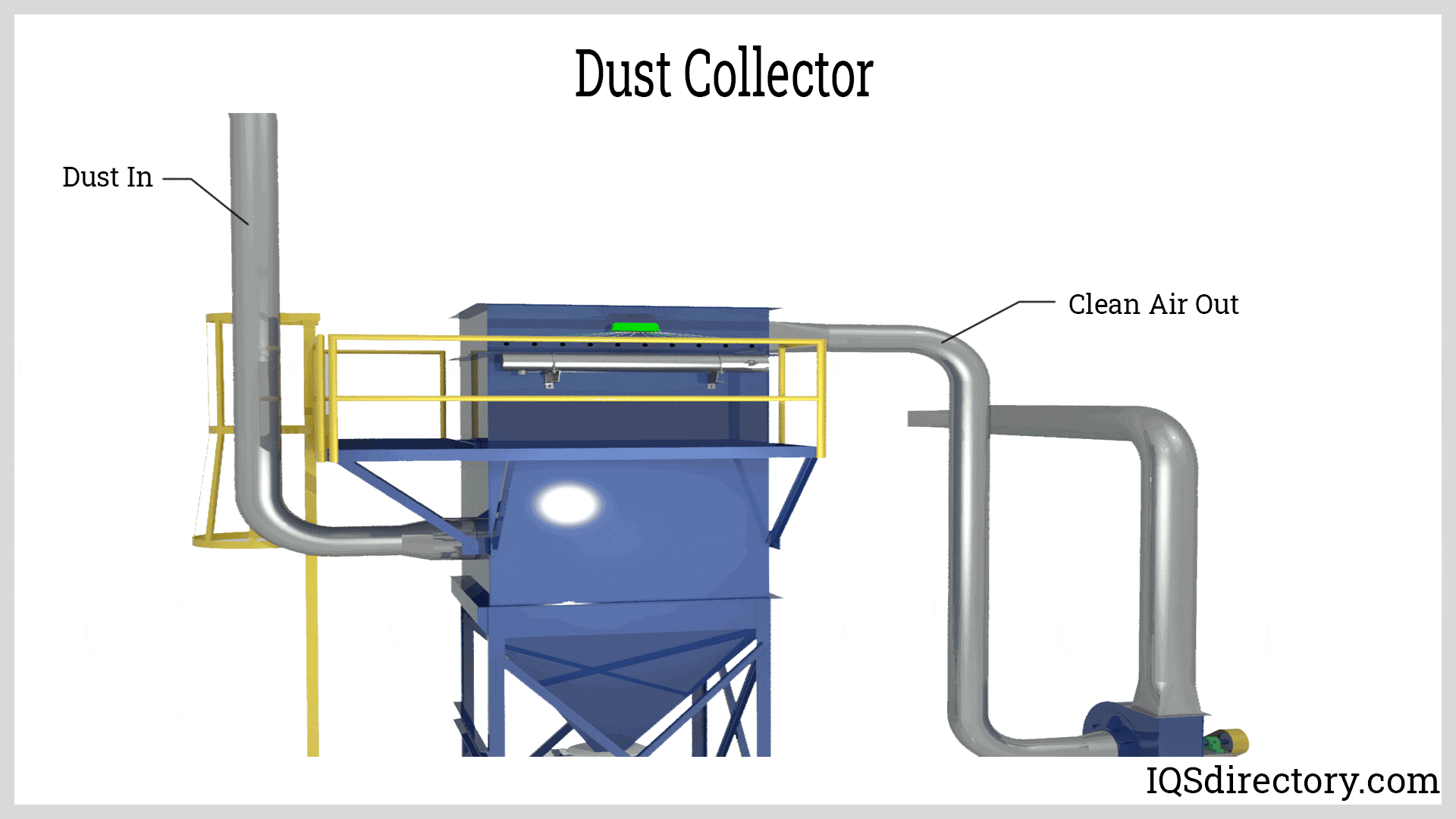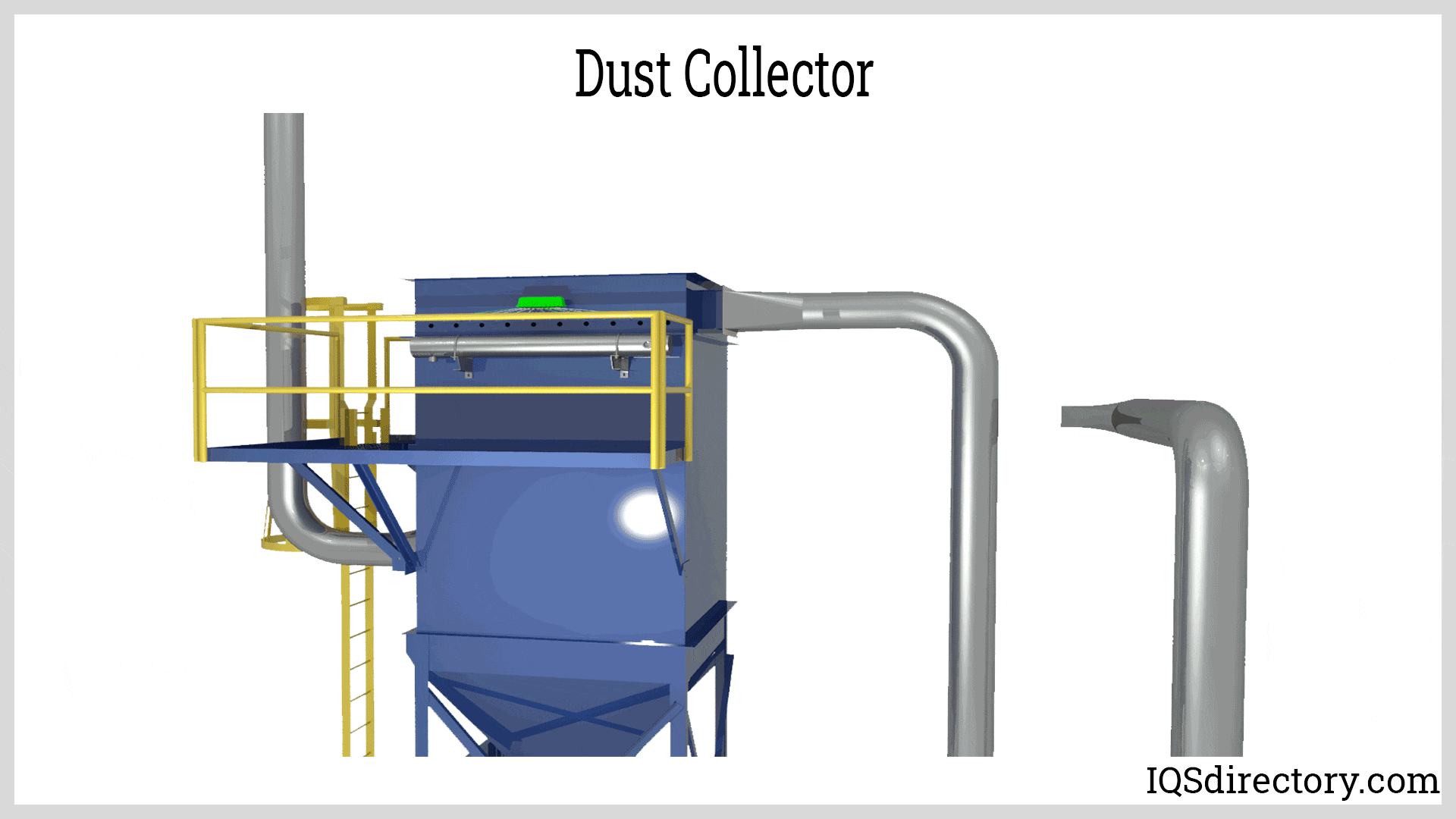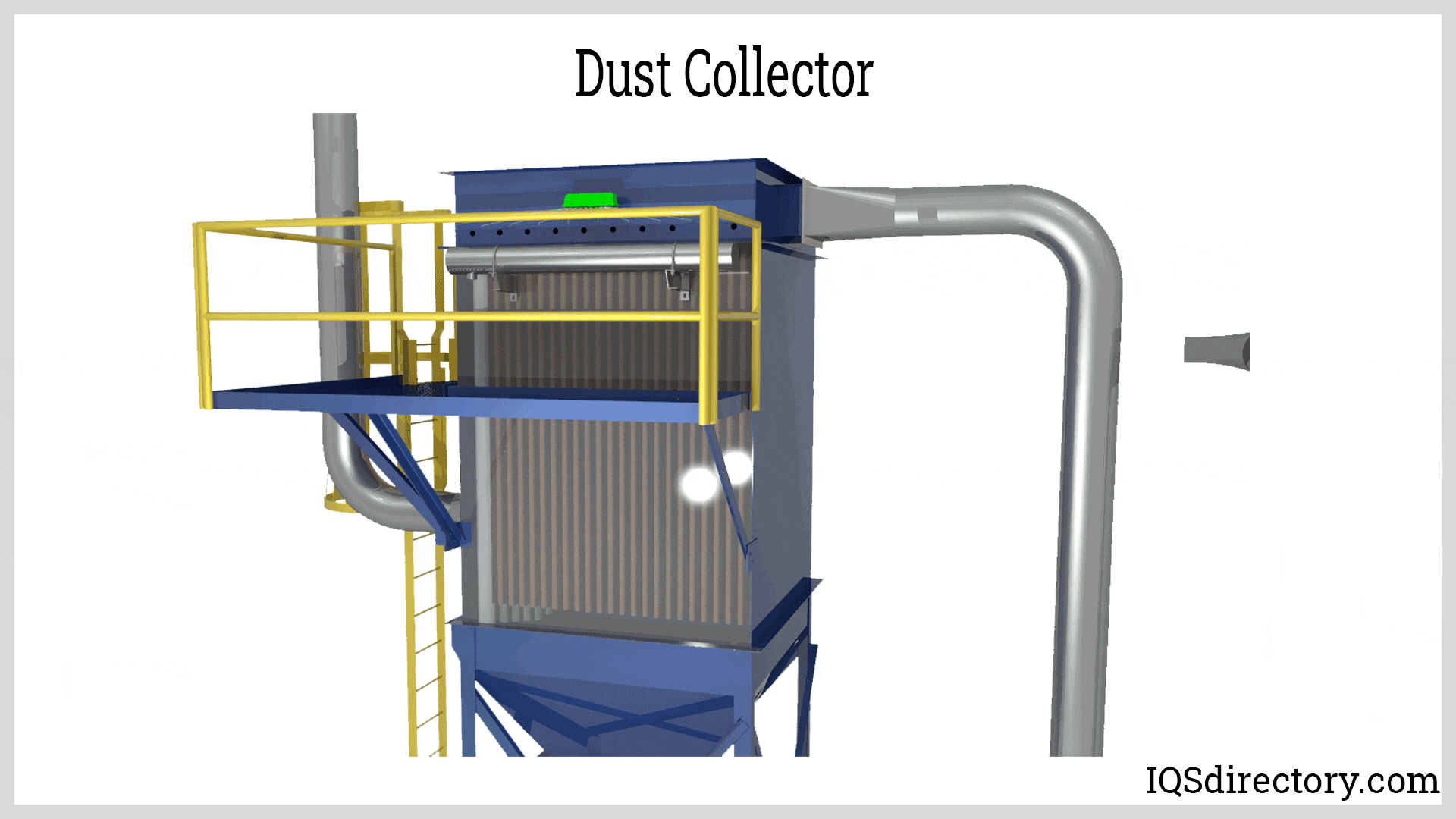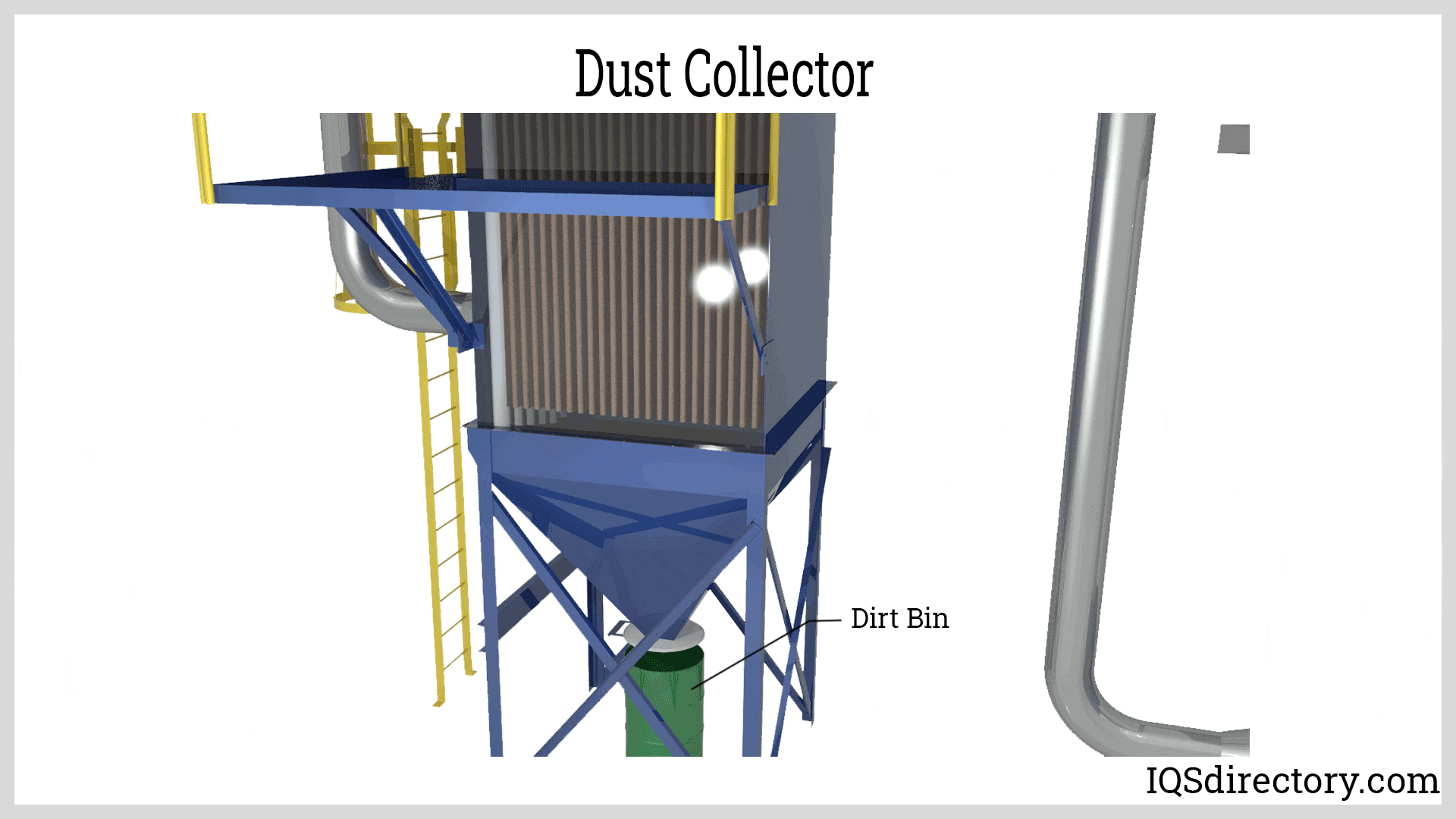
The Definitive Guide to Dust System Design: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dust system design
As global industries increasingly prioritize workplace safety and environmental sustainability, the demand for effective dust system design has surged. However, sourcing a reliable dust collection system that meets specific operational needs can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for international buyers navigating the complexities of dust system design, offering insights into various types of systems, their applications across industries, and strategies for supplier vetting.
From understanding the nuances of different dust collection technologies to evaluating costs and performance metrics, this guide empowers decision-makers with the knowledge required to make informed purchases. It covers critical aspects such as the importance of selecting the right size and type of dust collector, optimizing ductwork for maximum efficiency, and ensuring compliance with health regulations. By addressing common pain points and offering actionable solutions, this resource aims to streamline the procurement process, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately contribute to a safer working environment. Whether you’re in manufacturing, woodworking, or construction, this guide is designed to help you find the ideal dust collection solutions tailored to your unique needs and geographical context.
Understanding dust system design Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Stage Collectors | Simple design; dust passes through impeller; lower cost | Small workshops, woodworking shops | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to install. Cons: Less efficient filtration; can clog easily. |
| Cyclone Collectors | Uses centrifugal force to separate dust; keeps filters cleaner | Large manufacturing, metal shops | Pros: Better airflow; longer filter life. Cons: Higher initial investment; requires more space. |
| Portable Dust Collectors | Compact; designed for mobility; lower capacity | Construction sites, small jobs | Pros: Easy to transport; versatile. Cons: Limited capacity; not suitable for large operations. |
| Centralized Systems | Networked dust collection; multiple tools connected to one unit | Large factories, industrial settings | Pros: Efficient for multiple tools; reduces noise. Cons: High installation cost; complex design. |
| HEPA Filtration Systems | High-efficiency filters; captures fine particles | Laboratories, healthcare facilities | Pros: Superior air quality; protects worker health. Cons: Higher maintenance; more expensive filters. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Single-Stage Collectors?
Single-stage collectors are characterized by their straightforward design where dust-laden air passes through an impeller, depositing larger debris into a collection bag. They are particularly suitable for small workshops and woodworking applications, making them a popular choice for hobbyists and small-scale operations. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the collector’s horsepower and airflow capacity, as these factors significantly influence performance and efficiency.
How Do Cyclone Collectors Enhance Dust Collection Efficiency?
Cyclone collectors utilize centrifugal force to separate dust and debris, allowing heavier particles to fall into a collection bin while cleaner air moves through the filter. This design is ideal for larger manufacturing environments or metalworking shops where high volumes of dust are generated. Buyers should consider the initial investment and space requirements, as cyclone systems often demand a more substantial upfront cost but offer long-term efficiency and reduced maintenance.
What Makes Portable Dust Collectors Ideal for Job Sites?
Portable dust collectors are designed for mobility, featuring compact sizes and lower capacities, making them perfect for construction sites and small jobs. Their versatility allows for easy transport between different work locations. When purchasing, buyers should assess the collector’s suction power and filter quality to ensure it meets the demands of various tasks while remaining portable.
Why Choose Centralized Dust Collection Systems for Large Operations?
Centralized dust collection systems connect multiple tools to a single dust collector, making them suitable for large factories and industrial settings. They provide efficient dust management across various workstations while reducing noise levels. However, buyers must consider the higher installation costs and complexity of these systems, as they require careful planning and integration into existing workflows.
What Are the Benefits of HEPA Filtration Systems in Dust Collection?
HEPA filtration systems are designed to capture fine particles, providing superior air quality and worker protection, making them essential in laboratories and healthcare facilities. These systems ensure that harmful dust does not re-enter the workspace, thus safeguarding employee health. Buyers should weigh the benefits of improved air quality against the higher maintenance costs and the need for more expensive filters, which can impact overall budget considerations.
Key Industrial Applications of dust system design
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dust system design | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woodworking & Furniture | Whole-shop dust collection systems | Improved air quality, reduced health risks, and increased productivity | System compatibility, ductwork materials, and filter efficiency |
| Metal Fabrication | Dust extraction in welding and cutting | Enhanced worker safety, compliance with regulations, and reduced cleanup time | Collector power ratings, filter types, and duct configurations |
| Food Processing | Dust control in milling and packaging | Prevention of contamination, improved hygiene, and compliance with food safety standards | Hygienic design, material certifications, and ease of cleaning |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Dust containment during powder handling | Ensured product purity, reduced cross-contamination risks, and compliance with industry regulations | HEPA filter specifications, system scalability, and regulatory compliance |
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Dust suppression in crushing and screening | Enhanced worker safety, reduced environmental impact, and improved operational efficiency | System durability, adaptability to harsh conditions, and maintenance requirements |
How is ‘Dust System Design’ Applied in Key Industries?
How is dust system design utilized in woodworking and furniture industries?
In woodworking and furniture manufacturing, whole-shop dust collection systems are essential for capturing airborne particles generated by cutting, sanding, and finishing processes. These systems enhance air quality, significantly reducing respiratory health risks for workers. Buyers in this sector must consider system compatibility with existing machinery, the materials used for ductwork, and the efficiency of filters to ensure optimal performance in diverse shop layouts.
What are the dust control needs in metal fabrication?
Metal fabrication facilities face unique challenges with dust and fumes produced during welding, cutting, and grinding. Effective dust extraction systems not only enhance worker safety but also ensure compliance with stringent health and safety regulations. B2B buyers should focus on power ratings of collectors, types of filters that can handle metal dust, and the configuration of duct systems to accommodate various machinery setups.

Illustrative image related to dust system design
How is dust control critical in food processing applications?
In food processing, dust control systems are vital for maintaining hygiene standards during milling and packaging operations. These systems prevent contamination and ensure compliance with food safety regulations. Buyers must prioritize hygienic designs that facilitate easy cleaning, as well as material certifications that meet industry standards. Additionally, the effectiveness of dust collection systems in preventing cross-contamination is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
Why is dust containment important in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers require stringent dust containment solutions during powder handling to ensure product purity and compliance with regulatory standards. Dust systems must effectively capture fine particles to mitigate cross-contamination risks. Buyers should evaluate HEPA filter specifications, the scalability of systems to accommodate varying production volumes, and adherence to regulatory compliance requirements to ensure safe and efficient operations.
How does dust suppression benefit the mining and mineral processing industry?
In mining and mineral processing, dust suppression systems are critical for managing dust generated during crushing and screening operations. These systems enhance worker safety, reduce environmental impacts, and improve overall operational efficiency. When sourcing dust systems, businesses need to consider the durability of the equipment to withstand harsh conditions, adaptability to different materials, and the maintenance requirements to ensure long-term functionality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dust system design’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Dust Collection Leading to Health Concerns
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of inadequate dust collection systems that fail to effectively capture fine particles, posing significant health risks to workers. In environments such as woodworking shops or metal fabrication facilities, airborne dust can lead to chronic respiratory issues and decrease overall workplace safety. Buyers may realize that the existing systems do not meet the necessary standards for air quality, especially when regulatory compliance is a concern. This oversight can stem from using underpowered dust collectors or improperly sized ductwork, leaving employees exposed to hazardous dust levels.
The Solution:
To enhance dust collection efficiency and protect worker health, buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of their current dust collection system. Start by evaluating the airflow requirements in cubic feet per minute (CFM) for each tool in use. Opt for a dust collector that meets or exceeds these requirements, ideally with a minimum of 2 horsepower and a fan rated at least 1,300 CFM. Importantly, ensure that the entire ductwork system is designed with minimal bends and the largest diameter pipes possible to reduce resistance. Investing in HEPA filters can significantly improve air quality by capturing 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to inspect for leaks or blockages that could compromise system efficiency.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Poorly Designed Ductwork
The Problem:
Buyers frequently encounter high operational costs stemming from poorly designed ductwork that increases energy consumption. When duct systems are not optimized, they can create excessive friction and resistance, forcing dust collectors to work harder and consume more electricity. This inefficiency not only raises energy bills but can also lead to premature wear and tear on the equipment, necessitating more frequent replacements and repairs.
The Solution:
To mitigate operational costs, it is crucial to invest time in designing an efficient ductwork layout. Start by positioning the dust collector centrally within the workspace to minimize the length of duct runs. Utilize a combination of straight runs and gradual bends, opting for long-radius elbows instead of sharp turns. This will facilitate smoother airflow and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, consider implementing blast gates to control airflow to each tool, ensuring that the dust collector operates only when needed, further conserving energy. Regularly reviewing and refining the duct system based on changing shop layouts or new equipment can sustain efficiency and reduce costs over time.
Scenario 3: Difficulties in Connecting Handheld Tools to Dust Collection Systems
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers struggle with the challenge of connecting handheld tools—like sanders and routers—to centralized dust collection systems. These tools typically have small dust ports that can easily become clogged, limiting airflow and resulting in inefficient dust collection. This not only hampers productivity but also leads to increased cleanup times and potential safety hazards from dust accumulation.
The Solution:
To effectively connect handheld tools to dust collection systems, buyers should consider using portable dust extractors equipped with HEPA filters. These units are specifically designed to handle the lower airflow requirements of handheld tools while maintaining effective dust capture. Additionally, utilize flexible hoses that can be adapted to fit the various ports of different tools. Implementing shop-made or commercially available dust hoods can also help to capture dust at the source, improving overall efficiency. Regular training for operators on the importance of connecting tools to the dust collection system can further enhance compliance and reduce the likelihood of dust-related issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dust system design
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Dust System Design?
When designing a dust collection system, the choice of materials is crucial for ensuring performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Here are four common materials used in dust system design, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various dust collection applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and is typically rated for low-pressure systems.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to install, which makes it popular among small businesses and workshops. However, its lower temperature tolerance limits its use in high-heat applications, and it can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light.
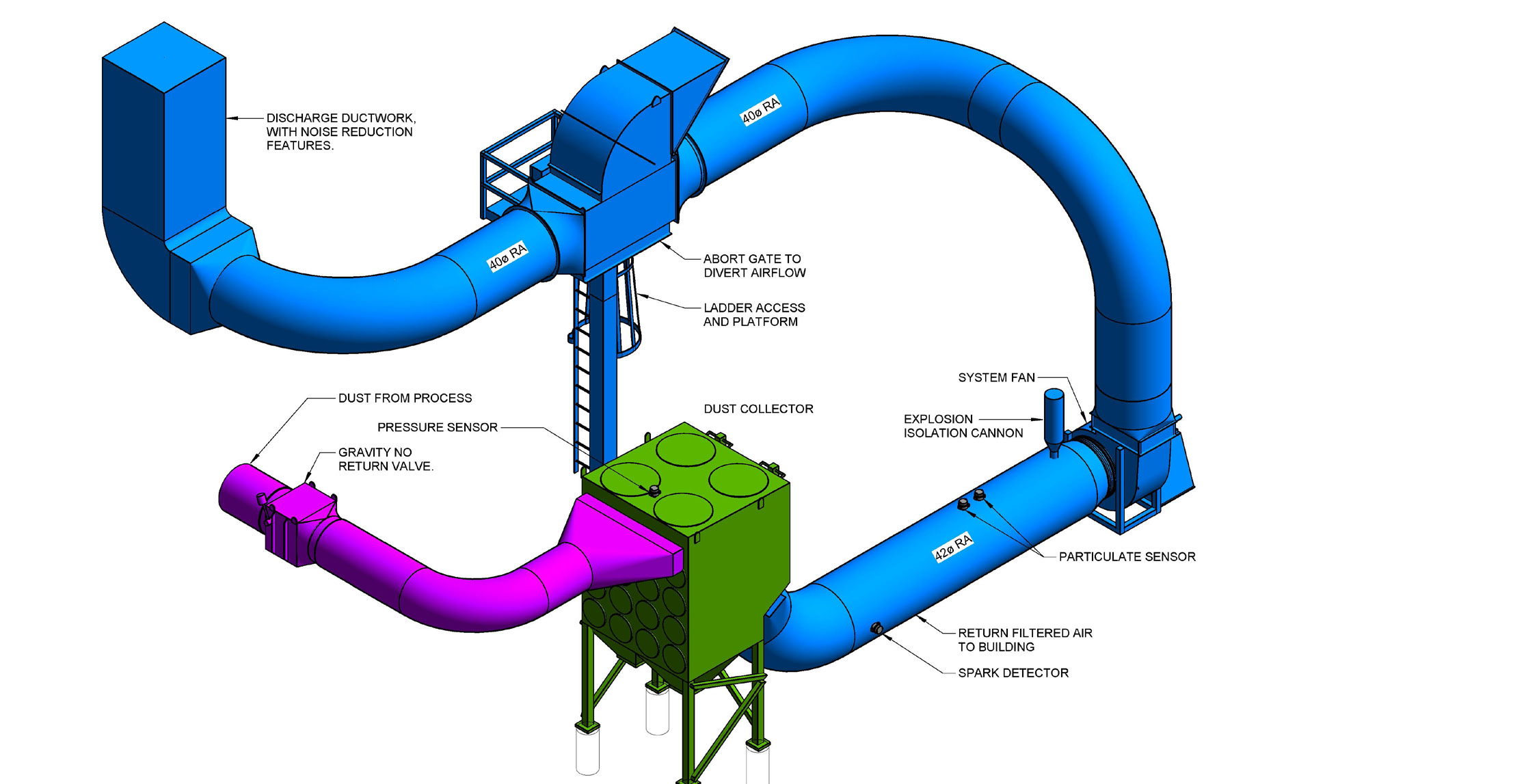
Illustrative image related to dust system design
Impact on Application: PVC is ideal for collecting wood dust and other non-corrosive materials. However, it is not suitable for abrasive or high-temperature dust, which can lead to system failures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards (such as ASTM in the U.S. or DIN in Europe) is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of PVC in their region, as import costs can vary significantly.
2. Galvanized Steel
Key Properties: Galvanized steel offers excellent durability and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is resistant to corrosion due to its zinc coating, making it suitable for various industrial environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of galvanized steel is its strength and longevity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it is more expensive than PVC and can be more challenging to install due to its weight.

Illustrative image related to dust system design
Impact on Application: This material is well-suited for systems handling abrasive dust, such as metal shavings or concrete dust. Its robust nature ensures that it can handle the wear and tear associated with these materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the galvanized steel meets local standards for corrosion resistance and durability. Additionally, they should consider the logistics of sourcing this material, as it may not be readily available in all regions.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. It is available in various grades, with 304 and 316 being the most common for dust collection systems.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is significantly more expensive than both PVC and galvanized steel, and its installation can be complex.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for collecting hazardous materials, including chemicals and corrosive dust. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not contaminate the collected dust.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards (like JIS in Japan or EN in Europe) is critical. Buyers should also be aware of the cost implications, as stainless steel may not be feasible for smaller operations.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can handle moderate temperatures and pressures. Its thermal conductivity allows for effective heat dissipation.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to install and maneuver. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be prone to dents and scratches, which may affect its performance over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for light to moderate dust collection applications, particularly in environments where weight is a concern. However, it may not be ideal for heavy-duty or abrasive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should consider the availability of aluminum and its compliance with regional standards. Additionally, they should evaluate the cost-effectiveness of aluminum in relation to its intended use.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for dust system design | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Wood dust collection | Cost-effective and easy to install | Limited temperature tolerance | Low |
| Galvanized Steel | Heavy-duty applications | Strong and durable | More expensive and heavier | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Hazardous material collection | Highly corrosion-resistant | High cost and complex installation | High |
| Aluminum | Light to moderate dust collection | Lightweight and easy to install | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in dust system design, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dust system design
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Dust Collection Systems?
The manufacturing process of dust collection systems involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers and their capabilities.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used in Dust System Manufacturing?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials include various metals, plastics, and composite materials. Steel and aluminum are frequently used for ductwork and collectors due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is often utilized for pipes and fittings because of its lightweight nature and resistance to chemical degradation.
Once the materials are sourced, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet international standards. This step often includes testing for tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and other physical properties that are crucial for the system’s performance.
How Are Dust Collection Components Formed and Shaped?
The forming stage involves various techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding. Laser cutting is commonly employed for precision parts, ensuring that the dimensions are exact for optimal airflow and connection integrity. After cutting, the materials may be bent or shaped using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, which provide high accuracy in creating ductwork and collector components.
Welding is another essential technique, especially for metal parts. It ensures strong joints that can withstand the pressure of airflow and resist wear over time. For plastics, processes like injection molding are often used to create fittings and connectors that are lightweight yet robust.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail in Dust System Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where all the components come together to form the complete dust collection system. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Component Integration: Individual parts such as ducts, collectors, and filters are connected using appropriate fasteners and fittings.
- Sealing and Insulation: To ensure no dust leaks occur, seals and gaskets are applied at joints. This is critical for maintaining system efficiency and protecting worker health.
- System Configuration: Depending on the specific requirements of the client, the system may be customized. This includes configuring the layout of ductwork to minimize airflow resistance.
Quality checks are conducted throughout the assembly process to ensure that all components fit properly and function as intended.
How Is Finishing Achieved in Dust Collection Systems?
Finishing involves applying protective coatings and conducting final inspections. Coatings, such as powder coating for metal parts, are essential for preventing corrosion and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the system.
Final inspections at this stage check for any defects or inconsistencies. This can include visual inspections, as well as more sophisticated methods like ultrasonic testing for weld integrity.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Dust System Manufacturers?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that dust collection systems meet safety and performance standards. Adhering to relevant international and industry-specific standards is essential for manufacturers aiming to serve a global market.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For dust collection systems, ISO 9001 is the primary standard for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have a robust framework for maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Additionally, certifications such as CE mark for European markets or API standards for specific industrial applications can be crucial. These certifications indicate that the products meet stringent safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Dust Collection System Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random checks are conducted to verify that production is in accordance with quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the system is assembled, a comprehensive inspection is performed to confirm that the final product meets all specifications and performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insight into the operational processes and quality management systems in place.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation such as quality assurance reports and compliance certificates can help verify adherence to international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an objective assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
International buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that can impact their purchasing decisions.
Are There Specific Regional Considerations for Quality Standards?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations governing dust collection systems. For instance, certain countries may require additional certifications that are not mandated elsewhere. Understanding these requirements is crucial for compliance and market acceptance.
How Do Cultural and Communication Factors Affect Quality Assurance?
Cultural differences can impact how quality is perceived and communicated. Clear, open lines of communication are essential for ensuring that both parties have a mutual understanding of quality expectations. It is advisable to establish a detailed quality agreement that outlines responsibilities, standards, and expectations.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in dust system design, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they select suppliers who meet their stringent quality and performance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dust system design’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure an effective dust system design. A well-designed dust collection system is essential for maintaining a safe and efficient work environment, particularly in industries prone to generating airborne particles. By following these steps, you can ensure that your dust system meets both regulatory standards and operational needs.
Step 1: Assess Your Operational Needs
Understanding your specific operational requirements is the first step in designing an effective dust collection system. Evaluate the types of machinery and processes that generate dust, as well as the volume of dust produced. This assessment will guide you in selecting the right size and type of dust collector to ensure optimal performance.
- Identify dust sources: List all tools and processes that produce dust, noting the volume and type of particles generated.
- Determine airflow requirements: Calculate the necessary cubic feet per minute (CFM) to effectively capture dust at the source.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Once you have assessed your needs, it’s crucial to define the technical specifications for your dust collection system. This includes factors such as the required airflow, static pressure, and filtration efficiency.
- Choose filter type: Decide between single-stage and cyclone collectors, based on your dust type and volume.
- Specify duct size and layout: Plan for duct diameter and layout to minimize airflow resistance, ensuring efficient dust transport.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. A well-vetted supplier can make a significant difference in the quality and reliability of your dust collection system.
- Evaluate reputation: Look for suppliers with proven experience in your industry and positive customer reviews.
- Request case studies: Ask for examples of previous installations that demonstrate their capability to meet your specific needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your shortlisted suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This step is vital for ensuring safety and quality in your dust collection system.
- Check for compliance: Confirm that suppliers adhere to local and international standards, such as OSHA or ISO certifications.
- Review filter efficiency ratings: Look for HEPA filters that guarantee high filtration efficiency to protect worker health.
Step 5: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have a shortlist of potential suppliers, request detailed proposals. This will help you compare offerings and understand the full scope of services and equipment provided.
- Include installation services: Ensure that proposals encompass installation, maintenance, and support options.
- Evaluate total cost: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also long-term operational costs, including energy consumption and filter replacements.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits and Demonstrations
If possible, arrange site visits or demonstrations with potential suppliers. This hands-on experience allows you to evaluate the equipment’s performance and suitability for your specific environment.
- Observe operational efficiency: Watch how the system operates in real-world conditions, paying attention to noise levels and dust capture efficiency.
- Ask for references: Speak to current users to gain insights into the system’s reliability and supplier support.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Installation
After selecting a supplier, finalize your purchase and plan for the installation of your dust collection system. Ensure that you have a clear timeline and understand the installation process.
- Coordinate with operations: Schedule installation during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to your operations.
- Plan for training: Arrange for training sessions for your staff on how to operate and maintain the new dust collection system effectively.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure they select and implement a dust system design that meets their operational needs while prioritizing health and safety.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dust system design Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Dust System Design Sourcing?
When considering the cost structure for dust system design, several components come into play. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials represent a significant portion of the costs, including ductwork (PVC, metal), dust collectors, filters, and various connectors and fittings. Opting for higher-quality materials, such as spiral ducts or HEPA filters, can enhance system efficiency but will increase upfront costs.
Illustrative image related to dust system design
Labor costs will vary depending on the complexity of the installation and the expertise required. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring the system is designed and installed correctly to optimize airflow and efficiency.
Manufacturing overhead accounts for the indirect costs related to production, including facility expenses, utilities, and administrative costs.
Tooling expenses involve the machinery and tools used to manufacture components. Investing in advanced tooling can improve production efficiency and reduce long-term costs.
Quality Control (QC) is crucial in ensuring that all components meet specified standards. A rigorous QC process can prevent costly failures and ensure compliance with health regulations, particularly important for international buyers concerned about safety standards.
Illustrative image related to dust system design
Logistics encompasses transportation and warehousing costs, which can vary significantly based on the geographic location of both suppliers and buyers.
Finally, the margin is influenced by competition and the perceived value of the products offered.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Pricing for Dust System Design?
Pricing in the dust system design market is highly influenced by volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ). Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their anticipated volume to maximize cost savings.
Specifications and customization also play a critical role. Tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements may incur additional costs. However, the investment can pay off in terms of improved efficiency and effectiveness of the dust collection system.
Material quality and certifications are vital factors as well. Systems that meet international standards or have certifications (like HEPA filters) typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to dust system design
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Dust System Design?
For B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of pricing can lead to significant cost savings.
Negotiation is crucial. Engaging suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially when placing large orders, can yield favorable terms. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts or additional services, such as free shipping or extended warranties.
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the initial purchase price but also operating costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. Investing in a higher-quality system may have a higher upfront cost but could result in lower operational costs and fewer interruptions over time.
For international buyers, understanding pricing nuances influenced by local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties is essential. Factors like Incoterms can significantly affect the final cost. For instance, choosing an Incoterm that places more responsibility on the supplier can simplify logistics but may raise costs.

Illustrative image related to dust system design
Is There a Disclaimer for Indicative Prices?
It’s important to note that prices for dust system components and installation can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing. Always account for potential fluctuations in raw material costs and labor rates, which can affect overall pricing in this dynamic market.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dust system design With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for Dust Collection
In the realm of industrial operations, efficient dust collection is critical for maintaining a safe and clean work environment. While traditional dust system designs are widely used, various alternative solutions can also achieve similar goals. Below, we compare dust system design with two viable alternatives: portable dust extractors and electrostatic precipitators. This analysis will help B2B buyers understand the strengths and weaknesses of each option to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Dust System Design | Portable Dust Extractors | Electrostatic Precipitators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, suitable for large areas; captures fine particles effectively. | Good for localized dust control; may struggle with fine particulate capture. | Highly effective for fine particles, especially in high-volume airflows. |
| Cost | Initial investment can be high; long-term savings due to durability. | Lower initial cost; may require frequent replacement or maintenance. | High upfront cost; energy-efficient but may have high maintenance costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful planning and installation; may need professional help. | Easy to set up and move around; ideal for smaller spaces. | Complex installation; may need specialized knowledge for setup. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance; filter changes and system checks necessary. | Minimal maintenance; filters need replacing regularly but are easy to access. | Requires regular cleaning of collector plates; can be labor-intensive. |
| Best Use Case | Large workshops and factories needing consistent dust control across multiple tools. | Small workshops or job sites where mobility is essential. | Industries dealing with high dust loads and fine particulates, like metalworking. |
Understanding Portable Dust Extractors: Pros and Cons
Portable dust extractors are compact units designed for flexibility and mobility. They are particularly useful in smaller workshops or job sites where space is limited. The main advantage of portable extractors is their lower initial cost and ease of setup. However, they may not effectively capture fine dust particles compared to larger systems, potentially impacting air quality over time. Frequent filter replacements can also add to ongoing costs, making them less economical in the long run for businesses with heavy dust loads.
Evaluating Electrostatic Precipitators: Pros and Cons
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) utilize electrical charges to remove dust and particulates from the air. They are exceptionally efficient at capturing fine particles, making them suitable for industries where air quality is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals or food processing. While ESPs can provide significant energy savings over time, their initial investment is high, and they require specialized installation and maintenance. Additionally, cleaning the collector plates can be labor-intensive, which may not be ideal for all operations.
Making the Right Choice: What Should B2B Buyers Consider?
When choosing a dust collection solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and space limitations. Dust system designs are ideal for larger operations requiring comprehensive dust control, while portable dust extractors offer flexibility for smaller setups. Electrostatic precipitators are best suited for environments where air quality is critical but come with higher costs and maintenance demands. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can select the most appropriate dust collection solution that aligns with their operational requirements and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dust system design
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Dust System Design?
When considering dust system design, various technical properties are crucial for ensuring efficiency and safety. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Airflow Capacity (CFM)
Airflow capacity, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), indicates how much air a dust collector can move. This metric is vital because insufficient airflow can lead to inadequate dust removal, compromising both equipment performance and workplace safety. Buyers should select systems that provide CFM ratings suitable for their specific applications, taking into account the number of tools and the length of ductwork involved.
2. Static Pressure (SP)
Static pressure refers to the resistance within the duct system that affects airflow. It is measured in inches of water column (in. WC) and is influenced by factors such as duct length, bends, and the type of fittings used. Understanding SP is essential for selecting the right dust collector; too much resistance can reduce efficiency and increase energy costs. B2B buyers should evaluate their ductwork design to minimize SP for optimal performance.
3. Filtration Efficiency
Filtration efficiency indicates how well a dust collector can trap particles of varying sizes. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are often recommended, as they can capture at least 99.97% of particles measuring 0.3 microns. Selecting a system with adequate filtration is crucial for protecting worker health, especially in industries where fine dust can pose serious respiratory risks.
4. Duct Diameter
The diameter of the ductwork impacts airflow velocity and overall system performance. Larger ducts can handle higher volumes of air, reducing the risk of clogs and ensuring effective dust collection. Buyers should consider the tool port sizes and choose duct diameters that match or exceed these specifications to maintain system efficiency.
5. Material Grade
The material grade of ductwork and components affects durability and resistance to corrosion or wear. Common materials include PVC and various metals. For B2B buyers, selecting high-grade materials can ensure a longer lifespan for the system, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
6. Noise Level
Noise levels produced by dust collection systems are measured in decibels (dB). Excessive noise can lead to a hazardous work environment and may require additional soundproofing measures. Evaluating noise levels is essential for compliance with occupational safety regulations and for maintaining worker comfort.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Dust System Design?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in dust system design. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In dust system design, knowing the OEM helps in sourcing quality components and ensuring compatibility between different system elements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when sourcing components for dust systems.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific products or services. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare quotes and negotiate terms, making it a critical step in the procurement process for dust system components.
Illustrative image related to dust system design
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can help B2B buyers minimize risks and ensure smoother international transactions.
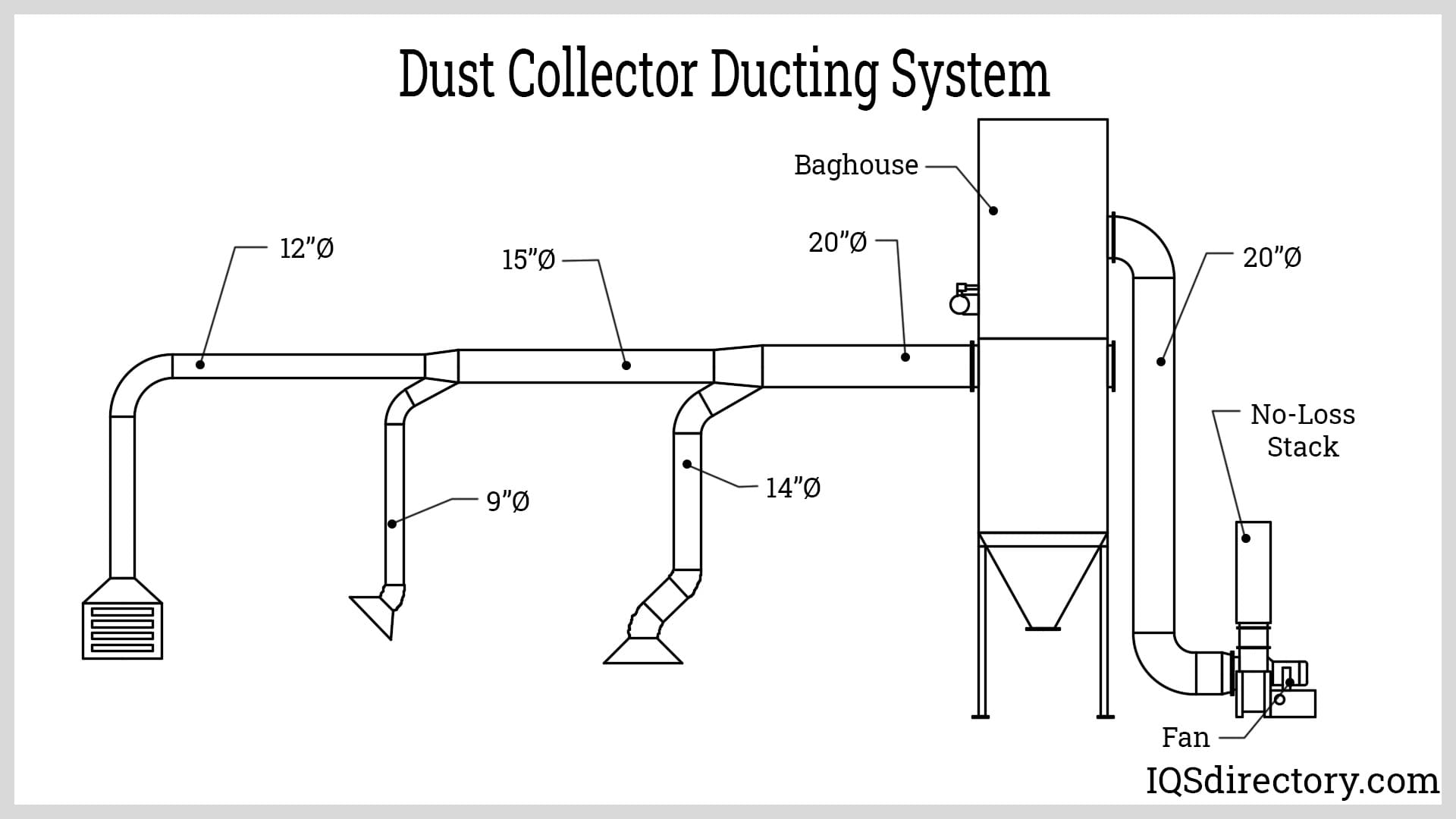
5. Ductwork Configuration
This term refers to the arrangement and design of duct systems used in dust collection. Proper ductwork configuration is vital for optimizing airflow and minimizing resistance, which directly impacts system efficiency.
6. Cyclone Separator
A cyclone separator is a type of dust collector that uses centrifugal force to separate dust from the air. Understanding this term is essential for B2B buyers considering different dust collection technologies, as cyclone systems often provide superior filtration and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to dust system design
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when designing or upgrading their dust collection systems. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to a safer working environment.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dust system design Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Dust System Design for B2B Buyers?
The dust system design sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing awareness of workplace safety and health regulations. Industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are adopting more stringent dust control measures to mitigate health risks associated with airborne particulate matter. This trend is further bolstered by the rising demand for advanced filtration technologies, such as HEPA filters, which are critical in ensuring clean air quality.
Emerging technologies, including smart dust collection systems equipped with IoT capabilities, are also reshaping the landscape. These systems allow for real-time monitoring and performance optimization, enabling businesses to enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. The integration of automation in dust collection processes is becoming a focal point, allowing companies to streamline operations and improve response times to dust-related issues.
Furthermore, international buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific industry needs. This demand for flexibility is particularly evident in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, where diverse manufacturing processes necessitate bespoke dust management systems. As a result, companies that can offer modular designs and scalable solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Dust System Design Solutions?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the dust system design sector. The environmental impact of dust collection systems is under scrutiny, with businesses seeking to minimize their carbon footprint. This has led to an increased focus on energy-efficient systems that reduce power consumption while maintaining high performance.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction as stakeholders demand transparency in supply chains. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers who prioritize sustainable materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled or eco-friendly materials in dust system design are becoming critical criteria in supplier selection.
In addition, the adoption of ‘green’ certifications is influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are looking for systems that not only comply with environmental regulations but also contribute positively to sustainability goals. As a result, manufacturers that can demonstrate their commitment to eco-friendly practices and provide certified products are likely to attract more business from conscientious buyers.
How Has the Dust System Design Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the dust system design sector reflects broader industrial trends and technological advancements. Historically, dust collection systems were rudimentary, often relying on basic filtration methods that were not particularly effective. However, as industries grew and the understanding of health impacts associated with dust exposure deepened, there was a shift towards more sophisticated solutions.
The introduction of cyclone separators and multi-stage filtration systems marked a significant turning point, allowing for higher efficiency in dust collection. Over the past few decades, the integration of automation and smart technology has further transformed the sector, enabling real-time monitoring and enhanced operational control.
Today, the focus is not just on efficiency but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing, which are reshaping the future of dust system design. As international B2B buyers prioritize these values, the sector continues to innovate, adapting to the changing demands of the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dust system design
-
How do I solve dust collection challenges in my facility?
Effective dust collection begins with a well-planned system tailored to your specific needs. Start by assessing the types of machinery in your facility and their dust output. Design a layout that minimizes duct length and resistance, using large-diameter pipes to enhance airflow. Consider investing in a high-efficiency filter, such as a HEPA filter, to ensure that even the smallest particles are captured. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the system will also help identify any inefficiencies or leaks, allowing for timely adjustments. -
What is the best dust collection system for woodworking applications?
The ideal dust collection system for woodworking typically includes a cyclone or a high-horsepower single-stage collector. Cyclones are preferred for their ability to separate larger debris before reaching the filter, maintaining airflow efficiency. Aim for a collector with a minimum of 1,300 CFM and a 2 HP motor for most woodworking shops. Additionally, ensure that the system is designed to minimize bends in ductwork to maintain optimal airflow. Engaging a professional for system design can also yield significant long-term benefits. -
What customization options are available for dust system designs?
Customization options for dust system designs can include tailored duct layouts, specific collector sizes, and specialized filtration systems. Many manufacturers offer services to create bespoke systems that fit the unique dimensions and operational needs of your facility. Additionally, options such as blast gates for airflow control and custom hoods for capturing dust from specific tools can enhance system performance. Discussing your requirements with a supplier can help you identify the best customization choices. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for dust collection systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for dust collection systems vary by supplier and region. Typically, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs due to production efficiencies, while smaller suppliers might be more flexible. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may accommodate lower quantities for custom systems. Understanding your facility’s requirements can help you negotiate better terms while ensuring you receive the necessary equipment. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing dust collection systems internationally?
Payment terms for international orders can range from upfront payment to net terms after delivery, depending on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment through letters of credit for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I vet suppliers for dust system design?
When vetting suppliers for dust system design, consider their industry experience, customer reviews, and certifications. Request case studies or references from previous clients to assess their capability and reliability. Evaluating their technical expertise in dust collection technology and understanding of local regulations can also be crucial. Additionally, visiting their facilities or attending trade shows can provide insights into their operations and product quality. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing dust collection systems?
Logistics for importing dust collection systems involve assessing shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work closely with your supplier to understand shipping timelines and packaging requirements to prevent damage during transit. Ensure that your chosen logistics partner is experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate customs efficiently. Planning for potential delays and understanding your responsibilities regarding import duties will help avoid unexpected costs. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for dust collection systems?
Quality assurance measures for dust collection systems should include thorough testing of equipment before shipment, adherence to industry standards, and certifications for safety and efficiency. Request documentation that outlines the testing procedures used by the manufacturer, including airflow and filtration efficiency tests. After installation, conducting regular inspections and maintenance checks will help ensure long-term performance and compliance with health and safety regulations.
Top 6 Dust System Design Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wood Magazine – Dust Collection System Guide
Domain: woodmagazine.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: A well-planned dust-collection system traps tiny particles before they become airborne. Key considerations include: 1. Layout: Select dust-collector location and lay out duct runs with minimal resistance. Use short duct runs and minimal turns. 2. Collector Location: Place the collector centrally to minimize duct lengths. 3. Tool Placement: Position tools that require the most airflow closest to th…
2. Spiral MFG – High Pressure Galvanized Pipe
Domain: spiralmfg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: HIGH PRESSURE GALVANIZED PIPE: Elbows, Tees, 90° Laterals, 30°/45°, Multi Branch Pant Wyes, Reducers, Fittings, Plugs, Caps & Couplings, Pickup Hoods, Weather Hoods, Rectangular & Round Transitions, Rectangular Duct, Single Wall Insulated Spiral Pipe, Dual Wall Insulated Spiral Pipe, Angle Rings & Flanges, Duct Sealants & Tapes, Hangers, Accessories, Clean Outs & Access Doors, Blast Gates & Contro…
3. AirHand – Dust Collection Systems
Domain: airhand.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Dust Collection System Information, CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute), FPM (Feet per Minute), SP (Static Pressure), VP (Velocity Pressure), Metalworking Dust Velocity: 4500 FPM in branches, 4000 FPM in main; Woodworking Dust Velocity: 4000 FPM in branches, 3500 FPM in main; Other Light Dust Velocity: 4000 FPM in branches, 3500 FPM in main. Recommendations for designing a dust collection system include d…
4. AirBestPractices – Compressed Air System Design for Dust Collectors
Domain: airbestpractices.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Compressed Air System Design for Dust Collectors involves the use of pulse jet dust collectors that utilize compressed air to remove dust from filter bags. Key specifications include:
– Compressed air inlet pressure is critical for effective dust removal.
– Pulse valves send a specific volume of air at a predetermined velocity to clear dust.
– The pulse of air typically ranges from 3 to 6 cubic…
5. Baghouse – Dust Collection Systems
Domain: baghouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Baghouse Dust Collection System, Dust Collector Filters, Baghouse Filters, PTFE Filters, Pleated Filters, Cartridge Filters, Dust Collector Filter Cages, Filter Hardware, Industrial Dust Collection Systems, Cartridge Collectors, Baghouse Collectors, Cyclone Collectors, Bin Vents, Oil Mist Collectors, Fire Suppression Accessories, Explosion Vents, Baghouse Spark Arrestors, Solenoid Valves, Pressure…
6. Reddit – DIY Dust Collection Systems
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: DIY dust collection systems, Thien baffle on trash can, shop vac for airflow, whirlwind chip separator, 4″ and 2.5″ dust collection hoses, air filtration for fine particulate, piping, connectors, and gates.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dust system design
In the competitive landscape of industrial operations, effective dust system design is crucial for ensuring workplace safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. By strategically sourcing high-quality dust collection systems, B2B buyers can significantly reduce health risks associated with airborne particles while enhancing productivity. Key considerations include selecting the right dust collector based on airflow requirements, optimizing ductwork layout to minimize resistance, and prioritizing high-efficiency filtration systems to protect both workers and equipment.
As businesses expand in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for advanced dust control solutions will continue to grow. Investing in robust and well-designed dust collection systems not only adheres to regulatory standards but also fosters a healthier work environment, ultimately leading to increased operational longevity and cost savings.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should leverage the insights shared in this guide to make informed decisions. Engage with trusted suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and expert guidance in dust system design. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can position themselves for success in an evolving market, ensuring a cleaner, safer, and more efficient future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.